REPREXAIN- hydrocodone bitartrate, ibuprofen tablet, film coated REPREXAIN- hydrocodone bitartrate, ibuprofen tablet
Reprexain by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Reprexain by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Stat Rx USA, STAT RX USA LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
DESCRIPTIONEach REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets) contains either: Hydrocodone Bitartrate, USP 2.5 mg and ibuprofen, USP 200 mg, Hydrocodone Bitartrate, USP 5 mg and ibuprofen, USP 200 mg or Hydrocodone Bitartrate, USP 10 mg and ibuprofen, USP 200 mg.
REPREXAIN™ is supplied in a fixed combination tablet form for oral administration.
REPREXAIN™ combines the opioid analgesic agent, hydrocodone bitartrate, with the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory (NSAID) agent, ibuprofen.
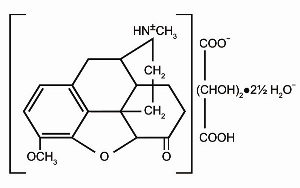
Hydrocodone bitartrate is a semisynthetic and centrally acting opioid analgesic. Its chemical name is: 4,5 a-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6-one tartrate (1:1) hydrate (2:5). Its chemical formula is: C18H 21NO3C4H6O62½H2O, and the molecular weight is 494.50. Its structural formula is:
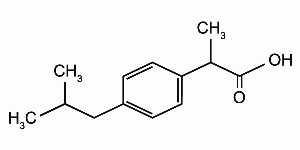
Ibuprofen is a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agent [non-selective COX inhibitor] with analgesic and antipyretic properties. Its chemical name is: (±)-2-(p-isobutylphenyl) propionic acid. Its chemical formula is: C13H18O2, and the molecular weight is: 206.29. Its structural formula is:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYHydrocodone Component
Hydrocodone is a semisynthetic opioid analgesic and antitussive with multiple actions qualitatively similar to those of codeine. Most of these involve the central nervous system and smooth muscle. The precise mechanism of action of hydrocodone and other opioids is not known, although it is believed to relate to the existence of opiate receptors in the central nervous system. In addition to analgesia, opioids may produce drowsiness, changes in mood, and mental clouding.
Ibuprofen Component
Ibuprofen is a non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent that possesses analgesic and antipyretic activities. Its mode action, like that of other NSAIDs, is not completely understood, but may be related to inhibition of cyclooxygenase activity and prostaglandin synthesis. Ibuprofen is a peripherally acting analgesic. Ibuprofen does not have any known effects on opiate receptors.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: After oral dosing with the REPREXAIN™tablet, a peak hydrocodone plasma level of 27 ng/mL is achieved at 1.7 hours, and a peak ibuprofen plasma level of 30 mcg/mL is achieved at 1.8 hours. The effect of food on the absorption of either component from the REPREXAIN™ tablet has not been established.
Distribution: Ibuprofen is highly protein-bound (99%) like most other non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agents. Although the extent of protein binding of hydrocodone in human plasma has not been definitely determined, structural similarities to related opioid analgesics suggest that hydrocodone is not extensively protein bound. As most agents in the 5-ring morphinan group of semi-synthetic opioids bind plasma protein to
a similar degree (range 19% [hydromorphone] to 45% [oxycodone]), hydrocodone is expected to fall within this range.
Metabolism: Hydrocodone exhibits a complex pattern of metabolism, including O-demethylation, N-demethylation, and 6-keto reduction to the corresponding 6-a-and 6-ßhydroxy metabolites. Hydromorphone, a potent opioid, is formed from the O -demethylation of hydrocodone and contributes to the total analgesic effect of hydrocodone. The O-and N -demethylation processes are mediated by separate P-450 isoenzymes: CYP2D6 and CYP3A4, respectively.
Ibuprofen is present in this product as a racemate, and following absorption it undergoes interconversion in the plasma from the R-isomer to the S-isomer. Both the R- and S-isomers are metabolized to two primary metabolites:
(+)-2-4’-(2hydroxy-2-methyl-propyl) phenyl propionic acid and (+)-2-4’-(2carboxypropyl) phenyl propionic acid, both of which
circulate in the plasma at low levels relative to the parent.
Elimination: Hydrocodone and its metabolites are eliminated primarily in the kidneys, with a mean plasma half-life of 4.5 hours. Ibuprofen is excreted in the urine, 50% to 60% as metabolites and approximately 15% as unchanged drug and conjugate. The plasma half-life is 2.2 hours.
