MAGNESIUM SULFATE IN WATER- magnesium sulfate heptahydrate injection, solution
Magnesium Sulfate in Water by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Magnesium Sulfate in Water by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by B. Braun Medical Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is a sterile, nonpyrogenic solution of magnesium sulfate heptahydrate in water for injection. May contain sulfuric acid and/or sodium hydroxide for pH adjustment. The pH is 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5). It is available in 4% and 8% concentrations. See HOW SUPPLIED section for the content and characteristics of available dosage forms and fill volumes. Magnesium Sulfate, USP heptahydrate is chemically designated MgSO4 7H2O, colorless crystals or white powder freely soluble in water.
Water for Injection, USP is chemically designated H2O.
Not made with natural rubber latex, DEHP or PVC.
The plastic container is a copolymer of ethylene and propylene formulated and developed for parenteral drugs. The copolymer contains no plasticizers. The safety of the plastic container has been confirmed by biological evaluation procedures. The material passes Class Vl testing as specified in the U.S. Pharmacopeia for Biological Tests — Plastic Containers.
The container/solution unit is a closed system and is not dependent upon entry of external air during administration. The container has two ports, one is for the intravenous administration set covered by a tamperproof barrier and the other is a blocked port. Refer to the DIRECTIONS FOR USE of the container to properly identify the ports.
No vapor barrier is necessary.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Magnesium (Mg++) is an important cofactor for enzymatic reactions and plays an important role in neurochemical transmission and muscular excitability.
Magnesium prevents or controls convulsions by blocking neuromuscular transmission and decreasing the amount of acetylcholine liberated at the end plate by the motor nerve impulse. Magnesium is said to have a depressant effect on the central nervous system, but it does not adversely affect the mother, fetus or neonate when used as directed in eclampsia or pre-eclampsia. Normal serum magnesium levels range from 1.3 to 2.1 mEq/liter.
As serum magnesium rises above 4 mEq/liter, the deep tendon reflexes are first decreased and then disappear as the serum level approaches 10 mEq/liter. At this level respiratory paralysis may occur. Heart block also may occur at this or lower serum levels of magnesium.
Magnesium acts peripherally to produce vasodilation. With low doses only flushing and sweating occur, but larger doses cause lowering of blood pressure. The central and peripheral effects of magnesium poisoning are antagonized to some extent by intravenous administration of calcium.
With intravenous administration the onset of anticonvulsant action is immediate and lasts about 30 minutes. Following intramuscular administration the onset of action occurs in about one hour and persists for three to four hours. Effective anticonvulsant serum levels range from 2.5 to 7.5 mEq/liter.
Pharmacokinetics:
Special Populations:
Renal Insufficiency:
Magnesium is excreted solely by the kidney. In patients with severe renal insufficiency, the dose should be lower and frequent serum magnesium levels must be obtained (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is indicated for the prevention and control of seizures in pre-eclampsia and eclampsia, respectively. When used judiciously it effectively prevents and controls the convulsions of eclampsia without producing deleterious depression of the central nervous system of the mother or infant. However, other effective drugs are available for this purpose.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
FETAL HARM: Continuous administration of magnesium sulfate beyond 5-7 days to pregnant women can lead to hypocalcemia and bone abnormalities in the developing fetus. These bone abnormalities include skeletal demineralization and osteopenia. In addition, cases of neonatal fracture have been reported. The shortest duration of treatment that can lead to fetal harm is not known. Magnesium sulfate should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. If magnesium sulfate is given for treatment of preterm labor, the woman should be informed that the efficacy and safety of such use have not been established and that use of magnesium sulfate beyond 5-7 days may cause fetal abnormalities.
Parenteral use in the presence of renal insufficiency may lead to magnesium intoxication.
-
PRECAUTIONS
Because magnesium is removed from the body solely by the kidneys, the drug should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment. Urine output should be maintained at a level of 100 mL every four hours. Monitoring serum magnesium levels and the patient’s clinical status is essential to avoid the consequences of overdosage in toxemia. Clinical indications of a safe dosage regimen include the presence of the patellar reflex (knee jerk) and absence of respiratory depression (approximately 16 breaths or more/minute). Serum magnesium levels usually sufficient to control convulsions range from 3 to 6 mg/100 mL (2.5 to 5 mEq/liter). The strength of the deep tendon reflexes begins to diminish when serum magnesium levels exceed 4 mEq/liter. Reflexes may be absent at 10 mEq magnesium/liter, where respiratory paralysis is a potential hazard. An injectable calcium salt should be immediately available to counteract the potential hazards of magnesium intoxication in eclampsia.
