METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, extended release
Methylphenidate hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Methylphenidate hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Alvogen Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE EXTENDED-RELEASE TABLETS.
METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE extended-release tablets, for oral use CII
Initial U.S. Approval: 2000WARNING: DRUG DEPENDENCE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets should be given cautiously to patients with a history of drug dependence or alcoholism. Chronic abusive use can lead to marked tolerance and psychological dependence, with varying degrees of abnormal behavior.
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets are a CNS stimulant indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children 6 years of age and older, adolescents, and adults up to the age of 65. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets should be taken once daily in the morning and swallowed whole with the aid of liquids. Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets should not be chewed or crushed. Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets may be taken with or without food. (2.1)
- For children and adolescents new to methylphenidate, the recommended starting dosage is 18 mg once daily. Dosage may be increased by 18 mg/day at weekly intervals and should not exceed 54 mg/day in children and 72 mg/day in adolescents. (2.2)
- For adult patients new to methylphenidate, the recommended starting dose is 18 mg/day or 36 mg/day. Dosage may be increased by 18 mg/day at weekly intervals and should not exceed 72 mg/day for adults. (2.2)
- For patients currently using methylphenidate, dosing is based on current dose regimen and clinical judgment. (2.3)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 18 mg, 27 mg, 36 mg, and 54 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Known hypersensitivity to the product (4.1)
- Marked anxiety, tension, or agitation (4.2)
- Glaucoma (4.3)
- Tics or a family history or diagnosis of Tourette's syndrome (4.4)
- Do not use methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in patients currently using or within 2 weeks of using an MAO inhibitor (4.5)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Cardiovascular Events: Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at usual doses in children and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. Sudden death, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults taking stimulant drugs at usual doses for ADHD. Stimulant products generally should not be used in patients with known structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart rhythm abnormalities, coronary artery disease, or other serious heart problems. (5.1)
- Increase in Blood Pressure: Monitor patients for changes in heart rate and blood pressure and use with caution in patients for whom an increase in blood pressure or heart rate would be problematic. (5.1)
- Psychiatric Adverse Events: Use of stimulants may cause treatment-emergent psychotic or manic symptoms in patients with no prior history, or exacerbation of symptoms in patients with preexisting psychiatric illness. Clinical evaluation for Bipolar Disorder is recommended prior to stimulant use. Monitor for aggressive behavior. (5.2)
- Seizures: Stimulants may lower the convulsive threshold. Discontinue in the presence of seizures. (5.3)
- Priapism: cases of painful and prolonged penile erections and priapism have been reported with methylphenidate products. Immediate medical attention should be sought if signs or symptoms of painful or prolonged penile erections or priapism are observed. (5.4)
- Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon: Stimulants used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. (5.5)
- Visual Disturbance: difficulties with accommodation and blurring of vision have been reported with stimulant treatment. (5.7)
- Long-Term Suppression of Growth: monitor height and weight at appropriate intervals in pediatric patients. (5.6)
- Gastrointestinal obstruction with preexisting GI narrowing. (5.8)
- Hematologic monitoring: Periodic CBC, differential, and platelet counts are advised during prolonged therapy. (5.9)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reaction in double-blind clinical trials (>5%) in children and adolescents was abdominal pain upper. The most common adverse reactions in double-blind clinical trials (>5%) in adult patients were decreased appetite, headache, dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, anxiety, dizziness, weight decreased, irritability, and hyperhidrosis. (6.1 and 6.2)
The most common adverse reactions associated with discontinuation (≥1%) from either pediatric or adult clinical trials were anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and blood pressure increased. (6.3)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Alvogen, Inc. at 1-866-770-3024 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Do not use methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in patients currently using or within 2 weeks of using an MAO inhibitor (7.1)
- Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets may increase blood pressure; use cautiously with vasopressors (7.2)
- Inhibition of metabolism of coumarin anticoagulants, anticonvulsants, and some antidepressants (7.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 10/2018
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: DRUG DEPENDENCE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Special Diagnostic Considerations
1.2 Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Patients New to Methylphenidate
2.3 Patients Currently Using Methylphenidate
2.4 Dose Titration
2.5 Maintenance/Extended Treatment
2.6 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Methylphenidate
4.2 Agitation
4.3 Glaucoma
4.4 Tics
4.5 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Cardiovascular Events
5.2 Psychiatric Adverse Events
5.3 Seizures
5.4 Priapism
5.5 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon
5.6 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
5.7 Visual Disturbance
5.8 Potential for Gastrointestinal Obstruction
5.9 Hematologic Monitoring
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
6.2 Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Clinical Trials
6.3 Discontinuation Due to Adverse Reactions
6.4 Tics
6.5 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
6.6 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 MAO Inhibitors
7.2 Vasopressor Agents
7.3 Coumarin Anticoagulants, Antidepressants, and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Labor and Delivery
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
9.2 Abuse
9.3 Dependence
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
10.2 Recommended Treatment
10.3 Poison Control Center
11 DESCRIPTION
11.1 System Components and Performance
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Children
14.2 Adolescents
14.3 Adults
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- BOXED WARNING (What is this?)
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are indicated for the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in children 6 years of age and older, adolescents, and adults up to the age of 65 [see Clinical Studies (14)].
A diagnosis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD; DSM-IV) implies the presence of hyperactive-impulsive or inattentive symptoms that caused impairment and were present before age 7 years. The symptoms must cause clinically significant impairment, e.g., in social, academic, or occupational functioning, and be present in two or more settings, e.g., school (or work) and at home. The symptoms must not be better accounted for by another mental disorder. For the Inattentive Type, at least six of the following symptoms must have persisted for at least 6 months: lack of attention to details/careless mistakes; lack of sustained attention; poor listener; failure to follow through on tasks; poor organization; avoids tasks requiring sustained mental effort; loses things; easily distracted; forgetful. For the Hyperactive-Impulsive Type, at least six of the following symptoms must have persisted for at least 6 months: fidgeting/squirming; leaving seat; inappropriate running/climbing; difficulty with quiet activities; "on the go;" excessive talking; blurting answers; can't wait turn; intrusive. The Combined Type requires both inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive criteria to be met.
1.1 Special Diagnostic Considerations
Specific etiology of this syndrome is unknown, and there is no single diagnostic test. Adequate diagnosis requires the use of medical and special psychological, educational, and social resources. Learning may or may not be impaired. The diagnosis must be based upon a complete history and evaluation of the patient and not solely on the presence of the required number of DSM-IV characteristics.
1.2 Need for Comprehensive Treatment Program
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are indicated as an integral part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include other measures (psychological, educational, social). Drug treatment may not be indicated for all patients with ADHD. Stimulants are not intended for use in patients who exhibit symptoms secondary to environmental factors and/or other primary psychiatric disorders, including psychosis. Appropriate educational placement is essential and psychosocial intervention is often helpful. When remedial measures alone are insufficient, the decision to prescribe stimulant medication will depend upon the physician's assessment of the chronicity and severity of the patient's symptoms.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be administered orally once daily in the morning with or without food.
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets must be swallowed whole with the aid of liquids, and must not be chewed, divided, or crushed [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
2.2 Patients New to Methylphenidate
The recommended starting dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets for patients who are not currently taking methylphenidate or stimulants other than methylphenidate is 18 mg once daily for children and adolescents and 18 mg once daily or 36 mg once daily for adults (see Table 1).
