ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE injection, solution
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is 3,4-Dihydroxy-α-[(isopropylamino)methyl] benzyl alcohol hydrochloride, a synthetic sympathomimetic amine that is structurally related to epinephrine but acts almost exclusively on beta receptors. The molecular formula is C11H17NO3 HCl. It has a molecular weight of 247.72 and the following structural formula:
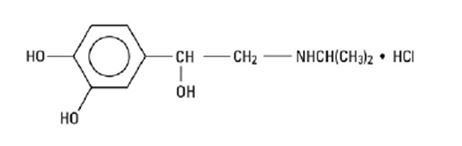
Isoproterenol hydrochloride is a racemic compound.
Isoproterenol hydrochloride, USP is white to practically white crystalline powder and freely soluble in water, soluble in alcohol, less soluble in dehydrated alcohol, insoluble in chloroform and in ether.
Each milliliter of the sterile solution contains:
Isoproterenol hydrochloride, USP
0.2 mg
Edetate Disodium (EDTA)
0.2 mg
Sodium Chloride
7.0 mg
Sodium Citrate, Dihydrate
2.07 mg
Citric Acid, Anhydrous
2.5 mg
Water for Injection
q.s.
The pH is adjusted between 2.5 and 4.5 with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide.
The sterile solution is nonpyrogenic and can be administered by the intravenous, intramuscular, subcutaneous, or intracardiac routes.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Isoproterenol is a potent nonselective beta-adrenergic agonist with very low affinity for alpha-adrenergic receptors. Intravenous infusion of isoproterenol in man lowers peripheral vascular resistance, primarily in skeletal muscle but also in renal and mesenteric vascular beds. Diastolic pressure falls. Renal blood flow is decreased in normotensive subjects but is increased markedly in shock. Systolic blood pressure may remain unchanged or rise, although mean arterial pressure typically falls. Cardiac output is increased because of the positive inotropic and chronotropic effects of the drug in the face of diminished peripheral vascular resistance. The cardiac effects of isoproterenol may lead to palpitations, sinus tachycardia, and more serious arrhythmias; large doses of isoproterenol may cause myocardial necrosis in animals.
Isoproterenol relaxes almost all varieties of smooth muscle when the tone is high, but this action is most pronounced on bronchial and gastrointestinal smooth muscle. It prevents or relieves bronchoconstriction, but tolerance to this effect develops with overuse of the drug.
In man, isoproterenol causes less hyperglycemia than does epinephrine. Isoproterenol and epinephrine are equally effective in stimulating the release of free fatty acids and energy production.
Absorption, Fate and Excretion
Isoproterenol is metabolized primarily in the liver and other tissues by COMT. Isoproterenol is a relatively poor substrate for MAO and is not taken up by sympathetic neurons to the same extent as are epinephrine and norepinephrine. The duration of action of isoproterenol may therefore be longer than that of epinephrine, but is still brief. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection is indicated:
- For mild or transient episodes of heart block that do not require electric shock or pacemaker therapy.
- For serious episodes of heart block and Adams-Stokes attacks (except when caused by ventricular tachycardia or fibrillation) (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- For use in cardiac arrest until electric shock or pacemaker therapy, the treatments of choice, is available (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
- For bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia.
- As an adjunct to fluid and electrolyte replacement therapy and the use of other drugs and procedures in the treatment of hypovolemic and septic shock, low cardiac output (hypoperfusion) states, congestive heart failure, and cardiogenic shock (see WARNINGS).
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection, by increasing myocardial oxygen requirements while decreasing effective coronary perfusion, may have a deleterious effect on the injured or failing heart. Most experts discourage its use as the initial agent in treating cardiogenic shock following myocardial infarction. However, when a low arterial pressure has been elevated by other means, isoproterenol hydrochloride injection may produce beneficial hemodynamic and metabolic effects.
In a few patients, presumably with organic disease of the AV node and its branches, isoproterenol hydrochloride injection has paradoxically been reported to worsen heart block or to precipitate Adams- Stokes attacks during normal sinus rhythm or transient heart block.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection should generally be started at the lowest recommended dose. This may be gradually increased if necessary while carefully monitoring the patient. Doses sufficient to increase the heart rate to more than 130 beats per minute may increase the likelihood of inducing ventricular arrhythmias. Such increases in heart rate will also tend to increase cardiac work and oxygen requirements which may adversely affect the failing heart or the heart with a significant degree of arteriosclerosis.
