PLUVICTO- lutetium lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan injection, solution
PLUVICTO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
PLUVICTO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc, Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PLUVICTO safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PLUVICTO.
PLUVICTO® (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan) injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2022RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PLUVICTO is a radioligand therapeutic agent indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) who have been treated with androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy, and
- are considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy, or
- have received prior taxane-based chemotherapy. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Select patients for treatment using LOCAMETZ® or another approved PSMA positron emission tomography (PET) product based on PSMA expression in tumors. (2.2)
- Recommended Dosage: Administer 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) every 6 weeks for 6 doses. (2.3)
- Dose interruption, reduction, or permanent discontinuation may be required due to adverse reactions. (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 1,000 MBq/mL (27 mCi/mL) in a single-dose vial. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Risk From Radiation Exposure: Minimize radiation exposure during and after treatment with PLUVICTO consistent with institutional good radiation safety practices and patient treatment procedures. Ensure patients increase oral fluid intake and advise patients to void as often as possible to reduce bladder radiation. (5.1)
- Myelosuppression: Perform complete blood counts. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue PLUVICTO based on severity. (2.4, 5.2)
- Renal Toxicity: Advise patients to remain well hydrated and to urinate frequently. Perform kidney function laboratory tests. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue PLUVICTO based on severity. (2.4, 5.3)
- Embryo-Fetal Toxicity: Can cause fetal harm. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception. (5.4, 8.1, 8.3)
- Infertility: PLUVICTO may cause temporary or permanent infertility. (5.5, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased lymphocytes, decreased hemoglobin, fatigue, dry mouth, decreased platelets, decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate, nausea, decreased neutrophils, decreased calcium, decreased sodium, increased aspartate aminotransferase, increased alkaline phosphatase, arthralgia, decreased appetite, increased potassium, constipation, and back pain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation at 1-888-669-6682 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 3/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Instructions
2.2 Patient Selection
2.3 Recommended Dosage
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
2.5 Preparation and Administration
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk From Radiation Exposure
5.2 Myelosuppression
5.3 Renal Toxicity
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
5.5 Infertility
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 Physical Characteristics
11.2 External Radiation
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 PSMA-Positive mCRPC Previously Treated With ARPI Therapy
14.2 PSMA-Positive mCRPC Previously Treated With ARPI Therapy and Taxane-Based Chemotherapy
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
PLUVICTO is indicated for the treatment of adult patients with prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-positive metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) who have been treated with androgen receptor pathway inhibitor (ARPI) therapy, and
- are considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy, or
- have received prior taxane-based chemotherapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Safety Instructions
PLUVICTO is a radiopharmaceutical; handle with appropriate safety measures to minimize radiation exposure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Use waterproof gloves and effective radiation shielding when handling PLUVICTO.
Radiopharmaceuticals, including PLUVICTO, should be used by or under the control of healthcare providers who are qualified by specific training and experience in the safe use and handling of radiopharmaceuticals, and whose experience and training have been approved by the appropriate governmental agency authorized to license the use of radiopharmaceuticals.
2.2 Patient Selection
Select patients with previously treated mCRPC for treatment with PLUVICTO using LOCAMETZ or another approved PSMA positron emission tomography (PET) product based on PSMA expression in tumors. Additional selection criteria were used in clinical studies [see Clinical Studies (14)].
2.3 Recommended Dosage
The recommended PLUVICTO dosage is 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) intravenously every 6 weeks for 6 doses, or until disease progression, or unacceptable toxicity.
2.4 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Recommended dosage modifications of PLUVICTO for adverse reactions are provided in Table 1. Management of adverse reactions may require temporary dose interruption, dose reduction or permanent discontinuation of treatment with PLUVICTO. If a treatment delay due to an adverse reaction persists for > 4 weeks, consider permanent discontinuation of PLUVICTO. The dose of PLUVICTO may be reduced by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi) once; do not re-escalate dose. If a patient has further adverse reactions that would require an additional dose reduction, treatment with PLUVICTO must be discontinued.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage Modifications of PLUVICTO for Adverse Reactions Abbreviations: CLcr, creatinine clearance; AST, aspartate aminotransferase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; ULN, upper limit of normal.
Grading according to most current Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE).Adverse reaction Severity Dosage modification Myelosuppression
(Anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, or neutropenia)
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]Grade 2 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement to Grade 1 or baseline. Grade ≥ 3 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement to Grade 1 or baseline.
Reduce PLUVICTO dose by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi).Recurrent Grade ≥ 3 myelosuppression after one dose reduction Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Renal toxicity
[see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]Defined as: - Confirmed serum creatinine increase (Grade ≥ 2)
- Confirmed CLcr < 30 mL/min; calculate using Cockcroft-Gault with actual body weight
Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement. Defined as: - Confirmed ≥ 40% increase from baseline serum creatinine
and - Confirmed > 40% decrease from baseline CLcr; calculate using Cockcroft-Gault with actual body weight
Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement or return to baseline.
Reduce PLUVICTO dose by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi).Grade ≥ 3 renal toxicity Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Recurrent renal toxicity after one dose reduction Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Dry mouth [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade 2 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement or return to baseline.
Consider reducing PLUVICTO dose by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi).Grade 3 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement or return to baseline.
Reduce PLUVICTO dose by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi).Recurrent Grade 3 dry mouth after one dose reduction Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Gastrointestinal toxicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade ≥ 3 (not amenable to medical intervention) Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement to Grade 2 or baseline.
Reduce PLUVICTO dose by 20% to 5.9 GBq (160 mCi).Recurrent Grade ≥ 3 gastrointestinal toxicity after one dose reduction Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Fatigue [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade ≥ 3 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement to Grade 2 or baseline. Electrolyte or metabolic abnormalities [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Grade ≥ 2 Withhold PLUVICTO until improvement to Grade 1 or baseline. Other non-hematologic toxicity [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)] Any unacceptable toxicity Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Any adverse reaction that requires treatment delay of > 4 weeks Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. Any recurrent Grade 3 or 4 or persistent and intolerable Grade 2 adverse reaction after one dose reduction Permanently discontinue PLUVICTO. 2.5 Preparation and Administration
Preparation Instructions
- Use aseptic technique and radiation shielding when handling or administering PLUVICTO, using tongs as needed to minimize radiation exposure.
