ZORVOLEX- diclofenac capsule
Zorvolex by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Zorvolex by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Zyla Life Sciences US Inc., Catalent CTS, LLC, Patheon. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ZORVOLEX® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ZORVOLEX.
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1988WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use (5.1)
- ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (4, 5.1)
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events (5.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Boxed Warning 5/2016 Warnings and Precautions, Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events (5.1) 5/2016 Warnings and Precautions, Heart Failure and Edema (5.5) 5/2016 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules: 18 mg and 35 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hepatotoxicity: Inform patients of warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity. Discontinue if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen or if clinical signs and symptoms of liver disease develop (5.3)
- Hypertension: Patients taking some antihypertensive medications may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. Monitor blood pressure (5.4, 7)
- Heart Failure and Edema: Avoid use of ZORVOLEX in patients with severe heart failure unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening heart failure (5.5)
- Renal Toxicity: Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia. Avoid use of ZORVOLEX in patients with advanced renal disease unless benefits are expected to outweigh risk of worsening renal function (5.6)
- Anaphylactic Reactions: Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs (5.7)
- Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity: ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma. Monitor patients with preexisting asthma (without aspirin sensitivity) (5.8)
- Serious Skin Reactions: Discontinue ZORVOLEX at first appearance of skin rash or other signs of hypersensitivity (5.9)
- Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus: Avoid use in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation (5.10, 8.1)
-
Hematologic Toxicity: Monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit in patients with any signs or symptoms of anemia (5.11, 7)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) are edema, nausea, headache, dizziness, vomiting, constipation, pruritus, diarrhea, flatulence, pain in extremity, abdominal pain, sinusitis, alanine aminotransferase increased, blood creatinine increased, hypertension, and dyspepsia. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Egalet US Inc., at 1-800-518-1084 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Drugs that Interfere with Hemostasis (e.g. warfarin, aspirin, SSRIs/SNRIs): Monitor patients for bleeding who are concomitantly taking ZORVOLEX with drugs that interfere with hemostasis. Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended (7)
- ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers (ARB), or Beta-Blockers: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX may diminish the antihypertensive effect of these drugs. Monitor blood pressure (7)
- ACE Inhibitors and ARBs: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX in elderly, volume depleted, or those with renal impairment may result in deterioration of renal function. In such high risk patients, monitor for signs of worsening renal function (7)
- Diuretics: NSAIDs can reduce natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazide diuretics. Monitor patients to assure diuretic efficacy including antihypertensive effects (7)
- Digoxin: Concomitant use with ZORVOLEX can increase serum concentration and prolong half-life of digoxin. Monitor serum digoxin levels (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: Use of NSAIDs during the third trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks gestation (5.10, 8.1)
Infertility: NSAIDs are associated with reversible infertility. Consider withdrawal of ZORVOLEX in women who have difficulties conceiving (8.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 3/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Instructions
2.2 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
2.3 Non-Interchangeability with Other Formulations of Diclofenac
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
5.4 Hypertension
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
5.6 Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
5.10 Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
5.11 Hematologic Toxicity
5.12 Masking of Inflammation and Fever
5.13 Laboratory Monitoring
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: RISK OF SERIOUS CARDIOVASCULAR AND GASTROINTESTINAL EVENTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) cause an increased risk of serious cardiovascular thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction and stroke, which can be fatal. This risk may occur early in treatment and may increase with duration of use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
- NSAIDs cause an increased risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach or intestines, which can be fatal. These events can occur at any time during use and without warning symptoms. Elderly patients and patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding are at greater risk for serious GI events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Instructions
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of ZORVOLEX and other treatment options before deciding to use ZORVOLEX. Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals [see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
The effectiveness of ZORVOLEX when taken with food has not been studied in clinical studies. Taking ZORVOLEX with food may cause a reduction in effectiveness compared to taking ZORVOLEX on an empty stomach [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)].
Acute Pain
For management of mild to moderate acute pain, the dosage is 18 mg or 35 mg orally three times daily.
Osteoarthritis Pain
For management of osteoarthritis pain, the dosage is 35 mg orally three times daily.
2.2 Dosage Adjustments in Patients with Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic disease may require reduced doses of ZORVOLEX compared to patients with normal hepatic function [see Clinical Pharmacology (12)]. As with other diclofenac products, start treatment at the lowest dose. If efficacy is not achieved with the lowest dose, discontinue use.
2.3 Non-Interchangeability with Other Formulations of Diclofenac
ZORVOLEX capsules are not interchangeable with other formulations of oral diclofenac even if the milligram strength is the same. ZORVOLEX capsules contain diclofenac free acid whereas other diclofenac products contain a salt of diclofenac, i.e., diclofenac potassium or sodium. A 35 mg dose of ZORVOLEX is approximately equal to 37.6 mg of sodium diclofenac or 39.5 mg of potassium diclofenac. Therefore, do not substitute similar dosing strengths of other diclofenac products without taking this into consideration.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in the following patients:
- Known hypersensitivity (e.g., anaphylactic reactions and serious skin reactions) to diclofenac or any components of the drug product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.9)]
- History of asthma, urticaria, or other allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, sometimes fatal, anaphylactic reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7, 5.8)]
- In the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, including myocardial infarction (MI) and stroke, which can be fatal. Based on available data, it is unclear that the risk for CV thrombotic events is similar for all NSAIDs. The relative increase in serious CV thrombotic events over baseline conferred by NSAID use appears to be similar in those with and without known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease. However, patients with known CV disease or risk factors had a higher absolute incidence of excess serious CV thrombotic events, due to their increased baseline rate. Some observational studies found that this increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events began as early as the first weeks of treatment. The increase in CV thrombotic risk has been observed most consistently at higher doses.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in NSAID-treated patients, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, throughout the entire treatment course, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID, such as diclofenac, increases the risk of serious gastrointestinal (GI) events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Status Post Coronary Artery Bypass Graft (CABG) Surgery
Two large, controlled clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10–14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke. NSAIDs are contraindicated in the setting of CABG [see Contraindications (4)].
Post-MI Patients
Observational studies conducted in the Danish National Registry have demonstrated that patients treated with NSAIDs in the post-MI period were at increased risk of reinfarction, CV-related death, and all-cause mortality beginning in the first week of treatment. In this same cohort, the incidence of death in the first year post-MI was 20 per 100 person years in NSAID-treated patients compared to 12 per 100 person years in non-NSAID exposed patients. Although the absolute rate of death declined somewhat after the first year post-MI, the increased relative risk of death in NSAID users persisted over at least the next four years of follow-up.
