BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE tablet, film coated
Bupropion Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Bupropion Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Contract Pharmacy Services-PA. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
Suicidality and Antidepressant Drugs
Use in Treating Psychiatric Disorders: Antidepressants increased the risk compared to placebo of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults in short-term studies of major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Anyone considering the use of bupropion hydrochloride tablets or any other antidepressant in a child, adolescent, or young adult must balance this risk with the clinical need. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction in risk with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older. Depression and certain other psychiatric disorders are themselves associated with increases in the risk of suicide. Patients of all ages who are started on antidepressant therapy should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, or unusual changes in behavior. Families and caregivers should be advised of the need for close observation and communication with the prescriber. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets is not approved for use in pediatric patients. (See WARNINGS: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk in Treating Psychiatric Disorders, PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients, and PRECAUTIONS: Pediatric Use.)
Use in Smoking Cessation Treatment: Bupropion hydrochloride, bupropion hydrochloride, the sustained-release formulation, and bupropion hydrochloride, the extended-release formulation, are not approved for smoking cessation treatment, but bupropion under the name ZYBAN® (bupropion hydrochloride) Sustained-Release Tablets is approved for this use. Serious neuropsychiatric events, including but not limited to depression, suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, and completed suicide have been reported in patients taking bupropion for smoking cessation. Some cases may have been complicated by the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal in patients who stopped smoking. Depressed mood may be a symptom of nicotine withdrawal. Depression, rarely including suicidal ideation, has been reported in smokers undergoing a smoking cessation attempt without medication. However, some of these symptoms have occurred in patients taking bupropion who continued to smoke.
All patients being treated with bupropion for smoking cessation treatment should be observed for neuropsychiatric symptoms including changes in behavior, hostility, agitation, depressed mood, and suicide-related events, including ideation, behavior, and attempted suicide. These symptoms, as well as worsening of pre-existing psychiatric illness and completed suicide have been reported in some patients attempting to quit smoking while taking ZYBAN in the postmarketing experience. When symptoms were reported, most were during treatment with ZYBAN, but some were following discontinuation of treatment with ZYBAN. These events have occurred in patients with and without pre-existing psychiatric disease; some have experienced worsening of their psychiatric illnesses. Patients with serious psychiatric illness such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder did not participate in the premarketing studies of ZYBAN.
Advise patients and caregivers that the patient using bupropion for smoking cessation should stop taking bupropion and contact a healthcare provider immediately if agitation, hostility, depressed mood, or changes in thinking or behavior that are not typical for the patient are observed, or if the patient develops suicidal ideation or suicidal behavior. In many postmarketing cases, resolution of symptoms after discontinuation of ZYBAN was reported, although in some cases the symptoms persisted; therefore, ongoing monitoring and supportive care should be provided until symptoms resolve.
The risks of using bupropion for smoking cessation should be weighed against the benefits of its use. bupropion hydrochloride tablets has been demonstrated to increase the likelihood of abstinence from smoking for as long as 6 months compared to treatment with placebo. The health benefits of quitting smoking are immediate and substantial. (See WARNINGS: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk in Treating Psychiatric Disorders and PRECAUTIONS: Information for Patients.)
-
DESCRIPTION
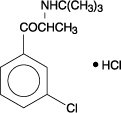
Bupropion hydrochloride, an antidepressant of the aminoketone class, is chemically unrelated to tricyclic, tetracyclic, selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitor, or other known antidepressant agents. Its structure closely resembles that of diethylpropion; it is related to phenylethylamines. It is designated as (±)-1-(3-chlorophenyl)-2-[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]-1-propanone hydrochloride. The molecular weight is 276.2. The molecular formula is C13H18CINOHCI. Bupropion hydrochloride powder is white, crystalline, and highly soluble in water. It has a bitter taste and produces the sensation of local anesthesia on the oral mucosa. It has the following structural formula:
Each bupropion hydrochloride tablet intended for oral administration contains 75 mg or 100 mg bupropion hydrochloride. In addition, each bupropion hydrochloride tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake, FD&C Red No. 40 aluminum lake, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, potassium chloride, pregelatinized starch, stearic acid, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
The neurochemical mechanism of the antidepressant effect of bupropion is not known. Bupropion is a relatively weak inhibitor of the neuronal uptake of norepinephrine and dopamine, and does not inhibit monoamine oxidase or the re-uptake of serotonin.
Bupropion produces dose-related central nervous system (CNS) stimulant effects in animals, as evidenced by increased locomotor activity, increased rates of responding in various schedule-controlled operant behavior tasks, and, at high doses, induction of mild stereotyped behavior.
Bupropion causes convulsions in rodents and dogs at doses approximately tenfold the dose recommended as the human antidepressant dose.
Pharmacokinetics
Bupropion is a racemic mixture. The pharmacological activity and pharmacokinetics of the individual enantiomers have not been studied. In humans, following oral administration of bupropion hydrochloride tablets, peak plasma bupropion concentrations are usually achieved within 2 hours, followed by a biphasic decline. The terminal phase has a mean half-life of 14 hours, with a range of 8 to 24 hours. The distribution phase has a mean half-life of 3 to 4 hours. The mean elimination half-life (±SD) of bupropion after chronic dosing is 21 (±9) hours, and steady-state plasma concentrations of bupropion are reached within 8 days. Plasma bupropion concentrations are dose-proportional following single doses of 100 to 250 mg; however, it is not known if the proportionality between dose and plasma level is maintained in chronic use.
Absorption
The absolute bioavailability of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in humans has not been determined because an intravenous formulation for human use is not available. However, it appears likely that only a small proportion of any orally administered dose reaches the systemic circulation intact.
Distribution
In vitro tests show that bupropion is 84% bound to human plasma protein at concentrations up to 200 mcg/mL. The extent of protein binding of the hydroxybupropion metabolite is similar to that for bupropion, whereas the extent of protein binding of the threohydrobupropion metabolite is about half that seen with bupropion.
Metabolism
Bupropion is extensively metabolized in humans. Three metabolites have been shown to be active: hydroxybupropion, which is formed via hydroxylation of the tert-butyl group of bupropion, and the amino-alcohol isomers threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion, which are formed via reduction of the carbonyl group. In vitro findings suggest that cytochrome P450IIB6 (CYP2B6) is the principal isoenzyme involved in the formation of hydroxybupropion, while cytochrome P450 isoenzymes are not involved in the formation of threohydrobupropion. Oxidation of the bupropion side chain results in the formation of a glycine conjugate of metachlorobenzoic acid, which is then excreted as the major urinary metabolite. The potency and toxicity of the metabolites relative to bupropion have not been fully characterized. However, it has been demonstrated in an antidepressant screening test in mice that hydroxybupropion is one-half as potent as bupropion, while threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion are 5-fold less potent than bupropion. This may be of clinical importance because their plasma concentrations are as high or higher than those of bupropion.
Because bupropion is extensively metabolized, there is the potential for drug-drug interactions, particularly with those agents that are metabolized by the cytochrome P450IIB6 (CYP2B6) isoenzyme. Although bupropion is not metabolized by cytochrome P450IID6 (CYP2D6), there is the potential for drug-drug interactions when bupropion is co-administered with drugs metabolized by this isoenzyme (see PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions).
Following a single dose in humans, peak plasma concentrations of hydroxybupropion occur approximately 3 hours after administration of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Peak plasma concentrations of hydroxybupropion are approximately 10 times the peak level of the parent drug at steady state. The elimination half-life of hydroxybupropion is approximately 20 (±5) hours, and its AUC at steady state is about 17 times that of bupropion. The times to peak concentrations for the erythrohydrobupropion and threohydrobupropion metabolites are similar to that of the hydroxybupropion metabolite. However, their elimination half-lives are longer, 33 (±10) and 37 (±13) hours, respectively, and steady-state AUCs are 1.5 and 7 times that of bupropion, respectively.
Bupropion and its metabolites exhibit linear kinetics following chronic administration of 300 to 450 mg/day.
Elimination
Following oral administration of 200 mg of 14C-bupropion in humans, 87% and 10% of the radioactive dose were recovered in the urine and feces, respectively. However, the fraction of the oral dose of bupropion hydrochloride tablets excreted unchanged was only 0.5%, a finding consistent with the extensive metabolism of bupropion.
Populations Subgroups
Factors or conditions altering metabolic capacity (e.g., liver disease, congestive heart failure [CHF], age, concomitant medications, etc.) or elimination may be expected to influence the degree and extent of accumulation of the active metabolites of bupropion. The elimination of the major metabolites of bupropion may be affected by reduced renal or hepatic function because they are moderately polar compounds and are likely to undergo further metabolism or conjugation in the liver prior to urinary excretion.
