These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS. TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1981
Trazodone Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Trazodone Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by REMEDYREPACK INC.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE- trazodone hydrochloride tablet, film coated
REMEDYREPACK INC.
----------
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE TABLETS.
TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE tablets, for oral use Initial U.S. Approval: 1981
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
|
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
WARNING: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS AND BEHAVIORS
Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients in short-term studies. Closely monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening, and for emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are not approved for use in pediatric patients
[see
Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults .
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dose Selection
An initial dose of 150 mg/day in divided doses is suggested. The dosage should be initiated at a low-dose and increased gradually, noting the clinical response and any evidence of intolerance. Occurrence of drowsiness may require the administration of a major portion of the daily dose at bedtime or a reduction of dosage.
The dose may be increased by 50 mg/day every 3 to 4 days. The maximum dose for outpatients usually should not exceed 400 mg/day in divided doses. Inpatients (i.e., more severely depressed patients) may be given up to but not in excess of 600 mg/day in divided doses.
Once an adequate response has been achieved, dosage may be gradually reduced, with subsequent adjustment depending on therapeutic response.
2.2 Important Administration Instructions
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets can be swallowed whole or administered as a half tablet by breaking the tablet along the score line. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be taken shortly after a meal or light snack.
2.3 Screen for Bipolar Disorder Prior to Starting Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets
Prior to initiating treatment with trazodone hydrochloride tablets or another antidepressant, screen patients for a personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
2.4 Switching to or from Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor Antidepressant
At least 14 days must elapse between discontinuation of a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI) antidepressant and initiation of trazodone hydrochloride tablets. In addition, at least 14 days must elapse after stopping trazodone hydrochloride tablets before starting an MAOI antidepressant [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.5 Dosage Recommendations for Concomitant Use with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors or Inducers
Coadministration with Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors
Consider reducing trazodone hydrochloride tablets dose based on tolerability when trazodone hydrochloride tablets are coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inhibitor [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Coadministration with Strong CYP3A4 Inducers
Consider increasing trazodone hydrochloride tablets dose based on therapeutic response when trazodone hydrochloride tablets are coadministered with a strong CYP3A4 inducer [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
2.6 Discontinuation of Treatment with Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets
Adverse reactions may occur upon discontinuation of trazodone hydrochloride tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]. Gradually reduce the dosage rather than stopping trazodone hydrochloride tablets abruptly whenever possible.
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are available in the following strengths:
50 mg - white, film-coated, round, convex, scored tablets, debossed “61” bisect “60” on one side and debossed “V” on the reverse side.
100 mg - white, film-coated, round, convex, scored tablets, debossed “61” bisect “61” on one side and debossed “V” on the reverse side.
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in:
-
Patients taking, or within 14 days of stopping, monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs), including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue, because of an increased risk of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors in Pediatric and Young Adult Patients
In pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and other antidepressant classes) that included approximately 77,000 adult patients and over 4,400 pediatric patients, the incidence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients was greater in antidepressant-treated patients than in placebo-treated patients. The drug-placebo differences in the number of cases of suicidal thoughts and behaviors per 1000 patients treated are provided in Table 1.
No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric studies. There were suicides in the adult studies, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about antidepressant drug effect on suicide.
Table 1: Risk Differences of the Number of Cases of Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors in the Pooled Placebo-Controlled Trials of Antidepressants in Pediatric and Adult Patients
| Age Range (years) | Drug-Placebo Difference in Number of Patients of Suicidal Thoughts or Behaviors per 1000 Patients Treated |
| Increases Compared to Placebo | |
| <18 | 14 additional patients |
| 18-24 | 5 additional patients |
| Decreases Compared to Placebo | |
| 25-64 | 1 fewer patient |
| ≥65 | 6 fewer patients |
It is unknown whether the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric and young adult patients extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond four months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with MDD that antidepressants delay the recurrence of depression.
Monitor all antidepressant-treated patients for clinical worsening and emergence of suicidal thoughts and behaviors, especially during the initial few months of drug therapy and at times of dosage changes. Counsel family members or caregivers of patients to monitor for changes in behavior and to alert the healthcare provider. Consider changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing trazodone hydrochloride tablets, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidal thoughts or behaviors.
