CARDURA XL- doxazosin mesylate tablet, film coated, extended release
Cardura by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Cardura by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Viatris Specialty LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use CARDURA XL safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for CARDURA XL.
CARDURA® XL (doxazosin) extended-release tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1990INDICATIONS AND USAGE
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 mg and 8 mg tablets (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients with known sensitivity to doxazosin, other quinazolines, or any of the inert ingredients (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Postural hypotension with or without syncope may occur in the first few hours after administration. (5.1)
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome has been observed during cataract surgery in some patients. Advise patients considering cataract surgery to tell their ophthalmologist that they have taken CARDURA XL tablets. (5.2)
Caution should be used when administering to patients with preexisting severe gastrointestinal narrowing or coronary insufficiency. (5.3, 5.7)
Advise patients to be screened for the presence of prostate cancer prior to treatment and at regular intervals afterwards. (5.4)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most commonly reported adverse reactions from clinical trials are asthenia, headache, hypotension, and dizziness. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Viatris at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX) or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Caution should be exercised when concomitantly administering CARDURA XL with a strong cytochrome P450 (CYP) 3A4 inhibitor. (7.1)
Concomitant administration of CARDURA XL with a phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitor can result in additive blood pressure lowering effects and symptomatic hypotension. (7.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Geriatric: Hypotension with CARDURA XL is more prevalent in patients 70 years or older. (8.5)
Hepatic Impairment: CARDURA XL is not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment and should be administered with caution to patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment. (8.6, 12.3)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 5/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
2.2 Patients Switching from CARDURA to CARDURA XL
2.3 Concomitant Administration with PDE-5 Inhibitors
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Postural Hypotension
5.2 Cataract Surgery
5.3 Gastrointestinal Disorders
5.4 Prostate Cancer
5.5 PDE-5 Inhibitors
5.6 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
5.7 Patients with Coronary Insufficiency
5.8 CYP 3A4 Inhibitors
5.9 Priapism
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP 3A4 Inhibitors
7.2 Antihypertensive Medications
7.3 PDE-5 Inhibitors
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Studies in Patients with BPH
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Postural Hypotension
17.2 Priapism
17.3 Tablet Administration
17.4 Dosing Interval
17.5 Tablet Elimination
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 General Dosing Information
The initial dose of CARDURA XL, 4 mg given once daily, should be administered with breakfast. Depending on the patient’s symptomatic response and tolerability, the dose may be increased to 8 mg, the maximum recommended dose. The recommended titration interval is 3-4 weeks. If CARDURA XL administration is discontinued for several days, therapy should be restarted using the 4 mg once daily dose. Tablets should be swallowed whole, and must not be chewed, divided, cut, or crushed.
2.2 Patients Switching from CARDURA to CARDURA XL
If switching from CARDURA immediate-release (IR) to CARDURA XL, therapy should be initiated with the lowest dose (4 mg once daily). Prior to starting therapy with CARDURA XL, the final evening dose of CARDURA should not be taken.
2.3 Concomitant Administration with PDE-5 Inhibitors
Concomitant administration of CARDURA XL with a PDE-5 inhibitor can result in additive blood pressure lowering effects and symptomatic hypotension; therefore, PDE-5 inhibitor therapy should be initiated at the lowest dose in patients taking CARDURA XL.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
CARDURA XL is contraindicated in patients with a known hypersensitivity to doxazosin, other quinazolines (e.g., prazosin, terazosin), or any of the inert ingredients. Allergic reactions to doxazosin and other quinazolines have included skin rash, urticaria, pruritus, angioedema, and respiratory symptoms [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Postural Hypotension
Postural hypotension with or without symptoms (e.g., dizziness) may develop within a few hours following administration of CARDURA XL. However, infrequently, symptomatic postural hypotension has also been reported later than a few hours after dosing. As with other alpha-blockers, there is a potential for syncope, especially after the initial dose or after an increase in dosage strength. Patients should be warned of the possible occurrence of such events and should avoid situations where injury could result should syncope occur. Care should be taken when CARDURA XL is administered to patients with symptomatic hypotension or patients who have had a hypotensive response to other medications.
5.2 Cataract Surgery
Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome (IFIS) has been observed during cataract surgery in some patients on or previously treated with alpha1 blockers. This variant of small pupil syndrome is characterized by the combination of a flaccid iris that billows in response to intraoperative irrigation currents, progressive intraoperative miosis despite preoperative dilation with standard mydriatic drugs, and potential prolapse of the iris toward the phacoemulsification incisions. The patient’s surgeon should be prepared for possible modifications to their surgical technique, such as the utilization of iris hooks, iris dilator rings, or viscoelastic substances. There does not appear to be a benefit from stopping alpha1 blocker therapy prior to cataract surgery.
5.3 Gastrointestinal Disorders
As with any other non-deformable material, caution should be used when administering CARDURA XL to patients with preexisting severe gastrointestinal narrowing (pathologic or iatrogenic). There have been rare reports of obstructive symptoms in patients with known strictures in association with the ingestion of another drug in this non-deformable extended-release formulation. Markedly increased GI retention times, as may occur in patients with chronic constipation, can increase systemic exposure to doxazosin and thereby potentially increase adverse reactions.