Special Populations: No significant pharmacokinetic differences based on age or gender have been demonstrated. The pharmacokinetics of hydrocodone and ibuprofen from REPREXAIN™ has not been evaluated in children.
Renal Impairment:The effect of renal insufficiency on the pharmacokinetics of the REPREXAIN™ dosage form has not been determined.
CLINICAL STUDIESIn single-dose studies of post surgical pain (abdominal, gynecological, orthopedic), 940 patients were studied at doses of one or two tablets. REPREXAIN™ produced greater efficacy than placebo and each of its individual components given at the same dose. No advantage was demonstrated for the two-tablet dose.
-
INDICATIONS & USAGE
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of REPREXAIN™ and other treatment options before deciding to use REPREXAIN™. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
REPREXAIN™ tablets are indicated for the short-term (generally less than 10 days) management of acute pain. REPREXAIN™ is not indicated for the treatment of such conditions as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
REPREXAIN™ is contraindicated in patients with known hypersensitivity to hydrocodone or ibuprofen. Patients known to be hypersensitive to other opioids may exhibit cross-sensitivity to hydrocodone. REPREXAIN™ should not be given to patients who have experienced asthma, urticaria, or allergic-type reactions after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Severe, rarely fatal, anaphylactic-like reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see WARNINGS – Anaphylactoid Reactions, and PRECAUTIONS - Pre-existing Asthma).
REPREXAIN™ is contraindicated for the treatment of peri-operative pain in the setting of coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery (see WARNINGS). -
WARNINGS
WARNINGS
CARDIOVASCULAR EFFECTS
Cardiovascular Thrombotic Events
Clinical trials of several COX-2 selective and nonselective NSAIDs of up to three years duration have shown an increased risk of serious cardiovascular (CV) thrombotic events, myocardial infarction, and stroke, which can be fatal. All NSAIDs, both COX-2 selective and nonselective, may have a similar risk. Patients with known CV disease or risk factors for CV disease may be at greater risk. To minimize the potential risk for an adverse CV event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest duration possible. Physicians and patients should remain alert for the development of such events, even in the absence of previous CV symptoms. Patients should be informed about the signs and/or symptoms of serious CV events and the steps to take if they occur.
There is no consistent evidence that concurrent use of aspirin mitigates the increased risk of serious CV thrombotic events associated with NSAID use. The concurrent use of aspirin and an NSAID does increase the risk of serious GI events (see GI WARNINGS).
Two large, controlled, clinical trials of a COX-2 selective NSAID for the treatment of pain in the first 10-14 days following CABG surgery found an increased incidence of myocardial infarction and stroke (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Hypertension
NSAID-containing products, including REPREXAIN™, can lead to onset of new hypertension or worsening of preexisting hypertension, either of which may contribute to the increased incidence of CV events. Patients taking thiazides or loop diuretics may have impaired response to these therapies when taking NSAIDs. NSAID-containing products, including REPREXAIN™, should be used with caution in patients with hypertension. Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored closely during the initiation of NSAID treatment and throughout the course of therapy.
Congestive Heart Failure and Edema
Fluid retention and edema have been observed in some patients taking NSAIDs. REPREXAIN™ should be used with caution in patients with fluid retention or heart failure.
Misuse Abuse and Diversion of Opioids
REPREXAIN™ contains hydrocodone an opioid agonist, and is a Schedule III controlled substance. Opioid agonists have the potential for being abused and are sought by abusers and people with addiction disorders, and are subject to diversion.
REPREXAIN™ can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit. This should be considered when prescribing or dispensing REPREXAIN™ in situations where the physician or pharmacist is concerned about an increased risk of misuse, abuse or diversion (see DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE).
Respiratory Depression
At high doses or in opioid-sensitive patients, hydrocodone may produce dose-related respiratory depression by acting directly on the brain stem respiratory centers. Hydrocodone also affects the center that controls respiratory rhythm, and may produce irregular and periodic breathing.
Head Injury and Increased Intracranial Pressure
The respiratory depressant effects of opioids and their capacity to elevate cerebrospinal fluid pressure may be markedly exaggerated in the presence of head injury, intracranial lesions or a pre-existing increase in intracranial pressure. Furthermore, opioids produce adverse reactions, which may obscure the clinical course of patients with head injuries.
Acute Abdominal Conditions
The administration of opioids may obscure the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions.