Table 1. Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Recommended Starting Doses and Dose Ranges Patient Age Recommended Starting Dose Dose Range Children 6 to 12 years of age 18 mg/day 18 mg/day to 54 mg/day Adolescents 13 to 17 years of age 18 mg/day 18 mg/day to 72 mg/day
not to exceed 2 mg/kg/dayAdults 18 to 65 years of age 18 mg/day or 36 mg/day 18 mg/day to 72 mg/day 2.3 Patients Currently Using Methylphenidate
The recommended dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets for patients who are currently taking methylphenidate twice daily or three times daily at doses of 10 mg/day to 60 mg/day is provided in Table 2. Dosing recommendations are based on current dose regimen and clinical judgment. Conversion dosage should not exceed 72 mg daily.
Table 2. Recommended Dose Conversion from Methylphenidate Regimens to Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Previous Methylphenidate Daily Dose Recommended Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Starting Dose 5 mg Methylphenidate twice daily or three times daily 18 mg every morning 10 mg Methylphenidate twice daily or three times daily 36 mg every morning 15 mg Methylphenidate twice daily or three times daily 54 mg every morning 20 mg Methylphenidate twice daily or three times daily 72 mg every morning Other methylphenidate regimens: Clinical judgment should be used when selecting the starting dose.
2.4 Dose Titration
Doses may be increased in 18 mg increments at weekly intervals for patients who have not achieved an optimal response at a lower dose. Daily dosages above 54 mg in children and 72 mg in adolescents have not been studied and are not recommended. Daily dosages above 72 mg in adults are not recommended.
A 27 mg dosage strength is available for physicians who wish to prescribe between the 18 mg and 36 mg dosages.
2.5 Maintenance/Extended Treatment
There is no body of evidence available from controlled trials to indicate how long the patient with ADHD should be treated with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. It is generally agreed, however, that pharmacological treatment of ADHD may be needed for extended periods.
The effectiveness of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets for long-term use, i.e., for more than 7 weeks, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. The physician who elects to use methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets for extended periods in patients with ADHD should periodically re-evaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient with trials off medication to assess the patient's functioning without pharmacotherapy. Improvement may be sustained when the drug is either temporarily or permanently discontinued.
2.6 Dose Reduction and Discontinuation
If paradoxical aggravation of symptoms or other adverse events occur, the dosage should be reduced, or, if necessary, the drug should be discontinued.
If improvement is not observed after appropriate dosage adjustment over a one-month period, the drug should be discontinued.
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets, USP are available in the following dosage strengths: 18 mg tablets are yellow, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side; 27 mg tablets are gray, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side; 36 mg tablets are white, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side and 54 mg tablets are orange, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
4.1 Hypersensitivity to Methylphenidate
Hypersensitivity reactions, such as angioedema and anaphylactic reactions, have been observed in patients treated with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Therefore, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients known to be hypersensitive to methylphenidate or other components of the product [see Adverse Reactions (6.6)].
4.2 Agitation
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with marked anxiety, tension, and agitation, since the drug may aggravate these symptoms.
4.3 Glaucoma
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with glaucoma.
4.4 Tics
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated in patients with motor tics or with a family history or diagnosis of Tourette's syndrome [see Adverse Reactions (6.4)].
4.5 Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are contraindicated during treatment with monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, and also within a minimum of 14 days following discontinuation of a MAO inhibitor (hypertensive crises may result) [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Serious Cardiovascular Events
Sudden Death and Preexisting Structural Cardiac Abnormalities or Other Serious Heart Problems
Children and Adolescents
Sudden death has been reported in association with CNS stimulant treatment at usual doses in children and adolescents with structural cardiac abnormalities or other serious heart problems. Although some serious heart problems alone carry an increased risk of sudden death, stimulant products generally should not be used in children or adolescents with known serious structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart rhythm abnormalities, or other serious cardiac problems that may place them at increased vulnerability to the sympathomimetic effects of a stimulant drug.
Adults
Sudden deaths, stroke, and myocardial infarction have been reported in adults taking stimulant drugs at usual doses for ADHD. Although the role of stimulants in these adult cases is also unknown, adults have a greater likelihood than children of having serious structural cardiac abnormalities, cardiomyopathy, serious heart rhythm abnormalities, coronary artery disease, or other serious cardiac problems. Adults with such abnormalities should also generally not be treated with stimulant drugs.
Hypertension and Other Cardiovascular Conditions
Stimulant medications cause a modest increase in average blood pressure (about 2 mm Hg to 4 mm Hg) and average heart rate (about 3 bpm to 6 bpm) [see Adverse Reactions (6.5)], and individuals may have larger increases. While the mean changes alone would not be expected to have short-term consequences, all patients should be monitored for larger changes in heart rate and blood pressure. Caution is indicated in treating patients whose underlying medical conditions might be compromised by increases in blood pressure or heart rate, e.g., those with preexisting hypertension, heart failure, recent myocardial infarction, or ventricular arrhythmia.
Assessing Cardiovascular Status in Patients Being Treated with Stimulant Medications
Children, adolescents, or adults who are being considered for treatment with stimulant medications should have a careful history (including assessment for a family history of sudden death or ventricular arrhythmia) and physical exam to assess for the presence of cardiac disease, and should receive further cardiac evaluation if findings suggest such disease (e.g., electrocardiogram and echocardiogram). Patients who develop symptoms such as exertional chest pain, unexplained syncope, or other symptoms suggestive of cardiac disease during stimulant treatment should undergo a prompt cardiac evaluation.
5.2 Psychiatric Adverse Events
Preexisting Psychosis
Administration of stimulants may exacerbate symptoms of behavior disturbance and thought disorder in patients with a preexisting psychotic disorder.
Bipolar Illness
Particular care should be taken in using stimulants to treat ADHD in patients with comorbid bipolar disorder because of concern for possible induction of a mixed/manic episode in such patients. Prior to initiating treatment with a stimulant, patients with comorbid depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression.
Emergence of New Psychotic or Manic Symptoms
Treatment-emergent psychotic or manic symptoms, e.g., hallucinations, delusional thinking, or mania in patients without a prior history of psychotic illness or mania can be caused by stimulants at usual doses. If such symptoms occur, consideration should be given to a possible causal role of the stimulant, and discontinuation of treatment may be appropriate. In a pooled analysis of multiple short-term, placebo-controlled studies, such symptoms occurred in about 0.1% (4 patients with events out of 3,482 exposed to methylphenidate or amphetamine for several weeks at usual doses) of stimulant-treated patients compared to 0 in placebo-treated patients.
Aggression
Aggressive behavior or hostility is often observed in patients with ADHD, and has been reported in clinical trials and the postmarketing experience of some medications indicated for the treatment of ADHD. Although there is no systematic evidence that stimulants cause aggressive behavior or hostility, patients beginning treatment for ADHD should be monitored for the appearance of or worsening of aggressive behavior or hostility.
5.3 Seizures
There is some clinical evidence that stimulants may lower the convulsive threshold in patients with prior history of seizures, in patients with prior EEG abnormalities in absence of seizures, and, very rarely, in patients without a history of seizures and no prior EEG evidence of seizures. In the presence of seizures, the drug should be discontinued.
5.4 Priapism
Prolonged and painful erections, sometimes requiring surgical intervention, have been reported with methylphenidate products, including methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, in both pediatric and adult patients [see Adverse Reactions (6.6)]. Priapism was not reported with drug initiation but developed after some time on the drug, often subsequent to an increase in dose. Priapism has also appeared during a period of drug withdrawal (drug holidays or during discontinuation). Patients who develop abnormally sustained or frequent and painful erections should seek immediate medical attention.
