Tretinoin by Oceanside Pharmaceuticals / DPT Laboratories, Ltd. / Bausch Health Companies Inc. TRETINOIN gel
Tretinoin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Tretinoin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Oceanside Pharmaceuticals, DPT Laboratories, Ltd., Bausch Health Companies Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Tretinoin Gel safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Tretinoin Gel.
Tretinoin Gel, 0.05%
For topical use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1973INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Tretinoin Gel is a retinoid indicated for topical treatment of acne vulgaris. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Gel, 0.05% (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Tretinoin Gel should not be used on eczematous or sunburned skin due to potential for severe irritation. (5.1)
- Topical over-the-counter acne preparations, concomitant topical medications, medicated cleansers, topical products with alcohol or astringents: Use with caution, irritation may occur. (5.1)
- Avoid unprotected exposure to sunlight including sunlamps (UV light) when using Tretinoin Gel due to potential for increased photosensitization. Use sunscreen of at least SPF 15 and protective clothing during exposure. (5.2)
- Avoid use of Tretinoin Gel with weather extremes, such as wind or cold due to potential for increased irritation. (5.2)
- Use Tretinoin Gel with caution if allergic to fish due to potential for allergenicity to fish protein. Patients who develop pruritus or urticaria should contact their healthcare provider. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) with Tretinoin Gel are dry skin, peeling/scaling/flaking skin, skin burning sensation, and erythema. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC at 1-800-321-4576 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 7/2016
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Skin Irritation
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
5.3 Fish Allergies
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For topical use only. Not for ophthalmic, oral, or intravaginal use.
Tretinoin Gel should be applied once daily, before bedtime, to the skin where acne lesions appear, using a thin layer to cover the entire affected area. Tretinoin Gel should be kept away from the eyes, the mouth, paranasal creases, and mucous membranes. Application of excessive amounts of gel will not provide incremental efficacy.
Patients treated with Tretinoin Gel may use cosmetics, but the areas to be treated should be cleansed thoroughly before the medication is applied.
When treating with Tretinoin Gel, caution should be exercised with the use of concomitant topical over-the-counter preparations, topical medications, medicated or abrasive soaps and cleansers, products that have strong drying effect, and products with high concentrations of alcohol, astringents, spices, or lime. Particular caution should be exercised with acne preparations containing benzoyl peroxide, sulfur, resorcinol, or salicylic acid. Allow the effects of such preparations to subside before use of Tretinoin Gel has begun.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Skin Irritation
The skin of certain individuals may become dry, red, or exfoliated while using Tretinoin Gel. If the degree of irritation warrants, patients should be directed to temporarily reduce the amount or frequency of application of the medication, discontinue use temporarily, or discontinue use all together. Efficacy at reduced frequencies of application has not been established. If a reaction suggesting sensitivity occurs, use of the medication should be discontinued. Mild to moderate skin dryness may also be experienced; if so, use of an appropriate moisturizer during the day may be helpful.
Tretinoin has been reported to cause severe irritation on eczematous or sunburned skin and should be used with caution in patients with these conditions.
To help limit skin irritation, patients must:
- wash the treated skin gently, using a mild, non-medicated soap, and pat it dry,
- avoid washing the treated skin too often and scrubbing the affected skin area, and
- avoid contact with the peels of limes.
5.2 Ultraviolet Light and Environmental Exposure
Unprotected exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps, should be minimized during the use of Tretinoin Gel. Patients who normally experience high levels of sun exposure, and those with inherent sensitivity to sun, should be warned to exercise caution. Use of sunscreen products of at least SPF 15 and protective clothing over treated areas is recommended when exposure cannot be avoided.
Weather extremes, such as wind or cold, also may be irritating to tretinoin-treated skin.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under prescribing conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two randomized, controlled trials, 674 subjects received treatment for up to 12 weeks with Tretinoin Gel [see Clinical Studies (14)]. In these studies, 50% of the subjects who were treated with Tretinoin Gel reported one or more adverse reactions; 30% of the subjects reported treatment-related adverse reactions. In the vehicle group, 29% of the 487 randomized subjects reported at least one adverse reaction; 5% of the subjects reported events that were treatment-related. There were no serious, treatment-related adverse reactions reported by subjects in any of the treatment groups.
