CIPROFLOXACIN by STAT RX USA LLC / STAT TX USA LLC CIPROFLOXACIN tablet
CIPROFLOXACIN by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
CIPROFLOXACIN by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by STAT RX USA LLC, STAT TX USA LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING:
Fluoroquinolones, including CIPROFLOXACIN TABLETS USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg, are
associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This risk is further
increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and
in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants (See WARNINGS). -
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg and other antibacterial drugs Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria. -
DESCRIPTION
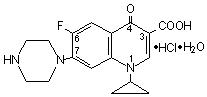
Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg are synthetic broad spectrum antimicrobial agents for oral administration. Ciprofloxacin hydrochloride, USP, a fluoroquinolone, is the monohydrochloride monohydrate salt of 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1, 4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. It is a faintly yellowish to light yellow crystalline substance with a molecular weight of 385.8. Its empirical formula is C17H18FN3O3HClH2O and its chemical structure is as follows:
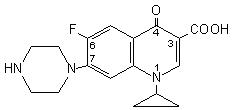
Ciprofloxacin is 1-cyclopropyl-6-fluoro-1,4-dihydro-4-oxo-7-(1-piperazinyl)-3-quinolinecarboxylic acid. Its empirical formula is C17H18FN3O3 and its molecular weight is 331.4. It is a faintly yellowish to light yellow crystalline substance and its chemical structure is as follows:
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP are film-coated tablets and are available in 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg (ciprofloxacin equivalent) strengths. Ciprofloxacin Tablets are white to slightly yellowish. The inactive ingredients are pregelatinized starch, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol and purified water. -
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Absorption:
Ciprofloxacin given as an oral tablet is rapidly and well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract after oral administration. The absolute bioavailability is approximately 70% with no substantial loss by first pass metabolism. Ciprofloxacin maximum serum concentrations and area under the curve are shown in the chart for the 250 mg to 1000 mg dose range.
Maximum serum concentrations are attained 1 to 2 hours after oral dosing. Mean concentrations 12 hours after dosing with 250, 500, or 750 mg are 0.1, 0.2, and 0.4 μg/mL, respectively. The serum elimination half-life in subjects with normal renal function is approximately 4 hours. Serum concentrations increase proportionately with doses up to 1000 mg.
Dose (mg)Maximum
Serum Concentrations
(μg/mL)Area
Under Curve
(AUC)
(μghr/mL)250
500
750
1000
1.2
2.4
4.3
5.4
4.8
11.6
20.2
30.8
A 500 mg oral dose given every 12 hours has been shown to produce an area under the serum concentration time curve (AUC) equivalent to that produced by an intravenous infusion of 400 mg ciprofloxacin given over 60 minutes every 12 hours. A 750 mg oral dose given every 12 hours has been shown to produce an AUC at steady-state equivalent to that produced by an intravenous infusion of 400 mg given over 60 minutes every 8 hours. A 750 mg oral dose results in a Cmax similar to that observed with a 400 mg I.V. dose. A 250 mg oral dose given every 12 hours produces an AUC equivalent to that produced by an infusion of 200 mg ciprofloxacin given every 12 hours.a AUC 0-12hSteady-state Pharmacokinetic Parameters
Following Multiple Oral and I.V. DosesParameters
AUC (μghr/mL)
Cmax (μg/mL)500 mg
q12h, P.O.
13.7a
2.97
400 mg
q12h, I.V.
12.7a
4.56
750 mg
q12h, P.O.
31.6b
3.59
400 mg
q8h, I.V.
32.9c
4.07
bAUC 24h=AUC0-12h x 2
cAUC 24h=AUC0-8h x 3Distribution:
The binding of ciprofloxacin to serum proteins is 20 to 40% which is not likely to be high enough to cause significant protein binding interactions with other drugs.
After oral administration, ciprofloxacin is widely distributed throughout the body. Tissue concentrations often exceed serum concentrations in both men and women, particularly in genital tissue including the prostate. Ciprofloxacin is present in active form in the saliva, nasal and bronchial secretions, mucosa of the sinuses, sputum, skin blister fluid, lymph, peritoneal fluid, bile, and prostatic secretions. Ciprofloxacin has also been detected in lung, skin, fat, muscle, cartilage, and bone. The drug diffuses into the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF); however, CSF concentrations are generally less than 10% of peak serum concentrations. Low levels of the drug have been detected in the aqueous and vitreous humors of the eye.
Metabolism:
Four metabolites have been identified in human urine which together account for approximately 15% of an oral dose. The metabolites have antimicrobial activity, but are less active than unchanged ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin is an inhibitor of human cytochrome P450 1A2 (CYP1A2) mediated metabolism. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin with other drugs primarily metabolized by CYP1A2 results in increased plasma concentrations of these drugs and could lead to clinically significant adverse events of the coadministered drug (see CONTRAINDICATIONS; WARNINGS; PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).Excretion:
The serum elimination half-life in subjects with normal renal function is approximately 4 hours. Approximately 40 to 50% of an orally administered dose is excreted in the urine as unchanged drug. After a 250 mg oral dose, urine concentrations of ciprofloxacin usually exceed 200 μg/mL during the first two hours and are approximately 30 μg/mL at 8 to 12 hours after dosing. The urinary excretion of ciprofloxacin is virtually complete within 24 hours after dosing. The renal clearance of ciprofloxacin, which is approximately 300 mL/minute, exceeds the normal glomerular filtration rate of 120 mL/minute. Thus, active tubular secretion would seem to play a significant role in its elimination. Co-administration of probenecid with ciprofloxacin results in about a 50% reduction in the ciprofloxacin renal clearance and a 50% increase in its concentration in the systemic circulation. Although bile concentrations of ciprofloxacin are several fold higher than serum concentrations after oral dosing, only a small amount of the dose administered is recovered from the bile as unchanged drug. An additional 1 to 2% of the dose is recovered from the bile in the form of metabolites. Approximately 20 to 35% of an oral dose is recovered from the feces within 5 days after dosing. This may arise from either biliary clearance or transintestinal elimination.
Drug-drug Interactions:
When Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg is given concomitantly with food, there is a delay in the absorption of the drug, resulting in peak concentrations that occur closer to 2 hours after dosing rather than 1 hour. The overall absorption of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg however, is not substantially affected. Concurrent administration of antacids containing magnesium hydroxide or aluminum hydroxide may reduce the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin by as much as 90%. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
The serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin and metronidazole were not altered when these two drugs were given concomitantly.
Concomitant administration with tizanidine is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Concomitant administration of ciprofloxacin with theophylline decreases the clearance of theophylline resulting in elevated serum theophylline levels and increased risk of a patient developing CNS or other adverse reactions. Ciprofloxacin also decreases caffeine clearance and inhibits the formation of paraxanthine after caffeine administration. (See WARNINGS: PRECAUTIONS.)Special Populations:
Pharmacokinetic studies of the oral (single dose) and intravenous (single and multiple dose) forms of ciprofloxacin indicate that plasma concentrations of ciprofloxacin are higher in elderly subjects (> 65 years) as compared to young adults. Although the Cmax is increased 16- 40%, the increase in mean AUC is approximately 30%, and can be at least partially attributed to decreased renal clearance in the elderly. Elimination half-life is only slightly (~20%) prolonged in the elderly. These differences are not considered clinically significant. (See PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use.)
In patients with reduced renal function, the half-life of ciprofloxacin is slightly prolonged. Dosage adjustments may be required. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
In preliminary studies in patients with stable chronic liver cirrhosis, no significant changes in ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics have been observed. The kinetics of ciprofloxacin in patients with acute hepatic insufficiency, however, have not been fully elucidated.
MICROBIOLOGY
Ciprofloxacin has in vitro activity against a wide range of gram-negative and gram-positive microorganisms. The bactericidal action of ciprofloxacin results from inhibition of the enzymes topoisomerase II (DNA gyrase) and topoisomerase IV, which are required for bacterial DNA replication, transcription, repair, and recombination. The mechanism of action of fluoroquinolones, including ciprofloxacin, is different from that of penicillins, cephalosporins, aminoglycosides, macrolides, and tetracyclines; therefore, microorganisms resistant to these classes of drugs may be susceptible to ciprofloxacin and other quinolones. There is no known cross-resistance between ciprofloxacin and other classes of antimicrobials. In vitro resistance to ciprofloxacin develops slowly by multiple step mutations.
Ciprofloxacin is slightly less active when tested at acidic pH. The inoculum size has little effect when tested in vitro. The minimal bactericidal concentration (MBC) generally does not exceed the minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) by more than a factor of 2.
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section of the package insert for Ciprofloxacin Hydrochloride Tablets USP, 250mg, 500mg and 750mg.Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Enterococcus faecalis (Many strains are only moderately susceptible.)
Staphylococcus aureus (methicillin-susceptible strains only)
Staphylococcus epidermidis (methicillin-susceptible strains only)
Staphylococcus saprophyticus
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only)
Streptococcus pyogenesAerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Campylobacter jejuni Proteus mirabilis
Citrobacter diversus Proteus vulgaris
Citrobacter freundii Providencia rettgeri
Enterobacter cloacae Providencia stuartii
Escherichia coli Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Haemophilus influenzae Salmonella typhi
Haemophilus parainfluenzae Serratia marcescens
Klebsiella pneumoniae Shigella boydii
Moraxella catarrhalis Shigella dysenteriae
Morganella morganii Shigella flexneri
Neisseria gonorrhoeae Shigella sonnei
Ciprofloxacin has been shown to be active against Bacillus anthracis both in vitro and by use of serum levels as a surrogate marker (see INDICATIONS AND USAGE and INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION).
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown.
Ciprofloxacin exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 1 μg/mL or less against most (≥ 90%) strains of the following microorganisms; however, the safety and effectiveness of ciprofloxacin in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Aerobic gram-positive microorganisms
Staphylococcus haemolyticus
Staphylococcus hominis
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-resistant strains only)
Aerobic gram-negative microorganisms
Acinetobacter Iwoffii Pasteurella multocida
Aeromonas hydrophila Salmonella enteritidis
Edwardsiella tarda Vibrio cholerae
Enterobacter aerogenes Vibrio parahaemolyticus
Klebsiella oxytoca Vibrio vulnificus
Legionella pneumophila Yersinia enterocolitica
Most strains of Burkholderia cepacia and some strains of Stenotrophomonas maltophilia are resistant to ciprofloxacin as are most anaerobic bacteria, including Bacteroides fragilis and Clostridium difficile.