5.5 Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon
Stimulants, including methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, used to treat ADHD are associated with peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon. Signs and symptoms are usually intermittent and mild; however, very rare sequelae include digital ulceration and/or soft tissue breakdown. Effects of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon, were observed in post-marketing reports at different times and at therapeutic doses in all age groups throughout the course of treatment. Signs and symptoms generally improve after reduction in dose or discontinuation of drug. Careful observation for digital changes is necessary during treatment with ADHD stimulants. Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
5.6 Long-Term Suppression of Growth
Careful follow-up of weight and height in children ages 7 to 10 years who were randomized to either methylphenidate or nonmedication treatment groups over 14 months, as well as in naturalistic subgroups of newly methylphenidate-treated and nonmedication-treated children over 36 months (to the ages of 10 to 13 years), suggests that consistently medicated children (i.e., treatment for 7 days per week throughout the year) have a temporary slowing in growth rate (on average, a total of about 2 cm less growth in height and 2.7 kg less growth in weight over 3 years), without evidence of growth rebound during this period of development. Published data are inadequate to determine whether chronic use of amphetamines may cause similar suppression of growth; however, it is anticipated that they likely have this effect as well. Therefore, growth should be monitored during treatment with stimulants, and patients who are not growing or gaining height or weight as expected may need to have their treatment interrupted.
5.7 Visual Disturbance
Difficulties with accommodation and blurring of vision have been reported with stimulant treatment.
5.8 Potential for Gastrointestinal Obstruction
Because the methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablet is nondeformable and does not appreciably change in shape in the GI tract, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should not ordinarily be administered to patients with preexisting severe gastrointestinal narrowing (pathologic or iatrogenic, for example: esophageal motility disorders, small bowel inflammatory disease, "short gut" syndrome due to adhesions or decreased transit time, past history of peritonitis, cystic fibrosis, chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction, or Meckel's diverticulum). There have been rare reports of obstructive symptoms in patients with known strictures in association with the ingestion of drugs in nondeformable controlled-release formulations. Due to the controlled-release design of the tablet, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used only in patients who are able to swallow the tablet whole [see Patient Counseling Information (17)].
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following are discussed in more detail in other sections of the labeling:
- Drug Dependence [see Box Warning]
- Hypersensitivity to Methylphenidate [see Contraindications (4.1)]
- Agitation [see Contraindications (4.2)]
- Glaucoma [see Contraindications (4.3)]
- Tics [see Contraindications (4.4)]
- Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors [see Contraindications (4.5) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
- Serious Cardiovascular Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Psychiatric Adverse Events [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Seizures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Long-Term Suppression of Growth [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Visual Disturbance [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Potential for Gastrointestinal Obstruction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Hematologic Monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)]
The most common adverse reaction in double-blind clinical trials (>5%) in pediatric patients (children and adolescents) was abdominal pain upper. The most common adverse reactions in double-blind clinical trials (>5%) in adult patients were decreased appetite, headache, dry mouth, nausea, insomnia, anxiety, dizziness, weight decreased, irritability, and hyperhidrosis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The most common adverse reactions associated with discontinuation (≥1%) from either pediatric or adult clinical trials were anxiety, irritability, insomnia, and blood pressure increased [see Adverse Reactions (6.3)].
The development program formethylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets included exposures in a total of 3,906 participants in clinical trials. Children, adolescents, and adults with ADHD were evaluated in 6 controlled clinical studies and 11 open-label clinical studies (see Table 3). Safety was assessed by collecting adverse events, vital signs, weights, and ECGs, and by performing physical examinations and laboratory analyses.
Table 3. Mehtylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Exposure in Double-Blind and Open-Label Clinical Studies Patient Population N Dose Range Children 2,216 18 mg to 54 mg once daily Adolescents 502 18 mg to 72 mg once daily Adults 1,188 18 mg to 108 mg once daily Adverse events during exposure were obtained primarily by general inquiry and recorded by clinical investigators using their own terminology. Consequently, to provide a meaningful estimate of the proportion of individuals experiencing adverse events, events were grouped in standardized categories using MedDRA terminology.
The stated frequencies of adverse events represent the proportion of individuals who experienced, at least once, a treatment-emergent adverse event of the type listed. An event was considered treatment-emergent if it occurred for the first time or worsened while receiving therapy following baseline evaluation.
Throughout this section, adverse reactions are reported. Adverse reactions are adverse events that were considered to be reasonably associated with the use of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets based on the comprehensive assessment of the available adverse event information. A causal association for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets often cannot be reliably established in individual cases. Further, because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The majority of adverse reactions were mild to moderate in severity.
6.1 Commonly Observed Adverse Reactions in Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials
Adverse reactions in either the pediatric or adult double-blind adverse reactions tables may be relevant for both patient populations.
Children and Adolescents
Table 4 lists the adverse reactions reported in 1% or more of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treated children and adolescent subjects in 4 placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials.
Table 4. Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥1% of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Treated Children and Adolescent Subjects in 4 Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trials of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets System/Organ Class
Adverse ReactionMethylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets
(n=321)
%Placebo
(n=318)
%- * Terms of Initial insomnia (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets=0.6%) and Insomnia (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets=2.2%) are combined into Insomnia.
Gastrointestinal Disorders Abdominal pain upper 6.2 3.8 Vomiting 2.8 1.6 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Pyrexia 2.2 0.9 Infections and Infestations Nasopharyngitis 2.8 2.2 Nervous System Disorders Dizziness 1.9 0 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia* * 2.8 0.3 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Cough 1.9 0.9 Oropharyngeal pain 1.2 0.9 * Terms of Initial insomnia (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets =0.6%) and Insomnia (Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets =2.2%) are combined into Insomnia.
The majority of adverse reactions were mild to moderate in severity.
Adults
Table 5 lists the adverse reactions reported in 1% or more of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treated adults in 2 placebo-controlled, double-blind clinical trials.
Table 5. Adverse Reactions Reported by ≥1% of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Treated Adult Subjects in 2 Placebo-Controlled, Double-Blind Clinical Trials* System/Organ Class
Adverse ReactionMethylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets
(n=415)
%Placebo
(n=212)
%- * * Included doses up to 108 mg.
Cardiac Disorders Tachycardia 4.8 0 Palpitations 3.1 0.9 Ear and Labyrinth Disorders Vertigo 1.7 0 Eye Disorders Vision blurred 1.7 0.5 Gastrointestinal Disorders Dry mouth 14.0 3.8 Nausea 12.8 3.3 Dyspepsia 2.2 0.9 Vomiting 1.7 0.5 Constipation 1.4 0.9 General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Irritability 5.8 1.4 Infections and Infestations Upper respiratory tract infection 2.2 0.9 Investigations Weight decreased 6.5 3.3 Metabolism and Nutrition Disorders Decreased appetite 25.3 6.6 Anorexia 1.7 0 Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Muscle tightness 1.9 0 Nervous System Disorders Headache 22.2 15.6 Dizziness 6.7 5.2 Tremor 2.7 0.5 Paresthesia 1.2 0 Sedation 1.2 0 Tension headache 1.2 0.5 Psychiatric Disorders Insomnia 12.3 6.1 Anxiety 8.2 2.4 Initial insomnia 4.3 2.8 Depressed mood 3.9 1.4 Nervousness 3.1 0.5 Restlessness 3.1 0 Agitation 2.2 0.5 Aggression 1.7 0.5 Bruxism 1.7 0.5 Depression 1.7 0.9 Libido decreased 1.7 0.5 Affect lability 1.4 0.9 Confusional state 1.2 0.5 Tension 1.2 0.5 Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Oropharyngeal pain 1.7 1.4 Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders Hyperhidrosis 5.1 0.9 * Included doses up to 108 mg.
The majority of ADRs were mild to moderate in severity.