- Inspect the product visually under a shielded screen for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Discard the vial if particulates and/or discoloration are present.
- Do not inject the PLUVICTO solution directly into any other intravenous solution.
- Confirm the amount of radioactivity of PLUVICTO delivered to the patient with an appropriately calibrated dose calibrator prior to and after each PLUVICTO administration.
- Dispose of any unused medicinal product or waste material in accordance with local and federal laws.
Administration Instructions
Prior to administration, flush the intravenous catheter used exclusively for PLUVICTO administration with ≥ 10 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to ensure patency and to minimize the risk of extravasation. Manage cases of extravasation as per institutional guidelines.
The recommended dosage of PLUVICTO may be administered intravenously as an injection using the syringe method, as an infusion using the gravity method, or as an infusion using the peristaltic pump method.
When using the gravity or peristaltic pump method, infuse PLUVICTO directly from its original container.
Use the syringe method or the peristaltic pump method when administering a reduced dose of PLUVICTO following a dosage modification for an adverse reaction. When using the gravity method for a reduced dose, adjust the PLUVICTO dose before the administration to avoid the delivery of an incorrect volume of PLUVICTO.
Intravenous Methods of Administration
Instructions for the Syringe Method
- Withdraw an appropriate volume of PLUVICTO solution to deliver the desired radioactivity by using a disposable syringe fitted with a syringe shield and a disposable sterile needle that is 9 cm, 18 gauge (long needle). To aid the withdrawal of the solution, a filtered 2.5 cm, 20 gauge needle (short venting needle) can be used to reduce the resistance from the pressurized vial. Ensure that the short needle does not touch the PLUVICTO solution in the vial.
- Administer PLUVICTO to the patient by slow intravenous push within approximately 1 to 10 minutes (either with a syringe pump or manually without a syringe pump) via an intravenous catheter that is primed with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and that is used exclusively for PLUVICTO administration to the patient.
- If using a syringe pump, fit the syringe into the shielded pump and include a 3-way stopcock valve between the syringe and an intravenous catheter primed with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and used for PLUVICTO administration to the patient.
- When the desired PLUVICTO radioactivity has been delivered, stop the syringe pump and then change the position of the 3-way stopcock valve to flush the syringe with 25 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Restart the syringe pump.
- After the flush of the syringe has been completed, perform an intravenous flush of ≥ 10 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP through the intravenous catheter to the patient.
Instructions for the Gravity Method
- Insert a 2.5 cm, 20 gauge needle (short needle) into the PLUVICTO vial and connect via a catheter to 500 mL 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP (used to transport the PLUVICTO solution during the infusion). Ensure that the short needle does not touch the PLUVICTO solution in the vial and do not connect the short needle directly to the patient. Do not allow the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to flow into the PLUVICTO vial prior to the initiation of the PLUVICTO infusion and do not inject the PLUVICTO solution directly into the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP.
- Insert a second needle that is 9 cm, 18 gauge (long needle) into the PLUVICTO vial, ensuring that the long needle touches and is secured to the bottom of the PLUVICTO vial during the entire infusion. Connect the long needle to the patient by an intravenous catheter that is primed with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and that is used exclusively for the PLUVICTO infusion into the patient.
- Use a clamp or an infusion pump to regulate the flow of the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP via the short needle into the PLUVICTO vial (the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP entering the vial through the short needle will carry the PLUVICTO solution from the vial to the patient via the intravenous catheter connected to the long needle within approximately 30 minutes).
- During the infusion, ensure that the level of solution in the PLUVICTO vial remains constant.
- Disconnect the vial from the long needle line and clamp the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP line once the level of radioactivity is stable for at least five minutes.
- Follow the infusion with an intravenous flush of ≥ 10 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP through the intravenous catheter to the patient.
Instructions for the Peristaltic Pump Method
- Insert a filtered 2.5 cm, 20 gauge needle (short venting needle) into the PLUVICTO vial. Ensure that the short needle does not touch the PLUVICTO solution in the vial and do not connect the short needle directly to the patient or to the peristaltic pump.
- Insert a second needle that is 9 cm, 18 gauge (long needle) into the PLUVICTO vial, ensuring that the long needle touches and is secured to the bottom of the PLUVICTO vial during the entire infusion. Connect the long needle and a 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP to a 3-way stopcock valve via appropriate tubing.
- Connect the output of the 3-way stopcock valve to tubing installed on the input side of the peristaltic pump according to manufacturer’s instructions.
- Prime the line by opening the 3-way stopcock valve and pumping the PLUVICTO solution through the tubing until it reaches the exit of the valve.
- Prime the intravenous catheter which will be connected to the patient by opening the 3-way stopcock valve to the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP and pumping the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP until it exits the end of the catheter tubing.
- Connect the primed intravenous catheter to the patient and set the 3-way stopcock valve such that the PLUVICTO solution is in line with the peristaltic pump.
- Infuse an appropriate volume of PLUVICTO solution at approximately 25 mL/h to deliver the desired radioactivity.
- When the desired PLUVICTO radioactivity has been delivered, stop the peristaltic pump and then change the position of the 3-way stopcock valve so that the peristaltic pump is in line with the 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP. Restart the peristaltic pump and infuse an intravenous flush of ≥ 10 mL of 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP through the intravenous catheter to the patient.
2.6 Radiation Dosimetry
Dosimetry of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan was collected in 29 patients in the VISION sub-study, in order to calculate whole body and organ radiation dosimetry. The mean and standard deviation (SD) of the estimated radiation absorbed doses to different organs for adults receiving PLUVICTO are shown in Table 2. The organs with the highest radiation absorbed doses are lacrimal glands, salivary glands, large intestine (left and right colon), kidneys, and urinary bladder wall. The maximum penetration of lutetium-177 in tissue is approximately 2 mm and the mean penetration is 0.67 mm.