Selected adverse reactions that occurred in at least 1% of subjects in the two trials combined are shown in Table 1 (below). Most skin-related adverse reactions first appear during the first two weeks of treatment with Tretinoin Gel, and the incidence rate for skin-related reactions peaks around the second and third week of treatment. In some subjects, the skin-related adverse reactions persist throughout the treatment period.
Table 1: Number of Subjects with Selected Adverse Reactions (Occurring in at Least 1% of Subjects) Event Tretinoin Gel
(n = 674)Vehicle Gel
(n = 487)Dry Skin
109 (16%)
8 (2%)
Peeling/Scaling/Flaking Skin
78 (12%)
7 (1%)
Skin Burning Sensation
53 (8%)
8 (2%)
Erythema
47 (7%)
1 (<1%)
Pruritus
11 (2%)
3 (1%)
Pain of Skin
7 (1%)
0 (0%)
Sunburn
7 (1%)
3 (1%)
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of Tretinoin Gel. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Temporary hyper- or hypopigmentation has been reported with repeated application of tretinoin.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
There are no well-controlled trials in pregnant women treated with Tretinoin Gel. Tretinoin Gel should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Tretinoin Gel at doses of 0.1, 0.3 and 1 g/kg/day was tested for maternal and developmental toxicity in pregnant Sprague-Dawley rats by dermal application. The dose of 1 g/kg/day was approximately 4 times the clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison. Possible tretinoin-associated teratogenic effects (craniofacial abnormalities (hydrocephaly), asymmetrical thyroids, variations in ossification, and increased supernumerary ribs) were noted in the fetuses of Tretinoin Gel treated animals. These findings were not observed in control animals. Other maternal and reproductive parameters in the Tretinoin Gel treated animals were not different from control. For purposes of comparison of the animal exposure to human exposure, the clinical dose is defined as 2 g of Tretinoin Gel applied daily to a 50 kg person.
Oral tretinoin has been shown to be teratogenic in rats, mice, rabbits, hamsters and nonhuman primates. Tretinoin was teratogenic in Wistar rats when given orally in doses greater than 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison). In the cynomolgus monkey, fetal malformations were reported for doses of 10 mg/kg/day, but none were observed at 5 mg/kg/day (approximately 80 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison), although increased skeletal variations were observed at all doses. Dose-related increases in embryolethality and abortion also were reported. Similar results have also been reported in pigtail macaques.
Topical tretinoin in a different formulation has generated equivocal results in animal teratogenicity tests. There is evidence for teratogenicity (shortened or kinked tail) of topical tretinoin in Wistar rats at doses greater than 1 mg/kg/day (approximately 8 times the clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison). Anomalies (humerus: short 13%, bent 6%, os parietal incompletely ossified 14%) have also been reported when 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 160 times the clinical dose assuming 100% absorption and based on body surface area comparison) was topically applied. Supernumerary ribs have been a consistent finding in rats when dams were treated topically or orally with retinoids.
With widespread use of any drug, a small number of birth defect reports associated temporally with the administration of the drug would be expected by chance alone. Cases of temporally associated congenital malformations have been reported with use of other topical tretinoin products. The significance of these spontaneous reports in terms of risk to the fetus is not known.
Nonteratogenic effects on fetuses: Oral tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic in rats when administered in doses 20 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison. Topical tretinoin has been shown to be fetotoxic in rabbits when administered in doses 8 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when Tretinoin Gel is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in children below the age of 10 have not been established.
A total of 381 pediatric subjects (aged 10 to 16 years) treated with Tretinoin Gel were enrolled into the two clinical studies. Across these two studies, comparable safety and efficacy were observed between pediatric and adult subjects.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Tretinoin Gel, 0.05% is a translucent to opaque, pale yellow gel containing 0.05% tretinoin, by weight for topical administration.
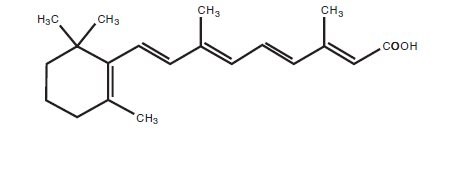
Chemically, tretinoin is all-trans-retinoic acid, also known as (all-E)-3,7-dimethyl-9-(2,6,6-trimethyl-1-cyclohexen-1-yl)-2,4,6,8-nonatetraenoic acid. It is a member of the retinoid class of compounds, and a metabolite of Vitamin A. Tretinoin has a molecular weight of 300.44, a molecular formula of C20H28O2 and the following structure:
Each gram of Tretinoin Gel, 0.05% contains 0.5 mg of tretinoin.