6.2 Other Adverse Reactions Observed in Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets Clinical Trials
This section includes adverse reactions reported by methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treated subjects in double-blind trials that do not meet the criteria specified for Table 4 or Table 5 and all adverse reactions reported by methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treated subjects who participated in open-label and postmarketing clinical trials.
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Leukopenia
Eye Disorders: Accommodation disorder, Dry eye
Vascular Disorders: Hot flush
Gastrointestinal Disorders: Abdominal discomfort, Abdominal pain, Diarrhea
General Disorders and Administrative Site Conditions: Asthenia, Fatigue, Feeling jittery, Thirst
Infections and Infestations: Sinusitis
Investigations: Alanine aminotransferase increased, Blood pressure increased, Cardiac murmur, Heart rate increased
Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders: Muscle spasms
Nervous System Disorders: Lethargy, Psychomotor hyperactivity, Somnolence
Psychiatric Disorders: Anger, Hypervigilance, Mood altered, Mood swings, Panic attack, Sleep disorder, Tearfulness, Tic
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Erectile dysfunction
Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders: Dyspnea
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Rash, Rash macular
Vascular Disorders: Hypertension
6.3 Discontinuation Due to Adverse Reactions
Adverse reactions in the 4 placebo-controlled studies of children and adolescents leading to discontinuation occurred in 2 methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets patients (0.6%) including depressed mood (1, 0.3%) and headache and insomnia (1, 0.3%), and 6 placebo patients (1.9%) including headache and insomnia (1, 0.3%), irritability (2, 0.6%), headache (1, 0.3%), psychomotor hyperactivity (1, 0.3%), and tic (1, 0.3%).
In the 2 placebo-controlled studies of adults, 25 methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets patients (6.0%) and 6 placebo patients (2.8%) discontinued due to an adverse reaction. Those events with an incidence of >0.5% in the methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets patients included anxiety (1.7%), irritability (1.4%), blood pressure increased (1.0%), and nervousness (0.7%). In placebo patients, blood pressure increased and depressed mood had an incidence of >0.5% (0.9%).
In the 11 open-label studies of children, adolescents, and adults, 266 methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets patients (7.0%) discontinued due to an adverse reaction. Those events with an incidence of >0.5% included insomnia (1.2%), irritability (0.8%), anxiety (0.7%), decreased appetite (0.7%), and tic (0.6%).
6.4 Tics
In a long-term uncontrolled study (n=432 children), the cumulative incidence of new onset of tics was 9% after 27 months of treatment with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
In a second uncontrolled study (n=682 children) the cumulative incidence of new-onset tics was 1% (9/682 children). The treatment period was up to 9 months with mean treatment duration of 7.2 months.
6.5 Blood Pressure and Heart Rate Increases
In the laboratory classroom clinical trials in children (Studies 1 and 2), both methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once daily and methylphenidate three times daily increased resting pulse by an average of 2 bpm to 6 bpm and produced average increases of systolic and diastolic blood pressure of roughly 1 mm Hg to 4 mm Hg during the day, relative to placebo. In the placebo-controlled adolescent trial (Study 4), mean increases from baseline in resting pulse rate were observed with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo at the end of the double-blind phase (5 beats/minute and 3 beats/minute, respectively). Mean increases from baseline in blood pressure at the end of the double-blind phase for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo-treated patients were 0.7 mm Hg and 0.7 mm Hg (systolic) and 2.6 mm Hg and 1.4 mm Hg (diastolic), respectively. In one placebo-controlled study in adults (Study 6), dose-dependent mean increases of 3.9 bpm to 9.8 bpm from baseline in standing pulse rate were observed with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets at the end of the double-blind treatment vs. an increase of 2.7 beats/minute with placebo. Mean changes from baseline in standing blood pressure at the end of double-blind treatment ranged from 0.1 mm Hg to 2.2 mm Hg (systolic) and -0.7 mm Hg to 2.2 mm Hg (diastolic) for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and was 1.1 mm Hg (systolic) and -1.8 mm Hg (diastolic) for placebo. In a second placebo-controlled study in adults (Study 5), mean changes from baseline in resting pulse rate were observed for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo at the end of the double-blind treatment (3.6 beats/minute and –1.6 beats/minute, respectively). Mean changes from baseline in blood pressure at the end of the double–blind treatment for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo-treated patients were –1.2 mm Hg and –0.5 mm Hg (systolic) and 1.1 mm Hg and 0.4 mm Hg (diastolic), respectively [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.6 Postmarketing Experience
The following additional adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency:
Blood and Lymphatic System Disorders: Pancytopenia, Thrombocytopenia, Thrombocytopenic purpura
Cardiac Disorders: Angina pectoris, Bradycardia, Extrasystoles, Supraventricular tachycardia, Ventricular extrasystoles
Eye Disorders: Diplopia, Mydriasis, Visual impairment
General Disorders: Chest pain, Chest discomfort, Drug effect decreased, Hyperpyrexia, Therapeutic response decreased
Hepatobiliary disorders: Hepatocellular injury, Acute hepatic failure
Immune System Disorders: Hypersensitivity reactions such as Angioedema, Anaphylactic reactions, Auricular swelling, Bullous conditions, Exfoliative conditions, Urticarias, Pruritus NEC, Rashes, Eruptions, and Exanthemas NEC
Investigations: Blood alkaline phosphatase increased, Blood bilirubin increased, Hepatic enzyme increased, Platelet count decreased, White blood cell count abnormal
Musculoskeletal, Connective Tissue and Bone Disorders: Arthralgia, Myalgia, Muscle twitching, Rhabdomyolysis
Nervous System Disorders: Convulsion, Grand mal convulsion, Dyskinesia, Serotonin syndrome in combination with serotonergic drugs
Psychiatric Disorders: Disorientation, Hallucination, Hallucination auditory, Hallucination visual, Mania, Logorrhea, Libido changes
Reproductive System and Breast Disorders: Priapism
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Alopecia, Erythema
Vascular Disorders: Raynaud's phenomenon
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 MAO Inhibitors
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should not be used in patients being treated (currently or within the preceding 2 weeks) with MAO inhibitors [see Contraindications (4.5)].
7.2 Vasopressor Agents
Because of possible increases in blood pressure, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used cautiously with vasopressor agents [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
7.3 Coumarin Anticoagulants, Antidepressants, and Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors
Human pharmacologic studies have shown that methylphenidate may inhibit the metabolism of coumarin anticoagulants, anticonvulsants (e.g., phenobarbital, phenytoin, primidone), and some antidepressants (tricyclics and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors). Downward dose adjustment of these drugs may be required when given concomitantly with methylphenidate. It may be necessary to adjust the dosage and monitor plasma drug concentrations (or, in the case of coumarin, coagulation times), when initiating or discontinuing concomitant methylphenidate.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
Methylphenidate has been shown to have teratogenic effects in rabbits when given in doses of 200 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 100 times and 40 times the maximum recommended human dose on a mg/kg and mg/m2 basis, respectively.
A reproduction study in rats revealed no evidence of harm to the fetus at oral doses up to 30 mg/kg/day, approximately 15-fold and 3-fold the maximum recommended human dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on a mg/kg and mg/m2 basis, respectively. The approximate plasma exposure to methylphenidate plus its main metabolite PPAA in pregnant rats was 1 to 2 times that seen in trials in volunteers and patients with the maximum recommended dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets based on the AUC.
The safety of methylphenidate for use during human pregnancy has not been established. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus
8.2 Labor and Delivery
The effect of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether methylphenidate is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised if methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are administered to a nursing woman.
In lactating female rats treated with a single oral dose of 5 mg/kg radiolabeled methylphenidate, radioactivity (representing methylphenidate and/or its metabolites) was observed in milk and levels were generally similar to those in plasma.