Gastrointestinal (GI) Effects - Risk of GI Ulceration, Bleeding and Perforation
NSAIDs, including REPREXAIN™, can cause serious gastrointestinal (GI) adverse events including inflammation, bleeding, ulceration, and perforation of the stomach, small intestine, or large intestine, which can be fatal. These serious adverse events can occur at any time, with or without warning symptoms, in patients treated with NSAIDs. Only one in five patients who develops a serious upper GI adverse event on NSAID therapy, is symptomatic. Upper GI ulcers, gross bleeding, or perforation caused by NSAIDs occur in approximately 1% of patients treated for 3-6 months, and in about 2-4% of patients treated for one year. These trends continue with longer duration of use, increasing the likelihood of developing a serious GI event at some time during the course of therapy. However, even short-term therapy is not without risk.
NSAIDs should be prescribed with extreme caution in those with a prior history of ulcer disease or gastrointestinal bleeding. Patients with a prior history of peptic ulcer disease and/or gastrointestinal bleeding who use NSAIDs have a greater than 10-fold increased risk for developing a GI bleed compared to patients with neither of these risk factors. Other factors that increase the risk for GI bleeding in patients treated with NSAIDs include concomitant use of oral corticosteroids or anticoagulants, longer duration of NSAID therapy, smoking, use of alcohol, older age, and poor general health status. Most spontaneous reports of fatal GI events are in elderly or debilitated patients and therefore, special care should be taken in treating this population.
To minimize the potential risk for an adverse GI event in patients treated with an NSAID, the lowest effective dose should be used for the shortest possible duration. Patients and physicians should remain alert for signs and symptoms of GI ulceration and bleeding during NSAID therapy and promptly initiate additional evaluation and treatment if a serious GI adverse event is suspected. This should include discontinuation of the NSAID until a serious GI adverse event is ruled out. For high-risk patients, alternate therapies that do not involve NSAIDs should be considered.
Renal Effects
Long-term administration of NSAIDs has resulted in renal papillary necrosis and other renal injury. Renal toxicity has also been seen in patients in whom renal prostaglandins have a compensatory role in the maintenance of renal perfusion. In these patients, administration of a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug may cause a dose-dependent reduction in prostaglandin formation and, secondarily, in renal blood flow, which may precipitate overt renal decompensation. Patients at greatest risk of this reaction are those with impaired renal function, heart failure, liver dysfunction, those taking diuretics and ACE inhibitors, and the elderly. Discontinuation of NSAID therapy is usually followed by recovery to the pretreatment state.
Advanced Renal Disease
No information is available from controlled clinical studies regarding the use of REPREXAIN™ in patients with advanced renal disease. Therefore, treatment with REPREXAIN™ is not recommended in patients with advanced renal disease. If REPREXAIN™ therapy must be initiated, close monitoring of the patient’s renal function is advisable.
Anaphylactoid Reactions
As with other NSAID-containing products, anaphylactoid reactions may occur in patients without known prior exposure to REPREXAIN™. REPREXAIN™ should not be given to patients with the aspirin triad. This symptom complex typically occurs in asthmatic patients who experience rhinitis with or without nasal polyps, or who exhibit severe, potentially fatal bronchospasm after taking aspirin or other NSAIDs. Fatal reactions to NSAIDs have been reported in such patients (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS - Pre-existing Asthma). Emergency help should be sought in cases where an anaphylactoid reaction occurs.
Skin Reactions
Products containing NSAIDs, including REPREXAIN™, can cause serious skin adverse events such as exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson Syndrome (SJS), and toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), which can be fatal. These serious events may occur without warning. Patients should be informed about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations and use of the drug should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Pregnancy
As with other NSAID-containing products, REPREXAIN™ should be avoided in late pregnancy because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
-
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
General
REPREXAIN™ cannot be expected to substitute for corticosteroids or to treat corticosteroid insufficiency. Abrupt discontinuation of corticosteroids may lead to disease exacerbation. Patients on prolonged corticosteroid therapy should have their therapy tapered slowly if a decision is made to discontinue corticosteroids. The pharmacological activity of REPREXAIN™ in reducing fever and inflammation may diminish the utility of these diagnostic signs in detecting complications of presumed noninfectious, painful conditions.
Special Risk Patients
As with any opioid analgesic agent, REPREXAIN™ should be used with caution in elderly or debilitated patients, and those with severe impairment of hepatic or renal function, hypothyroidism, Addison’s disease, prostatic hypertrophy or urethral stricture. The usual precautions should be observed and the possibility of respiratory depression should be kept in mind.