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution Techniques:
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method1 (broth or agar) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of ciprofloxacin powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For testing aerobic microorganisms other than Haemophilus influenzae , Haemophilus parainfluenzae, and Neisseria gonorrhoeaea:MIC (μg/mL) Interpretation ≤ 1
Susceptible (S)
2
Intermediate (I)
≥ 4
Resistant (R)
a These interpretive standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with streptococci using cation-adjusted Mueller-Hinton broth with 2-5% lysed horse blood.
For testing Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzaeb:MIC (μg/mL) Interpretation ≤ 1
Susceptible (S)
b This interpretive standard is applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae using Haemophilus Test Medium.1
The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than “Susceptible”. Strains yielding MIC results suggestive of a “nonsusceptible” category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing.
For testing Neisseria gonorrhoeaec:MIC (μg/mL) Interpretation ≤ 0.06
Susceptible (S)
0.12 – 0.5
Intermediate (I)
≥ 1
Resistant (R)
c This interpretive standard is applicable only to agar dilution test with GC agar base and 1% defined growth supplement.
A report of “Susceptible” indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable. A report of “Intermediate” indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone, which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of “Resistant” indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable; other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. Standard ciprofloxacin powder should provide the following MIC values:Organism MIC (μg/mL) E. faecalis
ATCC 29212
0.25 – 2
E. coli
ATCC 25922
0.004 – 0.015
H. influenzaea ATCC 49247
0.004 – 0.03
P. aeruginosa
ATCC 27853
0.25 – 1.0
S. aureus
ATCC 29213
0.12 – 0.5
C. jejunib
ATCC 33560
0.06 – 0.25 and 0.03 – 0.12
N. gonorrhoeaec
ATCC 49226
0.001– 0.008
a This quality control range is applicable to only H. influenzae ATCC 49247 tested by a broth microdilution procedure using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM)1.
b C. jejuni ATCC 33560 tested by broth microdilution procedure using cation adjusted Mueller Hinton broth with 2.5-5% lysed horse blood in a microaerophilic environment at 36-37°C for 48 hours and for 42°C at 24 hours2, respectively.
c N. gonorrhoeae ATCC 49226 tested by agar dilution procedure using GC agar and 1% defined growth supplement in a 5% CO2 environment at 35-37°C for 20-24 hours3.Diffusion Techniques:
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. One such standardized procedure3 requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 5-μg ciprofloxacin to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to ciprofloxacin.
Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 5-μg ciprofloxacin disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For testing Enterobacteriaceae, Enterococcus faecalis, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus species, penicillin-susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, Streptococcus pyogenes, and Pseudomonas aeruginosaa:Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥ 21
Susceptible (S)
16 – 20
Intermediate (I)
≤ 15
Resistant (R)
a These zone diameter standards are applicable only to tests performed for streptococci using Mueller-Hinton agar supplemented with 5% sheep blood incubated in 5% CO2.
For testing Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzaeb:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥ 21
Susceptible (S)
b This zone diameter standard is applicable only to tests with Haemophilus influenzae and Haemophilus parainfluenzae using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).3
The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than “Susceptible”. Strains yielding zone diameter results suggestive of a “nonsusceptible” category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing.
For testing Neisseria gonorrhoeaec:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥41
Susceptible (S)
28 – 40
Intermediate (I)
≤ 27
Resistant (R)
c This zone diameter standard is applicable only to disk diffusion tests with GC agar base and 1% defined growth supplement.
Interpretation should be as stated above for results using dilution techniques. Interpretation involves correlation of the diameter obtained in the disk test with the MIC for ciprofloxacin.
As with standardized dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms that are used to control the technical aspects of the laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 5-μg ciprofloxacin disk should provide the following zone diameters in these laboratory test quality control strains:
Organism Zone Diameter (mm) E. coli
ATCC 25922
30-40
H. influenzaea
ATCC 49247
34-42
N. gonorrhoeaeb
ATCC 49226
48-58
P. aeruginosa
ATCC 27853
25-33
S. aureus
ATCC 25923
22-30
a These quality control limits are applicable to only H. influenzae ATCC 49247 testing using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM).3
b These quality control limits are applicable only to tests conducted with N. gonorrhoeae ATCC 49226 performed by disk diffusion using GC agar base and 1% defined growth supplement. -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg is indicated for the treatment of infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions and patient populations listed below. Please see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for specific recommendations.Adult Patients:
Urinary Tract Infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, Proteus mirabilis, Providencia rettgeri, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter diversus, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis, Staphylococcus saprophyticus, or Enterococcus faecalis.
Acute Uncomplicated Cystitis in females caused by Escherichia coli or Staphylococcus saprophyticus.
Chronic Bacterial Prostatitis caused by Escherichia coli or Proteus mirabilis.
Lower Respiratory Tract Infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Haemophilus influenzae, Haemophilus parainfluenzae, or penicillin-susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae. Also, Moraxella catarrhalis for the treatment of acute exacerbations of chronic bronchitis.
NOTE: Although effective in clinical trials, ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the treatment of presumed or confirmed pneumonia secondary to Streptococcus pneumoniae.
Acute Sinusitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae, penicillin-susceptible Streptococcus pneumoniae, or Moraxella catarrhalis.
Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Enterobacter cloacae, Proteus mirabilis, Proteus vulgaris, Providencia stuartii, Morganella morganii, Citrobacter freundii, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus epidermidis, or Streptococcus pyogenes.
Bone and Joint Infections caused by Enterobacter cloacae, Serratia marcescens, or Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
Complicated Intra-Abdominal Infections (used in combination with metronidazole) caused by Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Proteus mirabilis, Klebsiella pneumoniae, or Bacteroides fragilis.
Infectious Diarrhea caused by Escherichia coli (enterotoxigenic strains), Campylobacter jejuni, Shigella boydii†, Shigella dysenteriae, Shigella flexneri or Shigella sonnei† when antibacterial therapy is indicated.
Typhoid Fever (Enteric Fever) caused by Salmonella typhi.
NOTE: The efficacy of ciprofloxacin in the eradication of the chronic typhoid carrier state has not been demonstrated.
Uncomplicated cervical and urethral gonorrhea due to Neisseria gonorrhoeae.Pediatric patients (1 to 17 years of age):
Complicated Urinary Tract Infections and Pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli.
NOTE: Although effective in clinical trials, ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the pediatric population due to an increased incidence of adverse events compared to controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues. (See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use, ADVERSE REACTIONS and CLINICAL STUDIES.)
Ciprofloxacin, like other fluoroquinolones, is associated with arthropathy and histopathological changes in weight-bearing joints of juvenile animals. (See ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY.)
Adult and Pediatric Patients:
Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure): To reduce the incidence or progression of disease following exposure to aerosolized Bacillus anthracis.
Ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans served as a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit and provided the initial basis for approval of this indication.5 Supportive clinical information for ciprofloxacin for anthrax post-exposure prophylaxis was obtained during the anthrax bioterror attacks of October 2001. (See also, INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION).
†Although treatment of infections due to this organism in this organ system demonstrated a clinically significant outcome, efficacy was studied in fewer than 10 patients.
If anaerobic organisms are suspected of contributing to the infection, appropriate therapy should be administered. Appropriate culture and susceptibility tests should be performed before treatment in order to isolate and identify organisms causing infection and to determine their susceptibility to ciprofloxacin. Therapy with Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg may be initiated before results of these tests are known; once results become available appropriate therapy should be continued. As with other drugs, some strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa may develop resistance fairly rapidly during treatment with ciprofloxacin. Culture and susceptibility testing performed periodically during therapy will provide information not only on the therapeutic effect of the antimicrobial agent but also on the possible emergence of bacterial resistance.
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg and other antibacterial drugs, Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy. -
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ciprofloxacin is contraindicated in persons with a history of hypersensitivity to ciprofloxacin, any member of the quinolone class of antimicrobial agents, or any of the product components.
Concomitant administration with tizanidine is contraindicated. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.) -
WARNINGS
Tendinopathy and Tendon Rupture:
Fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg, are associated with an increased risk of tendinitis and tendon rupture in all ages. This adverse reaction most frequently involves the Achilles tendon, and rupture of the Achilles tendon may require surgical repair. Tendinitis and tendon rupture in the rotator cuff (the shoulder), the hand, the biceps, the thumb, and other tendon sites have also been reported. The risk of developing fluoroquinolone-associated tendinitis and tendon rupture is further increased in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants. Factors, in addition to age and corticosteroid use, that may independently increase the risk of tendon rupture include strenuous physical activity, renal failure, and previous tendon disorders such as rheumatoid arthritis. Tendinitis and tendon rupture have also occurred in patients taking fluoroquinolones who do not have the above risk factors. Tendon rupture can occur during or after completion of therapy; cases occurring up to several months after completion of therapy have been reported. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should be discontinued if the patient experiences pain, swelling, inflammation or rupture of a tendon. Patients should be advised to rest at the first sign of tendinitis or tendon rupture, and to contact their healthcare provider regarding changing to a non-quinolone antimicrobial drug.