Table 2: Estimated Radiation Absorbed Dosea for PLUVICTO in VISION aRadiation absorbed dose estimates were derived using OLINDA v2.2 radiation dosimetry software, using measured time-activity data from patient imaging as input.
*Estimated radiation absorbed dose for bone marrow is not included given the wide expected variability based on location and burden of bone metastases between patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Absorbed dose per unit activity
(Gy/GBq)
N = 29Calculated absorbed dose
for 7.4 GBq
administration
(Gy)Calculated absorbed dose for
6 x 7.4 GBq
(44.4 GBq cumulative activity)
(Gy)Organ* Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Adrenals 0.033 0.025 0.24 0.19 1.5 1.1 Brain 0.007 0.005 0.049 0.035 0.30 0.22 Esophagus 0.025 0.026 0.18 0.19 1.1 1.1 Eyes 0.022 0.024 0.16 0.18 0.99 1.1 Gallbladder wall 0.028 0.026 0.20 0.19 1.2 1.1 Heart wall 0.17 0.12 1.2 0.83 7.8 5.2 Kidneys 0.43 0.16 3.1 1.2 19 7.3 Lacrimal glands 2.1 0.47 15 3.4 92 21 Left colon 0.58 0.14 4.1 1.0 26 6.0 Liver 0.090 0.044 0.64 0.32 4.0 2.0 Lungs 0.11 0.11 0.76 0.81 4.7 4.9 Pancreas 0.027 0.026 0.19 0.19 1.2 1.1 Prostate 0.027 0.026 0.19 0.19 1.2 1.1 Rectum 0.56 0.14 4.0 1.1 25 6.2 Right colon 0.32 0.078 2.3 0.58 14 3.4 Salivary glands 0.63 0.36 4.5 2.6 28 16 Small intestine 0.071 0.031 0.50 0.23 3.1 1.4 Spleen 0.067 0.027 0.48 0.20 3.0 1.2 Stomach wall 0.025 0.026 0.18 0.19 1.1 1.1 Testes 0.023 0.025 0.16 0.18 1.0 1.1 Thymus 0.025 0.026 0.18 0.19 1.1 1.1 Thyroid 0.26 0.37 1.8 2.7 11 16 Total body 0.037 0.027 0.27 0.20 1.6 1.2 Urinary bladder wall 0.32 0.025 2.3 0.19 14 1.1 - 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Risk From Radiation Exposure
PLUVICTO contributes to a patient’s overall long-term cumulative radiation exposure. Long-term cumulative radiation exposure is associated with an increased risk for cancer.
Minimize radiation exposure to patients, medical personnel, and others during and after treatment with PLUVICTO consistent with institutional good radiation safety practices, patient treatment procedures, Nuclear Regulatory Commission patient-release guidance, and instructions to the patient for follow-up radiation protection at home.
Ensure patients increase oral fluid intake and advise patients to void as often as possible to reduce bladder radiation.
Before the patient is released, inform patients about the necessary radioprotection precautions to follow to minimize radiation exposure to others [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
After each administration of PLUVICTO, advise patients to:
- Limit close contact (less than 3 feet) with others for 2 days or with children and pregnant women for 7 days.
- Refrain from sexual activity for 7 days.
- Sleep in a separate room from others for 3 days, from children for 7 days, or from pregnant women for 15 days.
5.2 Myelosuppression
PLUVICTO can cause severe and life-threatening myelosuppression, including anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, and neutropenia.
In the PSMAfore study, Grade 3 or 4 decreased hemoglobin (7%), decreased leukocytes (4.4%), decreased neutrophils (3.5%), and decreased platelets (2.7%) occurred in patients treated with PLUVICTO. One death occurred due to bone marrow failure during long-term follow-up in a patient who received PLUVICTO.
In the VISION study, Grade 3 or 4 decreased hemoglobin (15%), decreased platelets (9%), decreased leukocytes (7%), and decreased neutrophils (4.5%) occurred in patients treated with PLUVICTO. Grade ≥ 3 pancytopenia occurred in 1.1% (which includes two fatal events) of patients treated with PLUVICTO. Two deaths (0.4%) occurred due to intracranial hemorrhage and subdural hematoma in association with thrombocytopenia, one death (0.2%) occurred due to sepsis and concurrent neutropenia, and one death (0.2%) occurred due to bone marrow failure.
Perform complete blood counts before and during treatment with PLUVICTO. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue PLUVICTO based on the severity of myelosuppression [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.3 Renal Toxicity
PLUVICTO can cause severe renal toxicity.
In the PSMAfore study, Grade 3 or 4 acute kidney injury (1.3%) occurred in patients treated with PLUVICTO. In the VISION study, Grade 3 or 4 acute kidney injury (3.4%) occurred in patients treated with PLUVICTO.
Advise patients to remain well hydrated and to urinate frequently before and after administration of PLUVICTO. Perform kidney function laboratory tests, including serum creatinine and calculated creatinine clearance (CLcr), before and during treatment with PLUVICTO. Withhold, reduce dose, or permanently discontinue PLUVICTO based on the severity of renal toxicity [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)].
5.4 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
The safety and efficacy of PLUVICTO have not been established in females. Based on its mechanism of action, PLUVICTO can cause fetal harm [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. No animal studies using lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan have been conducted to evaluate its effect on female reproduction and embryo-fetal development; however, radioactive emissions, including those from PLUVICTO, can cause fetal harm. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PLUVICTO and for 14 weeks after the last dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In the pooled safety population for the PSMAfore and VISION studies (N = 756), the most common (≥ 20%) adverse reactions, including laboratory abnormalities, were decreased lymphocytes (83%), decreased hemoglobin (65%), fatigue (49%), dry mouth (46%), decreased platelets (40%), decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (37%), nausea (35%), decreased neutrophils (31%), decreased calcium (29%), decreased sodium (27%), increased aspartate aminotransferase (26%), increased alkaline phosphatase (24%), arthralgia (22%), decreased appetite (21%), increased potassium (21%), constipation (21%), and back pain (21%).