Avoid the use of ZORVOLEX in patients with a recent MI unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of recurrent CV thrombotic events. If ZORVOLEX is used in patients with a recent MI, monitor patients for signs of cardiac ischemia.
5.2 Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develop a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occurred in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2%-4% of patients treated for one year. However, even short-term NSAID therapy is not without risk.
Risk Factors for GI Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or GI bleeding who used NSAIDs had a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients without these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk of GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include longer duration of NSAID therapy; concomitant use of oral corticosteroids, aspirin, anticoagulants, or selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs); smoking; use of alcohol; older age; and poor general health status. Most postmarketing reports of fatal GI events occurred in elderly or debilitated patients. Additionally, patients with advanced liver disease and/or coagulopathy are at increased risk for GI bleeding.
Strategies to Minimize the GI Risks in NSAID-treated patients:
- Use the lowest effective dosage for the shortest possible duration.
- Avoid administration of more than one NSAID at a time.
- Avoid use in patients at higher risk unless benefits are expected to outweigh the increased risk of bleeding. For such patients, as well as those with active GI bleeding, consider alternate therapies other than NSAIDs.
- Remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy.
- If a serious GI adverse event is suspected, promptly initiate evaluation and treatment, and discontinue ZORVOLEX until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out.
- In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, monitor patients more closely for evidence of GI bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
5.3 Hepatotoxicity
In clinical trials of diclofenac-containing products, meaningful elevations (i.e., more than 3 times the ULN) of AST (SGOT) were observed in about 2% of approximately 5,700 patients at some time during diclofenac treatment (ALT was not measured in all studies).
In a large, open-label, controlled trial of 3,700 patients treated with oral diclofenac sodium for 2-6 months, patients were monitored first at 8 weeks and 1,200 patients were monitored again at 24 weeks. Meaningful elevations of ALT and/or AST occurred in about 4% of patients and included marked elevations (greater than 8 times the ULN) in about 1% of the 3,700 patients. In that open-label study, a higher incidence of borderline (less than 3 times the ULN), moderate (3-8 times the ULN), and marked (greater than 8 times the ULN) elevations of ALT or AST was observed in patients receiving diclofenac when compared to other NSAIDs. Elevations in transaminases were seen more frequently in patients with osteoarthritis than in those with rheumatoid arthritis.
Almost all meaningful elevations in transaminases were detected before patients became symptomatic. Abnormal tests occurred during the first 2 months of therapy with diclofenac in 42 of the 51 patients in all trials who developed marked transaminase elevations.
In postmarketing reports, cases of drug-induced hepatotoxicity have been reported in the first month, and in some cases, the first 2 months of therapy, but can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
Postmarketing surveillance has reported cases of severe hepatic reactions, including liver necrosis, jaundice, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, and liver failure. Some of these reported cases resulted in fatalities or liver transplantation.
In a European retrospective population-based, case-controlled study, 10 cases of diclofenac associated drug-induced liver injury with current use compared with non-use of diclofenac were associated with a statistically significant 4-fold adjusted odds ratio of liver injury. In this particular study, based on an overall number of 10 cases of liver injury associated with diclofenac, the adjusted odds ratio increased further with female gender, doses of 150 mg or more, and duration of use for more then 90 days.
Physicians should measure transaminases at baseline and periodically in patients receiving long-term therapy with ZORVOLEX, because severe hepatotoxicity may develop without a prodrome of distinguishing symptoms. The optimum times for making the first and subsequent transaminase measurements are not known. Based on clinical trial data and postmarketing experiences, transaminases should be monitored within 4 to 8 weeks after initiating treatment with diclofenac. However, severe hepatic reactions can occur at any time during treatment with diclofenac.
If abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, if clinical signs and/or symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, abdominal pain, diarrhea, dark urine, etc.), ZORVOLEX should be discontinued immediately.
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, diarrhea, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and "flu-like" symptoms). If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.), discontinue ZORVOLEX immediately, and perform a clinical evaluation of the patient.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse liver related event in patients treated with ZORVOLEX, use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration possible. Exercise caution when prescribing ZORVOLEX with concomitant drugs that are known to be potentially hepatotoxic (e.g., acetaminophen, antibiotics, and anti-epileptics).
5.4 Hypertension
NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, can lead to new onset of hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, thiazide diuretics, or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Monitor blood pressure (BP) during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
5.5 Heart Failure and Edema
The Coxib and traditional NSAID Trialists’ Collaboration meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials demonstrated an approximately two-fold increase in hospitalizations for heart failure in COX-2 selective-treated patients and nonselective NSAID-treated patients compared to placebo-treated patients. In a Danish National Registry study of patients with heart failure, NSAID use increased the risk of MI, hospitalization for heart failure, and death.
Additionally, fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients treated with NSAIDs. Use of diclofenac may blunt the CV effects of several therapeutic agents used to treat these medical conditions (e.g., diuretics, ACE inhibitors, or angiotensin receptor blockers [ARBs]) [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Avoid the use of ZORVOLEX in patients with severe heart failure unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening heart failure. If ZORVOLEX is used in patients with severe heart failure, monitor patients for signs of worsening heart failure.
5.6 Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia
Renal Toxicity
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury.
Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of an NSAID may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, dehydration, hypovolemia, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors or ARBs, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of ZORVOLEX in patients with advanced renal disease. The renal effects of ZORVOLEX may hasten the progression of renal dysfunction in patients with preexisting renal disease.
Correct volume status in dehydrated or hypovolemic patients prior to initiating ZORVOLEX. Monitor renal function in patients with renal or hepatic impairment, heart failure, dehydration, or hypovolemia during use of ZORVOLEX [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Avoid the use of ZORVOLEX in patients with advanced renal disease unless the benefits are expected to outweigh the risk of worsening renal function. If ZORVOLEX is used in patients with advanced renal disease, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function.
Hyperkalemia
Increases in serum potassium concentration, including hyperkalemia, have been reported with use of NSAIDs, even in some patients without renal impairment. In patients with normal renal function, these effects have been attributed to a hyporeninemic-hypoaldosteronism state.
