BALSALAZIDE DISODIUM capsule
Balsalazide Disodium by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Balsalazide Disodium by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
Balsalazide Disodium capsules
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use Balsalazide Disodium Capsules safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for Balsalazide Disodium Capsules.
Balsalazide Disodium capsules, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Balsalazide disodium capsules are a locally acting aminosalicylate indicated for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis in patients 5 years of age and older. ( 1)
- Limitations of Use: Safety and effectiveness of balsalazide beyond 8 weeks in children (ages 5 to17 years) and 12 weeks in adults have not been established. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Adult dose is three 750 mg balsalazide capsules 3 times a day (6.75 g/day) with or without food for 8 weeks. Some adult patients required treatment for up to 12 weeks. ( 2.1)
- Pediatric dose is EITHER: (2.2, 8.4)
- 1. Three 750 mg balsalazide capsules 3 times a day (6.75 g/day) with or without food for 8 weeks.
- OR:
- 2. One 750 mg balsalazide capsule 3 times a day (2.25 g/day) with or without food for up to 8 weeks.
- Capsules may be swallowed whole or may be opened and sprinkled on applesauce, then chewed or swallowed immediately. ( 2.3, 12.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Capsules: 750 mg ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with hypersensitivity to salicylates or to any of the components of balsalazide disodium capsules or balsalazide metabolites. Hypersensitivity reactions may include, but are not limited to the following: anaphylaxis, bronchospasm, and skin reaction. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥3%) are headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, respiratory infection, and arthralgia. Adverse reactions in children were similar. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact West-Ward Pharmaceuticals Corp. at 1-800-962-8364 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Renal Impairment: Use balsalazide with caution in patients with a history of renal disease. ( 5.3)
Revised: 8/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Dose
2.2 Pediatric Dose
2.3 Administration Alternatives
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Exacerbations of Ulcerative Colitis
5.2 Pyloric Stenosis
5.3 Renal
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Renal Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Studies
14.2 Pediatric Studies
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Adult Dose
For treatment of active ulcerative colitis in adult patients, the usual dose is three 750 mg balsalazide capsules to be taken 3 times a day (6.75 g per day) for up to 8 weeks. Some patients in the adult clinical trials required treatment for up to 12 weeks.
2.2 Pediatric Dose
For treatment of active ulcerative colitis in pediatric patients, aged 5 to 17 years, the usual dose is EITHER:
- three 750 mg balsalazide capsules 3 times a day (6.75 g per day) for up to 8 weeks;
- OR:
- one 750 mg balsalazide capsule 3 times a day (2.25 g per day) for up to 8 weeks.
Use of balsalazide in the pediatric population for more than 8 weeks has not been evaluated in clinical trials [see ClinicalStudies ( 14.2)] .
2.3 Administration Alternatives
Balsalazide capsules may also be administered by carefully opening the capsule and sprinkling the capsule contents on applesauce. The entire drug/applesauce mixture should be swallowed immediately; the contents may be chewed, if necessary, since contents of balsalazide are NOT coated beads/granules. Patients should be instructed not to store any drug/applesauce mixture for future use.
If the capsules are opened for sprinkling, color variation of the powder inside the capsules ranges from orange to yellow and is expected due to color variation of the active pharmaceutical ingredient.
Teeth and/or tongue staining may occur in some patients who use balsalazide in sprinkle form with food.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Exacerbations of Ulcerative Colitis
In the adult clinical trials, 3 out of 259 patients reported exacerbation of the symptoms of ulcerative colitis. In the pediatric clinical trials, 4 out of 68 patients reported exacerbation of the symptoms of ulcerative colitis.
Observe patients closely for worsening of these symptoms while on treatment.
5.2 Pyloric Stenosis
Patients with pyloric stenosis may have prolonged gastric retention of balsalazide capsules.
5.3 Renal
Renal toxicity has been observed in animals and patients given other mesalamine products. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering balsalazide to patients with known renal dysfunction or a history of renal disease [see Nonclinical Toxicology ( 13.2)] .
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Studies Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Adult Ulcerative Colitis:
During clinical development, 259 adult patients with active ulcerative colitis were exposed to 6.75 g/day balsalazide in 4 controlled trials.
