AMOXICILLIN powder, for suspension
Amoxicillin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Amoxicillin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use AMOXICILLIN FOR ORAL SUSPENSION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for AMOXICILLIN FOR ORAL SUSPENSION.
AMOXICILLIN for oral suspension
Dye free
Initial U.S. Approval:1974RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Drug-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (DIES) (5.3) 02/2024
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Amoxicillin is a penicillin-class antibacterial indicated for treatment of infections due to susceptible strains of designated microorganisms. (1)
Adults and Pediatric Patients (1)
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections of the Ear, Nose, and Throat
- Infections of the Genitourinary Tract
- Infections of the Skin and Skin Structure
- Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract
Adult Patients only (1)
- Helicobacter pylori Infection and Duodenal Ulcer Disease
Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of amoxicillin for oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, amoxicillin for oral suspension should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- In Adults, 750 to 1750 mg/day in divided doses every 8 to 12 hours.
- In Pediatric Patients over 3 Months of Age, 20 to 45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 to 12 hours. Refer to full prescribing information for specific dosing regimens. (2.2, 2.3)
- The upper dose for neonates and infants aged 3 months or younger is 30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours. (2.3)
- Dosing for H. pylori Infection (in Adults): Triple therapy: 1 gram amoxicillin, 500 mg clarithromycin, and 30 mg lansoprazole, all given twice daily (every 12 hours) for 14 days. Dual therapy: 1 gram amoxicillin and 30 mg lansoprazole, each given three times daily (every 8 hours) for 14 days. (2.4)
- Reduce the dose in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR greater than 30 mL/min). (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- For Oral Suspension:125 mg/5 mL, 250 mg/5 mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- History of a serious hypersensitivity reaction (e.g., anaphylaxis or Stevens-Johnson syndrome) to amoxicillin or to other beta-lactams (e.g., penicillins or cephalosporins). (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Anaphylactic reactions: Serious and occasionally fatal anaphylactic reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy, including amoxicillin. Discontinue amoxicillin if a reaction occurs. (5.1)
- Severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR): Monitor closely. Discontinue if rash progresses. (5.2)
- Drug-induced enterocolitis syndrome (DIES) has been reported with amoxicillin use. If this occurs, discontinue amoxicillin for oral suspension and institute appropriate therapy. (5.3)
- Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) (ranging from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis): Evaluate if diarrhea occurs. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (greater than 1%) observed in clinical trials of amoxicillin for oral suspension were diarrhea, rash, vomiting, and nausea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. at 1-877-233-2001 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Coadministration with probenecid is not recommended. (7.1)
- Concomitant use of amoxicillin and oral anticoagulants may increase the prolongation of prothrombin time. (7.2)
- Coadministration with allopurinol increases the risk of rash. (7.3)
- Amoxicillin may reduce the efficacy of oral contraceptives. (7.4)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 2/2024
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
2.2 Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months (12 weeks) and Older
2.3 Dosage in Pediatric Patients Aged Less than 12 Weeks (3 months)
2.4 Dosage for H. pylori Infection in Adults
2.5 Dosage in Renal Impairment for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Greater than 40 kg
2.6 Directions for Mixing Oral Suspension
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Anaphylactic Reactions
5.2 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
5.3 Drug-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (DIES)
5.4 Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
5.6 Skin Rash in Patients with Mononucleosis
5.7 Phenylketonurics
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Probenecid
7.2 Oral Anticoagulants
7.3 Allopurinol
7.4 Oral Contraceptives
7.5 Other Antibacterials
7.6 Effects on Laboratory Tests
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Dosing in Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
12.4 Microbiology
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 H. pylori Eradication to Reduce the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Adults and Pediatric Patients
- Upper Respiratory Tract Infections of the Ear, Nose, and Throat: Amoxicillin for oral suspension is indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase-negative) isolates of Streptococcus species. (α- and β-hemolytic isolates only), Streptococcus pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., or Haemophilus influenzae.
