XPOVIO- selinexor tablet, film coated
XPOVIO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
XPOVIO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use XPOVIO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for XPOVIO.
XPOVIO™ (selinexor) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2019INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XPOVIO is a nuclear export inhibitor indicated in combination with dexamethasone for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who have received at least four prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least two proteasome inhibitors, at least two immunomodulatory agents, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial (1).
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 20 mg (3).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4).
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Thrombocytopenia: Monitor platelet counts at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Manage with dose interruption, reduction, and supportive care (2.4, 5.1).
- Neutropenia: Monitor neutrophil counts at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Manage with dose interruption and/or reduction and granulocyte colony-stimulating factors (G-CSFs) (2.4, 5.2).
- Gastrointestinal Toxicity: Nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia, and weight loss may occur. Provide antiemetic prophylaxis. Manage with dose interruption and/or reduction, antiemetics, and supportive care (2.4, 5.3).
- Hyponatremia: Monitor serum sodium levels at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Correct for concurrent hyperglycemia and high serum paraprotein levels (2.4, 5.4).
- Infections: Monitor for signs/symptoms of infection and treat promptly (5.2, 5.5).
- Neurological Toxicity: Avoid taking XPOVIO with other medications that may cause dizziness or confusion. Avoid situations where dizziness or confusional state may be a problem. Optimize hydration status, blood counts and concomitant medications to avoid dizziness or confusion (5.6).
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise females of reproductive potential, and males with a female partner of reproductive potential, of the potential risk to a fetus and use of effective contraception (5.7, 8.1, 8.3).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥20%) are thrombocytopenia, fatigue, nausea, anemia, decreased appetite, decreased weight, diarrhea, vomiting, hyponatremia, neutropenia, leukopenia, constipation, dyspnea, and upper respiratory tract infection (6.1).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. at 1-888-209-9326 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 7/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
2.2 Recommended Monitoring for Safety
2.3 Recommended Concomitant Treatments
2.4 Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombocytopenia
5.2 Neutropenia
5.3 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
5.4 Hyponatremia
5.5 Infections
5.6 Neurological Toxicity
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
XPOVIO is indicated in combination with dexamethasone for the treatment of adult patients with relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma (RRMM) who have received at least four prior therapies and whose disease is refractory to at least two proteasome inhibitors, at least two immunomodulatory agents, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
This indication is approved under accelerated approval based on response rate. Continued approval for this indication may be contingent upon verification and description of clinical benefit in a confirmatory trial.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
The recommended starting dosage of XPOVIO is 80 mg (four 20 mg tablets) taken orally on Days 1 and 3 of each week until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
The recommended starting dosage of dexamethasone is 20 mg taken orally with each dose of XPOVIO on Days 1 and 3 of each week. For additional information regarding the administration of dexamethasone, refer to its prescribing information.
Each XPOVIO dose should be taken at approximately the same time of day, and each tablet should be swallowed whole with water. Do not break, chew, crush, or divide the tablets.
If a dose of XPOVIO is missed or delayed, instruct patients to take their next dose at the next regularly scheduled time. If a patient vomits a dose of XPOVIO, the patient should not repeat the dose and the patient should take the next dose on the next regularly scheduled day.
2.2 Recommended Monitoring for Safety
Monitor complete blood count (CBC), standard blood chemistry, and body weight at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated. Monitor more frequently during the first two months of treatment [see Warning and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, and 5.4)].
2.3 Recommended Concomitant Treatments
Advise patients to maintain adequate fluid and caloric intake throughout treatment.
Consider intravenous hydration for patients at risk of dehydration.
Provide prophylactic concomitant treatment with a 5-HT3 antagonist and/or other anti-nausea agents prior to and during treatment with XPOVIO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
2.4 Dosage Modification for Adverse Reactions
Recommended XPOVIO dosage reductions and dosage modifications for adverse reactions are presented in Table 1 and Table 2, respectively.
Refer to the dexamethasone prescribing information for dexamethasone dosage modifications due to adverse reactions.
Table 1: XPOVIO Dosage Reduction Steps for Adverse Reactions Recommended Starting Dosage First Reduction Second Reduction Third Reduction Discontinue 80 mg
Days 1 and 3 of each week
(160 mg total per week)100 mg
once weekly80 mg
once weekly60 mg
once weeklyTable 2: XPOVIO Dosage Modification Guidelines for Adverse Reactions a. National Cancer Institute Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (NCI CTCAE) version 4.03.
Adverse Reactiona Occurrence Action Hematologic Adverse Reactions Thrombocytopenia Platelet count 25,000 to less than 75,000/mcL Any - Reduce XPOVIO by 1 dose level (see Table 1).
Platelet count 25,000 to less than 75,000/mcL with concurrent bleeding Any - Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1), after bleeding has resolved.
Platelet count less than 25,000/mcL Any
- Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor until platelet count returns to at least 50,000/mcL.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Neutropenia Absolute neutrophil count of 0.5 to 1.0 x 109/L without fever Any - Reduce XPOVIO by 1 dose level (see Table 1).
Absolute neutrophil count less than 0.5 x 109/L
OR febrile neutropeniaAny
- Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor until neutrophil counts return to 1.0 x 109/L or higher.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Anemia Hemoglobin less than 8.0 g/dL Any - Reduce XPOVIO by 1 dose level (see Table 1).
- Administer blood transfusions and/or other treatments per clinical guidelines.
Life-threatening consequences
(urgent intervention indicated)Any - Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor hemoglobin until levels return to 8 g/dL or higher.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
- Administer blood transfusions and/or other treatments per clinical guidelines.
Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions Hyponatremia Sodium level 130 mmol/L or less Any - Interrupt XPOVIO and provide appropriate supportive care.
- Monitor until sodium levels return to 130 mmol/L or higher.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Fatigue Grade 2 lasting greater than 7 days
OR Grade 3Any
- Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor until fatigue resolves to Grade 1 or baseline.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Nausea and Vomiting Grade 1 or 2 nausea (oral intake decreased without significant weight loss, dehydration or malnutrition)
OR Grade 1 or 2 vomiting (5 or fewer episodes per day)Any - Maintain XPOVIO and initiate additional anti-nausea medications.
Grade 3 nausea (inadequate oral caloric or fluid intake)
OR Grade 3 or higher vomiting (6 or more episodes per day)Any - Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor until nausea or vomiting has resolved to Grade 2 or lower or baseline.