In the 4 controlled clinical trials patients receiving a balsalazide dose of 6.75 g/day most frequently reported the following adverse reactions: headache (8%), abdominal pain (6%), diarrhea (5%), nausea (5%), vomiting (4%), respiratory infection (4%), and arthralgia (4%). Withdrawal from therapy due to adverse reactions was comparable among patients on balsalazide and placebo.
Adverse reactions reported by 1% or more of patients who participated in the 4 well-controlled, Phase 3 trials are presented by treatment group (Table 1).
The number of placebo patients (35), however, is too small for valid comparisons. Some adverse reactions, such as abdominal pain, fatigue, and nausea were reported more frequently in women than in men. Abdominal pain, rectal bleeding, and anemia can be part of the clinical presentation of ulcerative colitis.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 1% of Adult Balsalazide Patients in Controlled Trials * - * Adverse reactions occurring in at least 1% of balsalazide patients which were less frequent than placebo for the same adverse reaction were not included in the table.
Adverse Reaction
Balsalazide 6.75 g/day (N=259)
Placebo (N=35)
Abdominal pain
16 (6%)
1 (3%)
Diarrhea
14 (5%)
1 (3%)
Arthralgia
9 (4%)
0%
Rhinitis
6 (2%)
0%
Insomnia
6 (2%)
0%
Fatigue
6 (2%)
0%
Flatulence
5 (2%)
0%
Fever
5 (2%)
0%
Dyspepsia
5 (2%)
0%
Pharyngitis
4 (2%)
0%
Coughing
4 (2%)
0%
Anorexia
4 (2%)
0%
Urinary tract infection
3 (1%)
0%
Myalgia
3 (1%)
0%
Flu-like disorder
3 (1%)
0%
Dry mouth
3 (1%)
0%
Cramps
3 (1%)
0%
Constipation
3 (1%)
0%
Pediatric Ulcerative Colitis:
In a clinical trial in 68 pediatric patients aged 5 to 17 years with mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis who received 6.75 g/day or 2.25 g/day balsalazide for 8 weeks, the most frequently reported adverse reactions were headache (15%), abdominal pain upper (13%), abdominal pain (12%), vomiting (10%), diarrhea (9%), colitis ulcerative (6%), nasopharyngitis (6%), and pyrexia (6%) [see Table 2].
One patient who received balsalazide 6.75 g/day and 3 patients who received balsalazide 2.25 g/day discontinued treatment because of adverse reactions. In addition, 2 patients in each dose group discontinued because of a lack of efficacy.
Adverse reactions reported by 3% or more of pediatric patients within either treatment group in the Phase 3 trial are presented in Table 2.
Table 2: Treatment-Emergent Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥3% of Patients in Either Treatment Group in a Controlled Study of 68 Pediatric Patients
Adverse Reaction
Balsalazide
6.75 g/day
[N = 33]
Balsalazide
2.25 g/day
[N = 35]
Total
[N = 68]
Headache
5 (15%)
5 (14%)
10 (15%)
Abdominal pain upper
3 (9%)
6 (17%)
9 (13%)
Abdominal pain
4 (12%)
4 (11%)
8 (12%)
Vomiting
1 (3%)
6 (17%)
7 (10%)
Diarrhea
2 (6%)
4 (11%)
6 (9%)
Colitis ulcerative
2 (6%)
2 (6%)
4 (6%)
Nasopharyngitis
3 (9%)
1 (3%)
4 (6%)
Pyrexia
0 (0%)
4 (11%)
4 (6%)
Hematochezia
0 (0%)
3 (9%)
3 (4%)
Nausea
0 (0%)
3 (9%)
3 (4%)
Influenza
1 (3%)
2 (6%)
3 (4%)
Fatigue
2 (6%)
1 (3%)
3 (4%)
Stomatitis
0 (0%)
2 (6%)
2 (3%)
Cough
0 (0%)
2 (6%)
2 (3%)
Pharyngolaryngeal pain
2 (6%)
0 (0%)
2 (3%)
Dysmenorrhea
2 (6%)
0 (0%)
2 (3%)
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of balsalazide in clinical practice. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Myocarditis, pericarditis, vasculitis, pruritus, pleural effusion, pneumonia (with and without eosinophilia), alveolitis, renal failure, interstitial nephritis, pancreatitis, and alopecia.
Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. These adverse reactions have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to balsalazide.