5.2 Serotonin Syndrome
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) and SSRIs, including trazodone hydrochloride tablets, can precipitate serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition. The risk is increased with concomitant use of other serotonergic drugs (including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, and St. John’s Wort) and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin, i.e., MAOIs [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Serotonin syndrome can also occur when these drugs are used alone.
Serotonin syndrome signs and symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, delirium, and coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, dizziness, diaphoresis, flushing, hyperthermia), neuromuscular symptoms (e.g., tremor, rigidity, myoclonus, hyperreflexia, incoordination), seizures, and gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea).
The concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets with MAOIs is contraindicated. In addition, do not initiate trazodone hydrochloride tablets in a patient being treated with MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue. No reports involved the administration of methylene blue by other routes (such as oral tablets or local tissue injection). If it is necessary to initiate treatment with an MAOI such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue in a patient taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets, discontinue trazodone hydrochloride tablets before initiating treatment with the MAOI [see Contraindications (4), Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Monitor all patients taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets for the emergence of serotonin syndrome. Discontinue treatment with trazodone hydrochloride tablets and any concomitant serotonergic agents immediately if the above symptoms occur, and initiate supportive symptomatic treatment. If concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets with other serotonergic drugs is clinically warranted, inform patients of the increased risk for serotonin syndrome and monitor for symptoms.
5.3 Cardiac Arrhythmias
Clinical studies indicate that trazodone hydrochloride may be arrhythmogenic in patients with preexisting cardiac disease. Arrhythmias identified include isolated PVCs, ventricular couplets, tachycardia with syncope, and torsade de pointes. Postmarketing events, including torsade de pointes have been reported at doses of 100 mg or less with the immediate-release form of trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets should also be avoided in patients with a history of cardiac arrhythmias, as well as other circumstances that may increase the risk of the occurrence of torsade de pointes and/or sudden death, including symptomatic bradycardia, hypokalemia or hypomagnesemia, and the presence of congenital prolongation of the QT interval. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are not recommended for use during the initial recovery phase of myocardial infarction. Caution should be used when administering trazodone hydrochloride tablets to patients with cardiac disease and such patients should be closely monitored, since antidepressant drugs (including trazodone hydrochloride tablets) may cause cardiac arrhythmias [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)] .
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets prolongs the QT/QT c interval. The use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be avoided in patients with known QT prolongation or in combination with other drugs that are inhibitors of CYP3A4 (e.g., itraconazole, clarithromycin, voriconazole), or known to prolong QT interval including Class 1A antiarrhythmics (e.g., quinidine, procainamide) or Class 3 antiarrhythmics (e.g., amiodarone, sotalol), certain antipsychotic medications (e.g., ziprasidone, chlorpromazine, thioridazine), and certain antibiotics (e.g., gatifloxacin). Concomitant administration of drugs may increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
5.4 Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope
Hypotension, including orthostatic hypotension and syncope has been reported in patients receiving trazodone hydrochloride. Concomitant use with an antihypertensive may require a reduction in the dose of the antihypertensive drug.
5.5 Increased Risk of Bleeding
Drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake inhibition, including trazodone hydrochloride tablets, increase the risk of bleeding events. Concomitant use of aspirin, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS), other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin, and other anticoagulants may add to this risk. Case reports and epidemiological studies (case-control and cohort design) have demonstrated an association between use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and the occurrence of gastrointestinal bleeding. Bleeding events related to drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake have ranged from ecchymosis, hematoma, epistaxis, and petechiae to life-threatening hemorrhages.
Inform patients about the risk of bleeding associated with the concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and antiplatelet agents or anticoagulants. For patients taking warfarin, carefully monitor coagulation indices when initiating, titrating, or discontinuing trazodone hydrochloride tablets.
5.6 Priapism
Cases of priapism (painful erections greater than 6 hours in duration) have been reported in men receiving trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Priapism, if not treated promptly, can result in irreversible damage to the erectile tissue. Men who have an erection lasting greater than 4 hours, whether painful or not, should immediately discontinue the drug and seek emergency medical attention [see Adverse Reactions (6.2), Overdosage (10)].
