Metaxalone by INA Pharmaceutics Inc METAXALONE tablet
Metaxalone by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Metaxalone by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by INA Pharmaceutics Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use METAXALONE TABLETS, 640 mg, safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for METAXALONE TABLETS, 640 mg.
METAXALONE tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1962INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, is a muscle relaxant, indicated as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomforts associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions in adult and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Recommended dosage in adults and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older is 640 mg taken orally, with or without food, three to four times a day ( 2)
- Maximum recommended daily dosage is 2,560 mg (one tablet four times a day) ( 2)
- Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg and SKELAXIN 800 mg tablets are not mutually substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis due to differences in pharmacokinetic profiles (
5.3,
12.3). When it is appropriate to switch a patient taking SKELAXIN 800 mg on an empty stomach to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg (
2):
- Stop SKELAXIN 800 mg threetimes a day and start Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg threetimes a day on an empty stomach OR
- Stop SKELAXIN 800 mg fourtimes a day and start Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg fourtimes a day on an empty stomach.
- For patients who have been taking either product with food, do not switch between SKELAXIN 800 mg and Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg ( 2).
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 640 mg. ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serotonin Syndrome: Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of metaxalone (within the recommended dosage range) and other serotonergic drugs and with the use of metaxalone as the only serotonergic drug taken at a dosage higher than the recommended dosage. If concomitant use with another serotonergic drug is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases. Discontinue Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg if serotonin syndrome is suspected or it occurs. ( 5.1, 7.1)
- Central Nervous System (CNS) Depression: Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle, and may enhance the effects of other CNS depressants including alcohol. Follow patients closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. If concomitant use with another CNS depressant is warranted, closely monitor for signs of respiratory depression and sedation, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases. ( 5.2, 7.2)
- Risk with Inappropriate Switching to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg Inappropriate switching on a mg-to-mg basis from SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg to achieve the same total daily metaxalone dosage may result in a clinically significant increase in metaxalone exposure which may increase the risk of metaxalone-associated adverse reactions including CNS depression. Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg are not mutually substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis ( 5.3, 12.3).
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg include drowsiness, dizziness, headache, and nervousness or “irritability”, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal upset. ( 6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact INA Pharmaceutics, Inc. at 1-866-835-0469 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Geriatric Use: Geriatric patients may be especially susceptible to CNS depression associated with Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg use. ( 8.5)
- Hepatic Impairment: Consider additional monitoring in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. ( 4, 8.6)
- Renal impairment: Consider additional monitoring in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment ( 4, 8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 5/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serotonin Syndrome
5.2 Central Nervous System Depression
5.3 Risk with Inappropriate Switching to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Serotonergic Drugs
7.2 Depressants
7.3 Interaction of Metaxalone with Benedict’s Tests
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
8.7 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The recommended dosage of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg in adults and pediatric patients 13 years of age and older is 640 mg taken orally with or without food, three to four times a day. The maximum recommended daily dosage is 2,560 mg (one tablet four times a day).
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and SKELAXIN 800 mg are not mutually substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis due to differences in pharmacokinetic profiles [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. When it is appropriate to switch a patient taking SKELAXIN 800 mg on an empty stomach to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg:
- Stop SKELAXIN 800 mg threetimes a day and start Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg threetimes a day on an empty stomach, OR
- Stop SKELAXIN 800 mg fourtimes a day and start Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg fourtimes a day on an empty stomach.
For patients who have been taking either product with food, do not switch between SKELAXIN 800 mg and Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serotonin Syndrome
Cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of metaxalone (within the recommended dosage range) and other serotonergic drugs [see Drug Interactions (7)] and with the use of metaxalone as the only serotonergic drug taken at a dosage higher than the recommended dosage [see Overdosage (10)] . Serotonergic drugs include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, opioids (particularly fentanyl, meperidine, and methadone), drugs that affect the serotonergic neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), and drugs that impair metabolism of serotonin (including monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, both those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue) [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
Serotonin syndrome symptoms may include mental status changes (e.g., agitation, hallucinations, coma), autonomic instability (e.g., tachycardia, labile blood pressure, hyperthermia), neuromuscular aberrations (e.g., hyperreflexia, incoordination, rigidity), and/or gastrointestinal symptoms (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea). The onset of symptoms generally occurs within several hours to a few days after initiation of a serotonergic drug but may occur later than that.
If concomitant use of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and another serotonergic drug is warranted, reassess the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage modification. Discontinue Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg if serotonin syndrome is suspected or occurs.
5.2 Central Nervous System Depression
Because of central nervous system (CNS) depressant effects, metaxalone may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle, especially when used with other CNS depressants including alcohol. Geriatric patients may be especially susceptible to CNS depression associated with metaxalone use. When used concomitantly, the sedative effects of metaxalone and other CNS depressants (e.g., alcohol, benzodiazepines, opioids, tricyclic antidepressants) may be additive [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Follow patients treated with Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg closely for signs and symptoms of respiratory depression and sedation. If concomitant use of metaxalone and another CNS depressant is warranted, closely monitor for signs of respiratory depression and sedation, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage increases.
