CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE- chloroquine phosphate tablet, film coated
Chloroquine phosphate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Chloroquine phosphate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Ranbaxy Pharmaceuticals Inc., Ipca Laboratories Ltd, Ohm Laboratories Inc., Ipca Laboratories Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- BOXED WARNING (What is this?)
-
DESCRIPTION
Chloroquine phosphate, USP is a 4-aminoquinoline compound for oral administration. It is a white crystalline powder; odorless; has a bitter taste, and is discolored slowly on exposure to light. It is freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in alcohol, in chloroform and in ether.
Chloroquine phosphate, USP is an antimalarial and amebicidal drug.
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 250 mg of chloroquine phosphate, USP (equivalent to 150 mg base).
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, corn starch, hypromellose, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, polyethylene glycol 400, polyethylene glycol 3350, polysorbate 80, povidone, sodium starch glycolate, talc, and titanium dioxide.
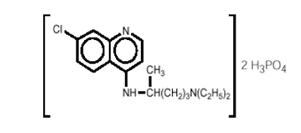
Chemically, it is 7-chloro-4-[[4-(diethylamino)-1-methylbutyl]amino] quinoline phosphate (1:2) and has the following molecular structure:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Chloroquine is rapidly and almost completely absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, and only a small proportion of the administered dose is found in the stools. Approximately 55% of the drug in the plasma is bound to nondiffusible plasma constituents. Excretion of chloroquine is quite slow, but is increased by acidification of the urine. Chloroquine is deposited in the tissues in considerable amounts. In animals, from 200 to 700 times the plasma concentration may be found in the liver, spleen, kidney, and lung; leukocytes also concentrate the drug. The brain and spinal cord, in contrast, contain only 10 to 30 times the amount present in plasma.
Chloroquine undergoes appreciable degradation in the body. The main metabolite is desethylchloroquine, which accounts for one fourth of the total material appearing in the urine; bisdesethylchloroquine, a carboxylic acid derivative, and other metabolic products as yet uncharacterized are found in small amounts. Slightly more than half of the urinary drug products can be accounted for as unchanged chloroquine.
Mechanism of Action: Chloroquine is an antimalarial agent. While the drug can inhibit certain enzymes, its effect is believed to result, at least in part from its interaction with DNA. However, the mechanism of plasmodicidal action of chloroquine is not completely certain.
Activity in vitro and in vivo: Chloroquine is active against the erythrocytic forms of Plasmodium vivax, Plasmodium malariae, and susceptible strains of Plasmodium falciparum (but not the gametocytes of P. falciparum). It is not effective against exoerythrocytic forms of the parasite.
In vitro studies with trophozoites of Entamoeba histolytica have demonstrated that chloroquine phosphate also possesses amebicidal activity comparable to that of emetine.
Drug Resistance: Resistance of Plasmodium falciparum to chloroquine is widespread and cases of Plasmodium vivax have been reported.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Chloroquine phosphate tablets are indicated for the suppressive treatment and for acute attacks of malaria due to P. vivax, P. malariae, P. ovale, and susceptible strains of P. falciparum. The drug is also indicated for the treatment of extraintestinal amebiasis.
Chloroquine phosphate tablets does not prevent relapses in patients with vivax or malariae malaria because it is not effective against exoerythrocytic forms of the parasite, nor will it prevent vivax or malariae infection when administered as a prophylactic. It is highly effective as a suppressive agent in patients with vivax or malariae malaria, in terminating acute attacks, and significantly lengthening the interval between treatment and relapse. In patients with falciparum malaria it abolishes the acute attack and effects complete cure of the infection, unless due to a resistant strain of P. falciparum.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Use of this drug is contraindicated in the presence of retinal or visual field changes either attributable to 4-aminoquinoline compounds or to any other etiology, and in patients with known hypersensitivity to 4-aminoquinoline compounds. However, in the treatment of acute attacks of malaria caused by susceptible strains of plasmodia, the physician may elect to use this drug after carefully weighing the possible benefits and risks to the patient.
-
WARNINGS
It has been found that certain strains of P. falciparum have become resistant to 4- aminoquinoline compounds (including chloroquine and hydroxychloroquine). Chloroquine resistance is widespread and, at present, is particularly prominent in various parts of the world including sub-Saharan Africa, Southeast Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and over large portions of South America, including the Amazon basin1.