Hepatic
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion was characterized in 2 single-dose studies, one in patients with alcoholic liver disease and one in patients with mild-to-severe cirrhosis. The first study showed that the half-life of hydroxybupropion was significantly longer in 8 patients with alcoholic liver disease than in 8 healthy volunteers (32 ± 14 hours versus 21 ± 5 hours, respectively). Although not statistically significant, the AUCs for bupropion and hydroxybupropion were more variable and tended to be greater (by 53% to 57%) in volunteers with alcoholic liver disease. The differences in half-life for bupropion and the other metabolites in the 2 patient groups were minimal.
The second study showed that there were no statistically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of bupropion and its active metabolites in 9 patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis compared to 8 healthy volunteers. However, more variability was observed in some of the pharmacokinetic parameters for bupropion (AUC, Cmax, and Tmax) and its active metabolites (t1/2) in patients with mild to moderate hepatic cirrhosis. In addition, in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis, the bupropion Cmax and AUC were substantially increased (mean difference: by approximately 70% and 3-fold, respectively) and more variable when compared to values in healthy volunteers; the mean bupropion half-life was also longer (29 hours in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis vs. 19 hours in healthy subjects). For the metabolite hydroxybupropion, the mean Cmax was approximately 69% lower. For the combined amino-alcohol isomers threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion, the mean Cmax was approximately 31% lower. The mean AUC increased by about 11/2-fold for hydroxybupropion and about 21/2-fold for threo/erythrohydrobupropion. The median Tmax was observed 19 hours later for hydroxybupropion and 31 hours later for threo/erythrohydrobupropion. The mean half-lives for hydroxybupropion and threo/erythrohydrobupropion were increased 5- and 2-fold, respectively, in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis compared to healthy volunteers (see WARNINGS, PRECAUTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Renal
There is limited information on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion in patients with renal impairment. An inter-study comparison between normal subjects and patients with end-stage renal failure demonstrated that the parent drug Cmax and AUC values were comparable in the 2 groups, whereas the hydroxybupropion and threohydrobupropion metabolites had a 2.3- and 2.8-fold increase, respectively, in AUC for patients with end-stage renal failure. A second study, comparing normal subjects and patients with moderate-to-severe renal impairment (GFR 30.9 ± 10.8 mL/min) showed that exposure to a single 150 mg dose of sustained-release bupropion was approximately 2-fold higher in patients with impaired renal function while levels of the hydroxybupropion and threo/erythrohydrobupropion (combined) metabolites were similar in the 2 groups. The elimination of bupropion and/or the major metabolites of bupropion may be reduced by impaired renal function (see PRECAUTIONS: Renal Impairment).
Left Ventricular Dysfunction
During a chronic dosing study in 14 depressed patients with left ventricular dysfunction (history of CHF or an enlarged heart on x-ray), no apparent effect on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion or its metabolites was revealed, compared to healthy volunteers.
Age
The effects of age on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion and its metabolites have not been fully characterized, but an exploration of steady-state bupropion concentrations from several depression efficacy studies involving patients dosed in a range of 300 to 750 mg/day, on a 3 times daily schedule, revealed no relationship between age (18 to 83 years) and plasma concentration of bupropion. A single-dose pharmacokinetic study demonstrated that the disposition of bupropion and its metabolites in elderly subjects was similar to that of younger subjects. These data suggest there is no prominent effect of age on bupropion concentration; however, another pharmacokinetic study, single and multiple dose, has suggested that the elderly are at increased risk for accumulation of bupropion and its metabolites (see PRECAUTIONS: Geriatric Use).
Gender
A single-dose study involving 12 healthy male and 12 healthy female volunteers revealed no sex-related differences in the pharmacokinetic parameters of bupropion.
Smokers
The effects of cigarette smoking on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion were studied in 34 healthy male and female volunteers; 17 were chronic cigarette smokers and 17 were nonsmokers. Following oral administration of a single 150 mg dose of bupropion, there were no statistically significant differences in Cmax, half-life, Tmax, AUC or clearance of bupropion or its active metabolites between smokers and nonsmokers.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are indicated for the treatment of major depressive disorder. A physician considering bupropion hydrochloride tablets for the management of a patient’s first episode of depression should be aware that the drug may cause generalized seizures in a dose-dependent manner with an approximate incidence of 0.4% (4/1,000). This incidence of seizures may exceed that of other marketed antidepressants by as much as 4-fold. This relative risk is only an approximate estimate because no direct comparative studies have been conducted (see WARNINGS).
The efficacy of bupropion hydrochloride tablets has been established in 3 placebo-controlled trials, including 2 of approximately 3 weeks’ duration in depressed inpatients and one of approximately 6 weeks’ duration in depressed outpatients. The depressive disorder of the patients studied corresponds most closely to the Major Depression category of the APA Diagnostic and Statistical Manual III.
Major Depression implies a prominent and relatively persistent depressed or dysphoric mood that usually interferes with daily functioning (nearly every day for at least 2 weeks); it should include at least 4 of the following 8 symptoms: change in appetite, change in sleep, psychomotor agitation or retardation, loss of interest in usual activities or decrease in sexual drive, increased fatigability, feelings of guilt or worthlessness, slowed thinking or impaired concentration, and suicidal ideation or attempts.
Effectiveness of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in long-term use, that is, for more than 6 weeks, has not been systematically evaluated in controlled trials. Therefore, the physician who elects to use bupropion hydrochloride tablets for extended periods should periodically reevaluate the long-term usefulness of the drug for the individual patient.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with a seizure disorder.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients treated with ZYBAN (bupropion hydrochloride) Sustained-Release Tablets; Wellbutrin SR (bupropion hydrochloride), the sustained-release formulation; Wellbutrin XL (bupropion hydrochloride), the extended-release formulation; or any other medications that contain bupropion because the incidence of seizure is dose dependent.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients with a current or prior diagnosis of bulimia or anorexia nervosa because of a higher incidence of seizures noted in such patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients undergoing abrupt discontinuation of alcohol or sedatives (including benzodiazepines).
The concurrent administration of bupropion hydrochloride tablets and a monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitor is contraindicated. At least 14 days should elapse between discontinuation of an MAO inhibitor and initiation of treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are contraindicated in patients who have shown an allergic response to bupropion or the other ingredients that make up bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
-
WARNINGS
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk in Treating Psychiatric Disorders
Patients with major depressive disorder (MDD), both adult and pediatric, may experience worsening of their depression and/or the emergence of suicidal ideation and behavior (suicidality) or unusual changes in behavior, whether or not they are taking antidepressant medications, and this risk may persist until significant remission occurs. Suicide is a known risk of depression and certain other psychiatric disorders, and these disorders themselves are the strongest predictors of suicide. There has been a long-standing concern, however, that antidepressants may have a role in inducing worsening of depression and the emergence of suicidality in certain patients during the early phases of treatment. Pooled analyses of short-term placebo-controlled trials of antidepressant drugs (SSRIs and others) showed that these drugs increase the risk of suicidal thinking and behavior (suicidality) in children, adolescents, and young adults (ages 18-24) with major depressive disorder (MDD) and other psychiatric disorders. Short-term studies did not show an increase in the risk of suicidality with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults beyond age 24; there was a reduction with antidepressants compared to placebo in adults aged 65 and older.
The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in children and adolescents with MDD, obsessive compulsive disorder (OCD), or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 24 short-term trials of 9 antidepressant drugs in over 4,400 patients. The pooled analyses of placebo-controlled trials in adults with MDD or other psychiatric disorders included a total of 295 short-term trials (median duration of 2 months) of 11 antidepressant drugs in over 77,000 patients. There was considerable variation in risk of suicidality among drugs, but a tendency toward an increase in the younger patients for almost all drugs studied. There were differences in absolute risk of suicidality across the different indications, with the highest incidence in MDD. The risk differences (drug vs placebo), however, were relatively stable within age strata and across indications. These risk differences (drug-placebo difference in the number of cases of suicidality per 1,000 patients treated) are provided in Table 1.
Table 1 Age Range Drug-Placebo Difference in
Number of Cases of Suicidality
per 1,000 Patients TreatedIncreases Compared to Placebo <18 14 additional cases 18-24 5 additional cases Decreases Compared to Placebo 25-64 1 fewer case ≥65 6 fewer cases No suicides occurred in any of the pediatric trials. There were suicides in the adult trials, but the number was not sufficient to reach any conclusion about drug effect on suicide.
