SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM suspension
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Physicians Total Care, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
-
DESCRIPTION
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is a synthetic antibacterial combination product containing 200 mg sulfamethoxazole and 40 mg trimethoprim per 5 mL for oral administration.
Sulfamethoxazole is N1-(5-methyl-3-isoxazolyl)sulfanilamide; the molecular formula is C10H11N3O3S. It is an almost white, odorless, tasteless compound with a molecular weight of 253.28 and the following structural formula is:
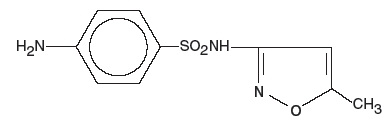
Trimethoprim is 2,4-diamino-5-(3,4,5- trimethoxybenzyl) pyrimidine; the molecular formula is C14H18N4O3. It is a white to light yellow, odorless, bitter compound with a molecular weight of 290.3 and. It has the following structural formula is:
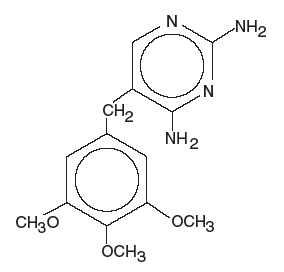
Inactive ingredients: alcohol 0.26%, methylparaben 0.1% and sodium benzoate 0.1% (added as preservatives), carboxymethylcellulose sodium, citric acid (anhydrous), glycerin, microcrystalline cellulose, polysorbate 80, purified water, saccharin sodium, and sorbitol. The light purple, grape flavored suspension contains the following additional inactive ingredients: FD&C Red No. 40, FD&C Blue No. 1 and natural and artificial grape flavor. The pink, cherry flavored suspension contains the following additional inactive ingredients: FD&C Red No. 40, FD&C Yellow No. 6 and artificial cherry flavor.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is rapidly absorbed following oral administration. Both sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim exist in the blood as unbound, protein-bound, and metabolized forms; sulfamethoxazole also exists as the conjugated form. The metabolism of sulfamethoxazole occurs predominantly by N4-acetylation, although the glucuronide conjugate has been identified. The principal metabolites of trimethoprim are the 1- and 3-oxides and the 3’- and 4’-hydroxy derivatives. The free forms of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are considered to be the therapeutically active forms. Approximately 70% of sulfamethoxazole and 44% of trimethoprim are bound to plasma proteins. The presence of 10 mg percent sulfamethoxazole in plasma decreases the protein binding of trimethoprim by an insignificant degree; trimethoprim does not influence the protein binding of sulfamethoxazole.
Peak blood levels for the individual components occur 1 to 4 hours after oral administration. The mean serum half-lives of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are 10 and 8 to 10 hours, respectively. However, patients with severely impaired renal function exhibit an increase in the half-lives of both components, requiring dosage regimen adjustment (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION section). Detectable amounts of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are present in the blood 24 hours after drug administration. During administration of 800 mg sulfamethoxazole and 160 mg trimethoprim b.i.d., the mean steady-state plasma concentration of trimethoprim was 1.72 μg/mL. The steady-state mean plasma levels of free and total sulfamethoxazole were 57.4 μg/mL and 68.0 μg/mL, respectively. These steady-state levels were achieved after three days of drug administration.1 Excretion of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is primarily by the kidneys through both glomerular filtration and tubular secretion. Urine concentrations of both sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are considerably higher than are the concentrations in the blood. The average percentage of the dose recovered in urine from 0 to 72 hours after a single oral dose of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is 84.5% for total sulfonamide and 66.8% for free trimethoprim. Thirty percent of the total sulfonamide is excreted as free sulfamethoxazole, with the remaining as N4-acetylated metabolite.2 When administered together as sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, neither sulfamethoxazole nor trimethoprim affects the urinary excretion pattern of the other.
Both sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim distribute to sputum, vaginal fluid and middle ear fluid; trimethoprim also distributes to bronchial secretions, and both pass the placental barrier and are excreted in human milk.
