CAZIANT TRIPHASIC REGIMEN- desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol kit
Caziant by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Caziant by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Mayne Pharma Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
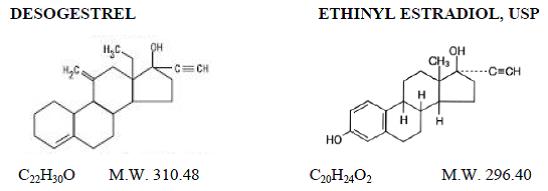
Caziant® (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP) is a triphasic oral contraceptive containing two active components, desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol, USP. Each 28 day treatment cycle pack consists of three active dosing phases: 7 beige tablets containing 0.1 mg desogestrel (13-ethyl-11-methylene-18,19-dinor-17α-pregn-4-en-20-yn-17-ol) and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP (19-nor-17α-pregna-1,3,5(10)-trien-20-yne-3, 17-diol); 7 orange tablets containing 0.125 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP, and 7 pink tablets containing 0.15 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP. Inactive ingredients include colloidal silicon dioxide, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, polyethylene glycol, polysorbate 80, povidone, pregelatinized corn starch, stearic acid, titanium dioxide and vitamin E. Beige tablets also contain iron oxide red and iron oxide yellow. Pink and orange tablets also contain FD&C Red No. 40 Aluminum Lake and FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake. Caziant also contains 7 white tablets with the following inert ingredients: lactose anhydrous, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose and pregelatinized corn starch. The structural formulas are as follows:
The 7 beige, 7 pink and 7 orange tablets meet Dissolution Test 2.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Combination oral contraceptives act by suppression of gonadotropins. Although the primary mechanism of this action is inhibition of ovulation, other alterations include changes in the cervical mucus (which increase the difficulty of sperm entry into the uterus) and the endometrium (which reduce the likelihood of implantation).
Receptor-binding studies, as well as studies in animals, have shown that etonogestrel, the biologically active metabolite of desogestrel, combines high progestational activity with minimal intrinsic androgenicity.91, 92 The relevance of this latter finding in humans is unknown.
Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
Desogestrel is rapidly and almost completely absorbed and converted into etonogestrel, its biologically active metabolite. Following oral administration, the relative bioavailability of desogestrel, based on the lowest and highest tablet strengths, 0.100 mg desogestrel/0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.150 mg desogestrel/0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, compared to solution, as measured by serum levels of etonogestrel, is approximately 100%. Ethinyl estradiol is rapidly and almost completely absorbed. When the lowest and highest tablet strengths, 0.100 mg desogestrel/0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol and 0.150 mg desogestrel/0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, were compared to solution, the relative bioavailability of ethinyl estradiol was 92% and 98%, respectively. The effect of food on the bioavailability of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets following oral administration has not been evaluated.
The pharmacokinetics of etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol following multiple dose administration of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets were determined during the third cycle in 21 subjects. After multiple dosing with desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets, plasma concentrations of etonogestrel reached steady-state after four days of treatment during dosing Phases 1 and 3. During dosing Phase 2, steady-state was reached after five days of treatment. The dose-normalized AUC0 to 24 for etonogestrel was increased approximately 20% from Phase 1 to Phase 2 and approximately 10% from Phase 2 to Phase 3. SHBG concentrations were shown to be induced by the daily administration of ethinyl estradiol. Steady state for ethinyl estradiol was reached after four days of dosing in all dosing phases. The pharmacokinetic parameters of etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol during the third cycle following multiple dose administration of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets are summarized in TABLE 1.
TABLE 1: MEAN (SD) PHARMACOKINETIC PARAMETERS OF DESOGESTREL AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL TABLETS OVER A 28 DAY DOSING PERIOD IN THE THIRD CYCLE (n = 21). Etonogestrel
Phase
Dose†
Cmax
tmax
n-AUC0 to 24
CL/F
(days)
mg
pg/mL
hr
pghr/mL/mcg
L/hr
1 (1 to 7)
0.100
2163.3 (856.4)
1.6 (0.7)
196 (75.4)
6.1 (2.3)
2 (8 to 14)
0.125
3241.5 (1296.5)a
1.1 (0.3)a
234.4 (85)a
5.1 (1.9)a
3 (15 to 21)
0.150
3855.7 (1273.1)
1.5 (0.8)
256.6 (104)
4.6 (1.6)
† Desogestrel
Ethinyl Estradiol
Phase
Dose
Cmax
tmax
n-AUC0 to 24
CL/F
(days)
mg
pg/mL
hr
pghr/mL/mcg
L/hr
1 (1 to 7)
0.025
85.4 (51.7)
1.5 (0.8)
26.4 (11.5)
43.5 (15)
2 (8 to 14)
0.025
91.3 (52.2)a
1.2 (1.2)a
29 (15.5)a
41.7 (15.5)a
3 (15 to 21)
0.025
90.1 (48.2)
1.2 (0.7)
28.3 (13.2)
42.5 (18.7)
a n = 20
Cmax – maximum serum drug concentration
tmax – time at which maximum serum drug concentration occurs
n-AUC0 to 24 – area under the concentration- vs. time curve -0 to 24 hours normalized to 1 mcg administered
CL/F – apparent clearance
Note: for information on t1/2 for Day 21, see the Excretion section.
Distribution
Etonogestrel, the active metabolite of desogestrel, was found to be 98% protein bound, primarily to sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG). Ethinyl estradiol is primarily bound to plasma albumin. Ethinyl estradiol does not bind to SHBG, but induces SHBG synthesis. Desogestrel, in combination with ethinyl estradiol, does not counteract the estrogen-induced increase in SHBG, resulting in lower serum levels of free testosterone.96 to 99
Metabolism
Desogestrel: Desogestrel is rapidly and completely metabolized by hydroxylation in the intestinal mucosa and on first pass through the liver to etonogestrel. In vitro data suggest an important role for the cytochrome P450 CYP2C9 in the bioactivation of desogestrel. Further metabolism of etonogestrel into 6β-hydroxy, etonogestrel and 6β-13ethyl-dihydroxylated metabolites as major metabolites is catalyzed by CYP3A4. Other metabolites (i.e., 3α-OH-desogestrel, 3β-OH-desogestrel, and 3α-OH-5α-H-desogestrel) also have been identified and these metabolites may undergo glucuronide and sulfate conjugation.