It is unknown whether the suicidality risk extends to longer-term use, i.e., beyond several months. However, there is substantial evidence from placebo-controlled maintenance trials in adults with depression that the use of antidepressants can delay the recurrence of depression.
All patients being treated with antidepressants for any indication should be monitored appropriately and observed closely for clinical worsening, suicidality, and unusual changes in behavior, especially during the initial few months of a course of drug therapy, or at times of dose changes, either increases or decreases.
The following symptoms, anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, and mania, have been reported in adult and pediatric patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder as well as for other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric. Although a causal link between the emergence of such symptoms and either the worsening of depression and/or the emergence of suicidal impulses has not been established, there is concern that such symptoms may represent precursors to emerging suicidality.
Consideration should be given to changing the therapeutic regimen, including possibly discontinuing the medication, in patients whose depression is persistently worse, or who are experiencing emergent suicidality or symptoms that might be precursors to worsening depression or suicidality, especially if these symptoms are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms.
Families and caregivers of patients being treated with antidepressants for major depressive disorder or other indications, both psychiatric and nonpsychiatric, should be alerted about the need to monitor patients for the emergence of agitation, irritability, unusual changes in behavior, and the other symptoms described above, as well as the emergence of suicidality, and to report such symptoms immediately to healthcare providers. Such monitoring should include daily observation by families and caregivers. Prescriptions for bupropion hydrochloride should be written for the smallest quantity of tablets consistent with good patient management, in order to reduce the risk of overdose.
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and Suicide Risk in Smoking Cessation Treatment
Bupropion hydrochloride, bupropion hydrochloride, the sustained-release formulation, and bupropion hydrochloride, the extended-release forumlation, are not approved for smoking cessation treatment, but bupropion under the name ZYBAN (bupropion hydrochloride) Sustained-Release Tablets is approved for this use. Serious neuropsychiatric symptoms have been reported in patients taking bupropion for smoking cessation (see BOXED WARNING, ADVERSE REACTIONS). These have included changes in mood (including depression and mania), psychosis, hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, homicidal ideation, hostility, agitation, aggression, anxiety, and panic, as well as suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, and completed suicide. Some reported cases may have been complicated by the symptoms of nicotine withdrawal in patients who stopped smoking. Depressed mood may be a symptom of nicotine withdrawal. Depression, rarely including suicidal ideation, has been reported in smokers undergoing a smoking cessation attempt without medication. However, some of these symptoms have occurred in patients taking bupropion who continued to smoke. When symptoms were reported, most were during bupropion treatment, but some were following discontinuation of bupropion therapy.
These events have occurred in patients with and without pre-existing psychiatric disease; some have experienced worsening of their psychiatric illnesses. All patients being treated with bupropion as part of smoking cessation treatment should be observed for neuropsychiatric symptoms or worsening of pre-existing psychiatric illness.
Patients with serious psychiatric illness such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depressive disorder did not participate in the pre-marketing studies of ZYBAN.
Advise patients and caregivers that the patient using bupropion for smoking cessation should stop taking bupropion and contact a healthcare provider immediately if agitation, depressed mood, or changes in behavior or thinking that are not typical for the patient are observed, or if the patient develops suicidal ideation or suicidal behavior. In many postmarketing cases, resolution of symptoms after discontinuation of ZYBAN was reported, although in some cases the symptoms persisted, therefore, ongoing monitoring and supportive care should be provided until symptoms resolve.
The risks of using bupropion for smoking cessation should be weighed against the benefits of its use. ZYBAN has been demonstrated to increase the likelihood of abstinence from smoking for as long as six months compared to treatment with placebo. The health benefits of quitting smoking are immediate and substantial.
Screening Patients for Bipolar Disorder
A major depressive episode may be the initial presentation of bipolar disorder. It is generally believed (though not established in controlled trials) that treating such an episode with an antidepressant alone may increase the likelihood of precipitation of a mixed/manic episode in patients at risk for bipolar disorder. Whether any of the symptoms described above represent such a conversion is unknown. However, prior to initiating treatment with an antidepressant, patients with depressive symptoms should be adequately screened to determine if they are at risk for bipolar disorder; such screening should include a detailed psychiatric history, including a family history of suicide, bipolar disorder, and depression. It should be noted that bupropion hydrochloride tablets is not approved for use in treating bipolar depression.
Bupropion-Containing Products
Patients should be made aware that bupropion hydrochloride tablets contain the same active ingredient found in ZYBAN, used as an aid to smoking cessation treatment, and that bupropion hydrochloride tablets should not be used in combination with ZYBAN, or any other medications that contain bupropion, such as Wellbutrin SR (bupropion hydrochloride), the sustained-release formulation or Wellbutrin XL (bupropion hydrochloride), the extended-release formulation.
Seizures
Bupropion is associated with seizures in approximately 0.4% (4/1,000) of patients treated at doses up to 450 mg/day. This incidence of seizures may exceed that of other marketed antidepressants by as much as 4-fold. This relative risk is only an approximate estimate because no direct comparative studies have been conducted. The estimated seizure incidence for bupropion hydrochloride tablets increases almost tenfold between 450 and 600 mg/day, which is twice the usually required daily dose (300 mg) and one and one-third the maximum recommended daily dose (450 mg). Given the wide variability among individuals and their capacity to metabolize and eliminate drugs this disproportionate increase in seizure incidence with dose incrementation calls for caution in dosing.
During the initial development, 25 among approximately 2,400 patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets experienced seizures. At the time of seizure, 7 patients were receiving daily doses of 450 mg or below for an incidence of 0.33% (3/1,000) within the recommended dose range. Twelve patients experienced seizures at 600 mg/day (2.3% incidence); 6 additional patients had seizures at daily doses between 600 and 900 mg (2.8% incidence).
A separate, prospective study was conducted to determine the incidence of seizure during an 8-week treatment exposure in approximately 3,200 additional patients who received daily doses of up to 450 mg. Patients were permitted to continue treatment beyond 8 weeks if clinically indicated. Eight seizures occurred during the initial 8-week treatment period and 5 seizures were reported in patients continuing treatment beyond 8 weeks, resulting in a total seizure incidence of 0.4%.
The risk of seizure appears to be strongly associated with dose. Sudden and large increments in dose may contribute to increased risk. While many seizures occurred early in the course of treatment, some seizures did occur after several weeks at fixed dose. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be discontinued and not restarted in patients who experience a seizure while on treatment.
The risk of seizure is also related to patient factors, clinical situations, and concomitant medications, which must be considered in selection of patients for therapy with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
- Patient factors: Predisposing factors that may increase the risk of seizure with bupropion use include history of head trauma or prior seizure, central nervous system (CNS) tumor, the presence of severe hepatic cirrhosis, and concomitant medications that lower seizure threshold.
- Clinical situations: Circumstances associated with an increased seizure risk include, among others, excessive use of alcohol or sedatives (including benzodiazepines); addiction to opiates, cocaine, or stimulants; use of over-the-counter stimulants and anorectics; and diabetes treated with oral hypoglycemics or insulin.
- Concomitant medications: Many medications (e.g., antipsychotics, antidepressants, theophylline, systemic steroids) are known to lower seizure threshold.
Recommendations for Reducing the Risk of Seizure
Retrospective analysis of clinical experience gained during the development of bupropion hydrochloride tablets suggests that the risk of seizure may be minimized if
- the total daily dose of bupropion hydrochloride tablets does not exceed 450 mg,
- the daily dose is administered 3 times daily, with each single dose not to exceed 150 mg to avoid high peak concentrations of bupropion and/or its metabolites, and
- the rate of incrementation of dose is very gradual.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be administered with extreme caution to patients with a history of seizure, cranial trauma, or other predisposition(s) toward seizure, or patients treated with other agents (e.g., antipsychotics, other antidepressants, theophylline, systemic steroids, etc.) that lower seizure threshold.
