PEDMARK- sodium thiosulfate injection, solution
PEDMARK by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PEDMARK by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Fennec Pharmaceuticals Inc., Cambrex Charles City, Inc., Cambrex Agawam MA, Berkshire Sterile Manufacturing, A+ Secure Packaging LLC, d/b/a Cardinal Health Packaging, SGS Life Science Services, Cambrex Durham, NC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PEDMARK safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PEDMARK.
PEDMARK® (sodium thiosulfate injection), for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1992INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PEDMARK is indicated to reduce the risk of ototoxicity associated with cisplatin in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with localized, non-metastatic solid tumors. (1)
Limitations of Use:
The safety and efficacy of PEDMARK have not been established when administered following cisplatin infusions longer than 6 hours. PEDMARK may not reduce the risk of ototoxicity when administered following longer cisplatin infusions, because irreversible ototoxicity may have already occurred.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
PEDMARK is not substitutable with other sodium thiosulfate products. (2)
The recommended dose of PEDMARK is based on surface area according to actual body weight.
- Administer PEDMARK as an intravenous infusion over 15 minutes starting 6 hours after completion of cisplatin infusion.
- For multiday cisplatin regimens, administer PEDMARK 6 hours after each cisplatin infusion but at least 10 hours before the next cisplatin infusion.
- Do not start PEDMARK if less than 10 hours before starting the next cisplatin infusion (2)
Actual Body Weight PEDMARK Dose Less than 5 kg 10 g/m2 5 to 10 kg 15 g/m2 Greater than 10 kg 20 g/m2 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 12.5 grams/100 mL in a single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
History of severe hypersensitivity to sodium thiosulfate or any components. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypersensitivity: Immediately discontinue PEDMARK and institute appropriate care. Administer premedications before each subsequent dose. PEDMARK may contain sodium sulfite; patients with sulfite sensitivity may have hypersensitivity reactions. (5.1)
- Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia: PEDMARK is not indicated for use in pediatric patients less than 1 month of age. Monitor serum sodium and potassium at baseline and as clinically indicated. Withhold PEDMARK in patients with serum sodium greater than 145 mmol/L (5.2)
- Nausea and Vomiting: Administer antiemetics prior to each PEDMARK administration. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Most common adverse reactions (≥ 25% with difference between arms of >5% compared to cisplatin alone) in SIOPEL 6 are vomiting, nausea, decreased hemoglobin, and hypernatremia. (6)
- Most common adverse reaction (≥25% with difference between arms of >5% compared to cisplatin alone) in COG ACCL0431 is hypokalemia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Fennec Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-833-336-6321, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 6/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
2.3 Recommended Premedications
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Preparation
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
5.2 Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia
5.3 Nausea and Vomiting
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience/Spontaneous Reports
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PEDMARK is indicated to reduce the risk of ototoxicity associated with cisplatin in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with localized, non-metastatic solid tumors.
Limitations of Use
The safety and efficacy of PEDMARK have not been established when administered following cisplatin infusions longer than 6 hours. PEDMARK may not reduce the risk of ototoxicity when administered following longer cisplatin infusions, because irreversible ototoxicity may have already occurred.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosing Information
PEDMARK is not substitutable with other sodium thiosulfate products.
Ensure serum sodium level is within normal range prior to initiating PEDMARK [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
2.2 Recommended Dosage and Administration
The recommended dose of PEDMARK is based on surface area according to actual body weight as summarized in Table 1.
Table 1. Recommended Dose for PEDMARK Actual Body Weight PEDMARK Dose Less than 5 kg 10 g/m2 5 to 10 kg 15 g/m2 Greater than 10 kg 20 g/m2 Administer PEDMARK as an intravenous infusion over 15 minutes, following cisplatin infusions that are 1 to 6 hours in duration [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Infuse PEDMARK as described below to minimize the potential interference with the antitumor activity of cisplatin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), Clinical Studies (14)].
- Administer PEDMARK 6 hours after completion of a cisplatin infusion.
- For multiday cisplatin regimens, administer PEDMARK 6 hours after completion of each cisplatin infusion and at least 10 hours before the next cisplatin infusion. Do not administer PEDMARK if the next cisplatin infusion is scheduled to begin in less than 10 hours [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3), Clinical Studies (14)].