-
9 DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
9.1 Controlled Substance
Methylphenidate is a Schedule II controlled substance under the Controlled Substances Act.
9.2 Abuse
As noted in the Box Warning, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be given cautiously to patients with a history of drug dependence or alcoholism. Chronic abusive use can lead to marked tolerance and psychological dependence with varying degrees of abnormal behavior. Frank psychotic episodes can occur, especially with parenteral abuse.
In two placebo-controlled human abuse potential studies, single oral doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were compared to single oral doses of immediate-release methylphenidate (IR MPH) and placebo in subjects with a history of recreational stimulant use to assess relative abuse potential. For the purpose of this assessment, the response for each of the subjective measures was defined as the maximum effect within the first 8 hours after dose administration.
In one study (n=40), both methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (108 mg) and 60 mg IR MPH compared to placebo produced statistically significantly greater responses on the five subjective measures suggestive of abuse potential. In comparisons between the two active treatments, however, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (108 mg) produced variable responses on positive subjective measures that were either statistically indistinguishable from (Abuse Potential, Drug Liking, Amphetamine, and Morphine Benzedrine Group [Euphoria]) or statistically less than (Stimulation – Euphoria) responses produced by 60 mg IR MPH.
In another study (n=49), both doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (54 mg and 108 mg) and both doses of IR MPH (50 mg and 90 mg) produced statistically significantly greater responses compared to placebo on the two primary scales used in the study (Drug Liking, Euphoria). When doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (54 mg and 108 mg) were compared to IR MPH (50 mg and 90 mg), respectively, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets produced statistically significantly lower subjective responses on these two scales than IR MPH. methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (108 mg) produced responses that were statistically indistinguishable from the responses on these two scales produced by IR MPH (50 mg). Differences in subjective responses to the respective doses should be considered in the context that only 22% of the total amount of methylphenidate in methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets is available for immediate release from the drug overcoat [see System Components and Performance (11.1)].
Although these findings reveal a relatively lower response to methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on subjective measures suggestive of abuse potential compared to IR MPH at roughly equivalent total MPH doses, the relevance of these findings to the abuse potential of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in the community is unknown.
9.3 Dependence
As noted in the Box Warning, careful supervision is required during withdrawal from abusive use since severe depression may occur. Withdrawal following chronic therapeutic use may unmask symptoms of the underlying disorder that may require follow-up.
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
10.1 Signs and Symptoms
Signs and symptoms of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets overdosage, resulting principally from overstimulation of the CNS and from excessive sympathomimetic effects, may include the following: vomiting, agitation, muscle twitching, convulsion, grand mal convulsion, confusional state, hallucinations (auditory and/or visual), hyperhidrosis, headache, pyrexia, tachycardia, palpitations, heart rate increased, sinus arrhythmia, hypertension, rhabdomyolysis, mydriasis, and dry mouth.
10.2 Recommended Treatment
Treatment consists of appropriate supportive measures. The patient must be protected against self-injury and against external stimuli that would aggravate overstimulation already present. Gastric contents may be evacuated by gastric lavage as indicated. Before performing gastric lavage, control agitation and seizures if present and protect the airway. Other measures to detoxify the gut include administration of activated charcoal and a cathartic. Intensive care must be provided to maintain adequate circulation and respiratory exchange; external cooling procedures may be required for pyrexia.
Efficacy of peritoneal dialysis or extracorporeal hemodialysis for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets overdosage has not been established.
The prolonged release of methylphenidate from methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be considered when treating patients with overdose.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets, USP are a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets, USP are available in four tablet strengths. Each extended-release tablet for once-a-day oral administration contains 18 mg, 27 mg, 36 mg, or 54 mg of methylphenidate HCl USP and is designed to have a 12-hour duration of effect. Chemically, methylphenidate HCl is d,l (racemic) methyl α-phenyl-2-piperidineacetate hydrochloride. Its empirical formula is C14H19NO2HCl. Its structural formula is:
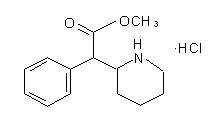
Methylphenidate HCl USP is a white, odorless crystalline powder. Its solutions are acid to litmus. It is freely soluble in water and in methanol, soluble in alcohol, and slightly soluble in chloroform and in acetone. Its molecular weight is 269.77.
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets, USP also contain the following inert ingredients: black iron oxide, butylated hydroxytoluene, cellulose acetate, citric acid, hypromellose, poloxamer, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, povidone, sodium chloride, stearic acid, succinic acid, and yellow iron oxide.
Tablets also contain black imprinting ink comprised of ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac.
Additionally, the 18 mg tablets contain D&C yellow # 10, hypromellose, FD&C yellow #6, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; the 27 mg tablets contain black iron oxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; the 36 mg tablets contain hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; and the 54 mg tablets contain FD&C yellow #6, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
11.1 System Components and Performance
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets uses osmotic pressure to deliver methylphenidate HCl at a controlled rate. The system, which resembles a conventional tablet in appearance, comprises an osmotically active bilayer core surrounded by a semipermeable membrane with an immediate-release drug overcoat. The bilayer core is composed of a drug layer containing the drug and excipients, and a push layer containing osmotically active components. There is a precision-laser drilled orifice on the drug-layer end of the tablet. In an aqueous environment, such as the gastrointestinal tract, the drug overcoat dissolves within one hour, providing an initial dose of methylphenidate. Water permeates through the membrane into the tablet core. As the osmotically active polymer excipients expand, methylphenidate is released through the orifice. The membrane controls the rate at which water enters the tablet core, which in turn controls drug delivery. Furthermore, the drug release rate from the system increases with time over a period of 6 to 7 hours. The biologically inert components of the tablet remain intact during gastrointestinal transit and are eliminated in the stool as a tablet shell along with insoluble core components. It is possible that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets may be visible on abdominal x-rays under certain circumstances, especially when digital enhancing techniques are utilized.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Methylphenidate HCl is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. The mode of therapeutic action in Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is not known. Methylphenidate is thought to block the reuptake of norepinephrine and dopamine into the presynaptic neuron and increase the release of these monoamines into the extraneuronal space.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Methylphenidate is a racemic mixture comprised of the d- and l-isomers. The d-isomer is more pharmacologically active than the l-isomer.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Methylphenidate is readily absorbed. Following oral administration of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, plasma methylphenidate concentrations increase rapidly, reaching an initial maximum at about 1 hour, followed by gradual ascending concentrations over the next 5 to 9 hours, after which a gradual decrease begins. Mean times to reach peak plasma concentrations across all doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets occurred between 6 and 10 hours.
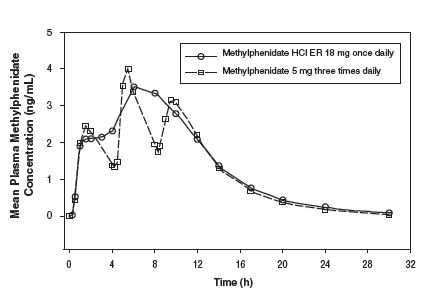
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once daily minimizes the fluctuations between peak and trough concentrations associated with immediate-release methylphenidate three times daily (see Figure 1). The relative bioavailability of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once daily and methylphenidate three times daily in adults is comparable
Figure 1. Mean methylphenidate plasma concentrations in 36 adults, following a single dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets18 mg once daily and immediate-release methylphenidate 5 mg three times daily administered every 4 hours.
The mean single-dose pharmacokinetic parameters in 36 healthy adults following the administration of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets 18 mg once daily and methylphenidate 5 mg three times daily are summarized in Table 6.