PSMAfore
The safety of PLUVICTO was evaluated in the PSMAfore study in patients with progressive, PSMA-positive mCRPC previously treated with ARPI therapy, for whom it was considered appropriate to delay taxane-based chemotherapy by the investigator [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Patients received at least one dose of either PLUVICTO 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) administered every 6 weeks (N = 227) or a change in ARPI (N = 232). The median duration of exposure to PLUVICTO was 8.4 months (range, 0.4 to 11.6), and the median number of doses of PLUVICTO received was 6 (range, 1 to 6). The median cumulative administered activity of PLUVICTO was 42.4 GBq (range, 7.0 to 45.4).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 20% of patients who received PLUVICTO. Serious adverse reactions in > 1% of patients who received PLUVICTO included anemia (1.8%), urinary tract infection (1.8%), hemorrhage (1.3%), and sepsis (1.3%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 1.8% of patients who received PLUVICTO, including COVID-19 pneumonia, cardiac arrest, intestinal ischemia, and sepsis (0.4% each).
PLUVICTO was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 6% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of PLUVICTO in ≥ 1% of patients who received PLUVICTO were thrombocytopenia (1.8%) and dry mouth (1.3%).
Adverse reactions leading to a dose interruption of PLUVICTO occurred in 12% of patients. The most frequent (≥ 1%) adverse reactions leading to a dose interruption of PLUVICTO in patients who received PLUVICTO were COVID-19 (3.1%) and anemia (1.8%).
Adverse reactions leading to a dose reduction of PLUVICTO occurred in 3.5% of patients. The most frequent (≥ 0.5%) adverse reaction leading to a dose reduction of PLUVICTO in patients who received PLUVICTO was dry mouth (0.9%).
Table 3 and Table 4 summarize the incidence of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in PSMAfore.
Table 3: Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients With PSMA-Positive mCRPC Who Received PLUVICTO in PSMAfore Abbreviation: ARPI, androgen receptor pathway inhibitor.
aIncludes multiple similar terms.Adverse reactions PLUVICTO
(N = 227)ARPI
(N = 232)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)Gastrointestinal disorders Dry moutha 61 0.9 2.6 0 Nausea 32 0 12 0.4 Constipation 22 0.4 14 0 Diarrhea 17 0 9 0.4 Vomiting 11 0 4.7 0 General disorders Fatiguea 53 1.3 53 5 Metabolism and nutrition disorders Decreased appetite 22 0 19 0.4 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Arthralgia 20 0 23 0.4 Back pain 14 1.3 20 2.6 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received PLUVICTO included dysgeusia, abdominal pain, peripheral edema, headache, acute kidney injury, weight decreased, urinary tract infection, dry eye, dizziness, dry skin, oral fungal infection, gastroesophageal reflux disease, pyrexia, vertigo, stomatitis, dysphagia, esophagitis, pancytopenia, and bone marrow failure.
Table 4: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) That Worsened From Baseline in Patients With PSMA-Positive mCRPC Who Received PLUVICTO or Change in ARPI (Between Arm Difference of ≥ 5% All Grades) in PSMAfore Abbreviation: ARPI, androgen receptor pathway inhibitor.
aThe denominator used to calculate the rate for each laboratory parameter was based on 226 patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
bThe denominator used to calculate the rate for each laboratory parameter varied from 231 to 232 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
cNo Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline were reported.Laboratory abnormalities PLUVICTOa ARPIb All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)Hematology Decreased lymphocytes 78 27 57 12 Decreased hemoglobin 67 7c 50 7c Decreased neutrophils 38 3.5 18 1.3 Decreased platelets 30 2.7 11 1.7 Chemistry Increased alkaline phosphatase 31 8 50 10c Decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 23 0.9c 22 3.5 Increased magnesium 19 0.9c 28 0c Decreased calcium 18 0.9 11 0.9 Decreased sodium 11 0c 18 0c Decreased potassium 6 0.9c 18 2.6 VISION
The safety of PLUVICTO was evaluated in the VISION study in patients with progressive, PSMA-positive mCRPC previously treated with ARPI therapy and taxane-based chemotherapy [see Clinical Studies (14.2)]. Patients received at least one dose of either PLUVICTO 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) administered every 6 weeks plus BSoC (N = 529) or BSoC alone (N = 205). The median duration of exposure to PLUVICTO plus BSoC was 7.8 months (range, 0.3 to 36.5). Among patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC, the median number of doses of PLUVICTO received was 5 (range, 1 to 6). The median cumulative administered activity of PLUVICTO was 37.5 GBq (range, 7.0 to 48.3).
Serious adverse reactions occurred in 37% of patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC. Serious adverse reactions in > 1% of patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC included musculoskeletal pain (4%), hemorrhage (4%), sepsis (3.2%), urinary tract infection (3%), anemia (2.8%), acute kidney injury (1.9%), pneumonia (1.7%), pyrexia (1.5%), pancytopenia (1.3%), spinal cord compression (1.1%), and pulmonary embolism (1.1%).
Fatal adverse reactions occurred in 3% of patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC, including sepsis (0.9%), pancytopenia (0.6%), hepatic failure (0.4%), intracranial hemorrhage (0.2%), subdural hematoma (0.2%), ischemic stroke (0.2%), COVID-19 (0.2%), and aspiration pneumonia (0.2%).
PLUVICTO was permanently discontinued due to adverse reactions in 12% of patients. Adverse reactions leading to permanent discontinuation of PLUVICTO in ≥ 1% of patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC were anemia (2.8%), thrombocytopenia (2.8%), and leukopenia (including neutropenia) (1.7%).