- Infections of the Genitourinary Tract: Amoxicillin for oral suspension is indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase-negative) isolates of Escherichia coli, Proteus mirabilis, or Enterococcus faecalis.
- Infections of the Skin and Skin Structure: Amoxicillin for oral suspension is indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase-negative) isolates of Streptococcus spp. (α- and β-hemolytic isolates only), Staphylococcus spp., or E. coli.
- Infections of the Lower Respiratory Tract: Amoxicillin for oral suspension is indicated in the treatment of infections due to susceptible (ONLY β-lactamase-negative) isolates of Streptococcus spp. (α- and β-hemolytic isolates only), S. pneumoniae, Staphylococcus spp., or H. influenzae.
Adult Patients Only
- Helicobacter pylori Infection and Duodenal Ulcer Disease:
Triple therapy for Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) with clarithromycin and lansoprazole:
Amoxicillin, in combination with clarithromycin plus lansoprazole as triple therapy, is indicated for the treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (active or 1-year history of a duodenal ulcer) to eradicate H. pylori. Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Dual therapy for H. pylori with lansoprazole:
Amoxicillin, in combination with lansoprazole delayed-release capsules as dual therapy, is indicated for the treatment of patients with H. pylori infection and duodenal ulcer disease (active or 1-year history of a duodenal ulcer) who are either allergic or intolerant to clarithromycin or in whom resistance to clarithromycin is known or suspected. (See the clarithromycin package insert, MICROBIOLOGY.) Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Usage
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of amoxicillin and other antibacterial drugs, amoxicillin should be used only to treat infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Administration Instructions
To minimize the potential for gastrointestinal intolerance, amoxicillin should be taken at the start of a meal.
2.2 Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months (12 weeks) and Older
- Treatment should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours beyond the time that the patient becomes asymptomatic, or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained.
- It is recommended that there be at least 10 days’ treatment for any infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes to prevent the occurrence of acute rheumatic fever.
- In some infections, therapy may be required for several weeks. It may be necessary to continue clinical and/or bacteriological follow-up for several months after cessation of therapy.
Table 1. Dosage Recommendations for Adult and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months (12 weeks) and Older
Infection Severitya Recommended Dosage for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Greater than 40 kg Recommended Dosage for Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Less than 40 kg Ear/Nose/Throat
Skin/Skin Structure
Genitourinary Tract
Mild/Moderate 500 mg every 12 hours or
250 mg every 8 hours
25 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours
or
20 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
Severe 875 mg every 12 hours or
500 mg every 8 hours
45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours
or
40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
Lower Respiratory
Tract
Mild/Moderate or Severe 875 mg every 12 hours or
500 mg every 8 hours45 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 12 hours
or
40 mg/kg/day in divided doses every 8 hours
a Dosage for infections caused by bacteria that are intermediate in their susceptibility to amoxicillin should follow the recommendations for severe infections.
2.3 Dosage in Pediatric Patients Aged Less than 12 Weeks (3 months)
- It is recommended that there be at least 10 days’ treatment for any infection caused by Streptococcus pyogenes to prevent the occurrence of acute rheumatic fever.
- Due to incompletely developed renal function affecting elimination of amoxicillin in this age group, the recommended upper dose of amoxicillin is 30 mg/kg/day divided every 12 hours. There are currently no dosing recommendations for pediatric patients with impaired renal function.
- Treatment should be continued for a minimum of 48 to 72 hours beyond the time that the patient becomes asymptomatic, or evidence of bacterial eradication has been obtained.
2.4 Dosage for H. pylori Infection in Adults
Triple therapy: The recommended adult oral dose is 1 gram amoxicillin, 500 mg clarithromycin, and 30 mg lansoprazole, all given twice daily (every 12 hours) for 14 days.
Dual therapy: The recommended adult oral dose is 1 gram amoxicillin and 30 mg lansoprazole, each given three times daily (every 8 hours) for 14 days.