Hepatic Impairment
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with extreme caution in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis. In these patients a reduced dose and/or frequency is required, as peak bupropion, as well as AUC, levels are substantially increased and accumulation is likely to occur in such patients to a greater extent than usual. The dose should not exceed 75 mg once a day in these patients (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, PRECAUTIONS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Potential for Hepatotoxicity
In rats receiving large doses of bupropion chronically, there was an increase in incidence of hepatic hyperplastic nodules and hepatocellular hypertrophy. In dogs receiving large doses of bupropion chronically, various histologic changes were seen in the liver, and laboratory tests suggesting mild hepatocellular injury were noted.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Agitation and Insomnia
A substantial proportion of patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets experience some degree of increased restlessness, agitation, anxiety, and insomnia, especially shortly after initiation of treatment. In clinical studies, these symptoms were sometimes of sufficient magnitude to require treatment with sedative/hypnotic drugs. In approximately 2% of patients, symptoms were sufficiently severe to require discontinuation of treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
Psychosis, Confusion, and Other Neuropsychiatric Phenomena
Depressed patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets have been reported to show a variety of neuropsychiatric signs and symptoms including delusions, hallucinations, psychosis, concentration disturbance, paranoia, and confusion. Because of the uncontrolled nature of many studies, it is impossible to provide a precise estimate of the extent of risk imposed by treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. In several cases, neuropsychiatric phenomena abated upon dose reduction and/or withdrawal of treatment.
Activation of Psychosis and/or Mania
Antidepressants can precipitate manic episodes in bipolar disorder patients during the depressed phase of their illness and may activate latent psychosis in other susceptible patients. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are expected to pose similar risks.
Altered Appetite and Weight
A weight loss of greater than 5 lbs occurred in 28% of patients receiving bupropion hydrochloride tablets. This incidence is approximately double that seen in comparable patients treated with tricyclics or placebo. Furthermore, while 35% of patients receiving tricyclic antidepressants gained weight, only 9.4% of patients treated with bupropion did. Consequently, if weight loss is a major presenting sign of a patient’s depressive illness, the anorectic and/or weight reducing potential of bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be considered.
Allergic Reactions
Anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions characterized by symptoms such as pruritus, urticaria, angioedema, and dyspnea requiring medical treatment have been reported in clinical trials with bupropion. In addition, there have been rare spontaneous postmarketing reports of erythema multiforme, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and anaphylactic shock associated with bupropion. A patient should stop taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets and consult a doctor if experiencing allergic or anaphylactoid/anaphylactic reactions (e.g., skin rash, pruritus, hives, chest pain, edema, and shortness of breath) during treatment.
Arthralgia, myalgia, and fever with rash and other symptoms suggestive of delayed hypersensitivity have been reported in association with bupropion. These symptoms may resemble serum sickness.
Cardiovascular Effects
In clinical practice, hypertension, in some cases severe, requiring acute treatment, has been reported in patients receiving bupropion alone and in combination with nicotine replacement therapy. These events have been observed in both patients with and without evidence of preexisting hypertension.
Data from a comparative study of the sustained-release formulation of bupropion (ZYBAN Sustained-Release Tablets), nicotine transdermal system (NTS), the combination of sustained-release bupropion plus NTS, and placebo as an aid to smoking cessation suggest a higher incidence of treatment-emergent hypertension in patients treated with the combination of sustained-release bupropion and NTS. In this study, 6.1% of patients treated with the combination of sustained-release bupropion and NTS had treatment-emergent hypertension compared to 2.5%, 1.6%, and 3.1% of patients treated with sustained-release bupropion, NTS, and placebo, respectively. The majority of these patients had evidence of preexisting hypertension. Three patients (1.2%) treated with the combination of ZYBAN and NTS and one patient (0.4%) treated with NTS had study medication discontinued due to hypertension compared to none of the patients treated with ZYBAN or placebo. Monitoring of blood pressure is recommended in patients who receive the combination of bupropion and nicotine replacement.
There is no clinical experience establishing the safety of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in patients with a recent history of myocardial infarction or unstable heart disease. Therefore, care should be exercised if it is used in these groups. Bupropion was well tolerated in depressed patients who had previously developed orthostatic hypotension while receiving tricyclic antidepressants and was also generally well tolerated in a group of 36 depressed inpatients with stable congestive heart failure (CHF). However, bupropion was associated with a rise in supine blood pressure in the study of patients with CHF, resulting in discontinuation of treatment in 2 patients for exacerbation of baseline hypertension.
Hepatic Impairment
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with extreme caution in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis. In these patients, a reduced dose and frequency is required. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment (including mild-to-moderate hepatic cirrhosis) and a reduced frequency and/or dose should be considered in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic cirrhosis.
All patients with hepatic impairment should be closely monitored for possible adverse effects that could indicate high drug and metabolite levels (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, WARNINGS, and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Renal Impairment
There is limited information on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion in patients with renal impairment. An inter-study comparison between normal subjects and patients with end-stage renal failure demonstrated that the parent drug Cmax and AUC values were comparable in the 2 groups, whereas the hydroxybupropion and threohydrobupropion metabolites had a 2.3- and 2.8-fold increase, respectively, in AUC for patients with end-stage renal failure. A second study, comparing normal subjects and patients with moderate-to-severe renal impairment (GFR 30.9 ± 10.8 mL/min) showed that exposure to a single 150 mg dose of sustained-release bupropion was approximately 2-fold higher in patients with impaired renal function while levels of the hydroxybupropion and threo/erythrohydrobupropion (combined) metabolites were similar in the 2 groups. Bupropion is extensively metabolized in the liver to active metabolites, which are further metabolized and subsequently excreted by the kidneys. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment and a reduced frequency and/or dose should be considered as bupropion and the metabolites of bupropion may accumulate in such patients to a greater extent than usual. The patient should be closely monitored for possible adverse effects that could indicate high drug or metabolite levels.
Information for Patients
Prescribers or other health professionals should inform patients, their families, and their caregivers about the benefits and risks associated with treatment with bupropion hydrochloride and should counsel them in its appropriate use. A patient Medication Guide about “Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions,” “Quitting Smoking, Quit-Smoking Medication, Changes in Thinking and Behavior, Depression, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions,” and “What Other Important Information Should I Know About Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets?” is available for bupropion hydrochloride tablets. The prescriber or health professional should instruct patients, their families, and their caregivers to read the Medication Guide and should assist them in understanding its contents. Patients should be given the opportunity to discuss the contents of the Medication Guide and to obtain answers to any questions they may have. The complete text of the Medication Guide is reprinted at the end of this document.
Patients should be advised of the following issues and asked to alert their prescriber if these occur while taking bupropion hydrochloride.
Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk in Treating Psychiatric Disorders
Patients, their families, and their caregivers should be encouraged to be alert to the emergence of anxiety, agitation, panic attacks, insomnia, irritability, hostility, aggressiveness, impulsivity, akathisia (psychomotor restlessness), hypomania, mania, other unusual changes in behavior, worsening of depression, and suicidal ideation, especially early during antidepressant treatment and when the dose is adjusted up or down. Families and caregivers of patients should be advised to look for the emergence of such symptoms on a day-to-day basis, since changes may be abrupt. Such symptoms should be reported to the patient’s prescriber or health professional, especially if they are severe, abrupt in onset, or were not part of the patient’s presenting symptoms. Symptoms such as these may be associated with an increased risk for suicidal thinking and behavior and indicate a need for very close monitoring and possibly changes in the medication.
Neuropsychiatric Symptoms and Suicide Risk in Smoking Cessation Treatment
Although bupropion hydrochloride tablets are not indicated for smoking cessation treatment, it contains the same active ingredient as ZYBAN which is approved for this use. Patients should be informed that quitting smoking, with or without ZYBAN, may be associated with nicotine withdrawal symptoms (including depression or agitation), or exacerbation of pre-existing psychiatric illness. Furthermore, some patients have experienced changes in mood (including depression and mania), psychosis, hallucinations, paranoia, delusions, homicidal ideation aggression, anxiety, and panic, as well as suicidal ideation, suicide attempt, and completed suicide when attempting to quit smoking while taking ZYBAN. If patients develop agitation, hostility, depressed mood, or changes in thinking or behavior that are not typical for them, or if patients develop suicidal ideation or behavior, they should be urged to report these symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately.
Bupropion-Containing Products
Patients should be made aware that bupropion hydrochloride tablets contain the same active ingredient found in ZYBAN, used as an aid to smoking cessation, and that bupropion hydrochloride tablets should not be used in combination with ZYBAN or any other medications that contain bupropion hydrochloride (such as Wellbutrin SR, the sustained-release formulation and Wellbutrin XL, the extended-release formulation).
Patients should be instructed to take bupropion hydrochloride tablets in equally divided doses 3 or 4 times a day to minimize the risk of seizure.
Patients should be told that bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be discontinued and not restarted if they experience a seizure while on treatment.
Patients should be told that any CNS-active drug like bupropion hydrochloride tablets may impair their ability to perform tasks requiring judgment or motor and cognitive skills. Consequently, until they are reasonably certain that bupropion hydrochloride tablets do not adversely affect their performance, they should refrain from driving an automobile or operating complex, hazardous machinery.