- Initiate additional anti-nausea medications.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Diarrhea Grade 2 (increase of 4 to 6 stools per day over baseline) 1st - Maintain XPOVIO and institute supportive care.
2nd and subsequent - Reduce XPOVIO by 1 dose level (see Table 1).
- Institute supportive care.
Grade 3 or higher (increase of 7 stools or more per day over baseline; hospitalization indicated) Any
- Interrupt XPOVIO and institute supportive care.
- Monitor until diarrhea resolves to Grade 2 or lower.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Weight Loss and Anorexia Weight loss of 10% to less than 20% OR anorexia associated with significant weight loss or malnutrition Any - Interrupt XPOVIO and institute supportive care.
- Monitor until weight returns to more than 90% of baseline weight.
- Restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
Other Non-Hematologic Adverse Reactions Grade 3 or 4 (life threatening) Any - Interrupt XPOVIO.
- Monitor until resolved to Grade 2 or lower, restart XPOVIO at 1 dose level lower (see Table 1).
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Thrombocytopenia
XPOVIO can cause thrombocytopenia, leading to potentially fatal hemorrhage. Thrombocytopenia was reported as an adverse reaction in 74% of patients, and severe (Grade 3-4) thrombocytopenia occurred in 61% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of the first event was 22 days. Bleeding occurred in 23% of patients with thrombocytopenia, clinically significant bleeding occurred in 5% of patients with thrombocytopenia and fatal hemorrhage occurred in <1% of patients.
Monitor platelet counts at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Monitor more frequently during the first two months of treatment. Institute platelet transfusion and/or other treatments as clinically indicated. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of bleeding and evaluate promptly. Interrupt and/or reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Neutropenia
XPOVIO can cause neutropenia, potentially increasing the risk of infection. Neutropenia was reported as an adverse reaction in 34% of patients, and severe (Grade 3-4) neutropenia occurred in 21% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of the first event was 25 days. Febrile neutropenia was reported in 3% of patients.
Obtain neutrophil counts at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Monitor more frequently during the first two months of treatment. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of concomitant infection and evaluate promptly. Consider supportive measures including antimicrobials for signs of infection and use of growth factors (e.g., G-CSF). Interrupt and/or reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.3 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Gastrointestinal toxicities occurred in patients treated with XPOVIO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Nausea/Vomiting
Nausea was reported as an adverse reaction in 72% of patients, and Grade 3 nausea occurred in 9% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of the first nausea event was 3 days.
Vomiting was reported in 41% of patients, and Grade 3 vomiting occurred in 4% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of the first vomiting event was 5 days.
Provide prophylactic 5-HT3 antagonists and/or other anti-nausea agents, prior to and during treatment with XPOVIO. Manage nausea/vomiting by dose interruption, reduction, and/or discontinuation. Administer intravenous fluids and replace electrolytes to prevent dehydration in patients at risk. Use additional anti-nausea medications as clinically indicated [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Diarrhea
Diarrhea was reported as an adverse reaction in 44% of patients, and Grade 3 diarrhea occurred in 6% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of diarrhea was 15 days.
Manage diarrhea by dose modifications and/or standard anti-diarrheal agents; administer intravenous fluids to prevent dehydration in patients at risk [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Anorexia/Weight Loss
Anorexia was reported as an adverse reaction in 53% of patients, and Grade 3 anorexia occurred in 5% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of anorexia was 8 days.
Weight loss was reported as an adverse reaction in 47% of patients, and Grade 3 weight loss occurred in 1% of patients treated with XPOVIO. The median time to onset of weight loss was 15 days.
Monitor patient weight at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Monitor more frequently during the first two months of treatment. Manage anorexia and weight loss with dose modifications, appetite stimulants, and nutritional support [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Hyponatremia
XPOVIO can cause hyponatremia; 39% of patients treated with XPOVIO experienced hyponatremia, 22% of patients experienced Grade 3 or 4 hyponatremia. The median time to onset of the first event was 8 days.
Monitor sodium level at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Monitor more frequently during the first two months of treatment. Correct sodium levels for concurrent hyperglycemia (serum glucose >150 mg/dL) and high serum paraprotein levels. Treat hyponatremia per clinical guidelines (intravenous saline and/or salt tablets), including dietary review. Interrupt and/or reduce dose, or permanently discontinue based on severity of adverse reaction [see Dosage and Administration (2.4) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.5 Infections
In patients receiving XPOVIO, 52% of patients experienced any grade of infection. Upper respiratory tract infection of any grade occurred in 21%, pneumonia in 13%, and sepsis in 6% of patients. Grade ≥3 infections were reported in 25% of patients, and deaths resulting from an infection occurred in 4% of patients. The most commonly reported Grade ≥3 infections were pneumonia in 9% of patients, followed by sepsis in 6%. The median time to onset was 54 days for pneumonia and 42 days for sepsis. Most infections were not associated with neutropenia and were caused by non-opportunistic organisms [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.6 Neurological Toxicity
Neurological toxicities occurred in patients treated with XPOVIO [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Neurological adverse reactions including dizziness, syncope, depressed level of consciousness, and mental status changes (including delirium and confusional state) occurred in 30% of patients, and severe events (Grade 3-4) occurred in 9% of patients treated with XPOVIO. Median time to the first event was 15 days.
Optimize hydration status, hemoglobin level, and concomitant medications to avoid exacerbating dizziness or mental status changes.
5.7 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on data from animal studies and its mechanism of action, XPOVIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Selinexor administration to pregnant animals during organogenesis resulted in structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at exposures below those occurring clinically at the recommended dose.
Advise pregnant women of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential and males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described in detail in other labeling sections:
- Thrombocytopenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Neutropenia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Gastrointestinal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- Hyponatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
- Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
- Neurological Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The data described below reflect exposure to XPOVIO plus dexamethasone in 202 patients with RRMM who received XPOVIO 80 mg in combination with dexamethasone 20 mg on Days 1 and 3 of every week.
The median duration of XPOVIO treatment was 8 weeks (range: 1 to 60 weeks). The median dose was 115.4 mg (range: 36 to 200 mg) per week.
The treatment discontinuation rate due to adverse reactions was 27%; 53% of patients had a reduction in the XPOVIO dose, and 65.3% had the dose of XPOVIO interrupted. The most frequent adverse reactions requiring permanent discontinuation in 4% or greater of patients who received XPOVIO included fatigue, nausea, and thrombocytopenia. The rate of fatal adverse reactions was 8.9%.