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in men who have conditions that might predispose them to priapism (e.g., sickle cell anemia, multiple myeloma, or leukemia), or in men with anatomical deformation of the penis (e.g., angulation, cavernosal fibrosis, or Peyronie’s disease).
5.7 Activation of Mania or Hypomania
In patients with bipolar disorder, treating a depressive episode with trazodone hydrochloride tablets or another antidepressant may precipitate a mixed/manic episode. Activation of mania/hypomania has been reported in a small proportion of patients with major affective disorder who were treated with antidepressants. Prior to initiating treatment with trazodone hydrochloride tablets, screen patients for any personal or family history of bipolar disorder, mania, or hypomania [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)] .
5.8 Discontinuation Syndrome
Adverse reactions after discontinuation of serotonergic antidepressants, particularly after abrupt discontinuation, include: nausea, sweating, dysphoric mood, irritability, agitation, dizziness, sensory disturbances (e.g., paresthesia, such as electric shock sensations), tremor, anxiety, confusion, headache, lethargy, emotional lability, insomnia, hypomania, tinnitus, and seizures. A gradual reduction in dosage rather than abrupt cessation is recommended whenever possible [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.9 Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets may cause somnolence or sedation and may impair the mental and/or physical ability required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks. Patients should be cautioned about operating hazardous machinery, including automobiles, until they are reasonably certain that the drug treatment does not affect them adversely.
5.10 Angle-Closure Glaucoma
The pupillary dilation that occurs following use of many antidepressant drugs including trazodone hydrochloride tablets may trigger an angle closure attack in a patient with anatomically narrow angles who does not have a patent iridectomy. Avoid use of antidepressants, including trazodone hydrochloride tablets, in patients with untreated anatomically narrow angles.
5.11 Hyponatremia
Hyponatremia may occur as a result of treatment with SNRIs and SSRIs, including trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Cases with serum sodium lower than 110 mmol/L have been reported. Signs and symptoms of hyponatremia include headache, difficulty concentrating, memory impairment, confusion, weakness, and unsteadiness, which can lead to falls. Signs and symptoms associated with more severe and/or acute cases have included hallucination, syncope, seizure, coma, respiratory arrest, and death. In many cases, this hyponatremia appears to be the result of the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion (SIADH).
In patients with symptomatic hyponatremia, discontinue trazodone hydrochloride tablets and institute appropriate medical intervention. Elderly patients, patients taking diuretics, and those who are volume-depleted may be at greater risk of developing hyponatremia with SSRIs and SNRIs [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)] .
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Suicidal Thoughts and Behavior in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults
[see
Boxed Warning and
Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Serotonin Syndrome
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
Cardiac Arrythmias
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Orthostatic Hypotension and Syncope
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
Increased Risk of Bleeding
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
Priapism
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Activation of Mania or Hypomania
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
Discontinuation Syndrome
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
Potential for Cognitive and Motor Impairment
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
Angle-Closure Glaucoma
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.10)]
Hyponatremia
[see
Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Table 2: Common Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 2% of Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets-treated Patients and Greater than the Rate of Placebo- Treated Patients as Observed in Controled Clinical Studies
|
Inpatients |
Outpatients |
|||
|
Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets N=142 |
Placebo N=95 |
Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets N=157 |
Placebo N=158 |
|
|
Allergic | ||||
|
Skin Condition/Edema |
3% |
1% |
7% |
1% |
|
Autonomic | ||||
|
Blurred Vision |
6% |
4% |
15% |
4% |
|
Constipation |
7% |
4% |
8% |
6% |
|
Dry Mouth |
15% |
8% |
34% |
20% |
|
Cardiovascular | ||||
|
Hypertension |
20% |
1% |
1% |
* |
|
Hypotension |
7% |
1% |
4% |
0 |
|
Syncope |
3% |
2% |
5% |
1% |
|
CNS | ||||
|
Confusion |
5% |
0 |
6% |
8% |
|
Decreased Concentration |
3% |
2% |
1% |
0 |
|
Disorientation |
2% |
0 |
* |
0 |
|
Dizziness/Light-Headedness |
20% |
5% |
28% |
15% |
|
Drowsiness |
24% |
6% |
41% |
20% |
|
Fatigue |