5.4 Prostate Cancer
Carcinoma of the prostate causes many of the same symptoms associated with BPH and the two disorders frequently co-exist. Carcinoma of the prostate should therefore be ruled out prior to commencing therapy with CARDURA XL.
5.5 PDE-5 Inhibitors
Concomitant administration of CARDURA XL with a PDE-5 inhibitor can result in additive blood pressure lowering effects and symptomatic hypotension. Pharmacodynamic interactions between CARDURA XL and antihypertensive medications or other vasodilating agents have not been determined.
5.6 Patients with Hepatic Impairment
CARDURA XL is not recommended for patients with severe hepatic impairment and should be administered with caution to patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Use in Specific Populations (8.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
5.7 Patients with Coronary Insufficiency
Patients with congestive heart failure, angina pectoris, or acute myocardial infarction within the last 6 months were excluded from the Phase 3 studies. If symptoms of angina pectoris should newly appear or worsen, CARDURA XL should be discontinued.
5.8 CYP 3A4 Inhibitors
Caution should be exercised when concomitantly administering CARDURA XL with a strong CYP 3A4 inhibitor, such as atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, or voriconazole.
5.9 Priapism
Rarely (probably less frequently than once in every several thousand patients), alpha-1 antagonists, including doxazosin, have been associated with priapism (painful penile erection, sustained for hours and unrelieved by sexual intercourse or masturbation). Because this condition can lead to permanent impotence if not promptly treated, patients must be advised about the seriousness of the condition.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in clinical practice.
The incidence of adverse reactions was derived from two controlled efficacy and safety trials involving 1473 BPH patients. In Study 1, CARDURA XL (n = 317) was compared to doxazosin IR tablets (n = 322) and to placebo (n = 156). In Study 2, CARDURA XL (n = 350) was compared just to doxazosin IR tablets (n = 330). In both of these studies, CARDURA XL was initiated at a dose of 4 mg, which could be increased by the investigator to 8 mg after seven weeks if an adequate response was not seen [see Clinical Studies (14.1)]. Similarly, doxazosin IR was begun at a dose of 1 mg, which was increased in all patients to 2 mg after 1 week, followed by the option to increase to 4 mg after 4 weeks, and 8 mg after 7 weeks.
The most commonly reported adverse reactions leading to discontinuation in the CARDURA XL group were dizziness, dyspnea, asthenia, headache, hypotension, postural hypotension, and somnolence. The rates of discontinuation for adverse reactions were 6%, 7% and 3% in the CARDURA XL, doxazosin IR, and placebo groups, respectively.
Table 1 lists the incidence rates of adverse reactions derived from all reported adverse events in the two controlled studies (Studies 1 and 2) combined, at a rate greater than placebo and in 1% or more of patients treated with CARDURA XL.
TABLE 1 Adverse Reactions, Derived from All Adverse Events Exceeding Placebo Rate and Occurring in ≥ 1% of BPH Patients Treated with CARDURA XL
Body System
CARDURA XL
(N = 666)
Doxazosin IR
(N = 651)
Placebo
(N = 156)
BODY AS A WHOLE
Abdominal Pain
1.8%
2.3%
0.6%
Asthenia
3.9%
6.9%
1.3%
Headache
6.0%
5.1%
4.5%
CARDIOVASCULAR
Hypotension
1.7%
1.8%
0.0%
Postural Hypotension
1.2%
2.2%
0.6%
DIGESTIVE
Dyspepsia
1.4%
1.2%
0.0%
Nausea
1.2%
2.3%
0.6%
MUSCULOSKELETAL
Myalgia
1.4%
0.5%
0.0%
NERVOUS
Dizziness
5.3%
9.1%
1.9%
Somnolence
1.5%
1.2%
0.0%
Vertigo
1.5%
4.1%
0.6%
RESPIRATORY
Dyspnea
1.2%
1.2%
0.0%
Respiratory Tract Infection
4.8%
4.5%
1.9%
UROGENITAL
Urinary Tract Infection
1.4%
0.8%
0.6%
Additional adverse events reported with CARDURA XL, reported by less than 1% of patients, and those of clinical interest include:
Cardiovascular System: angina pectoris, syncope, tachycardia, chest pain, palpitations;
Digestive System: diarrhea;
Musculoskeletal System: arthralgia;
Nervous System: libido decreased;
Urogenital System: impotence, dysuria.
In general, the adverse events reported in the open-label safety extension, in approximately 295 BPH patients treated for up to 37 weeks, were similar in type and frequency to the events described above in the controlled trials.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse events have been identified during post-approval use of doxazosin. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Autonomic Nervous System: priapism;
Cardiovascular System: cerebrovascular accidents, dizziness postural, myocardial infarction;
Central and Peripheral Nervous System: hypoesthesia, paresthesia;
Endocrine System: gynecomastia;
Gastrointestinal System: gastrointestinal obstruction, vomiting;
General Body System: fatigue, hot flushes, malaise;
Heart Rate/Rhythm: bradycardia, cardiac arrhythmias;
Hematopoietic: leukopenia, purpura, thrombocytopenia;
Liver/Biliary System: abnormal liver function tests, hepatitis, hepatitis cholestatic, jaundice;
Musculoskeletal System: muscle cramps, muscle weakness;
Psychiatric: agitation, anorexia, nervousness;
Respiratory System: bronchospasm aggravated;
Skin Disorders: alopecia, urticaria, skin rash, pruritus;
Special Senses: blurred vision, Intraoperative Floppy Iris Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)];
Urinary System: hematuria, micturition disorder, micturition frequency, nocturia, polyuria.