Ethinyl Estradiol: Ethinyl estradiol is subject to a significant degree of presystemic conjugation (phase II metabolism). Ethinyl estradiol, escaping gut wall conjugation, undergoes phase I metabolism and hepatic conjugation (phase II metabolism). Major phase I metabolites are 2-OH-ethinyl estradiol and 2-methoxy-ethinyl estradiol. Sulfate and glucuronide conjugates of both ethinyl estradiol and phase I metabolites, which are excreted in bile, can undergo enterohepatic circulation.
Excretion
Etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol are primarily eliminated in urine, bile and feces. At steady state, on Day 21, the elimination half-lives of etonogestrel and ethinyl estradiol are 37.1 ± 14.8 hours and 28.2 ± 10.5 hours, respectively.
Special Populations
Race
There is no information to determine the effect of race on the pharmacokinetics of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets.
Hepatic Insufficiency
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of hepatic disease on the disposition of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets. However, steroid hormones may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function (see PRECAUTIONS).
Renal Insufficiency
No formal studies were conducted to evaluate the effect of renal disease on the disposition of desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets.
Drug-Drug Interactions
Interactions between desogestrel/ethinyl estradiol and other drugs have been reported in the literature. No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets (see PRECAUTIONS).
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) is indicated for the prevention of pregnancy in women who elect to use this product as a method of contraception.
Oral contraceptives are highly effective. TABLE 2 lists the typical unintended pregnancy rates for users of combination oral contraceptives and other methods of contraception. The efficacy of these contraceptive methods, except sterilization, the IUD, and implants, depends upon the reliability with which they are used. Correct and consistent use of these methods can result in lower failure rates.
TABLE 2: PERCENTAGE OF WOMEN EXPERIENCING AN UNINTENDED PREGNANCY DURING THE FIRST YEAR OF TYPICAL USE AND THE FIRST YEAR OF PERFECT USE OF CONTRACEPTION AND THE PERCENTAGE CONTINUING USE AT THE END OF THE FIRST YEAR, UNITED STATES. - * Among couples attempting to avoid pregnancy, the percentage who continue to use a method for one year
- † Among typical couples who initiate use of a method (not necessarily for the first time), the percentage who experience an accidental pregnancy during the first year if they do not stop use for any other reason
- ‡ Among couples who initiate use of a method (not necessarily for the first time) and who use it perfectly (both consistently and correctly), the percentage who experience an accidental pregnancy during the first year if they do not stop use for any other reason
- § The percentage of women becoming pregnant noted in columns (2) and (3) are based on data from populations where contraception is not used and from women who cease using contraception in order to become pregnant. Among such populations, about 89% became pregnant in one year. This estimate was lowered slightly (to 85%) to represent the percentage that would become pregnant within one year among women now relying on reversible methods of contraception if they abandon contraception altogether
- ¶ Foams, creams, gels, vaginal suppositories and vaginal film
- # Cervical mucous (ovulation) method supplemented by calendar in the preovulatory and basal body temperature in the postovulatory phases
- Þ With spermicidal cream or jelly
- ß Without spermicides
- à The treatment schedule is one dose within 72 hours after unprotected intercourse and a second dose 12 hours after the first dose. The Food and Drug Administration has declared the following brands of oral contraceptives to be safe and effective for emergency contraception: Ovral® (1 dose is 2 white pills), Alesse® (1 dose is 5 pink pills), Nordette® or Levlen® (1 dose is 2 light orange pills), Lo/Ovral® (1 dose is 4 white pills), Triphasil® or Tri-Levlen® (1 dose is 4 yellow pills)
- è However, to maintain effective protection against pregnancy, another method of contraception must be used as soon as menstruation resumes, the frequency or duration of breastfeeds is reduced, bottle feeds are introduced or the baby reaches six months of age
% of Women Experiencing an Unintended Pregnancy within the First Year of Use
% of Women Continuing Use at One Year*
Method
Typical Use†
Perfect Use‡
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
Chance§
85
85
Spermicides¶
26
6
40
Periodic abstinence
25
63
Calendar
9
Ovulation
Method3
Sympto-Thermal#
2
Post-Ovulation
1
Withdrawal
19
4
CapÞ
Parous Women
40
26
42
Nulliparous
Women20
9
56
Sponge
Parous Women
40
20
42
Nulliparous
Women20
9
56
DiaphragmÞ
20
6
56
Condomß
Female (Reality)
21
5
56
Male
14
3
61
Pill
5
71
Progestin Only
0.5
Combined
0.1
IUD
Progesterone T
2.0
1.5
81
Copper T 380A
0.8
0.6
78
LNg 20
0.1
0.1
81
Depo-Provera
0.3
0.3
70
Norplant and
Norplant-20.05
0.05
88
Female sterilization
0.5
0.5
100
Male sterilization
0.15
0.10
100
Emergency Contraceptive Pills: Treatment initiated within 72 hours after unprotected
intercourse reduces risk of pregnancy by at least 75%à
Lactational Amenorrhea Method: LAM is a highly effective, temporary method of
contraception.è
Source: Trussell J, Stewart F, Contraceptive Efficacy. In Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Stewart F, Cates W, Stewart GK, Kowal D, Guest F, Contraceptive Technology: Seventeenth Revised Edition.
New York, NY: Irvington Publishers, 1998.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Oral contraceptives should not be used in women who currently have the following conditions:
- Thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- A past history of deep vein thrombophlebitis or thromboembolic disorders
- Cerebral vascular or coronary artery disease (current or history)
- Valvular heart disease with thrombogenic complications
- Severe hypertension
- Diabetes with vascular involvement
- Headaches with focal neurological symptoms
- Major surgery with prolonged immobilization
- Known or suspected carcinoma of the breast (or personal history of breast cancer)
- Carcinoma of the endometrium or other known or suspected estrogen-dependent neoplasia
- Undiagnosed abnormal genital bleeding
- Cholestatic jaundice of pregnancy or jaundice with prior hormonal contraceptive use
- Hepatic tumors (benign or malignant) or active liver disease
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Heavy smoking (≥ 15 cigarettes per day) and over age 35
- Hypersensitivity to any of the components of Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets)
- Are receiving Hepatitis C drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to the potential for ALT elevations (see WARNINGS, Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment).