Table 6. Pharmacokinetic Parameters (Mean ± SD) After Single Dose in Healthy Adults Parameters Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets
(18 mg once daily)
(n=36)Methylphenidate
(5 mg three times daily)
(n=35)Cmax (ng/mL) 3.7 ± 1.0 4.2 ± 1.0 Tmax (h) 6.8 ± 1.8 6.5 ± 1.8 AUCinf (ng∙h/mL) 41.8 ± 13.9 38.0 ± 11.0 t½ (h) 3.5 ± 0.4 3.0 ± 0.5 The pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were evaluated in healthy adults following single- and multiple-dose administration (steady state) of doses up to 144 mg/day. The mean half-life was about 3.6 hours. No differences in the pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were noted following single and repeated once-daily dosing, indicating no significant drug accumulation. The AUC and t1/2 following repeated once-daily dosing are similar to those following the first dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in a dose range of 18 mg to 144 mg.
Dose Proportionality
Following administration of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in single doses of 18 mg/day, 36 mg/day, and 54 mg/day to healthy adults, Cmax and AUC(0–inf) of d-methylphenidate were proportional to dose, whereas l-methylphenidate Cmax and AUC(0–inf) increased disproportionately with respect to dose. Following administration of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, plasma concentrations of the l-isomer were approximately 1/40 the plasma concentrations of the d-isomer.
In healthy adults, single and multiple dosing of once-daily methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets doses from 54 mg/day to 144 mg/day resulted in linear and dose-proportional increases in Cmax and AUCinf for total methylphenidate (MPH) and its major metabolite, α-phenyl-piperidine acetic acid (PPAA). There was no time dependency in the pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate. The ratio of metabolite (PPAA) to parent drug (MPH) was constant across doses from 54 mg/day to 144 mg/day, both after single dose and upon multiple dosing.
In a multiple-dose study in adolescent ADHD patients aged 13 to 16 administered their prescribed dose (18 mg/day to 72 mg/day) of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, mean Cmax and AUCTAU of d- and total methylphenidate increased proportionally with respect to dose.
Distribution
Plasma methylphenidate concentrations in adults and adolescents decline biexponentially following oral administration. The half-life of methylphenidate in adults and adolescents following oral administration of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets was approximately 3.5 hours.
Metabolism and Excretion
In humans, methylphenidate is metabolized primarily by de-esterification to PPAA, which has little or no pharmacologic activity. In adults the metabolism of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once daily as evaluated by metabolism to PPAA is similar to that of methylphenidate three times daily. The metabolism of single and repeated once-daily doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets is similar.
After oral dosing of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, about 90% of the radioactivity was recovered in urine. The main urinary metabolite was PPAA, accounting for approximately 80% of the dose.
Food Effects
In patients, there were no differences in either the pharmacokinetics or the pharmacodynamic performance of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets when administered after a high-fat breakfast. There is no evidence of dose dumping in the presence or absence of food.
Alcohol Effect
An in vitro study was conducted to explore the effect of alcohol on the release characteristics of methylphenidate from the methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets 18 mg tablet dosage form. At an alcohol concentration up to 40% there was no increased release of methylphenidate in the first hour. The results with the 18 mg tablet strength are considered representative of the other available tablet strengths.
Special Populations
Gender
In healthy adults, the mean dose-adjusted AUC (0–inf) values for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were 36.7 ng∙h/mL in men and 37.1 ng∙h/mL in women, with no differences noted between the two groups.
Race
In adults receiving methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, dose-adjusted AUC(0–inf) was consistent across ethnic groups; however, the sample size may have been insufficient to detect ethnic variations in pharmacokinetics.
Age
Increase in age resulted in increased apparent oral clearance (CL/F) (58% increase in adolescents compared to children). Some of these differences could be explained by body-weight differences among these populations. This suggests that subjects with higher body weight may have lower exposures of total methylphenidate at similar doses.
The pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets have not been studied in children less than 6 years of age.
Renal Insufficiency
There is no experience with the use of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in patients with renal insufficiency. After oral administration of radiolabeled methylphenidate in humans, methylphenidate was extensively metabolized and approximately 80% of the radioactivity was excreted in the urine in the form of PPAA. Since renal clearance is not an important route of methylphenidate clearance, renal insufficiency is expected to have little effect on the pharmacokinetics of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis
In a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in B6C3F1 mice, methylphenidate caused an increase in hepatocellular adenomas and, in males only, an increase in hepatoblastomas at a daily dose of approximately 60 mg/kg/day. This dose is approximately 30 times and 4 times the maximum recommended human dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on a mg/kg and mg/m2 basis, respectively. Hepatoblastoma is a relatively rare rodent malignant tumor type. There was no increase in total malignant hepatic tumors. The mouse strain used is sensitive to the development of hepatic tumors, and the significance of these results to humans is unknown. Methylphenidate did not cause any increases in tumors in a lifetime carcinogenicity study carried out in F344 rats; the highest dose used was approximately 45 mg/kg/day, which is approximately 22 times and 5 times the maximum recommended human dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on a mg/kg and mg/m2 basis, respectively.
In a 24-week carcinogenicity study in the transgenic mouse strain p53+/-, which is sensitive to genotoxic carcinogens, there was no evidence of carcinogenicity. Male and female mice were fed diets containing the same concentration of methylphenidate as in the lifetime carcinogenicity study; the high-dose groups were exposed to 60 mg/kg/day to 74 mg/kg/day of methylphenidate.
Mutagenesis
Methylphenidate was not mutagenic in the in vitro Ames reverse mutation assay or the in vitro mouse lymphoma cell forward mutation assay. Sister chromatid exchanges and chromosome aberrations were increased, indicative of a weak clastogenic response, in an in vitro assay in cultured Chinese Hamster Ovary cells. Methylphenidate was negative in vivo in males and females in the mouse bone marrow micronucleus assay.
Impairment of Fertility
Methylphenidate did not impair fertility in male or female mice that were fed diets containing the drug in an 18-week Continuous Breeding study. The study was conducted at doses up to 160 mg/kg/day, approximately 80-fold and 8-fold the highest recommended human dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets on a mg/kg and mg/m2 basis, respectively.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in 4 randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies in children and adolescents and 2 double-blind placebo-controlled studies in adults who met the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual 4th edition (DSM-IV) criteria for ADHD.
14.1 Children
Three double-blind, active- and placebo-controlled studies were conducted in 416 children aged 6 to 12 years. The controlled studies compared methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets given once daily (18 mg, 36 mg, or 54 mg), methylphenidate given three times daily over 12 hours (15 mg, 30 mg, or 45 mg total daily dose), and placebo in two single-center, 3-week crossover studies (Studies 1 and 2) and in a multicenter, 4-week, parallel-group comparison (Study 3). The primary comparison of interest in all three trials was methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets versus placebo.
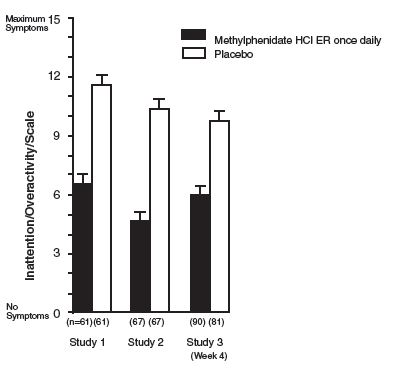
Symptoms of ADHD were evaluated by community schoolteachers using the Inattention/Overactivity with Aggression (IOWA) Conners scale. Statistically significant reduction in the Inattention/Overactivity subscale versus placebo was shown consistently across all three controlled studies for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. The scores for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo for the three studies are presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2. Mean Community School Teacher IOWA Conners Inattention/Overactivity Scores with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once daily (18, 36, or 54 mg) and placebo. Studies 1 and 2 involved a 3-way crossover of 1 week per treatment arm. Study 3 involved 4 weeks of parallel-group treatments with a Last Observation Carried Forward analysis at week 4. Error bars represent the mean plus standard error of the mean.
