EQUIOXX- firocoxib tablet, chewable
EQUIOXX by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
EQUIOXX by is a Animal medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
Description:
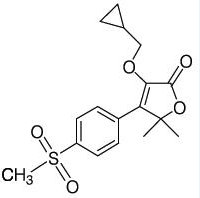
EQUIOXX (firocoxib) Tablets belongs to the coxib class of non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Firocoxib is a white crystalline compound described chemically as 3 (cyclopropylmethoxy)-4-(4-methylsulfonyl)phenyl)-5,5-dimethylfuranone. The empirical formula is C17H20O5S, and the molecular weight is 336.4 g/mol. The structural formula is shown below:
- Indications:
-
Dosage and Administration:
Always provide the Client Information Sheet with the prescription. The recommended dosage of EQUIOXX Tablets is one 57 mg tablet administered orally to horses weighing 800 – 1300 lbs, once daily for up to 14 days. For ease of administration, EQUIOXX Tablets may be given with food.
The overall duration of treatment with any firocoxib formulation in horses, including EQUIOXX Tablets, Injection or Oral Paste, should not exceed 14 days. Please see the package insert for EQUIOXX Injection or Oral Paste for appropriate prescribing information for those formulations.
- Contraindications:
- Warnings:
-
Precautions:
Horses should undergo a thorough history and physical examination before initiation of NSAID therapy. Appropriate laboratory tests should be conducted to establish hematological and serum biochemical baseline data before and periodically during administration of any NSAID. Clients should be advised to observe for signs of potential drug toxicity and be given a Client Information Sheet with each prescription. See Information for Owner or Person Treating Horse section of this package insert.
Treatment with EQUIOXX Tablets should be terminated if signs such as inappetence, colic, abnormal feces, or lethargy are observed.
As a class, cyclooxygenase inhibitory NSAIDs may be associated with gastrointestinal, renal, and hepatic toxicity. Sensitivity to drug-associated adverse events varies with the individual patient. Horses that have experienced adverse reactions from one NSAID may experience adverse reactions from another NSAID. Patients at greatest risk for adverse events are those that are dehydrated, on diuretic therapy, or those with existing renal, cardiovascular, and/or hepatic dysfunction. Concurrent administration of potentially nephrotoxic drugs should be carefully approached or avoided. NSAIDs may inhibit the prostaglandins that maintain normal homeostatic function. Such anti-prostaglandin effects may result in clinically significant disease in patients with underlying or pre-existing disease that has not been previously diagnosed. Since many NSAIDs possess the potential to produce gastrointestinal ulcerations and/or gastrointestinal perforation, concomitant use of EQUIOXX Tablets with other anti-inflammatory drugs, such as NSAIDs or corticosteroids, should be avoided.
The concomitant use of protein bound drugs with EQUIOXX Tablets has not been studied in horses. The influence of concomitant drugs that may inhibit the metabolism of EQUIOXX Tablets has not been evaluated. Drug compatibility should be monitored in patients requiring adjunctive therapy.
The safe use of EQUIOXX Tablets in horses less than one year in age, horses used for breeding, or in pregnant or lactating mares has not been evaluated.
Consider appropriate washout times when switching from one NSAID to another NSAID or corticosteroid.
-
Adverse Reactions:
The safety and effectiveness of EQUIOXX Tablets was established in a relative bioavailability study comparing EQUIOXX Tablets and EQUIOXX (firocoxib) Oral Paste. Therefore, additional field studies were not performed to support the effectiveness of EQUIOXX Tablets.