Adverse reactions leading to a dose interruption of PLUVICTO occurred in 16% of patients. The most frequent (≥ 3%) adverse reactions leading to a dose interruption of PLUVICTO in patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC were anemia (5%) and thrombocytopenia (3.6%).
Adverse reactions leading to a dose reduction of PLUVICTO occurred in 6% of patients. The most frequent (≥ 1%) adverse reactions leading to a dose reduction of PLUVICTO in patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC were thrombocytopenia (1.9%) and anemia (1.3%).
Table 5 and Table 6 summarize the incidence of adverse reactions and laboratory abnormalities, respectively, in VISION.
Table 5: Adverse Reactions (≥ 10%) in Patients With PSMA-Positive mCRPC Who Received PLUVICTO Plus BSoC in VISION Abbreviation: BSoC, best standard of care.
aIncludes multiple similar terms.Adverse reactions PLUVICTO plus BSoC
(N = 529)BSoC
(N = 205)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)General disorders Fatiguea 48 7 29 2.4 Decreased appetite 21 1.9 15 0.5 Weight decreased 11 0.4 10 0.5 Peripheral edemaa 10 0.4 7 1 Gastrointestinal disorders Dry moutha 39 0 1 0 Nausea 36 1.3 17 0.5 Constipation 20 1.1 11 0.5 Vomitinga 19 0.9 6 0.5 Diarrhea 19 0.8 2.9 0.5 Abdominal paina 12 1.3 6 0.5 Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders Back pain 24 3.6 15 3.9 Arthralgia 22 1.1 13 0.5 Bone pain 11 2.5 8 2.4 Renal and urinary disorders Urinary tract infectiona 12 3.8 1 0.5 Clinically relevant adverse reactions in < 10% of patients who received PLUVICTO plus BSoC included acute kidney injury, dizziness, dysgeusia, headache, pyrexia, dry eye, oral fungal infection, vertigo, gastroesophageal reflux disease, stomatitis, pancytopenia, dry skin, dysphagia, esophagitis, and bone marrow failure.
Table 6: Select Laboratory Abnormalities (≥ 10%) That Worsened From Baseline in Patients With PSMA-Positive mCRPC Who Received PLUVICTO Plus BSoC (Between Arm Difference of ≥ 5% All Grades) in VISION Abbreviation: BSoC, best standard of care.
aThe denominator used to calculate the rate for each laboratory parameter varied from 506 to 529 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
bThe denominator used to calculate the rate for each laboratory parameter varied from 194 to 198 based on the number of patients with a baseline value and at least one post-treatment value.
cNo Grade 4 laboratory abnormalities worsening from baseline were reported.Laboratory abnormalities PLUVICTO plus BSoCa BSoCb All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)All Grades
(%)Grades 3 or 4
(%)Hematology Decreased lymphocytes 85 47 51 18 Decreased hemoglobin 64 15c 34 7c Decreased platelets 45 9 20 2.5 Decreased neutrophils 28 4.7 9 0.5 Chemistry Decreased estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) 43 3.6 28 2.5 Decreased sodium 34 0.6c 23 1 Decreased calcium 34 1.9 18 1.5 Increased aspartate aminotransferase (AST) 29 1.1 18 1c Increased potassium 24 0.6 18 0.5c Increased sodium 11 0c 5 0c -
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of PLUVICTO have not been established in females. Based on its mechanism of action, PLUVICTO can cause fetal harm [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no available data on PLUVICTO use in pregnant females. No animal studies using lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan have been conducted to evaluate its effect on female reproduction and embryo-fetal development; however, all radioactive emissions, including those from PLUVICTO, can cause fetal harm.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
The safety and efficacy of PLUVICTO have not been established in females. There are no data on the presence of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan in human milk or its effects on the breastfed child or on milk production.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Contraception
Males
Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PLUVICTO and for 14 weeks after the last dose [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1), Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)].
Infertility
The recommended cumulative dose of 44.4 GBq of PLUVICTO results in a radiation absorbed dose to the testes within the range where PLUVICTO may cause temporary or permanent infertility.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of PLUVICTO in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Of the 227 patients who received at least one dose of PLUVICTO in the PSMAfore study, 177 patients (78%) were 65 years of age or older and 83 patients (37%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between patients ≥ 75 years of age and younger patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 20% of patients ≥ 75 years of age and in 20% of younger patients. Grade ≥ 3 adverse reactions occurred in 39% of patients ≥ 75 years of age and in 34% of younger patients.
Of the 529 patients who received at least one dose of PLUVICTO plus BSoC in the VISION study, 387 patients (73%) were 65 years of age or older and 143 patients (27%) were 75 years of age or older. No overall differences in effectiveness were observed between patients ≥ 75 years of age and younger patients. Serious adverse reactions occurred in 41% of patients ≥ 75 years of age and in 35% of younger patients. Grade ≥ 3 adverse reactions occurred in 56% of patients ≥ 75 years of age and in 53% of younger patients.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Exposure of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is expected to increase with the degree of renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. No dose adjustment is recommended for patients with mild (baseline CLcr 60 to 89 mL/min by Cockcroft-Gault) to moderate (CLcr 30 to 59 mL/min) renal impairment; however, patients with mild to moderate renal impairment may be at greater risk of toxicity. Frequently monitor renal function and adverse reactions in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.4)]. The pharmacokinetics and safety of PLUVICTO have not been studied in patients with severe (CLcr 15 to 29 mL/min) renal impairment or end-stage renal disease.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
In the event of administration of a radiation overdosage with PLUVICTO, reduce the radiation absorbed dose to the patient by increasing the elimination of the radionuclide from the body by frequent micturition or by forced diuresis and frequent bladder voiding. Estimate the effective radiation dose that was applied and treat with additional supportive care measures as clinically indicated.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
PLUVICTO (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan) is a radioligand therapeutic agent. Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is a PSMA-binding ligand bound to a DOTA chelator radiolabeled with lutetium-177.