5.7 Anaphylactic Reactions
Diclofenac has been associated with anaphylactic reactions in patients with and without known hypersensitivity to diclofenac and in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Seek emergency help if an anaphylactic reaction occurs.
5.8 Exacerbation of Asthma Related to Aspirin Sensitivity
A subpopulation of patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma which may include chronic rhinosinusitis complicated by nasal polyps; severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm; and/or intolerance to aspirin and other NSAIDs. Because cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity [see Contraindications (4)]. When ZORVOLEX is used in patients with preexisting asthma (without known aspirin sensitivity), monitor patients for changes in the signs and symptoms of asthma.
5.9 Serious Skin Reactions
NSAIDs, including diclofenac, can cause serious skin adverse reactions such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Inform patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin reactions, and to discontinue the use of ZORVOLEX at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity. ZORVOLEX is contraindicated in patients with previous serious skin reactions to NSAIDs [see Contraindications (4)].
5.10 Premature Closure of Fetal Ductus Arteriosus
Diclofenac may cause premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester) [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
5.11 Hematologic Toxicity
Anemia has occurred in NSAID-treated patients. This may be due to occult or gross blood loss, fluid retention, or an incompletely described effect on erythropoiesis. If a patient treated with ZORVOLEX has any signs or symptoms of anemia, monitor hemoglobin or hematocrit.
NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, may increase the risk of bleeding events. Co-morbid conditions, such as coagulation disorders, concomitant use of warfarin, other anticoagulants, antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) may increase this risk. Monitor these patients for signs of bleeding [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- GI Bleeding, Ulceration and Perforation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Hypertension [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Heart Failure and Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Renal Toxicity and Hyperkalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Anaphylactic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Serious Skin Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
- Hematologic Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
Adverse Reactions in Patients with Acute Pain
Two-hundred sixteen (216) patients received ZORVOLEX in the completed, 48-hour, double-blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of acute pain following bunionectomy. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1 Summary of Adverse Reactions (≥2% in ZORVOLEX 18 mg or 35 mg group) – Phase 3 Study in Patients With Postsurgical Pain *One tablet of hydrocodone/acetaminophen 10 mg/325 mg was permitted every 4 to 6 hours as rescue medication for pain management. There was a greater use of concomitant opioid rescue medication in placebo-treated patients than in ZORVOLEX-treated patients. About 82% of patients in the ZORVOLEX 35 mg group, 85% of the patients in the ZORVOLEX 18 mg group, and 97% of patients in the placebo group took rescue medication for pain management during the study.
Adverse Reactions ZORVOLEX 18 mg or 35 mg
three times daily*
N = 216Placebo*
N = 106Edema 33% 32% Nausea 27% 37% Headache 13% 15% Dizziness 10% 16% Vomiting 9% 12% Constipation 8% 4% Pruritus 7% 6% Flatulence 3% 2% Pain in Extremity 3% 1% Dyspepsia 2% 1% Adverse Reactions in Patients with Osteoarthritis Pain
Two-hundred two (202) patients received ZORVOLEX in the completed, 12-week, double- blind, placebo-controlled, clinical trial of osteoarthritis pain of the knee or hip. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2 Summary of Adverse Reactions (≥2%) – 12-week Phase 3 Study in Patients With Osteoarthritis Pain* * Adverse reactions that occurred in ≥2% of patients treated with ZORVOLEX and occurred more frequently than in patients treated with placebo
Adverse Reactions ZORVOLEX 35 mg
N=202Placebo
N=103Nausea 7% 2% Diarrhea 6% 3% Headache 4% 3% Abdominal Pain Upper 3% 1% Sinusitis 3% 1% Vomiting 3% 1% Alanine Aminotransferase Increased 2% 0 Blood Creatinine Increased 2% 0 Dyspepsia 2% 1% Flatulence 2% 0 Hypertension 2% 1% Six-hundred one (601) patients received ZORVOLEX 35 mg either twice or three times daily in a 52-week, open-label, clinical trial in osteoarthritis pain of the knee or hip. Of those, 360 (60%) patients completed the trial. The most frequent adverse reactions in this study are summarized in Table 3.
Table 3 Summary of Adverse Reactions (≥2%) – 52-week Open-label Study in Patients with Osteoarthritis Pain Adverse Reactions ZORVOLEX 35 mg
N=601Upper respiratory tract infection 8% Headache 8% Urinary tract infection 7% Diarrhea 6% Nasopharyngitis 6% Nausea 6% Constipation 5% Sinusitis 5% Osteoarthritis 5% Cough 4% Alanine aminotransferase increased 4% Back pain 3% Dyspepsia 3% Procedural pain 3% Bronchitis 3% Hypertension 3% Abdominal pain upper 3% Influenza 3% Arthralgia 3% Contusion 3% Vomiting 3% Abdominal discomfort 2% Aspartate aminotransferase increased 2% Dizziness 2% Fall 2% Abdominal pain 2% Adverse reactions reported for diclofenac and other NSAIDs:
In patients taking other NSAIDs, the most frequently reported adverse reactions occurring in approximately 1%-10% of patients are:
Gastrointestinal experiences including: abdominal pain, constipation, diarrhea, dyspepsia, flatulence, gross bleeding/perforation, heartburn, nausea, GI ulcers (gastric/duodenal) and vomiting.
Abnormal renal function, anemia, dizziness, edema, elevated liver enzymes, headaches, increased bleeding time, pruritus, rashes and tinnitus.
Additional adverse reactions reported occasionally include:
Body as a Whole: fever, infection, sepsis
Cardiovascular System: congestive heart failure, hypertension, tachycardia, syncope
Digestive System: dry mouth, esophagitis, gastric/peptic ulcers, gastritis, gastrointestinal bleeding, glossitis, hematemesis, hepatitis, jaundice
Hemic and Lymphatic System: ecchymosis, eosinophilia, leukopenia, melena, purpura, rectal bleeding, stomatitis, thrombocytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: weight changes
Nervous System: anxiety, asthenia, confusion, depression, dream abnormalities, drowsiness, insomnia, malaise, nervousness, paresthesia, somnolence, tremors, vertigo
Respiratory System: asthma, dyspnea
Skin and Appendages: alopecia, photosensitivity, sweating increased
Special Senses: blurred vision
Urogenital System: cystitis, dysuria, hematuria, interstitial nephritis, oliguria/polyuria, proteinuria, renal failureOther adverse reactions, which occur rarely are:
Body as a Whole: anaphylactic reactions, appetite changes, death
Cardiovascular System: arrhythmia, hypotension, myocardial infarction, palpitations, vasculitis
Digestive System: colitis, eructation, fulminant hepatitis with and without jaundice, liver failure, liver necrosis, pancreatitis
Hemic and Lymphatic System: agranulocytosis, hemolytic anemia, aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, pancytopenia
Metabolic and Nutritional: hyperglycemia
Nervous System: convulsions, coma, hallucinations, meningitis
Respiratory System: respiratory depression, pneumonia
Skin and Appendages: angioedema, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, urticaria
Special Senses: conjunctivitis, hearing impairment -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
See Table 4 for clinically significant drug interactions with diclofenac.