-
WARNINGS
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from oral contraceptive use. This risk increases with age and with heavy smoking (15 or more cigarettes per day) and is quite marked in women over 35 years of age. Women who use oral contraceptives should be strongly advised not to smoke.
The use of oral contraceptives is associated with increased risks of several serious conditions including venous and arterial thrombotic and thromboembolic events (such as myocardial infarction, thromboembolism, and stroke) hepatic neoplasia, gallbladder disease, and hypertension, although the risk of serious morbidity or mortality is very small in healthy women without underlying risk factors. The risk of morbidity and mortality increases significantly in the presence of other underlying risk factors such as certain inherited thrombophilias, hypertension, hyperlipidemias, obesity, and diabetes.
Practitioners prescribing oral contraceptives should be familiar with the following information relating to these risks. The information contained in this package insert is principally based on studies carried out in patients who used oral contraceptives with formulations of higher doses of estrogens and progestogens than those in common use today. The effect of long-term use of the oral contraceptives with formulations of lower doses of both estrogens and progestogens remains to be determined.
Throughout this labeling, epidemiologic studies reported are of two types: retrospective or case control studies and prospective or cohort studies. Case control studies provide a measure of the relative risk of a disease, namely, a ratio of the incidence of a disease among oral contraceptive users to that among non-users. The relative risk does not provide information on the actual clinical occurrence of a disease. Cohort studies provide a measure of attributable risk, which is the difference in the incidence of disease between oral contraceptive users and non-users. The attributable risk does provide information about the actual occurrence of a disease in the population (Adapted from refs. 2 and 3 with the authors’ permission). For further information, the reader is referred to a text on epidemiological methods.
1. Thromboembolic Disorders and Other Vascular Problems
a. Thromboembolism
An increased risk of thromboembolic and thrombotic disease associated with the use of oral contraceptives is well established. Case control studies have found the relative risk of users compared to non-users to be 3 for the first episode of superficial venous thrombosis, 4 to 11 for deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism, and 1.5 to 6 for women with predisposing conditions for venous thromboembolic disease.2, 3, 19 to 24 Cohort studies have shown the relative risk to be somewhat lower, about 3 for new cases and about 4.5 for new cases requiring hospitalization.25 The risk of thromboembolic disease associated with oral contraceptives is not related to length of use and disappears after pill use is stopped.2
Several epidemiologic studies indicate that third generation oral contraceptives, including those containing desogestrel, are associated with a higher risk of venous thromboembolism than certain second generation oral contraceptives.102 to 104 In general, these studies indicate an approximate two-fold increased risk, which corresponds to an additional 1 to 2 cases of venous thromboembolism per 10,000 women-years of use. However, data from additional studies have not shown this two-fold increase in risk.
A two- to four-fold increase in relative risk of post-operative thromboembolic complications has been reported with the use of oral contraceptives.9, 26 The relative risk of venous thrombosis in women who have predisposing conditions is twice that of women without such medical conditions.9, 26 If feasible, oral contraceptives should be discontinued at least four weeks prior to and for two weeks after elective surgery of a type associated with an increase in risk of thromboembolism and during and following prolonged immobilization. Since the immediate postpartum period is associated with an increased risk of thromboembolism, oral contraceptives should be started no earlier than four to six weeks after delivery in women who elect not to breastfeed.
b. Myocardial infarction
An increased risk of myocardial infarction has been attributed to oral contraceptive use. This risk is primarily in smokers or women with other underlying risk factors for coronary artery disease such as hypertension, hypercholesterolemia, morbid obesity, and diabetes. The relative risk of heart attack for current oral contraceptive users has been estimated to be two to six.4 to 10 The risk is very low in women under the age of 30.
Smoking in combination with oral contraceptive use has been shown to contribute substantially to the incidence of myocardial infarction in women in their mid-thirties or older with smoking accounting for the majority of excess cases.11 Mortality rates associated with circulatory disease have been shown to increase substantially in smokers over the age of 35 and non-smokers over the age of 40 (TABLE 3) among women who use oral contraceptives.
TABLE 3: CIRCULATORY DISEASE MORTALITY RATES PER 100,000 WOMAN-YEARS BY AGE, SMOKING STATUS, AND ORAL CONTRACEPTIVE USE.
AGEEVER-USERS NON-SMOKERS
EVER-USERS SMOKERS
CONTROLS NON-SMOKERS
CONTROLS SMOKERS
15 to 24
0
10.5
0
0
25 to 34
4.4
14.2
2.7
4.2
35 to 44
21.5
63.4
6.4
15.2
45+
52.4
206.7
11.4
27.9
Adapted from P.M. Layde and V. Beral, ref. #12.
Oral contraceptives may compound the effects of well-known risk factors, such as hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemias, age, and obesity.13 In particular, some progestogens are known to decrease HDL cholesterol and cause glucose intolerance, while estrogens may create a state of hyperinsulinism.14 to 18 Oral contraceptives have been shown to increase blood pressure among users (see section 10 in WARNINGS). Similar effects on risk factors have been associated with an increased risk of heart disease. Oral contraceptives must be used with caution in women with cardiovascular disease risk factors.
c. Cerebrovascular diseases
Oral contraceptives have been shown to increase both the relative and attributable risks of cerebrovascular events (thrombotic and hemorrhagic strokes), although, in general, the risk is greatest among older (> 35 years), hypertensive women who also smoke. Hypertension was found to be a risk factor for both users and non-users, for both types of strokes, while smoking interacted to increase the risk for hemorrhagic strokes.27 to 29
In a large study, the relative risk of thrombotic strokes has been shown to range from 3 for normotensive users to 14 for users with severe hypertension.30 The relative risk of hemorrhagic stroke is reported to be 1.2 for non-smokers who used oral contraceptives, 2.6 for smokers who did not use oral contraceptives, 7.6 for smokers who used oral contraceptives, 1.8 for normotensive users, and 25.7 for users with severe hypertension.30 The attributable risk is also greater in older women.3 Oral contraceptives also increase the risk for stroke in women with other underlying risk factors such as certain inherited or acquired thrombophilias, hyperlipidemias, and obesity. Women with migraine (particularly migraine with aura) who take combination oral contraceptives may be at an increased risk of stroke.
d. Dose-related risk of vascular disease from oral contraceptives
A positive association has been observed between the amount of estrogen and progestogen in oral contraceptives and the risk of vascular disease.31 to 33 A decline in serum high-density lipoproteins (HDL) has been reported with many progestational agents.14 to 16 A decline in serum high-density lipoproteins has been associated with an increased incidence of ischemic heart disease. Because estrogens increase HDL cholesterol, the net effect of an oral contraceptive depends on a balance achieved between doses of estrogen and progestogen and the nature and absolute amount of progestogens used in the contraceptives. The amount of both hormones should be considered in the choice of an oral contraceptive.