Geriatric Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of sulfamethoxazole 800 mg and trimethoprim 160 mg were studied in 6 geriatric subjects (mean age: 78.6 years) and 6 young healthy subjects (mean age: 29.3 years) using a non-U.S. approved formulation. Pharmacokinetic values for sulfamethoxazole in geriatric subjects were similar to those observed in young adult subjects. The mean renal clearance of trimethoprim was significantly lowered in geriatric subjects compared with young adult subjects (19 mL/h/kg vs. 55 mL/h/kg). However, after normalizing by body weight, the apparent total body clearance of trimethoprim was an average 19% lower in geriatric subjects compared with young adult subjects.3
Microbiology
Sulfamethoxazole inhibits bacterial synthesis of dihydrofolic acid by competing with para-aminobenzoic acid (PABA). Trimethoprim blocks the production of tetrahydrofolic acid from dihydrofolic acid by binding to and reversibly inhibiting the required enzyme, dihydrofolate reductase. Thus, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim blocks two consecutive steps in the biosynthesis of nucleic acids and proteins essential to many bacteria.
In vitro studies have shown that bacterial resistance develops more slowly with both sulfamethoxazole trimethoprim in combination than with either sulfamethoxazole or trimethoprim alone.
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim have been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section.
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms:
Escherichia coli (including susceptible enterotoxigenic strains implicated in traveler's diarrhea)
Klebsiella species
Enterobacter species
Haemophilus influenzae
Morganella morganii
Proteus mirabilis
Proteus vulgaris
Shigella flexneri
Shigella sonnei
Susceptibility Testing Methods:
Dilution Techniques:
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method4 (broth or agar) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For testing Enterobacteriaceae:
MIC (μg/mL) Interpretation ≤ 2/38 Susceptible (S) ≥ 4/76 Resistant (R) When testing either Haemophilus influenzaea or Streptococcus pneumoniaeb:
MIC (μg/mL) Interpretationb ≤ 0.5/9.5 Susceptible (S) 1/19 – 2/38 Intermediate (I) ≥ 4/76 Resistant (R) a.These interpretative standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Haemophilus influenzae using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).4
b.These interpretative standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests using cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with 2% to 5% lysed horse blood.4
A report of "Susceptible" indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable. A report of "Intermediate" indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of "Resistant" indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable; other therapy should be selected.
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. Standard sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim powder should provide the following range of values:
Microorganism MIC (μg/mL) Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 ≤ 0.5/9.5 Haemophilus influenzaec ATCC 49247 0.03/0.59 – 0.25/4.75 Streptococcus pneumoniaed ATCC 49619 0.12/2.4 – 1/19 c.This quality control range is applicable only to Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49247 tested by broth microdilution procedure using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).4
d.This quality control range is applicable to tests performed by the broth microdilution method only using cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with 2% to 5% lysed horse blood.4
Diffusion Techniques:
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. One such standardized procedure5 requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 1.25/23.75 μg of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 1.25/23.75 mcg of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For testing either Enterobacteriaceae or Haemophilus influenzaee:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥ 16 Susceptible (S) 11 – 15 Intermediate (I) ≤ 10 Resistant (R) e.These zone diameter standards are applicable only for disk diffusion testing with Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).5
When testing Streptococcus pneumoniaef:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥ 19 Susceptible (S) 16 – 18 Intermediate (I) ≤ 15 Resistant (R) f. These zone diameter interpretative standards are applicable only to tests performed using Mueller-Hinton agar supplemented with 5% defibrinated sheep blood when incubated in 5% CO2.5
Interpretation should be as stated above for results using dilution techniques. Interpretation involves correlation of the diameter obtained in the disk test with the MIC for sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
Quality Control
As with standardized dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms that are used to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 1.25/23.75 μg sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim disk* should provide the following zone diameters in these laboratory test quality control strains:
Microorganism Zone Diameter Range (mm) Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 23–29 Haemophilus influenzaeg ATCC 49247 24–32 Streptococcus pneumoniaeh ATCC 49619 20–28 * Mueller-Hinton agar should be checked for excessive levels of thymidine or thymine. To determine whether Mueller-Hinton medium has sufficiently low levels of thymidine and thymine, an Enterococcus faecalis (ATCC 29212 or ATCC 33186) may be tested with sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim disks. A zone of inhibition ≥20 mm that is essentially free of fine colonies indicates a sufficiently low level of thymidine and thymine.
g.This quality control range is applicable only to Haemophilus influenzae ATCC 49247 tested by a disk diffusion procedure using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).5
h.This quality control range is applicable only to tests performed by disk diffusion using Mueller-Hinton agar supplemented with 5% defibrinated sheep blood when incubated in 5% CO2.5
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension and other antibacterial drugs, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to empiric selection of therapy.