There have been rare reports of gastrointestinal irritation and gastrointestinal bleeding with use of another drug in this non-deformable sustained release formulation, although causal relationship to the drug is uncertain.
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 CYP 3A4 Inhibitors
No in vivo drug interaction studies were conducted with CARDURA XL.
In vitro studies suggest that doxazosin is a substrate of CYP 3A4. Caution should be exercised when concomitantly administering CARDURA XL with a strong CYP 3A4 inhibitor, such as atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, or voriconazole [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Antihypertensive Medications
Pharmacodynamic interactions between CARDURA XL and antihypertensive medications or other vasodilating agents have not been determined.
7.3 PDE-5 Inhibitors
Concomitant administration of CARDURA XL with a PDE-5 inhibitor can result in additive blood pressure lowering effects and symptomatic hypotension [see Dosage and Administration (2.3)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
CARDURA XL is not indicated for use in females and is not indicated for the treatment of hypertension. The limited available data with CARDURA XL in pregnant women are not sufficient to inform a drug-associated risk for major birth defects and miscarriage. No adverse developmental outcomes were observed in animal reproduction studies with oral administration of doxazosin to pregnant rats and rabbits at doses of up to 10 and 4 times, respectively, the 12 mg/day recommended dose. Postnatal development was delayed in rats at a dose of 8 times the 12 mg/day recommended dose [see Data].
Data
Animal Data
Radioactivity was found to cross the placenta following oral administration of labeled doxazosin to pregnant rats. Studies in pregnant rabbits and rats at daily oral doses of up to 41 and 20 mg/kg, respectively (plasma drug concentrations of 10 and 4 times, respectively, the human AUC exposures with a 12 mg/day therapeutic dose), during organogenesis have revealed no evidence of adverse developmental effects. A dosage regimen of 82 mg/kg/day in the rabbit was associated with reduced fetal survival. In peri- and postnatal studies in rats, postnatal development at maternal doses of 40 or 50 mg/kg/day of doxazosin (about 8 times human AUC exposure with a 12 mg/day therapeutic dose) was delayed, as evidenced by slower body weight gain and slightly later appearance of anatomical features and reflexes.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of CARDURA XL in pediatric patients have not been established.
8.5 Geriatric Use
The incidence of hypotension with CARDURA XL use appears to be age related and more prevalent in patients 70 years or older. At steady state, increases of 27% in maximum plasma concentrations (Cmax) and 34% in the area under the concentration-time curve (AUC) were seen in the elderly (> 65 years old) compared to the young [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Of the 666 patients with BPH who received CARDURA XL in the two controlled clinical efficacy and safety studies, 325 patients (49%) were 65 years of age or older. One hundred thirty-six patients treated with CARDURA XL (20%) were > 70 years of age.
In these two studies, the cumulative incidence of hypotension appeared to be age related. The reason for an increased incidence of hypotension in patients older than 70 years of age may be related to a modest increase in systemic exposure to doxazosin [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)], to an increased propensity to orthostasis in the elderly, or to an enhanced sensitivity to vasodilatory agents in the elderly. The incidence of hypotension reported as an adverse reaction was higher in patients 70 years of age and older (4/136; 2.9%) as compared to patients < 70 years of age (7/530; 1.3%).
8.6 Hepatic Impairment
Since there is no clinical experience in patients with severe hepatic impairment, use in these patients is not recommended. CARDURA XL should be administered with caution to patients with mild or moderate hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
There is no experience with CARDURA XL overdosage. Overdosage experience with the doxazosin IR is limited. Two adolescents who each intentionally ingested 40 mg doxazosin IR with diclofenac or paracetamol were treated with gastric lavage with activated charcoal and made full recoveries. A two-year-old child who accidentally ingested 4 mg doxazosin IR was treated with gastric lavage and remained normotensive during the five-hour emergency room observation period. A six-month-old child accidentally received a crushed 1 mg tablet of doxazosin IR and was reported to have been drowsy. A 32-year-old female with chronic renal failure, epilepsy, and depression intentionally ingested 60 mg doxazosin IR (blood level 0.9 µg/mL; normal values in hypertensives = 0.02 µg/mL); death was attributed to a grand mal seizure resulting from hypotension. A 39-year-old female who ingested 70 mg doxazosin IR, alcohol, and Dalmane® (flurazepam) developed hypotension which responded to fluid therapy.