2.3 Recommended Premedications
Administer antiemetics before each PEDMARK infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
For patients who experience a hypersensitivity reaction, administer antihistamines and glucocorticoids (if appropriate) before each subsequent PEDMARK infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
The recommended dosage modifications for adverse reactions are provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Recommended PEDMARK Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions Adverse Reaction Severity Dosage Modification Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)] Grade 3 or 4 Permanently discontinue PEDMARK. Hypernatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] >145 mmol/L Withhold PEDMARK until sodium is within normal limits. Resume at the same dose. Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] Grade 3 or 4 Withhold PEDMARK until potassium is within normal limits. Resume at the same dose. Other Adverse Reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 3 Withhold until ≤ Grade 1. Resume at the same dose. Grade 4 Permanently discontinue PEDMARK. 2.5 Preparation
- Calculate the dose (grams) and determine the number of vial(s) needed.
- Visually inspect the contents of the vial for particulate matter and discoloration. Discard the vial(s) if discolored or contains visible particulates.
- Withdraw the calculated dose from the vial(s) into a syringe or transfer the calculated dose into an empty infusion bag.
- Use immediately after withdrawing into a syringe or transferring to an empty infusion bag. If not used immediately, PEDMARK can be stored in an infusion bag for no more than 18 hours at 20°C to 22°C (68°F to 72°F). Discard unused portion.
No incompatibilities have been observed between PEDMARK with infusion bags made of polyvinyl chloride, ethylene vinyl acetate, or polyolephin.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
PEDMARK is contraindicated in patients with history of a severe hypersensitivity to sodium thiosulfate or any of its components [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity
Hypersensitivity reactions occurred in 8% to 13% of patients in clinical trials [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
PEDMARK is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity to sodium thiosulfate or its components [see Contraindications (4)].
Monitor patients for hypersensitivity reactions. Immediately discontinue PEDMARK and institute appropriate care if a hypersensitivity reaction occurs [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. Administer antihistamines or glucocorticoids (if appropriate) before each subsequent administration of PEDMARK [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
PEDMARK may contain sodium sulfite. Sulfite exposure can cause hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic symptoms and life-threatening or severe asthma episodes, in patients with sulfite sensitivity. The overall prevalence of sulfite sensitivity in the general population is unknown; sulfite sensitivity is seen more frequently in people with asthma compared to people without asthma.
5.2 Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia
At the recommended dosage of PEDMARK, a 20 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 162 mmol/m2, a 15 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 121 mmol/m2 and a 10 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 81 mmol/m2.
Hypernatremia occurred in 12% to 26% of patients in clinical trials, including a single Grade 3 case. Hypokalemia occurred in 15% to 27% of patients in clinical trials, with Grade 3 or 4 occurring in 9% to 27% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Pediatric patients younger than 1 month have less well-developed sodium homeostasis compared to other pediatric patients. PEDMARK is not indicated and not recommended for use in pediatric patients younger than 1 month of age.
Monitor serum sodium and potassium levels at baseline and as clinically indicated. Do not initiate PEDMARK infusions in patients with baseline serum sodium greater than 145 mmol/L [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2), Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
Withhold PEDMARK in patients with serum sodium greater than 145 mmol/L [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.2), Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypernatremia and hypokalemia. Provide supportive care and supplementation as appropriate.
5.3 Nausea and Vomiting
Nausea occurred in 8% to 40% of patients in clinical trials, with Grade 3 or 4 in 3.8 to 8%. Vomiting occurred in 7% to 85% of patients in clinical trials, with Grade 3 or 4 in 7% to 8% [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Administer antiemetics prior to each PEDMARK administration [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)]. Provide additional antiemetics and supportive care as appropriate.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Nausea and Vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
SIOPEL 6
The safety of PEDMARK was evaluated in SIOPEL 6 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients received cisplatin-based chemotherapy with or without PEDMARK administered at a dose of 10 g/m2, 15 g/m2, or 20 g/m2 (depending on body weight) as an intravenous infusion over 15 minutes starting 6 hours after completion of each cisplatin infusion. Patients received PEDMARK for a median of 6 cycles (range: 2 to 8 cycles) during a median of 94 days (range: 2.1 to 5.2 months) of cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 40% of patients who received PEDMARK in combination with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Serious adverse reactions in >5% of patients who received PEDMARK included infection, decreased neutrophil count, and pyrexia.