In controlled field studies, 127 horses (ages 3 to 37 years) were evaluated for safety when given EQUIOXX Oral Paste at a dose of 0.045 mg/lb (0.1 mg/kg) orally once daily for up to 14 days. The following adverse reactions were observed. Horses may have experienced more than one of the observed adverse reactions during the study.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Seen in U.S. Field Studies with EQUIOXX Oral Paste: Adverse Reactions EQUIOXX n = 127 Active Control n = 125 Abdominal pain
0
1
Diarrhea
2
0
Excitation
1
0
Lethargy
0
1
Loose stool
1
0
Polydipsia
0
1
Urticaria
0
1
In these field trials, EQUIOXX Oral Paste was safely used concomitantly with other therapies, including vaccines, anthelmintics, and antibiotics. The safety data sheet (SDS) contains more detailed occupational safety information.
- To report suspected adverse events, for technical assistance, or to obtain a copy of the SDS, contact Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. at 1-888-637-4251. For additional information about adverse drug experience reporting for animal drugs, contact FDA at 1-888-FDA-VETS or online at http://www.fda.gov/AnimalVeterinary/SafetyHealth.
-
Information for Owner or Person Treating Horse:
A Client Information Sheet should be provided to the person treating the horse. Treatment administrators and caretakers should be aware of the potential for adverse reactions and the clinical signs associated with NSAID intolerance. Adverse reactions may include erosions and ulcers of the gums, tongue, lips and face, weight loss, colic, diarrhea, or icterus. Serious adverse reactions associated with this drug class can occur without warning and, in some situations, result in death. Clients should be advised to discontinue NSAID therapy and contact their veterinarian immediately if any of these signs of intolerance are observed. The majority of patients with drug-related adverse reactions recover when the signs are recognized, drug administration is stopped, and veterinary care is initiated.
-
Clinical Pharmacology:
Relative Bioavailability Study
A pharmacokinetic study was conducted to compare the relative bioavailability of an oral firocoxib tablet containing 57 mg firocoxib (EQUIOXX Tablets) to the approved paste formulation (EQUIOXX Oral Paste; NADA 141-253). The criteria for the Test/Reference (T/R) ratios and the 90% Confidence Intervals (CI) of EQUIOXX Tablets (test product) were adjusted on the basis of the safety and effectiveness data for EQUIOXX Oral Paste (reference product). The lower bound of the 90% CI for effectiveness was defined by the minimal effective plasma concentration in the study used to support the dosage characterization of EQUIOXX Oral Paste. Effectiveness was based upon the area under the plasma drug concentration-time curve to the last quantifiable concentration (AUClast), with the effectiveness criteria set at a T/R ratio of greater than or equal to 0.77 and a corresponding lower bound for the 90% CI set at 0.71. The upper bound of the 90% CI for safety was defined by the maximum safe plasma concentration (Cmax) in the study used to establish a margin of safety for EQUIOXX Oral Paste Based upon that margin of safety, product safety was defined as a T/R of less than or equal to 1.53, with a corresponding upper bound for the 90% CI of 1.71.
The relative bioavailability study was a randomized, two period, two sequence crossover study in thirty horses. Each horse received a single tablet (57 mg firocoxib) and a single tube of paste (56.7 mg firocoxib). Blood samples were collected at 15 minutes, 45 minutes, 1, 1.5, 2, 3, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24, 32, 48, 72, 96 and 120 hours following each treatment. Samples were analyzed by LC-MS/MS for firocoxib concentrations. The results of the relative bioavailability study are summarized in Table 2. The Cmax and AUClast of EQUIOXX Tablets were within the adjusted 90% CI for safety and effectiveness and met the criteria established for successfully demonstrating that EQUIOXX Tablets will be safe and effective. Therefore, EQUIOXX Tablets and EQUIOXX Oral Paste are acceptable as pharmaceutical alternatives.
There was a substantial difference in the Tmax (time to maximum plasma concentration) between EQUIOXX Oral Paste and EQUIOXX Tablets. The Tmax ranged from 0.25-4 hours for EQUIOXX Oral Paste and 0.25-12 hours for EQUIOXX Tablets. The difference in the rate and extent of absorption was greatest within the first three hours after administration. The mean terminal elimination half-life of EQUIOXX Oral Paste (45.45 hours) was similar to that of EQUIOXX Tablet (44.49 hours).