The most likely manifestation of overdosage would be hypotension, for which the usual treatment would be intravenous infusion of fluid, keeping the patient in the supine position, and in certain circumstances, the administration of vasopressors. As doxazosin is highly protein bound, dialysis would not be indicated.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
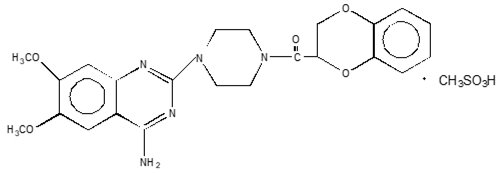
CARDURA XL contains doxazosin which is a quinazoline compound with the chemical name 1-(4-amino-6,7-dimethoxy-2-quinazolinyl)-4-(1,4-benzodioxan-2-ylcarbonyl) piperazine methanesulfonate. The empirical formula for doxazosin mesylate is C23H25N5O5 CH4O3S and the molecular weight is 547.6. It has the following structure:
CARDURA XL is an extended-release tablet for oral use and is designed to deliver 4 or 8 mg of doxazosin as the free base. Each 4 and 8 mg tablet contains 5.1 and 10.2 mg doxazosin mesylate (includes a 5% overage) to ensure the labeled dose of 4 and 8 mg doxazosin as the free base (equivalent to 4.9 and 9.8 mg of doxazosin mesylate), is delivered. The inactive ingredients for CARDURA XL are black iron oxide, cellulose acetate, hypromellose, Macrogol®, magnesium stearate, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene oxide, red ferric oxide, sodium chloride and titanium dioxide.
CARDURA XL System Components and Performance
CARDURA XL is similar in appearance to a conventional tablet. It consists, however, of an osmotically active drug core surrounded by a semipermeable membrane. The core itself is divided into two layers: an “active” layer containing the drug, and a “push” layer containing pharmacologically inert (but osmotically active) components. The membrane surrounding the tablet is permeable to water, but not to drug or osmotic excipients. As water from the gastrointestinal tract enters the tablet, pressure increases in the osmotic layer and “pushes” against the drug layer, resulting in the release of drug through a small, laser-drilled orifice in the membrane on the drug side of the tablet.
CARDURA XL utilizes GITS (Gastrointestinal Therapeutic System) which is designed to provide a controlled rate of delivery of doxazosin into the gastrointestinal lumen which is independent of pH or gastrointestinal (GI) motility. The function of CARDURA XL depends upon the existence of an osmotic gradient between the contents of the bi-layer core and fluid in the GI tract. Drug delivery is essentially constant as long as the osmotic gradient remains constant, and then gradually falls to zero. The biologically inert components of the tablet remain intact during GI transit and are eliminated in the feces as an insoluble shell.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
The symptoms associated with benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), such as urinary frequency, nocturia, weak stream, hesitancy, and incomplete emptying are related to two components, anatomical (static) and functional (dynamic). The static component is related to an increase in prostate size caused, in part, by a proliferation of smooth muscle cells in the prostatic stroma. However, the severity of BPH symptoms and the degree of urethral obstruction do not correlate well with the size of the prostate. The dynamic component of BPH is associated with an increase in smooth muscle tone in the prostate and bladder neck. The degree of tone in this area is mediated by the alpha1 adrenoceptor, which is present in high density in the prostatic stroma, prostatic capsule, and bladder neck. Blockade of the alpha1 receptor decreases urethral resistance and may relieve the BPH symptoms and improve urine flow. Doxazosin mesylate is a selective inhibitor of the alpha1-subtype of alpha adrenergic receptors. In the human prostate, doxazosin mesylate antagonizes phenylephrine (alpha1 agonist)-induced contractions, in vitro, and binds with high affinity to the alpha1A adrenoceptor.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Administration of CARDURA XL to patients with symptomatic BPH resulted in a statistically significant improvement in maximum urinary flow rate [see Clinical Studies (14.1)].
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of CARDURA XL is different from that of doxazosin IR. CARDURA XL provides a controlled release of doxazosin over a 24-hour period.
Absorption
Pharmacokinetic parameters describing absorption following 4 and 8 mg CARDURA XL daily doses are reported in Table 2 below. The relative bioavailability of CARDURA XL compared with doxazosin IR was 54% at the 4 mg dose and 59% for the 8 mg dose.