PEDMARK was permanently discontinued due to an adverse reaction in 1 patient; this patient discontinued PEDMARK for Grade 2 hypersensitivity.
The most common adverse reactions (≥25% with difference between arms of >5% compared to cisplatin alone) were vomiting, nausea, decreased hemoglobin, and hypernatremia.
Table 3 summarizes the adverse reactions reported in SIOPEL 6.
Table 3. Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients Who Received PEDMARK and Cisplatin with a Difference Between Arms of >5% Compared to Cisplatin Alone in SIOPEL 6 Adverse Reaction PEDMARK + Cisplatin
(N = 53)Cisplatin Alone
(N = 56)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)Gastrointestinal disorders Vomiting 85 8 54 3.6 Nausea 40 3.8 30 5 Investigations Decreased Hemoglobin 34 19 29 16 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Hypernatremia 26 1.9 3.6 0 Hypokalemia 15 9 1.8 0 Hypophosphatemia 15 9 1.8 0 Hypermagnesemia 11 9 5 3.6 General disorders Pyrexia 15 0 9 0 COG ACCL0431
The safety of PEDMARK was evaluated in COG ACCL0431 [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Patients received cisplatin-based chemotherapy with or without PEDMARK, administered at a dose that is bioequivalent to the recommended dose as an intravenous infusion over 15 minutes starting 6 hours after completion of each cisplatin infusion. Patients who received PEDMARK were treated for a median of 3 cycles (range: 1 to 6) during a median of 15 weeks of cisplatin-based chemotherapy.
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 36% of patients who received PEDMARK in combination with cisplatin-based chemotherapy. Serious adverse reactions in >5% of patients who received PEDMARK included febrile neutropenia, decreased neutrophil count, decreased platelet count, decreased white blood cell count, anemia, stomatitis, infections, decreased lymphocyte count, and increased alanine aminotransferase (ALT).
PEDMARK was permanently discontinued due to an adverse reaction in 1 patient; this patient discontinued PEDMARK for Grade 2 hypersensitivity.
The most common adverse reaction (≥25% with difference between arms of >5% compared to cisplatin alone) was hypokalemia.
Table 4 summarizes the adverse reactions reported in COG ACCL0431.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions (≥10%) in Patients Who Received PEDMARK and Cisplatin with a Difference Between Arms of >5% Compared to Cisplatin Alone in COG ACCL0431 Adverse Reaction PEDMARK + Cisplatin
(N = 59)Cisplatin Alone
(N = 64)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grade 3 or 4
(%)Metabolism and nutrition disorders Hypokalemia 27 27 20 20 Hypophosphatemia 20 20 11 11 Hyponatremia 14 12 6 6 Hypernatremia 12 0 6 0 Gastrointestinal disorders Stomatitis 14 14 6 6 6.2 Postmarketing Experience/Spontaneous Reports
The following adverse reactions have been identified from spontaneous reports based on medical literature. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular Disorders: hypertension, hypotension
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: metabolic acidosis, hypocalcemia
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on PEDMARK used in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk. Oral or intravenous administration of sodium thiosulfate during the period of organogenesis resulted in no signs of malformations or lethality, but at doses and exposures that were lower than those in humans (see Data).
PEDMARK is administered following cisplatin infusions, which can cause embryo-fetal harm. Refer to cisplatin prescribing information for additional information.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Animal Data
In animal studies, sodium thiosulfate was not embryotoxic or teratogenic in pregnant mice, rats, hamsters, or rabbits at daily (5 to 13 daily doses during the period of organogenesis) oral maternal doses of up to 550, 400, 400, and 580 mg/kg/day (0.08 to 0.35 times the highest clinical dose of 20 g/m2 based on body surface area [BSA]), respectively, of sodium thiosulfate; exposure in these animals compared to humans may be much lower due to poor oral bioavailability. Sodium thiosulfate was not embryotoxic or teratogenic in hamsters following a total daily dose of 1500 mg/kg (0.38 times the highest clinical dose of 20 g/m2 based on BSA). Additionally, an intravenous pharmacokinetic study in gravid ewes indicated that sodium thiosulfate does not cross the placenta.