11% |
4% |
6% |
3% |
|
Headache |
10% |
5% |
20% |
16% |
|
Nervousness |
15% |
11% |
6% |
8% |
|
Gastrointestinal | ||||
|
Abdominal/Gastric Disorder |
4% |
4% |
6% |
4% |
|
Diarrhea |
0 |
1% |
5% |
1% |
|
Nausea/Vomiting |
10% |
1% |
13% |
10% |
|
Musculoskeletal | ||||
|
Aches/Pains |
6% |
3% |
5% |
3% |
|
Neurological | ||||
|
Incoordination |
5% |
0 |
2% |
* |
|
Tremors |
3% |
1% |
5% |
4% |
|
Other | ||||
|
Eyes Red/Tired/Itching |
3% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Head Full-Heavy |
3% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Malaise |
3% |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Nasal/Sinus Congestion |
3% |
0 |
6% |
3% |
|
Weight Gain |
1% |
0 |
5% |
2% |
|
Weight Loss |
* |
3% |
6% |
3% |
|
*Incidence less than 1% | ||||
Other adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of <2% with the use of trazodone hydrochloride in the controlled clinical studies: akathisia, allergic reaction, anemia, chest pain, delayed urine flow, early menses, flatulence, hallucinations/delusions, hematuria, hypersalivation, hypomania, impaired memory, impaired speech, impotence, increased appetite, increased libido, increased urinary frequency, missed periods, muscle twitches, numbness, paresthesia, retrograde ejaculation, shortness of breath, and tachycardia/palpitations. Occasional sinus bradycardia has occurred in long-term studies.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
Blood and lymphatic system disorders: hemolytic anemia, leukocytosis
Cardiac disorders: cardiospasm, congestive heart failure, conduction block, orthostatic hypotension and syncope, palpitations, bradycardia, atrial fibrillation, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest, arrhythmia, ventricular ectopic activity, including ventricular tachycardia and QT prolongation. Prolonged QT interval, torsade de pointes, and ventricular tachycardia have been reported at doses of 100 mg per day or less [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Endocrine disorders: inappropriate ADH syndrome
Eye disorders: diplopia
Gastrointestinal disorders: increased salivation, nausea/vomiting
General disorders and administration site conditions: chills, edema, unexplained death, weakness
Hepatobiliary disorders: cholestasis, jaundice, hyperbilirubinemia, liver enzyme alterations
Investigations: increased amylase
Metabolism and nutrition disorders: methemoglobinemia
Nervous system disorders: aphasia, ataxia, cerebrovascular accident, extrapyramidal symptoms, grand mal seizures, paresthesia, tardive dyskinesia, vertigo
Psychiatric disorders: abnormal dreams, agitation, anxiety, hallucinations, insomnia, paranoid reaction, psychosis, stupor
Renal and urinary disorders: urinary incontinence, urinary retention
Reproductive system and breast disorders: breast enlargement or engorgement, clitorism, lactation, priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: apnea
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: alopecia, hirsutism, leukonychia, pruritus, psoriasis, rash, urticaria
Vascular disorders: vasodilation
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Drugs Having Clinically Important Interactions With Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets
Table 3: Clinically Important Drug Interactions with Trazodone Hydrochloride Tablets
|
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of MAOIs and serotonergic drugs including trazodone hydrochloride tablets increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients taking MAOIs, including MAOIs such as linezolid or intravenous methylene blue [see Contraindications (4), Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4), and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
|
Examples: |
isocarboxazid, moclobemide, phenelzine, selegiline, tranylcypromine |
|
Other Serotonergic Drugs |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of serotonergic drugs including trazodone hydrochloride tablets and other serotonergic drugs increases the risk of serotonin syndrome. |
|
Intervention: |
Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of serotonin syndrome, particularly during trazodone hydrochloride tablets initiation. If serotonin syndrome occurs, consider discontinuation of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and/or concomitant serotonergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. |
|
Examples: |
triptans, antidepressants (tricyclic and serotonin uptake inhibitors), fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, and St. John's Wort |
|
Antiplatelet Agents and Anticoagulants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. The concurrent use of an antiplatelet agent or anticoagulant with trazodone hydrochloride tablets may potentiate the risk of bleeding. |
|
Intervention: |
Inform patients of the increased risk of bleeding with the concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants. For patients taking warfarin, carefully monitor the international normalized ratio (INR) when initiating or discontinuing trazodone hydrochloride tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]. |
|
Examples: |
warfarin, rivaroxaban, dabigatran, clopidogrel |
|
Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and strong CYP3A4 inhibitors increased the exposure of trazodone compared to the use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets alone . |
|
Intervention: |
If trazodone hydrochloride tablets are used with a potent CYP3A4 inhibitor, the risk of adverse reactions, including cardiac arrhythmias, may be increased and a lower dose of trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be considered [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
Examples: |
itraconazole, ketoconazole, clarithromycin, indinavir |
|
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
The concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and strong CYP3A4 inducers decreased the exposure of trazodone compared to the use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets alone . |
|
Intervention: |
Patients should be closely monitored to see if there is a need for an increased dose of trazodone hydrochloride tablets when taking CYP3A4 inducers [see Dosage and Administration (2.5)]. |
|
Examples: |
rifampin, carbamazepine, phenytoin, St. John’s wort |
|
Digoxin and Phenytoin |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Digoxin and phenytoin are narrow therapeutic index drugs. Concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets can increase digoxin or phenytoin concentrations. |
|
Intervention: |
Measure serum digoxin or phenytoin concentrations before initiating concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Continue monitoring and reduce digoxin or phenytoin dose as necessary. |
|
Examples: |
digoxin, phenytoin |
|
Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets may enhance the response CNS depressants. |
|
Intervention: |
Patients should be counseled that trazodone hydrochloride tablets may enhance the response to alcohol, barbiturates, and other CNS depressants. |
|
Examples: |
alcohol, barbiturates |
|
QT Interval Prolongation |
|
|
Clinical Impact: |
Concomitant use of drugs that prolong the QT interval may add to the QT effects of trazodone hydrochloride tablets and increase the risk of cardiac arrhythmia. |
|
Intervention: |
Avoid the use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets in combination with other drugs known to prolong QTc [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. |
|
Examples: |
Class 1A antiarrhythmics: quinidine, procainamide, disopyramide; Class 3 antiarrhythmics: amiodarone, sotalol; Antipsychotics: ziprasidone, chlorpromazine, thioridazine; Antibiotics: gatifloxacin |
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Trazodone hydrochloride has been shown to cause increased fetal resorption and other adverse effects on the fetus in the rat when given at dose levels approximately 6 to 9 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 400 mg/day on mg/m 2 in adolescents. There was also an increase in congenital anomalies in the rabbit at approximately 6 to 17 times the MRHD on mg/m 2 basis in adolescents. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Trazodone hydrochloride should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Animal Data
No teratogenic effects were observed when trazodone was given to pregnant rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at oral doses up to 450 mg/kg/day. This dose is 9 and 17 times, in rats and rabbits, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 400 mg/day on mg/m 2 basis in adolescents. Increased fetal resorption and other adverse effects on the fetus in rats at 6 to 9 times the MRHD and increase in congenital anomalies in rabbits at 6 to 17 times the MRHD on mg/m 2 basis in adolescents were observed.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Trazodone and/or its metabolites have been found in the milk of lactating rats, suggesting that the drug may be secreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when trazodone is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established. Antidepressants increased the risk of suicidal thoughts and behaviors in pediatric patients [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Reported clinical literature and experience with trazodone has not identified differences in responses between elderly and younger patients. However, as experience in the elderly with trazodone hydrochloride is limited, it should be used with caution in geriatric patients.
Serotonergic antidepressants have been associated with cases of clinically significant hyponatremia in elderly patients, who may be at greater risk for this adverse reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
10 OVERDOSAGE
Death from overdose has occurred in patients ingesting trazodone hydrochloride tablets and other CNS depressant drugs concurrently (alcohol; alcohol and chloral hydrate and diazepam; amobarbital; chlordiazepoxide; or meprobamate).
The most severe reactions reported to have occurred with overdose of trazodone hydrochloride tablets alone have been priapism, respiratory arrest, seizures, and ECG changes, including QT prolongation. The reactions reported most frequently have been drowsiness and vomiting. Overdosage may cause an increase in incidence or severity of any of the reported adverse reactions.