Table 2: Relative Bioavailability Results for EQUIOXX Oral Paste (Reference) and EQUIOXX Tablets (Test) (n=30 horses) Parameter Units Reference Geometric Mean Test Geometric Mean Test/Reference Lower 90% CI Upper 90% CI Cmax= maximum observed plasma concentration
AUClast = Area Under the Curve to the last quantifiable time point
CI= Confidence IntervalCmax
ng/mL
78.44
58.85
0.75
67.92
82.88
AUC last
hr*ng/mL
2515.77
2336.32
0.93
86.37
99.85
The major metabolism mechanism of firocoxib in the horse is decyclopropylmethylation followed by glucuronidation of that metabolite. Based upon radiolabel studies done for the firocoxib paste formulation, the majority of firocoxib is eliminated in the urine as the decyclopropylmethylated metabolite. Despite a high degree of plasma protein binding (98%), firocoxib exhibits a large volume of distribution (mean Vd(ss) = 1652 mL/kg). The terminal elimination half-life (T1/2) in plasma averages 30-40 hours after IV, oral paste or tablet dosing. Therefore, drug accumulation occurs with repeated dose administrations and steady state concentrations are achieved beyond 6-8 daily oral doses in the horse.
Mode of Action
EQUIOXX (firocoxib) Tablets is a cyclooxygenase-inhibiting (coxib) class, non-narcotic, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antipyretic activity1 in animal models. Based on in vitro horse data, firocoxib is a selective inhibitor of prostaglandin biosynthesis through inhibition of the inducible cyclooxygenase-2-isoenzyme (COX-2)2,3. Firocoxib selectivity for the constitutive isoenzyme, cyclooxygenase-1 (COX-1) is relatively low. However, the clinical significance of these in vitro selectivity findings has not been established.
-
Effectiveness:
The effectiveness of EQUIOXX Tablets was established in a relative bioavailability study comparing EQUIOXX Tablets and EQUIOXX Oral Paste. Therefore, additional field studies were not performed to support the effectiveness of EQUIOXX Tablets. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Relative Bioavailability Study).
Two hundred fifty-three client-owned horses of various breeds, ranging in age from 2 to 37 years and weighing from 595 to 1638 lbs, were randomly administered EQUIOXX Oral Paste or an active control drug in multi-center field studies. Two hundred forty horses were evaluated for effectiveness and 252 horses were evaluated for safety. Horses were assessed for lameness, pain on manipulation, range of motion, joint swelling, and overall clinical improvement in a non-inferiority evaluation of EQUIOXX Oral Paste compared to an active control. At study's end, 84.4% of horses treated with EQUIOXX Oral Paste were judged improved on veterinarians' clinical assessment, and 73.8% were also rated improved by owners. Horses treated with EQUIOXX Oral Paste showed improvement in veterinarian-assessed lameness, pain on manipulation, range of motion, and joint swelling that was comparable to the active control.
-
Animal Safety:
The safety of EQUIOXX Tablets was supported by a relative bioavailability study comparing EQUIOXX Tablets and EQUIOXX Oral Paste (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, Relative Bioavailability Study), pharmacovigilance information, and target animal safety data for existing firocoxib containing products in horses. No additional target animal safety studies were conducted with EQUIOXX Tablets.
In a target animal safety study conducted to support the approval of EQUIOXX Oral Paste, firocoxib was administered orally to healthy adult horses (two male castrates and four females per group) at 0, 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg firocoxib/kg body weight (1, 3 and 5X the recommended dose) for 30 days. Administration of firocoxib at 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg body weight was associated with an increased incidence of oral ulcers as compared to the control group but, no oral ulcers were noted with 0.1 mg/kg. There were no other drug-related adverse findings in this study.