Cough Reflex
Hydrocodone suppresses the cough reflex; as with opioids, caution should be exercised when REPREXAIN™ is used postoperatively and in patients with pulmonary disease.
Hepatic Effects
Borderline elevations of one or more liver enzymes may occur in up to 15% of patients taking NSAIDs including ibuprofen as found in REPREXAIN™. These laboratory abnormalities may progress, may remain essentially unchanged, or may be transient with continued therapy. Notable elevations of SGPT (ALT) or SGOT (AST) (approximately three or more times the upper limit of normal) have been reported in approximately 1% of patients in clinical trials with NSAIDS. In addition, rare cases of severe hepatic reactions, including jaundice and fatal fulminant hepatitis, liver necrosis and hepatic failure, some of them with fatal outcomes have been reported.
A patient with symptoms and/or signs suggesting liver dysfunction, or in whom an abnormal liver test has occurred, should be evaluated for evidence of the development of more severe hepatic reactions while on REPREXAIN™ therapy. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop, or if systemic manifestations occur (e.g. eosinophilia, rash, etc.), REPREXAIN™ should be discontinued.
Hematological Effects
Anemia is sometimes seen in patients receiving NSAIDs including ibuprofen as found in REPREXAIN™. This may be due to fluid retention, occult or gross GI blood loss, or an incompletely described effect upon erythropoiesis. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs including ibuprofen, should have their hemoglobin or hematocrit checked if they exhibit any signs or symptoms of anemia.
NSAIDs inhibit platelet aggregation and have been shown to prolong bleeding time in some patients. Unlike aspirin, their effect on platelet function is quantitatively less, of shorter duration, and reversible. Patients receiving REPREXAIN™ who may be adversely affected by alterations in platelet function, such as those with coagulation disorders or patients receiving anticoagulants, should be carefully monitored.
Pre-existing Asthma
Patients with asthma may have aspirin-sensitive asthma. The use of aspirin in patients with aspirin-sensitive asthma has been associated with severe bronchospasm, which may be fatal. Since cross-reactivity between aspirin and other NSAIDs has been reported in such aspirin-sensitive patients, REPREXAIN™ should not be administered to patients with this form of aspirin sensitivity and should be used with caution in patients with pre-existing asthma.
Aseptic Meningitis
Aseptic meningitis with fever and coma has been observed on rare occasions in patients on ibuprofen therapy as found in REPREXAIN™. Although it is probably more likely to occur in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and related connective tissue diseases, it has been reported in patients who do not have an underlying chronic disease. If signs or symptoms of meningitis develop in a patient on REPREXAIN™, the possibility of its being related to ibuprofen should be considered.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reactions
REPREXAIN™ was administered to approximately 300 pain patients in a safety study that employed dosages and a duration of treatment sufficient to encompass the recommended usage (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). Adverse event rates generally increased with increasing daily dose. The event rates reported below are from approximately 150 patients who were in a group that received one tablet of REPREXAIN™ an average of three to four times daily. The overall incidence rates of adverse experiences in the trials were fairly similar for this patient group and those who received the comparison treatment, acetaminophen 600 mg with codeine 60 mg.
Drug Abuse and Dependence
The following lists adverse events that occurred with an incidence of 1% or greater in clinical trials of REPREXAIN™, without regard to the causal relationship of the events to the drug. To distinguish different rates of occurrence in clinical studies, the adverse events are listed as follows:
name of adverse event = less than 3%
adverse events marked with an asterisk * = 3% to 9%
adverse event rates over 9% are in parentheses.
Body as a Whole: Abdominal pain*; Asthenia*; Fever; Flu syndrome; Headache (27%); Infection*; Pain.
Cardiovascular: Palpitations; Vasodilation.
Central Nervous System: Anxiety*; Confusion; Dizziness (14%); Hypertonia; Insomnia*; Nervousness*; Paresthesia; Somnolence (22%); Thinking abnormalities.
Digestive: Anorexia; Constipation (22%); Diarrhea*; Dry mouth*; Dyspepsia (12%); Flatulence*; Gastritis; Melena; Mouth ulcers; Nausea (21%); Thirst; Vomiting*.
Metabolic and Nutritional Disorders: Edema*.
Respiratory: Dyspnea; Hiccups; Pharyngitis; Rhinitis.
Skin and Appendages: Pruritus*; Sweating*.
Special Senses: Tinnitus.
Urogenital: Urinary frequency.