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection should be administered slowly to avoid producing hypermagnesemia.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Studies with Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential, mutagenic potential or effects on fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects:
See WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection, can cause fetal abnormalities when administered beyond 5-7 days to pregnant women.
There are retrospective epidemiological studies and case reports documenting fetal abnormalities such as hypocalcemia, skeletal demineralizations, osteopenia and other skeletal abnormalities with continuous maternal administration of magnesium sulfate for more than 5-7 days.1-12 Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed. If this drug is used during pregnancy the woman should be apprised of the potential harm to the fetus.
Nonteratogenic Effects:
When administered by continuous I.V. infusion (especially for more than 24 hours preceding delivery) to control convulsions in a toxemic woman, the newborn may show signs of magnesium toxicity, including neuromuscular or respiratory depression. (See OVERDOSAGE.)
Labor and Delivery:
Continuous administration of magnesium sulfate is an unapproved treatment for preterm labor. The safety and efficacy of such use have not been established. The administration of Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection outside of its approved indication in pregnant women should be by trained obstetrical personnel in a hospital setting with appropriate obstetrical care facilities.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The adverse effects of parenterally administered magnesium usually are the result of magnesium intoxication. These include flushing, sweating, hypotension, depressed reflexes, flaccid paralysis, hypothermia, circulatory collapse, cardiac and central nervous system depression proceeding to respiratory paralysis.
Hypocalcemia with signs of tetany secondary to magnesium sulfate therapy for eclampsia has been reported.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Magnesium intoxication is manifested by a sharp drop in blood pressure and respiratory paralysis. Disappearance of the patellar reflex is a useful clinical sign to detect the onset of magnesium intoxication. In the event of overdosage, artificial ventilation must be provided until a calcium salt can be injected I.V. to antagonize the effects of magnesium.
For Treatment of Overdose
Artificial respiration is often required. Intravenous calcium, 10 to 20 mL of a 5% solution (diluted if desirable with isotonic sodium chloride for injection) is used to counteract effects of hypermagnesemia. Subcutaneous physostigmine, 0.5 to 1 mg may be helpful.
Hypermagnesemia in the newborn may require resuscitation and assisted ventilation via endotracheal intubation or intermittent positive pressure ventilation as well as I.V. calcium.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is intended for intravenous use only. For the management of pre-eclampsia or eclampsia, intravenous infusions of dilute solutions of magnesium (1% to 8%) are often given in combination with intramuscular injections of 50% Magnesium Sulfate Injection, USP. Therefore, in the clinical conditions cited below, both forms of therapy are noted, as appropriate.
Continuous maternal administration of magnesium sulfate in pregnancy beyond 5-7 days can cause fetal abnormalities.
In Eclampsia
In severe pre-eclampsia or eclampsia, the total initial dose is 10 to 14 g of magnesium sulfate. To initiate therapy, 4 g of Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection may be administered intravenously. The rate of I.V. infusion should generally not exceed 150 mg/minute, or 3.75 mL of a 4% concentration (or its equivalent) per minute, except in severe eclampsia with seizures. Simultaneously, 4 to 5 g (32.5 to 40.6 mEq) of magnesium sulfate may be administered intramuscularly into each buttock using undiluted 50% Magnesium Sulfate Injection, USP. After the initial I.V. dose, some clinicians administer 1 to 2 g/hour by constant I.V. infusion.
Subsequent intramuscular doses of 4 to 5 g of magnesium sulfate may be injected into alternate buttocks every four hours, depending on the continuing presence of the patellar reflex, adequate respiratory function, and absence of signs of magnesium toxicity. Therapy should continue until paroxysms cease.
A serum magnesium level of 6 mg/100 mL is considered optimal for control of seizures. A total daily (24 hr) dose of 30 to 40 g magnesium sulfate should not be exceeded. In the presence of severe renal insufficiency, frequent serum magnesium concentrations must be obtained and the maximum dosage of magnesium sulfate is 20 g per 48 hours.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
Do not administer unless solution is clear. Discard unused portion.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Magnesium Sulfate in Water for Injection is supplied in 100 mL fill and 50 mL fill PAB® containers packaged 24 per case as follows:
- * As the heptahydrate.
- † Partial fill container 100 mL in 150 mL container.
- ‡ Partial fill container 50 mL in 100 mL container.