The chemical name is 2-[4-[2-[[4-[[(2S)-1-[[(5S)-5-carboxy-5-[[(1S)-1,3-dicarboxy propyl]carbamoylamino]pentyl]amino]-3-naphthalen-2-yl-1-oxopropan-2-yl]carbamoyl]cyclohexyl]methylamino]-2-oxoethyl]-4,7,10-tris(carboxylatomethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetrazacyclododec-1-yl]acetate; lutetium-177(3+). The molecular mass is 1216.06 g/mol and the molecular formula is C49H68177LuN9O16. The chemical structure for lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is shown below:
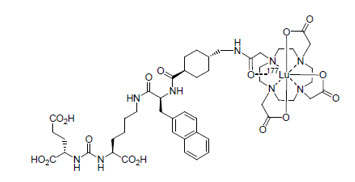
PLUVICTO (lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan) 1,000 MBq/mL (27 mCi/mL) Injection is supplied as a sterile, clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution for intravenous use. Each single-dose vial contains acetic acid (0.30 mg/mL), sodium acetate (0.41 mg/mL), gentisic acid (0.39 mg/mL), sodium ascorbate (50.0 mg/mL), pentetic acid (0.10 mg/mL), and water for injection (q.s. to 1 mL). The pH range of the solution is 4.5 to 7.0.
11.1 Physical Characteristics
Lutetium-177 decays to a stable hafnium-177 with a physical half-life of 6.647 days by emitting beta-minus radiation with a maximum energy of 498 keV (79%) and photonic radiation (γ) of 208 keV (11%) and 113 keV (6.4%).
The main radiations of lutetium-177 are detailed in Table 7.
Table 7: Lutetium-177 Main Radiations Radiation Energy (keV) Iβ-% Iγ% β- 176.5 12.2 β- 248.1 0.05 β- 384.9 9.1 β- 497.8 78.6 γ 71.6 0.15 γ 112.9 6.40 γ 136.7 0.05 γ 208.4 11.0 γ 249.7 0.21 γ 321.3 0.22 11.2 External Radiation
Table 8 summarizes the radioactive decay properties of lutetium-177.
Table 8: Physical Decay Chart: Lutetium-177 Physical Half-life = 6.647 days Hours Fraction remaining 0 1.000 1 0.996 2 0.991 5 0.979 10 0.958 24 (1 day) 0.901 48 (2 days) 0.812 72 (3 days) 0.731 120 (5 days) 0.594 168 (7 days) 0.482 336 (14 days) 0.232 720 (30 days) 0.044 1080 (45 days) 0.009 -
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is a radioligand therapeutic agent. The active moiety of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is the radionuclide lutetium-177 which is linked to a moiety that binds to PSMA, a transmembrane protein that is expressed in prostate cancer, including mCRPC. Upon binding of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan to PSMA-expressing cells, the beta-minus emission from lutetium-177 delivers radiation to PSMA-expressing cells, as well as to surrounding cells, and induces DNA damage which can lead to cell death.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan exposure-efficacy relationships and the time course of pharmacodynamic response have not been fully characterized.
Cardiac Electrophysiology
At the recommended dosage, PLUVICTO does not cause large mean increases (> 20 ms) in the QTc interval.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Pharmacokinetics of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan are expressed as geometric mean (geometric mean coefficient of variation) unless otherwise specified.
The blood lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan area under the curve (AUC) is 52.3 ng.h/mL (31.4%) and the maximum blood concentration (Cmax) is 6.58 ng/mL (43.5%) at the recommended dosage.
Distribution
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan volume of distribution is 123 L (78.1%).
Within 2.5 hours after administration, lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan distributes in gastrointestinal tract, liver, lungs, kidneys, heart wall, bone marrow, and salivary glands.
Vipivotide tetraxetan and non-radioactive lutetium vipivotide tetraxetan are 60% to 70% bound to human plasma proteins.
Elimination
The lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan terminal elimination half-life is 41.6 hours (68.8%) and the clearance (CL) is 2.04 L/h (31.5%).
Metabolism
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan does not undergo hepatic or renal metabolism.
Excretion
Lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is primarily eliminated renally.
Specific Populations
Exposure (AUC) of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan increased with decreasing creatinine clearance (CLcr). The effect of baseline CLcr < 54 mL/min on lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies
CYP450 enzymes: Vipivotide tetraxetan is not a substrate of cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzymes. Vipivotide tetraxetan did not induce CYP1A2, 2B6 or 3A4; and did not inhibit CYP1A2, 2B6, 2C8, 2C9, 2C19, 2D6 or 3A in vitro.
Transporters: Vipivotide tetraxetan is not a substrate of BCRP, P-gp, MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3 or OCT2. Vipivotide tetraxetan did not inhibit BCRP, P-gp, MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1 or OCT2 in vitro.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenicity and mutagenicity studies have not been conducted with lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan; however, radiation is a carcinogen and mutagen.
No animal studies were conducted to determine the effects of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan on fertility.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 PSMA-Positive mCRPC Previously Treated With ARPI Therapy
PSMAfore
The efficacy of PLUVICTO was evaluated in PSMAfore (NCT04689828), a randomized (1:1), multicenter, open-label trial that evaluated PLUVICTO (N = 234) versus a change in ARPI (N = 234) in patients with progressive, PSMA-positive mCRPC. Randomization was stratified by setting of prior ARPI use [castration-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC) vs. hormone-sensitive prostate cancer (HSPC)] and by symptomatology [asymptomatic or mildly symptomatic vs. symptomatic]. Patients were required to have a castrate level of serum/plasma testosterone by either medical castration or prior orchiectomy at study entry. Patients were required to have progressed only once on an ARPI (abiraterone acetate, enzalutamide, darolutamide, or apalutamide). Prior taxane-based chemotherapy was only allowed in the adjuvant or neoadjuvant setting greater than 12 months before enrollment. Patients were considered appropriate for delay of taxane-based chemotherapy by the investigator. Patients were required to have PSMA-positive mCRPC defined as having at least one tumor lesion (soft tissue or bone) with gallium Ga 68 gozetotide uptake greater than in normal liver. Patients were considered ineligible if any intraprostatic lesion or any one lesion larger than size criteria [organs ≥ 1 cm in longest diameter, lymph nodes ≥ 2.5 cm in short axis, bones (soft tissue component) ≥ 1 cm in longest diameter] had gallium Ga 68 gozetotide uptake less than or equal to uptake in normal liver.