Urinary Tract Infections
For the treatment of urinary tract infections due to susceptible strains of the following organisms: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella species, Enterobacter species, Morganella morganii, Proteus mirabilis and Proteus vulgaris. It is recommended that initial episodes of uncomplicated urinary tract infections be treated with a single effective antibacterial agent rather than the combination.
Acute Otitis Media
For the treatment of acute otitis media in pediatric patients due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when in the judgment of the physician sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim offers some advantage over the use of other antimicrobial agents. To date, there are limited data on the safety of repeated use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in pediatric patients under two years of age. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is not indicated for prophylactic or prolonged administration in otitis media at any age.
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults
For the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis due to susceptible strains of Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae when in the judgment of the physician sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim offers some advantage over the use of a single antimicrobial agent.
Shigellosis
For the treatment of enteritis caused by susceptible strains of Shigella flexneri and Shigella sonnei when antibacterial therapy is indicated.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to trimethoprim or sulfonamides, in patients with a history of drug-induced immune thrombocytopenia with use of trimethoprim and/or sulfonamides, and in patients with documented megaloblastic anemia due to folate deficiency. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is also contraindicated in pregnant patients and nursing mothers, because sulfonamides pass the placenta and are excreted in the milk and may cause kernicterus. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension is contraindicated in pediatric patients less than 2 months of age. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is also contraindicated in patients with marked hepatic damage or with severe renal insufficiency when renal function status cannot be monitored.
-
WARNINGS
FATALITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF SULFONAMIDES, ALTHOUGH RARE, HAVE OCCURRED DUE TO SEVERE REACTIONS, INCLUDING STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, FULMINANT HEPATIC NECROSIS, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, APLASTIC ANEMIA AND OTHER BLOOD DYSCRASIAS.
SULFONAMIDES, INCLUDING SULFONAMIDE-CONTAINING PRODUCTS SUCH AS SULFAMETHOXAZOLE/TRIMETHOPRIM, SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED AT THE FIRST APPEARANCE OF SKIN RASH OR ANY SIGN OF ADVERSE REACTION. In rare instances, a skin rash may be followed by a more severe reaction, such as Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, hepatic necrosis and serious blood disorders (see PRECAUTIONS). Clinical signs, such as rash, sore throat, fever, arthralgia, pallor, purpura or jaundice may be early indications of serious reactions.
Cough, shortness of breath, and pulmonary infiltrates are hypersensitivity reactions of the respiratory tract that have been reported in association with sulfonamide treatment.
Thrombocytopenia
Sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim-induced thrombocytopenia may be an immune-mediated disorder. Severe cases of thrombocytopenia that are fatal or life threatening have been reported. Thrombocytopenia usually resolves within a week upon discontinuation of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim.
The sulfonamides should not be used for the treatment of group A β-hemolytic streptococcal infections. In an established infection, they will not eradicate the streptococcus and, therefore, will not prevent sequelae such as rheumatic fever.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antiobiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Prescribing sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension should be given with caution to patients with impaired renal or hepatic function, to those with possible folate deficiency (e.g., the elderly, chronic alcoholics, patients receiving anticonvulsant therapy, patients with malabsorption syndrome, and patients in malnutrition states) and to those with severe allergies or bronchial asthma. In glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficient individuals, hemolysis may occur. This reaction is frequently dose-related (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGYand DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Use in the Elderly
Cases of hypoglycemia in non-diabetic patients treated with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are seen rarely, usually occurring after a few days of therapy. Patients with renal dysfunction, liver disease, malnutrition or those receiving high doses of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim are particularly at risk.
Hematological changes indicative of folic acid deficiency may occur in elderly patients or in patients with preexisting folic acid deficiency or kidney failure. These effects are reversible by folinic acid therapy.
Trimethoprim has been noted to impair phenylalanine metabolism, but this is of no significance in phenylketonuric patients on appropriate dietary restriction.
As with all drugs containing sulfonamides, caution is advisable in patients with porphyria or thyroid dysfunction.