8.2 Lactation
There are no data on the presence of sodium thiosulfate in human milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production.
PEDMARK is administered in combination with cisplatin. Refer to cisplatin prescribing information for additional information.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PEDMARK have been established to reduce the risk of ototoxicity associated with cisplatin in pediatric patients 1 month of age and older with localized, non-metastatic solid tumors.
The safety and effectiveness of PEDMARK have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 1 month old or in pediatric patients with metastatic cancer.
PEDMARK is not recommended in pediatric patients younger than 1 month old due to the increased risk of hypernatremia [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Sodium thiosulfate is substantially excreted by the kidney [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with renal impairment or end-stage renal disease. Monitor for signs and symptoms of hypernatremia and hypokalemia more closely if the GFR falls below 60 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Sodium thiosulfate anhydrous is an inorganic salt with a molecular formula of Na2S2O3 and a molecular weight of 158.11 g/mol. The structural formula is:
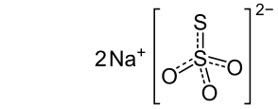
It is a white to off-white crystalline solid that is soluble in water, but insoluble in alcohol. The aqueous solution has a pH ranging from 6.5 to 8.0.
PEDMARK (sodium thiosulfate injection) is a sterile, preservative-free, clear, colorless solution in a single-dose vial for intravenous use with a pH between 7 and 9. Each vial contains the equivalent of 12.5 grams of sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate (provided as sodium thiosulfate anhydrous 8 grams) in 100 mL solution (125 mg/mL). Each mL contains the equivalent of 125 mg of sodium thiosulfate pentahydrate (provided as sodium thiosulfate anhydrous 80 mg) and 0.25 mg boric acid. Sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid may have been used for pH adjustment.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Cisplatin-induced ototoxicity is caused by irreversible damage to hair cells in the cochlea hypothesized to be due to a combination of reactive oxygen species (ROS) production and direct alkylation of DNA leading to cell death. Sodium thiosulfate interacts directly with cisplatin to produce an inactive platinum species. In addition, sodium thiosulfate can enter cells through the sodium sulfate cotransporter 2 and cause intracellular effects such as the increase in antioxidant glutathione levels and inhibition of intracellular oxidative stress. Both activities may contribute to the ability of sodium thiosulfate to reduce the risk of ototoxicity.
Concurrent incubation of sodium thiosulfate with cisplatin decreased the in vitro cytotoxicity of cisplatin to tumor cells; delaying the addition of sodium thiosulfate to these cultures prevented the protective effect.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Serum Sodium Level
A 20 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 162 mmol/m2, a 15 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 121 mmol/m2, and a 10 g/m2 dose delivers a sodium load of 81 mmol/m2. In SIOPEL 6, the recommended dosage resulted in an average transient increase in serum sodium levels of approximately 6 mmol/L at 1 hour after infusion [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)] and levels had returned to baseline by 18 hours or 24 hours after administration.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics (PK) of thiosulfate was assessed in pediatric patients. At the recommended dosage, the mean (±SD) maximum concentration (Cmax) was 13 ± 1.2 mM. The Cmax of thiosulfate increased proportionally to dose over the range of 4 g/m2 to 20 g/m2. No accumulation of thiosulfate is expected following administration of PEDMARK on two consecutive days.
Distribution
Sodium thiosulfate does not bind to human plasma proteins. Sodium thiosulfate is an inorganic salt and thiosulfate anions do not readily cross cell membranes. The mean volume of distribution of thiosulfate is 0.23 L/kg.
Elimination
The mean half-life (t1/2) of thiosulfate is approximately 20 minutes to 50 minutes. The mean total clearance of thiosulfate is 2.2 mL/min/kg in patients with fully developed renal function (age approximately 1 year). Renal clearance accounts for approximately 50% of total clearance in patients with fully developed renal function.