Adequate filling of the intravascular compartment by suitable volume expanders is of primary importance in most cases of shock and should precede the administration of vasoactive drugs. In patients with normal cardiac function, determination of central venous pressure is a reliable guide during volume replacement. If evidence of hypoperfusion persists after adequate volume replacement, isoproterenol hydrochloride injection may be given.
In addition to the routine monitoring of systemic blood pressure, heart rate, urine flow, and the electrocardiograph, monitor the response to therapy by frequent determination of the central venous pressure and blood gases. Closely observe patients in shock during isoproterenol hydrochloride injection administration. If the heart rate exceeds 110 beats per minute, it may be advisable to decrease the infusion rate or temporarily discontinue the infusion. Determinations of cardiac output and circulation time may also be helpful. Take appropriate measures to ensure adequate ventilation. Pay attention to acid-base balance and to the correction of electrolyte disturbances.
Drug Interactions
Isoproterenol hydrochloride injection and epinephrine should not be administered simultaneously because both drugs are direct cardiac stimulants and their combined effects may induce serious arrhythmias. The drugs may, however, be administered alternately provided a proper interval has elapsed between doses.
Avoid isoproterenol hydrochloride when potent inhalational anesthetics such as halothane are employed because of potential to sensitize the myocardium to effects of sympathomimetic amines.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of isoproterenol hydrochloride have not been done. Mutagenic potential and effect on fertility have not been determined. There is no evidence from human experience that isoproterenol hydrochloride injection may be carcinogenic or mutagenic or that it impairs fertility.
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with isoproterenol hydrochloride. It is also not known whether isoproterenol hydrochloride can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Isoproterenol hydrochloride should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when isoproterenol hydrochloride injection is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy of isoproterenol in pediatric patients have not been established.
Intravenous infusions of isoproterenol in refractory asthmatic children at rates of 0.05 to 2.7 mcg/kg/min have caused clinical deterioration, myocardial necrosis, congestive heart failure and death. The risks of cardiac toxicity appear to be increased by some factors [acidosis, hypoxemia, co-administration of corticosteroids, co-administration of methylxanthines (theophylline, theobromine) or aminophylline] that are especially likely to be present in these patients. If I.V. isoproterenol is used in children with refractory asthma, patient monitoring must include continuous assessment of vital signs, frequent electrocardiography, and daily measurements of cardiac enzymes, including CPK-MB.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of isoproterenol hydrochloride did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects in clinical circumstances. There are, however, some data that suggest that elderly healthy or hypertensive patients are less responsive to beta-adrenergic stimulation than are younger subjects. In general, dose selection for elderly patients should usually start at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function and of concomitant diseases or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following reactions to isoproterenol hydrochloride injection have been reported:
CNS: Nervousness, headache, dizziness, nausea, visual blurring.
Cardiovascular: Tachycardia, palpitations, angina, Adams-Stokes attacks, pulmonary edema, hypertension, hypotension, ventricular arrhythmias, tachyarrhythmias.
In a few patients, presumably with organic disease of the AV node and its branches, isoproterenol hydrochloride injection has been reported to precipitate Adams-Stokes seizures during normal sinus rhythm or transient heart block.
Respiratory: Dyspnea.
Other: Flushing of the skin, sweating, mild tremors, weakness, pallor.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amneal Biosciences at 1-855-266-3251 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
-
OVERDOSAGE
The acute toxicity of isoproterenol hydrochloride in animals is much less than that of epinephrine.
Excessive doses in animals or man can cause a striking drop in blood pressure, and repeated large doses in animals may result in cardiac enlargement and focal myocarditis.
In case of accidental overdosage as evidenced mainly by tachycardia or other arrhythmias, palpitations, angina, hypotension, or hypertension, reduce rate of administration or discontinue isoproterenol hydrochloride injection until patient’s condition stabilizes. Blood pressure, pulse, respiration, and ECG should be monitored.
It is not known whether isoproterenol hydrochloride is dialyzable.
The oral LD50 of isoproterenol hydrochloride in mice is 3,850 mg/kg ± 1,190 mg/kg of pure drug in solution.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Start isoproterenol hydrochloride injection at the lowest recommended dose and increase the rate of administration gradually if necessary while carefully monitoring the patient. The usual route of administration is by intravenous infusion or bolus intravenous injection. In dire emergencies, the drug may be administered by intracardiac injection. If time is not of the utmost importance, initial therapy by intramuscular or subcutaneous injection is preferred.