Table 4 Clinically Significant Drug Interactions with Diclofenac Drugs That Interfere with Hemostasis Clinical Impact: - Diclofenac and anticoagulants such as warfarin have a synergistic effect on bleeding. The concomitant use of diclofenac and anticoagulants have an increased risk of serious bleeding compared to the use of either drug alone.
- Serotonin release by platelets plays an important role in hemostasis. Case-control and cohort epidemiological studies showed that concomitant use of drugs that interfere with serotonin reuptake and an NSAID may potentiate the risk of bleeding more than an NSAID alone.
Intervention: Monitor patients with concomitant use of ZORVOLEX with anticoagulants (e.g., warfarin), antiplatelet agents (e.g., aspirin), selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), and serotonin norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) for signs of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]. Aspirin Clinical Impact: Controlled clinical studies showed that the concomitant use of NSAIDs and analgesic doses of aspirin does not produce any greater therapeutic effect than the use of NSAIDs alone. In a clinical study, the concomitant use of an NSAID and aspirin was associated with a significantly increased incidence of GI adverse reactions as compared to use of the NSAID alone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Intervention: Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and analgesic doses of aspirin is not generally recommended because of the increased risk of bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)].
ZORVOLEX is not a substitute for low dose aspirin for cardiovascular protection.ACE Inhibitors, Angiotensin Receptor Blockers, and Beta-Blockers Clinical Impact: - NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs), or beta-blockers (including propranolol).
- In patients who are elderly, volume-depleted (including those on diuretic therapy), or have renal impairment, co-administration of an NSAID with ACE inhibitors or ARBs may result in deterioration of renal function, including possible acute renal failure. These effects are usually reversible.
Intervention: - During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and ACE-inhibitors, ARBs, or beta- blockers, monitor blood pressure to ensure that the desired blood pressure is obtained.
- During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and ACE-inhibitors or ARBs in patients who are elderly, volume-depleted, or have impaired renal function, monitor for signs of worsening renal function [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
- When these drugs are administered concomitantly, patients should be adequately hydrated. Assess renal function at the beginning of the concomitant treatment and periodically thereafter.
Diuretics Clinical Impact: The concomitant use of diclofenac with digoxin has been reported to increase the serum concentration and prolong the half-life of digoxin. Intervention: During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and digoxin, monitor serum digoxin levels. Lithium Clinical Impact: NSAIDs have produced elevations in plasma lithium levels and reductions in renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15%, and the renal clearance decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to NSAID inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. Intervention: During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and lithium, monitor patients for signs of lithium toxicity. Methotrexate Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of NSAIDs and methotrexate may increase the risk for methotrexate toxicity (e.g., neutropenia, thrombocytopenia, renal dysfunction). Intervention: During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and methotrexate, monitor patients for methotrexate toxicity. Cyclosporine Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and cyclosporine may increase cyclosporine’s nephrotoxicity. Intervention: During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and cyclosporine, monitor patients for signs of worsening renal function. NSAIDs and Salicylates Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) increases the risk of GI toxicity, with little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Intervention: The concomitant use of diclofenac with other NSAIDs or salicylates is not recommended. Pemetrexed Clinical Impact: Concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and pemetrexed may increase the risk of pemetrexed- associated myelosuppression, renal, and GI toxicity (see the pemetrexed prescribing information). Intervention: During concomitant use of ZORVOLEX and pemetrexed, in patients with renal impairment whose creatinine clearance ranges from 45 to 79 mL/min, monitor for myelosuppression, renal and GI toxicity.
NSAIDs with short elimination half-lives (e.g., diclofenac, indomethacin) should be avoided for a period of two days before, the day of, and two days following administration of pemetrexed.
In the absence of data regarding potential interaction between pemetrexed and NSAIDs with longer half-lives (e.g., meloxicam, nabumetone), patients taking these NSAIDs should interrupt dosing for at least five days before, the day of, and two days following pemetrexed administration.Inhibitors or Inducers of Cytochrome P450 2C9 Clinical Impact: Diclofenac is metabolized by cytochrome P450 enzymes, predominantly by CYP2C9. Co-administration of diclofenac with CYP2C9 inhibitors (e.g. voriconazole) may enhance the exposure and toxicity of diclofenac whereas co- administration with CYP2C9 inducers (e.g. rifampin) may lead to compromised efficacy of diclofenac. Intervention: A dosage adjustment may be warranted when diclofenac is administered with CYP2C9 inhibitors or inducers [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C prior to 30 weeks gestation; Category D starting 30 weeks gestation.
Risk Summary
Use of NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, during the third trimester of pregnancy increases the risk of premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus. Avoid use of NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, in pregnant women starting at 30 weeks of gestation (third trimester).
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ZORVOLEX in pregnant women. Data from observational studies regarding potential embryofetal risks of NSAID use in women in the first or second trimesters of pregnancy are inconclusive. In the general U.S. population, all clinically recognized pregnancies, regardless of drug exposure, have a background rate of 2-4% for major malformations, and 15-20% for pregnancy loss.
In animal reproduction studies, no evidence of teratogenicity was observed in mice, rats, and rabbits given diclofenac during the period of organogenesis at doses approximately 1, 1, and 2 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of ZORVOLEX despite the presence of maternal and fetal toxicity at these doses [see Data]. Based on animal data, prostaglandins have been shown to have an important role in endometrial vascular permeability, blastocyst implantation, and decidualization. In animal studies, administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors such as diclofenac, resulted in increased pre- and post- implantation loss.