Incidence less than 1%
Body as a Whole: Allergic reaction.
Cardiovascular: Arrhythmia; Hypotension; Tachycardia.
Central Nervous System: Agitation; Abnormal dreams; Decreased libido; Depression; Euphoria; Mood changes; Neuralgia; Slurred speech; Tremor, Vertigo.
Digestive: Chalky stool; “Clenching teeth”; Dysphagia; Esophageal spasm; Esophagitis; Gastroenteritis; Glossitis; Liver enzyme elevation.
Metabolic and Nutritional: Weight decrease.
Musculoskeletal: Arthralgia; Myalgia.
Respiratory: Asthma; Bronchitis; Hoarseness; Increased cough; Pulmonary congestion; Pneumonia; Shallow breathing; Sinusitis.
Skin and Appendages: Rash; Urticaria.
Special Senses: Altered vision; Bad taste; Dry eyes.
Urogenital: Cystitis; Glycosuria; Impotence; Urinary incontinence; Urinary retention.
Misuse Abuse and Diversion of Opioids
REPREXAIN™ contains hydrocodone, an opioid agonist, and is a Schedule III controlled substance. REPREXAIN™, and other opioids used in analgesia can be abused and are subject to criminal diversion.
Addiction is a primary, chronic, neurobiologic disease, with genetic, psychosocial, and environmental factors influencing its development and manifestations. It is characterized by behaviors that include one or more of the following: impaired control over drug use, compulsive use, continued use despite harm, and craving. Drug addiction is a treatable disease utilizing a multidisciplinary approach, but relapse is common.
“Drug seeking” behavior is very common in addicts and drug abusers. Drug-seeking tactics include emergency calls or visits near the end of office hours, refusal to undergo appropriate examination, testing or referral, repeated “loss” of prescriptions, tampering with prescriptions and reluctance to provide prior medical records or contact information for other treating physician(s). “Doctor shopping” to obtain additional prescriptions is common among drug abusers and people suffering from untreated addiction.
Abuse and addiction are separate and distinct from physical dependence and tolerance. Physical dependence usually assumes clinically significant dimensions only after several weeks of continued opioid use, although a mild degree of physical dependence may develop after a few days of opioid therapy. Tolerance, in which increasingly large doses are required in order to produce the same degree of analgesia, is manifested initially by a shortened duration of analgesic effect, and subsequently by decreases in the intensity of analgesia. The rate of development of tolerance varies among patients. Physicians should be aware that abuse of opioids can occur in the absence of true addiction and is characterized by misuse for nonmedical purposes, often in combination with other psychoactive substances. REPREXAIN™, like other opioids, may be diverted for non-medical use. Record-keeping of prescribing information, including quantity, frequency, and renewal requests is strongly advised.
Proper assessment of the patient, proper prescribing practices, periodic re-evaluation of therapy, and proper dispensing and storage are appropriate measures that help to limit abuse of opioid drugs. -
OVERDOSAGE
OVERDOSAGE
Following an acute overdosage, toxicity may result from hydrocodone and/or ibuprofen.
Signs and Symptoms
Hydrocodone Component
Serious overdose with hydrocodone is characterized by respiratory depression (a decrease in respiratory rate and/or tidal volume, Cheyne-Stokes respiration, cyanosis) extreme somnolence progressing to stupor or coma, skeletal muscle flaccidity, cold and clammy skin, and sometimes bradycardia and hypotension. In severe overdosage, apnea, circulatory collapse, cardiac arrest and death may occur.
Ibuprofen Component
Symptoms include gastrointestinal irritation with erosion and hemorrhage or perforation, kidney damage, liver damage, heart damage, hemolytic anemia, agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia, aplastic anemia, and meningitis. Other symptoms may include headache, dizziness, tinnitus, confusion, blurred vision, mental disturbances, skin rash, stomatitis, edema, reduced retinal sensitivity, corneal deposits, and hyperkalemia.