Metabolism
Thiosulfate is an endogenous intermediate product of sulfur-containing amino acid metabolism. Thiosulfate is metabolized through thiosulfate sulfur transferase and thiosulfate reductase to sulfite, which is oxidized to sulfate.
Excretion
After administration of sodium thiosulfate, approximately 50% of the administered sodium thiosulfate was excreted unchanged in urine and >95% of the dose excreted in urine occurs within the first 4 hours after administration.
Specific Populations
Patients with Renal Impairment
Thiosulfate Cmax increased approximately 25% and AUC increased approximately 2-fold in subjects on hemodialysis (GFR 0 to 6 mL/min/1.72 m2, estimated by the modification of diet in renal disease [MDRD] equation) compared to subjects with normal renal function (GFR >70 mL/min/1.72 m2, MDRD).
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
Cytochrome P450 Enzymes: Sodium thiosulfate is an inducer of CYP2B6 but not of CYP1A2 or CYP3A4. Sodium thiosulfate is not an inhibitor of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6 or CYP3A4 at clinically relevant concentrations.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate the potential carcinogenicity of sodium thiosulfate. In an in vitro Bacterial Reverse Mutation Assay (Ames Assay), sodium thiosulfate was not mutagenic in the absence of metabolic activation in S. typhimurium strains TA98, TA100, TA1535, TA1537, or TA1538, nor in the presence of metabolic activation in strains TA98, TA1535, TA1537, or TA1538 or E. coli strain WP2. Sodium thiosulfate at up to 1000 µM did not increase the frequency of sister chromatid exchanges in human lymphocytes in vitro.
There are no animal studies examining the effects of sodium thiosulfate on fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of PEDMARK in reducing the risk of cisplatin-associated ototoxicity was evaluated in two multicenter studies: SIOPEL 6 and COG ACCL0431.
SIOPEL 6
SIOPEL 6 (NCT00652132) was a multicenter, randomized, controlled, open-label study. Eligible patients were between 1 month and 18 years of age and were receiving cisplatin-based chemotherapy for standard-risk hepatoblastoma. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive 6 cycles of perioperative cisplatin-based chemotherapy without (cisplatin alone arm) or with PEDMARK (PEDMARK + cisplatin arm). Patients received PEDMARK at a dose based on body weight administered intravenously over 15 minutes, beginning 6 hours after completion of each cisplatin infusion. Doses of PEDMARK were 10 g/m2 for patients weighing <5 kg; 15 g/m2 for patients weighing 5 kg to 10 kg; and 20 g/m2 for patients weighing >10 kg. Randomization was stratified by country, age (above vs below 15 months), and PRETEXT (I and II vs III). The major efficacy outcome measure was hearing loss defined as a Brock Grade ≥1; hearing was assessed using pure tone audiometry after study treatment or at an age of at least 3.5 years, whichever was later.
A total of 114 patients were randomized, 61 patients to the PEDMARK + cisplatin arm and 53 patients to the cisplatin alone arm. The median age was 1.1 years (range: 1.2 months to 8.2 years); 55% were male; 60% were White, 11% were Asian, and 1.8% were Black or African American.
The incidence of hearing loss was lower in the PEDMARK + cisplatin arm compared with the cisplatin alone arm. Efficacy results are provided in Table 5.
Table 5: Efficacy Results for SIOPEL 6 Patients Who Experienced Hearing Loss PEDMARK + Cisplatin
(N = 61*)Cisplatin Alone
(N = 53*)- * 6 patients who received PEDMARK + cisplatin and 7 patients who received cisplatin alone did not have hearing assessed and were assumed to have hearing loss.