Clinical Considerations
Labor or Delivery
There are no studies on the effects of ZORVOLEX during labor or delivery. In animal studies, NSAIDs, including diclofenac, inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, cause delayed parturition, and increase the incidence of stillbirth.
Animal data
Reproductive and developmental studies in animals demonstrated that diclofenac sodium administration during organogenesis did not produce teratogenicity despite the induction of maternal toxicity and fetal toxicity in mice at oral doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (approximately equivalent to the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of ZORVOLEX, 105 mg/day, based on body surface area (BSA) comparison), and in rats and rabbits at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 1 and 2 times, respectively, the MRHD based on BSA comparison). In rats, maternally toxic doses were associated with dystocia, prolonged gestation, reduced fetal weights and growth, and reduced fetal survival. Diclofenac has been shown to cross the placental barrier in mice, rats, and humans.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Based on available data, diclofenac may be present in human milk. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for ZORVOLEX and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from the ZORVOLEX or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
One woman treated orally with a diclofenac salt, 150 mg/day, had a milk diclofenac level of 100 mcg/L, equivalent to an infant dose of about 0.03 mg/kg/day. Diclofenac was not detectable in breast milk in 12 women using diclofenac (after either 100 mg/day orally for 7 days or a single 50 mg intramuscular dose administered in the immediate postpartum period).
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Infertility
Females
Based on the mechanism of action, the use of prostaglandin-mediated NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, may delay or prevent rupture of ovarian follicles, which has been associated with reversible infertility in some women. Published animal studies have shown that administration of prostaglandin synthesis inhibitors has the potential to disrupt prostaglandin- mediated follicular rupture required for ovulation. Small studies in women treated with NSAIDs have also shown a reversible delay in ovulation. Consider withdrawal of NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, in women who have difficulties conceiving or who are undergoing investigation of infertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of ZORVOLEX in pediatric patients has not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Elderly patients, compared to younger patients, are at greater risk for NSAID-associated serious cardiovascular, gastrointestinal, and/or renal adverse reactions. If the anticipated benefit for the elderly patient outweighs these potential risks, start dosing at the low end of the dosing range, and monitor patients for adverse effects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.6, 5.13)].
Diclofenac is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Symptoms following acute NSAID overdosages have been typically limited to lethargy, drowsiness, nausea, vomiting, and epigastric pain, which have been generally reversible with supportive care. Gastrointestinal bleeding has occurred. Hypertension, acute renal failure, respiratory depression, and coma have occurred, but were rare [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.2, 5.4, 5.6)].
Manage patients with symptomatic and supportive care following an NSAID overdosage. There are no specific antidotes. Consider emesis and/or activated charcoal (60 to 100 grams in adults, 1 to 2 grams per kg of body weight in pediatric patients) and/or osmotic cathartic in symptomatic patients seen within four hours of ingestion or in patients with a large overdosage (5 to 10 times the recommended dosage). Forced diuresis, alkalinization of urine, hemodialysis, or hemoperfusion may not be useful due to high protein binding.
For additional information about overdosage treatment contact a poison control center (1- 800-222-1222).
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules are a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, available as hard gelatin capsules of 18 mg and 35 mg for oral administration. The chemical name is 2- [(2, 6-dichlorophenyl) amino] benzeneacetic acid. The molecular weight is 296.15. Its molecular formula is C14H11C12NO2, and it has the following chemical structure.
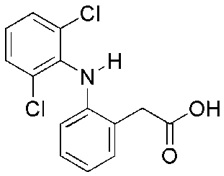
Diclofenac acid is a white to slight yellowish crystalline powder. Diclofenac acid has a pKa of 4.18 and a logP of 3.03. It is practically insoluble in water and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
The inactive ingredients in ZORVOLEX include a combination of lactose monohydrate, sodium lauryl sulfate, microcrystalline cellulose, croscarmellose sodium and sodium stearyl fumarate. The capsule shells contain gelatin, titanium dioxide, and dyes FD&C blue #1, FD&C blue #2, FDA/E172 Yellow Iron Oxide and FDA/E172 Black Iron Oxide. The imprinting on the gelatin capsules is white edible ink. The 18 mg capsules have a blue body imprinted with IP-203 and light green cap imprinted with 18 mg in white ink. The 35 mg capsules have a blue body imprinted with IP-204 and green cap imprinted with 35 mg in white ink.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Diclofenac has analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antipyretic properties.
The mechanism of action of ZORVOLEX, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood but involves inhibition of cyclooxygenase (COX-1 and COX-2).
Diclofenac is a potent inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis in vitro. Diclofenac concentrations reached during therapy have produced in vivo effects. Prostaglandins sensitize afferent nerves and potentiate the action of bradykinin in inducing pain in animal models. Prostaglandins are mediators of inflammation. Because diclofenac is an inhibitor of prostaglandin synthesis, its mode of action may be due to a decrease of prostaglandins in peripheral tissues.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The relative bioavailability of ZORVOLEX 35 mg capsules was compared to diclofenac potassium immediate-release (IR) tablets 50 mg in 39 healthy subjects under fasted and fed conditions in a single-dose crossover study.
ZORVOLEX 35 mg capsules do not result in an equivalent systemic exposure to 50 mg diclofenac potassium IR tablets.
When taken under fasted conditions, a 20% lower dose of diclofenac in ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in a 23% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 26% lower mean peak concentration (Cmax) compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets. The time to reach peak concentration (Tmax) was similar for ZORVOLEX and diclofenac potassium IR tablets and was ~1 hour for both.
When taken under fed conditions, a 20% lower dose of diclofenac in ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in a 23% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 48% lower mean Cmax compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets. The Tmax for ZORVOLEX was delayed by approximately 1 hour compared to diclofenac potassium IR tablets (3.32 hours vs. 2.33 hours, respectively).
When taken under fed conditions, ZORVOLEX capsules resulted in an 11% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and a 60% lower mean Cmax compared to fasted conditions. Whereas diclofenac potassium IR tablets under fed conditions resulted in 8% - 10% lower mean systemic exposure (AUCinf) and 28% - 43% lower mean Cmax compared to fasted conditions, based on the results from two individual food effect studies. The Tmax for ZORVOLEX was delayed by approximately 2.32 hours under fed conditions compared to fasted conditions (3.32 hours vs. 1.00 hour, respectively), while the Tmax for diclofenac potassium IR tablets was delayed by approximately 1.00 - 1.33 hours under fed conditions compared to fasted conditions (1.70 vs. 0.74 hours and 2.33 vs. 1.00 hours, respectively in two studies).