Please refer to clarithromycin and lansoprazole full prescribing information.
2.5 Dosage in Renal Impairment for Adults and Pediatric Patients Aged 3 Months and Older and Weight Greater than 40 kg
- Patients with impaired renal function do not generally require a reduction in dose unless the impairment is severe. Renal impairment patients with a glomerular filtration rate of less than 30 mL/min should NOT receive the 875 mg dose. See dosage regimens in patients with severe renal impairment provided in Table 2.
Table 2. Dosing in Patients with Severe Renal Impairment
Patients with Renal Impairment Dosage Regimen GFR 10 to 30 mL/min 500 mg or 250 mg every 12 hours, depending on the severity of the infection GFR less than 10 mL/min 500 mg or 250 mg every 24 hours, depending on the severity of the infection Hemodialysis 500 mg or 250 mg every 24 hours, depending on severity of the infection
Administer an additional dose both during and at the end of dialysis
2.6 Directions for Mixing Oral Suspension
Prepare a suspension at time of dispensing as follows: Tap bottle until all powder flows freely. Measure the total amount of water (see Table 3). Add approximately 1/3 of the water to powder. Replace cap and shake vigorously to wet powder. Add remaining water. Replace cap and shake vigorously.
Table 3. Amount of Water for Mixing for Oral Suspension
Strength Bottle Size Total Amount of Water Required for Reconstitution For Oral Suspension 125 mg/5 mL 80 mL 66 mL 100 mL 83 mL 150 mL 125 mL For Oral Suspension 250 mg/5 mL 80 mL 59 mL 100 mL 73 mL 150 mL 110 mL After reconstitution, the required amount of suspension should be placed directly on the child’s tongue for swallowing. Alternate means of administration are to add the required amount of suspension to formula, milk, fruit juice, water, ginger ale, or cold drinks. These preparations should then be taken immediately.
SHAKE ORAL SUSPENSION WELL BEFORE USING. Keep bottle tightly closed. Any unused portion of the reconstituted suspension must be discarded after 14 days. Refrigeration is preferable, but not required.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Anaphylactic Reactions
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions have been reported in patients on penicillin therapy including amoxicillin. Although anaphylaxis is more frequent following parenteral therapy, it has occurred in patients on oral penicillins. These reactions are more likely to occur in individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity and/or a history of sensitivity to multiple allergens.
There have been reports of individuals with a history of penicillin hypersensitivity who have experienced severe reactions when treated with cephalosporins. Before initiating therapy with amoxicillin, careful inquiry should be made regarding previous hypersensitivity reactions to penicillins, cephalosporins, or other allergens. If an allergic reaction occurs, amoxicillin should be discontinued, and appropriate therapy instituted.
5.2 Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions
Amoxicillin may cause severe cutaneous adverse reactions (SCAR), such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome (SJS), toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN), drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), and acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP). If patients develop skin rash they should be monitored closely, and amoxicillin discontinued if lesions progress.
5.3 Drug-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (DIES)
Drug-induced enterocolitis syndrome (DIES) has been reported with amoxicillin use [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)], with most cases occurring in pediatric patients ≤18 years of age. DIES is a non-IgE mediated hypersensitivity reaction characterized by protracted vomiting occurring 1 to 4 hours after drug ingestion in the absence of skin or respiratory symptoms. DIES may be associated with pallor, lethargy, hypotension, shock, diarrhea within 24 hours after ingesting amoxicillin, and leukocytosis with neutrophilia. If DIES occurs, discontinue amoxicillin for oral suspension and institute appropriate therapy.
5.4 Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD)
Clostridioides difficile-associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including amoxicillin, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin-producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibacterial use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over 2 months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibacterial use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibacterial treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
5.5 Development of Drug-Resistant Bacteria
Prescribing amoxicillin in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Anaphylactic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Drug-Induced Enterocolitis Syndrome (DIES) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Clostridioides difficile-Associated Diarrhea (CDAD) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The most common adverse reactions (greater than 1%) observed in clinical trials of amoxicillin capsules, tablets or oral suspension were diarrhea, rash, vomiting, and nausea.
