FELANORM- methimazole solution
Felanorm by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Felanorm by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Norbrook Laboratories Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- DESCRIPTION:
- INDICATION:
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION:
Always include the Instructions for Preparing a Dose of Felanorm (methimazole) Oral Solution and the Information for Cat Owners with the prescription. The starting dose of Felanorm is 2.5 mg administered every 12 hours. Following 3 weeks of treatment, the dose should be titrated to effect based on individual serum total T4 (TT4) levels and clinical response. Dose adjustments should be made in 2.5 mg increments. The maximum total dosage is 20 mg per day divided, not to exceed 10 mg as a single administration.
Hematology, biochemistry, and TT4 should be evaluated prior to initiating treatment and monitored after 3 weeks and 6 weeks of treatment. Thereafter, bloodwork should be monitored every 3 months and the dose adjusted as necessary. Cats receiving doses greater than 10 mg per day should be monitored more frequently.
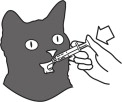
The product should be administered orally using the enclosed graduated dosing syringe. The syringe has measurements representing the mg dose of the product. Rinse/clean the oral dosing syringe between uses. (See the Instructions for Preparing a Dose of Felanorm (methimazole) Oral Solution).
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS:
Do not use in cats with hypersensitivity to methimazole or carbimazole. Do not use in cats with primary liver disease or renal failure.
Do not use in cats with autoimmune disease. See ADVERSE REACTIONS.
Do not use in cats with hematological disorders (such as anemia, neutropenia, lymphopenia, or thrombocytopenia) or coagulopathies. See ADVERSE REACTIONS.
Do not use in pregnant or lactating queens. Laboratory studies in rats and mice have shown evidence of teratogenic and embryotoxic effects of methimazole.
-
WARNINGS:
Methimazole has anti-vitamin K activity and may induce bleeding diathesis without evidence of thrombocytopenia. See ADVERSE REACTIONS.
Keep Felanorm in a secure location out of reach of dogs, cats, and other animals to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
-
HUMAN WARNINGS:
Not for use in humans. Keep out of reach of children. For use in cats only. Wear protective single use, impermeable (e.g., latex or nitrile) gloves when administering the solution. Wash hands with soap and water after administration to avoid exposure to drug. Wear protective gloves to prevent direct contact with litter, feces, urine, or vomit of treated cats, and the solution. Wash hands after contact with the litter of treated cats.
Methimazole is a human teratogen and crosses the placenta concentrating in the fetal thyroid gland. There is also a high rate of transfer into breast milk. Pregnant women or women who may become pregnant, and nursing mothers should wear gloves when handling the solution, litter or bodily fluids of treated cats. Individuals with an endocrine disorder that could be impacted by methimazole should use similar precautions.
Methimazole may cause vomiting, gastric distress, headache, fever, arthralgia, pruritus, and pancytopenia. In the event of accidental ingestion/overdose, seek medical advice immediately and show the product label to the physician.
Avoid skin and oral exposure, including hand-to-mouth contact. Wash any spillages or splatter from the skin immediately. Do not eat, drink, smoke/vape, or use smokeless tobacco while handling the product or used litter.
Felanorm may cause skin or eye irritation. Avoid eye contact, including hand-to-eye contact. In case of accidental eye contact, rinse eyes immediately with clean running water. If irritation develops, seek medical advice.
-
PRECAUTIONS:
Use of Felanorm in cats with renal dysfunction should be carefully evaluated. Reversal of hyperthyroidism may be associated with decreased glomerular filtration rate and a decline in renal function, unmasking the presence of underlying renal disease. Due to potentially serious adverse reactions such as hepatopathy, immune-mediated anemia, thrombocytopenia, and agranulocytosis, cats on methimazole therapy should be monitored closely for any sign of illness including anorexia, vomiting, head/facial pruritus or edema, depression/lethargy, weight loss, anemia, skin lesions, diarrhea, fever, or lymphadenopathy. If a cat becomes ill while on Felanorm, the drug should be stopped and appropriate hematological and biochemical testing should be done (see ANIMAL SAFETY and POST APPROVAL EXPERIENCE). Anticoagulants may be potentiated by the anti-vitamin K activity of Felanorm. Concurrent use of phenobarbital may reduce the clinical effectiveness of Felanorm.
A reduction in dose of certain drugs (β-adrenergic blocking agents, digitalis glycosides, and theophylline) may be needed when the patient becomes euthyroid.
Methimazole is known to reduce the hepatic oxidation of benzimidazole anthelmintics (e.g. fenbendazole), leading to increased plasma concentration of these anthelmintics when administered concurrently.