Use in the Treatment of and Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia in Patients with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS)
AIDS patients may not tolerate or respond to sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in the same manner as non-AIDS patients. The incidence of side effects, particularly rash, fever, leukopenia and elevated aminotransferase (transaminase) values, with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim therapy in AIDS patients who are being treated for Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia has been reported to be greatly increased compared with the incidence normally associated with the use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in non-AIDS patients. The incidence of hyperkalemia appears to be increased in AIDS patients receiving sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Adverse effects are generally less severe in patients receiving sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim for prophylaxis. A history of mild intolerance to sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension in AIDS patients does not appear to predict intolerance of subsequent secondary prophylaxis.6 However, if a patient develops skin rash or any sign of adverse reaction, therapy with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim should be reevaluated (see WARNINGS).
High dosage of trimethoprim, as used in patients with Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia, induces a progressive but reversible increase of serum potassium concentrations in a substantial number of patients. Even treatment with recommended doses may cause hyperkalemia when trimethoprim is administered to patients with underlying disorders of potassium metabolism, with renal insufficiency, or if drugs known to induce hyperkalemia are given concomitantly. Close monitoring of serum potassium is warranted in these patients.
During treatment, adequate fluid intake and urinary output should be ensured to prevent crystalluria. Patients who are "slow acetylators" may be more prone to idiosyncratic reactions to sulfonamides.
Information for patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension or other antibaceterial drugs in the future.
Patients should be instructed to maintain an adequate fluid intake in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with and without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Laboratory tests
Complete blood counts should be done frequently in patients receiving sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim; if a significant reduction in the count of any formed blood element is noted, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim should be discontinued. Urinalyses with careful microscopic examination and renal function tests should be performed during therapy, particularly for those patients with impaired renal function.
Drug Interactions
In elderly patients concurrently receiving certain diuretics, primarily thiazides, an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia with purpura has been reported.
It has been reported that sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may prolong the prothrombin time in patients who are receiving the anticoagulant warfarin. This interaction should be kept in mind when sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is given to patients already on anticoagulant therapy, and the coagulation time should be reassessed.
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may inhibit the hepatic metabolism of phenytoin. Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, given at a common clinical dosage, increased the phenytoin half-life by 39% and decreased the phenytoin metabolic clearance rate by 27%. When administering these drugs concurrently, one should be alert for possible excessive phenytoin effect.
Sulfonamides can also displace methotrexate from plasma protein binding sites and can compete with the renal transport of methotrexate, thus increasing free methotrexate concentrations.
There have been reports of marked but reversible nephrotoxicity with coadministration of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim and cyclosporine in renal transplant recipients.
Increased digoxin blood levels can occur with concomitant sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim therapy, especially in elderly patients. Serum digoxin levels should be monitored. Increased sulfamethoxazole blood levels may occur in patients who are also receiving indomethacin.
Occasional reports suggest that patients receiving pyrimethamine as malaria prophylaxis in doses exceeding 25 mg weekly may develop megaloblastic anemia if sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is prescribed.
The efficacy of tricyclic antidepressants can decrease when coadministered with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
Like other sulfonamide-containing drugs, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim potentiates the effect of oral hypoglycemics.
In the literature, a single case of toxic delirium has been reported after concomitant intake of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and amantadine.
In the literature, three cases of hyperkalemia in elderly patients have been reported after concomitant intake of sulfamethoxazole/trimethoprim and an angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor.7,8
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, specifically the trimethoprim component, can interfere with a serum methotrexate assay as determined by the competitive binding protein technique (CBPA) when a bacterial dihydrofolate reductase is used as the binding protein. No interference occurs, however, if methotrexate is measured by a radioimmunoassay (RIA).
The presence of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may also interfere with the Jaffé alkaline picrate reaction assay for creatinine, resulting in overestimations of about 10% in the range of normal values.
Carcinogenesis, mutagenesis, impairment of fertility
Carcinogenesis
Long-term studies in animals to evaluate carcinogenic potential have not been conducted with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
Mutagenesis
Bacterial mutagenic studies have not been performed with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in combination. Trimethoprim was demonstrated to be nonmutagenic in the Ames assay. No chromosomal damage was observed in human leukocytes cultured in vitro with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim alone or in combination; the concentrations used exceeded blood levels of these compounds following therapy with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. Observations of leukocytes obtained from patients treated with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim revealed no chromosomal abnormalities.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic effects
Pregnancy Category C. In rats, oral doses of 533 mg/kg or 200 mg/kg produced teratologic effects manifested mainly as cleft palates.