Pregnant Women:
THE SAFETY AND EFFECTIVENESS OF CIPROFLOXACIN IN PREGNANT AND LACTATING WOMEN HAVE NOT BEEN ESTABLISHED. (See PRECAUTIONS: Pregnancy, and Nursing Mothers subsections.)Pediatrics:
Ciprofloxacin should be used in pediatric patients (less than 18 years of age) only for infections listed in the INDICATIONS AND USAGE section. An increased incidence of adverse events compared to controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues, has been observed. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
In pre-clinical studies, oral administration of ciprofloxacin caused lameness in immature dogs. Histopathological examination of the weight-bearing joints of these dogs revealed permanent lesions of the cartilage. Related quinolone-class drugs also produce erosions of cartilage of weight-bearing joints and other signs of arthropathy in immature animals of various species. (See ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY.)Cytochrome P450 (CYP450):
Ciprofloxacin is an inhibitor of the hepatic CYP1A2 enzyme pathway. Coadministration of ciprofloxacin and other drugs primarily metabolized by CYP1A2 (e.g. theophylline, methylxanthines, tizanidine) results in increased plasma concentrations of the coadministered drug and could lead to clinically significant pharmacodynamic side effects of the coadministered drug.Central Nervous System Disorders:
Convulsions, increased intracranial pressure, and toxic psychosis have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin may also cause central nervous system (CNS) events including: dizziness, confusion, tremors, hallucinations, depression, and, rarely, suicidal thoughts or acts. These reactions may occur following the first dose. If these reactions occur in patients receiving ciprofloxacin, the drug should be discontinued and appropriate measures instituted. As with all quinolones, ciprofloxacin should be used with caution in patients with known or suspected CNS disorders that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (e.g. severe cerebral arteriosclerosis, epilepsy), or in the presence of other risk factors that may predispose to seizures or lower the seizure threshold (e.g. certain drug therapy, renal dysfunction). (See PRECAUTIONS: General, Information for Patients, Drug Interactions and ADVERSE REACTIONS.)Theophylline:
SERIOUS AND FATAL REACTIONS HAVE BEEN REPORTED IN PATIENTS RECEIVING CONCURRENT ADMINISTRATION OF CIPROFLOXACIN AND THEOPHYLLINE. These reactions have included cardiac arrest, seizure, status epilepticus, and respiratory failure. Although similar serious adverse effects have been reported in patients receiving theophylline alone, the possibility that these reactions may be potentiated by ciprofloxacin cannot be eliminated. If concomitant use cannot be avoided, serum levels of theophylline should be monitored and dosage adjustments made as appropriate.Hypersensitivity Reactions:
Serious and occasionally fatal hypersensitivity (anaphylactic) reactions, some following the first dose, have been reported in patients receiving quinolone therapy. Some reactions were accompanied by cardiovascular collapse, loss of consciousness, tingling, pharyngeal or facial edema, dyspnea, urticaria, and itching. Only a few patients had a history of hypersensitivity reactions. Serious anaphylactic reactions require immediate emergency treatment with epinephrine. Oxygen, intravenous steroids, and airway management, including intubation, should be administered as indicated.
Other serious and sometimes fatal events, some due to hypersensitivity, and some due to uncertain etiology, have been reported rarely in patients receiving therapy with quinolones, including ciprofloxacin. These events may be severe and generally occur following the administration of multiple doses. Clinical manifestations may include one or more of the following:- fever, rash, or severe dermatologic reactions (e.g., toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome);
- vasculitis; arthralgia; myalgia; serum sickness;
- allergic pneumonitis;
- interstitial nephritis; acute renal insufficiency or failure;
- hepatitis; jaundice; acute hepatic necrosis or failure;
- anemia, including hemolytic and aplastic; thrombocytopenia, including thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; leukopenia; agranulocytosis; pancytopenia; and/or other hematologic abnormalities.
The drug should be discontinued immediately at the first appearance of a skin rash, jaundice, or any other sign of hypersensitivity and supportive measures instituted (See PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients and ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Pseudomembranous Colitis:
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
Peripheral neuropathy:
Rare cases of sensory or sensorimotor axonal polyneuropathy affecting small and/or large axons resulting in paresthesias, hypoesthesias, dysesthesias and weakness have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including ciprofloxacin. Ciprofloxacin should be discontinued if the patient experiences symptoms of neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness, and/or weakness, or is found to have deficits in light touch, pain, temperature, position sense, vibratory sensation, and/or motor strength in order to prevent the development of an irreversible condition.Syphilis:
Ciprofloxacin has not been shown to be effective in the treatment of syphilis. Antimicrobial agents used in high dose for short periods of time to treat gonorrhea may mask or delay the symptoms of incubating syphilis. All patients with gonorrhea should have a serologic test for syphilis at the time of diagnosis. Patients treated with ciprofloxacin should have a follow-up serologic test for syphilis after three months. -
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Crystals of ciprofloxacin have been observed rarely in the urine of human subjects but more frequently in the urine of laboratory animals, which is usually alkaline. (See ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY.) Crystalluria related to ciprofloxacin has been reported only rarely in humans because human urine is usually acidic. Alkalinity of the urine should be avoided in patients receiving ciprofloxacin. Patients should be well hydrated to prevent the formation of highly concentrated urine.
Central Nervous System:
Quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, may also cause central nervous system (CNS) events, including: nervousness, agitation, insomnia, anxiety, nightmares or paranoia. (See WARNINGS, Information for Patients, and Drug Interactions.)
Renal Impairment:
Alteration of the dosage regimen is necessary for patients with impairment of renal function. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Photosensitivity/Phototoxicity:
Moderate to severe photosensitivity/phototoxicity reactions, the latter of which may manifest as exaggerated sunburn reactions (e.g., burning, erythema, exudation, vesicles, blistering, edema) involving areas exposed to light (typically the face, “V” area of the neck, extensor surfaces of the forearms, dorsa of the hands), can be associated with the use of quinolones after sun or UV light exposure. Therefore, excessive exposure to these sources of light should be avoided. Drug therapy should be discontinued if phototoxicity occurs (See ADVERSE REACTIONS/Post-Marketing Adverse Events).
As with any potent drug, periodic assessment of organ system functions, including renal, hepatic, and hematopoietic function, is advisable during prolonged therapy.
Prescribing Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.Information for Patients:
Patients should be advised:- to contact their healthcare provider if they experience pain, swelling, or inflammation of a tendon, or weakness or inability to use one of their joints; rest and refrain from exercise; and discontinue Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg treatment. The risk of severe tendon disorder with fluoroquinolones is higher in older patients usually over 60 years of age, in patients taking corticosteroid drugs, and in patients with kidney, heart or lung transplants.
- that antibacterial drugs including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
- that ciprofloxacin may be taken with or without meals and to drink fluids liberally. As with other quinolones, concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin with magnesium/aluminum antacids, or sucralfate, Videx® (didanosine) chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder, other highly buffered drugs, or with other products containing calcium, iron or zinc should be avoided. Ciprofloxacin may be taken two hours before or six hours after taking these products. Ciprofloxacin should not be taken with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone since absorption of ciprofloxacin may be significantly reduced; however, ciprofloxacin may be taken with a meal that contains these products.
- that ciprofloxacin may be associated with hypersensitivity reactions, even following a single dose, and to discontinue the drug at the first sign of a skin rash or other allergic reaction.
- that photosensitivity/phototoxicity has been reported in patients receiving quinolones. Patients should minimize or avoid exposure to natural or artificial sunlight (tanning beds or UVA/B treatment) while taking quinolones. If patients need to be outdoors while using quinolones, they should wear loose-fitting clothes that protect skin from sun exposure and discuss other sun protection measures with their physician. If a sunburn-like reaction or skin eruption occurs, patients should contact their physician.
- that peripheral neuropathies have been associated with ciprofloxacin use. If symptoms of peripheral neuropathy including pain, burning, tingling, numbness and/or weakness develop, they should discontinue treatment and contact their physicians.
- that ciprofloxacin may cause dizziness and lightheadedness; therefore, patients should know how they react to this drug before they operate an automobile or machinery or engage in activities requiring mental alertness or coordination.
- that ciprofloxacin increases the effects of tizanidine (Zanaflex®). Patients should not use ciprofloxacin if they are already taking tizanidine.
- that ciprofloxacin may increase the effects of theophylline and caffeine. There is a possibility of caffeine accumulation when products containing caffeine are consumed while taking quinolones.
- that convulsions have been reported in patients receiving quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, and to notify their physician before taking this drug if there is a history of this condition.
- that ciprofloxacin has been associated with an increased rate of adverse events involving joints and surrounding tissue structures (like tendons) in pediatric patients (less than 18 years of age). Parents should inform their child’s physician if the child has a history of joint-related problems before taking this drug. Parents of pediatric patients should also notify their child’s physician of any joint-related problems that occur during or following ciprofloxacin therapy. (See WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use and ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
- that diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Drug Interactions:
In a pharmacokinetic study, systemic exposure of tizanidine (4 mg single dose) was significantly increased (Cmax 7-fold, AUC 10-fold) when the drug was given concomitantly with ciprofloxacin (500 mg bid for 3 days). The hypotensive and sedative effects of tizanidine were also potentiated. Concomitant administration of tizanidine and ciprofloxacin is contraindicated.
As with some other quinolones, concurrent administration of ciprofloxacin with theophylline may lead to elevated serum concentrations of theophylline and prolongation of its elimination half-life. This may result in increased risk of theophylline-related adverse reactions. (See WARNINGS.) If concomitant use cannot be avoided, serum levels of theophylline should be monitored and dosage adjustments made as appropriate.
Some quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, have also been shown to interfere with the metabolism of caffeine. This may lead to reduced clearance of caffeine and a prolongation of its serum half-life.
Concurrent administration of a quinolone, including ciprofloxacin, with multivalent cation-containing products such as magnesium/aluminum antacids, sucralfate, Videx® (didanosine) chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder, other highly buffered drugs, or products containing calcium, iron, or zinc may substantially decrease its absorption, resulting in serum and urine levels considerably lower than desired. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION for concurrent administration of these agents with ciprofloxacin.)
Histamine H2-receptor antagonists appear to have no significant effect on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin.
Altered serum levels of phenytoin (increased and decreased) have been reported in patients receiving concomitant ciprofloxacin.
The concomitant administration of ciprofloxacin with the sulfonylurea glyburide has, on rare occasions, resulted in severe hypoglycemia.
Some quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, have been associated with transient elevations in serum creatinine in patients receiving cyclosporine concomitantly.
Quinolones, including ciprofloxacin, have been reported to enhance the effects of the oral anticoagulant warfarin or its derivatives. When these products are administered concomitantly, prothrombin time or other suitable coagulation tests should be closely monitored.
Probenecid interferes with renal tubular secretion of ciprofloxacin and produces an increase in the level of ciprofloxacin in the serum. This should be considered if patients are receiving both drugs concomitantly.