There is no specific antidote for trazodone hydrochloride overdose. In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug involvement. For current information on the management of poisoning or overdose, contact a poison control center (1-800-222-1222 or www.poison.org).
11 DESCRIPTION
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets for oral administration contain trazodone hydrochloride, a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor and 5HT2 receptor antagonist. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are a triazolopyridine derivative designated as 2-[3-[4-(3-chlorophenyl)-1-piperazinyl]propyl]-1,2,4-triazolo [4,3-a]pyridin-3(2 H)-one hydrochloride. It is a white odorless crystalline powder which is freely soluble in water. The structural formula is represented as follows:
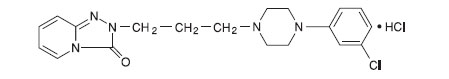
Molecular Formula: C 19H 22ClN 5OHCl
Molecular Weight: 408.33
Each tablet, for oral administration, contains 50 mg or 100 mg of trazodone hydrochloride, USP. In addition, each tablet contains hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, pregelatinized corn starch, silicon dioxide, and titanium dioxide.
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of trazodone’s antidepressant action is not fully understood, but is thought to be related to its enhancement of serotonergic activity in the CNS. Trazodone is both a selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) and a 5HT2 receptor antagonist and the net result of this action on serotonergic transmission and its role in trazodone’s antidepressant effect is unknown.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Preclinical studies have shown that trazodone selectively inhibits neuronal reuptake of serotonin (Ki = 367 nM) and acts as an antagonist at 5-HT-2A (Ki = 35.6 nM) serotonin receptors. Trazodone is also an antagonist at several other monoaminergic receptors including 5-HT2B (Ki = 78.4 nM), 5-HT2C (Ki = 224 nM), α1A (Ki = 153 nM), α2C (Ki = 155 nM) receptors and it is a partial agonist at 5-HT1A (Ki = 118 nM) receptor.
Trazodone antagonizes alpha 1-adrenergic receptors, a property which may be associated with postural hypotension.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In humans, trazodone hydrochloride is absorbed after oral administration without selective localization in any tissue. When trazodone hydrochloride is taken shortly after ingestion of food, there may be an increase in the amount of drug absorbed, a decrease in maximum concentration and a lengthening in the time to maximum concentration. Peak plasma levels occur approximately one hour after dosing when trazodone hydrochloride is taken on an empty stomach or 2 hours after dosing when taken with food.
Metabolism
In vitro studies in human liver microsomes show that trazodone is metabolized, via oxidative cleavage, to an active metabolite, m- chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) by CYP3A4. Other metabolic pathways that may be involved in the metabolism of trazodone have not been well characterized. Trazodone is extensively metabolized; less than 1% of an oral dose is excreted unchanged in the urine.
Elimination
In some patients trazodone may accumulate in the plasma.
Protein Binding
Trazodone is 89 to 95% protein bound
in vitro at concentrations attained with therapeutic doses in humans.
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
Carcinogenesis
No drug- or dose-related occurrence of carcinogenesis was evident in rats receiving trazodone in daily oral doses up to 7.3 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRSD) of 400 mg/day on mg/m 2 basis.
Mutagenesis
No genotoxicity studies were conducted with trazodone.
Impairment of Fertility
Trazodone has no effect on fertility in rats at doses up to 6 times the MRHD on mg/m 2 basis in adolescents.
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy and safety of trazodone hydrochloride were established from inpatient and outpatient trials of the trazodone immediate release formulation in the treatment of major depressive disorder.
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets USP, 50 mg are white, film-coated, round, convex, scored tablets, debossed “61” bisect “60” on one side and debossed “V” on the reverse side. They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC: 0603-6160-21
Bottles of 500: NDC: 0603-6160-28
Bottles of 1000: NDC: 0603-6160-32
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets USP, 100 mg are white, film-coated, round, convex, scored tablets, debossed “61” bisect “61” on one side and debossed “V” on the reverse side. They are available as follows:
Bottles of 100: NDC: 0603-6161-21
Bottles of 500: NDC: 0603-6161-28
Bottles of 1000: NDC: 0603-6161-32
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense contents with a child-resistant closure (as required) and in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP/NF.