Triple therapy: The most frequently reported adverse events for patients who received triple therapy (amoxicillin/clarithromycin/ lansoprazole) were diarrhea (7%), headache (6%), and taste perversion (5%).
Dual therapy: The most frequently reported adverse events for patients who received double therapy amoxicillin/lansoprazole were diarrhea (8%) and headache (7%). For more information on adverse reactions with clarithromycin or lansoprazole, refer to the Adverse Reactions section of their package inserts.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
In addition to adverse events reported from clinical trials, the following events have been identified during postmarketing use of penicillins. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made.
These events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of their seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to amoxicillin.
- Infections and Infestations: Mucocutaneous candidiasis.
- Gastrointestinal: Drug-induced enterocolitis syndrome (DIES), black hairy tongue, and hemorrhagic/pseudomembranous colitis.
- Immune: Hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions (including shock), angioedema, serum sickness-like reactions (urticaria or skin rash accompanied by arthritis, arthralgia, myalgia, and frequently fever), hypersensitivity vasculitis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Skin and Appendages: Rashes, pruritus, urticaria, erythema multiforme, SJS, TEN, DRESS, AGEP, exfoliative dermatitis, and linear IgA bullous dermatosis.
- Liver: A moderate rise in AST and/or ALT has been noted, but the significance of this finding is unknown. Hepatic dysfunction including cholestatic jaundice, hepatic cholestasis and acute cytolytic hepatitis have been reported.
- Renal: Crystalluria has been reported [see Overdosage (10)].
- Hemic and Lymphatic Systems: Anemia, including hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, thrombocytopenic purpura, eosinophilia, leukopenia, and agranulocytosis have been reported. These reactions are usually reversible on discontinuation of therapy and are believed to be hypersensitivity phenomena.
- Central Nervous System: Reversible hyperactivity, agitation, anxiety, insomnia, confusion, convulsions, behavioral changes, aseptic meningitis, and/or dizziness have been reported.
- Miscellaneous: Tooth discoloration (brown, yellow, or gray staining) has been reported. Most reports occurred in pediatric patients. Discoloration was reduced or eliminated with brushing or dental cleaning in most cases.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Probenecid
Probenecid decreases the renal tubular secretion of amoxicillin. Concurrent use of amoxicillin and probenecid may result in increased and prolonged blood levels of amoxicillin.
7.2 Oral Anticoagulants
Abnormal prolongation of prothrombin time (increased international normalized ratio [INR]) has been reported in patients receiving amoxicillin and oral anticoagulants.
Appropriate monitoring should be undertaken when anticoagulants are prescribed concurrently. Adjustments in the dose of oral anticoagulants may be necessary to maintain the desired level of anticoagulation.
7.3 Allopurinol
The concurrent administration of allopurinol and amoxicillin increases the incidence of rashes in patients receiving both drugs as compared to patients receiving amoxicillin alone. It is not known whether this potentiation of amoxicillin rashes is due to allopurinol or the hyperuricemia present in these patients.
7.4 Oral Contraceptives
Amoxicillin may affect the intestinal flora, leading to lower estrogen reabsorption and reduced efficacy of combined oral estrogen/progesterone contraceptives.
7.5 Other Antibacterials
Chloramphenicol, macrolides, sulfonamides, and tetracyclines may interfere with the bactericidal effects of penicillin. This has been demonstrated in vitro; however, the clinical significance of this interaction is not well documented.
7.6 Effects on Laboratory Tests
High urine concentrations of ampicillin may result in false-positive reactions when testing for the presence of glucose in urine using CLINITEST®, Benedict’s Solution, or Fehling’s Solution. Since this effect may also occur with amoxicillin, it is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions (such as CLINISTIX®) be used.