Renal tubular transport of methotrexate may be inhibited by concomitant administration of ciprofloxacin potentially leading to increased plasma levels of methotrexate. This might increase the risk of methotrexate associated toxic reactions. Therefore, patients under methotrexate therapy should be carefully monitored when concomitant ciprofloxacin therapy is indicated.
Metoclopramide significantly accelerates the absorption of oral ciprofloxacin resulting in shorter time to reach maximum plasma concentrations. No significant effect was observed on the bioavailability of ciprofloxacin.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (but not acetyl salicylic acid) in combination of very high doses of quinolones have been shown to provoke convulsions in pre-clinical studies.Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Eight in vitro mutagenicity tests have been conducted with ciprofloxacin, and the test results are listed below:
Salmonella/Microsome Test (Negative)
E. coli DNA Repair Assay (Negative)
Mouse Lymphoma Cell Forward Mutation Assay (Positive)
Chinese Hamster V79 Cell HGPRT Test (Negative)
Syrian Hamster Embryo Cell Transformation Assay (Negative)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Point Mutation Assay (Negative)
Saccharomyces cerevisiae Mitotic Crossover and Gene Conversion Assay (Negative)
Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay (Positive)
Thus, 2 of the 8 tests were positive, but results of the following 3 in vivo test systems gave negative results:
Rat Hepatocyte DNA Repair Assay
Micronucleus Test (Mice)
Dominant Lethal Test (Mice)
Long-term carcinogenicity studies in rats and mice resulted in no carcinogenic or tumorigenic effects due to ciprofloxacin at daily oral dose levels up to 250 and 750 mg /kg to rats and mice, respectively (approximately 1.7- and 2.5-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2).
Results from photo co-carcinogenicity testing indicate that ciprofloxacin does not reduce the time to appearance of UV-induced skin tumors as compared to vehicle control. Hairless (Skh-1) mice were exposed to UVA light for 3.5 hours five times every two weeks for up to 78 weeks while concurrently being administered ciprofloxacin. The time to development of the first skin tumors was 50 weeks in mice treated concomitantly with UVA and ciprofloxacin (mouse dose approximately equal to maximum recommended human dose based upon mg/m2), as opposed to 34 weeks when animals were treated with both UVA and vehicle. The times to development of skin tumors ranged from 16-32 weeks in mice treated concomitantly with UVA and other quinolones.4
In this model, mice treated with ciprofloxacin alone did not develop skin or systemic tumors. There are no data from similar models using pigmented mice and/or fully haired mice. The clinical significance of these findings to humans is unknown.
Fertility studies performed in rats at oral doses of ciprofloxacin up to 100 mg/kg (approximately 0.7-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2) revealed no evidence of impairment.Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C:
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. An expert review of published data on experiences with ciprofloxacin use during pregnancy by TERIS - the Teratogen Information System - concluded that therapeutic doses during pregnancy are unlikely to pose a substantial teratogenic risk (quantity and quality of data=fair), but the data are insufficient to state that there is no risk.8
A controlled prospective observational study followed 200 women exposed to fluoroquinolones (52.5% exposed to ciprofloxacin and 68% first trimester exposures) during gestation.9 In utero exposure to fluoroquinolones during embryogenesis was not associated with increased risk of major malformations. The reported rates of major congenital malformations were 2.2% for the fluoroquinolone group and 2.6% for the control group (background incidence of major malformations is 1-5%). Rates of spontaneous abortions, prematurity and low birth weight did not differ between the groups and there were no clinically significant musculoskeletal dysfunctions up to one year of age in the ciprofloxacin exposed children.
Another prospective follow-up study reported on 549 pregnancies with fluoroquinolone exposure (93% first trimester exposures).10 There were 70 ciprofloxacin exposures, all within the first trimester. The malformation rates among live-born babies exposed to ciprofloxacin and to fluoroquinolones overall were both within background incidence ranges. No specific patterns of congenital abnormalities were found. The study did not reveal any clear adverse reactions due to in utero exposure to ciprofloxacin.
No differences in the rates of prematurity, spontaneous abortions, or birth weight were seen in women exposed to ciprofloxacin during pregnancy.8,9 However, these small post-marketing epidemiology studies, of which most experience is from short term, first trimester exposure, are insufficient to evaluate the risk for less common defects or to permit reliable and definitive conclusions regarding the safety of ciprofloxacin in pregnant women and their developing fetuses. Ciprofloxacin should not be used during pregnancy unless the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to both fetus and mother (see WARNINGS).
Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and mice using oral doses up to 100 mg/kg (0.6 and 0.3 times the maximum daily human dose based upon body surface area, respectively) and have revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus due to ciprofloxacin. In rabbits, oral ciprofloxacin dose levels of 30 and 100 mg/kg (approximately 0.4- and 1.3-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2) produced gastrointestinal toxicity resulting in maternal weight loss and an increased incidence of abortion, but no teratogenicity was observed at either dose level. After intravenous administration of doses up to 20 mg/kg (approximately 0.3-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2) no maternal toxicity was produced and no embryotoxicity or teratogenicity was observed. (See WARNINGS.)Nursing Mothers:
Ciprofloxacin is excreted in human milk. The amount of ciprofloxacin absorbed by the nursing infant is unknown. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in infants nursing from mothers taking ciprofloxacin, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.Pediatric Use:
Ciprofloxacin, like other quinolones, causes arthropathy and histological changes in weight-bearing joints of juvenile animals resulting in lameness. (See ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY.)Inhalational Anthrax (Post-Exposure)
Ciprofloxacin is indicated in pediatric patients for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure). The risk-benefit assessment indicates that administration of ciprofloxacin to pediatric patients is appropriate. For information regarding pediatric dosing in inhalational anthrax (post-exposure), see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis
Ciprofloxacin is indicated for the treatment of complicated urinary tract infections and pyelonephritis due to Escherichia coli. Although effective in clinical trials, ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the pediatric population due to an increased incidence of adverse events compared to the controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues. The rates of these events in pediatric patients with complicated urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis within six weeks of follow-up were 9.3% (31/335) versus 6% (21/349) for control agents. The rates of these events occurring at any time up to the one year follow-up were 13.7% (46/335) and 9.5% (33/349), respectively. The rate of all adverse events regardless of drug relationship at six weeks was 41% (138/335) in the ciprofloxacin arm compared to 31% (109/349) in the control arm. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS and CLINICAL STUDIES.)
Cystic Fibrosis
Short-term safety data from a single trial in pediatric cystic fibrosis patients are available. In a randomized, double-blind clinical trial for the treatment of acute pulmonary exacerbations in cystic fibrosis patients (ages 5-17 years), 67 patients received ciprofloxacin I.V. 10 mg/kg/dose q8h for one week followed by ciprofloxacin tablets 20 mg/kg/dose q12h to complete 10-21 days treatment and 62 patients received the combination of ceftazidime I.V. 50 mg/kg/dose q8h and tobramycin I.V. 3 mg/kg/dose q8h for a total of 10-21 days. Patients less than 5 years of age were not studied. Safety monitoring in the study included periodic range of motion examinations and gait assessments by treatment-blinded examiners. Patients were followed for an average of 23 days after completing treatment (range 0-93 days). This study was not designed to determine long term effects and the safety of repeated exposure to ciprofloxacin. Musculoskeletal adverse events in patients with cystic fibrosis were reported in 22% of the patients in the ciprofloxacin group and 21% in the comparison group. Decreased range of motion was reported in 12% of the subjects in the ciprofloxacin group and 16% in the comparison group. Arthralgia was reported in 10% of the patients in the ciprofloxacin group and 11% in the comparison group. Other adverse events were similar in nature and frequency between treatment arms. One of sixty-seven patients developed arthritis of the knee nine days after a ten day course of treatment with ciprofloxacin. Clinical symptoms resolved, but an MRI showed knee effusion without other abnormalities eight months after treatment. However, the relationship of this event to the patient’s course of ciprofloxacin can not be definitively determined, particularly since patients with cystic fibrosis may develop arthralgias/arthritis as part of their underlying disease process.Geriatric Use:
Geriatric patients are at increased risk for developing severe tendon disorders including tendon rupture when being treated with a fluoroquinolone such as Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg. This risk is further increased in patients receiving concomitant corticosteroid therapy. Tendinitis or tendon rupture can involve the Achilles, hand, shoulder, or other tendon sites and can occur during or after completion of therapy; cases occurring up to several months after fluoroquinolone treatment have been reported. Caution should be used when prescribing Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg to elderly patients especially those on corticosteroids. Patients should be informed of this potential side effect and advised to discontinue Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg and contact their healthcare provider if any symptoms of tendinitis or tendon rupture occur (See BOXED WARNING, WARNINGS, and ADVERSE REACTIONS/Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports).
In a retrospective analysis of 23 multiple-dose controlled clinical trials of ciprofloxacin encompassing over 3500 ciprofloxacin treated patients, 25% of patients were greater than or equal to 65 years of age and 10% were greater than or equal to 75 years of age. No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals on any drug therapy cannot be ruled out. Ciprofloxacin is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of adverse reactions may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. No alteration of dosage is necessary for patients greater than 65 years of age with normal renal function. However, since some older individuals experience reduced renal function by virtue of their advanced age, care should be taken in dose selection for elderly patients, and renal function monitoring may be useful in these patients. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
In general, elderly patients may be more susceptible to drug-associated effects on the QT interval. Therefore, precaution should be taken when using Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg with concomitant drugs that can result in prolongation of the QT interval (e.g., class IA or class III antiarrhythmics) or in patients with risk factors for torsade de pointes (e.g., known QT prolongation, uncorrected hypokalemia). -
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Adverse Reactions in Adult Patients:
During clinical investigations with oral and parenteral ciprofloxacin, 49,038 patients received courses of the drug. Most of the adverse events reported were described as only mild or moderate in severity, abated soon after the drug was discontinued, and required no treatment. Ciprofloxacin was discontinued because of an adverse event in 1% of orally treated patients.
The most frequently reported drug related events, from clinical trials of all formulations, all dosages, all drug-therapy durations, and for all indications of ciprofloxacin therapy were nausea (2.5%), diarrhea (1.6%), liver function tests abnormal (1.3%), vomiting (1%), and rash (1%).
Additional medically important events that occurred in less than 1% of ciprofloxacin patients are listed below.