Hepatic:
Postmarketing adverse reactions of hepatotoxicity have been reported for products which contain (or are metabolized to) mesalamine, including elevated liver function tests (SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT, GGT, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin), jaundice, cholestatic jaundice, cirrhosis, hepatocellular damage including liver necrosis and liver failure. Some of these cases were fatal; however, no fatalities associated with these adverse reactions were reported in balsalazide clinical trials. One case of Kawasaki-like syndrome which included hepatic function changes was also reported, however, this adverse reaction was not reported in balsalazide clinical trials.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary:
Published data from meta-analyses, cohort studies and case series on the use of mesalamine, the active moiety of balsalazide, during pregnancy have not reliably informed an association with mesalamine and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes (see Data). There are adverse effects on maternal and fetal outcomes associated with ulcerative colitis in pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). In animal reproduction studies, there were no adverse developmental effects observed after oral administration of balsalazide disodium in pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses up to 2.4 and 4.7 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations:
Disease-associated maternal and embryo/fetal risk:
Published data suggest that increased disease activity is associated with the risk of developing adverse pregnancy outcomes in women with ulcerative colitis. Adverse pregnancy outcomes include preterm delivery (before 37 weeks of gestation), low birth weight (less than 2500 g) infants, and small for gestational age at birth.
Data:
Human Data:
Published data from meta-analyses, cohort studies and case series on the use of mesalamine, the active moiety of balsalazide, during early pregnancy (first trimester) and throughout pregnancy have not reliably informed an association of mesalamine and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes. There is no clear evidence that mesalamine exposure in early pregnancy is associated with an increase risk in major congenital malformations, including cardiac malformations. Published epidemiologic studies have important methodological limitations which hinder interpretation of the data, including inability to control for confounders, such as underlying maternal disease, and maternal use of concomitant medications, and missing information on the dose and duration of use for mesalamine products.
Animal Data:
Reproduction studies were performed in rats and rabbits following administration of balsalazide during organogenesis at oral doses up to 2 g/kg/day, 2.4 and 4.7 times the MRHD based on body surface area for the rat and rabbit, respectively, and revealed no adverse embryofetal developmental effects due to balsalazide disodium.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary:
Data from published literature report the presence of mesalamine and its metabolite, N acetyl-5 aminosalicylic acid, in human milk in small amounts with relative infant doses (RID) of 0.1% or less for mesalamine (see Data). There are case reports of diarrhea in breastfed infants exposed to mesalamine (see Clinical Considerations). There is no information on the effects of the drug on milk production. The lack of clinical data during lactation precludes a clear determination of the risk of balsalazide to an infant during lactation; therefore, the developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother’s clinical need for balsalazide and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from balsalazide or from the underlying maternal condition.
Clinical Considerations:
Advise the caregiver to monitor breastfed infants for diarrhea.
Data:
In published lactation studies, maternal mesalamine doses from various oral and rectal mesalamine formulations and products ranged from 500 mg to 4.8 g daily. The average concentration of mesalamine in milk ranged from non-detectable to 0.5 mg/L. The average concentration of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid in milk ranged from 0.2 to 9.3 mg/L. Based on these concentrations, estimated infant daily dosages for an exclusively breastfed infant are 0 to 0.075 mg/kg/day (RID 0 to 0.1%) of mesalamine and 0.03 to 1.4 mg/kg/day of N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Use of balsalazide in pediatric and adolescent patients 5 to 17 years of age for the treatment of mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis is supported by:
- extrapolation of results from clinical studies that supported the approval of balsalazide for adults.
- a clinical trial of 68 patients ages 5-17 years comparing two doses of balsalazide (6.75 g/day and 2.25 g/day), and
- a pharmacokinetic study performed on a subset of the pediatric study population [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1), Clinical Pharmacology ( 12.3), and Clinical Studies ( 14.2)] .
Based on the limited data available, dosing can be initiated at either 6.75 or 2.25 g/day.
Safety and efficacy of balsalazide in pediatric patients below the age of 5 years have not been established.
8.5 Renal Impairment
Renal toxicity has been observed in animals and patients given other mesalamine products. Mesalamine is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney. Therefore, caution should be exercised when administering balsalazide to patients with known renal dysfunction or a history of renal disease [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3), Nonclinical Toxicology ( 13.2)] .
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
No case of overdose has occurred with balsalazide. A 3-year-old boy is reported to have ingested 2 g of another mesalamine product. He was treated with ipecac and activated charcoal with no adverse reactions.