TABLE 2 Mean (±SD) Plasma Concentration of Doxazosin at Steady State in Healthy Volunteers: Pharmacokinetic Parameters
Parameter
CARDURA XL
(4 mg)
CARDURA XL
(8 mg)
Cmax (ng/mL)
10.1 ± 5.6
25.8 ± 12.1
AUC(0 - ∞)
183 ± 85.5
472 ± 170.8
Tmax (h)
8 ± 3.7
9 ± 4.7
Food Effect
As illustrated in Figure 1, the plasma Cmax and AUC were approximately 32% and 18% higher, respectively, after CARDURA XL was administered in the fed state compared with the fasted state. In order to provide the most consistent exposure, CARDURA XL should be administered with breakfast [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
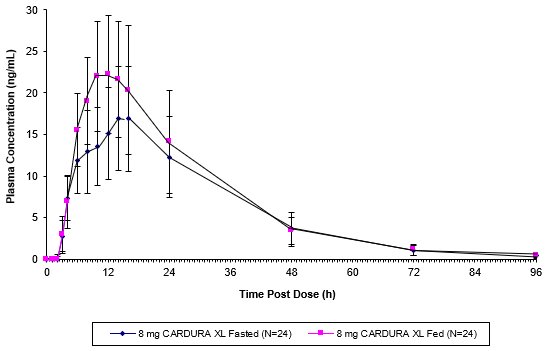
Figure 1: Mean (+SD) Plasma Concentration of Doxazosin Following Single Oral Doses of 8 mg CARDURA XL (Fed and Fasted)
GI Retention Time Effect
Markedly reduced GI retention times (e.g., short bowel syndrome) may influence the pharmacokinetics of CARDURA XL and possibly result in lower plasma concentrations. Conversely, markedly prolonged GI retention times (e.g., chronic constipation) can increase systemic exposure to doxazosin and potentially result in increased adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
Distribution
At the plasma concentrations achieved by therapeutic doses, approximately 98% of the circulating drug is bound to plasma proteins.
Metabolism
Doxazosin is extensively metabolized in the liver. In vitro studies suggest that the primary pathway for elimination is via CYP 3A4; however, CYP 2D6 and CYP 2C9 metabolic pathways also exist to a lesser extent. No in vivo drug interaction studies have been performed with CARDURA XL. Although several active metabolites of doxazosin have been identified, the pharmacokinetics of these metabolites has not been characterized [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Excretion
In a study of two subjects administered radiolabeled doxazosin IR 2 mg orally and 1 mg intravenously on two separate occasions, approximately 63% of the dose was eliminated in the feces and 9% of the dose was found in the urine. On average, only 4.8% of the dose was excreted as unchanged drug in the feces and only a trace of the total radioactivity in the urine was attributed to unchanged drug. The apparent elimination half-life of CARDURA XL is 15-19 hours.
Drug-Drug Interactions
No in vivo drug-drug interaction studies have been performed to assess the effect of concomitant medications on the pharmacokinetics of CARDURA XL or to assess the effect of CARDURA XL on the pharmacokinetics of other drugs. In vitro studies suggest that doxazosin is a substrate of CYP 3A4. Caution should be exercised when concomitantly administering CARDURA XL with a strong CYP 3A4 inhibitor, such as atazanavir, clarithromycin, indinavir, itraconazole, ketoconazole, nefazodone, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, telithromycin, or voriconazole.
In one placebo-controlled trial in normal volunteers, the administration of a single 1 mg dose of doxazosin IR on day 1 of a four-day regimen of cimetidine (400 mg twice daily) resulted in a 10% increase in the mean AUC of doxazosin, a 6% increase in mean Cmax of doxazosin, and no significant change in mean half-life of doxazosin. Based upon the differences in dose and formulation, the applicability of these results to CARDURA XL is unknown. Otherwise, the interaction potential with other inhibitors or substrates of CYP enzymes has not been determined. Pharmacodynamic interactions between CARDURA XL and anti-hypertensive medications or other vasodilating agents have also not been determined. Finally, drugs which reduce gastrointestinal motility leading to markedly prolonged GI retention times (e.g., anticholinergic agents) may increase systemic exposure to doxazosin.
Use in Specific Populations
Geriatric
In a study to assess the effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of CARDURA XL, increases of 27% in plasma Cmax and 34% in the plasma AUC were seen at steady state in the elderly (> 65 years old) compared to the young [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Hepatic Impairment
Administration of a single 2 mg dose of doxazosin IR to patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A) showed a 40% increase in exposure to doxazosin compared to patients without hepatic impairment. No studies have been performed to assess the effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of CARDURA XL. Use in patients with severe hepatic impairment is not recommended. CARDURA XL should be administered with caution to patients with evidence of mild or moderately impaired hepatic function or to patients receiving drugs known to influence hepatic metabolism.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Carcinogenesis and Mutagenesis
Doxazosin mesylate was not carcinogenic to rats or mice when administered daily for 2 years at doses up to 40 mg/kg/day or 120 mg/kg/day, respectively. Systemic drug exposures, as measured by AUC, were approximately 34-fold in rats and 16-fold in mice above the exposures at the maximum human recommended dose (MHRD) of 8 mg CARDURA XL.
Doxazosin base was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial Ames assays, the chromosomal aberration assay in human lymphocytes, or the mouse lymphoma assay. Doxazosin was not clastogenic in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay. Doxazosin mesylate has not been evaluated for genotoxicity.