Patients should be told that the excessive use or abrupt discontinuation of alcohol or sedatives (including benzodiazepines) may alter the seizure threshold. Some patients have reported lower alcohol tolerance during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Patients should be advised that the consumption of alcohol should be minimized or avoided.
Patients should be advised to inform their physicians if they are taking or plan to take any prescription or over-the-counter drugs. Concern is warranted because bupropion hydrochloride tablets and other drugs may affect each other’s metabolism.
Patients should be advised to notify their physicians if they become pregnant or intend to become pregnant during therapy.
Drug Interactions
Few systemic data have been collected on the metabolism of bupropion following concomitant administration with other drugs or, alternatively, the effect of concomitant administration of bupropion on the metabolism of other drugs.
Because bupropion is extensively metabolized, the coadministration of other drugs may affect its clinical activity. In vitro studies indicate that bupropion is primarily metabolized to hydroxybupropion by the CYP2B6 isoenzyme. Therefore, the potential exists for a drug interaction between bupropion hydrochloride tablets and drugs that are substrates or inhibitors of the CYP2B6 isoenzyme (e.g., orphenadrine, thiotepa, and cyclophosphamide). In addition, in vitro studies suggest that paroxetine, sertraline, norfluoxetine, and fluvoxamine as well as nelfinavir, ritonavir, and efavirenz inhibit the hydroxylation of bupropion. No clinical studies have been performed to evaluate this finding. The threohydrobupropion metabolite of bupropion does not appear to be produced by the cytochrome P450 isoenzymes. The effects of concomitant administration of cimetidine on the pharmacokinetics of bupropion and its active metabolites were studied in 24 healthy young male volunteers. Following oral administration of two 150 mg sustained-release tablets with and without 800 mg of cimetidine, the pharmacokinetics of bupropion and hydroxybupropion were unaffected. However, there were 16% and 32% increases in the AUC and Cmax, respectively, of the combined moieties of threohydrobupropion and erythrohydrobupropion.
While not systematically studied, certain drugs may induce the metabolism of bupropion (e.g., carbamazepine, phenobarbital, phenytoin).
Multiple oral doses of bupropion had no statistically significant effects on the single dose pharmacokinetics of lamotrigine in 12 healthy volunteers.
Animal data indicated that bupropion may be an inducer of drug-metabolizing enzymes in humans. In one study, following chronic administration of bupropion, 100 mg 3 times daily to 8 healthy male volunteers for 14 days, there was no evidence of induction of its own metabolism. Nevertheless, there may be the potential for clinically important alterations of blood levels of coadministered drugs.
Drugs Metabolized by Cytochrome P450IID6 (CYP2D6)
Many drugs, including most antidepressants (SSRIs, many tricyclics), beta-blockers, antiarrhythmics, and antipsychotics are metabolized by the CYP2D6 isoenzyme. Although bupropion is not metabolized by this isoenzyme, bupropion and hydroxybupropion are inhibitors of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme in vitro. In a study of 15 male subjects (ages 19 to 35 years) who were extensive metabolizers of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme, daily doses of bupropion given as 150 mg twice daily followed by a single dose of 50 mg desipramine increased the Cmax, AUC, and t1/2 of desipramine by an average of approximately 2-, 5- and 2-fold, respectively. The effect was present for at least 7 days after the last dose of bupropion. Concomitant use of bupropion with other drugs metabolized by CYP2D6 has not been formally studied.
Therefore, co-administration of bupropion with drugs that are metabolized by CYP2D6 isoenzyme including certain antidepressants (e.g., nortriptyline, imipramine, desipramine, paroxetine, fluoxetine, sertraline), antipsychotics (e.g., haloperidol, risperidone, thioridazine), beta-blockers (e.g., metoprolol), and Type 1C antiarrhythmics (e.g., propafenone, flecainide), should be approached with caution and should be initiated at the lower end of the dose range of the concomitant medication. If bupropion is added to the treatment regimen of a patient already receiving a drug metabolized by CYP2D6, the need to decrease the dose of the original medication should be considered, particularly for those concomitant medications with a narrow therapeutic index.
MAO Inhibitors
Studies in animals demonstrate that the acute toxicity of bupropion is enhanced by the MAO inhibitor phenelzine (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Levodopa and Amantadine
Limited clinical data suggest a higher incidence of adverse experiences in patients receiving bupropion concurrently with either levodopa or amantadine. Administration of bupropion hydrochloride tablets to patients receiving either levodopa or amantadine concurrently should be undertaken with caution, using small initial doses and small gradual dose increases.
Drugs that Lower Seizure Threshold
Concurrent administration of bupropion hydrochloride tablets and agents (e.g., antipsychotics, other antidepressants, theophylline, systemic steroids, etc.) that lower seizure threshold should be undertaken only with extreme caution (see WARNINGS). Low initial dosing and small gradual dose increases should be employed.
Alcohol
In post-marketing experience, there have been rare reports of adverse neuropsychiatric events or reduced alcohol tolerance in patients who were drinking alcohol during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets. The consumption of alcohol during treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be minimized or avoided (also see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Lifetime carcinogenicity studies were performed in rats and mice at doses up to 300 and 150 mg/kg/day, respectively. In the rat study there was an increase in nodular proliferative lesions of the liver at doses of 100 to 300 mg/kg/day; lower doses were not tested. The question of whether or not such lesions may be precursors of neoplasms of the liver is currently unresolved. Similar liver lesions were not seen in the mouse study, and no increase in malignant tumors of the liver and other organs was seen in either study.
Bupropion produced a borderline positive response (2 to 3 times control mutation rate) in some strains in the Ames bacterial mutagenicity test, and a high oral dose (300 mg/kg, but not 100 or 200 mg/kg) produced a low incidence of chromosomal aberrations in rats. The relevance of these results in estimating the risk of human exposure to therapeutic doses is unknown.
A fertility study was performed in rats; no evidence of impairment of fertility was encountered at oral doses up to 300 mg/kg/day.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
In studies conducted in rats and rabbits, bupropion was administered orally at doses up to 450 and 150 mg/kg/day, respectively (approximately 11 and 7 times the maximum recommended human dose [MRHD], respectively, on a mg/m2 basis), during the period of organogenesis. No clear evidence of teratogenic activity was found in either species; however, in rabbits, slightly increased incidences of fetal malformations and skeletal variations were observed at the lowest dose tested (25 mg/kg/day, approximately equal to the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) and greater. Decreased fetal weights were seen at 50 mg/kg and greater.
When rats were administered bupropion at oral doses of up to 300 mg/kg/day (approximately 7 times the MRHD on a mg/m2 basis) prior to mating and throughout pregnancy and lactation, there were no apparent adverse effects on offspring development.
One study has been conducted in pregnant women. This retrospective, managed-care database study assessed the risk of congenital malformations overall and cardiovascular malformations specifically, following exposure to bupropion in the first trimester compared to the risk of these malformations following exposure to other antidepressants in the first trimester and bupropion outside of the first trimester. This study included 7,005 infants with antidepressant exposure during pregnancy, 1,213 of whom were exposed to bupropion in the first trimester. The study showed no greater risk for congenital malformations overall or cardiovascular malformations specifically, following first trimester bupropion exposure compared to exposure to all other antidepressants in the first trimester, or bupropion outside of the first trimester. The results of this study have not been corroborated. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Labor and Delivery
The effect of bupropion hydrochloride tablets on labor and delivery in humans is unknown.
Nursing Mothers
Like many other drugs, bupropion hydrochloride tablets and its metabolites are secreted in human milk. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from bupropion, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness in the pediatric population have not been established (see BOX WARNING and WARNINGS: Clinical Worsening and Suicide Risk in Treating Psychiatric Disorders). Anyone considering the use of bupropion hydrochloride tablets in a child or adolescent must balance the potential risks with the clinical need.
Geriatric Use
Of the approximately 6,000 patients who participated in clinical trials with bupropion sustained-release tablets (depression and smoking cessation studies), 275 were 65 and over and 47 were 75 and over. In addition, several hundred patients 65 and over participated in clinical trials using the immediate-release formulation of bupropion (depression studies). No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients, but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out.
A single-dose pharmacokinetic study demonstrated that the disposition of bupropion and its metabolites in elderly subjects was similar to that of younger subjects; however, another pharmacokinetic study, single and multiple dose, has suggested that the elderly are at increased risk for accumulation of bupropion and its metabolites (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY).