The highest dose which did not cause cleft palates in rats was 512 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole or 192 mg/kg trimethoprim when administered separately. In two studies in rats, no teratology was observed when 512 mg/kg of sulfamethoxazole was used in combination with 128 mg/kg of trimethoprim. In one study, however, cleft palates were observed in one litter out of 9 when 355 mg/kg of sulfamethoxazole was used in combination with 88 mg/kg of trimethoprim.
In some rabbit studies, an overall increase in fetal loss (dead and resorbed and malformed conceptuses) was associated with doses of trimethoprim 6 times the human therapeutic dose.
While there are no large, well-controlled studies on the use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim in pregnant women, Brumfitt and Pursell,9 in a retrospective study, reported the outcome of 186 pregnancies during which the mother received either placebo or sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. The incidence of congenital abnormalities was 4.5% (3 of 66) in those who received placebo and 3.3% (4 of 120) in those receiving sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim. There were no abnormalities in the 10 children whose mothers received the drug during the first trimester. In a separate survey, Brumfitt and Pursell also found no congenital abnormalities in 35 children whose mothers had received oral sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim at the time of conception or shortly thereafter.
Because sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may interfere with folic acid metabolism, sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Pediatric use
Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim is not recommended for infants younger than 2 months of age (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE and CONTRAINDICATIONS section).
Geriatric use
Clinical studies of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
There may be an increased risk of severe adverse reactions in elderly patients, particularly when complicating conditions exist, e.g., impaired kidney and/or liver function, possible folate deficiency, or concomitant use of other drugs. Severe skin reactions, generalized bone marrow suppression (see WARNINGSand ADVERSE REACTIONS sections), a specific decrease in platelets (with or without purpura), and hyperkalemia are the most frequently reported severe adverse reactions in elderly patients. In those concurrently receiving certain diuretics, primarily thiazides, an increased incidence of thrombocytopenia with purpura has been reported. Increased digoxin blood levels can occur with concomitant sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim therapy, especially in elderly patients. Serum digoxin levels should be monitored. Hematological changes indicative of folic acid deficiency may occur in elderly patients. These effects are reversible by folinic acid therapy. Appropriate dosage adjustments should be made for patients with impaired kidney function and duration of use should be as short as possible to minimize risks of undesired reactions (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION sections). The trimethoprim component of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim may cause hyperkalemia when administered to patients with underlying disorders of potassium metabolism, with renal insufficiency or when given concomitantly with drugs known to induce hyperkalemia, such as angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors. Close monitoring of serum potassium is warranted in these patients. Discontinuation of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim treatment is recommended to help lower potassium serum levels.
Pharmacokinetics parameters for sulfamethoxazole were similar for geriatric subjects and younger adult subjects. The mean maximum serum trimethoprim concentration was higher and mean renal clearance of trimethoprim was lower in geriatric subjects compared with younger subjects (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Geriatric Pharmacokinetics).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal disturbances (nausea, vomiting, anorexia) and allergic skin reactions (such as rash and urticaria). FATALITIES ASSOCIATED WITH THE ADMINISTRATION OF SULFONAMIDES, ALTHOUGH RARE, HAVE OCCURRED DUE TO SEVERE REACTIONS, INCLUDING STEVENS-JOHNSON SYNDROME, TOXIC EPIDERMAL NECROLYSIS, FULMINANT HEPATIC NECROSIS, AGRANULOCYTOSIS, APLASTIC ANEMIA AND OTHER BLOOD DYSCRASIAS (SEE WARNINGS SECTION).
Hematologic
Agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, neutropenia, hemolytic anemia, megaloblastic anemia, hypoprothrombinemia, methemoglobinemia, eosinophilia.
Allergic Reactions
Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, anaphylaxis, allergic myocarditis, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, angioedema, drug fever, chills, Henoch-Schönlein purpura, serum sickness-like syndrome, generalized allergic reactions, generalized skin eruptions, photosensitivity, conjunctival and scleral injection, pruritus, urticaria and rash. In addition, periarteritis nodosa and systemic lupus erythematosus have been reported.
Gastrointestinal
Hepatitis (including cholestatic jaundice and hepatic necrosis) elevation of serum transaminase and bilirubin, pseudomembranous enterocolitis, pancreatitis, stomatitis, glossitis, nausea, emesis, abdominal pain, diarrhea, anorexia.
Genitourinary
Renal failure, interstitial nephritis, BUN and serum creatinine elevation, toxic nephrosis with oliguria and anuria, crystalluria and nephrotoxicity in association with cyclosporine.