Fertility in Males
Studies in rats after oral administration of doxazosin base showed reduced fertility in males, which was reversible after two weeks of treatment termination at doxazosin base exposure of 13-fold above the human exposure (AUC) at the MHRD of 8 mg CARDURA XL. There have been no reports of any effects of doxazosin on male fertility in humans.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and Pharmacology
Studies in Sprague-Dawley rats after 6, 12, and 18 months, and in CD-1 mice after 18 months of dietary administration, showed an increased incidence of myocardial necrosis or fibrosis at doxazosin base exposure of 26-fold above the human exposure (AUC) at the MHRD of 8 mg CARDURA XL. No cardiotoxicity was observed in dogs or Wistar rats after 12 months of oral dosing at doxazosin base exposures of 65- and 85-fold, respectively, above the human exposure (Cmax) at the MHRD of 8 mg CARDURA XL. There is no evidence that similar lesions occur in humans.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Studies in Patients with BPH
Two controlled clinical studies were conducted with CARDURA XL in BPH patients, followed by an open-label extension study. Study 1 was a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, placebo- and active-controlled study that compared the safety and efficacy of CARDURA XL (4 or 8 mg/day) with that of doxazosin IR (1, 2, 4, or 8 mg/day) and placebo over 13 weeks in 795 BPH patients, of whom 317 were randomized to CARDURA XL. Study 2 was a randomized, double-blind, parallel-group, active-controlled study that compared the safety and efficacy of CARDURA XL (4 or 8 mg/day) with that of doxazosin IR (1, 2, 4, or 8 mg/day) over 13 weeks in 680 BPH patients, of whom 350 were randomized to CARDURA XL.
In both studies, men aged 50-80 years with symptomatic benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) were enrolled. Symptomatic BPH was defined as a total score of at least 12 points on the 35-point International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and a maximum urinary flow rate of ≤ 15 mL/sec but no less than 5 mL/sec (total voided volume ≥ 150 mL). In these two studies, conducted in a total of 1475 patients, the mean age was 64 years (range 47-83 years). Patients were Caucasian (96%), Black (1.5%), Asian (1.5%), and of Other ethnicity (1%).
In both studies, CARDURA XL dosing was initiated after a 2-week placebo run-in period at 4 mg per day increasing to 8 mg per day after 7 weeks of treatment if adequate response (defined as having both an increase in maximum urinary flow rate of at least 3 mL/sec and a decrease in total IPSS of at least 30% from baseline) was not seen. Doxazosin IR was titrated from an initial dose of 1 mg daily to 2 mg daily after 1 week with the option to increase to 4 mg daily after 3 weeks and then to a maximum of 8 mg daily after 7 weeks if an adequate response was not seen. The final daily dose of CARDURA XL was 4 mg in 43% of patients and 8 mg in 57% of patients. The final daily dose of doxazosin IR was 1 mg in 1%, 2 mg in 12%, 4 mg in 30%, and 8 mg in 57% of patients.
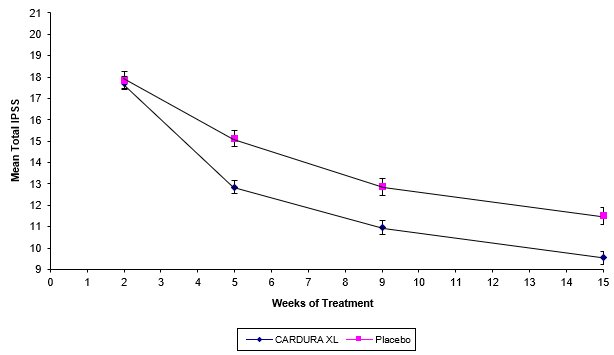
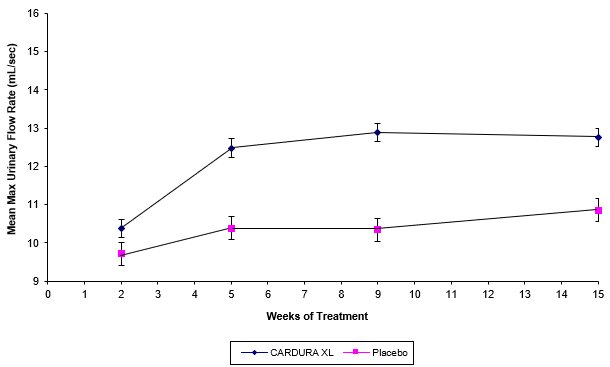
There were two primary efficacy variables in each of these two controlled clinical studies: the total International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) and the peak urinary flow rate (Qmax). The IPSS consists of seven questions that assess the severity of both irritative (frequency, urgency, nocturia) and obstructive (incomplete emptying, stopping and starting, weak stream, and pushing or straining) symptoms, with possible total scores ranging from 0 to 35. The Qmax was measured in both studies just prior to the next dose. The results for total symptom score are given in Table 3, and for maximum urinary flow rate in Table 4.
TABLE 3 - * Derived from IPSS questionnaire (range 0-35)
- † Mean change from baseline to Week 13
- ‡ Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) vs. placebo
TOTAL INTERNATIONAL PROSTATE SYMPTOM SCORE (IPSS)*
N
MEAN BASELINE
(± SD)
MEAN CHANGE
(± SE)†
STUDY 1
Placebo
151
17.9 ± 4.3
-6.1 ± 0.41
CARDURA XL
310
17.7 ± 4.3
-8.0 ± 0.30‡
Doxazosin IR
311
17.8 ± 4.5
-8.4 ± 0.29‡
STUDY 2
CARDURA XL
330
18.4 ± 5.0
-8.1 ± 0.30
Doxazosin IR
313
18.4 ± 4.8
-7.9 ± 0.31
TABLE 4 - * Mean change from baseline to Week 13
- † Statistically significant difference (p < 0.001) vs. placebo
MAXIMUM FLOW RATE (mL/sec)
N
MEAN BASELINE
(± SD)
MEAN CHANGE
(± SE)*
STUDY 1
Placebo
151
9.8 ± 2.6
0.8 ± 0.32
CARDURA XL
300
10.3 ± 2.6
2.6 ± 0.24†
Doxazosin IR
303
10.1 ± 2.7
2.2 ± 0.23†
STUDY 2
CARDURA XL
322
10.5 ± 2.6
2.7 ± 0.27
Doxazosin IR
314
10.6 ± 2.6
2.7 ± 0.27
Mean changes in IPSS scores for CARDURA XL and placebo in Study 1 are summarized in Figure 2.