Treatment
Primary attention should be given to the re-establishment of adequate respiratory exchange through provision of a patent airway and the institution of assisted or controlled ventilation. Naloxone, a narcotic antagonist, can reverse respiratory depression and coma associated with opioid overdose or unusual sensitivity to opioids, including hydrocodone. Therefore, an appropriate dose of naloxone hydrochloride should be administered intravenously with simultaneous efforts at respiratory resuscitation. Since the duration of action of hydrocodone may exceed that of the naloxone, the patient should be kept under continuous surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration. Supportive measures should be employed as indicated. Gastric emptying may be useful in removing unabsorbed drug. In cases where consciousness is impaired it may be inadvisable to perform gastric lavage. If gastric lavage is performed, little drug will likely be recovered if more than an hour has elapsed since ingestion. Ibuprofen is acidic and is excreted in the urine; therefore, it may be beneficial to administer alkali and induce diuresis. In addition to supportive measures the use of oral activated charcoal may help to reduce the absorption and reabsorption of ibuprofen. Dialysis is not likely to be effective for removal of ibuprofen because it is very highly bound to plasma proteins. -
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Carefully consider the potential benefits and risks of REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets) and other treatment options before deciding to use REPREXAIN™. Use the lowest effective dose for the shortest duration consistent with individual patient treatment goals (see WARNINGS).
After observing the response to initial therapy with REPREXAIN™, the dose and frequency should be adjusted to suit an individual patient’s needs.
For the short-term (generally less than 10 days) management of acute pain, the recommended dose of REPREXAIN™ is one tablet every 4 to 6 hours, as necessary. Dosage should not exceed 5 tablets in a 24-hour period. It should be kept in mind that tolerance to hydrocodone can develop with continued use and that the incidence of untoward effects is dose related.
The lowest effective dose or the longest dosing interval should be sought for each patient (see WARNINGS), especially in the elderly. After observing the initial response to therapy with REPREXAIN™, the dose and frequency of dosing should be adjusted to suit the individual patient’s need, without exceeding the total daily dose recommended. -
HOW SUPPLIED
HOW SUPPLIED
REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets) are available as:
Storage
2.5 mg/200 mg: white capsule shaped, film coated tablets, debossed “IP 116” on obverse and plain on reverse.
Bottles of 100: NDC 63717-900-01
Sample boxes of 10 tablets: NDC: 63717-900-99
5 mg/200 mg: white, oval shaped, film coated tablets, debossed “IP 146” on obverse and plain on reverse.
Bottles of 100: NDC: 63717-901-01
Sample boxes of 10 tablets: NDC: 63717-901-99
10 mg/200 mg: yellow, round shaped, film coated tablets, debossed “IP 117” on obverse and plain on reverse.
Bottles of 100: NDC 63717-902-01
Sample boxes of 10 tablets: NDC: 63717-902-99
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C
(59°-86°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container.
A Schedule CS-III Controlled Substance.
Manufactured For:
Hawthorn Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Madison, MS 39110
Rev. 12/08 HI251
NDC: 63717-900-01
Reprexain™ CIII
(hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablet)
2.5 mg/200 mg
Rx only
100 Tablets
Hawthorn Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Each tablet contains:
Hydrocodone bitartrate USP, 2.5 mg
Ibuprofen USP, 200 mg
Usual Dosage: See package insert.
Dispense in light resistant container as defined in the USP.
Store at 25oC (77oF); excursions permitted to controlled room temperature 15o-30oC
(59o-86oF).
Mfd. for: Hawthorn Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
Madison, Ms 39110
HI200 11/05
-
INFORMATION FOR PATIENTS
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the following information before initiating therapy with an NSAID and periodically during the course of ongoing therapy. Patients should also be encouraged to read the REPREXAIN™ Medication Guide that accompanies each prescription dispensed.
Laboratory Tests
1. REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets), like other opioid-containing analgesics, may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery; patients should be cautioned accordingly.
2. Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression, when taken with this combination product, and should be avoided.
3. REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets) can be abused in a manner similar to other opioid agonists, legal or illicit. REPREXAIN™ may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed.
4. REPREXAIN™, like other NSAID-containing products, may cause serious CV side effects, such as MI or stroke, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious CV events can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of chest pain, shortness of breath, weakness, slurring of speech, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Cardiovascular Effects).
5. REPREXAIN™, like other NSAID-containing products, can cause GI discomfort and serious GI side effects, such as ulcers and bleeding, which may result in hospitalization and even death. Although serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of ulcerations and bleeding, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative sign or symptoms including epigastric pain, dyspepsia, melena, and hematemesis. Patients should be apprised of the importance of this follow-up (see WARNINGS, Gastrointestinal Effects: Risk of Ulceration, Bleeding, and Perforation).