The population had a median age of 64 years (range: 35 to 86 years), 54% were male, and the majority (73%) were White (17% were Black or African American).
Table 3 summarizes the most common (≥10% of patients) adverse reactions reported in patients with RRMM who received XPOVIO and dexamethasone.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions with XPOVIO 80 mg and Dexamethasone 20 mg Administered Twice Weekly a. Thrombocytopenia includes thrombocytopenia and platelet count decreased.
b. Fatigue includes fatigue and asthenia.
c. Anemia includes anemia and hematocrit decreased.
d. Neutropenia includes neutropenia and neutrophil count decreased.
e. Dyspnea includes dyspnea, dyspnea exertional, and dyspnea at rest.
f. Upper respiratory tract infection includes upper respiratory tract infection, respiratory tract infection, pharyngitis, nasopharyngitis, bronchitis, bronchiolitis, respiratory syncytial virus infection, parainfluenza virus infection, rhinitis, rhinovirus infection, and adenovirus infection.
g. Cough includes cough, productive cough, and upper-airway cough syndrome.
h. Mental status changes includes mental status changes, confusional state, and delirium.
i. Hypercreatininemia includes hypercreatininemia and hypercreatinemia.
j. Pneumonia includes pneumonia, atypical pneumonia, lung infection, lower respiratory tract infection, pneumocystis jirovecii pneumonia, pneumonia aspiration, pneumonia influenzal, and pneumonia viral.
k. Includes fatal event.
Adverse Reaction Any Grade
(N = 202)
n (%)Grade ≥3
(N = 202)
n (%)Thrombocytopeniaa 149 (74) 124 (61) Fatigueb 147 (73) 44 (22) Nausea 146 (72) 18 (9) Anemiac 119 (59) 81 (40) Decreased appetite 108 (53) 9 (4.5) Weight decreased 95 (47) 1 (0.5) Diarrhea 89 (44) 13 (6) Vomiting 82 (41) 7 (3.5) Hyponatremia 78 (39) 44 (22) Neutropeniad 68 (34) 43 (21) Leukopenia 57 (28) 23 (11) Constipation 50 (25) 3 (1.5) Dyspneae 48 (24) 7 (3.5)k Upper respiratory tract infectionf 42 (21) 6 (3) Coughg 33 (16) 0 Mental status changesh 33 (16) 14 (7) Pyrexia 32 (16) 1 (0.5) Hyperglycemia 31 (15) 15 (7) Dizziness 30 (15) 0 Insomnia 30 (15) 4 (2) Lymphopenia 30 (15) 20 (10) Dehydration 28 (14) 7 (3.5) Hypercreatininemiai 28 (14) 4 (2) Pneumoniaj 26 (13) 18 (9)k Epistaxis 25 (12) 1 (0.5) Hypokalemia 25 (12) 7 (3.5) Dysgeusia 22 (11) 0 Vision blurred 21 (10) 1 (0.5) Headache 20 (10) 0 -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on findings in animal studies and its mechanism of action [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)], XPOVIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. There are no available data in pregnant women to inform the drug-associated risk. In animal reproduction studies, administration of selinexor to pregnant rats during organogenesis resulted in structural abnormalities and alterations to growth at exposures that were below those occurring clinically at the recommended dose (see Data). Advise pregnant women of the risks to a fetus.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal data
In an embryo-fetal development study in pregnant rats, daily oral administration of selinexor at 0, 0.25, 0.75, or 2 mg/kg throughout organogenesis caused incomplete or delayed ossification, skeletal variations, and reduced fetal weight compared with controls at a dose of 0.75 mg/kg (approximately 0.08-fold of human area under the curve [AUC] at the recommended dose). Malformations were observed at 2 mg/kg, including microphthalmia, fetal edema, malpositioned kidney, and persistent truncus arteriosus.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of selinexor or its metabolites in human milk, or their effects on the breastfed child or milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the last dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating XPOVIO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
XPOVIO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Infertility
Females and Males
Based on findings in animals, XPOVIO may impair fertility in females and males of reproductive potential [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of XPOVIO have not been established in pediatric patients.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 202 patients with RRMM who received XPOVIO, 49% were 65 years of age and over, while 11% were 75 years of age and over. No overall difference in effectiveness was observed in patients over 65 years of age, including patients over 75 years of age, when compared with younger patients. When comparing patients 75 years of age and older to younger patients, older patients had a higher incidence of discontinuation due to an adverse reaction (44% vs 27%), higher incidence of serious adverse reactions (70% vs 58%), and higher incidence of fatal adverse reactions (17% vs 9%).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
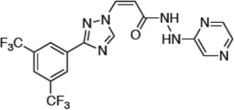
XPOVIO (selinexor) is an orally available nuclear export inhibitor.
Selinexor is (2Z)-3-{3-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-yl}-N'-(pyrazin-2-yl)prop-2-enehydrazide. It is a white to off-white powder and has the molecular formula C17H11F6N7O and a molecular mass of 443.31 g/mol.
The molecular structure is shown below:
Each XPOVIO (selinexor) tablet contains 20 mg of selinexor as the active ingredient.
XPOVIO tablets are blue, round, bi-convex, film-coated tablets with “K20” debossed on one side and nothing on the other side. The inactive ingredients are colloidal silicon dioxide, croscarmellose sodium, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, Opadry 200 clear, Opadry II blue, povidone K30, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
In nonclinical studies, selinexor reversibly inhibits nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins (TSPs), growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins by blocking exportin 1 (XPO1). XPO1 inhibition by selinexor leads to accumulation of TSPs in the nucleus, reductions in several oncoproteins, such as c-myc and cyclin D1, cell cycle arrest, and apoptosis of cancer cells. Selinexor demonstrated pro-apoptotic activity in vitro in multiple myeloma cell lines and patient tumor samples, and in murine xenograft models.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
XPOVIO exposure-response relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic responses are unknown.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
The effect of multiple doses of XPOVIO, up to 175 mg (2.2 times the approved recommended dose) twice weekly, on the QTc interval was evaluated in patients with heavily pretreated hematologic malignancies. XPOVIO had no large effect (i.e. no greater than 20 ms) on QTc interval at the therapeutic dose level.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following a single-dose administration of XPOVIO 80 mg, the mean (standard deviation) peak plasma concentration (Cmax) was 680 (124) ng/mL and the mean AUC was 5386 (1116) ngh/mL. Selinexor Cmax and AUC increased proportionally over doses from 3 mg/m2 to 85 mg/m2 (0.06 to 1.8 times the approved recommended dose based on 1.7 m2 body surface area). No clinically relevant accumulation at steady state was observed.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution of selinexor is 125 L in patients with cancer. The protein binding of selinexor is 95%.