Mean changes in maximum urinary flow rate (Qmax) for both CARDURA XL and placebo in Study 1 are summarized in Figure 3.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
CARDURA XL (doxazosin) extended-release tablets is available as 4 mg (white, imprinted with CXL 4) and 8 mg (white, imprinted with CXL 8) tablets.
Bottle of 30: 4 mg (NDC: 58151-078-93)
Bottle of 30: 8 mg (NDC: 58151-079-93)Storage
Recommended Storage: Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15-30°C (59-86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information)
17.1 Postural Hypotension
Patients should be told about the possible occurrence of symptoms related to postural hypotension, such as dizziness or syncope, when beginning therapy or when increasing dosage strength of CARDURA XL. Patients should be cautioned about driving, operating machinery, or performing hazardous tasks during this period, until the drug’s effect has been determined.
17.2 Priapism
Inform the patient about the possibility of priapism as a result of treatment with CARDURA XL extended-release tablets and other similar medications. Patients should be informed that this reaction is extremely rare, but if not brought to immediate medical attention, can lead to permanent erectile dysfunction.
17.3 Tablet Administration
Patients should be informed that CARDURA XL extended-release tablets should be swallowed whole. Patients should not chew, divide, cut, or crush tablets.
17.5 Tablet Elimination
Patients should not be concerned if they occasionally notice in their stool something that looks like a tablet. In the CARDURA XL extended-release tablet, the medication is contained within a nonabsorbable shell designed to release the drug at a controlled rate. When this process is completed, the empty tablet is eliminated from the body.
Distributed by:
Viatris Specialty LLC
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.© 2023 Viatris Inc.
CARDURA is a registered trademark of Viatris Specialty LLC, a Viatris Company
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
UPJ:CRDAXL:R1
-
PATIENT INFORMATION
CARDURA® XL (kar-DUR-a eks el)
(doxazosin)
TabletsRead this Patient Information leaflet before you start taking CARDURA XL and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking to your healthcare provider about your medical condition or your treatment.
What is CARDURA XL?
CARDURA XL is a prescription medicine called an “alpha-blocker”. CARDURA XL is used to treat the symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). CARDURA XL may help to relax the muscles in the prostate and the bladder which may lessen the symptoms of BPH and improve urine flow.
Before prescribing CARDURA XL, your healthcare provider may examine your prostate gland and do a blood test called a prostate specific antigen (PSA) test to check for prostate cancer. Prostate cancer and BPH can cause the same symptoms. Prostate cancer needs a different treatment.
Some medicines called “alpha-blockers” are used to treat high blood pressure. CARDURA XL is not for the treatment of high blood pressure.
It is not known if CARDURA XL is safe and effective in children.
Who should not take CARDURA XL?
Do not take CARDURA XL if you are allergic to doxazosin, other medications called quinazolines, or any of the ingredients in CARDURA XL. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in CARDURA XL.
What should I tell my healthcare provider before taking CARDURA XL?
Before you take CARDURA XL, tell your healthcare provider if you:
- have or have had low blood pressure, especially after taking another medicine. Signs of low blood pressure are fainting, dizziness, and lightheadedness.
- plan to have cataract surgery
- have stomach problems
- have prostate cancer
- have liver problems
- have heart problems
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
CARDURA XL may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how CARDURA XL works.
Especially tell your healthcare provider if you take:
- a medicine to treat an infection
- a medicine to treat HIV
- a medicine to treat depression
- a medicine to treat erectile dysfunction (ED)
Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist if you are not sure if your medicine is one of those listed above.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of them to show your healthcare provider and pharmacist when you get a new medicine.
How should I take CARDURA XL?
- Take CARDURA XL exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take CARDURA XL 1 time each day with your breakfast.
- Take CARDURA XL tablets whole. Do not chew, divide, cut, or crush CARDURA XL tablets before swallowing. If you cannot swallow CARDURA XL tablets whole, tell your healthcare provider. You may need a different medicine.
- CARDURA XL tablets have an outside shell that helps to release the medicine inside over time. You may see the empty CARDURA XL tablet in your stool (bowel movement). This is normal.
- If you take too much CARDURA XL, call your healthcare provider or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What should I avoid while taking CARDURA XL?
Do not drive, operate machinery, or do other dangerous activities until you know how CARDURA XL affects you. CARDURA XL can cause dizziness, weakness, or fainting.