Methimazole caused delayed maturation of the testes in young male cats in the 12-week safety study. See ANIMAL SAFETY. The safety of Felanorm has not been evaluated in male cats intended for breeding.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS:
In a US field study with 113 cats, the most common adverse reactions included change in food consumption (increase or decrease), lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea/loose stool, skin lesions, and abnormal vocalization. Three cats were withdrawn early from the study, one due to unmasking of latent renal disease and two due to the development of skin lesions. Over the course of the study, there was a decreasing trend in the mean counts of red blood cells, lymphocytes, neutrophils and monocytes; however, means remained within or near normal ranges for the testing laboratory. In the extended use phase of the US field study with 101 cats, the most common adverse reactions reported in the study above (lethargy, anorexia) were also observed. Additional signs occurring more frequently in the long-term study were:
depression/withdrawn behavior, weight loss, hair coat abnormalities, increased blood urea nitrogen (BUN), weakness, agitation and diarrhea. Most of the adverse reactions reported were mild and transient.
Serum chemistry and hematology results in the extended use study were consistent with the trends noted during the field study. The mean alanine transaminase (ALT) was above the reference range at the first two quarterly visits, but within the normal reference range (10-100 U/L) through the next two quarterly visits.
Mean lymphocyte counts decreased consistently during the study period, to slightly below the reference range (1200-8000 cells/mcL) at the fourth quarterly visit.
Sixteen cats experienced elevated antinuclear antibody (ANA) titers at one or more points during long-term therapy with methimazole, but the significance was not determined. Eighteen cats died or were euthanized during the extended use study, four of which may have been related to methimazole due to the unmasking/acceleration of chronic renal failure. See PRECAUTIONS.
In a foreign field study with 26 cats using a starting dose of 5 mg twice daily (twice the recommended starting dose), one cat was withdrawn due to lethargy, vomiting and facial excoriations. Marked thrombocytopenia was reported in two cats; the platelet count returned to normal in one cat when methimazole tablets were discontinued. Two cats collapsed and died within 12 days of starting methimazole at a dose of 5 mg twice daily. Both cats were reported with lethargy, vomiting, anorexia, and bloody diarrhea; one cat also had pallor.
In a second foreign field study with 78 cats using a starting dose of 2.5 mg twice daily, 4 cats were withdrawn due to suspected adverse reactions to methimazole including anemia, cholangiohepatitis, excoriations, vomiting, lethargy, jaundice, and anorexia. One cat receiving 2.5 mg three times daily collapsed and died after 8 weeks of treatment. Adverse reactions included pallor, anorexia, dehydration, jaundice, bleeding diathesis, and anemia. The most frequently reported adverse reactions included mild, transient, self-limiting vomiting, lethargy, and anorexia.
Foreign Market Experience: The following events were reported voluntarily during post-approval use of methimazole in foreign markets: facial pruritus, self-induced excoriations of the head and neck, generalized lymphadenopathy, thrombocytopenia, hematemesis, epistaxis, and elevation of serum liver enzymes and bilirubin.
If overdosage occurs, stop treatment and give symptomatic and supportive care.
POST APPROVAL EXPERIENCE (revised 2015): The following adverse events are based on voluntary, post approval reporting. Not all adverse events are reported to FDA/CVM. It is not always possible to reliably estimate the adverse event frequency or establish a causal relationship to product exposure using these data. The following adverse events are listed in decreasing order of reporting frequency: Anorexia, vomiting, head/facial pruritus or edema, depression/lethargy, weight loss, anemia, elevated liver enzymes, skin lesions, elevated BUN, diarrhea, and thrombocytopenia. In some reported cases, the patients recovered after adverse signs were recognized, the drug was withdrawn, and veterinary care was applied. In some cases, death (or euthanasia) has been reported as an outcome of the adverse reactions listed above.
-
CONTACT INFORMATION:
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Norbrook at 1-866-591-5777.
For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY:
Methimazole is an antithyroid drug that acts by blocking the biosynthesis of thyroid hormone in vivo. The primary action is to inhibit binding of iodide to the enzyme thyroid peroxidase, thereby preventing the catalyzed iodination of thyroglobulin and T3 and T4 synthesis.
Methimazole is well absorbed following oral administration. Maximum plasma concentrations are achieved within 1-1 1/2 hours after dosing and methimazole is rapidly eliminated from the blood (T1/2 is approximately 3 hours). Administration of methimazole in a fasted state enhances absorption.