If an overdose occurs with balsalazide, treatment should be supportive, with particular attention to correction of electrolyte abnormalities.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
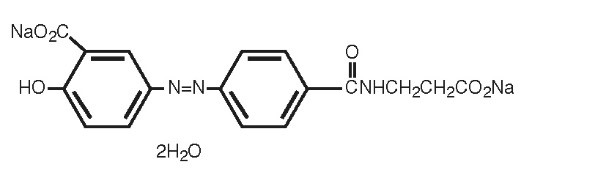
Each Balsalazide Disodium Capsule USP contains 750 mg of balsalazide disodium, a prodrug that is enzymatically cleaved in the colon to produce mesalamine (5-aminosalicylic acid or 5-ASA), an anti-inflammatory drug. Each capsule of balsalazide (750 mg) is equivalent to 267 mg of mesalamine. Balsalazide disodium has the chemical name (E)-5-[[-4-[[(2-carboxyethyl) amino]carbonyl] phenyl]azo]-2-hydroxybenzoic acid, disodium salt, dihydrate. Its structural formula is:
Molecular Weight: 437.31
Molecular Formula: C 17H 13N 3O 6Na 22H 2O
Balsalazide disodium is a yellow to orange crystalline powder. It is freely soluble in water and isotonic saline and DMSO, sparingly soluble in methanol and ethanol, and practically insoluble in all other organic solvents.
The inactive ingredients in Balsalazide Disodium Capsules USP are colloidal silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. Additionally, the capsule shell contains FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Red #40, FD&C Yellow #6, gelatin, and titanium dioxide. The black monogramming ink contains ammonium hydroxide, iron oxide black, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac glaze. The sodium content of each capsule is approximately 79 mg.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Balsalazide disodium is delivered intact to the colon where it is cleaved by bacterial azoreduction to release equimolar quantities of mesalamine, which is the therapeutically active portion of the molecule, and the 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine carrier moiety. The carrier moiety released when balsalazide disodium is cleaved is only minimally absorbed and is largely inert.
The mechanism of action of 5-ASA is unknown, but appears to be local to the colonic mucosa rather than systemic. Mucosal production of arachidonic acid metabolites, both through the cyclooxygenase pathways, i.e., prostanoids, and through the lipoxygenase pathways, i.e., leukotrienes and hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids, is increased in patients with chronic inflammatory bowel disease, and it is possible that 5-ASA diminishes inflammation by blocking production of arachidonic acid metabolites in the colon.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Balsalazide capsules contain a powder of balsalazide disodium that is insoluble in acid and designed to be delivered to the colon as the intact prodrug. Upon reaching the colon, bacterial azoreductases cleave the compound to release 5-ASA, the therapeutically active portion of the molecule, and 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine. The 5-ASA is further metabolized to yield N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA), a second key metabolite.
Absorption:
In a study of adult patients with ulcerative colitis, who received balsalazide, 1.5 g twice daily, for over 1 year, systemic drug exposure, based on mean AUC values, was up to 60 times greater (0.008 mcg·hr/mL to 0.480 mcg·hr/mL) when compared to that obtained in healthy subjects who received the same dose.
Effect of Food:
The plasma pharmacokinetics of balsalazide and its key metabolites from a crossover study in healthy volunteers are summarized in Table 3. In this study, a single oral dose of balsalazide 2.25 g was administered to healthy volunteers as intact capsules (3 x 750 mg) under fasting conditions, as intact capsules (3 x 750 mg) after a high-fat meal, and unencapuslated (3 x 750 mg) as sprinkles on applesauce.