Minimizing exposure to estrogen and progestogen is in keeping with good principles of therapeutics. For any particular estrogen/progestogen combination, the dosage regimen prescribed should be one which contains the least amount of estrogen and progestogen that is compatible with a low failure rate and the needs of the individual patient. New acceptors of oral contraceptive agents should be started on a product containing the lowest hormone content that provides satisfactory results in the individual.
e. Persistence of risk of vascular disease
There are two studies which have shown persistence of risk of vascular disease for ever-users of oral contraceptives. In a study in the United States, the risk of developing myocardial infarction after discontinuing oral contraceptives persists for at least 9 years for women 40 to 49 years old who had used oral contraceptives for five or more years, but this increased risk was not demonstrated in other age groups.8 In another study in Great Britain, the risk of developing cerebrovascular disease persisted for at least 6 years after discontinuation of oral contraceptives, although excess risk was very small.34 However, both studies were performed with oral contraceptive formulations containing 50 micrograms or more of estrogens.
2. Estimates of Mortality from Contraceptive Use
One study gathered data from a variety of sources which have estimated the mortality rate associated with different methods of contraception at different ages (TABLE 4). These estimates include the combined risk of death associated with contraceptive methods plus the risk attributable to pregnancy in the event of method failure. Each method of contraception has its specific benefits and risks. The study concluded that with the exception of oral contraceptive users 35 and older who smoke and 40 and older who do not smoke, mortality associated with all methods of birth control is low and below that associated with childbirth.
The observation of a possible increase in risk of mortality with age for oral contraceptive users is based on data gathered in the 1970’s - but not reported until 1983.35 However, current clinical practice involves the use of lower estrogen formulations combined with careful restriction of oral contraceptive use to women who do not have the various risk factors listed in this labeling.
Because of these changes in practice and, also, because of some limited new data which suggest that the risk of cardiovascular disease with the use of oral contraceptives may now be less than previously observed,100, 101 the Fertility and Maternal Health Drugs Advisory Committee was asked to review the topic in 1989. The Committee concluded that although cardiovascular disease risks may be increased with oral contraceptive use after age 40 in healthy non-smoking women (even with the newer low-dose formulations), there are also greater potential health risks associated with pregnancy in older women and with the alternative surgical and medical procedures which may be necessary if such women do not have access to effective and acceptable means of contraception.
Therefore, the Committee recommended that the benefits of low-dose oral contraceptive use by healthy non-smoking women over 40 may outweigh the possible risks. Of course, older women, as all women who take oral contraceptives, should take the lowest possible dose formulation that is effective and meets the individual patient needs.
TABLE 4: ANNUAL NUMBER OF BIRTH-RELATED OR METHOD-RELATED DEATHS ASSOCIATED WITH CONTROL OF FERTILITY PER 100,000 NON-STERILE WOMEN, BY FERTILITY CONTROL METHOD ACCORDING TO AGE. Method of control and outcome
15 to 19
20 to 24
25 to 29
30 to 34
35 to 39
40 to 44
No fertility control methods1
7
7.4
9.1
14.8
25.7
28.2
Oral contraceptives
non-smoker20.3
0.5
0.9
1.9
13.8
31.6
Oral contraceptives
smoker22.2
3.4
6.6
13.5
51.1
117.2
IUD2
0.8
0.8
1
1
1.4
1.4
Condom1
1.1
1.6
0.7
0.2
0.3
0.4
Diaphragm/
spermicide11.9
1.2
1.2
1.3
2.2
2.8
Periodic abstinence1
2.5
1.6
1.6
1.7
2.9
3.6
1. Deaths are birth related
2. Deaths are method relatedAdapted from H.W. Ory, ref. #35.
3. Carcinoma of the Reproductive Organs and Breasts
Numerous epidemiologic studies have been performed on the incidence of breast, endometrial, ovarian, and cervical cancer in women using oral contraceptives. Although the risk of breast cancer may be slightly increased among current users of oral contraceptives (RR = 1.24), this excess risk decreases over time after oral contraceptive discontinuation and by 10 years after cessation the increased risk disappears. The risk does not increase with duration of use, and no relationships have been found with dose or type of steroid. The patterns of risk are also similar regardless of a woman's reproductive history or her family breast cancer history. The subgroup for whom risk has been found to be significantly elevated is women who first used oral contraceptives before age 20, but because breast cancer is so rare at these young ages, the number of cases attributable to this early oral contraceptive use is extremely small. Breast cancers diagnosed in current or previous oral contraceptive users tend to be less advanced clinically than in never-users. Women who currently have or have had breast cancer should not use oral contraceptives because breast cancer is a hormone-sensitive tumor.
Some studies suggest that combination oral contraceptive use has been associated with an increase in the risk of cervical intra-epithelial neoplasia in some populations of women.45 to 48 However, there continues to be controversy about the extent to which such findings may be due to differences in sexual behavior and other factors.
In spite of many studies of the relationship between oral contraceptive use and breast and cervical cancers, a cause-and-effect relationship has not been established.
4. Hepatic Neoplasia
Benign hepatic adenomas are associated with oral contraceptive use, although the incidence of benign tumors is rare in the United States. Indirect calculations have estimated the attributable risk to be in the range of 3.3 cases/100,000 for users, a risk that increases after four or more years of use especially with oral contraceptives of higher dose.49 Rupture of rare, benign, hepatic adenomas may cause death through intra-abdominal hemorrhage.50, 51
Studies from Britain have shown an increased risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma52 to 54 in long-term (> 8 years) oral contraceptive users. However, these cancers are extremely rare in the U.S. and the attributable risk (the excess incidence) of liver cancers in oral contraceptive users approaches less than one per million users.
5. Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment
During clinical trials with the Hepatitis C combination drug regimen that contains ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, ALT elevations greater than 5 times the upper limit of normal (ULN), including some cases greater than 20 times the ULN, were significantly more frequent in women using ethinyl estradiol-containing medications such as COCs. Discontinue Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) prior to starting therapy with the combination drug regimen ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir [see CONTRAINDICATIONS]. Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) can be restarted approximately 2 weeks following completion of treatment with the combination drug regimen.
6. Ocular Lesions
There have been clinical case reports of retinal thrombosis associated with the use of oral contraceptives. Oral contraceptives should be discontinued if there is unexplained partial or complete loss of vision; onset of proptosis or diplopia; papilledema; or retinal vascular lesions. Appropriate diagnostic and therapeutic measures should be undertaken immediately.
7. Oral Contraceptive Use Before or During Early Pregnancy
Extensive epidemiologic studies have revealed no increased risk of birth defects in women who have used oral contraceptives prior to pregnancy.55 to 57 Studies also do not suggest a teratogenic effect, particularly in so far as cardiac anomalies and limb reduction defects are concerned,55, 56, 58, 59 when oral contraceptives are taken inadvertently during early pregnancy.
The administration of oral contraceptives to induce withdrawal bleeding should not be used as a test for pregnancy. Oral contraceptives should not be used during pregnancy to treat threatened or habitual abortion. It is recommended that for any patient who has missed two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, the possibility of pregnancy should be considered at the first missed period. Oral contraceptive use should be discontinued if pregnancy is confirmed.
8. Gallbladder Disease
Earlier studies have reported an increased lifetime relative risk of gallbladder surgery in users of oral contraceptives and estrogens.60, 61 More recent studies, however, have shown that the relative risk of developing gallbladder disease among oral contraceptive users may be minimal.62 to 64 The recent findings of minimal risk may be related to the use of oral contraceptive formulations containing lower hormonal doses of estrogens and progestogens.
9. Carbohydrate and Lipid Metabolic Effects
Oral contraceptives have been shown to cause a decrease in glucose tolerance in a significant percentage of users.17 Oral contraceptives containing greater than 75 micrograms of estrogens cause hyperinsulinism, while lower doses of estrogen cause less glucose intolerance.65 Progestogens increase insulin secretion and create insulin resistance, this effect varying with different progestational agents.17, 66 However, in the non-diabetic woman, oral contraceptives appear to have no effect on fasting blood glucose.67 Because of these demonstrated effects, prediabetic and diabetic women should be carefully monitored while taking oral contraceptives.
A small proportion of women will have persistent hypertriglyceridemia while on the pill. As discussed earlier (see WARNINGS 1.a. and 1.d.), changes in serum triglycerides and lipoprotein levels have been reported in oral contraceptive users.
10. Elevated Blood Pressure
Women with severe hypertension should not be started on hormonal contraceptives. An increase in blood pressure has been reported in women taking oral contraceptives68 and this increase is more likely in older oral contraceptive users69 and with continued use.61 Data from the Royal College of General Practitioners12 and subsequent randomized trials have shown that the incidence of hypertension increases with increasing quantities of progestogens.
Women with a history of hypertension or hypertension-related diseases, or renal disease70 should be encouraged to use another method of contraception. If women elect to use oral contraceptives, they should be monitored closely and if significant elevation of blood pressure occurs, oral contraceptives should be discontinued. For most women, elevated blood pressure will return to normal after stopping oral contraceptives,69 and there is no difference in the occurrence of hypertension between ever- and never-users.68, 70, 71
11. Headache
The onset or exacerbation of migraine or development of headache with a new pattern which is recurrent, persistent, or severe requires discontinuation of oral contraceptives and evaluation of the cause.
12. Bleeding Irregularities
Breakthrough bleeding and spotting are sometimes encountered in patients on oral contraceptives, especially during the first three months of use. If bleeding persists or recurs, non-hormonal causes should be considered and adequate diagnostic measures taken to rule out malignancy or pregnancy, as in the case of any abnormal vaginal bleeding. If pathology has been excluded, time or a change to another formulation may solve the problem. In the event of amenorrhea, pregnancy should be ruled out.
Some women may encounter post-pill amenorrhea or oligomenorrhea, especially when such a condition was pre-existent.
-
PRECAUTIONS
1. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
Patients should be counseled that this product does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
2. Physical Examination and Follow Up
It is good medical practice for all women to have annual history and physical examinations, including women using oral contraceptives. The physical examination, however, may be deferred until after initiation of oral contraceptives if requested by the woman and judged appropriate by the clinician. The physical examination should include special reference to blood pressure, breasts, abdomen and pelvic organs, including cervical cytology, and relevant laboratory tests. In case of undiagnosed, persistent or recurrent abnormal vaginal bleeding, appropriate measures should be conducted to rule out malignancy. Women with a strong family history of breast cancer or who have breast nodules should be monitored with particular care.
3. Lipid Disorders
Women who are being treated for hyperlipidemias should be followed closely if they elect to use oral contraceptives. Some progestogens may elevate LDL levels and may render the control of hyperlipidemias more difficult.
In patients with familial defects of lipoprotein metabolism receiving estrogen-containing preparations, there have been case reports of significant elevations of plasma triglycerides leading to pancreatitis.
4. Liver Function
If jaundice develops in any woman receiving oral contraceptives, the medication should be discontinued. The hormones in Caziant may be poorly metabolized in patients with impaired liver function.
5. Fluid Retention
Oral contraceptives may cause some degree of fluid retention. They should be prescribed with caution, and only with careful monitoring, in patients with conditions which might be aggravated by fluid retention.
6. Emotional Disorders
Patients becoming significantly depressed while taking oral contraceptives should stop the medication and use an alternate method of contraception in an attempt to determine whether the symptom is drug related. Women with a history of depression should be carefully observed and the drug discontinued if depression recurs to a serious degree.