BODY AS A WHOLE: headache, abdominal pain/discomfort, foot pain, pain, pain in extremities, injection site reaction (ciprofloxacin intravenous)
CARDIOVASCULAR: palpitation, atrial flutter, ventricular ectopy, syncope, hypertension, angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, cardiopulmonary arrest, cerebral thrombosis, phlebitis, tachycardia, migraine, hypotension
CENTRAL NERVOUS SYSTEM: restlessness, dizziness, lightheadedness, insomnia, nightmares, hallucinations, manic reaction, irritability, tremor, ataxia, convulsive seizures, lethargy, drowsiness, weakness, malaise, anorexia, phobia, depersonalization, depression, paresthesia, abnormal gait, grand mal convulsion
GASTROINTESTINAL: painful oral mucosa, oral candidiasis, dysphagia, intestinal perforation, gastrointestinal bleeding, cholestatic jaundice, hepatitis
HEMIC/LYMPHATIC: lymphadenopathy, petechia
METABOLIC/NUTRITIONAL: amylase increase, lipase increase
MUSCULOSKELETAL: arthralgia or back pain, joint stiffness, achiness, neck or chest pain, flare up of gout
RENAL/UROGENITAL: interstitial nephritis, nephritis, renal failure, polyuria, urinary retention, urethral bleeding, vaginitis, acidosis, breast pain
RESPIRATORY: dyspnea, epistaxis, laryngeal or pulmonary edema, hiccough, hemoptysis, bronchospasm, pulmonary embolism
SKIN/HYPERSENSITIVITY: allergic reaction, pruritus, urticaria, photosensitivity/phototoxicity reaction, flushing, fever, chills, angioedema, edema of the face, neck, lips, conjunctivae or hands, cutaneous candidiasis, hyperpigmentation, erythema nodosum, sweating
SPECIAL SENSES: blurred vision, disturbed vision (change in color perception, overbrightness of lights), decreased visual acuity, diplopia, eye pain, tinnitus, hearing loss, bad taste, chromatopsia
In several instances nausea, vomiting, tremor, irritability, or palpitation were judged by investigators to be related to elevated serum levels of theophylline possibly as a result of drug interaction with ciprofloxacin.
In randomized, double-blind controlled clinical trials comparing ciprofloxacin tablets (500 mg BID) to cefuroxime axetil (250 mg-500 mg BID) and to clarithromycin (500 mg BID) in patients with respiratory tract infections, ciprofloxacin demonstrated a CNS adverse event profile comparable to the control drugs.Adverse Reactions in Pediatric Patients:
Ciprofloxacin, administered I.V. and /or orally, was compared to a cephalosporin for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) or pyelonephritis in pediatric patients 1 to 17 years of age (mean age of 6 ± 4 years). The trial was conducted in the US, Canada, Argentina, Peru, Costa Rica, Mexico, South Africa, and Germany. The duration of therapy was 10 to 21 days (mean duration of treatment was 11 days with a range of 1 to 88 days). The primary objective of the study was to assess musculoskeletal and neurological safety within 6 weeks of therapy and through one year of follow-up in the 335 ciprofloxacin- and 349 comparator-treated patients enrolled.
An Independent Pediatric Safety Committee (IPSC) reviewed all cases of musculoskeletal adverse events as well as all patients with an abnormal gait or abnormal joint exam (baseline or treatment-emergent). These events were evaluated in a comprehensive fashion and included such conditions as arthralgia, abnormal gait, abnormal joint exam, joint sprains, leg pain, back pain, arthrosis, bone pain, pain, myalgia, arm pain, and decreased range of motion in a joint. The affected joints included: knee, elbow, ankle, hip, wrist, and shoulder. Within 6 weeks of treatment initiation, the rates of these events were 9.3% (31/335) in the ciprofloxacin-treated group versus 6% (21/349) in comparator-treated patients. The majority of these events were mild or moderate in intensity. All musculoskeletal events occurring by 6 weeks resolved (clinical resolution of signs and symptoms), usually within 30 days of end of treatment. Radiological evaluations were not routinely used to confirm resolution of the events. The events occurred more frequently in ciprofloxacin-treated patients than control patients, regardless of whether they received I.V. or oral therapy. Ciprofloxacin-treated patients were more likely to report more than one event and on more than one occasion compared to control patients. These events occurred in all age groups and the rates were consistently higher in the ciprofloxacin group compared to the control group. At the end of 1 year, the rate of these events reported at any time during that period was 13.7% (46/335) in the ciprofloxacin-treated group versus 9.5% (33/349) comparator-treated patients.
An adolescent female discontinued ciprofloxacin for wrist pain that developed during treatment. An MRI performed 4 weeks later showed a tear in the right ulnar fibrocartilage. A diagnosis of overuse syndrome secondary to sports activity was made, but a contribution from ciprofloxacin cannot be excluded. The patient recovered by 4 months without surgical intervention.
Findings Involving Joint or Peri-articular Tissues as Assessed by the IPSC Ciprofloxacin Comparator *The study was designed to demonstrate that the arthropathy rate for the ciprofloxacin group did not exceed
that of the control group by more than + 6%. At both the 6 week and 1 year evaluations, the 95% confidence
interval indicated that it could not be concluded that ciprofloxacin group had findings comparable to the control group.
All Patients (within 6 weeks)
31/335 (9.3%)
21/349 (6%)
95% Confidence Interval*
(-0.8%, +7.2%)
Age Group
≥ 12 months < 24 months
1/36 (2.8%)
0/41
≥ 2 years < 6 years
5/124 (4%)
3/118 (2.5%)
≥ 6 years < 12 years
18/143 (12.6%)
12/153 (7.8%)
≥ 12 years to 17 years
7/32 (21.9%)
6/37 (16.2 %)
All Patients (within 1 year)
46/335 (13.7%)
33/349 (9.5%)
95% Confidence Interval*
(-0.6%, + 9.1%)
The incidence rates of neurological events within 6 weeks of treatment initiation were 3% (9/335) in the ciprofloxacin group versus 2% (7/349) in the comparator group and included dizziness, nervousness, insomnia, and somnolence.
In this trial, the overall incidence rates of adverse events regardless of relationship to study drug and within 6 weeks of treatment initiation were 41% (138/335) in the ciprofloxacin group versus 31% (109/349) in the comparator group. The most frequent events were gastrointestinal: 15% (50/335) of ciprofloxacin patients compared to 9% (31/349) of comparator patients. Serious adverse events were seen in 7.5% (25/335) of ciprofloxacin-treated patients compared to 5.7% (20/349) of control patients. Discontinuation of drug due to an adverse event was observed in 3% (10/335) of ciprofloxacin-treated patients versus 1.4% (5/349) of comparator patients. Other adverse events that occurred in at least 1% of ciprofloxacin patients were diarrhea 4.8%, vomiting 4.8%, abdominal pain 3.3%, accidental injury 3%, rhinitis 3%, dyspepsia 2.7%, nausea 2.7%, fever 2.1%, asthma 1.8% and rash 1.8%.
In addition to the events reported in pediatric patients in clinical trials, it should be expected that events reported in adults during clinical trials or post-marketing experience may also occur in pediatric patients.Post-Marketing Adverse Event Reports:
The following adverse events have been reported from worldwide marketing experience with quinolones, including ciprofloxacin. Because these events are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure. Decisions to include these events in labeling are typically based on one or more of the following factors: (1) seriousness of the event, (2) frequency of the reporting, or (3) strength of causal connection to the drug.
Agitation, agranulocytosis, albuminuria, anaphylactic reactions (including life-threatening anaphylactic shock), anosmia, candiduria, cholesterol elevation (serum), confusion, constipation, delirium, dyspepsia, dysphagia, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, fixed eruption, flatulence, glucose elevation (blood), hemolytic anemia, hepatic failure (including fatal cases), hepatic necrosis, hyperesthesia, hypertonia, hypesthesia, hypotension (postural), jaundice, marrow depression (life threatening), methemoglobinemia, moniliasis (oral, gastrointestinal, vaginal), myalgia, myasthenia, myasthenia gravis (possible exacerbation), myoclonus, nystagmus, pancreatitis, pancytopenia (life threatening or fatal outcome), peripheral neuropathy, phenytoin alteration (serum), photosensitivity/phototoxicity reaction, potassium elevation (serum), prothrombin time prolongation or decrease, pseudomembranous colitis (The onset of pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may occur during or after antimicrobial treatment.), psychosis (toxic), renal calculi, serum sickness like reaction, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, taste loss, tendinitis, tendon rupture, torsade de pointes, toxic epidermal necrolysis (Lyell’s Syndrome), triglyceride elevation (serum), twitching, vaginal candidiasis, and vasculitis. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Adverse events were also reported by persons who received ciprofloxacin for anthrax post-exposure prophylaxis following the anthrax bioterror attacks of October 2001. (See also INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.)Adverse Laboratory Changes:
Changes in laboratory parameters listed as adverse events without regard to drug relationship are listed below:
Hepatic – Elevations of ALT (SGPT) (1.9%), AST (SGOT) (1.7%), alkaline phosphatase (0.8%), LDH (0.4%), serum bilirubin (0.3%).
Hematologic – Eosinophilia (0.6%), leukopenia (0.4%), decreased blood platelets (0.1%), elevated blood platelets (0.1%), pancytopenia (0.1%).
Renal – Elevations of serum creatinine (1.1%), BUN (0.9%), CRYSTALLURIA, CYLINDRURIA, AND HEMATURIA HAVE BEEN REPORTED.
Other changes occurring in less than 0.1% of courses were: elevation of serum gammaglutamyl transferase, elevation of serum amylase, reduction in blood glucose, elevated uric acid, decrease in hemoglobin, anemia, bleeding diathesis, increase in blood monocytes, leukocytosis. -
OVERDOSAGE
In the event of acute overdosage, reversible renal toxicity has been reported in some cases. The stomach should be emptied by inducing vomiting or by gastric lavage. The patient should be carefully observed and given supportive treatment, including monitoring of renal function and administration of magnesium, aluminum, or calcium containing antacids which can reduce the absorption of ciprofloxacin. Adequate hydration must be maintained. Only a small amount of ciprofloxacin (< 10%) is removed from the body after hemodialysis or peritoneal dialysis.