-
EFFECTIVENESS:
In a US effectiveness field study with 113 cats, the product was considered effective if both the TT4 concentration was ≤ 4.0 mcg/dL, and the Investigator's clinical assessment documented clinical improvement. Of the 105 evaluable cases, 64 (61%) were considered treatment successes. The decrease in TT4 concentration was significant from the pre-enrollment visit to the Day 42 visit. A TT4 of ≤ 4.0 mcg/dL occurred in 59.1% and 61.9% of cats on Day 21 and Day 42, respectively. Investigators assessed 91.8% and 87.6% of cats as clinically improved on Days 21 and 42, respectively.
In the extended use phase of the US effectiveness field study with 101 cats, effectiveness was based on a combination of lnvestigator's clinical assessment, maintenance of TT4 concentrations at or near the laboratory reference range of 0.8-4.0 mcg/dL, and the presence or absence of adverse reactions. Mean TT4 concentrations were within or near the laboratory reference range during the first four quarterly visits. At the first quarterly visit, Investigators categorized 80.9% of cats as stable or improved relative to their baseline assessment. By the fourth quarterly visit, 75.8% were deemed to be stable or improved.
The average maintenance dose required in the extended use phase was 2.5 mg twice daily, with a minimum of 2.5 mg per cat and a maximum of 15 mg per cat on a daily basis.
-
ANIMAL SAFETY:
ANIMAL SAFETY STUDIES: In a 12-week safety study, healthy young cats were dosed with 0, 10, 20, and 30 mg methimazole per day, divided into two doses. Cats in all treated, groups experienced anorexia, vomiting, loose stool and lethargy. Cats in the 20 and 30 mg/day groups also had facial excoriations, pruritus, and lymphadenopathy. The following hematological changes were seen: neutropenia, lymphopenia, anemia, and thrombocytopenia. The following biochemical changes were seen: increased globulin, increased magnesium, increased blood urea nitrogen, increased creatinine and decreased phosphorus. There was a dose-dependent occurrence of antinuclear antibodies. Most of the clinical pathology changes were mild in nature. One cat dosed with 20 mg/day experienced a six-fold increase in ALT during the study. This cat had loose stool, but was otherwise healthy throughout the study. Hepatomegaly was seen in this cat at necropsy and the histopathological examination was comparable to other treated cats with hepatomegaly and normal ALT.
Gross necropsy findings in all treated groups included hepatomegaly, thymus atrophy and thyroid hyperplasia and darkening. Some treated males had delayed maturation of the testes. The 30 mg/day dose was poorly tolerated and resulted in the clinical deterioration and euthanasia of four of the six cats in that group. Two of the cats showed signs of immune-mediated hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia and severe clinical deterioration. One had been on the drug for 34 days, the other for 9 weeks. The drug was discontinued in a third cat treated with 30 mg/day while it received supportive care. It was euthanized on day 55 after becoming anorexic. This cat had anemia (HCT 21.6%) and red blood cell agglutination. Necropsy showed inflammation of the muscular layer of the stomach and a small erosion in the stomach. A fourth cat treated with 30 mg/day was euthanized after several days of anorexia when the decision was made to discontinue dosing in this group. All 30 mg/day cats that died had generalized lymphadenopathy. Necropsies revealed reactive lymph nodes and varying degrees of inflammation throughout the body. The remaining 2 cats in the 30 mg/day group were taken off methimazole at week 9 and fully recovered.
- STORAGE INFORMATION:
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Felanorm is available at 5mg/mL in bottles containing 30 or 100mL with 1mL dosing syringe.
Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-771
TAKE TIME
OBSERVE LABEL
DIRECTIONSManufactured by:
Norbrook Laboratories Limited
Newry, Co. Down, BT35 6QQ, Northern Ireland
Felanorm® is a trademark of Norbrook Laboratories Limited
US Patent Numbers: 10,045,967, US 11,123,327 and US 11,738,005
Rev. 08/2024
317670I04
Norbrook® -
INSTRUCTIONS FOR USE
Instructions for Preparing a Dose of Felanorm (methimazole) Oral Solution
To draw up a dose, carefully follow these instructions. Prior to preparing a dose, carefully read the Special precautions to be taken when administering Felanorm in the Information for Cat Owners.
- Always wear protective single use, impermeable (e.g., latex or nitrile) gloves when preparing and administering the cat's dose of this medicine.
- Push and turn the screw cap to open the bottle. Attach the dosing syringe to the bottle by gently pushing the end onto the top of the bottle.
Note: Always cap the bottle after use. - Check that the plunger of the oral dosing syringe (included with the product bottle) is pushed all the way down.
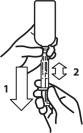
- Turn the bottle/syringe upside down. Pull the plunger back/down until the oral dosing syringe fills with medicine.