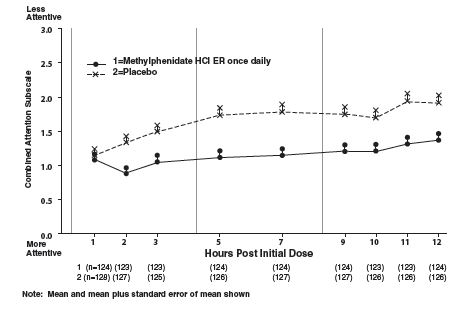
In Studies 1 and 2, symptoms of ADHD were evaluated by laboratory schoolteachers using the SKAMP1 laboratory school rating scale. The combined results from these two studies demonstrated statistically significant improvements in attention and behavior in patients treated with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets versus placebo that were maintained through 12 hours after dosing. Figure 3 presents the laboratory schoolteacher SKAMP ratings for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and placebo.
Figure 3. Laboratory School Teacher SKAMP Ratings: Mean (SEM) of Combined Attention (Studies 1 and 2)
- 1 Swanson, Kotkin, Agler, M-Fynn, and Pelham
14.2 Adolescents
In a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled trial (Study 4) involving 177 patients, methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets was demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of ADHD in adolescents aged 13 to 18 years at doses up to 72 mg/day (1.4 mg/kg/day). Of 220 patients who entered an open 4-week titration phase, 177 were titrated to an individualized dose (maximum of 72 mg/day) based on meeting specific improvement criteria on the ADHD Rating Scale and the Global Assessment of Effectiveness with acceptable tolerability. Patients who met these criteria were then randomized to receive either their individualized dose of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets (18 mg/day to 72 mg/day, n=87) or placebo (n=90) during a two-week double-blind phase. At the end of this phase, mean scores for the investigator rating on the ADHD Rating Scale demonstrated that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
14.3 Adults
Two double-blind, placebo-controlled studies were conducted in 627 adults aged 18 to 65 years. The controlled studies compared methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets administered once daily and placebo in a multicenter, parallel-group, 7-week dose-titration study (Study 5) (36 mg/day to 108 mg/day) and in a multicenter, parallel-group, 5-week, fixed-dose study (Study 6) (18 mg/day, 36 mg/day, and 72 mg/day).
Study 5 demonstrated the effectiveness of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in the treatment of ADHD in adults aged 18 to 65 years at doses from 36 mg/day to 108 mg/day based on the change from baseline to final study visit on the Adult ADHD Investigator Rating Scale (AISRS). Of 226 patients who entered the 7-week trial, 110 were randomized to methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and 116 were randomized to placebo. Treatment was initiated at 36 mg/day and patients continued with incremental increases of 18 mg/day (36 mg/day to 108 mg/day) based on meeting specific improvement criteria with acceptable tolerability. At the final study visit, mean change scores (LS Mean, SEM) for the investigator rating on the AISRS demonstrated that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets was statistically significantly superior to placebo.
Study 6 was a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-response study (5-week duration) with 3 fixed-dose groups (18 mg, 36 mg, and 72 mg). Patients were randomized to receive methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets administered at doses of 18 mg (n=101), 36 mg (n=102), 72 mg/day (n=102), or placebo (n=96). All three doses of methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets were statistically significantly more effective than placebo in improving CAARS (Conners' Adult ADHD Rating Scale) total scores at double-blind end point in adult subjects with ADHD.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets, USP are available in 18 mg, 27 mg, 36 mg, and 54 mg dosage strengths. The 18 mg tablets are yellow, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side. The 27 mg tablets are gray, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side. The 36 mg tablets are white, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side. The 54 mg tablets are orange, round, biconvex coated tablets, “AL” printed in black ink on one side and blank on the other side, with a laser-drilled hole on one side. All four dosage strengths are supplied in bottles containing 100 tablets.
18 mg 100-count bottle NDC: 47781-415-01 27 mg 100-count bottle NDC: 47781-416-01 36 mg 100-count bottle NDC: 47781-417-01 54 mg 100-count bottle NDC: 47781-418-01 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See Medication Guide
Priapism
Advise patients, caregivers, and family members of the possibility of painful or prolonged penile erections (priapism). Instruct the patient to seek immediate medical attention in the event of priapism [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Circulation Problems in Fingers and Toes [Peripheral Vasculopathy, including Raynaud's Phenomenon]
Instruct patients beginning treatment with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets about the risk of peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon, and associated signs and symptoms: fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful, and/or may change color from pale, to blue, to red.
Instruct patients to report to their physician any new numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in fingers or toes.
Instruct patients to call their physician immediately with any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Further clinical evaluation (e.g., rheumatology referral) may be appropriate for certain patients.
General Considerations
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with methylphenidate and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide is available for methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Administration Instructions
Patients should be informed that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole with the aid of liquids. Tablets should not be chewed, divided, or crushed. The medication is contained within a nonabsorbable shell designed to release the drug at a controlled rate. The tablet shell, along with insoluble core components, is eliminated from the body; patients should not be concerned if they occasionally notice in their stool something that looks like a tablet.
Driving or Operating Heavy Machinery
Stimulants may impair the ability of the patient to operate potentially hazardous machinery or vehicles. Patients should be cautioned accordingly until they are reasonably certain that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets does not adversely affect their ability to engage in such activities.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
Methylphenidate Hydrochloride
(meth'' il fen' i date hye'' droe klor' ide)
Extended-Release Tablets CIIRead the Medication Guide that comes with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets before you or your child starts taking it and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This Medication Guide does not take the place of talking to your doctor about your or your child's treatment with methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
What is the most important information I should know about Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
The following have been reported with use of methylphenidate HCl and other stimulant medicines:
1. Heart-related problems:
- sudden death in patients who have heart problems or heart defects
- stroke and heart attack in adults
- increased blood pressure and heart rate
Tell your doctor if you or your child has any heart problems, heart defects, high blood pressure, or a family history of these problems.
Your doctor should check you or your child carefully for heart problems before starting starting methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Your doctor should check your or your child's blood pressure and heart rate regularly during treatment with starting methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Call your doctor right away if you or your child has any signs of heart problems such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or fainting while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
2. Mental (Psychiatric) problems:
All Patients
- new or worse behavior and thought problems
- new or worse bipolar illness
- new or worse aggressive behavior or hostility
Children and Teenagers
- new psychotic symptoms (such as hearing voices, believing things that are not true, are suspicious) or new manic symptoms
Tell your doctor about any mental problems you or your child have, or about a family history of suicide, bipolar illness, or depression.
Call your doctor right away if you or your child has any new or worsening mental symptoms or problems while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, especially seeing or hearing things that are not real, believing things that are not real, or are suspicious.
3. Painful and prolonged erections (priapism)
Painful and prolonged erections (priapism) have occurred with methylphenidate. If you or your child develop priapism, seek medical help right away. Because of the potential for lasting damage, priapism should be evaluated by a doctor immediately.
4. Circulation problems in fingers and toes [Peripheral vasculopathy, including Raynaud's phenomenon]:
- fingers or toes may feel numb, cool, painful
- fingers or toes may change color from pale, to blue, to red
Tell your doctor if you have or your child has numbness, pain, skin color change, or sensitivity to temperature in your fingers or toes.