Single doses of ciprofloxacin were relatively non-toxic via the oral route of administration in mice, rats, and dogs. No deaths occurred within a 14-day post treatment observation period at the highest oral doses tested; up to 5000 mg/kg in either rodent species, or up to 2500 mg/kg in the dog. Clinical signs observed included hypoactivity and cyanosis in both rodent species and severe vomiting in dogs. In rabbits, significant mortality was seen at doses of ciprofloxacin > 2500 mg/kg. Mortality was delayed in these animals, occurring 10-14 days after dosing.
In mice, rats, rabbits and dogs, significant toxicity including tonic/clonic convulsions was observed at intravenous doses of ciprofloxacin between 125 and 300 mg/kg. -
DOSAGE & ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - ADULTS
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should be administered orally to adults as described in the Dosage Guidelines table.
The determination of dosage for any particular patient must take into consideration the severity and nature of the infection, the susceptibility of the causative organism, the integrity of the patient’s host-defense mechanisms, and the status of renal function and hepatic function.
The duration of treatment depends upon the severity of infection. The usual duration is 7 to 14 days; however, for severe and complicated infections more prolonged therapy may be required. Ciprofloxacin should be administered at least 2 hours before or 6 hours after magnesium/aluminum antacids, or sucralfate, Videx® (didanosine) chewable/buffered tablets or pediatric powder for oral solution, other highly buffered drugs, or other products containing calcium, iron or zinc.
ADULT DOSAGE GUIDELINES Infection Severity Dose Frequency Usual Durations† * used in conjunction with metronidazole
† Generally ciprofloxacin should be continued for at least 2 days after the signs and symptoms of infection
have disappeared, except for inhalational anthrax (post-exposure).
** Drug administration should begin as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed exposure.
This indication is based on a surrogate endpoint, ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans,
reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit.4 For a discussion of ciprofloxacin serum concentrations in various
human populations, see INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.
Urinary Tract
Acute Uncomplicated
250 mg
q 12 h
3 Days
Mild/Moderate
250 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 Days
Severe/Complicated
500 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 Days
Chronic Bacterial Prostatits
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
28 Days
Lower Respiratory Tract
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 days
Severe/Complicated
750 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 days
Acute Sinusitis
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
10 days
Skin and Skin Structure
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 Days
Severe/Complicated
750 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 Days
Bone and Joint
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
≥4 to 6 weeks
Severe/Complicated
750 mg
q 12 h
≥4 to 6 weeks
Intra-Abdominal*
Complicated
500 mg
q 12 h
7 to 14 Days
Infectious Diarrhea
Mild/Moderate/Severe
500 mg
q 12 h
5 to 7 Days
Typhoid Fever
Mild/Moderate
500 mg
q 12 h
10 Days
Urethral and Cervical
Gonococcal Infections
Uncomplicated
250 mg
single dose
single dose
Inhalational anthrax (post-exposure)**
500 mg
q 12 h
60 Days
Conversion of I.V. to Oral Dosing in Adults:
Patients whose therapy is started with CIPRO I.V. may be switched to Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg when clinically indicated at the discretion of the physician (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and table below for the equivalent dosing regimens).
Equivalent AUC Dosing Regimens Cipro Oral Dosage Equivalent Cipro I.V. Dosage 250 mg Tablet q 12 h
200 mg I.V. q 12 h
500 mg Tablet q 12 h
400 mg I.V. q 12 h
750 mg Tablet q 12 h
400 mg I.V. q 8 h
Adults with Impaired Renal Function:
Ciprofloxacin is eliminated primarily by renal excretion; however, the drug is also metabolized and partially cleared through the biliary system of the liver and through the intestine. These alternative pathways of drug elimination appear to compensate for the reduced renal excretion in patients with renal impairment. Nonetheless, some modification of dosage is recommended, particularly for patients with severe renal dysfunction. The following table provides dosage guidelines for use in patients with renal impairment:
RECOMMENDED STARTING AND MAINTENANCE DOSES FOR PATIENTS WITH IMPAIRED RENAL FUNCTION Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Dose > 50
See Usual Dosage.
30-50
250-500 mg q 12 h
5-29
250-500 mg q 18 h
Patients on hemodialysis
or Peritoneal dialysis
250-500 mg q 24 h
(after dialysis)
When only the serum creatinine concentration is known, the following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance.
Weight (kg) x (140 - age)
Men: Creatinine clearance (mL/min) = 72 x serum creatinine (mg/dL)
Women: 0.85 x the value calculated for men.
The serum creatinine should represent a steady state of renal function.
In patients with severe infections and severe renal impairment, a unit dose of 750 mg may be administered at the intervals noted above. Patients should be carefully monitored.DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION - PEDIATRICS
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg should be administered orally as described in the Dosage Guidelines table. An increased incidence of adverse events compared to controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues, has been observed. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS and CLINICAL STUDIES.)
Dosing and initial route of therapy (i.e., I.V. or oral) for complicated urinary tract infection or pyelonephritis should be determined by the severity of the infection. In the clinical trial, pediatric patients with moderate to severe infection were initiated on 6 to 10 mg/kg I.V. every 8 hours and allowed to switch to oral therapy (10 to 20 mg/kg every 12 hours), at the discretion of the physician.
PEDIATRIC DOSAGE GUIDELINES Infection Route of
AdministrationDose
(mg/kg)Frequency Total
Duration* The total duration of therapy for complicated urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis in
the clinical trial was determined by the physician. The mean duration of treatment was
11 days (range 10 to 21 days).
** Drug administration should begin as soon as possible after suspected or confirmed
exposure to Bacillus anthracis spores. This indication is based on a surrogate endpoint,
ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans, reasonably likely to predict
clinical benefit.5 For a discussion of ciprofloxacin serum concentrations in various
human populations, see INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION.
Complicated
Urinary Tract or
Pyelonephritis
Intravenous
6 to 10 mg/kg
(maximum 400 mg
per dose; not to be exceeded
even in patients weighing
> 51 kg)
Every 8 hours
10-21 days*
(patients from
1 to 17 years of
age)
Oral
10 mg/kg to 20 mg/kg
(maximum 750 mg per
dose; not to be exceeded
even in patients weighing
> 51 kg)
Every 12 hours
Inhalational
Anthrax
(Post-Exposure)**
Intravenous
10 mg/kg
(maximum 400 mg per
dose)
Every 12 hours
60 days
Oral
15 mg/kg
(maximum 500 mg per dose)
Every 12 hours
Pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency were excluded from the clinical trial of complicated urinary tract infection and pyelonephritis. No information is available on dosing adjustments necessary for pediatric patients with moderate to severe renal insufficiency (i.e., creatinine clearance of < 50 mL/min/1.73m2). -
HOW SUPPLIED
Ciprofloxacin Tablets are available as round biconvex white to slightly yellowish film coated tablets containing 250 mg of ciprofloxacin. The 250 mg tablet is embossed with the word "P" on one side and "250" on reverse side. The 500 mg and 750 mg tablet are available as capsule shaped, white to slightly yellowish film coated tablets with the word "P" embossed on one side and "500" or "750" on reverse side, respectively.
Strength NDC Code Tablet Identification Bottles of 50: 250 mg
500 mg
750 mgNDC: 16571-411-05
NDC: 16571-412-05
NDC: 16571-413-05P 250
P 500
P 750Bottles of 100: 250 mg
500 mg
750 mgNDC: 16571-411-10
NDC: 16571-412-10
NDC: 16571-413-10P 250
P 500
P 750Bottles of 500: 250 mg
500 mg
750 mgNDC: 16571-411-50
NDC: 16571-412-50
NDC: 16571-413-50P 250
P 500
P 750Store below 30°C (86°F).
Manufactured by:
Unique Pharmaceutical Laboratories
Neelam Centre, Hind Cycle Road
Worli, Mumbai 400 025, IndiaDistributed by:
PACK Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Buffalo Grove, IL 60089 USA -
ANIMAL PHARMACOLOGY
Ciprofloxacin and other quinolones have been shown to cause arthropathy in immature animals of most species tested. (See WARNINGS.) Damage of weight bearing joints was observed in juvenile dogs and rats. In young beagles, 100 mg/kg ciprofloxacin, given daily for 4 weeks, caused degenerative articular changes of the knee joint. At 30 mg/kg, the effect on the joint was minimal. In a subsequent study in young beagle dogs, oral ciprofloxacin doses of 30 mg/kg and 90 mg/kg ciprofloxacin (approximately 1.3- and 3.5-times the pediatric dose based upon comparative plasma AUCs) given daily for 2 weeks caused articular changes which were still observed by histopathology after a treatment-free period of 5 months. At 10 mg/kg (approximately 0.6-times the pediatric dose based upon comparative plasma AUCs), no effects on joints were observed. This dose was also not associated with arthrotoxicity after an additional treatment-free period of 5 months. In another study, removal of weight bearing from the joint reduced the lesions but did not totally prevent them.
Crystalluria, sometimes associated with secondary nephropathy, occurs in laboratory animals dosed with ciprofloxacin. This is primarily related to the reduced solubility of ciprofloxacin under alkaline conditions, which predominate in the urine of test animals; in man, crystalluria is rare since human urine is typically acidic. In rhesus monkeys, crystalluria without nephropathy was noted after single oral doses as low as 5 mg/kg. (approximately 0.07-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2). After 6 months of intravenous dosing at 10 mg/kg/day, no nephropathological changes were noted; however, nephropathy was observed after dosing at 20 mg/kg/day for the same duration (approximately 0.2-times the highest recommended therapeutic dose based upon mg/m2).
In dogs, ciprofloxacin at 3 and 10 mg/kg by rapid I.V. injection (15 sec.) produces pronounced hypotensive effects. These effects are considered to be related to histamine release, since they are partially antagonized by pyrilamine, an antihistamine. In rhesus monkeys, rapid I.V. injection also produces hypotension but the effect in this species is inconsistent and less pronounced.
In mice, concomitant administration of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs such as phenylbutazone and indomethacin with quinolones has been reported to enhance the CNS stimulatory effect of quinolones.