What are the possible side effects of CARDURA XL?
CARDURA XL may cause serious side effects including:
-
a sudden drop in blood pressure (postural hypotension). Postural hypotension can happen at any time while you take CARDURA XL. The chance of having postural hypotension is higher a few hours after you take CARDURA XL or if you start taking a higher dose.
Symptoms of postural hypotension may happen after you stand up from a lying or sitting position and may include:- o dizziness or
- o fainting or
- o feeling light-headed
- You should get up slowly from a chair or bed until you know how CARDURA XL will affect you. If you begin to feel dizzy or lightheaded, sit or lie down with your legs and feet up. If your symptoms do not get better call your healthcare provider.
- intraoperative floppy iris syndrome (IFIS). IFIS can happen during eye surgery to people who are taking or have taken alpha-blockers such as CARDURA XL. If you have an eye surgery for a clouding of the eye (cataract) planned, tell your eye doctor that you are using CARDURA XL or have taken an alpha-blocker before.
- blockage of the digestive tract. There have been rare reports of symptoms of blockage in the digestive tract in patients with prior history of narrowing or blockage of the digestive tract. These symptoms are severe and persistent abdominal pain/cramping/bloating. If you know you have a narrowing of your digestive tract and you experience these symptoms, contact your healthcare provider.
- prolonged erection of the penis. Extremely rarely, CARDURA XL and similar medications have caused painful erection of the penis, sustained for hours and unrelieved by sexual intercourse or masturbation. This condition is serious, and if untreated it can be followed by permanent inability to have an erection. If you have a prolonged abnormal erection, call your doctor or go to an emergency room as soon as possible.
The most common side effects of CARDURA XL include:
- tiredness
- headache
- low blood pressure
- dizziness
Call your healthcare provider if you get any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of CARDURA XL. For more information ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store CARDURA XL?
- Store CARDURA XL at 59°F to 86°F (15°C to 30°C).
Keep CARDURA XL and all medicines out of reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of CARDURA XL.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use CARDURA XL for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give CARDURA XL to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about CARDURA XL. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for information about CARDURA XL that is written for health professionals.
For more information, call Viatris at 1-877-446-3679 (1-877-4-INFO-RX).
What are the ingredients in CARDURA XL?
Active Ingredient: doxazosin
Inactive Ingredients: black iron oxide, cellulose acetate, hypromellose, Macrogol®, magnesium stearate, pharmaceutical glaze, polyethylene oxide, red ferric oxide, sodium chloride and titanium dioxide.
Distributed by:
Viatris Specialty LLC
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.© 2023 Viatris Inc.
CARDURA is a registered trademark of Viatris Specialty LLC, a Viatris Company
The brands listed are trademarks of their respective owners.
UPJ:PL:CRDAXL:R1
Revised: 5/2023 -
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 4 mg
NDC: 58151-078-93
Cardura® XL
(doxazosin)
extended-release tablets
4 mg*30 Tablets Rx only
Store at 25ºC (77ºF);
excursions permitted to
15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
[see USP Controlled Room
Temperature].PROTECT FROM MOISTURE
AND HUMIDITY.DOSAGE AND USE
See accompanying
prescribing information.*Each tablet contains 5.1 mg
doxazosin mesylate which
includes an overage to provide
4 mg doxazosin as a free base.Distributed by:
Viatris Specialty LLC
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.© 2023 Viatris Inc.
RUPJ078H
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 8 mg
NDC: 58151-079-93
Cardura® XL
(doxazosin)
extended-release tablets
8 mg*30 Tablets Rx only
Store at 25ºC (77ºF);
excursions permitted to
15-30ºC (59-86ºF)
[see USP Controlled Room
Temperature].PROTECT FROM MOISTURE
AND HUMIDITY.DOSAGE AND USE
See accompanying
prescribing information.*Each tablet contains 10.2 mg
doxazosin mesylate which
includes an overage to provide
8 mg doxazosin as a free base.Distributed by:
Viatris Specialty LLC
Morgantown, WV 26505 U.S.A.© 2023 Viatris Inc.
RUPJ079H
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CARDURA XL
doxazosin mesylate tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58151-078 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DOXAZOSIN MESYLATE (UNII: 86P6PQK0MU) (DOXAZOSIN - UNII:NW1291F1W8) DOXAZOSIN 4 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) CELLULOSE ACETATE (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code CXL;4 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58151-078-93 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 04/23/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021269 04/23/2024 CARDURA XL
doxazosin mesylate tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 58151-079 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DOXAZOSIN MESYLATE (UNII: 86P6PQK0MU) (DOXAZOSIN - UNII:NW1291F1W8) DOXAZOSIN 8 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) CELLULOSE ACETATE (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code CXL;8 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 58151-079-93 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/04/2024 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA021269 01/04/2024 Labeler - Viatris Specialty LLC (117455616)
Trademark Results [Cardura]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 CARDURA 73528813 1360101 Live/Registered |
PFIZER INC. 1985-03-25 |
 CARDURA 72144546 0747425 Live/Registered |
Shell Oil Comany 1962-05-14 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.