In another target animal safety study, firocoxib was administered orally to healthy adult horses (four males or male castrates and four females per group) at 0, 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg firocoxib/kg body weight (1, 3 and 5X the recommended dose) for 42 days. Administration of firocoxib at 0.1, 0.3 and 0.5 mg/kg body weight was associated with delayed healing of pre-existing oral (lip, tongue, gingival) ulcers. In addition, the incidence of oral ulcers was higher in all treated groups as compared to the control group.
Clinical chemistry and coagulation abnormalities were seen in several horses in the 0.5 mg/kg (5X) group. One 5X male horse developed a mildly elevated BUN and creatinine over the course of the study, prolonged buccal mucosal bleeding time (BMBT), and a dilated pelvis of the right kidney. Another 5X male had a similar mild increase in creatinine during the study but did not have any gross abnormal findings. One female in the 5X group had a prolonged BMBT, bilateral tubulointerstitial nephropathy and bilateral papillary necrosis.
Tubulointerstitial nephropathy occurred in one 3X female, two 3X male horses, and the 5X female horse discussed above with the prolonged BMBT. Papillary necrosis was present in one 1X male horse and the 5X female horse discussed above. Despite the gross and microscopic renal lesions, all of the horses were clinically healthy and had normal hematology, clinical chemistry and urinalysis values.
In another target animal safety study, firocoxib was administered orally to healthy adult horses (three females, two male castrates and one male per group) at 0, 0.25 mg/kg, 0.75 mg/kg and 1.25 mg/kg (2.5, 7.5 and 12.5X the recommended dose of 0.1 mg/kg) for 92 days. An additional group of three females, two male castrates and one male per group, was dosed at 1.25 mg/kg for 92 days but was monitored until Days 147-149. There were treatment-related adverse events in all treated groups. These consisted of ulcers of the lips, gingiva and tongue and erosions of the skin of the mandible and head. Gross and microscopic lesions of the kidneys consistent with tubulointerstitial nephropathy were seen in all treated groups. Papillary necrosis was seen in the 2.5X and 12.5X groups. In addition, several 12.5X horses had elevated liver enzymes (GGT, SDH, AST and ALT). One 2.5X horse had increased urine GGT and urine protein levels which was due to renal hemorrhage and nephropathy. Gastric ulcers of the margo plicatus and glandular area were more prevalent in the 2.5X and 7.5X groups, but not seen in the 12.5X group. The group of horses that were monitored until Days 147-149 showed partial to full recovery from oral and skin ulcers, but no recovery from tubulointerstitial nephropathy.
In a target animal safety study conducted to assess the safety of EQUIOXX Injection followed by EQUIOXX Oral Paste in the horse, thirty-two clinically healthy adult horses received EQUIOXX Injection intravenously once daily for five days at doses of either 0 mg/kg (control group); 0.09 mg/kg (1X); 0.27 mg/kg (3X); or 0.45 mg/kg (5X the recommended dose). This was followed by once daily oral administration of EQUIOXX Oral paste for nine days at doses of either 0 mg/kg (control group); 0.1 mg/kg (1X); 0.3 mg/kg (3X); or 0.5 mg/kg (5X the recommended dose). This sequence (five days of EQUIOXX Injection followed by nine days EQUIOXX Oral Paste, for a total of 14 days) was repeated three times for a total treatment duration of 42 days (3X the recommended treatment duration of 14 days). Two male 5X horses demonstrated a white focus in the renal cortex which correlated with tubulointerstitial nephropathy microscopically. The presence of tubulointerstitial nephropathy was considered treatment-related. One horse from the control group and two horses from the 5X group had injection site swellings during treatment. Injection site changes characterized by inflammatory cell influx and rarely tissue necrosis were seen in all study groups including the control group. There was a dose-dependent increase in the incidence of oral ulcers and erosions. Elevated hepatic enzymes (GGT or AST) were noted in all study groups at one or more time points. One male 5X horse with an elevated GGT value on Day 42 was noted to have tubulointerstitial nephropathy at the time of necropsy. For all horses, these hepatic enzyme elevations generally returned to the reference range by the next time point.