Call your doctor right away if you have or your child has any signs of unexplained wounds appearing on fingers or toes while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
What are Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are a central nervous system stimulant prescription medicine. It is used for the treatment of attention deficit and hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets may help increase attention and decrease impulsiveness and hyperactivity in patients with ADHD.
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should be used as a part of a total treatment program for ADHD that may include counseling or other therapies.
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are a federally controlled substance (CII) because it can be abused or lead to dependence. Keep methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in a safe place to prevent misuse and abuse. Selling or giving away methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets may harm others, and is against the law.
Tell your doctor if you or your child has (or has a family history of) ever abused or been dependent on alcohol, prescription medicines, or street drugs.
Who should not take Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should not be taken if you or your child:
- is very anxious, tense, or agitated
- has an eye problem called glaucoma
- has tics or Tourette's syndrome, or a family history of Tourette's syndrome. Tics are hard-to-control repeated movements or sounds.
- is taking or has taken within the past 14 days an antidepression medicine called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor or MAOI.
- is allergic to anything in methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients.
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets should not be used in children less than 6 years old because it has not been studied in this age group.
Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets may not be right for you or your child. Before starting methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets, tell your or your child's doctor about all health conditions (or a family history of) including:
- heart problems, heart defects, or high blood pressure
- mental problems including psychosis, mania, bipolar illness, or depression
- tics or Tourette's syndrome
- seizures or have had an abnormal brain wave test (EEG)
- circulation problems in fingers and toes
- esophagus, stomach, or small or large intestine problems
Tell your doctor if you or your child is pregnant, planning to become pregnant, or breastfeeding.
Can methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets be taken with other medicines?
Tell your doctor about all of the medicines that you or your child takes including prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and some medicines may interact with each other and cause serious side effects. Sometimes the doses of other medicines will need to be adjusted while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets.
Your doctor will decide whether methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets can be taken with other medicines.
Especially tell your doctor if you or your child takes:
- antidepression medicines including MAOIs
- seizure medicines
- blood thinner medicines
- blood pressure medicines
- cold or allergy medicines that contain decongestants
Know the medicines that you or your child takes. Keep a list of your medicines with you to show your doctor and pharmacist.
Do not start any new medicine while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets without talking to your doctor first.
How shouldmethylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets be taken?
- Take methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets exactly as prescribed. Your doctor may adjust the dose until it is right for you or your child.
- Do not chew, crush, or divide the tablets. Swallow methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets tablets whole with water or other liquids. Tell your doctor if you or your child cannot swallow methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets whole. A different medicine may need to be prescribed.
- Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets can be taken with or without food.
- Take methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets once each day in the morning. Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets are an extended-release tablet. It releases medication into your or your child's body throughout the day.
- The methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablet does not dissolve completely in the body after all the medicine has been released. You or your child may sometimes notice the empty tablet in a bowel movement. This is normal.
- From time to time, your doctor may stop methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treatment for a while to check ADHD symptoms.
- Your doctor may do regular checks of the blood, heart, and blood pressure while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Children should have their height and weight checked often while taking methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. Methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets treatment may be stopped if a problem is found during these check-ups.
- If you or your child takes too much methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets or overdoses, call your doctor or poison control center right away, or get emergency treatment.
What are possible side effects of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
See "What is the most important information I should know about Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?" for information on reported heart and mental problems.
Other serious side effects include:
- slowing of growth (height and weight) in children
- seizures, mainly in patients with a history of seizures
- eyesight changes or blurred vision
- blockage of the esophagus, stomach, small or large intestine in patients who already have a narrowing in any of these organs
Common side effects include: - decreased appetite
- dry mouth
- trouble sleeping
- dizziness
- stomach ache
- increased sweating
- headache
- nausea
- anxiety
- weight loss
- irritability
Stimulants may impair the ability of you or your child to operate potentially hazardous machinery or vehicles. You or your child should exercise caution until you or your child is reasonably certain that methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets does not adversely affect your or your child's ability to engage in such activities.
Talk to your doctor if you or your child has side effects that are bothersome or do not go away.
This is not a complete list of possible side effects. Ask your doctor or pharmacist for more information.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
You may also report side effects to Alvogen, Inc. at 1-866-770-3024.
How should I store Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
- Store methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets in a safe place at room temperature, 59° to 86°F (15° to 30°C). Protect from moisture.
- Keep methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition. It may harm them and it is against the law.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets that was written for healthcare professionals. For more information about methylphenidate hydrochloride extended-release tablets call 1-866-770-3024.
What are the ingredients in Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Tablets?
Active Ingredient: methylphenidate HCl
Inactive Ingredients: black iron oxide, butylated hydroxytoluene, cellulose acetate, citric acid, hypromellose, poloxamer, polyethylene glycol, polyethylene oxide, povidone, sodium chloride, stearic acid, succinic acid, and yellow iron oxide.
Tablets also contain black imprinting ink comprised of ammonium hydroxide, black iron oxide, isopropyl alcohol, n-butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, and shellac.
Additionally, the 18 mg tablets contain D&C yellow # 10, hypromellose, FD&C yellow #6, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; the 27 mg tablets contain , black iron oxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; the 36 mg tablets contain hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin; and the 54 mg tablets contain FD&C yellow #6, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Alvogen, Inc.
Pine Brook, NJ 07058 USAPL415-00
Revised January 2018
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 18 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 27 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 36 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 54 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE
methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 47781-415 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Methylphenidate hydrochloride (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (Methylphenidate - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) Methylphenidate hydrochloride 18 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) succinic acid (UNII: AB6MNQ6J6L) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) Anhydrous Citric Acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) Poloxamer 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) D&C Yellow No. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) Fd&C Yellow No. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 7000000 (UNII: G3MS6M810Y) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 100000 (UNII: V46Y6OJ5QB) Product Characteristics Color YELLOW Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code AL Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 47781-415-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210818 11/30/2018 METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE
methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 47781-416 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Methylphenidate hydrochloride (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (Methylphenidate - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) Methylphenidate hydrochloride 27 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) succinic acid (UNII: AB6MNQ6J6L) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) Anhydrous Citric Acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) Poloxamer 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 100000 (UNII: V46Y6OJ5QB) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 7000000 (UNII: G3MS6M810Y) Product Characteristics Color GRAY Score no score Shape ROUND Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code AL Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 47781-416-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210818 11/30/2018 METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE
methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 47781-417 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Methylphenidate hydrochloride (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (Methylphenidate - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) Methylphenidate hydrochloride 36 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) succinic acid (UNII: AB6MNQ6J6L) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) Anhydrous Citric Acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) Poloxamer 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 7000000 (UNII: G3MS6M810Y) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 100000 (UNII: V46Y6OJ5QB) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code AL Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 47781-417-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210818 11/30/2018 METHYLPHENIDATE HYDROCHLORIDE
methylphenidate hydrochloride tablet, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 47781-418 Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Methylphenidate hydrochloride (UNII: 4B3SC438HI) (Methylphenidate - UNII:207ZZ9QZ49) Methylphenidate hydrochloride 54 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxytoluene (UNII: 1P9D0Z171K) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) sodium chloride (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) stearic acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) succinic acid (UNII: AB6MNQ6J6L) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) Anhydrous Citric Acid (UNII: XF417D3PSL) Poloxamer 188 (UNII: LQA7B6G8JG) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Fd&C Yellow No. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) Butyl Alcohol (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 100000 (UNII: V46Y6OJ5QB) POLYETHYLENE OXIDE 7000000 (UNII: G3MS6M810Y) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code AL Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 47781-418-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/09/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA210818 11/30/2018 Labeler - Alvogen Inc. (008057330)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.