There were no differences in elimination half-life between ZORVOLEX and diclofenac potassium IR tablets under fasted or fed conditions.
Absorption
Diclofenac is 100% absorbed after oral administration compared to IV administration as measured by urine recovery. However, due to first-pass metabolism, only about 50% of the absorbed dose is systemically available. After repeated oral administration, no accumulation of diclofenac in plasma occurred.
Administration of ZORVOLEX capsules 18 mg and 35 mg was associated with dose proportional pharmacokinetics.
Taking ZORVOLEX with food causes a significant decrease in the rate but not the overall extent of systemic absorption of diclofenac compared with taking ZORVOLEX on an empty stomach. ZORVOLEX capsules results in 60% lower Cmax, 11% lower AUCinf, and 2.32 hours delayed Tmax (1.0 hour during fasted versus 3.32 hours during fed) under the fed condition compared to the fasted condition. The effectiveness of ZORVOLEX when taken with food has not been studied in clinical studies. The decreased Cmax may be associated with decreased effectiveness. Taking ZORVOLEX with food may cause a reduction in effectiveness compared to taking ZORVOLEX on an empty stomach.
Distribution
The apparent volume of distribution (V/F) of diclofenac potassium is 1.3 L/kg. Diclofenac is more than 99% bound to human serum proteins, primarily to albumin. Serum protein binding is constant over the concentration range (0.15-105 mg/mL) achieved with recommended doses.
Diclofenac diffuses into and out of the synovial fluid. Diffusion into the joint occurs when plasma levels are higher than those in the synovial fluid, after which the process reverses and synovial fluid levels are higher than plasma levels. It is not known whether diffusion into the joint plays a role in the effectiveness of diclofenac.
Elimination
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. The terminal half-life of unchanged diclofenac is approximately 2 hours.
Metabolism
Five diclofenac metabolites have been identified in human plasma and urine. The metabolites include 4'-hydroxy-, 5-hydroxy-, 3'-hydroxy-, 4',5-dihydroxy- and 3'- hydroxy-4'-methoxy diclofenac. The major diclofenac metabolite, 4'-hydroxy-diclofenac, has very weak pharmacologic activity. The formation of 4'-hydroxy-diclofenac is primarily mediated by CYP2C9. Both diclofenac and its oxidative metabolites undergo glucuronidation or sulfation followed by biliary excretion. Acylglucuronidation mediated by UGT2B7 and oxidation mediated by CYP2C8 may also play a role in diclofenac metabolism. CYP3A4 is responsible for the formation of minor metabolites, 5-hydroxy and 3'-hydroxy-diclofenac. In patients with renal dysfunction, peak concentrations of metabolites 4'-hydroxy and 5-hydroxy-diclofenac were approximately 50% and 4% of the parent compound after single oral dosing compared to 27% and 1% in normal healthy subjects.
Excretion
Diclofenac is eliminated through metabolism and subsequent urinary and biliary excretion of the glucuronide and the sulfate conjugates of the metabolites. Little or no free unchanged diclofenac is excreted in the urine. Approximately 65% of the dose is excreted in the urine, and approximately 35% in the bile as conjugates of unchanged diclofenac plus metabolites. Because renal elimination is not a significant pathway of elimination for unchanged diclofenac, dosing adjustment in patients with mild to moderate renal dysfunction is not necessary. The terminal half-life of unchanged diclofenac is approximately 2 hours.
Specific Populations
Pediatric: The pharmacokinetics of ZORVOLEX has not been investigated in pediatric patients.
Race: Pharmacokinetic differences due to race/ethnicity have not been identified.
Hepatic Impairment: No dedicated diclofenac pharmacokinetics studies in patients with hepatic impairment were conducted. Hepatic metabolism accounts for almost 100% of diclofenac elimination. Therefore, in patients with hepatic impairment, start with the lowest dose and if efficacy is not achieved, consider use of an alternate product [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Renal Impairment: Diclofenac pharmacokinetics has been investigated in subjects with renal insufficiency. No differences in the pharmacokinetics of diclofenac have been detected in studies of patients with renal impairment. In patients with renal impairment (inulin clearance 60-90, 30-60, and less than 30 mL/min; N=6 in each group), AUC values and elimination rate were comparable to those in healthy subjects [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Drug Interaction Studies
Aspirin: When NSAIDs were administered with aspirin, the protein binding of NSAIDs were reduced, although the clearance of free NSAID was not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known. See Table 4 for clinically significant drug interactions of NSAIDs with aspirin [see Drug Interactions (7)].
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats given diclofenac sodium up to 2 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.2 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD] of ZORVOLEX based on body surface area [BSA] comparison) have revealed no significant increase in tumor incidence. A 2-year carcinogenicity study conducted in mice employing diclofenac sodium at doses up to 0.3 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.014 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) in males and 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.04 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) in females did not reveal any oncogenic potential.
Mutagenesis
Diclofenac sodium did not show mutagenic activity in in vitro point mutation assays in mammalian (mouse lymphoma) and microbial (yeast, Ames) test systems and was nonmutagenic in several mammalian in vitro and in vivo tests, including dominant lethal and male germinal epithelial chromosomal aberration studies in Chinese hamsters.
Impairment of Fertility
Diclofenac sodium administered to male and female rats at 4 mg/kg/day (approximately 0.4 times the MRHD based on BSA comparison) did not affect fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Acute Pain
The efficacy of ZORVOLEX in the management of acute pain was demonstrated in a single multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel arm study comparing ZORVOLEX 18 mg and 35 mg taken three times a day, placebo, and celecoxib in patients with pain following bunionectomy. The study enrolled 428 patients with a mean age of 40 years (range 18 to 65 years) and a minimum pain intensity rating of at least 40 mm on a 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS) during the 9-hour period after discontinuation of the anesthetic block following bunionectomy surgery. Patients were randomized equally across the treatment groups.