Ocular toxicity seen with some related drugs has not been observed in ciprofloxacin-treated animals. -
CLINICAL STUDIES
Complicated Urinary Tract Infection and Pyelonephritis – Efficacy in Pediatric Patients:
NOTE: Although effective in clinical trials, ciprofloxacin is not a drug of first choice in the pediatric population due to an increased incidence of adverse events compared to controls, including events related to joints and/or surrounding tissues.
Ciprofloxacin, administered I.V. and/or orally, was compared to a cephalosporin for treatment of complicated urinary tract infections (cUTI) and pyelonephritis in pediatric patients 1 to 17 years of age (mean age of 6 ± 4 years). The trial was conducted in the US, Canada, Argentina, Peru, Costa Rica, Mexico, South Africa, and Germany. The duration of therapy was 10 to 21 days (mean duration of treatment was 11 days with a range of 1 to 88 days). The primary objective of the study was to assess musculoskeletal and neurological safety.
Patients were evaluated for clinical success and bacteriological eradication of the baseline organism(s) with no new infection or superinfection at 5 to 9 days post-therapy (Test of Cure or TOC). The Per Protocol population had a causative organism(s) with protocol specified colony count(s) at baseline, no protocol violation, and no premature discontinuation or loss to follow-up (among other criteria).
The clinical success and bacteriologic eradication rates in the Per Protocol population were similar between ciprofloxacin and the comparator group as shown below.
Clinical Success and Bacteriologic Eradication at Test of Cure (5 to 9 Days Post-Therapy) Ciprofloxacin Comparator * Patients with baseline pathogen(s) eradicated and no new infections or
superinfections/total number of patients. There were 5.5% (6/211) ciprofloxacin and
9.5% (22/231) comparator patients with superinfections or new infections.
Randomized Patients
337
352
Per Protocol Patients
211
231
Clinical Response at 5 to 9 Days
Post-Treatment
95.7% (202/211)
92.6% (214/231)
95% CI [-1.3%, 7.3%]
Bacteriologic Eradication by
Patient at 5 to 9 Days
Post-Treatment*
84.4% (178/211)
78.3% (181/231)
95% CI [-1.3%, 13.1%]
Bacteriologic Eradication of the
Baseline Pathogen at 5 to 9 Days
Post-Treatment
Escherichia coli
156/178 (88%)
161/179 (90%)
INHALATIONAL ANTHRAX IN ADULTS AND PEDIATRICS – ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
The mean serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin associated with a statistically significant improvement in survival in the rhesus monkey model of inhalational anthrax are reached or exceeded in adult and pediatric patients receiving oral and intravenous regimens. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) Ciprofloxacin pharmacokinetics have been evaluated in various human populations. The mean peak serum concentration achieved at steady-state in human adults receiving 500 mg orally every 12 hours is 2.97 μg/mL, and 4.56 μg/mL following 400 mg intravenously every 12 hours. The mean trough serum concentration at steady-state for both of these regimens is 0.2 μg/mL. In a study of 10 pediatric patients between 6 and 16 years of age, the mean peak plasma concentration achieved is 8.3 μg/mL and trough concentrations range from 0.09 to 0.26 μg/mL, following two 30-minute intravenous infusions of 10 mg/kg administered 12 hours apart. After the second intravenous infusion patients switched to 15 mg/kg orally every 12 hours achieve a mean peak concentration of 3.6 μg/mL after the initial oral dose. Long-term safety data, including effects on cartilage, following the administration of ciprofloxacin to pediatric patients are limited. (For additional information, see PRECAUTIONS, Pediatric Use.) Ciprofloxacin serum concentrations achieved in humans serve as a surrogate endpoint reasonably likely to predict clinical benefit and provide the basis for this indication.5
A placebo-controlled animal study in rhesus monkeys exposed to an inhaled mean dose of 11 LD50 (~5.5 x 105 spores (range 5-30 LD50) of B. anthracis was conducted. The minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of ciprofloxacin for the anthrax strain used in this study was 0.08 μg/mL. In the animals studied, mean serum concentrations of ciprofloxacin achieved at expected Tmax (1 hour post-dose) following oral dosing to steady-state ranged from 0.98 to 1.69 μg/mL. Mean steady-state trough concentrations at 12 hours post-dose ranged from 0.12 to 0.19 μg/mL.6 Mortality due to anthrax for animals that received a 30-day regimen of oral ciprofloxacin beginning 24 hours post-exposure was significantly lower (1/9), compared to the placebo group (9/10) [p=0.001]. The one ciprofloxacin-treated animal that died of anthrax did so following the 30-day drug administration period.7
More than 9300 persons were recommended to complete a minimum of 60 days of antibiotic prophylaxis against possible inhalational exposure to B. anthracis during 2001. Ciprofloxacin was recommended to most of those individuals for all or part of the prophylaxis regimen. Some persons were also given anthrax vaccine or were switched to alternative antibiotics. No one who received ciprofloxacin or other therapies as prophylactic treatment subsequently developed inhalational anthrax. The number of persons who received ciprofloxacin as all or part of their post-exposure prophylaxis regimen is unknown.
Among the persons surveyed by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, over 1000 reported receiving ciprofloxacin as sole post-exposure prophylaxis for inhalational anthrax. Gastrointestinal adverse events (nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, or stomach pain), neurological adverse events (problems sleeping, nightmares, headache, dizziness or lightheadedness) and musculoskeletal adverse events (muscle or tendon pain and joint swelling or pain) were more frequent than had been previously reported in controlled clinical trials. This higher incidence, in the absence of a control group, could be explained by a reporting bias, concurrent medical conditions, other concomitant medications, emotional stress or other confounding factors, and/or a longer treatment period with ciprofloxacin. Because of these factors and limitations in the data collection, it is difficult to evaluate whether the reported symptoms were drug-related. -
REFERENCES:
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically-Fifth Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M7-A5, Vol. 20, No. 2, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 2000.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, Methods for Antimicrobial Dilution and Disk Susceptibility Testing of Infrequently Isolated or Fastidious Bacteria; Approved Guideline., CLSI Document M45-A, Vol. 26, No. 19, CLSI, Wayne, PA, 2006.
- National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests-Seventh Edition. Approved Standard NCCLS Document M2-A7, Vol. 20, No. 1, NCCLS, Wayne, PA, January, 2000.
- Report presented at the FDA’s Anti-Infective Drug and Dermatological Drug Product’s Advisory Committee meeting, March 31, 1993, Silver Spring, MD. Report available from FDA, CDER, Advisors and Consultants Staff, HFD-21, 1901 Chapman Avenue, Room 200, Rockville, MD 20852, USA.
- 21 CFR 314.510 (Subpart H – Accelerated Approval of New Drugs for Life-Threatening Illnesses).
- Kelly DJ, et al. Serum concentrations of penicillin, doxycycline, and ciprofloxacin during prolonged therapy in rhesus monkeys. J Infect Dis 1992; 166:1184-7.
- Friedlander AM, et al. Postexposure prophylaxis against experimental inhalational anthrax. J Infect Dis 1993; 167:1239-42.
- Friedman J, Polifka J. Teratogenic effects of drugs: a resource for clinicians (TERIS). Baltimore, Maryland: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2000:149-195.
- Loebstein R, Addis A, Ho E, et al. Pregnancy outcome following gestational exposure to fluoroquinolones: a multicenter prospective controlled study. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1998;42(6):1336-1339.
- Schaefer C, Amoura-Elefant E, Vial T, et al. Pregnancy outcome after prenatal quinolone exposure. Evaluation of a case registry of the European network of teratology information services (ENTIS). Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 1996;69:83-89.
-
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, 250 mg, 500 mg and 750 mg
Read the Medication Guide that comes with Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP before you start taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is the most important information I should know about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP ?
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP belongs to a class of antibiotics called fluoroquinolones. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP can cause side effects that may be serious or even cause death. If you get any of the following serious side effects, get medical help right away. Talk with your healthcare provider about whether you should continue to take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP.
Tendon rupture or swelling of the tendon (tendinitis)
- Tendons are tough cords of tissue that connect muscles to bones.
- Pain, swelling, tears and inflammation of tendons including the back of the ankle (Achilles), shoulder, hand, or other tendon sites can happen in people of all ages who take fluoroquinolone antibiotics, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. The risk of getting tendon problems is higher if you:
- are over 60 years of age
- are taking steroids (corticosteroids)
- have had a kidney, heart or lung transplant
- Swelling of the tendon (tendinitis) and tendon rupture (breakage) have also happened in patients who take fluoroquinolones who do not have the above risk factors.
- Other reasons for tendon ruptures can include:
- physical activity or exercise
- kidney failure
- tendon problems in the past, such as in people with rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Call your healthcare provider right away at the first sign of tendon pain, swelling or inflammation. Stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP until tendinitis or tendon rupture has been ruled out by your healthcare provider. Avoid exercise and using the affected area. The most common area of pain and swelling is the Achilles tendon at the back of your ankle. This can also happen with other tendons. Talk to your healthcare provider about the risk of tendon rupture with continued use of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. You may need a different antibiotic that is not a fluoroquinolone to treat your infection.
- Tendon rupture can happen while you are taking or after you have finished taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Tendon ruptures have happened up to several months after patients have finished taking their fluoroquinolone.
- Get medical help right away if you get any of the following signs or symptoms of a tendon rupture:
- hear or feel a snap or pop in a tendon area
- bruising right after an injury in a tendon area
- unable to move the affected area or bear weight
- See the section “What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?” for more information about side effects.
What is Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic medicine used to treat certain infections caused by certain germs called bacteria.
Children less than 18 years of age have a higher chance of getting bone, joint, or tendon (musculoskeletal) problems such as pain or swelling while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP should not be used as the first choice of antibiotic medicine in children under 18 years of age.
Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP should not be used in children under 18 years old, except to treat specific serious infections, such as complicated urinary tract infections and to prevent anthrax disease after breathing the anthrax bacteria germ (inhalational exposure). It is not known if Ciprofloxacin Extended Release Tablets are safe and work in children under 18 years of age.
Sometimes infections are caused by viruses rather than by bacteria. Examples include viral infections in the sinuses and lungs, such as the common cold or flu. Antibiotics, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, do not kill viruses.
Call your healthcare provider if you think your condition is not getting better while you are taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP.