- Storage Information:
- How Supplied:
-
REFERENCES
1McCann ME, Rickes EL, Hora DF, Cunningham PK et al. In vitro effects and in vivo efficacy of a novel cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor in cats with lipopolysaccharide-induced pyrexia. Am J Vet Res. 2005 Jul;66 (7):1278-84
2McCann ME, Anderson DR, Brideau C et al. In vitro activity and in vivo efficacy of a novel COX-2 inhibitor in the horse. Proceedings of the Academy of Veterinary Internal Medicine. 2002. Abstract 114, p.789.
3Data on file
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Equioxx®
(firocoxib) Tablets
57 mgNon-steroidal Anti-inflammatory drug
Information for Horse Owners
EQUIOXX Tablets are administered once daily for up to 14 days for the control of pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis in horses.
This summary contains important information about EQUIOXX Tablets. You should read this information before you start giving your horse EQUIOXX Tablets and review it each time your prescription is refilled. This sheet is provided only as a summary and does not take the place of instructions from your veterinarian. Talk to your veterinarian if you need clarification, have questions, or you want to know more about EQUIOXX Tablets.
What is EQUIOXX Tablets?
EQUIOXX Tablets is a veterinary prescription non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) of the coxib class used to control pain and inflammation associated with osteoarthritis in horses. Osteoarthritis (OA) is a painful condition caused by progressive "wear and tear" of cartilage and other parts of the joints that may result in the following changes or signs in your horse:
- Limping or lameness.
- Decreased activity or exercise (reluctance to stand, walk, trot or run, or difficulty performing these activities).
- Stiffness or decreased movement of joints.
How to give EQUIOXX Tablets to your horse.
EQUIOXX Tablets should be given according to your veterinarian's instructions. Do not change the way you give EQUIOXX Tablets to your horse without first speaking with your veterinarian. Do not exceed 14 days of treatment.
EQUIOXX Tablets may be given with or without food. Do not give PREVICOX® (firocoxib) Chewable Tablets for Dogs to horses, as overdoses may occur and result in serious side effects.
What kind of results can I expect when my horse is on EQUIOXX Tablets for OA?
While EQUIOXX Tablets are not a cure for osteoarthritis, it can control the pain and inflammation associated with OA and can improve your horse's mobility.
Which horses should not receive EQUIOXX Tablets?
Your horse should not be given EQUIOXX Tablets if he/she:
- Has an allergic reaction to firocoxib, the active ingredient in EQUIOXX Tablets.
- Has previously had an allergic reaction (such as hives, facial or lower limb swelling, or red or itchy skin) to aspirin or other NSAIDs.
- Is presently taking aspirin, phenylbutazone, flunixin meglumine, diclofenac, ketoprofen, or other NSAIDs or corticosteroids.
- The safety of EQUIOXX Tablets has not been determined in horses less than one year of age or in breeding horses, pregnant or lactating mares.
EQUIOXX Tablets should only be given orally to horses.
- 1. EQUIOXX Tablets is not for use in horses intended for human food consumption.
- 2. People should not take EQUIOXX Tablets. Keep EQUIOXX Tablets and all medications out of the reach of children. Consult a physician in case of accidental ingestion by humans.
- 3. Store EQUIOXX Tablets out of reach of dogs and other pets in a secured location in order to prevent accidental ingestion or overdose.
What to tell/ask your veterinarian before giving EQUIOXX Tablets.
Talk to your veterinarian about:
- The signs of OA you have observed in your horse, such as limping or stiffness.
- If any tests, such as X-rays, will be done before EQUIOXX Tablets is prescribed.
- How often your horse may need to be examined by your veterinarian.
- The risks and benefits of using EQUIOXX Tablets.
Tell your veterinarian if your horse has ever had the following medical problems:
- Any side effects from taking EQUIOXX Tablets or other NSAIDs, such as aspirin or phenylbutazone.