Elimination
Following a single dose of XPOVIO, the mean half-life is 6 to 8 hours. The apparent total clearance of selinexor is 17.9 L/h in patients with cancer.
Metabolism
Selinexor is metabolized by CYP3A4, multiple UDP-glucuronosyltransferases (UGTs) and glutathione S-transferases (GSTs).
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of selinexor were observed based on age (18 to 94 years old), sex, ethnicity, mild to severe renal impairment (CLCR: 15 to 89 mL/min, estimated by the Cockcroft-Gault equation). The effect of end-stage renal disease (CLCR <15 mL/min) or hemodialysis on selinexor pharmacokinetics is unknown. Mild hepatic impairment had no clinically significant effect on the pharmacokinetics of selinexor. The effect of moderate and severe hepatic impairment on selinexor pharmacokinetics is unknown.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity studies have not been conducted with selinexor.
Selinexor was not mutagenic in vitro in a bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay and was not clastogenic in either the in vitro cytogenetic assay in human lymphocytes or in the in vivo rat micronucleus assay.
Fertility studies in animals have not been conducted with selinexor. In repeat-dose oral toxicity studies, selinexor was administered for up to 13 weeks in rats and monkeys. Reduced sperm, spermatids, and germ cells in epididymides and testes were observed in rats at ≥1 mg/kg, decreased ovarian follicles were observed in rats at ≥2 mg/kg, and single cell necrosis of testes was observed in monkeys at ≥1.5 mg/kg. These dose levels resulted in systemic exposures approximately 0.11, 0.28, and 0.53 times, respectively, the exposure (AUClast) in humans at the recommended human dose of 80 mg.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Relapsed Refractory Multiple Myeloma
The efficacy of XPOVIO plus dexamethasone was evaluated in STORM (KCP-330-012; NCT02336815). STORM was a multicenter, single-arm, open-label study of patients with RRMM. STORM Part 2 included 122 patients with RRMM who had previously received three or more anti-myeloma treatment regimens including an alkylating agent, glucocorticoids, bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody; and whose myeloma was documented to be refractory to glucocorticoids, a proteasome inhibitor, an immunomodulatory agent, an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody, and to the last line of therapy.
In STORM Part 2, a total of 122 patients were treated with XPOVIO (80 mg) in combination with dexamethasone (20 mg) on Days 1 and 3 of every week. Eighty-three patients had RRMM that was refractory to bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and daratumumab. Baseline patient demographics and disease characteristics of these 83 patients are summarized in Table 4 and Table 5, respectively. Treatment continued until disease progression, death, or unacceptable toxicity.
The major efficacy outcome measure was overall response rate (ORR), as assessed by an Independent Review Committee (IRC) based on the International Myeloma Working Group (IMWG) Uniform Response Criteria for Multiple Myeloma. The approval of XPOVIO was based upon the efficacy and safety in a prespecified subgroup analysis of the 83 patients whose disease was refractory to bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and daratumumab, as the benefit-risk ratio appeared to be greater in this more heavily pretreated population than in the overall trial population. Overall response rate results are presented in Table 6. The median time to first response was 4 weeks (range: 1 to 10 weeks). The median duration of response was 3.8 months (95% CI: 2.3, not estimable).
Table 4: Baseline Demographics (STORM) Demographic STORM
(N = 83)Median age, years (range) 65 (40, 86) Age category, n (%) <65 years 40 (48) 65 – 74 years 31 (37) ≥75 years 12 (15) Sex, n (%) Male 51 (61) Female 32 (39) Race, n (%) White 58 (70) Black or African American 13 (16) Asian 2 (2) Native Hawaiian or other Pacific Islander 1 (1) Other 6 (7) Missing 3 (4) Table 5: Disease Characteristics (STORM) a. Includes any of del(17p)/p53, t(14; 16), t(4; 14), 1q21.
Parameter STORM
(N = 83)Median years from diagnosis to start of study treatment (range) 7 (1, 23) Prior treatment regimens, median (range) 8 (4, 18) Documented refractory status, n (%) Lenalidomide 83 (100) Pomalidomide 83 (100) Bortezomib 83 (100) Carfilzomib 83 (100) Daratumumab 83 (100) Documented refractory status to specific combinations, n (%) Bortezomib, carfilzomib, lenalidomide, pomalidomide, and daratumumab 83 (100) Daratumumab in any combination 57 (69) Daratumumab as single agent (+/- dexamethasone) 26 (31) Previous stem cell transplant, n (%) 67 (81) Revised International Staging System at Baseline, n (%) I 10 (12) II 56 (68) III 17 (21) Unknown 0 High-risk cytogeneticsa, n (%) 47 (57) Table 6: Overall Response (STORM) as Assessed by the IRC per IMWG Criteria a. Includes sCR + CR + VGPR + PR.
Response STORM
(N = 83)Overall Response Rate (ORR)a, n (%) 21 (25.3) 95% CI 16.4, 36 Stringent Complete Response (sCR) 1 (1) Complete Response (CR) 0 Very Good Partial Response (VGPR) 4 (5) Partial Response (PR) 16 (19) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
XPOVIO (selinexor) are blue, round, bi-convex, and film-coated 20 mg tablets with “K20” debossed on one side and nothing on the other side. Tablets are packaged in a child-resistant blister pack. Four blister packs are supplied per carton. The following four dose presentations are available:
Weekly dose Strength per tablet Carton Blister Pack NDC 80 mg twice weekly 20 mg 4 blister packs (32 tablets total in the carton) Each blister has eight 20 mg tablets Outer carton NDC: 72237-101-04
Blister pack NDC: 72237-101-14100 mg once weekly 20 mg 4 blister packs (20 tablets total in the carton) Each blister has five 20 mg tablets Outer carton NDC: 72237-101-05
Blister pack NDC: 72237-101-1580 mg once weekly 20 mg 4 blister packs (16 tablets total in the carton) Each blister has four 20 mg tablets Outer carton NDC: 72237-101-02
Blister pack NDC: 72237-101-1260 mg once weekly 20 mg 4 blister packs (12 tablets total in the carton) Each blister has three 20 mg tablets Outer carton NDC: 72237-101-01
Blister pack NDC: 72237-101-11 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide).