Other components of this formulation are benzyl alcohol, butylparaben, butylated hydroxytoluene, carbomer homopolymer Type C, ethylparaben, fish collagen hydrolyzates, glycerin, isobutylparaben, methylparaben, octoxynol 9, phenoxyethanol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium hyaluronate, and trolamine. The contribution to efficacy of individual components of the vehicle has not been evaluated.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Tretinoin is a metabolite of Vitamin A that binds with high affinity to specific retinoic acid receptors located in both the cytosol and nucleus, but cutaneous levels of tretinoin in excess of physiologic concentrations occur following application of a tretinoin-containing topical drug product.
Although tretinoin activates three members of the retinoid acid (RAR) nuclear receptors (RARα, RARβ, and RARγ) which act to modify gene expression, subsequent protein synthesis, and epithelial cell growth and differentiation, it has not been established whether the clinical effects of tretinoin are mediated through activation of retinoic acid receptors, other mechanisms, or both.
Although the exact mode of action of tretinoin is unknown, current evidence suggests that topical tretinoin decreases cohesiveness of follicular epithelial cells with decreased microcomedo formation. Additionally, tretinoin stimulates mitotic activity and increased turnover of follicular epithelial cells causing extrusion of the comedones.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
In two (2) studies, the plasma levels of tretinoin and its major metabolites (13-cis-retinoic acid and 4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid) were investigated in a total of 14 patients (age: 13 – 25 years) with severe acne, who applied 4 g ± 0.5 g (range 3.5 g – 4.5 g) of Tretinoin Gel once daily to face, back and chest, as compared to a mean of 0.71 g (range of 0.07 – 3.71 g) applied in the controlled clinical trials. Blood samples were taken at baseline and immediately prior to treatment on days 1, 5, 10 and 14. On Day 14, the final study day, samples also were taken 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 16, and 24 hours, post-treatment.
The plasma concentrations of tretinoin and its metabolites could be measured (LOQ = 0.5 ng/mL for all three analytes) in all patients at all time points. The range of plasma concentrations of tretinoin and its metabolites, 13-cis-retinoic acid and all-trans-4-oxo-retinoic acid at baseline and after multiple once daily applications of Tretinoin Gel for 14 days are given in Table 2 (below). Although some patients had increased concentrations of tretinoin or its metabolites over baseline values, no consistent increase in these concentrations were observed across patients.
Table 2: Concentrations of Active and Metabolites at Baseline and at Day 14 After Exposure to Tretinoin Gel 0.05% Compound Baseline Concentration
Range (ng/mL)Day 14 Concentration
Range (ng/mL)Tretinoin
0.68-1.62
0.69-2.88
13-cis-retinoic acid
0.67-1.79
0.51-2.26
4-oxo-13-cis-retinoic acid
0.82-5.92
0.59-6.96
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A 2-year dermal mouse carcinogenicity study was initiated with topical administration of 0.005%, 0.025% and 0.05% Tretinoin Gel. Although no drug-related tumors were observed in surviving animals, the irritating nature of the drug product precluded daily dosing, confounding data interpretation and reducing the biological significance of these results.
Studies in hairless albino mice with a different formulation suggest that concurrent exposure to tretinoin may enhance the tumorigenic potential of carcinogenic doses of UVB and UVA light from a solar simulator. This effect was confirmed in a later study in pigmented mice, and dark pigmentation did not overcome the enhancement of photocarcinogenesis by 0.05% tretinoin. Although the significance of these studies to humans is not clear, patients should minimize exposure to sunlight or artificial ultraviolet irradiation sources.
The genotoxic potential of tretinoin was evaluated in an in vitro bacterial reversion test, an in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes and an in vivo rat micronucleus assay. All tests were negative.
In dermal fertility studies of another tretinoin formulation in rats, slight (not statistically significant) decreases in sperm count and motility were seen at 0.5 mg/kg/day (3 mg/m2, approximately 4 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison), and slight (not statistically significant) increases in the number and percent of nonviable embryos in females treated with 0.25 mg/kg/day and above (1.5 mg/m2, approximately 2 times the clinical dose based on body surface area comparison) were observed.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of Tretinoin Gel used once daily before bedtime for the treatment of mild to moderate acne vulgaris were assessed in two 12-week prospective, multi-center, randomized, controlled trials. Subjects in these two trials ranged from 10 to 65 years of age, were approximately 52% female, 48% male, and were 74% Caucasian, 15% Black or African American, 3% Asian, and 8% Other.