Patients received PLUVICTO 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) every 6 weeks for 6 doses or a change in ARPI. Supportive care administered at the investigator’s discretion included bone-targeted agents; androgen deprivation therapy (ADT); or palliative radiotherapy.
The median age was 72 years (range, 43 to 94 years); 91% were White; 2.6% Black or African American; 0.6% Asian; 6% were Hispanic or Latino; 99% had ECOG PS0-1.
The major efficacy outcome measure was radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS) as determined by blinded independent central review (BICR) per Prostate Cancer Working Group 3 (PCWG3)-modified Response Evaluation Criteria in Solid Tumors (RECIST) v1.1 criteria. Additional efficacy outcome measures were Overall Survival (OS) and Overall Response Rate (ORR).
PSMAfore demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in rPFS for PLUVICTO compared to a change in ARPI.
Of patients that were randomized to receive a change in ARPI, 141 patients (60%) crossed over to receive PLUVICTO after confirmation of radiographic disease progression by BICR.
Efficacy results for PSMAfore are presented in Table 9 and Figure 1.
Table 9: Efficacy Results in PSMAfore ARPI = androgen receptor pathway inhibitor; NE = Not estimable; NS = Not statistically significant
aBy BICR per PCWG3-modified RECIST v1.1 criteria.
bExcludes one patient in the PLUVICTO arm who was randomized after the data cut-off for the rPFS primary analysis.
cBased on Kaplan-Meier estimate.
dHazard ratio based on the stratified Cox PH model.
eStratified log-rank test one-sided p-value.
fResponses are based on soft tissue and bone lesion assessment.PLUVICTO ARPI Radiographic progression-free survival (rPFS)a N = 233b N = 234 Events (progression or death), n (%) 60 (26) 106 (45) Median, months (95% CI)c 9.3 (7, NE) 5.6 (4, 6) Hazard ratio (95% CI)d 0.41 (0.29, 0.56) P-valuee < 0.0001 Overall survival (OS) N = 234 N = 234 Deaths, n (%) 142 (61) 157 (67) Median, months (95% CI)c 24.5 (19.5, 28.9) 23.1 (19.6, 25.5) Hazard ratio (95% CI)d 0.91 (0.72, 1.14) P-valuee NS Overall response rate (ORR)a,f Patients with measurable disease at baseline N = 72 N = 72 ORR (CR + PR), n (%) (95% CI) 35 (49)
(37, 61)10 (14)
(7, 24)Complete response (CR), n (%) 15 (21) 2 (2.8) Partial response (PR), n (%) 20 (28) 8 (11) Figure 1. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Radiographic Progression-Free Survival in PSMAfore
14.2 PSMA-Positive mCRPC Previously Treated With ARPI Therapy and Taxane-Based Chemotherapy
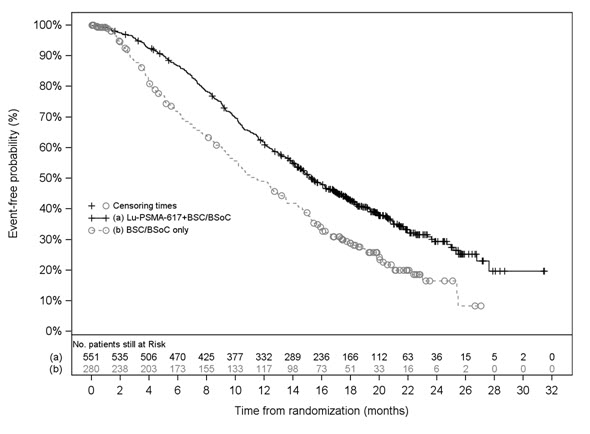
VISION
The efficacy of PLUVICTO was evaluated in VISION (NCT03511664), a randomized (2:1), multicenter, open-label trial of PLUVICTO plus BSoC (N = 551) versus BSoC alone (N = 280) in patients with progressive, PSMA-positive mCRPC. Randomization was stratified by baseline lactase dehydrogenase (LDH ≤ 260 IU/L vs. > 260 IU/L), presence of liver metastases (yes vs. no), ECOG PS score (0 or 1 vs. 2), and inclusion of an AR pathway inhibitor as part of BSoC (yes vs. no) at the time of randomization. Patients were required to have a castrate level of serum/plasma testosterone by either medical castration or prior orchiectomy at study entry. Patients were required to have received at least one ARPI, and 1 or 2 prior taxane-based chemotherapy regimens. Eligible patients were required to have PSMA-positive mCRPC defined as having at least one tumor lesion (soft tissue or bone) with gallium Ga 68 gozetotide uptake greater than in normal liver. Patients were considered ineligible if any one lesion larger than size criteria [organs ≥ 1 cm in short axis, lymph nodes ≥ 2.5 cm in short axis, bones (soft tissue component) ≥ 1 cm in short axis] had gallium Ga 68 gozetotide uptake less than or equal to uptake in normal liver.
Patients received PLUVICTO 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) every 6 weeks for up to a total of 6 doses plus BSoC or BSoC alone. BSoC administered at the investigator’s discretion included ketoconazole; radiation therapy to localized prostate cancer targets; bone-targeted agents; ADT; ARPIs. Patients continued treatment for up to 4-6 doses, or until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity. Patients with stable disease or partial response after 4 doses of PLUVICTO plus BSoC received up to 2 additional doses per investigator’s discretion.