7. Contact Lenses
Contact lens wearers who develop visual changes or changes in lens tolerance should be assessed by an ophthalmologist.
8. Drug Interactions
Changes in contraceptive effectiveness associated with coadministration of other drugs:
a. Anti-infective agents and anticonvulsants
Contraceptive effectiveness may be reduced when hormonal contraceptives are coadministered with some antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and other drugs that increase metabolism of contraceptive steroids. This could result in unintended pregnancy or breakthrough bleeding. Examples include barbiturates, rifampin, phenylbutazone, phenytoin, carbamazepine, felbamate, oxcarbazepine, topiramate, and griseofulvin.
Since desogestrel is mainly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 2C9 enzyme (CYP 2C9) to form etonogestrel, the active progestin, there is a possibility of interaction with CYP 2C9 substrates or inhibitors (such as: ibuprofen, piroxicam, naproxen, phenytoin, fluconazole, diclofenac, tolbutamide, glipizide, celecoxib, sulfamethoxazole, isoniazid, torsemide, irbesartan, losartan, and valsartan). The clinical relevance of these interactions is unknown.
b. Anti-HIV protease inhibitors
Several of the anti-HIV protease inhibitors have been studied with coadministration of oral combination hormonal contraceptives; significant changes (increase and decrease) in the plasma levels of the estrogen and progestin have been noted in some cases. The efficacy and safety of these oral contraceptive products may be affected with coadministration of anti-HIV protease inhibitors. Healthcare providers should refer to the label of the individual anti-HIV protease inhibitors for further drug-drug interaction information.
Concomitant Use with HCV Combination Therapy – Liver Enzyme Elevation
Do not co-administer Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) with HCV drug combinations containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir, due to potential for ALT elevations (see WARNINGS, Risk of Liver Enzyme Elevations with Concomitant Hepatitis C Treatment).
c. Herbal products
Herbal products containing St. John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum) may induce hepatic enzymes (cytochrome P450) and p-glycoprotein transporter and may reduce the effectiveness of contraceptive steroids. This may also result in breakthrough bleeding.
Increase in plasma hormone levels associated with coadministered drugs:
Coadministration of atorvastatin and certain ethinyl estradiol containing oral contraceptives increased AUC values for ethinyl estradiol by approximately 20%. Ascorbic acid and acetaminophen may increase plasma ethinyl estradiol levels, possibly by inhibition of conjugation. CYP 3A4 inhibitors such as itraconazole or ketoconazole may increase plasma hormone levels.
Changes in plasma levels of coadministered drugs:
Combination hormonal contraceptives containing some synthetic estrogens (e.g., ethinyl estradiol) may inhibit the metabolism of other compounds. Increased plasma concentrations of cyclosporine, prednisolone, and theophylline have been reported with concomitant administration of oral contraceptives. Decreased plasma concentrations of acetaminophen and increased clearance of temazepam, salicylic acid, morphine, and clofibric acid have been noted when these drugs were administered with oral contraceptives.
No formal drug-drug interaction studies were conducted with Caziant.
9. Interactions with Laboratory Tests
Certain endocrine and liver function tests and blood components may be affected by oral contraceptives:
- Increased prothrombin and factors VII, VIII, IX and X; decreased antithrombin 3; increased norepinephrine-induced platelet aggregability.
- Increased thyroid binding globulin (TBG) leading to increased circulating total thyroid hormone, as measured by protein-bound iodine (PBI), T4 by column or by radioimmunoassay. Free T3 resin uptake is decreased, reflecting the elevated TBG; free T4 concentration is unaltered.
- Other binding proteins may be elevated in serum.
- Sex hormone-binding globulins are increased and result in elevated levels of total circulating sex steroids; however, free or biologically active levels either decrease or remain unchanged.
- Triglycerides may be increased, and levels of various other lipids and lipoproteins may be affected.
- Glucose tolerance may be decreased.
- Serum folate levels may be depressed by oral contraceptive therapy. This may be of clinical significance if a woman becomes pregnant shortly after discontinuing oral contraceptives.
12. Nursing Mothers
Small amounts of oral contraceptive steroids have been identified in the milk of nursing mothers and a few adverse effects on the child have been reported, including jaundice and breast enlargement. In addition, combination oral contraceptives given in the postpartum period may interfere with lactation by decreasing the quantity and quality of breast milk. If possible, the nursing mother should be advised not to use oral contraceptives but to use other forms of contraception until she has completely weaned her child.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
An increased risk of the following serious adverse reactions has been associated with the use of oral contraceptives (see WARNINGS section):
- Thrombophlebitis and venous thrombosis with or without embolism
- Arterial thromboembolism
- Pulmonary embolism
- Myocardial infarction
- Cerebral hemorrhage
- Cerebral thrombosis
- Hypertension
- Gallbladder disease
- Hepatic adenomas or benign liver tumors
There is evidence of an association between the following conditions and the use of oral contraceptives:
- Mesenteric thrombosis
- Retinal thrombosis
The following adverse reactions have been reported in patients receiving oral contraceptives and are believed to be drug-related:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Gastrointestinal symptoms (such as abdominal pain, cramps and bloating)
- Breakthrough bleeding
- Spotting
- Change in menstrual flow
- Amenorrhea
- Temporary infertility after discontinuation of treatment
- Edema/fluid retention
- Melasma/chloasma which may persist
- Breast changes: tenderness, pain, enlargement, and secretion
- Decrease in serum folate levels
- Exacerbation of porphyria
- Aggravation of varicose veins
- Change in weight or appetite (increase or decrease)
- Change in cervical ectropion and secretion
- Possible diminution in lactation when given immediately postpartum
- Cholestatic jaundice
- Migraine headache
- Rash (allergic)
- Mood changes, including depression
- Vaginitis, including candidiasis
- Change in corneal curvature (steepening)
- Intolerance to contact lenses
- Exacerbation of systemic lupus erythematosus
- Exacerbation of chorea
- Anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, including urticaria, angioedema, and severe reactions with respiratory and circulatory symptoms
The following adverse reactions have been reported in users of oral contraceptives and the association has been neither confirmed nor refuted:
- Pre-menstrual syndrome
- Cataracts
- Cystitis-like syndrome
- Headache
- Nervousness
- Dizziness
- Hirsutism
- Loss of scalp hair
- Erythema multiforme
- Dysmenorrhea
- Pancreatitis
- Erythema nodosum
- Hemorrhagic eruption
- Impaired renal function
- Hemolytic uremic syndrome
- Acne
- Changes in libido
- Colitis
- Budd-Chiari Syndrome
- Optic neuritis, which may lead to partial or complete loss of vision
-
OVERDOSAGE
Serious ill effects have not been reported following acute ingestion of large doses of oral contraceptives by young children. Overdosage may cause nausea, and withdrawal bleeding may occur in females.