5.3 Risk with Inappropriate Switching to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg
Inappropriate switching on a mg-to-mg basis from SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg to achieve the same total daily metaxalone dosage may result in a clinically significant increase in metaxalone exposure which may increase the risk of metaxalone-associated adverse reactions including CNS depression. For example, it is inappropriate to switch from four SKELAXIN 800 mg tablets (3,200 mg) per day to five tablets of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg (3,200 mg) per day [1.25 times the maximum recommended daily dosage of 2,560 mg] [see Dosage and Administration (2)]. Metaxalone Tablets 640 mg and SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg are not mutually substitutable on a mg-to-mg basis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
It is generally inappropriate to switch between Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and SKELAXIN 800 mg to mediate metaxalone-associated adverse reactions.
For recommendations on how to switch from SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg, to Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, see Dosage and Administration (2).
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of metaxalone were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. The most frequent reactions to metaxalone were:
- CNS: drowsiness, dizziness, headache, and nervousness or “irritability”
- Digestive: nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal upset.
Other adverse reactions were:
- Allergic: anaphylaxis have been reported with metaxalone.
- CNS: cases of serotonin syndrome, a potentially life-threatening condition, have been reported during concomitant use of metaxalone (within the recommended dosage range) and other serotonergic drugs and with the use of metaxalone as the only serotonergic drug taken at a dosage higher than the recommended dosage [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.2), and Overdosage (10)].
- Hematologic: leucopenia; hemolytic anemia.
- Hepatobiliary: jaundice.
- Immune System: hypersensitivity reaction, rash with or without pruritus.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Serotonergic Drugs
If concomitant use of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and another serotonergic drug is warranted, carefully observe the patient, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage modification. Discontinue Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg if serotonin syndrome is suspected or if it occurs.
Serotonin syndrome has resulted from concomitant use of metaxalone (within the recommended dosage range) and other serotonergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Serotonergic drugs include selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs), serotonin and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs), tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs), triptans, 5-HT3 receptor antagonists, opioids (particularly fentanyl, meperidine, and methadone), drugs that affect the serotonin neurotransmitter system (e.g., mirtazapine, trazodone, tramadol), monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors (those intended to treat psychiatric disorders and also others, such as linezolid and intravenous methylene blue).
7.2 Depressants
If concomitant use of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg and another CNS depressant is warranted, closely monitor for signs of respiratory depression and sedation, particularly during treatment initiation and dosage modification.
Due to the additive pharmacologic effect, concomitant use of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg with other CNS depressants may increase the risk of sedation and respiratory depression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on metaxalone use in pregnancy to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes despite decades of metaxalone use. Reproduction studies in rats have not revealed evidence of impaired fertility or harm to fetus due to metaxalone.
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of metaxalone or its metabolite in either human or animal milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for metaxalone and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from metaxalone or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg are indicated as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomforts associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions in pediatric patients 13 years of age and older.
The safety and effectiveness of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg in pediatric patients less than 13 years of age have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg did not include sufficient numbers of patients 65 years of age and older to determine whether they respond differently from younger adult patients. The effects of age on the pharmacokinetics of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg have not been evaluated. Geriatric patients may be especially susceptible to CNS depression associated with metaxalone use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Metaxalone Tablets. 640 mg are contraindicated in patients with severe hepatic impairment . Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg should be used with caution and additional monitoring should be considered in patients with mild to moderate hepatic impairment. The effect of hepatic impairment on metaxalone pharmacokinetics is unknown; however, metaxalone undergoes extensive hepatic metabolism [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
8.7 Renal Impairment
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg are contraindicated in patients with severe renal impairment . Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg should be used with caution and additional monitoring should be considered in patients with mild to moderate renal impairment. The effect of renal impairment on metaxalone pharmacokinetics is unknown; however, metaxalone undergoes renal excretion as unidentified metabolites [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)] .
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Clinical Presentations of Metaxalone Overdose
Cardiovascular effects may include tachycardia and hypertension; hypotension has also been reported. CNS manifestations may include CNS depression, agitation, hallucinations, delusions, seizures, respiratory depression, and coma. Deaths by deliberate or accidental overdose may occur with metaxalone, particularly in combination with other CNS depressants (including alcohol). Serotonin syndrome, leading to muscle rigidity, tremor, and hyperthermia, has been reported [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.1, 7.2)].
Treatment of Overdose
The standard of treatment is supportive care. Monitor for CNS and respiratory depression and, manage airway with oxygen as needed. Gastrointestinal decontamination procedures (including emesis) should generally be avoided because aspiration may result from CNS depression and seizures. Extracorporeal elimination such as hemodialysis or plasmapheresis have no proven clinical benefit.
Consider contacting the Poison Help line (1-800-222-1222) or a medical toxicologist for additional overdose management recommendations.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg for oral administration, are available as 640 mg oval, peach-colored tablets, debossed with M640 on one side and no markings on the other side. Each tablet contains 640 mg metaxalone, a muscle relaxant, and the following inactive ingredients: alginic acid, FD&C yellow #6, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, propylene glycol alginate and povidone.