Efficacy results at Week 12 are presented in Table 3. Success on the 6-point Global Severity Score is defined as a score of 0 (clear) or 1 (very mild). In Trial 2, subjects were also required to have at least two grades reduction from baseline for success. 'Very mild' acne is defined as: skin almost clear; rare non-inflammatory lesions present, with rare non-inflamed papules (papules may be hyperpigmented, though not pink-red, less than 4 lesions). The database was not large enough to assess whether there were differences in effects in age, gender, or race subgroups.
Table 3: Efficacy Results at Week 12 in Trials 1 and 2 - * Success was defined as 0 (clear) or 1 (very mild)
- † Success was defined as 0 (clear) or 1 (very mild) with at least 2 grades reduction from baseline
Trial 1
Tretinoin Gel
N=375Vehicle
N=185Global Severity Score Success*
78 (21%)
23 (12%)
Non-Inflammatory Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
50.7
52.4
Mean Absolute Reduction
21.8
10.3
Mean Percent Reduction
43%
21%
Inflammatory Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
23.4
23.9
Mean Absolute Reduction
9.7
5.8
Mean Percent Reduction
41%
26%
Total Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
74.1
76.3
Mean Absolute Reduction
31.4
16.1
Mean Percent Reduction
43%
22%
Trial 2
Tretinoin Gel
N=299Vehicle
N=302Global Severity Score Success†
69 (23%)
42 (14%)
Non-Inflammatory Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
51.9
52.7
Mean Absolute Reduction
18.7
10.8
Mean Percent Reduction
37%
20%
Inflammatory Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
22.9
23.4
Mean Absolute Reduction
7.0
4.0
Mean Percent Reduction
30%
17%
Total Facial Lesions
Mean Baseline Count
74.8
76.1
Mean Absolute Reduction
25.7
14.7
Mean Percent Reduction
35%
19%
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Tretinoin Gel, 0.05% is a translucent to opaque, pale yellow topical gel and available as:
- 45 g tube (NDC: 68682-800-45)
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-Approved Patient Labeling (Patient Information)
Instruct patients to clean the affected areas with an appropriate cleanser before applying Tretinoin Gel.
Patients may use moisturizers that are noncomedogenic and should avoid products that could be drying or irritating.
Patients may also wear cosmetics while being treated with Tretinoin Gel; however, they should be instructed to remove the cosmetics and clean the area thoroughly before applying Tretinoin Gel.
Warn patients of the drying and irritation effects often seen during treatment. Continue use of the medication if these effects are tolerable.
Caution patients against application of Tretinoin Gel around the eyes, mouth, paranasal creases, and mucous membranes as the skin is especially prone to irritation.
Minimize exposure to sunlight, including sunlamps. Recommend the use of sunscreen products and protective apparel (e.g., hat) when exposure cannot be avoided.
Rx onlyManufactured for:
Oceanside Pharmaceuticals, a division of
Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
By:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, Canada
©Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Product/brand names are trademarks of their respective owners.9571700
Rev. 07/2016 -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Tretinoin Gel, 0.05%
For topical useImportant information: Tretinoin Gel is for use on skin only. Do not get Tretinoin Gel in your mouth, eyes, vagina, or the corners of your nose.
What is Tretinoin Gel?
Tretinoin Gel is a prescription medicine used on the skin (topical) to treat acne. Acne is a condition in which the skin has blackheads, whiteheads, and other pimples.
It is not known if Tretinoin Gel is safe and effective in children under 10 years of age.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before using Tretinoin Gel?
Before using Tretinoin Gel, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you:
- are allergic to fish. Tretinoin Gel contains fish proteins. Tell your healthcare provider if you get hives or itching during treatment with Tretinoin Gel.
- have a skin condition called eczema.
- have a sunburn.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if Tretinoin Gel will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if Tretinoin Gel passes into your breast milk.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, herbal supplements, and any skin products that you use.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you use any other medicines to treat your acne, including medicated cleansers or soaps. Using other topical acne products may increase the irritation of your skin when used with Tretinoin Gel.
How should I use Tretinoin Gel?