The median age was 71 years (range, 40 to 94 years); 87% White; 7% Black or African American; 2.4% Asian; 1.7% were Hispanic or Latino; 92% had ECOG PS0-1; 8% had ECOG PS2. All patients had received at least one prior taxane-based chemotherapy regimen and 41% of patients received two. One prior ARPI had been administered to 51% of patients, 41% of patients had received 2, and 8% of patients had received 3 or more. During the treatment period, 53% of patients in the PLUVICTO plus BSoC arm and 68% of patients in the BSoC alone arm received at least one ARPI.
The major efficacy outcome measures were OS and rPFS as determined by BICR per PCWG3-modified RECIST v1.1 criteria. An additional efficacy outcome measure was ORR.
VISION demonstrated a statistically significant improvement in both major efficacy outcome measures of OS and rPFS by BICR with PLUVICTO plus BSoC compared to treatment with BSoC alone. Interpretation of the magnitude of the rPFS effect was limited due to a high degree of censoring from early drop out in the control arm.
Efficacy results for VISION are presented in Table 10 and Figure 2.
Table 10: Efficacy Results in VISION aBased on Kaplan-Meier estimate.
bHazard ratio based on the stratified Cox PH model.
cStratified log-rank test two-sided p-value.
dResponses are based on soft tissue and bone lesion assessment.
eBy BICR per PCWG3-modified RECIST v1.1 criteria.
fStratified Wald’s Chi-square test two-sided p-value.PLUVICTO plus BSoC BSoC Overall survival (OS) N = 551 N = 280 Deaths, n (%) 343 (62) 187 (67) Median, months (95% CI)a 15.3 (14.2, 16.9) 11.3 (9.8, 13.5) Hazard ratio (95% CI)b 0.62 (0.52, 0.74) P-valuec < 0.001 Overall response rate (ORR)d,e Patients with measurable disease at baseline N = 184 N = 64 ORR (CR + PR), n (%) (95% CI) 91 (49)
(42, 57)1 (1.6)
(0, 8)Complete response (CR), n (%) 17 (9) 0 (0) Partial response (PR), n (%) 74 (40) 1 (1.6) P-valuef < 0.001 Figure 2. Kaplan-Meier Plot of Overall Survival in VISION

-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
PLUVICTO Injection containing 1,000 MBq/mL (27 mCi/mL) of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan is a sterile, preservative-free and clear, colorless to slightly yellow solution for intravenous use supplied in a clear, colorless Type I glass 30 mL single-dose vial containing 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) ± 10% of lutetium Lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan at the date and time of administration (NDC# 69488-010-61). The solution volume in the vial can range from 7.5 mL to 12.5 mL in order to provide a total of 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) of radioactivity at the date and time of administration.
The product vial is enclosed within a lead shielded container (NDC# 69488-010-61) for protective shielding and placed in a plastic sealed container. The product is shipped in a type A package (NDC# 69488-010-61).
The shelf life is 120 hours (5 days) from the date and time of calibration.
Store below 30°C (86°F). Do not freeze. Store in the original package to protect from ionizing radiation (lead shielding).
Store PLUVICTO in accordance with local and federal laws on radioactive materials.
Do not use PLUVICTO after the expiration date and time which are stated on the label.
Dispose of any unused medicinal product or waste material in accordance with local and federal laws.
Lutetium-177 for PLUVICTO may be prepared using two different sources of stable nuclides (either lutetium-176 or ytterbium-176) that require different waste management. Lutetium-177 for PLUVICTO is prepared using ytterbium-176 (“non-carrier added”) unless otherwise communicated on the product batch release certificate.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Risk From Radiation Exposure
Ensure patients increase oral fluid intake and advise patients to void as often as possible to reduce bladder radiation.
Before the patient is released, inform patients about the necessary radioprotection precautions to follow to minimize radiation exposure to others.
After each administration of PLUVICTO, advise patients to:
- Limit close contact (less than 3 feet) with others for 2 days or with children and pregnant women for 7 days.
- Refrain from sexual activity for 7 days.
- Sleep in a separate room from others for 3 days, from children for 7 days, or from pregnant women for 15 days [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Myelosuppression
Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of myelosuppression, such as tiredness, weakness, pale skin, shortness of breath, bleeding or bruising more easily than normal or difficulty to stop bleeding, or frequent infections with signs, such as fever, chills, sore throat or mouth ulcers [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Renal Toxicity
Advise patients to remain well hydrated and to urinate frequently before and after administration of PLUVICTO. Advise patients to contact their healthcare provider for any signs or symptoms of renal toxicity, such as passing urine less often than usual or passing much smaller amounts of urine than usual [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Advise males that PLUVICTO can cause fetal harm [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Advise male patients with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with PLUVICTO and for 14 weeks after the last dose [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
Infertility
Advise males of reproductive potential that PLUVICTO may cause temporary or permanent infertility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Distributed by:
Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation
East Hanover, NJ 07936©2025 Novartis
PLUVICTO® is a registered trademark of Novartis AG and/or its affiliates.
U.S. Patents 10398791; 10406240; 11318121; 12208102
T2025-17
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PLUVICTO
lutetium lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69488-010 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LUTETIUM LU-177 VIPIVOTIDE TETRAXETAN (UNII: G6UF363ECX) (LUTETIUM LU-177 VIPIVOTIDE TETRAXETAN - UNII:G6UF363ECX) LUTETIUM LU-177 VIPIVOTIDE TETRAXETAN 27 mCi in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ACETIC ACID (UNII: Q40Q9N063P) SODIUM ACETATE (UNII: 4550K0SC9B) GENTISIC ACID (UNII: VP36V95O3T) SODIUM ASCORBATE (UNII: S033EH8359) PENTETIC ACID (UNII: 7A314HQM0I) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69488-010-61 1 in 1 PACKAGE 03/23/2022 1 7.5 mL in 1 VIAL, GLASS; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA215833 03/23/2022 Labeler - Advanced Accelerator Applications USA, Inc (051714355) Registrant - Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation (002147023)
Trademark Results [PLUVICTO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 PLUVICTO 88758613 not registered Live/Pending |
ENDOCYTE, INC. 2020-01-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