Following administration of ampicillin or amoxicillin to pregnant women, a transient decrease in plasma concentration of total conjugated estriol, estriol-glucuronide, conjugated estrone, and estradiol has been noted.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects: Reproduction studies have been performed in mice and rats at doses up to 2000 mg/kg (3 and 6 times the 3 g human dose, based on body surface area). There was no evidence of harm to the fetus due to amoxicillin. There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, amoxicillin should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
8.2 Labor and Delivery
Oral ampicillin is poorly absorbed during labor. It is not known whether use of amoxicillin in humans during labor or delivery has immediate or delayed adverse effects on the fetus, prolongs the duration of labor, or increases the likelihood of the necessity for an obstetrical intervention.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
Penicillins have been shown to be excreted in human milk. Amoxicillin use by nursing mothers may lead to sensitization of infants. Caution should be exercised when amoxicillin is administered to a nursing woman.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of amoxicillin for the treatment of upper respiratory tract infections, and infections of the genitourinary tract, skin and skin structure and lower respiratory tract have been established in pediatric patients.
The safety and effectiveness of amoxicillin for the treatment of H. Pylori infection have not been established in pediatric patients.
Because of incompletely developed renal function in neonates and young infants, the elimination of amoxicillin may be delayed. Dosing of amoxicillin should be modified in pediatric patients 12 weeks or younger (3 months or younger) [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
An analysis of clinical studies of amoxicillin was conducted to determine whether subjects aged 65 and over respond differently from younger subjects. These analyses have not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but a greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
8.6 Dosing in Renal Impairment
Amoxicillin is primarily eliminated by the kidney and dosage adjustment is usually required in patients with severe renal impairment (GFR less than 30 mL/min). See Dosing in Renal Impairment (2.5) for specific recommendations in patients with renal impairment.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
In case of overdosage, discontinue amoxicillin, treat symptomatically, and institute supportive measures as required. A prospective study of 51 pediatric patients at a poison-control center suggested that overdosages of less than 250 mg/kg of amoxicillin are not associated with significant clinical symptoms.
Interstitial nephritis resulting in oliguric renal failure has been reported in a small number of patients after overdosage with amoxicillin1.
Crystalluria, in some cases leading to renal failure, has also been reported after amoxicillin overdosage in adult and pediatric patients. In case of overdosage, adequate fluid intake and diuresis should be maintained to reduce the risk of amoxicillin crystalluria.
Renal impairment appears to be reversible with cessation of drug administration. High blood levels may occur more readily in patients with impaired renal function because of decreased renal clearance of amoxicillin. Amoxicillin may be removed from circulation by hemodialysis.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Amoxicillin, USP is a semisynthetic antibacterial (amoxicillin), an analog of ampicillin, with a broad spectrum of bactericidal activity against many Gram-positive and Gram-negative microorganisms. Chemically, it is (2S,5R,6R)-6-[(R)-(-)-2-amino-2-(p-hydroxyphenyl)acetamido]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid trihydrate. It may be represented structurally as:
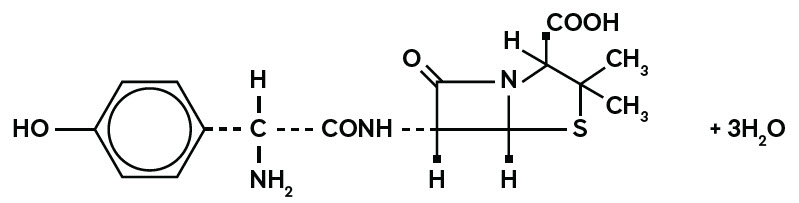
The amoxicillin, USP molecular formula is C16H19N3O5S3H2O, and the molecular weight is 419.45.
Amoxicillin for Oral Suspension, USP: Each 5 mL of reconstituted suspension contains 125 mg, 250 mg amoxicillin as the trihydrate. Each 5 mL of the 125 mg, 250 mg reconstituted suspension contains 0.1898 mEq (4.3635 mg) of sodium.