Bupropion is extensively metabolized in the liver to active metabolites, which are further metabolized and excreted by the kidneys. The risk of toxic reaction to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function (see PRECAUTIONS: Renal Impairment and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
(See also WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS)
Adverse events commonly encountered in patients treated with bupropion hydrochloride tablets are agitation, dry mouth, insomnia, headache/migraine, nausea/vomiting, constipation, and tremor.
Adverse events were sufficiently troublesome to cause discontinuation of treatment with bupropion hydrochloride tablets in approximately 10% of the 2,400 patients and volunteers who participated in clinical trials during the product’s initial development. The more common events causing discontinuation include neuropsychiatric disturbances (3.0%), primarily agitation and abnormalities in mental status; gastrointestinal disturbances (2.1%), primarily nausea and vomiting; neurological disturbances (1.7%), primarily seizures, headaches, and sleep disturbances; and dermatologic problems (1.4%), primarily rashes. It is important to note, however, that many of these events occurred at doses that exceed the recommended daily dose.
Accurate estimates of the incidence of adverse events associated with the use of any drug are difficult to obtain. Estimates are influenced by drug dose, detection technique, setting, physician judgments, etc. Consequently, Table 2 is presented solely to indicate the relative frequency of adverse events reported in representative controlled clinical studies conducted to evaluate the safety and efficacy of bupropion hydrochloride tablets under relatively similar conditions of daily dosage (300 to 600 mg), setting, and duration (3 to 4 weeks). The figures cited cannot be used to predict precisely the incidence of untoward events in the course of usual medical practice where patient characteristics and other factors must differ from those which prevailed in the clinical trials. These incidence figures also cannot be compared with those obtained from other clinical studies involving related drug products as each group of drug trials is conducted under a different set of conditions.
Finally, it is important to emphasize that the tabulation does not reflect the relative severity and/or clinical importance of the events. A better perspective on the serious adverse events associated with the use of bupropion hydrochloride tablets is provided in WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
Table 2. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Experience Incidence in Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials (Percent of Patients Reporting) Adverse Experience Bupropion
Hydrochloride
Tablets
Patients
(n = 323)Placebo
Patients
(n = 185)CARDIOVASCULAR Cardiac arrhythmias 5.3 4.3 Dizziness 22.3 16.2 Hypertension 4.3 1.6 Hypotension 2.5 2.2 Palpitations 3.7 2.2 Syncope 1.2 0.5 Tachycardia 10.8 8.6 DERMATOLOGIC Pruritus 2.2 0.0 Rash 8.0 6.5 GASTROINTESTINAL Anorexia 18.3 18.4 Appetite increase 3.7 2.2 Constipation 26.0 17.3 Diarrhea 6.8 8.6 Dyspepsia 3.1 2.2 Nausea/vomiting 22.9 18.9 Weight gain 13.6 22.7 Weight loss 23.2 23.2 GENITOURINARY Impotence 3.4 3.1 Menstrual complaints 4.7 1.1 Urinary frequency 2.5 2.2 Urinary retention 1.9 2.2 MUSCULOSKELETAL Arthritis 3.1 2.7 NEUROLOGICAL Akathisia 1.5 1.1 Akinesia/bradykinesia 8.0 8.6 Cutaneous temperature disturbance 1.9 1.6 Dry mouth 27.6 18.4 Excessive sweating 22.3 14.6 Headache/migraine 25.7 22.2 Impaired sleep quality 4.0 1.6 Increased salivary flow 3.4 3.8 Insomnia 18.6 15.7 Muscle spasms 1.9 3.2 Pseudoparkinsonism 1.5 1.6 Sedation 19.8 19.5 Sensory disturbance 4.0 3.2 Tremor 21.1 7.6 NEUROPSYCHIATRIC Agitation 31.9 22.2 Anxiety 3.1 1.1 Confusion 8.4 4.9 Decreased libido 3.1 1.6 Delusions 1.2 1.1 Disturbed concentration 3.1 3.8 Euphoria 1.2 0.5 Hostility 5.6 3.8 NONSPECIFIC Fatigue 5.0 8.6 Fever/chills 1.2 0.5 RESPIRATORY Upper respiratory complaints 5.0 11.4 SPECIAL SENSES Auditory disturbance 5.3 3.2 Blurred vision 14.6 10.3 Gustatory disturbance 3.1 1.1 Other Events Observed During the Development of Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets
The conditions and duration of exposure to bupropion hydrochloride tablets varied greatly, and a substantial proportion of the experience was gained in open and uncontrolled clinical settings. During this experience, numerous adverse events were reported; however, without appropriate controls, it is impossible to determine with certainty which events were or were not caused by bupropion hydrochloride tablets. The following enumeration is organized by organ system and describes events in terms of their relative frequency of reporting in the data base. Events of major clinical importance are also described in WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS.
The following definitions of frequency are used: Frequent adverse events are defined as those occurring in at least 1/100 patients. Infrequent adverse events are those occurring in 1/100 to 1/1,000 patients, while rare events are those occurring in less than 1/1,000 patients.
Cardiovascular
Frequent was edema; infrequent were chest pain, electrocardiogram (ECG) abnormalities (premature beats and nonspecific ST-T changes), and shortness of breath/dyspnea; rare were flushing, pallor, phlebitis, and myocardial infarction.
Dermatologic
Frequent were nonspecific rashes; infrequent were alopecia and dry skin; rare were change in hair color, hirsutism, and acne.
Gastrointestinal
Infrequent were dysphagia, thirst disturbance, and liver damage/jaundice; rare were rectal complaints, colitis, gastrointestinal bleeding, intestinal perforation, and stomach ulcer.
Genitourinary
Frequent was nocturia; infrequent were vaginal irritation, testicular swelling, urinary tract infection, painful erection, and retarded ejaculation; rare were dysuria, enuresis, urinary incontinence, menopause, ovarian disorder, pelvic infection, cystitis, dyspareunia, and painful ejaculation.
Neurological
(See WARNINGS)
Frequent were ataxia/incoordination, seizure, myoclonus, dyskinesia, and dystonia; infrequent were mydriasis, vertigo, and dysarthria; rare were electroencephalogram (EEG) abnormality, abnormal neurological exam, impaired attention, sciatica, and aphasia.
Neuropsychiatric
(See PRECAUTIONS)
Frequent were mania/hypomania, increased libido, hallucinations, decrease in sexual function, and depression; infrequent were memory impairment, depersonalization, psychosis, dysphoria, mood instability, paranoia, formal thought disorder, and frigidity; rare was suicidal ideation.
Oral Complaints
Frequent was stomatitis; infrequent were toothache, bruxism, gum irritation, and oral edema; rare was glossitis.
Postintroduction Reports
Voluntary reports of adverse events temporally associated with bupropion that have been received since market introduction and which may have no causal relationship with the drug include the following:
Body (General)
Arthralgia, myalgia, and fever with rash and other symptoms suggestive of delayed hypersensitivity. These symptoms may resemble serum sickness (see PRECAUTIONS).
Cardiovascular
Hypertension (in some cases severe, see PRECAUTIONS), orthostatic hypotension, third degree heart block
Hemic and Lymphatic
Ecchymosis, leukocytosis, leukopenia, thrombocytopenia. Altered PT and/or INR, infrequently associated with hemorrhagic or thrombotic complications, were observed when bupropion was coadministered with warfarin.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Humans
Controlled clinical studies conducted in normal volunteers, in subjects with a history of multiple drug abuse, and in depressed patients showed some increase in motor activity and agitation/excitement.
In a population of individuals experienced with drugs of abuse, a single dose of 400 mg of bupropion hydrochloride tablets produced mild amphetamine-like activity as compared to placebo on the Morphine-Benzedrine Subscale of the Addiction Research Center Inventories (ARCI) and a score intermediate between placebo and amphetamine on the Liking Scale of the ARCI. These scales measure general feelings of euphoria and drug desirability.
Findings in clinical trials, however, are not known to predict the abuse potential of drugs reliably. Nonetheless, evidence from single-dose studies does suggest that the recommended daily dosage of bupropion when administered in divided doses is not likely to be especially reinforcing to amphetamine or stimulant abusers. However, higher doses that could not be tested because of the risk of seizure might be modestly attractive to those who abuse stimulant drugs.