- † From Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test stratified by country group, age group, and PRETEXT group
Yes, n (%) 24 (39) 36 (68) No, n (%) 37 (61) 17 (32) Unadjusted relative risk (95% CI) 0.58 (0.40, 0.83) Adjusted relative risk (95% CI)† 0.58 (0.41, 0.81) COG ACCL0431
COG ACCL0431 (NCT00716976) was a multicenter, randomized, controlled, open-label study. Eligible patients were between 1 and 18 years of age and were receiving a chemotherapy regimen that included a cumulative cisplatin dose of 200 mg/m2 or higher, with individual cisplatin doses to be infused over 6 hours or less. Patients were randomized 1:1 to receive cisplatin-based chemotherapy without (cisplatin alone arm) or with PEDMARK (PEDMARK + cisplatin arm). Cisplatin was administered according to each site's disease-specific treatment protocols. Patients received PEDMARK intravenously starting 6 hours after the completion of each cisplatin infusion, at a dose bioequivalent to the recommended dose. The PEDMARK infusion must have been completed at least 10 hours before the next cisplatin infusion if the treatment protocol required multiple daily doses of cisplatin. Randomization was stratified by prior cranial radiation (yes vs no); for patients without prior cranial radiation, randomization was further stratified by age (<5 years vs ≥5 years) and duration of cisplatin infusion (<2 hours vs ≥2 hours). The major efficacy outcome measure was hearing loss assessed by American Speech-Language-Hearing Association (ASHA) criteria; hearing was assessed at baseline and 4 weeks after the final course of cisplatin.
A total of 125 pediatric patients were randomized, 61 patients to the PEDMARK + cisplatin arm and 64 patients to the cisplatin alone arm. The efficacy was evaluated in patients with localized disease in the ITT population (n = 77). The median age was 8 years (range: 1 to 18); 61% were male; 62% were White, 14% were Black or African American, and 2.6% were Asian. The median Karnofsky or Lansky performance status was 90 (range: 50 to 100). Underlying diagnosis included medulloblastoma (27%), osteosarcoma (26%), germ cell tumor (23%), neuroblastoma (10%), hepatoblastoma (8%), atypical teratoid/rhabdoid tumor (2.6%), choroid plexus carcinoma (1.3%), and anaplastic astrocytoma (1.3%); 7% had prior cranial radiation.
The incidence of hearing loss was lower in the PEDMARK + cisplatin arm compared with the cisplatin alone arm. Efficacy results are provided in Table 6.
Table 6: Efficacy Results for COG ACCL0431 – Patients with Localized Disease Patients Who Experienced Hearing Loss PEDMARK + Cisplatin
(N = 39*)Cisplatin Alone
(N = 38*)- * 8 patients who received PEDMARK + cisplatin and 5 patients who received cisplatin alone did not have hearing assessed and were assumed to have hearing loss.
- † From Cochran-Mantel-Haenszel test stratified by prior cranial irradiation, age group, and duration of cisplatin infusion