Inactive ingredients: colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, sodium benzoate, sucrose, trisodium citrate dihydrate, tutti frutti flavor and xanthan gum.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption: Amoxicillin is stable in the presence of gastric acid and is rapidly absorbed after oral administration. The effect of food on the absorption of amoxicillin from the tablets and suspension of amoxicillin has been partially investigated; 400 mg and 875 mg formulations have been studied only when administered at the start of a light meal.
Orally administered doses of 250 mg and 500 mg amoxicillin capsules result in average peak blood levels 1 to 2 hours after administration in the range of 3.5 mcg/mL to 5.0 mcg/mL and 5.5 mcg/mL to 7.5 mcg/mL, respectively.
Mean amoxicillin pharmacokinetic parameters from an open, two-part, single-dose crossover bioequivalence study in 27 adults comparing 875 mg of amoxicillin with 875 mg of amoxicillin/clavulanate potassium showed that the 875 mg tablet of amoxicillin produces an AUC0-∞ of 35.4 ± 8.1 mcghr/mL and a Cmax of 13.8 ± 4.1 mcg/mL. Dosing was at the start of a light meal following an overnight fast.
Orally administered doses of amoxicillin suspension, 125 mg/5 mL and 250 mg/5 mL, result in average peak blood levels 1 to 2 hours after administration in the range of 1.5 mcg/mL to 3.0 mcg/mL and 3.5 mcg/mL to 5.0 mcg/mL, respectively.
Oral administration of single doses of 400 mg chewable tablets and 400 mg/5 mL suspension of amoxicillin to 24 adult volunteers yielded comparable pharmacokinetic data:
Table 4: Mean Pharmacokinetic Parameters of Amoxicillin (400 mg chewable tablets and 400 mg/5 mL suspension) in Healthy Adults
Dose* AUC0-∞ (mcghr/mL) Cmax (mcg/mL)† Amoxicillin Amoxicillin (±S.D.) Amoxicillin (±S.D.) 400 mg (5 mL of suspension) 17.1 (3.1) 5.92 (1.62) 400 mg (1 chewable tablet) 17.9 (2.4) 5.18 (1.64) * Administered at the start of a light meal.
† Mean values of 24 normal volunteers. Peak concentrations occurred approximately 1 hour after the dose.Distribution: Amoxicillin diffuses readily into most body tissues and fluids, with the exception of brain and spinal fluid, except when meninges are inflamed. In blood serum, amoxicillin is approximately 20% protein-bound. Following a 1-gram dose, and utilizing a special skin window technique to determine levels of the antibiotic, it was noted that therapeutic levels were found in the interstitial fluid.
Metabolism and Excretion: The half-life of amoxicillin is 61.3 minutes. Approximately 60% of an orally administered dose of amoxicillin is excreted in the urine within 6 to 8 hours. Detectable serum levels are observed up to 8 hours after an orally administered dose of amoxicillin. Since most of the amoxicillin is excreted unchanged in the urine, its excretion can be delayed by concurrent administration of probenecid [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
12.4 Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Amoxicillin is similar to penicillin in its bactericidal action against susceptible bacteria during the stage of active multiplication. It acts through the inhibition of cell wall biosynthesis that leads to the death of the bacteria.
Resistance
Resistance to amoxicillin is mediated primarily through enzymes called beta-lactamases that cleave the beta-lactam ring of amoxicillin, rendering it inactive.
Antimicrobial Activity
Amoxicillin has been shown to be active against most isolates of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections [see Indications and Usage (1)].
Gram-Positive Bacteria Gram-Negative Bacteria Enterococcus faecalis
Staphylococcus spp.