- Carefully expel any large bubbles by pushing and pulling the plunger a few times with the bottle upside down. The presence of a few tiny bubbles is not important for dosing accuracy.
- Fill the syringe with the dose of medicine prescribed by your veterinarian by pulling the plunger back/down slowly. The scale on the oral dosing syringe corresponds to the milligram (mg) dose. The end of plunger nearest the tip of the syringe should be level with the measurement (line) corresponding to the correct mg dose.
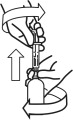
- Turn the bottle right way up and with a twisting movement, separate the dosing syringe from the bottle.
Note: If the prescribed dose is more than one syringe-full (5 mg or 1 milliliter (mL) of solution), you will need to reload the syringe with additional medication to provide the full dose. In this case, the total dose will need to be given via multiple fillings of the dosing syringe. For instance, if the dose is 7.5 mg, then you will need to give one syringe-full (5 mg) plus an additional 2.5 mg to provide the full dose.
- Push the plunger to empty the content of the syringe directly in the cat's mouth.
The product should be administered slowly and gently, allowing the cat to swallow the product. The product is administered by pushing it out of the syringe with the syringe plunger.
Following administration, any residual product remaining on the tip of the dosing syringe should be wiped clean with a disposable item (napkin, paper towel, or tissue). The contaminated item (napkin, paper towel, or tissue) should be disposed of immediately in a trash receptacle. To avoid contamination of the product bottle, the dosing syringe should be rinsed externally, cleaned, and dried between doses and between individual fillings (when multiple fillings of the dosing syringe are needed to provide a single dose). The bottle cap should be screwed back on the product bottle tightly, and the dosing syringe should be stored with the product bottle in the original carton.
Wash your hands with soap and water after administration to avoid exposure to the drug.
Keep out of reach of children.
-
INFORMATION FOR OWNERS/CAREGIVERS
Felanorm (methimazole) oral solution
Information for Cat Owners
This summary contains important information about Felanorm. You should read this information before starting your cat on Felanorm and review it each time the prescription is refilled. This sheet is provided only as a summary and does not take the place of instructions from your veterinarian. Talk to your veterinarian if you do not understand any of this information or if you want to know more about Felanorm.
What is Felanorm?
Felanorm is a prescription oral solution containing methimazole and is used for the treatment of hyperthyroidism in cats.
Hyperthyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland over-produces thyroid hormone and is a lifelong condition that requires treatment. Felanorm reduces the production of thyroid hormone. Common signs of hyperthyroidism include weight loss, and an increase in appetite, thirst, and urination. Other signs may include vomiting, diarrhea, hyperactivity, and unkempt coat.
What kind of results can I expect when my cat takes Felanorm for the control of hyperthyroidism?
Felanorm controls hyperthyroidism but does not cure the disease. It may take several weeks for the medication to normalize the thyroid hormone levels. Improvement in signs may include: weight gain or cessation of weight loss, a decrease in excessive appetite, water consumption, and urination, and a decrease in vomiting, diarrhea, and hyperactivity. Your veterinarian will evaluate your cat several weeks after starting treatment and on a regular basis thereafter to determine if dose adjustments are needed. Dose adjustment should only be carried out in consultation with your veterinarian.
What cats should not take Felanorm?
Your cat should not be given Felanorm if s/he:
- Is hypersensitive to methimazole
- Has been diagnosed with primary liver disease or kidney failure
- Has been diagnosed with an autoimmune disease
- Has been diagnosed with a blood disorder (such as anemia or low blood cell counts) or a clotting disorder
- Is pregnant or nursing
What to discuss with your veterinarian before giving Felanorm to your cat.
Tell your veterinarian about:
- Any serious disease or health conditions your cat has had
- Any previous treatments for hyperthyroidism, including methimazole treatment or radioactive iodine, and any side effects related to those treatments
- Any allergies that your cat has now or has had
- All medications that you are giving your cat or plan to give your cat, including those you can get without prescription (over-the-counter) and any dietary supplements
- If you plan to breed your cat, or if your cat is pregnant or nursing
Talk to your veterinarian about:
- What tests might be done before Felanorm is prescribed
- The potential side effects your cat may experience while taking Felanorm
- How often your cat may need to be examined by your veterinarian
- The risks and benefits of using Felanorm, including human user safety risks
What are the possible side effects that may occur in my cat during therapy with Felanorm?
Felanorm, like all other drugs, may cause side effects in individual cats. These are normally mild, but serious side effects have been reported in cats taking methimazole. Serious side effects can, in rare situations, result in death. It is important to stop the medication and contact your veterinarian immediately if you think your cat may have a medical problem or side effect while on Felanorm.