Yes, n (%) 17 (44) 22 (58) No, n (%) 22 (56) 16 (42) Unadjusted relative risk (95% CI) 0.75 (0.48, 1.18) Adjusted relative risk (95% CI)† 0.84 (0.53, 1.35) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PEDMARK (sodium thiosulfate injection) is a clear, colorless, sterile solution in a Type 1 Plus borosilicate glass single-dose vial with rubber stopper and capped with aluminum overseal, supplied as:
- 12.5 grams/100 mL (125 mg/mL) single-dose vial, NDC: 73077-010-01
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Hypersensitivity
Inform patients and caregivers that PEDMARK can cause hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Hypernatremia and Hypokalemia
Inform patients and caregivers that PEDMARK can cause hypernatremia and hypokalemia, and to promptly report signs and symptoms consistent with these electrolyte abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Nausea and Vomiting
Inform patients and caregivers that PEDMARK can cause nausea and vomiting [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 mL Vial Box
100 mL
SterileNDC: 73077-010-01
pedmark®
(sodium thiosulfate injection)12.5 grams/100 mL (125 mg/mL)
For Intravenous Use Only
Single-Dose Vial. Discard Unused
Portion.Rx Only
Do Not Substitute with Other
Sodium Thiosulfate Products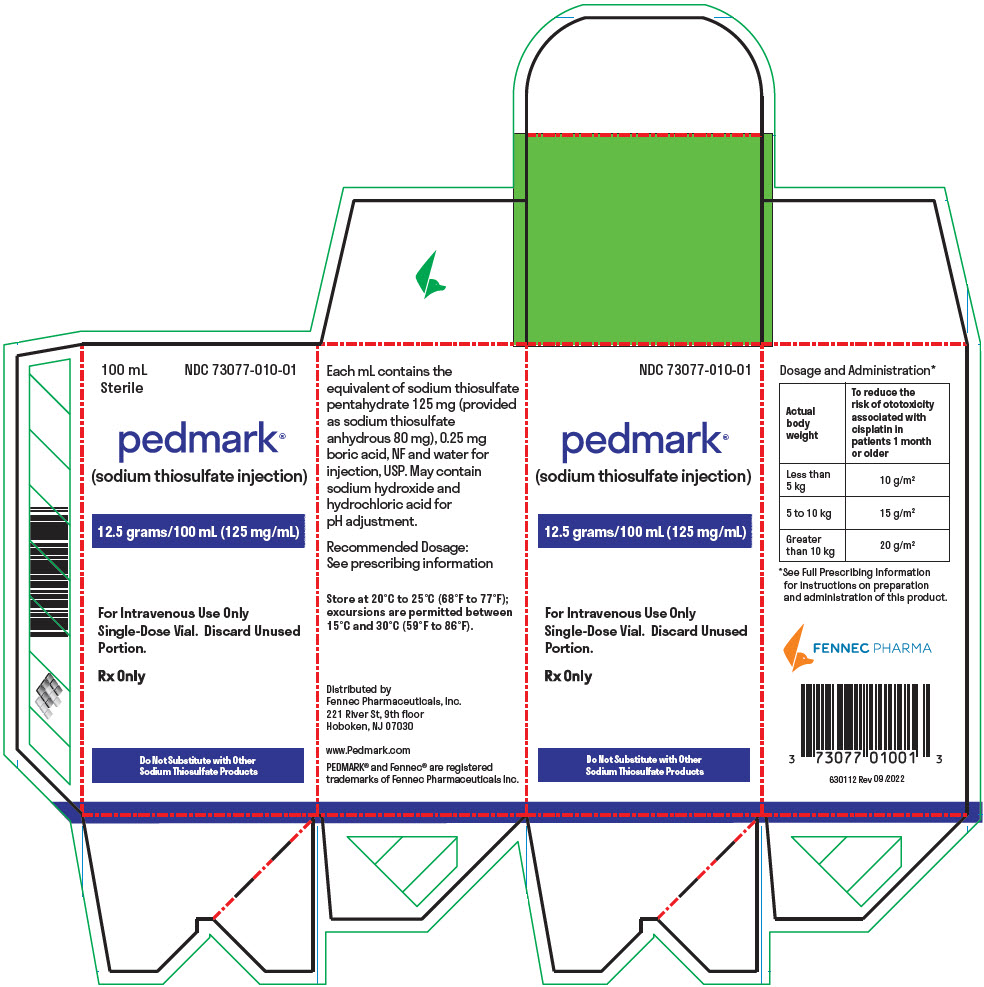
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PEDMARK
sodium thiosulfate injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 73077-010 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SODIUM THIOSULFATE (UNII: HX1032V43M) (THIOSULFATE ION - UNII:LLT6XV39PY) THIOSULFATE ION 12.5 g in 100 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength BORIC ACID (UNII: R57ZHV85D4) SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 73077-010-01 1 in 1 BOX, UNIT-DOSE 10/03/2022 1 100 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212937 10/03/2022 Labeler - Fennec Pharmaceuticals Inc. (159861132) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cambrex Charles City, Inc. 782974257 API MANUFACTURE(73077-010) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cambrex Agawam MA 079509111 ANALYSIS(73077-010) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sharp Sterile Manufacturing 079589218 MANUFACTURE(73077-010) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations A+ Secure Packaging LLC, d/b/a Cardinal Health Packaging 963589036 PACK(73077-010) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations SGS Life Science Services 049859261 ANALYSIS(73077-010) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Cambrex Durham, NC 108353231 ANALYSIS(73077-010)
Trademark Results [PEDMARK]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PEDMARK 90071857 not registered Live/Pending |
Fennec Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2020-07-24 |
 PEDMARK 87305680 not registered Live/Pending |
Fennec Pharmaceuticals, Inc. 2017-01-18 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.