Dosing Instructions [see Dosage and Administration (2)]:
- Instruct patients to take XPOVIO exactly as prescribed.
- Advise patients to swallow the tablet whole with water. The tablet should not be broken, chewed, crushed, or divided.
- If a patient misses a dose, advise them to take their next dose at its regularly scheduled time. If a patient vomits or misses a dose of XPOVIO, advise them to take the next dose on the next regularly scheduled day.
- Advise patients that XPOVIO comes in a child-resistant blister pack.
- Advise patients to take their prescribed dexamethasone and prophylactic anti-nausea medications exactly as prescribed [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
- Advise patients that blood tests and body weight will be monitored at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated, with more frequent monitoring during the first two months of treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
- Advise patients to maintain appropriate fluid and caloric intake throughout their treatment [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Hematologic Adverse Reactions
Thrombocytopenia
Advise patients that they may develop low platelet counts (thrombocytopenia). Symptoms of thrombocytopenia may include bleeding and easy bruising. Advise patients that platelet counts will be monitored at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated, with more frequent monitoring during the first 2 months of treatment. Advise patients to report signs of bleeding right away [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Anemia
Advise patients that they may develop anemia. Symptoms of anemia may include fatigue and shortness of breath. Advise patients to report signs or symptoms of anemia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Neutropenia
Advise patients that they may develop low neutrophil counts which may increase their susceptibility to infection [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Advise patients that neutrophil counts will be monitored at baseline, during treatment, and as clinically indicated, with more frequent monitoring during the first 2 months of treatment.
Gastrointestinal Adverse Reactions
Advise patients they may experience nausea/vomiting or diarrhea and to contact their physician if these adverse reactions occur or persist [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Anorexia/Weight Loss
Advise patients that they may experience weight loss or decreased appetite. Advise patients to report decreased appetite and weight loss [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Confusional State and Dizziness
Advise patients that they may experience confusion and dizziness. Advise patients not to operate motorized vehicles until they know how XPOVIO affects their abilities. Advise patients to report symptoms of neurological toxicity right away. Advise patients to avoid driving or operating machinery until they know how XPOVIO affects their abilities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Hyponatremia
Advise patients that they may develop low sodium levels (hyponatremia). Most cases of hyponatremia were not associated with specific symptoms. Advise patients that levels of sodium will be monitored at baseline and during treatment as clinically indicated, with more frequent monitoring during the first two months of treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Infections
Advise patients of the possibility of serious infections. Instruct patients to report infection-related signs or symptoms (e.g., chills, fever) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females to contact their healthcare provider if they become pregnant, or if pregnancy is suspected, during treatment with XPOVIO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Advise females of reproductive potential and males with a female partner of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the final dose of XPOVIO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Lactation
Advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with XPOVIO and for 1 week after the final dose of XPOVIO [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Concomitant Medications
Advise patients to take 5-HT3 antagonist prophylactic treatment and/or other anti-nausea agents prior to and during treatment with XPOVIO [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Advise patients to speak with their physician about other medications they are currently taking and before starting any new medication.
Manufactured for and marketed by: Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc., 85 Wells Avenue, Newton, MA, 02459.
XPOVIO is a trademark of Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.
©2019 Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc.
For more information, call 1-888-209-9326 or go to www.XPOVIO.com. -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
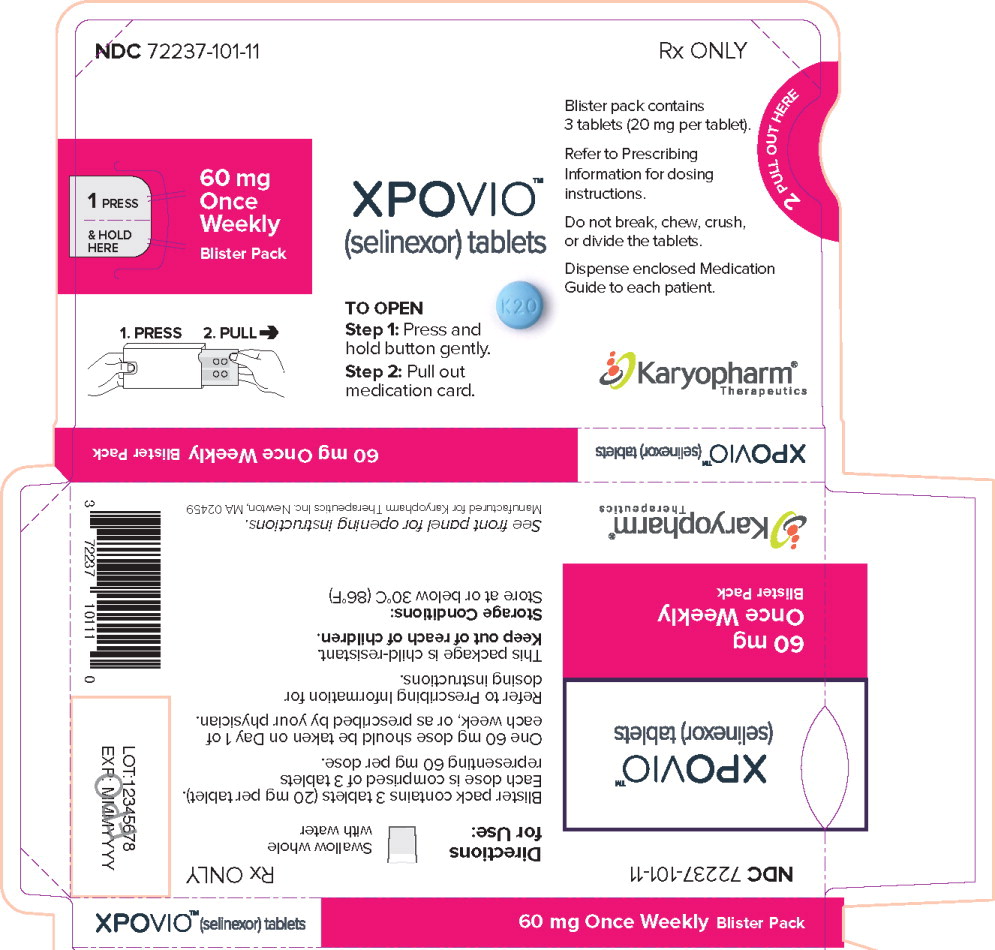
Principal Display Panel – 60 mg Carton Label
NDC: 72237-101-01
Rx ONLY
60 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister PacksXPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
Contents: 4 individual weekly
blister packs. Each blister pack
contains 3 tablets (20 mg per tablet).12 film-coated tablets
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 60 mg Blister Sleeve Label
NDC 72237-101-11
Rx ONLY
1 PRESS
& HOLD
HERE60 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister Pack1. PRESS 2. PULL
XPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
TO OPEN
Step 1: Press and
hold button gently.Step 2: Pull out
medication card.Blister pack contains
3 tablets (20 mg per tablet).Refer to Prescribing
Information for dosing
instructions.Do not break, chew, crush,
or divide the tablets.Dispense enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
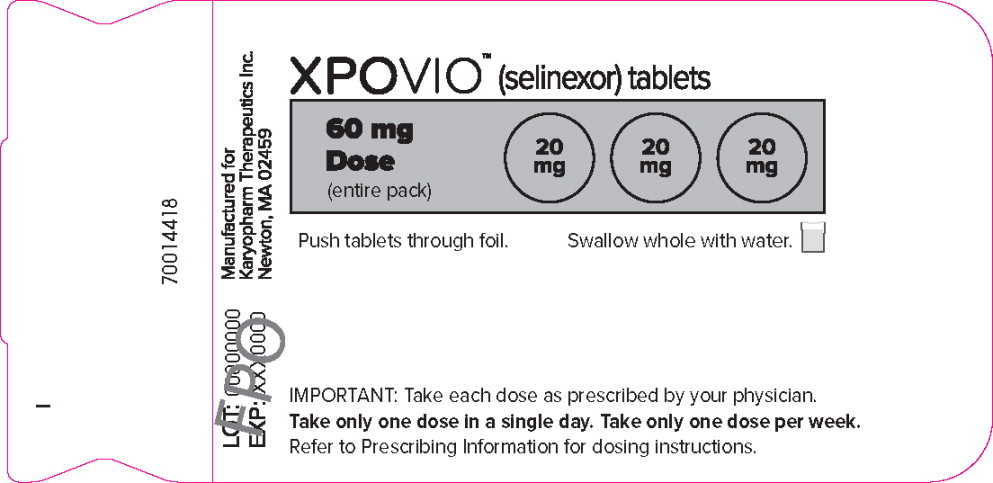
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 60 mg Blister Pack Label
XPOVIO™(selinexor tablets)
60 mg
Dose
(entire pack)Push tablets through foil.
Swallow whole with water.
IMPORTANT: Take each dose as prescribed by your physician.
Take only one dose in a single day. Take only one dose per week.
Refer to Prescribing Information for dosing instructions.
-
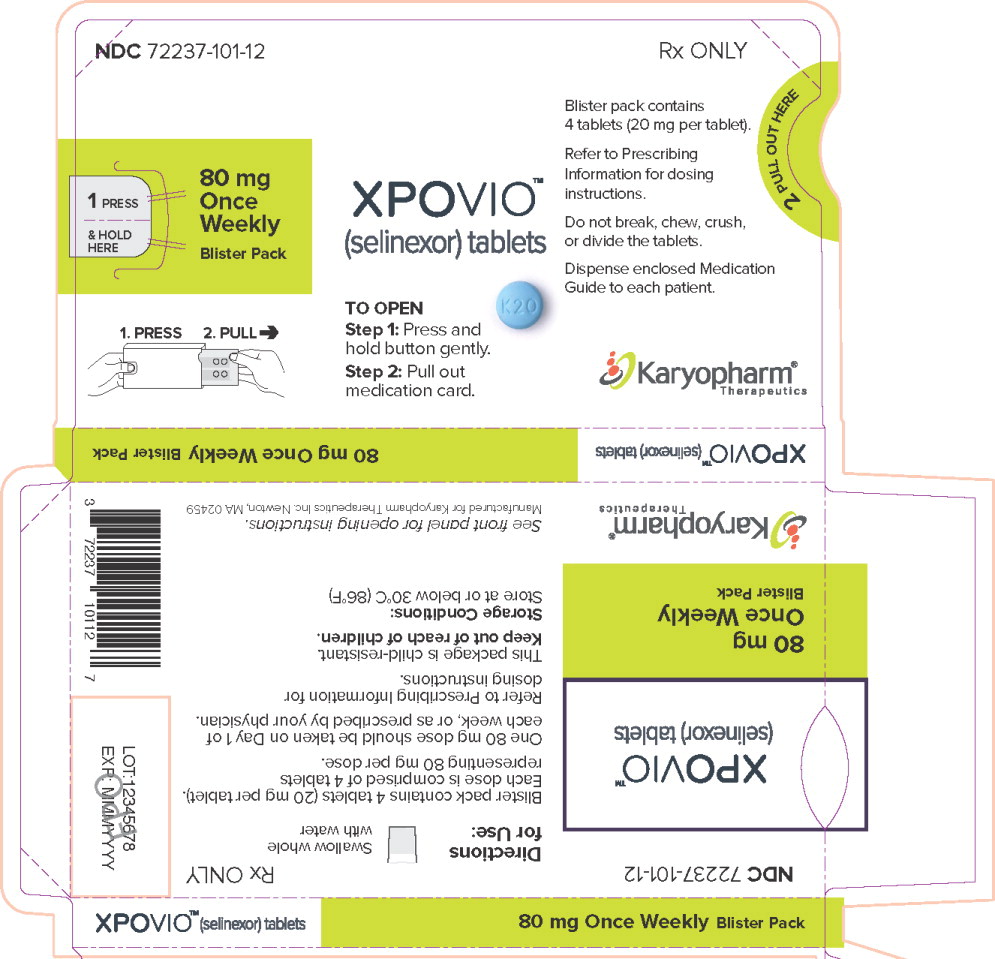
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 80 mg Carton Label
NDC: 72237-101-02
Rx ONLY
80 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister PacksXPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
Contents: 4 individual weekly
blister packs. Each blister pack
contains 4 tablets (20 mg per tablet).16 film-coated tablets
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 80 mg Blister Sleeve Label
NDC 72237-101-12
Rx ONLY
1 PRESS
& HOLD
HERE80 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister Pack1. PRESS 2. PULL
XPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
TO OPEN
Step 1: Press and
hold button gently.Step 2: Pull out
medication card.Blister pack contains
4 tablets (20 mg per tablet).Refer to Prescribing
Information for dosing
instructions.Do not break, chew, crush,
or divide the tablets.Dispense enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
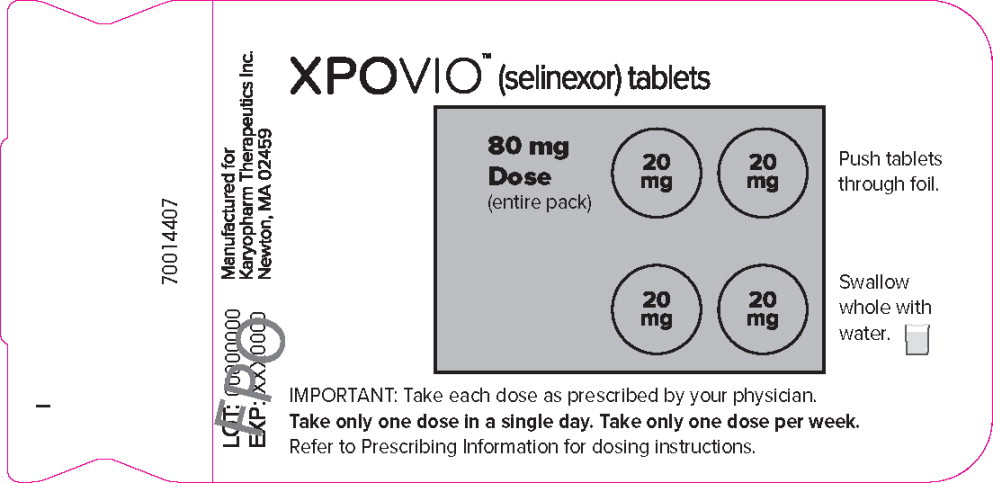
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 80 mg Blister Pack Label
XPOVIO™(selinexor tablets)
80 mg
Dose
(entire pack)Push tablets
through foil.Swallow
whole with
water.IMPORTANT: Take each dose as prescribed by your physician.