Before using chloroquine for prophylaxis, it should be ascertained whether chloroquine is appropriate for use in the region to be visited by the traveler. Chloroquine should not be used for treatment of P.falciparum infections acquired in areas of chloroquine resistance or malaria occurring in patients where chloroquine prophylaxis has failed.
Patients infected with a resistant strain of plasmodia as shown by the fact that normally adequate doses have failed to prevent or cure clinical malaria or parasitemia should be treated with another form of antimalarial therapy.
Retinopathy/maculopathy, as well as macular degeneration have been reported (see ADVERSE REACTIONS), and irreversible retinal damage has been observed in some patients who had received long-term or high-dosage 4-aminoquinoline therapy. Retinopathy has been reported to be dose related. Risk factors for the development of retinopathy include age, duration of treatment, high daily and/or cumulated doses.
When prolonged therapy with any antimalarial compound is contemplated, initial (base line) and periodic ophthalmologic examinations (including visual acuity, expert slit-lamp, funduscopic, and visual field tests) should be performed.
If there is any indication (past or present) of abnormality in the visual acuity, visual field, or retinal macular areas (such as pigmentary changes, loss of foveal reflex), or any visual symptoms (such as light flashes and streaks) which are not fully explainable by difficulties of accommodation or corneal opacities, the drug should be discontinued immediately and the patient closely observed for possible progression. Retinal changes (and visual disturbances) may progress even after cessation of therapy.
Acute extrapyramidal disorders may occur with chloroquine (see ADVERSE REACTIONS and OVERDOSE). These adverse reactions usually resolve after treatment discontinuation and/or symptomatic treatment.
All patients on long-term therapy with this preparation should be questioned and examined periodically, including testing knee and ankle reflexes, to detect any evidence of muscular weakness. If weakness occurs, discontinue the drug.
A number of fatalities have been reported following the accidental ingestion of chloroquine, sometimes in relatively small doses (0.75 g or 1 g chloroquine phosphate in one 3-year-old child). Patients should be strongly warned to keep this drug out of the reach of children because they are especially sensitive to the 4-aminoquinoline compounds.
Use of chloroquine phosphate in patients with psoriasis may precipitate a severe attack of psoriasis. When used in patients with porphyria the condition may be exacerbated. The drug should not be used in these conditions unless in the judgment of the physician the benefit to the patient outweighs the potential risks.
Usage in Pregnancy: Radioactively tagged chloroquine administered intravenously to pregnant pigmented CBA mice passed rapidly across the placenta and accumulated selectively in the melanin structures of the fetal eyes. It was retained in the ocular tissues for five months after the drug had been eliminated from the rest of the body2. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies evaluating the safety and efficacy of chloroquine in pregnant women. Usage of chloroquine during pregnancy should be avoided except in the suppression or treatment of malaria when in the judgment of the physician the benefit outweighs the potential risk to the fetus.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Hematological Effects/Laboratory Tests
Complete blood cell counts should be made periodically if patients are given prolonged therapy. If any severe blood disorder appears which is not attributable to the disease under treatment, discontinuance of the drug should be considered.
The drug should be administered with caution to patients having G-6-PD (glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase) deficiency.
Auditory Effects
In patients with preexisting auditory damage, chloroquine should be administered with caution. In case of any defects in hearing, chloroquine should be immediately discontinued, and the patient closely observed (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Hepatic Effects
Since this drug is known to concentrate in the liver, it should be used with caution in patients with hepatic disease or alcoholism or in conjunction with known hepatotoxic drugs.
Central Nervous System Effects
Patients with a history of epilepsy should be advised about the risk of chloroquine provoking seizures.
Drug Interactions
Antacids and kaolin: Antacids and kaolin can reduce absorption of chloroquine; an interval of at least 4 hours between intake of these agents and chloroquine should be observed.
Cimetidine: Cimetidine can inhibit the metabolism of chloroquine, increasing its plasma level. Concomitant use of cimetidine should be avoided.