Animals
Studies in rodents have shown that bupropion exhibits some pharmacologic actions common to psychostimulants including increases in locomotor activity and the production of a mild stereotyped behavior and increases in rates of responding in several schedule-controlled behavior paradigms. Drug discrimination studies in rats showed stimulus generalization between bupropion and amphetamine and other psychostimulants. Rhesus monkeys have been shown to self-administer bupropion intravenously.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Human Overdose Experience
Overdoses of up to 30 g or more of bupropion have been reported. Seizure was reported in approximately one-third of all cases. Other serious reactions reported with overdoses of bupropion alone included hallucinations, loss of consciousness, sinus tachycardia, and ECG changes such as conduction disturbances (including QRS prolongation) or arrhythmias. Fever, muscle rigidity, rhabdomyolysis, hypotension, stupor, coma, and respiratory failure have been reported mainly when bupropion was part of multiple drug overdoses.
Although most patients recovered without sequelae, deaths associated with overdoses of bupropion alone have been reported in patients ingesting large doses of the drug. Multiple uncontrolled seizures, bradycardia, cardiac failure, and cardiac arrest prior to death were reported in these patients.
Overdosage Management
Ensure an adequate airway, oxygenation, and ventilation. Monitor cardiac rhythm and vital signs. EEG monitoring is also recommended for the first 48 hours post-ingestion. General supportive and symptomatic measures are also recommended. Induction of emesis is not recommended.
Activated charcoal should be administered. There is no experience with the use of forced diuresis, dialysis, hemoperfusion, or exchange transfusion in the management of bupropion overdoses. No specific antidotes for bupropion are known.
Due to the dose-related risk of seizures with bupropion hydrochloride tablets, hospitalization following suspected overdose should be considered. Based on studies in animals, it is recommended that seizures be treated with intravenous benzodiazepine administration and other supportive measures, as appropriate.
In managing overdosage, consider the possibility of multiple drug involvement. The physician should consider contacting a poison control center for additional information on the treatment of any overdose. Telephone numbers for certified poison control centers are listed in the Physicians’ Desk Reference (PDR).
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General Dosing Considerations
It is particularly important to administer bupropion hydrochloride tablets in a manner most likely to minimize the risk of seizure (see WARNINGS). Increases in dose should not exceed 100 mg/day in a 3-day period. Gradual escalation in dosage is also important if agitation, motor restlessness, and insomnia, often seen during the initial days of treatment, are to be minimized. If necessary, these effects may be managed by temporary reduction of dose or the short-term administration of an intermediate to long-acting sedative hypnotic. A sedative hypnotic usually is not required beyond the first week of treatment. Insomnia may also be minimized by avoiding bedtime doses. If distressing, untoward effects supervene, dose escalation should be stopped.
No single dose of bupropion hydrochloride tablets should exceed 150 mg. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be administered 3 times daily, preferably with at least 6 hours between successive doses.
Usual Dosage for Adults
The usual adult dose is 300 mg/day, given 3 times daily. Dosing should begin at 200 mg/day, given as 100 mg twice daily. Based on clinical response, this dose may be increased to 300 mg/day, given as 100 mg 3 times daily, no sooner than 3 days after beginning therapy (see Table 3).
Table 3. Dosing Regimen Treatment
DayTotal
Daily DoseTablet
StrengthNumber of Tablets Morning Midday Evening 1 200 mg 100 mg 1 0 1 4 300 mg 100 mg 1 1 1 Increasing the Dosage Above 300 mg/Day
As with other antidepressants, the full antidepressant effect of bupropion hydrochloride tablets may not be evident until 4 weeks of treatment or longer. An increase in dosage, up to a maximum of 450 mg/day, given in divided doses of not more than 150 mg each, may be considered for patients in whom no clinical improvement is noted after several weeks of treatment at 300 mg/day. Dosing above 300 mg/day may be accomplished using the 75 or 100 mg tablets. The 100 mg tablet must be administered 4 times daily with at least 4 hours between successive doses, in order not to exceed the limit of 150 mg in a single dose. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be discontinued in patients who do not demonstrate an adequate response after an appropriate period of treatment at 450 mg/day.
Maintenance Treatment
The lowest dose that maintains remission is recommended. Although it is not known how long the patient should remain on bupropion hydrochloride tablets, it is generally recognized that acute episodes of depression require several months or longer of antidepressant drug treatment.
Dosage Adjustment for Patients with Impaired Hepatic Function
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with extreme caution in patients with severe hepatic cirrhosis. The dose should not exceed 75 mg once a day in these patients. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in patients with hepatic impairment (including mild-to-moderate hepatic cirrhosis) and a reduced frequency and/or dose should be considered in patients with mild-to-moderate hepatic cirrhosis (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY, WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS).
Dosage Adjustment for Patients with Impaired Renal Function
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets should be used with caution in patients with renal impairment and a reduced frequency and/or dose should be considered (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets, USP are supplied as:
75 mg: Lavender, round, film-coated tablets, debossed GG 929 on one side and plain on the reverse side.
NDC: 67046-044-30 in blisters of 30 tablets
100 mg:
Lavender, round, film-coated tablets, debossed GG 930 on one side and plain on the reverse side.
NDC: 67046-045-30 in blisters of 30 tablets
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
BuPROPion Hydrochloride Tablets, USP
Read this Medication Guide carefully before you start using bupropion hydrochloride tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. If you have any questions about bupropion hydrochloride tablets, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
IMPORTANT: Be sure to read the three sections of this Medication Guide. The first section is about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines; the second section is about the risk of changes in thinking and behavior, depression and suicidal thoughts or actions with medicines used to quit smoking; and the third section is entitled “What Other Important Information Should I Know About Bupropion Hydrochloride Tablets?”
Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
This section of the Medication Guide is only about the risk of suicidal thoughts and actions with antidepressant medicines. Talk to your, or your family member’s healthcare provider about:
- all risks and benefits of treatment with antidepressant medicines
- all treatment choices for depression or other serious mental illness
What is the most important information I should know about antidepressant medicines, depression and other serious mental illnesses, and suicidal thoughts or actions?
- Antidepressant medicines may increase suicidal thoughts or actions in some children, teenagers, and young adults within the first few months of treatment.
- Depression and other serious mental illnesses are the most important causes of suicidal thoughts and actions. Some people may have a particularly high risk of having suicidal thoughts or actions. These include people who have (or have a family history of) bipolar illness (also called manic-depressive illness) or suicidal thoughts or actions.
-
How can I watch for and try to prevent suicidal thoughts and actions in myself or a family member?
- Pay close attention to any changes, especially sudden changes, in mood, behaviors, thoughts, or feelings. This is very important when an antidepressant medicine is started or when the dose is changed.
- Call the healthcare provider right away to report new or sudden changes in mood, behavior, thoughts, or feelings.
- Keep all follow-up visits with the healthcare provider as scheduled. Call the healthcare provider between visits as needed, especially if you have concerns about symptoms.
Call a healthcare provider right away if you or your family member has any of the following symptoms, especially if they are new, worse, or worry you:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- feeling very agitated or restless
- panic attacks
- trouble sleeping (insomnia)
- new or worse irritability
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
What else do I need to know about antidepressant medicines?
- Never stop an antidepressant medicine without first talking to a healthcare provider. Stopping an antidepressant medicine suddenly can cause other symptoms.
- Antidepressants are medicines used to treat depression and other illnesses. It is important to discuss all the risks of treating depression and also the risks of not treating it. Patients and their families or other caregivers should discuss all treatment choices with the healthcare provider, not just the use of antidepressants.
- Antidepressant medicines have other side effects. Talk to the healthcare provider about the side effects of the medicine prescribed for you or your family member.
- Antidepressant medicines can interact with other medicines. Know all of the medicines that you or your family member takes. Keep a list of all medicines to show the healthcare provider. Do not start new medicines without first checking with your healthcare provider.
- Not all antidepressant medicines prescribed for children are FDA approved for use in children. Talk to your child’s healthcare provider for more information.
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets have not been studied in children under the age of 18 and are not approved for use in children and teenagers.
Quitting Smoking, Quit-Smoking Medications, Changes in Thinking and Behavior, Depression, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions
This section of the Medication Guide is only about the risk of changes in thinking and behavior, depression and suicidal thoughts or actions with drugs used to quit smoking.
Although bupropion hydrochloride tablets is not a treatment for quitting smoking, it contains the same active ingredient (bupropion hydrochloride) as ZYBAN® which is used to help patients quit smoking.
Some people have had changes in behavior, hostility, agitation, depression, suicidal thoughts or actions while taking bupropion to help them quit smoking. These symptoms can develop during treatment with bupropion or after stopping treatment with bupropion.