6. REPREXAIN™, like other NSAID-containing products, can cause serious skin side effects such as exfoliative dermatitis, SJS, and TEN, which may result in hospitalizations and even death. Although serious skin reactions may occur without warning, patients should be alert for the signs and symptoms of skin rash and blisters, fever, or other signs of hypersensitivity such as itching, and should ask for medical advice when observing any indicative signs or symptoms. Patients should be advised to stop the drug immediately if they develop any type of rash and contact their physicians as soon as possible.
7. Patients should promptly report signs or symptoms of unexplained weight gain or edema to their physicians.
8. Patients should be informed of the warning signs and symptoms of hepatotoxicity (e.g., nausea, fatigue, lethargy, pruritus, jaundice, right upper quadrant tenderness, and “flu-like” symptoms). If these occur, patients should be instructed to stop therapy and seek immediate medical therapy.
9. Patients should be informed of the signs of an anaphylactoid reaction (e.g., difficulty breathing, swelling of the face or throat). If these occur, patients should be instructed to seek immediate emergency help (see WARNINGS).
10. In late pregnancy, as with other NSAIDs, REPREXAIN™ should be avoided because it may cause premature closure of the ductus arteriosus.
11. Patients should be instructed to report any signs of blurred vision or other eye symptoms.
Because serious GI tract ulcerations and bleeding can occur without warning symptoms, physicians should monitor for signs or symptoms of GI bleeding. Patients on long-term treatment with NSAIDs should have their CBC and a chemistry profile checked periodically. If clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver or renal disease develop, systemic manifestations occur (e.g., eosinophilia, rash, etc.) or if abnormal liver tests persist or worsen, REPREXAIN™ should be discontinued.
Drug InteractionsACE-inhibitors: Reports suggest that NSAIDs may diminish the antihypertensive effect of ACE-inhibitors. This interaction should be given consideration in patients taking REPREXAIN™ concomitantly with ACE-inhibitors.
Anticholinergics: The concurrent use of anticholinergics with hydrocodone preparations may produce paralytic ileus.
Antidepressants: The use of Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) or tricyclic antidepressants with REPREXAIN™ may increase the effect of either the antidepressant or hydrocodone.
MAOIs have been reported to intensify the effects of at least one opioid drug causing anxiety, confusion and significant depression of respiration or coma. The use of hydrocodone is not recommended for patients taking MAOIs or within 14 days of stopping such treatment.
Aspirin: When REPREXAIN™ is administered with aspirin, the protein binding of aspirin is reduced, although the clearance of free REPREXAIN™ is not altered. The clinical significance of this interaction is not known; however, as with other NSAID-containing products, concomitant administration of REPREXAIN™ and aspirin is not generally recommended because of the potential of increased adverse effects.
CNS Depressants: Patients receiving other opioids, antihistamines, antipsychotics, antianxiety agents, or other CNS depressants (including alcohol) concomitantly with REPREXAIN™ may exhibit an additive CNS depression. When combined therapy is contemplated, the dose of one or both agents should be reduced.
Diuretics: Ibuprofen has been shown to reduce the natriuretic effect of furosemide and thiazides in some patients. This response has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis. During concomitant therapy with REPREXAIN™ the patient should be observed closely for signs of renal failure (see WARNINGS - Renal Effects), as well as diuretic efficacy.
Lithium: Ibuprofen has been shown to elevate plasma lithium concentration and reduce renal lithium clearance. The mean minimum lithium concentration increased 15% and the renal clearance was decreased by approximately 20%. This effect has been attributed to inhibition of renal prostaglandin synthesis by ibuprofen. Thus, when REPREXAIN™ and lithium are administered concurrently, patients should be observed for signs of lithium toxicity.
Methotrexate: Ibuprofen, as well as other NSAIDs, has been reported to competitively inhibit methotrexate accumulation in rabbit kidney slices. This may indicate that ibuprofen could enhance the toxicity of methotrexate. Caution should be used when REPREXAIN™ is administered concomitantly with methotrexate.
Mixed Agonist/Antagonist Opioid Analgesics: Agonist/antagonist analgesics (i.e., pentazocine, nalbuphine, butorphanol and buprenorphine) should be administered with caution to patients who have received or are receiving a course of therapy with a pure opioid agonist analgesic such as hydrocodone. In this situation, mixed agonist/antagonist analgesics may reduce the analgesic effect of hydrocodone and/or may precipitate withdrawal symptoms in these patients.
Neuromuscular Blocking Agents: Hydrocodone, as well as other opioid analgesics, may enhance the neuromuscular blocking action of skeletal muscle relaxants and produce an increased degree of respiratory depression.