Metabolic and Nutritional
Hyperkalemia (see PRECAUTIONS: Use in the Treatment of and Prophylaxis for Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia in Patients with Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome (AIDS).
Neurologic
Aseptic meningitis, convulsions, peripheral neuritis, ataxia, vertigo, tinnitus, headache.
Endocrine
The sulfonamides bear certain chemical similarities to some goitrogens, diuretics (acetazolamide and the thiazides) and oral hypoglycemic agents. Cross-sensitivity may exist with these agents. Diuresis and hypoglycemia have occurred rarely in patients receiving sulfonamides.
Musculoskeletal
Arthralgia and myalgia. Isolated cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported with sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim, mainly in AIDS patients.
Miscellaneous
Weakness, fatigue, insomnia.
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole. Because these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure:
- Σ Thrombotic thrombocytopenia purpura
- Σ Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
-
OVERDOSAGE
Acute
The amount of a single dose of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim that is either associated with symptoms of overdosage or is likely to be life-threatening has not been reported. Signs and symptoms of overdosage reported with sulfonamides include anorexia, colic, nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, drowsiness and unconsciousness. Pyrexia, hematuria and crystalluria may be noted. Blood dyscrasias and jaundice are potential late manifestations of overdosage.
Signs of acute overdosage with trimethoprim include nausea, vomiting, dizziness, headache, mental depression, confusion and bone marrow depression.
General principles of treatment include the institution of gastric lavage or emesis, forcing oral fluids, and the administration of intravenous fluids if urine output is low and renal function is normal. Acidification of the urine will increase renal elimination of trimethoprim. The patient should be monitored with blood counts and appropriate blood chemistries, including electrolytes. If a significant blood dyscrasia or jaundice occurs, specific therapy should be instituted for these complications. Peritoneal dialysis is not effective and hemodialysis is only moderately effective in eliminating sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim.
Chronic
Use of sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim at high doses and/or for extended periods of time may cause bone marrow depression manifested as thrombocytopenia, leukopenia and/or megaloblastic anemia. If signs of bone marrow depression occur, the patient should be given leucovorin 5 to 15 mg daily until normal hematopoiesis is restored.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Not recommended for use in pediatric patients less than 2 months of age.
Urinary Tract Infections and Shigellosis in Adults and Pediatric Patients, and Acute Otitis Media in Children
Adults
The usual adult dosage in the treatment of urinary tract infections is four teaspoonfuls (20mL) Sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension every 12 hours for 10 to 14 days. An identical daily dosage is used for 5 days in the treatment of shigellosis.
Children
The recommended dose for children with urinary tract infections or acute otitis media is 40 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole and 8 mg/kg trimethoprim per 24 hours, given in two divided doses every 12 hours for 10 days. An identical daily dosage is used for 5 days in the treatment of shigellosis. The following table is a guideline for the attainment of this dosage:
Children 2 months of age or older:
Weight Dose - every 12 hours lb kg Teaspoonfuls 22 10 1 (5 mL) 44 20 2 (10 mL) 66 30 3 (15 mL) 88 40 4 (20 mL) For Patients with Impaired Renal Function: When renal function is impaired, a reduced dosage should be employed using the following table:
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Recommended Dosage Regimen Above 30 Use standard regimen 15 to 30 ½ the usual regimen Below 15 Use not recommended Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis in Adults
The usual adult dosage in the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis is four teaspoonfuls (20 mL) sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim oral suspension every 12 hours for 14 days.
Pneumocystis Carinii Pneumonia
Treatment
Adults and Children: The recommended dosage for treatment of patients with documented Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia is 75 to 100 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole and 15 to 20 mg/kg trimethoprim per 24 hours given in equally divided doses every 6 hours for 14 to 21 days.10 The following table is a guideline for the upper limit of this dosage:
Weight Dose - every 6 hours lb kg Teaspoonfuls 18 8 1 (5 mL) 35 16 2 (10 mL) 53 24 3 (15 mL) 70 32 4 (20 mL) 88 40 5 (25 mL) 106 48 6 (30 mL) 141 64 8 (40 mL) 176 80 10 (50 mL) For the lower limit dose (75 mg/kg sulfamethoxazole and 15 mg/kg trimethoprim per 24 hours) administer 75% of the dose in the above table.