If you, your family member, or your caregiver notice agitation, hostility, depression, or changes in thinking or behavior that are not typical for you, or you have any of the following symptoms, stop taking bupropion and call your healthcare provider right away:
- thoughts about suicide or dying
- attempts to commit suicide
- new or worse depression
- new or worse anxiety
- panic attacks
- feeling very agitated or restless
- acting aggressive, being angry, or violent
- acting on dangerous impulses
- an extreme increase in activity and talking (mania)
- abnormal thoughts or sensations
- seeing or hearing things that are not there (hallucinations)
- feeling people are against you (paranoia)
- feeling confused
- other unusual changes in behavior or mood
When you try to quit smoking, with or without bupropion, you may have symptoms that may be due to nicotine withdrawal, including urge to smoke, depressed mood, trouble sleeping, irritability, frustration, anger, feeling anxious, difficulty concentrating, restlessness, decreased heart rate, and increased appetite or weight gain. Some people have even experienced suicidal thoughts when trying to quit smoking without medication. Sometimes quitting smoking can lead to worsening of mental health problems that you already have, such as depression.
Before taking bupropion, tell your healthcare provider if you have ever had depression or other mental illnesses. You should also tell your doctor about any symptoms you had during other times you tried to quit smoking, with or without bupropion.
What other important information should I know about bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Seizures. There is a chance of having a seizure (convulsion, fit) with bupropion hydrochloride tablets, especially in people:
- with certain medical problems.
- who take certain medicines.
The chance of having seizures increases with higher doses of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. For more information, see the sections “Who should not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?” and “What should I tell my doctor before using bupropion hydrochloride tablets?” Tell your doctor about all of your medical conditions and all the medicines you take. Do not take any other medicines while you are using bupropion hydrochloride tablets unless your doctor has said it is okay to take them.
If you have a seizure while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets, stop taking the tablets and call your doctor right away. Do not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets again if you have a seizure.
- High blood pressure (hypertension). Some people get high blood pressure, that can be severe, while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets. The chance of high blood pressure may be higher if you also use nicotine replacement therapy (such as a nicotine patch) to help you stop smoking.
- Severe allergic reactions. Some people have severe allergic reaction to bupropion hydrochloride tablets. Stop taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets and call your doctor right away if you get a rash, itching, hives, fever, swollen lymph glands, painful sores in the mouth or around the eyes, swelling of the lips or tongue, chest pain, or have trouble breathing. These could be signs of a serious allergic reaction.
- Unusual thoughts or behaviors. Some patients have unusual thoughts or behaviors while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets, including delusions (believe you are someone else), hallucinations (seeing or hearing things that are not there), paranoia (feeling that people are against you), or feeling confused. If this happens to you, call your doctor.
What are bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets are a prescription medicine used to treat adults with a certain type of depression called major depressive disorder.
Who should not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Do not take bupropion hydrochloride tablets if you
- have or had a seizure disorder or epilepsy.
- are taking ZYBAN (used to help people stop smoking) or any other medicines that contain bupropion hydrochloride, such as Wellbutrin SR Sustained-Release Tablets or Wellbutrin XL Extended-Release Tablets. Bupropion is the same ingredient that is in bupropion hydrochloride tablets, USP.
- drink a lot of alcohol and abruptly stop drinking, or use medicines called sedatives (these make you sleepy) or benzodiazepines and you stop using them all of a sudden.
- have taken within the last 14 days medicine for depression called a monoamine oxidase inhibitor (MAOI), such as NARDIL® (phenelzine sulfate), PARNATE® (tranylcypromine sulfate), or MARPLAN® (isocarboxazid).
- have or had an eating disorder such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia.
- are allergic to the active ingredient in bupropion hydrochloride tablets, bupropion, or to any of the inactive ingredients. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before using bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Tell your doctor if you have ever had depression, suicidal thoughts or actions, or other mental health problems. See “Antidepressant Medicines, Depression and Other Serious Mental Illnesses, and Suicidal Thoughts or Actions.”
- Tell your doctor about your medical conditions including if you:
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if bupropion hydrochloride tablets can harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets passes through your milk. It is not known if bupropion hydrochloride can harm your baby.
- have liver problems, especially cirrhosis of the liver.
- have kidney problems.
- have an eating disorder, such as anorexia nervosa or bulimia.
- have had a head injury.
- have had a seizure (convulsion, fit).
- have a tumor in your nervous system (brain or spine).
- have had a heart attack, heart problems, or high blood pressure.
- are a diabetic taking insulin or other medicines to control your blood sugar.
- drink a lot of alcohol.
- abuse prescription medicines or street drugs.
- Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and non-prescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements. Many medicines increase your chances of having seizures or other serious side effects if you take them while you are using bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
How should I take bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Take bupropion hydrochloride tablets exactly as prescribed by your doctor.
- Take bupropion hydrochloride tablets at the same time each day.
- Take your doses of bupropion hydrochloride tablets at least 6 hours apart.
- You may take bupropion hydrochloride tablets with or without food.
- If you miss a dose, do not take an extra tablet to make up for the dose you forgot. Wait and take your next tablet at the regular time. This is very important. Too many bupropion hydrochloride tablets can increase your chance of having a seizure.
- If you take too many bupropion hydrochloride tablets, or overdose, call your local emergency room or poison control center right away.
- Do not take any other medicines while using bupropion hydrochloride tablets unless your doctor has told you it is okay.
- It may take several weeks for you to feel that bupropion hydrochloride tablets are working. Once you feel better, it is important to keep taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets exactly as directed by your doctor. Call your doctor if you do not feel bupropion hydrochloride tablets are working for you.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets without talking with your doctor first.
What should I avoid while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Do not drink a lot of alcohol while taking bupropion hydrochloride tablets. If you usually drink a lot of alcohol, talk with your doctor before suddenly stopping. If you suddenly stop drinking alcohol, you may increase your risk of having seizures.
- Do not drive a car or use heavy machinery until you know how bupropion hydrochloride tablets affects you. Bupropion hydrochloride tablets can impair your ability to perform these tasks.
What are possible side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Bupropion hydrochloride tablets can cause serious side effects. Read this entire Medication Guide for more information about these serious side effects.
The most common side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets are nervousness, constipation, trouble sleeping, dry mouth, headache, nausea, vomiting, and shakiness (tremor).
If you have nausea, you may want to take your medicine with food. If you have trouble sleeping, do not take your medicine too close to bedtime.
These are not all the side effects of bupropion hydrochloride tablets. For a complete list, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
- Store bupropion hydrochloride tablets at room temperature. Store out of direct sunlight. Keep bupropion hydrochloride tablets in its tightly closed bottle.
General Information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets.
- Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use bupropion hydrochloride tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give bupropion hydrochloride tablets to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them. Keep bupropion hydrochloride tablets out of the reach of children.
This Medication Guide summarizes important information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets. For more information, talk to your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about bupropion hydrochloride tablets that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in bupropion hydrochloride tablets?
Active ingredient: bupropion hydrochloride.
Inactive ingredients: FD&C Blue No. 2 aluminum lake, FD&C Red No. 40 aluminum lake, hydroxypropyl methylcellulose, microcrystalline cellulose, potassium chloride, pregelatinized starch, stearic acid, titanium dioxide, and triethyl citrate.
The following are registered trademarks of their respective manufacturers: NARDIL®/Warner Lambert Company; MARPLAN®/Oxford Pharmaceutical Services, Inc.; PARNATE®, Wellbutrin SR®, Wellbutrin ER®, ZYBAN®/GlaxoSmith Kline.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
08-2009M
7334
Sandoz Inc.
Princeton, NJ 08540
Repackaged by:
Contract Pharmacy Services-PA
125 Titus Ave Suite 200
Warrington, PA 18976 USAOriginal--10/2009--NJW
Update--03/2010--NJW
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE
bupropion hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67046-044(NDC: 0781-1053) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: ZG7E5POY8O) (BUPROPION - UNII:01ZG3TPX31) BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE 75 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (15 CPS) (UNII: 36SFW2JZ0W) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) Product Characteristics Color purple (Lavender) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code GG929 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67046-044-30 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA075584 08/02/2002 BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE
bupropion hydrochloride tablet, film coatedProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 67046-045(NDC: 0781-1064) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: ZG7E5POY8O) (BUPROPION - UNII:01ZG3TPX31) BUPROPION HYDROCHLORIDE 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (15 CPS) (UNII: 36SFW2JZ0W) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) POTASSIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 660YQ98I10) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) TRIETHYL CITRATE (UNII: 8Z96QXD6UM) Product Characteristics Color pink (light pink colored) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code GG930 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 67046-045-30 30 in 1 BLISTER PACK Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA075584 07/02/2002 Labeler - Contract Pharmacy Services-PA (945429777)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.