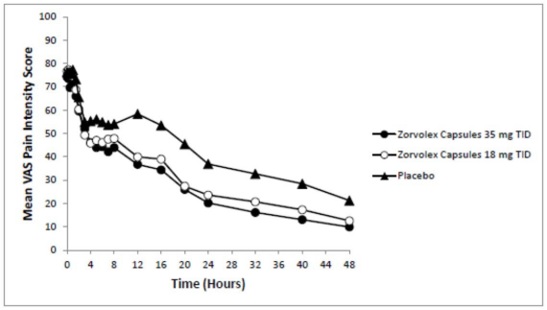
The mean and range (in parenthesis) of pain intensities on the VAS at baseline were 74 mm (44 to 100 mm), 77 mm (41 to 100 mm), and 76 mm (40 to 100 mm) for the ZORVOLEX 35 mg, ZORVOLEX 18 mg, and placebo groups, respectively. One tablet of hydrocodone/acetaminophen 10 mg/325 mg was permitted every 4 to 6 hours as rescue medication. About 82% of patients in the ZORVOLEX 35 mg group, 85% of the patients in the ZORVOLEX 18 mg group, and 97% of patients in the placebo group took rescue medication for pain management during the study.
The average pain intensities over time are depicted for the treatment groups in Figure 1. Both ZORVOLEX 18 mg and 35 mg demonstrated efficacy in pain intensity reduction compared with placebo, as measured by the sum of pain intensity difference over 0 to 48 hours after the first dose.
Figure 1 Average Pain Intensity Over 48 Hours for ZORVOLEX 18 mg, ZORVOLEX 35 mg, and Placebo Groups
Osteoarthritis Pain
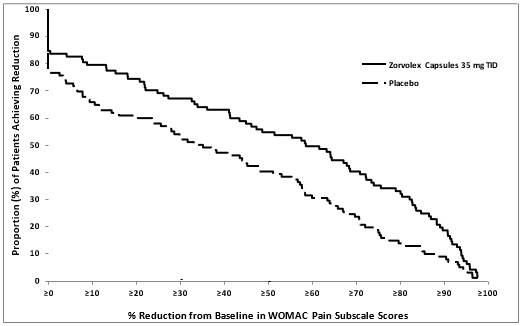
The efficacy of ZORVOLEX in the management of osteoarthritis pain was demonstrated in a single multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-arm study comparing ZORVOLEX 35 mg taken twice a day or three times a day and placebo in patients with osteoarthritis of the knee or hip. The study enrolled 305 patients with a mean age of 62 (range 41 to 90 years). Osteoarthritis pain was measured using the Western Ontario and McMaster University Osteoarthritis Index Pain Subscale (WOMAC Pain Subscale). Mean baseline WOMAC Pain Subscale Score across treatment groups was 75 mm using a 0 to 100 mm visual analog scale.
The primary efficacy parameter was the change from baseline at 12 weeks in the WOMAC Pain Subscale. ZORVOLEX 35 mg three times a day reduced osteoarthritis pain compared with placebo, as measured by WOMAC Pain Subscale Score. The distribution (%) of patients achieving various percentage reductions in pain intensity at Week 12 are depicted in Figure 2.
Figure 2 Distribution (%) of Patients Achieving Various Percentage Reductions in Pain Intensity at Week 12
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ZORVOLEX (diclofenac) capsules are supplied as:
- 18 mg - blue body and light green cap (imprinted IP-203 on the body and 18 mg on the cap in white ink)
- NDC (69344-203-29), Bottles of 90 capsules
- 35 mg - blue body and green cap (imprinted IP-204 on the body and 35 mg on the cap in white ink)
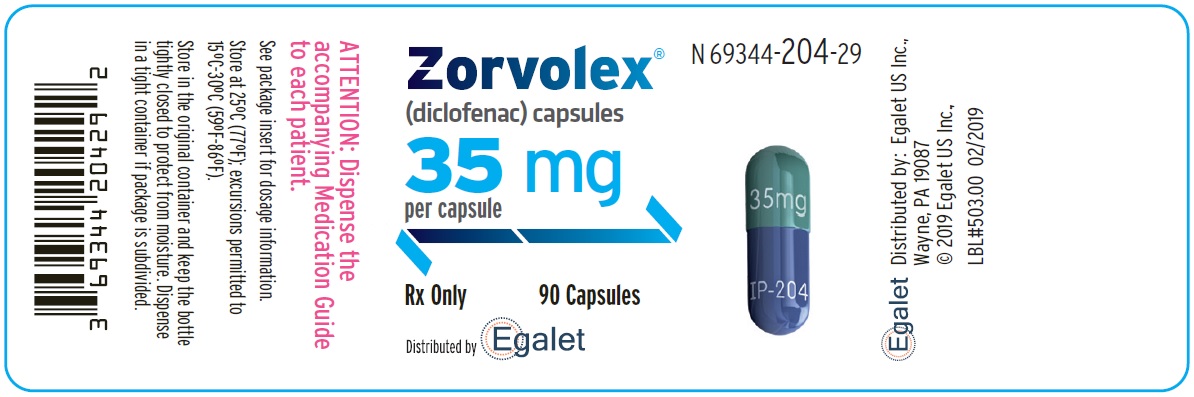
- NDC (69344-204-29), Bottles of 90 capsules
Storage
Store at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F); excursions permitted between 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store in the original container and keep the bottle tightly closed to protect from moisture. Dispense in a tight container if package is subdivided.
- 18 mg - blue body and light green cap (imprinted IP-203 on the body and 18 mg on the cap in white ink)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide) that accompanies each prescription dispensed. Inform patients, families, or their caregivers of the following information before initiating therapy with ZORVOLEX and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy.
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of cardiovascular thrombotic events, including chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, or slurring of speech, and to report any of these symptoms to their health care provider immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gastrointestinal Bleeding, Ulceration, and Perforation
Advise patients to report symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis to their health care provider. In the setting of concomitant use of low-dose aspirin for cardiac prophylaxis, inform patients of the increased risk for and the signs and symptoms of GI bleeding [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatotoxicity
Inform patients of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, diarrhea, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, instruct patients to stop ZORVOLEX and seek immediate medical therapy [see Warnings and Precautions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Heart Failure and Edema
Advise patients to be alert for the symptoms of congestive heart failure including shortness of breath, unexplained weight gain, or edema and to contact their healthcare provider if such symptoms occur [see Warnings and Precautions (see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Anaphylactic Reactions
Inform patients of the signs of an anaphylactic reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). Instruct patients to seek immediate emergency help if these occur [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Serious Skin Reactions
Advise patients to stop ZORVOLEX immediately if they develop any type of rash and to contact their healthcare provider as soon as possible [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Female Fertility
Advise females of reproductive potential who desire pregnancy that NSAIDs, including ZORVOLEX, may be associated with a reversible delay in ovulation [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Fetal Toxicity
Inform pregnant women to avoid use of ZORVOLEX and other NSAIDs starting at 30 weeks gestation because of the risk of the premature closing of the fetal ductus arteriosus [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Avoid Concomitant Use of NSAIDs
Inform patients that the concomitant use of ZORVOLEX with other NSAIDs or salicylates (e.g., diflunisal, salsalate) is not recommended due to the increased risk of gastrointestinal toxicity, and little or no increase in efficacy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Drug Interactions (7)]. Alert patients that NSAIDs may be present in “over the counter” medications for treatment of colds, fever, or insomnia.