Recommended dosage for adults with heart block, Adams-Stokes attacks, and cardiac arrest:
Route of
Administration
Preparation of Dilution
Initial Dose
Subsequent
Dose Range*
Bolus
intravenous
injection
Dilute 1 mL (0.2 mg) in 9 mL of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
0.02 mg to 0.06 mg
(1 mL to 3 mL of
diluted solution)
0.01 mg to 0.2 mg
(0.5 mL to 10 mL
of diluted solution)
Intravenous
infusion
Dilute 10 mL (2 mg) in 500 mL
of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
5 mcg/min. (1.25 mL
of diluted solution
per minute)
Intramuscular
Use Solution undiluted
0.2 mg (1 mL)
0.02 mg to 1 mg
(0.1 mL to 5 mL)
Subcutaneous
Use Solution undiluted
0.2 mg (1 mL)
0.15 mg to 0.2 mg
(0.75 mL to 1 mL)
Intracardiac
Use Solution undiluted
0.02 mg (0.1 mL)
* Subsequent dosage and method of administration depend on the ventricular rate and the rapidity with which the cardiac pacemaker can take over when the drug is gradually withdrawn.
There are no well-controlled studies in children to establish appropriate dosing; however, the American Heart Association recommends an initial infusion rate of 0.1 mcg/kg/min, with the usual range being 0.1 mcg/kg/min to 1 mcg/kg/min.
Recommended dosage for adults with shock and hypoperfusion states:
Recommended dosage for adults with bronchospasm occurring during anesthesia:Route of Administration
Preparation of Dilution†
Infusion Rate††
Intravenous infusion
Dilute 5 mL (1 mg) in 500 mL
of 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
0.5 mcg to 5 mcg per minute
(0.25 mL to 2.5 mL of diluted solution)
† Concentrations up to 10 times greater have been used when limitation of volume is essential.
†† Rates over 30 mcg per minute have been used in advanced stages of shock. The rate of infusion should be adjusted on the basis of heart rate, central venous pressure, systemic blood pressure, and urine flow. If the heart rate exceeds 110 beats per minute, it may be advisable to decrease or temporarily discontinue the infusion.
Route of
Administration
Preparation of Dilution
Initial Dose
Subsequent
Dose
Bolus
intravenous injection
Dilute 1 mL (0.2 mg) in
9 mL of Sodium Chloride Injection, USP, or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP
0.01 mg to 0.02 mg
(0.5 mL to 1 mL of
diluted solution)
The initial dose may
be repeated when
necessary
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit. Such solution should not be used.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection, USP is clear, colorless or practically colorless to slightly yellow color liquid. Each mL contains Isoproterenol Hydrochloride USP, 0.2 mg.
It is available as follows:
0.2 mg/mL (1 mL)
1 mL Single-Dose Vial: NDC: 70121-1604-1
10 Vials in a Carton: NDC: 70121-1604-7
1 mg/5 mL (0.2 mg/mL) (5 mL)
5 mL Single-Dose Vial: NDC: 70121-1605-1
10 Vials in a Carton: NDC: 70121-1605-7
Store at 20º to 25ºC (68º to 77ºF) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light. Keep in opaque container until used.
Do not use if the injection is pinkish or darker than slightly yellow or contains a precipitate.
Manufactured by:
Amneal Pharmaceuticals Pvt. Ltd.