NON-CONTRACEPTIVE HEALTH BENEFITS
The following non-contraceptive health benefits related to the use of oral contraceptives are supported by epidemiologic studies which largely utilized oral contraceptive formulations containing estrogen doses exceeding 0.035 mg of ethinyl estradiol or 0.05 mg of mestranol.73 to 78
Effects on menses:
- increased menstrual cycle regularity
- decreased blood loss and decreased incidence of iron deficiency anemia
- decreased incidence of dysmenorrhea
Effects related to inhibition of ovulation:
- decreased incidence of functional ovarian cysts
- decreased incidence of ectopic pregnancies
Effects from long-term use:
- decreased incidence of fibroadenomas and fibrocystic disease of the breast
- decreased incidence of acute pelvic inflammatory disease
- decreased incidence of endometrial cancer
- decreased incidence of ovarian cancer
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
To achieve maximum contraceptive effectiveness, Caziant tablets must be taken exactly as directed, at the same time every day, and at intervals not exceeding 24 hours. Caziant tablets may be initiated using either a Sunday start or a Day 1 start.
NOTE: Seven different "day label strips" are provided to accommodate the selected start regimen. The patient should place the self-adhesive "day label strip" that corresponds to her starting day on the blister card above the first row of tablets.
During the First Cycle of Use
IMPORTANT: The possibility of ovulation and conception prior to initiation of use of Caziant tablets should be considered. A woman can begin to take Caziant tablets either on the first Sunday after the onset of her menstrual period (Sunday Start) or on the first day of her menstrual period (Day 1 Start). When switching from another oral contraceptive, Caziant tablets should be started on the same day that a new pack of the previous oral contraceptive would have been started.
Sunday Start
When initiating a Sunday start regimen, another method of contraception, such as condoms or spermicide, should be used for the first 7 consecutive days of taking Caziant tablets.
Using a Sunday start, tablets are taken daily without interruption as follows: The first beige tablet should be taken on the first Sunday after menstruation begins (if menstruation begins on Sunday, the first beige tablet is taken on that day). Tablets are then taken sequentially following the arrows marked on the dispenser. One beige tablet is taken daily for 7 days, followed by 1 orange tablet daily for 7 days, 1 pink tablet daily for 7 days, and then 1 white (inactive) tablet daily for 7 days. For all subsequent cycles, the patient then begins a new 28 tablet regimen on the next day (Sunday) after taking the last white (inactive) tablet. [If switching from a Sunday Start oral contraceptive, the first Caziant tablet should be taken on the second Sunday after the last tablet of a 21 day oral contraceptive regimen or should be taken on the first Sunday after the last inactive tablet of a 28 day regimen.]
If a patient misses 1 active tablet in Weeks 1, 2, or 3, she should take the missed tablet as soon as she remembers. If the patient misses 2 consecutive active tablets in Week 1 or Week 2, the patient should take 2 tablets the day she remembers and 2 tablets the next day; thereafter, the patient should resume taking 1 tablet daily until she finishes the cycle pack. The patient should be instructed to use a back-up method of birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) if she has intercourse in the 7 days after she restarts her pills. If the patient misses 2 consecutive pink (active) tablets in the third week or misses 3 or more active tablets in a row at any time during the cycle, the patient should keep taking 1 active tablet daily until the next Sunday. On Sunday the patient should throw out the rest of that cycle pack and start a new cycle pack that same day. The patient should be instructed to use a back-up method of birth control if she has intercourse in the 7 days after restarting her pills.
Complete instructions to facilitate patient counseling on proper pill usage can be found in Detailed Patient Labeling ("HOW TO TAKE THE PILL" section).
Day 1 Start
Counting the first day of menstruation as "Day 1", the first beige tablet should be taken on the first day of menstrual bleeding. Tablets are then taken sequentially without interruption as follows: One beige tablet daily for 7 days, then 1 orange tablet daily for 7 days, followed by 1 pink tablet daily for 7 days and then 1 white (inactive) tablet daily for 7 days. For all subsequent cycles, the patient then begins a new 28 tablet regimen on the next day after taking the last white (inactive) tablet. [If switching directly from another oral contraceptive, the first beige tablet should be taken on the same day that a new pack of the previous oral contraceptive would have been started.]
If a patient misses 1 active tablet in Weeks 1, 2, or 3, she should take the missed tablet as soon as she remembers. If the patient misses 2 consecutive active tablets in Week 1 or Week 2, the patient should take 2 tablets the day she remembers and 2 tablets the next day; thereafter, the patient should resume taking 1 tablet daily until she finishes the cycle pack. The patient should be instructed to use a back-up method of birth control (such as condoms or spermicide) if she has intercourse in the 7 days after she restarts her pills. If the patient misses 2 consecutive pink tablets in the third week or misses 3 or more active tablets in a row at any time during the cycle, the patient should throw out the rest of that cycle pack and start a new cycle pack that same day. The patient should be instructed to use a back-up method of birth control if she has intercourse in the 7 days after restarting her pills.
Complete instructions to facilitate patient counseling on proper pill usage can be found in Detailed Patient Labeling ("HOW TO TAKE THE PILL" section).
ADDITIONAL INSTRUCTIONS FOR BOTH SUNDAY AND DAY 1 STARTS
If Spotting or Breakthrough Bleeding Occurs
Breakthrough bleeding, spotting, and amenorrhea are frequent reasons for patients discontinuing oral contraceptives. In breakthrough bleeding, as in all cases of irregular bleeding from the vagina, non-functional causes should be considered. In undiagnosed persistent or recurrent abnormal bleeding from the vagina, adequate diagnostic measures are indicated to rule out pregnancy or malignancy. If both pregnancy and pathology have been excluded, time or a change to another preparation may solve the problem. Changing to an oral contraceptive with a higher estrogen content, while potentially useful in minimizing menstrual irregularity, should be done only if necessary since this may increase the risk of thromboembolic disease.