Who should not take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
Do not take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP if you:
- have ever had a severe allergic reaction to an antibiotic known as a fluoroquinolone, or are allergic to any of the ingredients in Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure. See the list of ingredients in Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP at the end of this Medication Guide.
- also take a medicine called tizanidine (Zanaflex®). Serious side effects from tizanidine are likely to happen.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
See “What is the most important information I should know about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
Tell your healthcare provider about all your medical conditions, including if you:
- have tendon problems
- have central nervous system problems (such as epilepsy)
- have nerve problems
- have or anyone in your family has an irregular heartbeat, especially a condition called “QT prolongation”
- have a history of seizures
- have kidney problems. You may need a lower dose of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP if your kidneys do not work well.
- have rheumatoid arthritis (RA) or other history of joint problems
- have trouble swallowing pills
- are pregnant or planning to become pregnant. It is not known if Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP will harm your unborn child.
- are breast-feeding or planning to breast-feed. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP passes into breast milk. You and your healthcare provider should decide whether you will take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP or breast-feed.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins and herbal and dietary supplements. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and other medicines can affect each other causing side effects. Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- an NSAID (Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drug). Many common medicines for pain relief are NSAIDs. Taking an NSAID while you take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP or other fluoroquinolones may increase your risk of central nervous system effects and seizures. See “What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
- a blood thinner (warfarin, Coumadin®, Jantoven®)
- tizanidine (Zanaflex®). You should not take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP if you are already taking tizanidine. See “Who should not take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
- theophylline (Theo-24®, Elixophyllin®, Theochron®, Uniphyl®, Theolair®)
- glyburide (Micronase®, Glynase®, Diabeta®, Glucovance®). See “What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
- phenytoin (Fosphenytoin Sodium®, Cerebyx®, Dilantin-125®, Dilantin®, Extended Phenytoin Sodium®, Prompt Penytoin Sodium®, Phenytek®)
- products that contain caffeine
- a medicine to control your heart rate or rhythm (antiarrhythmics) See “What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
- an anti-psychotic medicine
- a tricyclic antidepressant
- a water pill (diuretic)
- a steroid medicine. Corticosteroids taken by mouth or by injection may increase the chance of tendon injury. See “What is the most important information I should know about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
- methotrexate (Trexall®)
- Probenecid (Probalan®, Col-probenecid®)
- Metoclopromide (Reglan®, Reglan ODT®)
- Certain medicines may keep Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP from working correctly.
Take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP either 2 hours before or 6 hours after taking
these products:
- an antacid, multivitamin, or other product that has magnesium, calcium, aluminum, iron, or zinc
- sucralfate (Carafate®)
- didanosine (Videx®, Videx EC®)
Ask your healthcare provider if you are not sure if any of your medicines are listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
- Take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP in the morning and evening at about the same time each day. Swallow the tablet whole. Do not split, crush or chew the tablet. Tell your healthcare provider if you can not swallow the tablet whole.
- Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP can be taken with or without food.
- Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP should not be taken with dairy products (like milk or yogurt) or calcium-fortified juices alone, but may be taken with a meal that contains these products.
- Drink plenty of fluids while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP.
- Do not skip any doses, or stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP even if you begin to feel better, until you finish your prescribed treatment, unless:
- you have tendon effects (see “What is the most important information I should know about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”),
- you have a serious allergic reaction (see “What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”), or
- your healthcare provider tells you to stop.
- This will help make sure that all of the bacteria are killed and lower the chance that the bacteria will become resistant to Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. If this happens, Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and other antibiotic medicines may not work in the future.
- If you miss a dose of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, take it as soon as you remember. Do not take two doses at the same time, and do not take more than two doses in one day.
- If you take too much, call your healthcare provider or get medical help immediately.
If you have been prescribed Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP after being exposed to anthrax:
- Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP has been approved to lessen the chance of getting anthrax disease or worsening of the disease after you are exposed to the anthrax bacteria germ.
- Take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Do not stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP without talking with your healthcare provider. If you stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP too soon, it may not keep you from getting the anthrax disease.
- Side effects may happen while you are taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. When taking your Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP to prevent anthrax infection, you and your healthcare provider should talk about whether the risks of stopping Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP too soon are more important than the risks of side effects with Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP.
- If you are pregnant, or plan to become pregnant while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, you and your healthcare provider should decide whether the benefits of taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP for anthrax are more important than the risks.
What should I avoid while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
- Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP can make you feel dizzy and lightheaded. Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other activities that require mental alertness or coordination until you know how Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP affects you.
- Avoid sunlamps, tanning beds, and try to limit your time in the sun. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP can make your skin sensitive to the sun (photosensitivity) and the light from sunlamps and tanning beds. You could get severe sunburn, blisters or swelling of your skin. If you get any of these symptoms while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, call your healthcare provider right away. You should use a sunscreen and wear a hat and clothes that cover your skin if you have to be in sunlight.
What are the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
- Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP can cause side effects that may be serious or even cause death. See “What is the most important information I should know about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?”
Other serious side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP include:
-
Central Nervous System effects: Seizures have been reported in people who take
fluoroquinolone antibiotics including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Tell your
healthcare provider if you have a history of seizures. Ask your healthcare provider
whether taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP will change your risk of having a
seizure.
Central Nervous System (CNS) side effects may happen as soon as after taking the first dose of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Talk to your healthcare provider right away if you get any of these side effects, or other changes in mood or behavior:- feel dizzy
- seizures
- hear voices, see things, or sense things that are not there (hallucinations)
- feel restless
- tremors
- feel anxious or nervous
- confusion
- depression
- trouble sleeping
- nightmares
- feel more suspicious (paranoia)
- suicidal thoughts or acts
-
Serious allergic reactions: Allergic reactions can happen in people taking
fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP, even after only one dose.
Stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and get emergency medical help right away if
you get any of the following symptoms of a severe allergic reaction:
- hives
- trouble breathing or swallowing
- swelling of the lips, tongue, face
- throat tightness, hoarseness
- rapid heartbeat
- faint
- yellowing of the skin or eyes. Stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and tell your healthcare provider right away if you get yellowing of your skin or white part of your eyes, or if you have dark urine. These can be signs of a serious reaction to Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP (a liver problem).
-
Skin rash
Skin rash may happen in people taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP even after only one dose. Stop taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP at the first sign of a skin rash and call your healthcare provider. Skin rash may be a sign of a more serious reaction to Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. -
Serious heart rhythm changes (QT prolongation and torsade de pointes)
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have a change in your heart beat (a fast or irregular heartbeat), or if you faint. Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP may cause a rare heart problem known as prolongation of the QT interval. This condition can cause an abnormal heartbeat and can be very dangerous. The chances of this event are higher in people:- who are elderly
- with a family history of prolonged QT interval
- with low blood potassium (hypokalemia)
- who take certain medicines to control heart rhythm (antiarrhythmics)
-
Intestine infection (Pseudomembranous colitis)
Pseudomembranous colitis can happen with most antibiotics, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Call your healthcare provider right away if you get watery diarrhea, diarrhea that does not go away, or bloody stools. You may have stomach cramps and a fever. Pseudomembranous colitis can happen 2 or more months after you have finished your antibiotic. -
Changes in sensation and possible nerve damage (Peripheral Neuropathy)
Damage to the nerves in arms, hands, legs, or feet can happen in people who take fluoroquinolones, including Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Talk with your healthcare provider right away if you get any of the following symptoms of peripheral neuropathy in your arms, hands, legs, or feet:- pain
- burning
- tingling
- numbness
- weakness
Ciprofloxacin tablets may need to be stopped to prevent permanent nerve damage. -
Low blood sugar (hypoglycemia)
People who take Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and other fluoroquinolone medicines with the oral anti-diabetes medicine glyburide (Micronase, Glynase, Diabeta, Glucovance) can get low blood sugar (hypoglycemia) which can sometimes be severe. Tell your healthcare provider if you get low blood sugar with CIPRO. Your antibiotic medicine may need to be changed. -
Sensitivity to sunlight (photosensitivity)
See “What should I avoid while taking Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?” -
Joint Problems
Increased chance of problems with joints and tissues around joints in children under 18 years old. Tell your child’s healthcare provider if your child has any joint problems during or after treatment with Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP.
The most common side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP include:- nausea
- headache
- diarrhea
- vomiting
- vaginal yeast infection
- changes in liver function tests
- pain or discomfort in the abdomen
These are not all the possible side effects of Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. Tell your healthcare provider about any side effect that bothers you, or that does not go away.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
- Store Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP below 86°F (30°C)
Keep Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP for a condition for which it is not prescribed. Do not give Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP. If you would like more information about CIPRO, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP that is written for healthcare professionals.
For more information 1-(866)-562-4597
What are the ingredients in Ciprofloxacin Tablets USP?
- Active ingredient: ciprofloxacin
- Inactive ingredients: pregelatinized starch, microcrystalline cellulose, colloidal silicon dioxide, crospovidone, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, titanium dioxide, polyethylene glycol and purified water
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured by:
Unique Pharmaceutical Laboratories
(A Div. of J. B. Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd)
Mumbai 400 030, IndiaDistributed by:
PACK Pharmaceuticals, LLC,
Buffalo Grove, IL 60089 USA - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CIPROFLOXACIN
ciprofloxacin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16590-054(NDC:16571-412) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 4BA73M5E37) (CIPROFLOXACIN - UNII:5E8K9I0O4U) CIPROFLOXACIN HYDROCHLORIDE 500 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) CROSPOVIDONE (UNII: 68401960MK) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSE (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color white (WHITE TO SLIGHTLY YELLOWISH) Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code P;500 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16590-054-10 10 in 1 BOTTLE 2 NDC: 16590-054-14 14 in 1 BOTTLE 3 NDC: 16590-054-20 20 in 1 BOTTLE 4 NDC: 16590-054-28 28 in 1 BOTTLE 5 NDC: 16590-054-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE 6 NDC: 16590-054-40 40 in 1 BOTTLE 7 NDC: 16590-054-71 100 in 1 BOTTLE 7 NDC: 16590-054-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE 8 NDC: 16590-054-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076639 09/10/2004 Labeler - STAT RX USA LLC (786036330) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations STAT TX USA LLC 786036330 repack, relabel
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
 CIPROFLOXACIN 500MG LABEL IMAGE
CIPROFLOXACIN 500MG LABEL IMAGE