Ampicillin: In a study of healthy volunteers, chloroquine significantly reduced the bioavailability of ampicillin. An interval of at least two hours between intake of this agent and chloroquine should be observed.
Cyclosporine: After introduction of chloroquine (oral form), a sudden increase in serum cyclosporine level has been reported. Therefore, close monitoring of serum cyclosporine level is recommended and, if necessary, chloroquine should be discontinued.
Mefloquine: Co-administration of chloroquine and mefloquine may increase the risk of convulsions.
The blood concentrations of chloroquine and desethylchloroquine (the major metabolite of chloroquine, which also has antimalarial properties) were negatively associated with log antibody titers. Chloroquine taken in the dose recommended for malaria prophylaxis can reduce the antibody response to primary immunization with intradermal human diploid-cell rabies vaccine.
Nursing Mothers
Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from chloroquine, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the potential clinical benefit of the drug to the mother.
The excretion of chloroquine and the major metabolite, desethylchloroquine, in breast milk was investigated in eleven lactating mothers following a single oral dose of chloroquine (600 mg base). The maximum daily dose of the drug that the infant can receive from breastfeeding was about 0.7% of the maternal start dose of the drug in malaria chemotherapy. Separate chemoprophylaxis for the infant is required. See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of chloroquine phosphate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. However, this drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Special Senses:Ocular: Maculopathy and macular degeneration have been reported and may be irreversible (see WARNINGS); irreversible retinal damage in patients receiving long-term or high-dosage 4-aminoquinoline therapy; visual disturbances (blurring of vision and difficulty of focusing or accommodation); nyctalopia; scotomatous vision with field defects of paracentral, pericentral ring types, and typically temporal scotomas, e.g., difficulty in reading with words tending to disappear, seeing half an object, misty vision, and fog before the eyes. Reversible corneal opacities have also been reported.
Auditory: Nerve type deafness; tinnitus, reduced hearing in patients with preexisting auditory damage.
Musculoskeletal System: Skeletal muscle myopathy or neuromyopathy leading to progressive weakness and atrophy of proximal muscle groups, which may be associated with mild sensory changes, depression of tendon reflexes and abnormal nerve conduction, have been noted.
Gastrointestinal system: Hepatitis, increased liver enzymes, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramps.
Skin and appendages: Rare reports of erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, exfoliative dermatitis and similar desquamation-type events. Pleomorphic skin eruptions, skin and mucosal pigmentary changes; lichen planus-like eruptions, pruritus, urticaria, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reaction including angioedema; drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS syndrome); photosensitivity and hair loss and bleaching of hair pigment.
Hematologic system: Rarely, pancytopenia, aplastic anemia, reversible agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia and neutropenia.
Nervous system: Convulsive seizures, mild and transient headache, polyneuritis. Acute extrapyramidal disorders (such as dystonia, dyskinesia, tongue protrusion, torticollis) (see WARNINGS and OVERDOSE). Neuropsychiatric changes including psychosis, delirium, anxiety, agitation, insomnia, confusion, hallucinations, personality changes, and depression.
Cardiac system: Rarely, hypotension, electrocardiographic change (particularly, inversion or depression of the T-wave with widening of the QRS complex), and cardiomyopathy.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms: Chloroquine is very rapidly and completely absorbed after ingestion. Toxic doses of chloroquine can be fatal. As little as 1 g may be fatal in children. Toxic symptoms can occur within minutes. These consist of headache, drowsiness, visual disturbances, nausea and vomiting, cardiovascular collapse, shock and convulsions followed by sudden and early respiratory and cardiac arrest. Hypokalemia has been observed with arrhythmias in cases of intoxication. The electrocardiogram may reveal atrial standstill, nodal rhythm, prolonged intraventricular conduction time, and progressive bradycardia leading to ventricular fibrillation and/or arrest. Cases of extrapyramidal disorders have also been reported in the context of chloroquine overdose (see WARNINGS and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Treatment: Treatment is symptomatic and must be prompt with immediate evacuation of the stomach by emesis (at home, before transportation to the hospital) or gastric lavage until the stomach is completely emptied. If finely powdered, activated charcoal is introduced by stomach tube, after lavage, and within 30 minutes after ingestion of the antimalarial, it may inhibit further intestinal absorption of the drug. To be effective, the dose of activated charcoal should be at least five times the estimated dose of chloroquine ingested.