Warfarin: The effects of warfarin and NSAIDs on GI bleeding are synergistic, such that users of both drugs together have a risk of serious GI bleeding higher than users of either drug alone.
Carcinogenesis, Mutangenicity, and Impairment of Fertility
Pregnancy
The carcinogenic and mutagenic potential of REPREXAIN™ has not been investigated. The ability of REPREXAIN™ to impair fertility has not been assessed.
Pregnancy Category C.
Teratogenic Effects: Reproductive studies conducted in rats and rabbits have not demonstrated evidence of developmental abnormalities.
REPREXAIN™, administered to rabbits at 95 mg/kg (5.72 and 1.9 times the maximum clinical dose based on body weight and surface area, respectively), a maternally toxic dose, resulted in an increase in the percentage of litters and fetuses with any major abnormality and an increase in the number of litters and fetuses with one or more nonossified metacarpals (a minor abnormality). REPREXAIN™, administered to rats at 166 mg/kg (10.0 and 1.66 times the maximum clinical dose based on body weight and surface area, respectively), a maternally toxic dose, did not result in any reproductive toxicity. However, animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. REPREXAIN™ should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Labor and Delivery
Nonteratogenic Effects: Because of the known effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on the fetal cardiovascular system (closure of the ductus arteriosus), use during pregnancy (particularly late pregnancy) should be avoided. Babies born to mothers who have been taking opioids regularly prior to delivery will be physically dependent. The withdrawal signs include irritability and excessive crying, tremors, hyperactive reflexes, increased respiratory rate, increased stools, sneezing, yawning, vomiting, and fever. The intensity of the syndrome does not always correlate with the duration of maternal opioid use or dose. There is no consensus on the best method of managing withdrawal.
Nursing Mothers
Labor and Delivery
As with other drugs known to inhibit prostaglandin synthesis, an increased incidence of dystocia and delayed parturition occurred in rats. Administration of REPREXAIN™ is not recommended during labor and delivery. The effects of REPREXAIN™ on labor and delivery in pregnant women are unknown.
It is not known whether hydrocodone is excreted in human milk. In limited studies, an assay capable of detecting 1 mcg/mL did not demonstrate ibuprofen in the milk of lactating mothers. However, because of the limited nature of the studies, and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from REPREXAIN™, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of REPREXAIN™ in pediatric patients below the age of 16 have not been established.
Geriatric Use
In controlled clinical trials there was no difference in tolerability between patients less than 65 years of age and those more than or equal to 65, apart from an increased tendency of the elderly to develop constipation. However, because the elderly may be more sensitive to the renal and gastrointestinal effects of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents as well as possible increased risk of respiratory depression with opioids, extra caution and reduced dosages should be used when treating the elderly with REPREXAIN™ (hydrocodone bitartrate and ibuprofen tablets).
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
REPREXAIN
hydrocodone bitartrate, ibuprofen tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16590-878(NDC: 63717-901) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Hydrocodone Bitartrate (UNII: NO70W886KK) (Hydrocodone - UNII:6YKS4Y3WQ7) Hydrocodone Bitartrate 5 mg Ibuprofen (UNII: WK2XYI10QM) (Ibuprofen - UNII:WK2XYI10QM) Ibuprofen 200 mg Product Characteristics Color white Score no score Shape OVAL Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code IP;146 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16590-878-20 20 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 16590-878-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 16590-878-40 40 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076642 12/16/2008 REPREXAIN
hydrocodone bitartrate, ibuprofen tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16590-276(NDC: 63717-902) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Hydrocodone Bitartrate (UNII: NO70W886KK) (Hydrocodone - UNII:6YKS4Y3WQ7) Hydrocodone Bitartrate 10 mg Ibuprofen (UNII: WK2XYI10QM) (Ibuprofen - UNII:WK2XYI10QM) Ibuprofen 200 mg Product Characteristics Color yellow Score no score Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code IP;117 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16590-276-30 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 16590-276-40 40 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 3 NDC: 16590-276-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 4 NDC: 16590-276-71 100 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 5 NDC: 16590-276-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076642 12/16/2008 Labeler - Stat Rx USA (786036330) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations STAT RX USA LLC 786036330 repack, relabel
Trademark Results [Reprexain]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 REPREXAIN 76584625 2978031 Live/Registered |
AMNEAL PHARMACEUTICALS LLC 2004-03-25 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
 Label Image
Label Image REPREXAIN 10-200 MG LABEL
REPREXAIN 10-200 MG LABEL