Take only one dose in a single day. Take only one dose per week.
Refer to Prescribing Information for dosing instructions.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 100 mg Carton Label
NDC: 72237-101-05
Rx ONLY
100 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister PacksXPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
Contents: 4 individual weekly
blister packs. Each blister pack
contains 5 tablets (20 mg per tablet).20 film-coated tablets
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
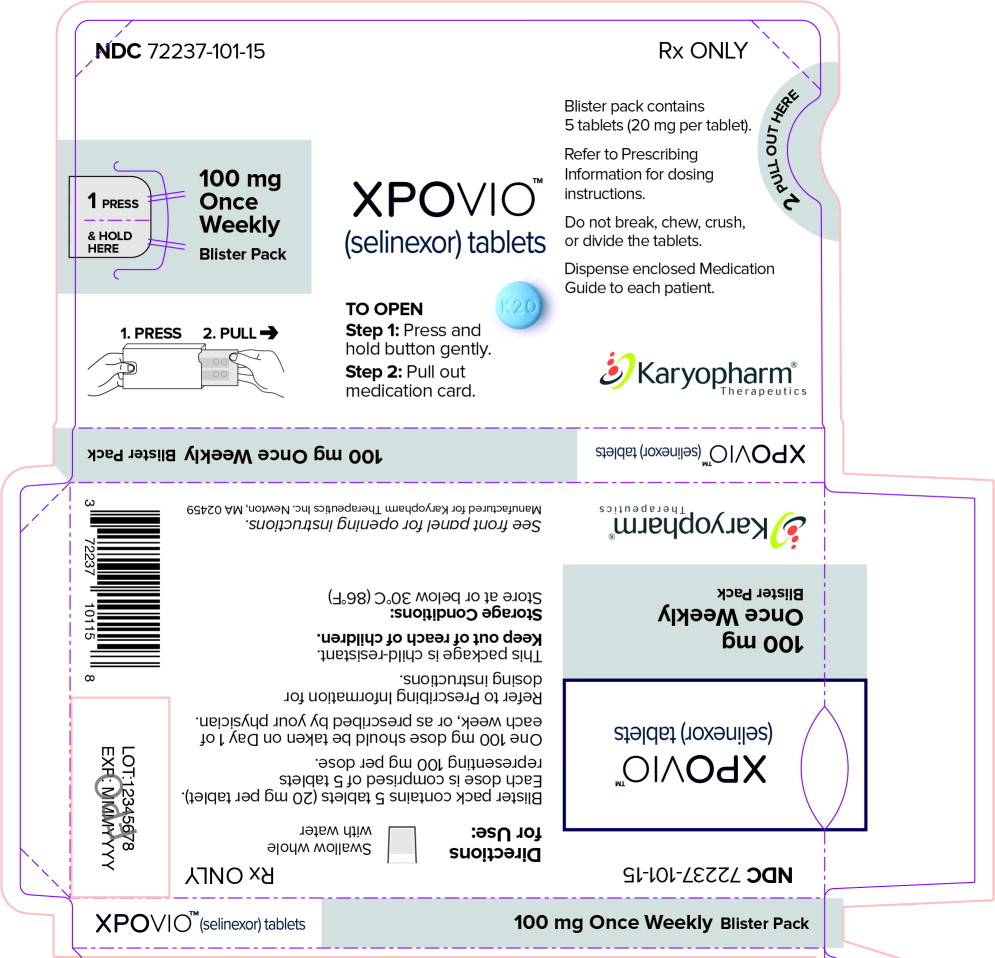
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 100 mg Blister Sleeve Label
NDC 72237-101-15
Rx ONLY
1 PRESS
& HOLD
HERE100 mg
Once
Weekly
Blister Pack1. PRESS 2. PULL
XPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
TO OPEN
Step 1: Press and
hold button gently.Step 2: Pull out
medication card.Blister pack contains
5 tablets (20 mg per tablet).Refer to Prescribing
Information for dosing
instructions.Do not break, chew, crush,
or divide the tablets.