Table 3: Plasma Pharmacokinetics for Balsalazide and Key Metabolites (5-ASA and N-Ac-5-ASA) with Administration of Balsalazide Following a Fast, a High-Fat Meal, and Drug Contents Sprinkled on Applesauce (Mean ± SD) Fasting
N=17
High-fat Meal
N=17
Sprinkled
N=17
C max (mcg/mL)
Balsalazide
0.51 ± 0.32
0.45 ± 0.39
0.21 ± 0.12
5-ASA
0.22 ± 0.12
0.11 ± 0.136
0.29 ± 0.17
N-Ac-5-ASA
0.88 ± 0.39
0.64 ± 0.534
1.04 ± 0.57
AUC last (mcg·hr/mL)
Balsalazide
1.35 ± 0.73
1.52 ± 1.01
0.87 ± 0.48
5-ASA
2.59 ± 1.46
2.10 ± 2.58
2.99 ± 1.70
N-Ac-5-ASA
17.8 ± 8.14
17.7 ± 13.7
20.0 ± 11.4
T max (h)
Balsalazide
0.8 ± 0.85
1.2 ± 1.11
1.6 ± 0.44
5-ASA
8.2 ± 1.98
22.0 ± 8.23
8.7 ± 1.99
N-Ac-5-ASA
9.9 ± 2.49
20.2 ± 8.94
10.8 ± 5.39
A relatively low systemic exposure was observed under all three administered conditions (fasting, fed with high-fat meal, sprinkled on applesauce), which reflects the variable, but minimal absorption of balsalazide disodium and its metabolites. The data indicate that both C max and AUC last were lower, while T max was markedly prolonged, under fed (high-fat meal) compared to fasted conditions. Moreover, the data suggest that dosing balsalazide disodium as a sprinkle or as a capsule provides highly variable, but relatively similar mean pharmacokinetic parameter values. No inference can be made as to how the systemic exposure differences of balsalazide and its metabolites in this study might predict the clinical efficacy under different dosing conditions (i.e., fasted, fed with high-fat meal, or sprinkled on applesauce) since clinical efficacy after balsalazide disodium administration is presumed to be primarily due to the local effects of 5-ASA on the colonic mucosa.
Distribution:
The binding of balsalazide to human plasma proteins was ≥ 99%.
Elimination:
Metabolism:
The products of the azoreduction of this compound, 5-ASA and 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine, and their N-acetylated metabolites have been identified in plasma, urine and feces.
Excretion:
Following single-dose administration of 2.25 g balsalazide (three 750 mg capsules) under fasting conditions in healthy subjects, mean urinary recovery of balsalazide, 5-ASA, and N-Ac-5-ASA was 0.20%, 0.22% and 10.2%, respectively.
In a multiple-dose study in healthy subjects receiving a balsalazide dose of two 750 mg capsules twice daily (3 g/day) for 10 days, mean urinary recovery of balsalazide, 5-ASA, and N-Ac-5-ASA was 0.1%, 0%, and 11.3%, respectively. During this study, subjects received their morning dose 0.5 hours after being fed a standard meal, and subjects received their evening dose 2 hours after being fed a standard meal.
In a study with 10 healthy volunteers, 65% of a single 2.25 g dose of balsalazide was recovered as 5-ASA, 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine, and the N-acetylated metabolites in feces, while <1% of the dose was recovered as parent compound.
In a study that examined the disposition of balsalazide in patients who were taking 3 to 6 g of balsalazide daily for more than 1 year and who were in remission from ulcerative colitis, less than 1% of an oral dose was recovered as intact balsalazide in the urine. Less than 4% of the dose was recovered as 5-ASA, while virtually no 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine was detected in urine. The mean urinary recovery of N-Ac-5-ASA and N-acetyl-4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine comprised <16% and <12% of the balsalazide dose, respectively. No fecal recovery studies were performed in this population.
Use in Specific Populations:
Pediatric Patients:
In studies of pediatric patients with mild-to-moderate active ulcerative colitis receiving three 750 mg balsalazide capsules 3 times daily (6.75 g/day) for 8 weeks, steady state was reached within 2 weeks, as observed in adult patients. Likewise, the pharmacokinetics of balsalazide, 5-ASA, and N-Ac-5-ASA were characterized by very large inter-patient variability, which is also similar to that seen in adult patients.
The pro-drug moiety, balsalazide, appeared to exhibit dose-independent (i.e., dose-linear) kinetics in children, and the systemic exposure parameters (C max and AUC 0-8) increased in an almost dose-proportional fashion after the 6.75 g/day versus the 2.25 g/day doses. However, the absolute magnitude of these exposure parameters was greater relative to adults. The C max and AUC 0-8 observed in pediatric patients were 26% and 102% greater than those observed in adult patients at the 6.75 g/day dosage level. In contrast, the systemic exposure parameters for the active metabolites, 5-ASA and N-Ac-5‑ASA, in pediatric patients increased in a less than dose-proportional manner after the 6.75 g/day dose versus the 2.25 g/day dose. Additionally, the magnitude of these exposure parameters was decreased for both metabolites relative to adults. For the metabolite of key safety concern from a systemic exposure perspective, 5-ASA, the C max and AUC 0-8 observed in pediatric patients were 67% and 64% lower than those observed in adult patients at the 6.75 g/day dosage level. Likewise, for N-Ac-5-ASA, the C max and AUC 0-8 observed in pediatric patients were 68% and 55% lower than those observed in adult patients at the 6.75 g/day dosage level.