- Any kidney disease.
- Any liver disease.
- Any gastrointestinal ulcer
Tell your veterinarian about:
- Other medical problems or allergies that your horse has now, or has had in the past.
- All medicines that you are giving or plan to give to your horse, including those you can get without a prescription and any dietary supplements.
Tell your veterinarian if you plan to breed your horse, or if your mare is pregnant or nursing a foal.
What are the possible side effects that may occur in my horse during EQUIOXX Tablets therapy?
EQUIOXX Tablets, like other NSAIDS, may cause some side effects. Serious side effects associated with NSAID therapy in horses can occur with or without warning. The most common side effects associated with EQUIOXX Tablets therapy involve the tongue, lips and skin of the mouth and face (erosions and ulcers of the mucosa and skin) and the kidney. Gastrointestinal, kidney and liver problems have also been reported with other NSAIDs. Look for the following side effects that may indicate your horse is having a problem with EQUIOXX or may have another medical problem:
- Sores or ulcers on the tongue and inside of mouth.
- Sores, scabs, redness, or rubbing of the facial skin, particularly around the mouth.
- Change in eating or drinking habits (frequency or amount consumed).
- Change in urination habits (frequency or color).
- Yellowing of gums, skin, or whites of the eyes (jaundice).
- Unexpected weight loss.
- Change in behavior (such as increased or decreased activity level).
It is important to stop therapy and contact your veterinarian if you think your horse has a medical problem or side effect while taking EQUIOXX Tablets. If you have additional questions about possible side effects, talk with your veterinarian or call 1-888-637-4251.
Can EQUIOXX Tablets be given with other medications?
EQUIOXX® should not be given with other NSAIDs (for example, aspirin, phenylbutazone, diclofenac, ketoprofen or flunixin) or systemic corticosteroids (for example, prednisone, cortisone, dexamethasone, or triamcinolone).
Tell your veterinarian about all medications that you have given your horse in the past, and any medications you are planning to give with EQUIOXX Tablets. This should include other medicines that you can get without a prescription or any dietary supplements. Your veterinarian may want to check that all of your horse's medicines can be given together.
What do I do in case my horse receives more than the prescribed amount of EQUIOXX Tablets?
- Consult your veterinarian if your horse receives more than the prescribed amount of EQUIOXX Tablets.
What else should I know about EQUIOXX Tablets?
- This sheet provides a summary of information about EQUIOXX Tablets and general information about NSAIDs. If you have any questions or concerns about EQUIOXX Tablets or osteoarthritis pain, talk with your veterinarian.
- As with all prescribed medicines, EQUIOXX Tablets should only be given to the horse for which it is prescribed. It should be given to your horse only for the condition for which it is prescribed, at the labeled dose and duration.
- It is important to periodically discuss your horse's response to EQUIOXX Tablets. Your veterinarian will determine if your horse is responding as expected and if your horse should continue receiving EQUIOXX Tablets.
Rev. 11-2018
- Principal Display Panel - 57 mg, 60 Tablet Bottle Carton
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EQUIOXX
firocoxib tablet, chewableProduct Information Product Type PRESCRIPTION ANIMAL DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 0010-3309 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength firocoxib (UNII: Y6V2W4S4WT) (firocoxib - UNII:Y6V2W4S4WT) firocoxib 57 mg Product Characteristics Color BROWN (tan/beige) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code M;57 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 0010-3309-01 1 in 1 CARTON 1 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC 2 NDC: 0010-3309-02 1 in 1 CARTON 2 180 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NADA NADA141458 07/14/2020 Labeler - Boehringer Ingelheim Animal Health USA Inc. (007134091)
Trademark Results [EQUIOXX]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 EQUIOXX 79031787 3298365 Live/Registered |
Merial, Inc. 2006-06-10 |
 EQUIOXX 76274709 2926131 Dead/Cancelled |
MERIAL LIMITED 2001-06-20 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.