Dispense enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
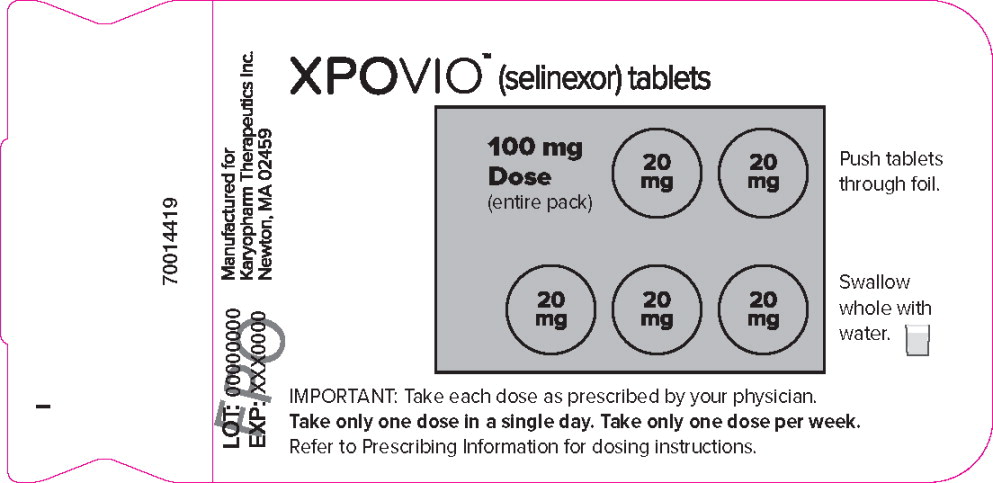
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 100 mg Blister Pack Label
XPOVIO™(selinexor tablets)
100 mg
Dose
(entire pack)Push tablets
through foil.Swallow
whole with
water.IMPORTANT: Take each dose as prescribed by your physician.
Take only one dose in a single day. Take only one dose per week.
Refer to Prescribing Information for dosing instructions.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 160 mg Carton Label
NDC: 72237-101-04
Rx ONLY
80 mg
Twice
Weekly
Blister Packs(160 mg total
weekly dose)XPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
Contents: 4 individual weekly
blister packs. Each blister pack
contains 8 tablets (20 mg per tablet).32 film-coated tablets
Dispense enclosed Medication Guide
to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 160 mg Blister Sleeve Label
NDC 72237-101-14
Rx ONLY
1 PRESS
& HOLD
HERE80 mg
Twice
Weekly
Blister Pack1. PRESS 2. PULL
(160 mg total
weekly dose)XPOVIO™
(selinexor) tablets
TO OPEN
Step 1: Press and
hold button gently.Step 2: Pull out
medication card.Blister pack contains
8 tablets (20 mg per tablet).Refer to Prescribing
Information for dosing
instructions.Do not break, chew, crush,
or divide the tablets.Dispense enclosed Medication
Guide to each patient.Karyopharm®
Therapeutics -
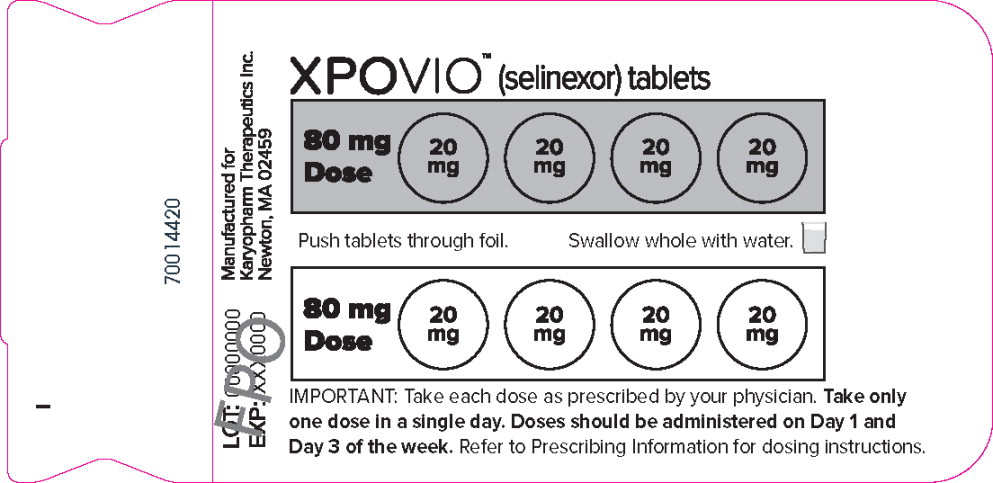
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
Principal Display Panel – 160 mg Blister Pack Label
XPOVIO™(selinexor tablets)
80 mg
DosePush tablets through foil.
Swallow whole with water.
80 mg
DoseIMPORTANT: Take each dose as prescribed by your physician. Take only
one dose in a single day. Doses should be administered on Day 1 and
Day 3 of the week. Refer to Prescribing Information for dosing instructions. -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
XPOVIO
selinexor tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 72237-101 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength selinexor (UNII: 31TZ62FO8F) (selinexor - UNII:31TZ62FO8F) selinexor 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose 101 (UNII: 7T9FYH5QMK) Microcrystalline Cellulose 102 (UNII: PNR0YF693Y) Croscarmellose Sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) Povidone K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (UNII: 368GB5141J) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Magnesium Stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) POLYVINYL ALCOHOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 532B59J990) GLYCERYL MONOSTEARATE (UNII: 230OU9XXE4) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 3350 (UNII: G2M7P15E5P) FD&C BLUE NO. 2--ALUMINUM LAKE (UNII: 4AQJ3LG584) FD&C BLUE NO. 1--ALUMINUM LAKE (UNII: J9EQA3S2JM) Product Characteristics Color blue (blue) Score no score Shape ROUND (ROUND) Size 7mm Flavor Imprint Code K20 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 72237-101-04 4 in 1 CARTON 07/10/2019 1 NDC: 72237-101-14 8 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 72237-101-05 4 in 1 CARTON 07/10/2019 2 NDC: 72237-101-15 5 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 3 NDC: 72237-101-02 4 in 1 CARTON 07/10/2019 3 NDC: 72237-101-12 4 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 4 NDC: 72237-101-01 4 in 1 CARTON 07/10/2019 4 NDC: 72237-101-11 3 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212306 07/10/2019 Labeler - Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. (061317680) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Carton Service, Incorporated 928861723 LABEL(72237-101) , PACK(72237-101) , RELABEL(72237-101) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent CTS, LLC 962674474 MANUFACTURE(72237-101) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Integrated Commercialization Solutions, LLC 038187093 RELABEL(72237-101) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Integrated Commercialization Solutions, LLC 832820588 RELABEL(72237-101)
Trademark Results [XPOVIO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 XPOVIO 87719728 not registered Live/Pending |
Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. 2017-12-13 |
 XPOVIO 86418181 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Karyopharm Therapeutics Inc. 2014-10-08 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.