HYOSCYAMINE- hyoscyamine sulfate liquid
Hyoscyamine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Hyoscyamine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Patrin Pharma. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Hyoscyamine Sulfate Oral Drops contains 0.125 mg Hyoscyamine Sulfate per mL with 5% v/v alcohol for oral administration.
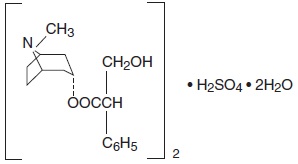
Hyoscyamine Sulfate is one of the principal anticholinergic/antispasmodic components of belladonna alkaloids. The empirical formula is (C17H23NO3)2 H2SO4 2H2O and the molecular weight is 712.85. Chemically, it is benzeneacetic acid, (α-(hydroxymethyl)-,8-methyl-8-azabicyclo [3.2.1.] oct-3-yl ester, [3(S)-endo]-,sulfate (2:1), dihydrate with the following structure:
HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE ORAL DROPS also contain as inactive ingredients: Alcohol, FD&C red #40, FD&C yellow #6, flavor, glycerin, purified water, benzoic acid, sodium citrate, sorbitol solution, and sucrose.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Hyoscyamine Sulfate inhibits the actions of acetylcholine on structures innervated by postganglionic cholinergic nerves and on smooth muscles that respond to acetylcholine but lack cholinergic innervation. These peripheral cholinergic receptors are present in the autonomic effector cells of the smooth muscle, cardiac muscle, the sinoatrial node, the atrioventricular node, and the exocrine glands. At therapeutic doses, it is completely devoid of any action on autonomic ganglia. Hyoscyamine Sulfate inhibits gastrointestinal propulsive motility and decreases gastric acid secretion. Hyoscyamine Sulfate also controls excessive pharyngeal, tracheal and bronchial secretions.
Hyoscyamine Sulfate is absorbed totally and completely by oral administration. Once absorbed, Hyoscyamine Sulfate disappears rapidly from the blood and is distributed throughout the entire body. The half-life of Hyoscyamine Sulfate is 2 to 3 1/2 hours. Hyoscyamine Sulfate is partly hydrolyzed to tropic acid and tropine but the majority of the drug is excreted in the urine unchanged within the first 12 hours. Only traces of this drug are found in breast milk. Hyoscyamine Sulfate passes the blood brain barrier and the placental barrier.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hyoscyamine Sulfate is effective as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of peptic ulcer. It can also be used to control gastric secretion, visceral spasm and hypermotility in spastic colitis, spastic bladder, cystitis, pylorospasm, and associated abdominal cramps. May be used in functional intestinal disorders to reduce symptoms such as those seen in mild dysenteries, diverticulitis, and acute enterocolitis. For use as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of irritable bowel syndrome (irritable colon, spastic colon, mucous colitis) and functional gastrointestinal disorders. Also used as adjunctive therapy in the treatment of neurogenic bladder and neurogenic bowel disturbances (including the splenic flexure syndrome and neurogenic colon). Also used in the treatment of colic (elixir and drops). Hyoscyamine Sulfate is indicated along with morphine or other narcotics in symptomatic relief of biliary and renal colic; as a "drying agent" in the relief of symptoms of acute rhinitis; in the therapy of parkinsonism to reduce rigidity and tremors and to control associated sialorrhea and hyperhidrosis. May be used in the therapy of poisoning by anticholinesterase agents.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Glaucoma; obstructive uropathy (for example, bladder neck obstruction due to prostatic hypertrophy); obstructive disease of the gastrointestinal tract (as in achalasia, pyloroduodenal stenosis); paralytic ileus, intestinal atony of elderly or debilitated patients; unstable cardiovascular status in acute hemorrhage; severe ulcerative colitis; toxic megacolon complicating ulcerative colitis; myasthenia gravis.
-
WARNINGS
In the presence of high environmental temperature, heat prostration can occur with drug use (fever and heat stroke due to decreased sweating). Diarrhea may be an early symptom of incomplete intestinal obstruction, especially in patients with ileostomy or colostomy. In this instance, treatment with this drug would be inappropriate and possibly harmful. Like other anticholinergic agents, Hyoscyamine Sulfate may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. In this event, the patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug.
Psychosis has been reported in sensitive individuals given anticholinergic drugs. CNS signs and symptoms include confusion, disorientation, short term memory loss, hallucinations, dysarthria, ataxia, coma, euphoria, decreased anxiety, fatigue, insomnia, agitation and mannerisms, and inappropriate affect. These CNS signs and symptoms usually resolve within 12 to 48 hours after discontinuation of the drug.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Use with caution in patients with: autonomic neuropathy, hyperthyroidism, coronary heart disease , congestive heart failure, cardiac arrhythmias, hypertension, and renal disease. Investigate any tachycardia before giving any anticholinergic drug since they may increase the heart rate. Use wit h caution in patients with hiatal hernia associated with reflux esophagitis.
Information for Patients:
Like other anticholinergic agents, Hyoscyamine Sulfate may produce drowsiness, dizziness or blurred vision. In this event, the patient should be warned not to engage in activities requiring mental alertness such as operating a motor vehicle or other machinery or to perform hazardous work while taking this drug.
Use of Hyoscyamine Sulfate may decrease sweating resulting in heat prostration, fever or heat stroke; febrile patients or those who may be exposed to elevated environmental temperatures should use caution.
Drug Interactions:
Pregnancy Category C.
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with this product. It is also not known whether this product can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. Hyoscyamine crosses the placenta. This product should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers:
This product is excreted in human milk. This product should not be administered to a nursing mother.