Chemically, metaxalone is 5-[(3, 5- dimethylphenoxy) methyl]-2-oxazolidinone. The empirical formula is C 12H 15NO 3, which corresponds to a molecular weight of 221.25. The structural formula is:
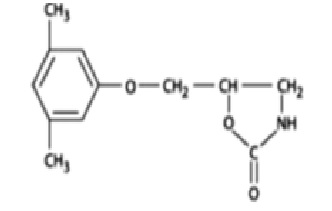
Metaxalone is a white to almost white, odorless crystalline powder freely soluble in chloroform, soluble in methanol and in 96% ethanol, but practically insoluble in ether or water.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of action of metaxalone as an adjunct to rest, physical therapy, and other measures for the relief of discomfort associated with acute, painful musculoskeletal conditions has not been established, but may be due to general CNS depression. Metaxalone has no direct action on the contractile mechanism of striated muscle, the motor end plate, or the nerve fiber.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The exposure-response relationship and time course of pharmacodynamic response for the safety and effectiveness of metaxalone not been fully characterized.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
In a relative bioavailability study in healthy adult volunteers, the C max (peak plasma concentration) and AUC (extent of absorption) values of metaxalone from Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg were found to be similar to those from SKELAXIN 800 mg tablets. After a single dose of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, under fasted conditions, mean C max and AUC values were 2 mcg/mL and 16 mcg*h/mL, respectively. The time-to-peak plasma concentration (T max) occurred at 3.5 hours (range 1.5-12 hours). The plasma half-life in adult healthy subjects was approximately 5 hours after administration of Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg.
Effect of Food: Table 1 displays the effect of a high fat meal on the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone.
Table 1: Effect of a High Fat Meal on the Pharmacokinetics of Metaxalone Metaxalone Product C max1 AUC 0-t1 AUC 0-inf1 T max2 Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg 23% Increase 7% Increase 6% Increase 8 hours
(3.5-24 hours)SKELAXIN (metaxalone) tablets, 800 mg 76% Increase 32% Increase 32% Increase 5 hours
(2.5-24 hours)1= Presented as ratio fed/fasted groups. Fed group received a high fat meal.
2= Presented as median (range) under fed state.Distribution
For Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, the metaxalone apparent volume of distribution (V/F) was approximately 800 Liters. Metaxalone plasma protein binding is unknown.
Elimination
For Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, the metaxalone plasma half-life was approximately 5 hours.
Metabolism: Metaxalone is metabolized by the liver. CYP1A2, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 and, to a lesser extent, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, and CYP2C19 are involved in metaxalone metabolism.
Excretion: Metaxalone is excreted in the urine as unidentified metabolites.
Specific Populations
For Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg, the effect of age, renal impairment, and hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of metaxalone is unknown.
Males and Females:The metaxalone Cmax increased by 36% and AUC inf by 31%, in females compared to males following administration of 640 mg of Metaxalone Tablets. These data were not adjusted for other factors (e.g., weight, renal function). The clinical significance of these findings is unknown.
Drug Interaction Studies
In Vitro Studies: Metaxalone does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2A6, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1, and CYP3A4 or induce CYP1A2, CYP2B6, and CYP3A4.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies to evaluate the carcinogenic potential of metaxalone have not been conducted.
Mutagenesis
Studies to evaluate the mutagenic potential of metaxalone have not been conducted.
Impairment of Fertility
Reproduction studies in rats have not revealed evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus due to metaxalone.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg are available as oval, peach-colored tablets, debossed with M640 on one side and no markings on the other side. Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg are packaged as a bottle of 60 tablets, NDC: 74157-018-60
Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F), excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F). [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Serotonin Syndrome
Inform patients that Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg could cause a rare but potentially life-threatening condition called serotonin syndrome. Warn patients of the symptoms of serotonin syndrome and to seek medical attention right away if symptoms develop. Instruct patients to inform their healthcare providers if they are taking, or plan to take, serotonergic drugs [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.1)] .
Central Nervous System Depression
Advise patients that Metaxalone Tablets, 640 mg may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for performance of hazardous tasks, such as operating machinery or driving a motor vehicle, especially when used with alcohol and other CNS depressants [see Drug Interactions (7.2)] .
Manufactured for: INA Pharmaceutics, Inc., Fairmont, WV 26554
U.S. Patents: 11,918,559; Patents Pending
21507-03 01/26
1274E## - Product label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
METAXALONE
metaxalone tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 74157-018 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METAXALONE (UNII: 1NMA9J598Y) (METAXALONE - UNII:1NMA9J598Y) METAXALONE 640 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ALGINIC ACID (UNII: 8C3Z4148WZ) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POVIDONE (UNII: FZ989GH94E) PROPYLENE GLYCOL ALGINATE (UNII: 26CD3J2R0C) Product Characteristics Color pink (light pink to pink) Score no score Shape OVAL Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code M640 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 74157-018-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/10/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022503 02/10/2025 Labeler - INA Pharmaceutics Inc (117466866)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