Parenteral Unit
Ahmedabad 382213, INDIA
Distributed by:
Amneal Biosciences LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807
Rev. 08-2018-00
-
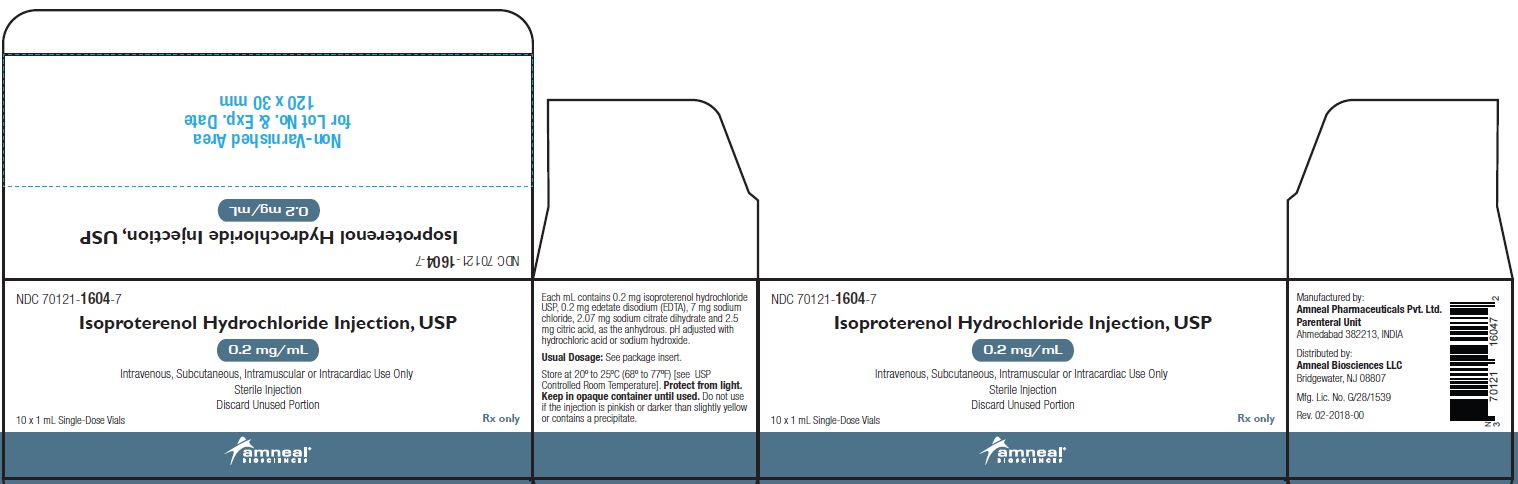
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 70121-1604-1
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection USP, 0.2 mg/mL
Rx only
Vial Label
Amneal Biosciences LLC

NDC: 70121-1604-7
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection USP, 0.2 mg/mL
Rx only
Carton Label
Amneal Biosciences LLC
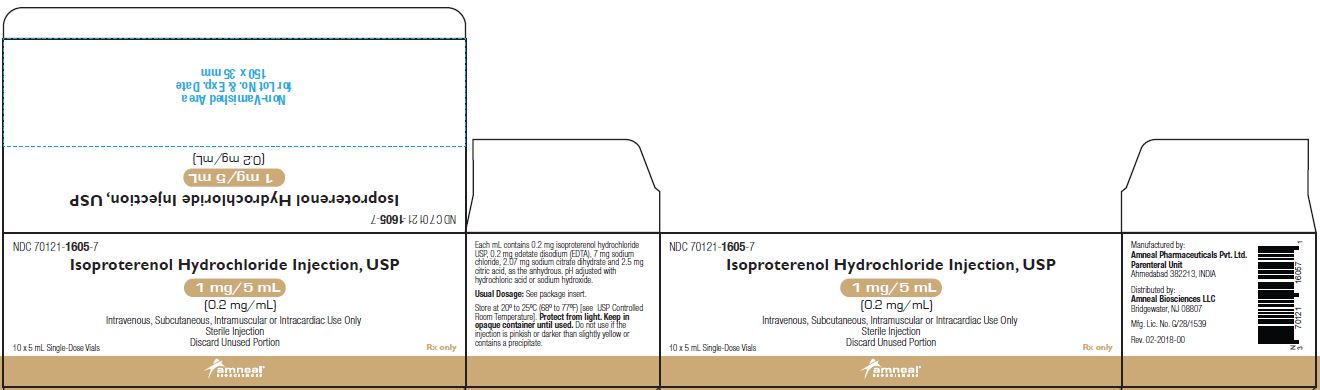
NDC: 70121-1605-1
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection USP, 1 mg/ 5 mL
Rx only
Vial Label
Amneal Biosciences LLC

NDC: 70121-1605-7
Isoproterenol Hydrochloride Injection USP, 1 mg/ 5 mL
Rx only
Carton Label
Amneal Biosciences LLC
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE
isoproterenol hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70121-1604 Route of Administration INTRACARDIAC, INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: DIA2A74855) (ISOPROTERENOL - UNII:L628TT009W) ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE 0.2 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70121-1604-7 10 in 1 CARTON 10/22/2018 1 NDC: 70121-1604-1 1 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210576 10/22/2018 ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE
isoproterenol hydrochloride injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70121-1605 Route of Administration INTRACARDIAC, INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: DIA2A74855) (ISOPROTERENOL - UNII:L628TT009W) ISOPROTERENOL HYDROCHLORIDE 1 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) EDETATE DISODIUM (UNII: 7FLD91C86K) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70121-1605-7 10 in 1 CARTON 10/22/2018 1 NDC: 70121-1605-1 5 mL in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210576 10/22/2018 Labeler - Amneal Pharmaceuticals LLC (827748190)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.