NDC REF Fill Volume Total
Magnesium
Sulfate*Total Magnesium
IonMagnesium Sulfate*
ConcentrationMagnesium
Ion
ConcentrationOsmolarity
(calc.)0264-4206-54 D4206-54 100 mL† 4 g 32.5 mEq 4% (40 mg/mL) 32.5 mEq/100 mL 325 mOsmol/Liter 0264-4204-52 D4204-52 50 mL‡ 2 g 16.25 mEq 4% (40 mg/mL) 16.25 mEq/50 mL 325 mOsmol/Liter 0264-4205-52 D4205-52 50 mL‡ 4 g 32.5 mEq 8% (80 mg/mL) 32.5 mEq/50 mL 649 mOsmol/Liter Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.] Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing.
-
REFERENCES
- Yokoyama K, Takahashi N, Yada Y. Prolonged maternal magnesium administration and bone metabolism in neonates. Early Human Dev. 2010; 86(3):187-91. Epub 2010 Mar 12.
- Wedig KE, Kogan J, Schorry EK et al. Skeletal demineralization and fractures caused by fetal magnesium toxicity. J Perinatol. 2006; 26(6):371-4.
- Nassar AH, Sakhel K, Maarouf H, et al. Adverse maternal and neonatal outcome of prolonged course of magnesium sulfate tocolysis. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scan. 2006; 85(9):1099-103.
- Malaeb SN, Rassi A, Haddad MC. Bone mineralization in newborns whose mothers received magnesium sulphate for tocolysis of premature labor. Pediatr Radiol. 2004; 34(5):384-6. Epub 2004 Feb 18.
- Matsuda Y, Maeda Y, Ito M, et al. Effect of magnesium sulfate treatment on neonatal bone abnormalities. Gynecol Obstet Invest.1997; 44(2):82-8.
- Schanler RJ, Smith LG, Burns PA. Effects of long-term maternal intravenous magnesium sulfate therapy on neonatal calcium metabolism and bone mineral content. Gynecol Obstet Invest. 1997; 43(4):236-41.
- Santi MD, Henry GW, Douglas GL. Magnesium sulfate treatment of preterm labor as a cause of abnormal neonatal bone mineralization. J Pediatr Orthop. 1994; 14(2):249-53.
- Holocomb WL, Shackelford GD, Petrie RH. Magnesium tocolysis and neonatal bone abnormalities: a controlled study. Obstet Gynecol. 1991; 78(4):611-4.
- Cumming WA, Thomas VJ. Hypermagnesemia: a cause of abnormal metaphyses in the neonate. Am J Roentgenol. 1989; 152(5):1071-2.
- Lamm CL, Norton KL, Murphy RJ. Congenital rickets associated with magnesium sulfate infusion for tocolysis. J Pediatr. 1988;113(6):1078-82.
- McGuinness GA, Weinstein MM, Cruikshank DP, et al. Effects of magnesium sulfate treatment on perinatal calcium metabolism. II. Neonatal responses. Obstet Gynecol. 1980; 56(5):595-600.
- Riaz M, Porat R, Brodsky NL, et al. The effect of maternal magnesium sulfate treatment on newborns: a prospective controlled study. J Perinatol. 1998; 18(6 pt 1):449-54.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Directions For Use of PAB® Container
CAUTION: DO NOT ADD SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICATION. WHENEVER POSSIBLE USE CENTRAL ROUTE.
Aseptic technique is required.
Before use, perform the following checks: Read the label. Ensure solution is the one ordered and is within the expiration date.
Inspect the solution in good light for cloudiness, haze or particulate matter; check the container for leakage or damage. Any container which is suspect should not be used.
Use only if solution is clear and container and seals are intact. Single dose plastic container. Discard unused portion. Consult Package Insert for complete product information.
WARNING: DO NOT USE PLASTIC CONTAINER IN SERIES CONNECTION.
This solution is intended for intravenous administration using sterile equipment. It is recommended that intravenous administration apparatus be replaced at least once every 24 hours.
-
Identify Two Ports (See Figure A).
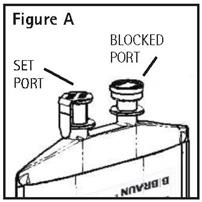
-
To Attach Administration Set
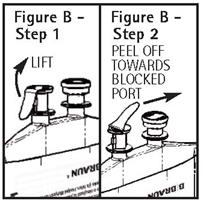
To aseptically remove the set port closure: hold container below the set port and grasp the foil tab between the thumb and forefinger then pull the tab in two steps as shown in Figure B Steps 1 and 2.
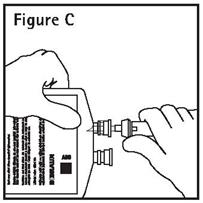
- Push spike through the diaphragm of the port (See Figure C). Hang container using hole on the lower flap. Prime set in accordance with the Directions for Use provided with the set in use.