All pharmacokinetic studies with balsalazide are characterized by large variability in the plasma concentration versus time profiles for balsalazide and its metabolites, thus half-life estimates of these analytes are indeterminate.
Drug Interaction Studies:
In Vitro Data:
In an in vitro study using human liver microsomes, balsalazide and its metabolites [5- aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA), N‑acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid (N-Ac-5-ASA), 4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine (4-ABA) and N-acetyl-4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine (N-Ac-4-ABA)] were not shown to inhibit the major CYP enzymes evaluated (CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, and CYP3A4/5). Therefore, balsalazide and its metabolites are not expected to inhibit the metabolism of other drugs which are substrates of CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A4/5.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a 24-month rat (Sprague Dawley) carcinogenicity study, oral (dietary) balsalazide disodium at doses up to 2 g/kg/day was not tumorigenic. For a 50 kg person of average height this dose represents 2.4 times the recommended human dose on a body surface area basis. Balsalazide disodium was not genotoxic in the following in vitro or in vivo tests: Ames test, human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration test, and mouse lymphoma cell (L5178Y/TK+/-) forward mutation test, or mouse micronucleus test. However, it was genotoxic in the in vitro Chinese hamster lung cell (CH V79/HGPRT) forward mutation test.
4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine, a metabolite of balsalazide disodium, was not genotoxic in the Ames test and the mouse lymphoma cell (L5178Y/TK+/-) forward mutation test but was positive in the human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration test. N-acetyl-4-aminobenzoyl-ß-alanine, a conjugated metabolite of balsalazide disodium, was not genotoxic in Ames test, the mouse lymphoma cell (L5178Y/TK+/-) forward mutation test, or the human lymphocyte chromosomal aberration test. Balsalazide disodium at oral doses up to 2 g/kg/day, 2.4 times the recommended human dose based on body surface area, was found to have no effect on fertility and reproductive performance in rats.
13.2 Animal Toxicology
Renal Toxicity:
In animal studies conducted at doses up to 2000 mg/kg (approximately 21 times the recommended 6.75 g/day dose on a mg/kg basis for a 70 kg person), balsalazide demonstrated no nephrotoxic effects in rats or dogs.
Overdosage:
A single oral dose of balsalazide disodium at 5 g/kg or 4-aminobenzoyl-β-alanine, a metabolite of balsalazide disodium, at 1 g/kg was non-lethal in mice and rats. No symptoms of acute toxicity were seen at these doses.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Adult Studies
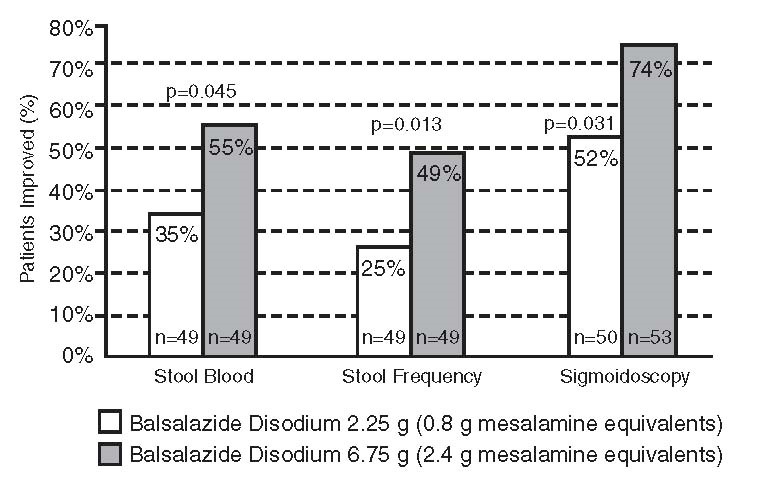
Two randomized, double-blind studies were conducted in adults. In the first trial, 103 patients with active mild-to-moderate ulcerative colitis with sigmoidoscopy findings of friable or spontaneously bleeding mucosa were randomized and treated with balsalazide 6.75 g/day or balsalazide 2.25 g/day. The primary efficacy endpoint was reduction of rectal bleeding and improvement of at least one of the other assessed symptoms (stool frequency, patient functional assessment, abdominal pain, sigmoidoscopic grade, and physician’s global assessment [PGA]). Outcome assessment for rectal bleeding at each interim period (week 2, 4, and 8) encompassed a 4-day period (96 hours). Results demonstrated a statistically significant difference between high and low doses of balsalazide ( Figure 1).