Pediatric Use:
Young children are especially susceptible to the toxic effects of anticholinergics. Close supervision is recommended for children with spastic paralysis or brain damage since an increased response to anticholinergics has been reported in these patients and dosage adjustments are often required. When anticholinergics are given to children where the environmental temperature is high, there is a risk of a rapid increase in body temperature because of these medications' suppression of sweat gland activity.
A paradoxical reaction characterized by hyperexcitability may occur in children taking large doses of anticholinergics.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
No long-term studies in animals have been performed to determine the carcinogenic, mutagenic or impairment of fertility potential of Hyoscyamine Sulfate; however, 40 years of marketing experience with Hyoscyamine Sulfate shows no demonstrable evidence of a problem.
Geriatric Use:
Reported clinical experience has not identified differences in safety between patients aged 65 and over and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
This drug is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
Additive adverse effects resulting from cholinergic blockade may occur when Hyoscyamine Sulfate is administered concomitantly with other antimuscarinics, amantadine, haloperidol, phenothiazines, monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors, tricyclic antidepressants or some antihistamines.
Antacids may interfere with the absorption of Hyoscyamine Sulfate. Administer Hyoscyamine Sulfate before meals; antacids after meals.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions have been reported for Hyoscyamine Sulfate and for pharmacologically similar drugs with anticholinergic/antispasmodic action. Adverse reactions may include dryness of the mouth; urinary hesitancy and retention; blurred vision; tachycardia; palpitations; mydriasis; cycloplegia; increased ocular tension; loss of taste; headache; nervousness; drowsiness; weakness; fatigue; dizziness; insomnia; nausea; vomiting; impotence; suppression of lactation; constipation; bloated feeling; abdominal pain; diarrhea; allergic reactions or drug idiosyncrasies; urticaria and other dermal manifestations; ataxia; speech disturbance; some degree of mental confusion and/or excitement (especially in elderly persons); short-term memory loss; hallucinations; and decreased sweating.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older: 1 to 2 mL every four hours or a s directed by physician. Do not exceed 12 mL in 24 hours.
Pediatric patients 2 years to 12 years of age: 1/4 to 1 mL every four hours or as directed b y physician. Do not exceed 6 mL in 24 hours.
Patients less than 2 years of age: Use as directed by physician with a dosage administered in drops.
The package of Hyoscyamine Sulfate Oral Drops includes a dropper having markings of 3, 4, 5 DROPS, and 0.25 mL. The approximate equivalent amount of Hyoscyamine Sulfate drops (mL) and its equivalent amount of Hyoscyamine Sulfate (mg) for each marking are in the table below. Rinse the dropper after every use and store the bottle using the original cap. Do not leave dropper in the bottle.
Approximate Equivalent Amount Marking on Dropper Hyoscyamine Sulfate Oral
Drops Solution (mL)Hyoscyamine Sulfate (mg) 3 DROPS 0.08 mL 0.01 mg 4 DROPS 0.11 mL 0.01375 mg 5 DROPS 0.14 mL 0.0175 mg 0.25 mL 0.25 mL 0.03125 mg The doses may be repeated every four hours or as needed. Dosage may be adjusted according to the severity of symptoms or as directed by a health care provider. Measure dosage very carefully.
-
OVERDOSAGE
The signs and symptoms of overdose are headache, nausea, vomiting, blurred vision, dilated pupils, hot dry skin, dizziness, dryness of the mouth, difficulty in swallowing and CNS stimulation.
Measures to be taken are immediate lavage of the stomach and injection of physostigmine 0.5 to 2 mg intravenously and repeated as necessary up to a total of 5 mg. Fever may be treated symptomatically (tepid water sponge baths, hypothermic blanket). Excitement to a degree which demands attention may be managed with sodium thiopental 2% solution given slowly intravenously or chloral hydrate (100-200 mL of a 2% solution) by rectal infusion. In the event of progression of the curare-like effect to paralysis of the respiratory muscles, artificial respiration should be instituted and maintained until effective respiratory action returns.
In rats, the LD50 for hyoscyamine is 375 mg/kg. Hyoscyamine Sulfate is dialyzable.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE ORAL DROPS (Hyoscyamine Sulfate 0.125 mg per mL) is orange colored, flavored, and contains 5% alcohol. It is supplied in a 15 mL bottle with a calibrated dropper.
Store at controlled room temperature 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursion permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F). Please refer to current USP.
NDC# 39328-047-15
Also, available as Hyoscyamine Elixir as NDC # 39328-048-16
KEEP OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN
Made for:
Patrin Pharma
P.O. Box 1481
Skokie, Illinois 60076
U.S.A.
For inquiries call toll free 800-936-3088Rev 2.0118
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PABEL - 15 mL BOTTLE CARTON
Rx only
NDC: 39328-047-15HYOSCYAMINE
ORAL DROPS0.125 mg/mL
Hyoscyamine Sulfate Oral Drops
Each mL contains:
Active: Hyoscyamine Sulfate 0.125 mg
Alcohol 5% v/v15 mL (1/2 fl oz)
PATRIN
PHARMA
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
HYOSCYAMINE
hyoscyamine sulfate liquidProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 39328-047 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE (UNII: F2R8V82B84) (HYOSCYAMINE - UNII:PX44XO846X) HYOSCYAMINE SULFATE 0.125 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Glycerin (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) Sucrose (UNII: C151H8M554) SORBITOL (UNII: 506T60A25R) SODIUM CITRATE, UNSPECIFIED FORM (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) ORANGE (UNII: 5EVU04N5QU) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Benzoic Acid (UNII: 8SKN0B0MIM) Alcohol (UNII: 3K9958V90M) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color orange Score Shape Size Flavor ORANGE Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 39328-047-15 15 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 09/04/2011 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date unapproved drug other 09/04/2011 Labeler - Patrin Pharma (806841677)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.