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling ( Medication Guide).
Suicidal Thoughts and Behaviors
Advise patients and caregivers to look for the emergence of suicidality, especially early during treatment and when the dosage is adjusted up or down and instruct them to report such symptoms to the healthcare provider [ see Box Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Dosage and Administration
Advise patients that trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be taken shortly after a meal or light snack. Advise patients regarding the importance of following dosage titration instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2)] .
Serotonin Syndrome
Caution patients about the risk of serotonin syndrome, particularly with the concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets with other serotonergic drugs including triptans, tricyclic antidepressants, fentanyl, lithium, tramadol, tryptophan, buspirone, amphetamines, St. John’s Wort, and with drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (in particular, MAOIs, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid). Patients should contact their health care provider or report to the emergency room if they experience signs or symptoms of serotonin syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7)] .
Activation of Mania/Hypomania
Advise patients and their caregivers to observe for signs of activation of mania/hypomania and instruct them to report such symptoms to the healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)] .
Increased Risk of Bleeding
Inform patients about the concomitant use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets with aspirin, NSAIDs, other antiplatelet drugs, warfarin, or other anticoagulants because the combined use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and these medications has been associated with an increased risk of bleeding. Advise them to inform their health care providers if they are taking or planning to take any prescription or over-the-counter medications that increase the risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)] .
Discontinuation Syndrome
Advise patients not to abruptly discontinue trazodone hydrochloride tablets and to discuss any tapering regimen with their healthcare provider. Adverse reactions can occur when trazodone hydrochloride tablets are discontinued [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to inform their health care providers if they are taking, or plan to take any prescription or over-the-counter medications since there is a potential for interactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
MEDICATION GUIDE
What is the most important information I should know about trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
Antidepressant medicines, depression or other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions: Talk to your healthcare provider about:
- All risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
- All treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illnesses
1. Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
2. Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a higher risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have or have a family history of bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
3. How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call your healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with your healthcare provider as scheduled. Call your healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you are worried about symptoms.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you have any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- Thoughts about suicide or dying
- Attempts to commit suicide
- New or worse depression
- New or worse anxiety
- Feeling very agitated or restless
- Panic attacks
- Trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- New or worse irritability
- Acting aggressive, being angry or violent
- Acting on dangerous impulses
- An extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- Other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
-
Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
-
Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. You should discuss all treatment choices with your healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
-
Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to your healthcare provider about the side effects of your medicines.
-
Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you take. Keep a list of all medicines to show your healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
It is not known if trazodone hydrochloride tablets are safe and effective in children.
What are trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets are a prescription medicine used in adults to treat major depressive disorder (MDD). Trazodone hydrochloride tablets belong to a class of medicines known as SSRIs (or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors).
Do not take trazodone hydrochloride tablets:
-
If you take a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI). Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if you take an MAOI, including the antibiotic linezolid, and intravenous methylene blue.
-
Do not take an MAOI within 2 weeks of stopping trazodone hydrochloride tablets unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider.
Do not start trazodone hydrochloride tablets if you stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks unless directed to do so by your healthcare provider.
Before you take trazodone hydrochloride tablets tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
-
have heart problems, including QT prolongation or a family history of it
-
have ever had a heart attack
-
have bipolar disorder
-
have liver or kidney problems
-
have other serious medical conditions
-
are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets may harm your unborn baby. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant.
-
are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if trazodone hydrochloride passes into your breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide if you will take trazodone hydrochloride tablets or breastfeed.
-
have taken a Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitor (MAOI) or if you have stopped taking an MAOI in the last 2 weeks.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Using trazodone hydrochloride tablets with certain other medicines can affect each other causing serious side effects.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
-
triptans used to treat migraine headache
-
medicines used to treat mood, anxiety, psychotic or thought disorders, including tricyclics, lithium, SSRIs, SNRIs, buspirone, or antipsychotics
-
tramadol
-
over-the-counter supplements such as tryptophan or St. John’s Wort
-
nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
-
aspirin
-
warfarin (Coumadin, Jantoven)
-
phenytoin (Mesantoin)
-
diuretics
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
- Take trazodone hydrochloride tablets exactly as your healthcare provider tells you.
- Trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be taken shortly after a meal or light snack.
- If you feel drowsy after taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets, talk to your healthcare provider. Your healthcare provider may change your dose or the time of day you take your trazodone hydrochloride tablets.
- Do not stop taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets without talking to your healthcare provider.
- Trazodone hydrochloride tablets should be swallowed whole or broken in half along the score line. Do not chew or crush trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Tell your healthcare provider if you cannot swallow trazodone either whole or as a half tablet.
- If you take too much trazodone hydrochloride tablets, call your healthcare provider, your Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222, or go to the nearest emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
- Do not drive, operate heavy machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how trazodone hydrochloride tablets affects you. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets can slow your thinking and motor skills.
- Do not drink alcohol or take other medicines that make you sleepy or dizzy while taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets until you talk with your healthcare provider. Trazodone hydrochloride tablets may make your sleepiness or dizziness worse if you take it with alcohol or other medicines that cause sleepiness or dizziness.
What are the possible side effects of trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
Trazodone hydrochloride tablets can cause serious side effects or death, including:
-
See “What is the most important information I should know about trazodone hydrochloride tablets?”
-
Serotonin syndrome. Symptoms of serotonin syndrome include: agitation, hallucinations, problems with coordination, fast heartbeat, tight muscles, trouble walking, sweating, fever, nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea.
-
Irregular or fast heartbeat or faint (QT prolongation)
-
Low blood pressure. You feel dizzy or faint when you change positions (go from sitting to standing)
-
Unusual bruising or bleeding
-
Erection lasting for more than 6 hours (priapism)
-
Feeling high or in a very good mood, then becoming irritable, or having too much energy, feeling like you have to keep talking or do not sleep (mania).
-
Withdrawal symptoms. Symptoms of withdrawal can include anxiety, agitation, and sleep problems. Do not stop taking trazodone hydrochloride tablets without talking to your healthcare provider.
-
Visual problems.
-
eye pain
-
changes in vision
-
swelling or redness in or around the eye
Only some people are at risk for these problems. You may want to undergo an eye examination to see if you are at risk and receive preventative treatment if you are.
-
-
Low sodium in your blood (hyponatremia). Symptoms of hyponatremia include: headache, feeling weak, feeling confused, trouble concentrating, memory problems and feeling unsteady when you walk.
Get medical help right away, if you have any of the symptoms listed above.
The most common side effects of trazodone hydrochloride tablets include:
-
swelling
-
blurred vision
-
dizziness
-
sleepiness
-
tiredness
-
diarrhea
-
stuffy nose
-
weight loss
These are not all the possible side effects of trazodone hydrochloride tablets. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
-
Store trazodone hydrochloride tablets at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
-
Keep in tight container
-
Keep out of the light
-
Safely throw away medicine that is out of date or no longer needed.
Keep trazodone hydrochloride tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of trazodone hydrochloride tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use trazodone hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give trazodone hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about trazodone hydrochloride tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in trazodone hydrochloride tablets?
Active ingredient: trazodone hydrochloride, USP
Inactive ingredients: 50 mg and 100 mg: hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, povidone, pregelatinized corn starch, silicon dioxide, and titanium dioxide.
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
DRUG: Trazodone Hydrochloride
GENERIC: Trazodone Hydrochloride
DOSAGE: TABLET, FILM COATED
ADMINSTRATION: ORAL
NDC: 70518-0160-0
COLOR: white
SHAPE: ROUND
SCORE: Two even pieces
SIZE: 11 mm
IMPRINT: 61;61;V
PACKAGING: 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK
ACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE 100mg in 1
INACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- HYPROMELLOSES
- STARCH, CORN
- POVIDONE
- SILICON DIOXIDE
- POLYETHYLENE GLYCOLS
- LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE
- MAGNESIUM STEARATE
- POLYDEXTROSE
- TITANIUM DIOXIDE

| TRAZODONE HYDROCHLORIDE
trazodone hydrochloride tablet, film coated |
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||||||||||||
| Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556) |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.