Figure 1: Percentage of Patients Improved at 8 weeks
A second study, conducted in Europe, confirmed findings of symptomatic improvement.
14.2 Pediatric Studies
A clinical trial was conducted comparing two doses (6.75 g/day and 2.25 g/day) of balsalazide in 68 pediatric patients (age 5 to 17, 23 males and 45 females) with mildly to moderately active ulcerative colitis. 28/33 (85%) patients randomized to 6.75 g/day and 25/35 (71%) patients randomized to 2.25 g/day completed the study. The primary endpoint for this study was the proportion of subjects with clinical improvement (defined as a reduction of at least 3 points in the Modified Sutherland Ulcerative Colitis Activity Index [MUCAI] from baseline to 8 weeks). Fifteen (45%) patients in the balsalazide 6.75 g/day group and 13 (37%) patients in the balsalazide 2.25 g/day group showed this clinical improvement. In both groups, patients with higher MUCAI total scores at baseline were likely to experience greater improvement.
Rectal bleeding improved in 64% of patients treated with balsalazide 6.75 g/day and 54% of patients treated with balsalazide 2.25 g/day. Colonic mucosal appearance upon endoscopy improved in 61% of patients treated with balsalazide 6.75 g/day and 46% of patients treated with balsalazide 2.25 g/day.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Balsalazide Disodium Capsules USP
The 750 mg capsule is supplied as a light orange opaque capsule with “54 795” printed in black ink on cap and body, containing a yellow-orange powder.
NDC: 60429-952-28: Bottle of 280 capsules
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Important Precautions Regarding Balsalazide:
- Instruct patients not to take balsalazide if they have a hypersensitivity to salicylates (e.g., aspirin).
- Patients should be instructed to contact their health care provider under the following circumstances:
- If they experience a worsening of their ulcerative colitis symptoms.
- If they are diagnosed with pyloric stenosis, because balsalazide capsules may be slow to pass through their digestive tract.
- If they are diagnosed with renal dysfunction. Damage to the kidney has been observed in people given medications similar to balsalazide.
What Patients Should Know About Adverse Reactions:
- In adult clinical trials the most common adverse reactions were headache, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, respiratory infection, and arthralgia.
- In the pediatric clinical trial the most common adverse reactions were headache, abdominal pain, vomiting, diarrhea, ulcerative colitis, nasopharyngitis, and pyrexia.
- Inform patients that this listing of adverse reactions is not complete and not all adverse reactions can be anticipated. If appropriate, a more comprehensive list of adverse reactions can be discussed with patients.
What Patients Should Know About Taking Balsalazide with Other Medication:
- Based upon limited studies conducted in a test tube, balsalazide is not believed to interfere with other drugs by preventing how the liver functions. However, as the studies were limited in scope, you should always consult your doctor and discuss potential interactions prior to initiating any new drug.
Distr. by: West-Ward
Pharmaceuticals Corp.
Eatontown, NJ 07724
10003708/08
Marketed/Packaged by:
GSMS, Inc.Camarillo, CA USA 93012
Revised August 2019
- PACKAGE/LABEL PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BALSALAZIDE DISODIUM
balsalazide disodium capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60429-952(NDC:0054-0079) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BALSALAZIDE DISODIUM (UNII: 1XL6BJI034) (BALSALAZIDE - UNII:P80AL8J7ZP) BALSALAZIDE DISODIUM 750 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) BUTYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Product Characteristics Color orange Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 1mm Flavor Imprint Code 54;795 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60429-952-28 280 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/26/2018 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA077806 12/28/2007 Labeler - Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. (603184490) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. 603184490 relabel(60429-952) , repack(60429-952)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.