Use of NSAIDs and Low-Dose Aspirin
Inform patients not to use low-dose aspirin concomitantly with ZORVOLEX until they talk to their healthcare provider [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Manufactured (under license from iCeutica Pty Ltd.) for and Distributed by:
Egalet US Inc., Wayne, PA 19087
©2019 Egalet Corporation. All rights reserved.
US Patent Nos. 8679544, 8999387, 9017721, 9173854, 9180095, 9180096, and 9186328
03/2019
LBL# 501.00
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Revised: 03/2019
Medication Guide for Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
What is the most important information I should know about medicines called Nonsteroidal Anti- inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)?
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:
-
Increased risk of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
- with increasing doses of NSAIDs
- with longer use of NSAIDs
Avoid taking NSAIDs after a recent heart attack, unless your healthcare provider tells you to. You may have an increased risk of another heart attack if you take NSAIDs after a recent heart attack. -
Increased risk of bleeding, ulcers, and tears (perforation) of the esophagus (tube leading from the mouth to the stomach), stomach and intestines:
- anytime during use
- without warning symptoms
- that may cause death
The risk of getting an ulcer or bleeding increases with:- past history of stomach ulcers, or stomach or intestinal bleeding with use of NSAIDs
- taking medicines called “corticosteroids”, “anticoagulants”, “SSRIs”, or “SNRIs”
- increasing doses of NSAIDs
- longer use of NSAIDs
- smoking
- drinking alcohol
- older age
- poor health
- advanced liver disease
- bleeding problems
NSAIDs should only be used:- exactly as prescribed
- at the lowest dose possible for your treatment
- for the shortest time needed
What are NSAIDs?
NSAIDs are used to treat pain and redness, swelling, and heat (inflammation) from medical conditions such as different types of arthritis, menstrual cramps, and other types of short-term pain.Who should not take NSAIDs?
Do not take NSAIDs:- if you have had an asthma attack, hives, or other allergic reaction with aspirin or any other NSAIDs.
- right before or after heart bypass surgery.
Before taking NSAIDs, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- have liver or kidney problems
- have high blood pressure
- have asthma
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Talk to your healthcare provider if you are considering taking NSAIDs during pregnancy. You should not take NSAIDs after 29 weeks of pregnancy.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breast feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all of the medicines you take, including prescription or over-the- counter medicines, vitamins or herbal supplements. NSAIDs and some other medicines can interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start taking any new medicine without talking to your healthcare provider first.
What are the possible side effects of NSAIDs?
NSAIDs can cause serious side effects, including:- new or worse high blood pressure
- heart failure
- liver problems including liver failure
- kidney problems including kidney failure
- low red blood cells (anemia)
- life-threatening skin reactions
- life-threatening allergic reactions
- Other side effects of NSAIDs include: stomach pain, constipation, diarrhea, gas, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, and dizziness.
Get emergency help right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing
- chest pain
- weakness in one part or side of your body
- slurred speech
- swelling of the face or throat
Stop taking your NSAID and call your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms:
- nausea
- more tired or weaker than usual
- diarrhea
- itching
- your skin or eyes look yellow
- indigestion or stomach pain
- flu-like symptoms
- vomit blood
- there is blood in your bowel movement or it is black and sticky like tar
- unusual weight gain
- skin rash or blisters with fever
- swelling of the arms, legs, hands and feet
If you take too much of your NSAID, call your healthcare provider or get medical help right away.
These are not all the possible side effects of NSAIDs. For more information, ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist about NSAIDs.Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Other information about NSAIDs
- Aspirin is an NSAID but it does not increase the chance of a heart attack. Aspirin can cause bleeding in the brain, stomach, and intestines. Aspirin can also cause ulcers in the stomach and intestines.
- Some NSAIDs are sold in lower doses without a prescription (over-the-counter). Talk to your healthcare provider before using over-the-counter NSAIDs for more than 10 days.
General information about the safe and effective use of NSAIDs
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use NSAIDs for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give NSAIDs to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.If you would like more information about NSAIDs, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about NSAIDs that is written for health professionals.
Distributed by: Egalet US Inc., Wayne, PA 19087
For more information, go to WWW.ZORVOLEX.COM or call 1-800-518-1084.
-
Increased risk of a heart attack or stroke that can lead to death. This risk may happen early in treatment and may increase:
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 69344-203-29 - 18 mg 90-count Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - NDC: 69344-204-29 - 35 mg 90-count Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ZORVOLEX
diclofenac capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69344-203 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DICLOFENAC (UNII: 144O8QL0L1) (DICLOFENAC - UNII:144O8QL0L1) DICLOFENAC 18 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) SODIUM STEARYL FUMARATE (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color BLUE (blue body) , GREEN (light green cap) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code IP;203;18;mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69344-203-29 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/04/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA204592 02/04/2019 ZORVOLEX
diclofenac capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69344-204 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DICLOFENAC (UNII: 144O8QL0L1) (DICLOFENAC - UNII:144O8QL0L1) DICLOFENAC 35 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) SODIUM STEARYL FUMARATE (UNII: 7CV7WJK4UI) GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color BLUE (blue body) , GREEN (green cap) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code IP;204;35;mg Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69344-204-29 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/04/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA204592 02/04/2019 Labeler - Egalet US Inc. (079581441) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Catalent CTS, LLC 962674474 MANUFACTURE(69344-203, 69344-204) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon 005286822 LABEL(69344-203, 69344-204) , PACK(69344-203, 69344-204)
Trademark Results [Zorvolex]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ZORVOLEX 85413540 4505759 Live/Registered |
ZYLA LIFE SCIENCES US INC. 2011-09-01 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.