Convulsions, if present, should be controlled before attempting gastric lavage. If due to cerebral stimulation, cautious administration of an ultra short-acting barbiturate may be tried but, if due to anoxia, it should be corrected by oxygen administration and artificial respiration, monitor ECG. In shock with hypotension, a potent vasopressor should be administered. Replace fluids and electrolytes as needed. Cardiac compressing or pacing may be indicated to sustain the circulation. Because of the importance of supporting respiration, tracheal intubation or tracheostomy, followed by gastric lavage, may also be necessary. Peritoneal dialysis and exchange transfusions have also been suggested to reduce the level of the drug in the blood.
Intervention options can involve: diazepam for life-threatening symptoms, seizures and sedation, epinephrine for treatment of vasodilation and myocardial depression, potassium replacement with close monitoring of serum potassium levels.
A patient who survives the acute phase and is asymptomatic should be closely observed for at least six hours. Fluids may be forced, and sufficient ammonium chloride (8 g daily in divided doses for adults) may be administered for a few days to acidify the urine to help promote urinary excretion in cases of both overdosage or sensitivity.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dosage of chloroquine phosphate is often expressed or calculated as the base. Each 250 mg tablet of chloroquine phosphate is equivalent to 150 mg base. In infants and children the dosage is preferably calculated on the body weight.
Malaria: Suppression— Adult Dose: 500 mg (= 300 mg base) on exactly the same day of each week.
Pediatric Dose: The weekly suppressive dosage is 5 mg calculated as base, per kg of body weight, but should not exceed the adult dose regardless of weight.
If circumstances permit, suppressive therapy should begin two weeks prior to exposure. However, failing this in adults, an initial double (loading) dose of 1 g (= 600 mg base), or in children 10 mg base/kg may be taken in two divided doses, six hours apart. The suppressive therapy should be continued for eight weeks after leaving the endemic area.
For Treatment of Acute Attack:
Adults: An initial dose of 1 g (= 600 mg base) followed by an additional 500 mg (= 300 mg base) after six to eight hours and a single dose of 500 mg (= 300 mg base) on each of two consecutive days. This represents a total dose of 2.5 g chloroquine phosphate or 1.5 g base in three days.
The dosage for adults of low body weight and for infants and children should be determined as follows:
First dose: 10 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 600 mg base).
Second dose: (6 hours after first dose) 5 mg base per kg (but not exceeding a single dose of 300 mg base).
Third dose: (24 hours after first dose) 5 mg base per kg.
Fourth dose: (36 hours after first dose) 5 mg base per kg.
For radical cure of vivax and malariae malaria concomitant therapy with an 8-aminoquinoline compound is necessary.
Extraintestinal Amebiasis: Adults:1 g (600 mg base) daily for two days, followed by 500 mg (300 mg base) daily for at least two to three weeks. Treatment is usually combined with an effective intestinal amebicide.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Chloroquine phosphate tablets, USP 250 mg are white to off-white, round, film-coated tablets, debossed with “RF” and “27” on one side and break line on the other side.
NDC: 63304-460-03 Bottles of 10
NDC: 63304-460-50 Bottles of 50
NDC: 63304-460-10 Bottles of 1000
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Store at 20 - 25° C (68 - 77° F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
- REFERENCES
-
PACKAGE LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 63304-460-03
CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE TABLETS,USP
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE
chloroquine phosphate tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63304-460 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE (UNII: 6E17K3343P) (CHLOROQUINE - UNII:886U3H6UFF) CHLOROQUINE PHOSPHATE 250 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) POVIDONES (UNII: FZ989GH94E) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A POTATO (UNII: 5856J3G2A2) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code RF27 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63304-460-03 10 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 63304-460-10 1000 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 63304-460-50 50 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA090610 03/15/2011 Labeler - Ranbaxy Pharmaceuticals Inc. (937890044) Registrant - Ipca Laboratories Ltd (650387009) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ohm Laboratories Inc. 184769029 manufacture(63304-460) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Ipca Laboratories Limited 862179827 api manufacture(63304-460)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.