Prophylaxis
Adults
The recommended dosage for prophylaxis in adults is four teaspoonfuls (20 mL) of the oral suspension daily.11
Children
For children, the recommended dose is 750 mg/m2/day sulfamethoxazole with 150 mg/m2/day trimethoprim given orally in equally divided doses twice a day, on 3 consecutive days per week. The total daily dose should not exceed 1600 mg sulfamethoxazole and 320 mg trimethoprim.12 The following table is a guideline for the attainment of this dosage in children:
Body Surface Area Dose - every 12 hours (m2) Teaspoonfuls 0.26 ½ (2.5 mL) 0.53 1 (5 mL) 1.06 2 (10 mL) -
HOW SUPPLIED
Sulfamethoxazole and Trimethoprim Oral Suspension, USP is supplied in a purple grape-flavored suspension containing 200 mg sulfamethoxazole and 40 mg trimethoprim per 5 mL (teaspoonful) packaged in 1 pint (473 mL) bottles - NDC: 54868-0276-0.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP, with a child-resistant closure (as required).
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hi-Tech Pharmacal Co., Inc. at 1-800-262-9010 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Rx only
-
REFERENCES
- Kremers P, Duvivier J, Heusghem C. Pharmacokinetic Studies of Co-Trimoxazole in Man after Single and Repeated Doses. J Clin Pharmacol. Feb-Mar 1974; 14:112–117.
- Kaplan SA, et al. Pharmacokinetic Profile of Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole in Man. J Infect Dis. Nov 1973; 128 (Suppl): S547–S555.
- Varoquaux O, et al. Pharmacokinetics of the trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole combination in the elderly. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1985;20:575–581.
- Rudoy RC, Nelson JD, Haltalin KC. Antimicrobial Agents Chemother. May 1974;5:439–443.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria that Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard – Fourth Edition. NCCLS Document M7–A4, Vol.17, No. 2, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 1997.
- Hardy DW, et al. A controlled trial of trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole or aerosolized pentamidine for secondary prophylaxis of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327: 1842–1848.
- Marinella Mark A. 1999. Trimethoprim-induced hyperkalemia: An analysis of reported cases. Gerontol. 45:209–212.
- Margassery, S. and B. Bastani. 2002. Life threatening hyperkalemia and acidosis secondary to trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole treatment. J. Nephrol. 14:410–414.
- Brumfitt W, Pursell R. Trimethoprim/Sulfamethoxazole in the Treatment of Bacteriuria in Women. J Infect Dis. Nov 1973; 128 (Suppl):S657–S663.
- Masur H. Prevention and treatment of Pneumocystis pneumonia. N Engl J Med. 1992; 327: 1853–1880.
- Recommendations for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia for adults and adolescents infected with human immunodeficiency virus. MMWR. 1992; 41(RR-4):1–11.
- CDC Guidelines for prophylaxis against Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia for children infected with human immunodeficiency virus. MMWR. 1991; 40(RR-2):1–13.
Manufactured by:
Hi-Tech Pharmacal Co., Inc.
Amityville, New York 11701
Rev. 823:07 7/11
-
PRINCPAL DISPLAY PANEL

SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM ORAL SUSPENSION, USP
200 mg/40 mg per 5 mL
Grape Flavor
Each teaspoonful (5 mL) contains:
Sulfamethoxazole.......................................200 mg
Trimethoprim..............................................40 mg
Alcohol........................................................0.26 %
USUAL DOSAGE: See package insert for dosage and full prescribing information. Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP. Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Protect from light.
SHAKE WELL BEFORE USING.
Rx only
16 fl oz (473 mL)
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SULFAMETHOXAZOLE AND TRIMETHOPRIM
sulfamethoxazole and trimethoprim suspensionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 54868-0276(NDC:50383-823) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SULFAMETHOXAZOLE (UNII: JE42381TNV) (SULFAMETHOXAZOLE - UNII:JE42381TNV) SULFAMETHOXAZOLE 200 mg in 5 mL TRIMETHOPRIM (UNII: AN164J8Y0X) (TRIMETHOPRIM - UNII:AN164J8Y0X) TRIMETHOPRIM 40 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE SODIUM (UNII: K679OBS311) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) CHERRY (UNII: BUC5I9595W) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor CHERRY Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 54868-0276-0 1 in 1 CARTON 1 473 mL in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA074650 12/29/1997 Labeler - Physicians Total Care, Inc. (194123980) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Physicians Total Care, Inc. 194123980 relabel(54868-0276)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.