- Use Tretinoin Gel exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to use it.
- Before you apply Tretinoin Gel, gently wash the affected skin area with a mild, non-medicated soap. Rinse and pat your skin dry.
- Apply Tretinoin Gel 1 time a day before bedtime.
- Apply a thin layer of Tretinoin Gel to cover the affected skin areas. Gently rub Tretinoin Gel into your skin.
- Do not use more Tretinoin Gel than you need to cover the affected area and do not apply Tretinoin Gel more than 1 time a day. Using too much Tretinoin Gel may irritate or increase the irritation of your skin, and will not give faster or better results.
- You may use moisturizers and cosmetics.
What should I avoid while using Tretinoin Gel?
- Avoid washing your skin too often and scrubbing the affected skin area.
- You should avoid sunlamps, tanning beds, and ultraviolet light during treatment with Tretinoin Gel.
- Minimize exposure to sunlight.
- If you have to be in the sunlight or are sensitive to sunlight, use a sunscreen with a SPF (sun protection factor) of 15 or more and wear protective clothing, and a wide brimmed hat to cover the treated areas.
- If you do get sunburned, stop using Tretinoin Gel until your skin has healed and is back to normal.
- Cold weather and wind may irritate skin treated with Tretinoin Gel. Skin treated with Tretinoin Gel may dry out or get wind burned more easily. Talk to your healthcare provider about ways to manage skin irritation.
- Avoid contact with the peels of limes.
What are the possible side effects of Tretinoin Gel?
Tretinoin Gel may cause skin irritation, including: skin dryness, burning, redness, excessive flaking or peeling. If you develop these symptoms, your healthcare provider may tell you to stop using Tretinoin Gel for a while, decrease the number of times you apply Tretinoin Gel, or completely stop treatment with Tretinoin Gel. It is not known if Tretinoin Gel is effective when used less than 1 time a day.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all of the side effects possible with Tretinoin Gel.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Tretinoin Gel?
- Store Tretinoin Gel at room temperature, 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Protect from freezing.
Keep Tretinoin Gel and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of Tretinoin Gel
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use Tretinoin Gel for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give Tretinoin Gel to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about Tretinoin Gel that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients of Tretinoin Gel?
Active ingredient: tretinoin
Inactive ingredients: benzyl alcohol, butylparaben, butylated hydroxytoluene, carbomer homopolymer Type C, ethylparaben, fish collagen hydrolyzates, glycerin, isobutylparaben, methylparaben, octoxynol 9, phenoxyethanol, propylparaben, purified water, sodium hyaluronate, and trolamine.Manufactured for:
Oceanside Pharmaceuticals, a division of
Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Bridgewater, NJ 08807 USA
By:
Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc.
Laval, Quebec H7L 4A8, CanadaFor more information, call 1-800-321-4576.
©Valeant Pharmaceuticals North America LLC
Product/brand names are trademarks of their respective owners.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.9571700
Rev. 07/2016
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRETINOIN
tretinoin gelProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68682-800 Route of Administration TOPICAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Tretinoin (UNII: 5688UTC01R) (Tretinoin - UNII:5688UTC01R) Tretinoin 0.05 g in 100 g Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength benzyl alcohol (UNII: LKG8494WBH) butylparaben (UNII: 3QPI1U3FV8) butylated hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) CARBOMER HOMOPOLYMER TYPE C (ALLYL PENTAERYTHRITOL CROSSLINKED) (UNII: 4Q93RCW27E) ethylparaben (UNII: 14255EXE39) MARINE COLLAGEN, SOLUBLE (UNII: 8JC99XGU4W) glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) isobutylparaben (UNII: 0QQJ25X58G) methylparaben (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) octoxynol-9 (UNII: 7JPC6Y25QS) phenoxyethanol (UNII: HIE492ZZ3T) propylparaben (UNII: Z8IX2SC1OH) water (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) hyaluronate sodium (UNII: YSE9PPT4TH) trolamine (UNII: 9O3K93S3TK) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68682-800-45 1 in 1 PACKAGE 07/26/2007 1 45 g in 1 TUBE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA authorized generic NDA022070 07/26/2007 Labeler - Oceanside Pharmaceuticals (832011691) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations DPT Laboratories, Ltd. 832224526 MANUFACTURE(68682-800) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Valeant Pharmaceuticals International, Inc. 245141858 MANUFACTURE(68682-800)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.