PAB® containers can be safely transported in a standard 6-inch carrier through a pneumatic tube system that is well maintained and running properly.
-
Identify Two Ports (See Figure A).
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 0264-4204-52
Magnesium Sulfate
In Water for Injection
2 g/50 mL (40 mg/mL)
(0.325 mEq Mg++/mL)2 g Total
50 mL PAB® Container
Each 50 mL contains Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate 2 g (equivalent to 16.25 mEq
Magnesium) in Water for Injection. May contain Sulfuric Acid and/or Sodium
Hydroxide for pH adjustment.pH 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5); 325 mOsmol/liter (Calc.)
Single dose container. Discard unused portion. For Intravenous Use Only. Usual
dosage: See prescribing information. Sterile, nonpyrogenic. Use only if solution
is clear and container is undamaged. Must not be used in series connections.CAUTION: DO NOT ADD SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICATION. WHENEVER
POSSIBLE USE CENTRAL ROUTE.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between
15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing.REF D4204-52
Not made with natural rubber latex, DEHP or PVC.
Rx only
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524 USA
1-800-227-2862. Prepared in USA.
API from USA or Czech Republic.
Y94-003-507 LD-476-2
LOT
EXP

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC 0264-4205-52
Magnesium Sulfate
In Water for Injection
4 g/50 mL (80 mg/mL)
(0.65 mEq Mg++/mL)
4 g Total
50 mL PAB® Container
Each 50 mL contains Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate 4 g (equivalent to 32.5 mEq
Magnesium) in Water for Injection. May contain Sulfuric Acid and/or Sodium
Hydroxide for pH adjustment.pH 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5); 649 mOsmol/liter (Calc.)
Single dose container. Discard unused portion. For Intravenous Use Only. Usual
dosage: See prescribing information. Sterile, nonpyrogenic. Use only if solution
is clear and container is undamaged. Must not be used in series connections.CAUTION: DO NOT ADD SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICATION. WHENEVER
POSSIBLE USE CENTRAL ROUTE.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between
15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing.REF D4205-52
Not made with natural rubber latex, DEHP or PVC.
Rx only
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524 USA
1-800-227-2862. Prepared in USA.
API from USA or Czech Republic.
Y94-003-508 LD-477-2
LOT
EXP

-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 0264-4206-54
Magnesium Sulfate
In Water for Injection
4 g/100 mL (40 mg/mL)
(0.325 mEq Mg++/mL)
4 g Total
100 mL PAB® Container
Each 100 mL contains Magnesium Sulfate Heptahydrate 4 g
(equivalent to 32.5 mEq Magnesium) in Water for Injection.
May contain Sulfuric Acid and/or Sodium Hydroxide for pH adjustment.pH 4.5 (3.5 to 6.5); 325 mOsmol/liter (Calc.)
Single dose container. Discard unused portion. For Intravenous
Use Only. Usual dosage: See prescribing information.
Sterile, nonpyrogenic. Use only if solution is clear and container
is undamaged. Must not be used in series connections.CAUTION: DO NOT ADD SUPPLEMENTARY MEDICATION.
WHENEVER POSSIBLE USE CENTRAL ROUTE.Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted between
15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Avoid excessive heat. Protect from freezing.REF D4206-54
Not made with natural rubber latex, DEHP or PVC.
Rx only
B. Braun Medical Inc.
Bethlehem, PA 18018-3524 USA
1-800-227-2862
Prepared in USA.
API from USA or Czech Republic.Y94-003-509 LD-478-2
LOT
EXP

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
MAGNESIUM SULFATE IN WATER
magnesium sulfate heptahydrate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-4204 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE (UNII: SK47B8698T) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 2 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SULFURIC ACID (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-4204-52 24 in 1 CASE 04/26/2021 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA207967 04/26/2021 MAGNESIUM SULFATE IN WATER
magnesium sulfate heptahydrate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-4205 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE (UNII: SK47B8698T) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 4 g in 50 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SULFURIC ACID (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-4205-52 24 in 1 CASE 04/26/2021 1 50 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA207967 04/26/2021 MAGNESIUM SULFATE IN WATER
magnesium sulfate heptahydrate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0264-4206 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE (UNII: SK47B8698T) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM SULFATE HEPTAHYDRATE 4 g in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SULFURIC ACID (UNII: O40UQP6WCF) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0264-4206-54 24 in 1 CASE 04/26/2021 1 100 mL in 1 CONTAINER; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA207967 04/26/2021 Labeler - B. Braun Medical Inc. (002397347)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.