Possible side effects include loss of appetite, lethargy, vomiting, diarrhea/loose stool, head and facial itchiness or swelling, skin lesions, weight loss, elevated liver enzymes, elevated kidney enzymes, abnormal vocalization, and low counts of red cells, white cells, and platelets. Methimazole may cause your cat to bleed or bruise more easily. In some cases, patients recovered after side effects from methimazole were recognized, methimazole was withdrawn, and veterinary care was administered. In some cases, death (or euthanasia) was the outcome of the side effects.
To report suspected adverse drug events, for technical assistance or to obtain a copy of the Safety Data Sheet (SDS), contact Norbrook at 1-866-591-5777. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or http://www.fda.gov/reportanimalae.
Felanorm should only be given to cats.
People should not take Felanorm. Keep Felanorm and all medication out of reach of children. Call your physician immediately if you accidentally swallow Felanorm.
How to give Felanorm to your cat.
Felanorm should be given as prescribed by your veterinarian and according to your veterinarian's instructions. Your veterinarian will tell you what amount of Felanorm is right for your cat. Whenever possible, you should administer Felanorm on a consistent schedule with regard to time of day. Do not change the way you give Felanorm to your cat without first speaking with your veterinarian. If a dose is missed, resume dosing based on your cat's regular dosing schedule. Do not give double the dose the next time. If your cat is due to have a monitoring blood test within a couple of days of missing a dose, make sure you tell your veterinarian as it could affect the blood results.
Advice on Correct Administration.
See Instructions for Preparing a Dose of Felanorm (methimazole) Oral Solution.
How to Store Felanorm.
Felanorm should be stored in the original container at room temperature (77°F), however temperatures between 59°-86°F are permitted.
Special precautions to be taken when administering Felanorm.
Methimazole can cause or increase the risk of birth defects in human babies.
Always wear protective single use, impermeable (e.g., latex or nitrile) gloves when administering Felanorm or to prevent direct contact with litter, feces, urine, or vomit of treated cats. Wash your hands with soap and water after administration of Felanorm or after contact with the litter of treated cats to avoid exposure to Felanorm. This is especially important if you are pregnant, become pregnant, are nursing, or have an endocrine disorder that could be impacted by Felanorm.
Avoid skin and oral exposure, including hand-to-mouth contact. Wash any spillages or splatter from the skin immediately. Do not eat, drink, smoke/vape, or use smokeless tobacco while handling the product or used litter. In the event of accidental ingestion, seek medical advice immediately and show the product label to the physician.
Felanorm may cause skin or eye irritation. Avoid eye contact, including hand-to-eye contact. In case of accidental eye contact, rinse eyes immediately with clean running water. If irritation develops, seek medical advice.
Can Felanorm be given with other medications?
Interactions with certain medications are possible. Always tell your veterinarian about all medications, including those you can get without a prescription (over-the-counter), that you have given your cat in the past and all medications that you are planning to give with Felanorm.
What can I do if my cat gets more than the prescribed amount of Felanorm?
Contact your veterinarian immediately if your cat gets more than the prescribed amount of Felanorm.
What else should I know about Felanorm?
This sheet provides a summary of information about Felanorm. If you have any questions or concerns about Felanorm or hyperthyroidism in cats, talk to your veterinarian.
As with all prescribed medications, Felanorm should only be given to the cat and condition for which it was prescribed, at the prescribed dose, and as directed by your veterinarian.
-
Principal Display Panel – 100 mL Carton Label
NDC: 55529-170-02
5 mg of methimazole/mL
Felanorm®
(methimazole)Oral Solution
5 mg of
methimazole/mL100 mL
For oral use in cats only
CAUTION: Federal law restricts this drug to use by
or on the order of a licensed veterinarian.Approved by FDA under ANADA # 200-771
Norbrook®
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FELANORM
methimazole solutionProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55529-170 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHIMAZOLE (UNII: 554Z48XN5E) (METHIMAZOLE - UNII:554Z48XN5E) METHIMAZOLE 5 mg in 1 mL Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor HONEY (Honey) Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55529-170-14 1 in 1 CARTON 1 30 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 55529-170-02 1 in 1 CARTON 2 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANADA ANADA200771 07/10/2024 Labeler - Norbrook Laboratories Limited (214580029) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Norbrook Laboratories Limited 211218325 MANUFACTURE, ANALYSIS, PACK, LABEL
Trademark Results [Felanorm]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 FELANORM 97042298 not registered Live/Pending |
Norbrook Laboratories Limited 2021-09-23 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.