Streptococcus pneumoniae
Streptococcus spp. (alpha and beta-hemolytic)
Escherichia coli
Haemophilus influenzae
Helicobacter pylori
Proteus mirabilisSusceptibility Testing:
For specific information regarding susceptibility test interpretive criteria and associated test methods and quality control standards recognized by FDA for this drug, please see: https://www.fda.gov/STIC. -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Long-term studies in animals have not been performed to evaluate carcinogenic potential. Studies to detect mutagenic potential of amoxicillin alone have not been conducted; however, the following information is available from tests on a 4:1 mixture of amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was non-mutagenic in the Ames bacterial mutation assay, and the yeast gene conversion assay.
Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was weakly positive in the mouse lymphoma assay, but the trend toward increased mutation frequencies in this assay occurred at doses that were also associated with decreased cell survival. Amoxicillin and potassium clavulanate was negative in the mouse micronucleus test and in the dominant lethal assay in mice. Potassium clavulanate alone was tested in the Ames bacterial mutation assay and in the mouse micronucleus test and was negative in each of these assays. In a multi-generation reproduction study in rats, no impairment of fertility or other adverse reproductive effects were seen at doses up to 500 mg/kg (approximately 2 times the 3 g human dose based on body surface area).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 H. pylori Eradication to Reduce the Risk of Duodenal Ulcer Recurrence
Randomized, double-blind clinical studies performed in the United States in patients with H. pylori and duodenal ulcer disease (defined as an active ulcer or history of an ulcer within 1 year) evaluated the efficacy of lansoprazole in combination with amoxicillin capsules and clarithromycin tablets as triple 14-day therapy, or in combination with amoxicillin capsules as dual 14-day therapy, for the eradication of H. pylori. Based on the results of these studies, the safety and efficacy of 2 different eradication regimens were established: Triple therapy: Amoxicillin 1 gram twice daily/clarithromycin 500 mg twice daily/lansoprazole 30 mg twice daily (see Table 5). Dual therapy: Amoxicillin 1 gram three times daily/lansoprazole 30 mg three times daily (see Table 6). All treatments were for 14 days. H. pylori eradication was defined as 2 negative tests (culture and histology) at 4 to 6 weeks following the end of treatment. Triple therapy was shown to be more effective than all possible dual therapy combinations. Dual therapy was shown to be more effective than both monotherapies. Eradication of H. pylori has been shown to reduce the risk of duodenal ulcer recurrence.
Table 5. H. pylori Eradication Rates When Amoxicillin is Administered as Part of a Triple Therapy Regimen
Study Triple Therapy Triple Therapy Evaluable Analysisa
[95% Confidence Interval]
(number of patients)Intent-to-Treat Analysisb
[95% Confidence Interval]
(number of patients)
Study 1 92
[80.0 to 97.7]
(n equals 48)86
[73.3 to 93.5]
(n equals 55)
Study 2 86
[75.7 to 93.6]
(n equals 66)83
[72.0 to 90.8]
(n equals 70)
a This analysis was based on evaluable patients with confirmed duodenal ulcer (active or within 1 year) and H. pylori infection at baseline defined as at least 2 of 3 positive endoscopic tests from CLOtest®, histology, and/or culture. Patients were included in the analysis if they completed the study. Additionally, if patients dropped out of the study due to an adverse event related to the study drug, they were included in the analysis as failures of therapy.
b Patients were included in the analysis if they had documented H. pylori infection at baseline as defined above and had a confirmed duodenal ulcer (active or within 1 year). All dropouts were included as failures of therapy.
Table 6. H. pylori Eradication Rates When Amoxicillin is Administered as Part of a Dual Therapy Regimen
Study Dual Therapy Dual Therapy Evaluable Analysisa
[95% Confidence Interval]
(number of patients)
Intent-to-Treat Analysisb
[95% Confidence Interval]
(number of patients)
Study 1 77
[62.5 to 87.2]
(n equals 51)
70
[56.8 to 81.2]
(n equals 60)
Study 2 66
[51.9 to 77.5]
(n equals 58)
61
[48.5 to 72.9]
(n equals 67)
a This analysis was based on evaluable patients with confirmed duodenal ulcer (active or within 1 year) and H. pylori infection at baseline defined as at least 2 of 3 positive endoscopic tests from CLOtest®, histology, and/or culture. Patients were included in the analysis if they completed the study. Additionally, if patients dropped out of the study due to an adverse event related to the study drug, they were included in the analysis as failures of therapy.
b Patients were included in the analysis if they had documented H. pylori infection at baseline as defined above and had a confirmed duodenal ulcer (active or within 1 year). All dropouts were included as failures of therapy.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Amoxicillin for Oral Suspension, USP: Each 5 mL of reconstituted fruity-flavored suspension contains 125 mg, 250 mg amoxicillin as the trihydrate.
Amoxicillin for Oral Suspension USP, 125 mg/5mL
80 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9888-80
100 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9888-01
150 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9888-15Amoxicillin for Oral Suspension USP, 250 mg/5mL
80 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9889-80
100 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9889-01
150 mL Bottle NDC: 0143-9889-15Store dry powder at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Shake well before using. Refrigeration is preferable but not required.
Discard suspension after 14 days. Keep container tightly closed.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Administration Instructions
Advise patients that amoxicillin for oral suspension may be taken every 8 hours or every 12 hours, depending on the dose prescribed.
Allergic Reactions
Counsel patients that amoxicillin contains a penicillin class drug product that can cause allergic reactions in some individuals.
Severe Cutaneous Adverse Reactions (SCAR)
Advise patients about the signs and symptoms of serious skin manifestations. Instruct patients to stop taking amoxicillin immediately and promptly report the first signs or symptoms of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Diarrhea
Counsel patients that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibacterial drugs which usually ends when the antibacterial drug is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibacterial drugs, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as 2 or more months after having taken their last dose of the antibacterial drug. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Antibacterial Resistance
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs, including amoxicillin, should only be used to treat or prevent bacterial infections. Antibacterial drugs do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When amoxicillin tablets, amoxicillin for oral suspension, amoxicillin tablets (chewable), and amoxicillin capsules are prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may: (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment, and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by amoxicillin or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Storage and Special Handling Instructions
It is preferable to refrigerate amoxicillin suspensions, but not required. Shake oral suspensions well before each use. Keep bottle tightly closed. When dosing a child with the suspension (liquid), use a calibrated oral syringe. Be sure to rinse the calibrated oral syringe after each use. Bottles of suspension of amoxicillin may contain more liquid than required. Follow your doctor’s instructions about the amount to use and the days of treatment your child requires. Discard any unused portion of the suspension after 14 days.
Brands listed are the trademarks of their respective owners.
Distributed by:
Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc.
Berkeley Heights, NJ 07922Manufactured by:
Hikma Pharmaceuticals
P.O. Box 182400
Amman 11118 − Jordan2INAMOXU12N
Revised February 2024
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
AMOXICILLIN
amoxicillin powder, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0143-9888 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AMOXICILLIN (UNII: 804826J2HU) (AMOXICILLIN ANHYDROUS - UNII:9EM05410Q9) AMOXICILLIN ANHYDROUS 125 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor TUTTI FRUTTI Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0143-9888-80 80 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 2 NDC: 0143-9888-01 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 3 NDC: 0143-9888-15 150 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA065322 06/19/2006 AMOXICILLIN
amoxicillin powder, for suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0143-9889 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength AMOXICILLIN (UNII: 804826J2HU) (AMOXICILLIN ANHYDROUS - UNII:9EM05410Q9) AMOXICILLIN ANHYDROUS 250 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) XANTHAN GUM (UNII: TTV12P4NEE) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor TUTTI FRUTTI Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0143-9889-80 80 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 2 NDC: 0143-9889-01 100 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 3 NDC: 0143-9889-15 150 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/19/2006 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA065322 06/19/2006 Labeler - Hikma Pharmaceuticals USA Inc. (001230762)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.