Use of Caziant in The Event of a Missed Menstrual Period
1. If the patient has not adhered to the prescribed schedule, the possibility of pregnancy should be considered at the time of the first missed period and oral contraceptive use should be discontinued if pregnancy is confirmed.
2. If the patient has adhered to the prescribed regimen and misses two consecutive periods, pregnancy should be ruled out. Oral contraceptive use should be discontinued if pregnancy is confirmed..
Use of Caziant Postpartum
The use of Caziant for contraception may be initiated 4 to 6 weeks postpartum in women who elect not to breastfeed. When the tablets are administered during the postpartum period, the increased risk of thromboembolic disease associated with the postpartum period must be considered (see CONTRAINDICATIONS and WARNINGS concerning thromboembolic disease. See also PRECAUTIONS, Nursing Mothers).
If the patient starts on Caziant postpartum, and has not yet had a period, she should be instructed to use another method of contraception until a beige tablet has been taken daily for 7 consecutive days.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Caziant® (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP - triphasic regimen) is available in a 28 day blister card tablet dispenser. Each 28 day treatment cycle pack consists of four different dosing phases, as follows: 7 beige, round, film-coated, biconvex, unscored tablets (debossed with stylized b on one side and 333 on the other side) containing 0.1 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP; 7 orange, round, film-coated, biconvex, unscored tablets (debossed with stylized b on one side and 332 on the other side) containing 0.125 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP; 7 pink, round, film-coated, biconvex, unscored tablets (debossed with stylized b on one side and 335 on the other side) containing 0.15 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol, USP and seven white, round, biconvex, unscored tablets (debossed with stylized b on one side and 334 on the other side) containing inert ingredients.
Boxes of 3 NDC: 51862-238-03
Storage
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
-
REFERENCES
1. Hatcher RA, Trussell J, Stewart F et al. Contraceptive Technology: Seventeenth Revised Edition, New York: Irvington Publishers, 1998, in press. 2. Stadel BV. Oral contraceptives and cardiovascular disease. (Pt. 1). N Engl J Med 1981; 305:612–618. 3. Stadel BV. Oral contraceptives and cardiovascular disease. (Pt. 2). N Engl J Med 1981; 305:672–677. 4. Adam SA, Thorogood M. Oral contraception and myocardial infarction revisited: the effects of new preparations and prescribing patterns. Br J Obstet and Gynecol 1981; 88:838–845. 5. Mann JI, Inman WH. Oral contraceptives and death from myocardial infarction. Br Med J 1975; 2(5965):245–248. 6. Mann JI, Vessey MP, Thorogood M, Doll R. Myocardial infarction in young women with special reference to oral contraceptive practice. Br Med J 1975; 2(5956):241–245. 7. Royal College of General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study: Further analyses of mortality in oral contraceptive users. Lancet 1981; 1:541–546. 8. Slone D, Shapiro S, Kaufman DW, Rosenberg L, Miettinen OS, Stolley PD. Risk of myocardial infarction in relation to current and discontinued use of oral contraceptives. N Engl J Med 1981; 305:420–424. 9. Vessey MP. Female hormones and vascular disease—an epidemiological overview. Br J Fam Plann 1980; 6:1–12. 10. Russell-Briefel RG, Ezzati TM, Fulwood R, Perlman JA, Murphy RS. Cardiovascular risk status and oral contraceptive use, United States, 1976–80. Prevent Med 1986; 15:352–362. 11. Goldbaum GM, Kendrick JS, Hogelin GC, Gentry EM. The relative impact of smoking and oral contraceptive use on women in the United States. JAMA 1987; 258:1339–1342. 12. Layde PM, Beral V. Further analyses of mortality in oral contraceptive users: Royal College General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study. (Table 5) Lancet 1981; 1:541–546. 13. Knopp RH. Arteriosclerosis risk: the roles of oral contraceptives and postmenopausal estrogens. J Reprod Med 1986; 31(9) (Supplement):913–921. 14. Krauss RM, Roy S, Mishell DR, Casagrande J, Pike MC. Effects of two low-dose oral contraceptives on serum lipids and lipoproteins: Differential changes in high-density lipoproteins subclasses. Am J Obstet 1983; 145:446–452. 15. Wahl P, Walden C, Knopp R, Hoover J, Wallace R, Heiss G, Rifkind B. Effect of estrogen/progestin potency on lipid/lipoprotein cholesterol. N Engl J Med 1983; 308:862–867. 16. Wynn V, Niththyananthan R. The effect of progestin in combined oral contraceptives on serum lipids with special reference to high-density lipoproteins. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982; 142:766–771. 17. Wynn V, Godsland I. Effects of oral contraceptives and carbohydrate metabolism. J Reprod Med 1986; 31 (9) (Supplement):892–897. 18. LaRosa JC. Atherosclerotic risk factors in cardiovascular disease. J Reprod Med 1986; 31 (9) (Supplement):906–912. 19. Inman WH, Vessey MP. Investigation of death from pulmonary, coronary, and cerebral thrombosis and embolism in women of child-bearing age. Br Med J 1968; 2 (5599):193–199. 20. Maguire MG, Tonascia J, Sartwell PE, Stolley PD, Tockman MS. Increased risk of thrombosis due to oral contraceptives: a further report. Am J Epidemiol 1979; 110 (2):188–195. 21. Pettiti DB, Wingerd J, Pellegrin F, Ramacharan S. Risk of vascular disease in women: smoking, oral contraceptives, noncontraceptive estrogens, and other factors. JAMA 1979; 242:1150–1154. 22. Vessey MP, Doll R. Investigation of relation between use of oral contraceptives and thromboembolic disease. Br Med J 1968; 2 (5599):199–205. 23. Vessey MP, Doll R. Investigation of relation between use of oral contraceptives and thromboembolic disease. A further report. Br Med J 1969; 2 (5658):651–657. 24. Porter JB, Hunter JR, Danielson DA, Jick H, Stergachis A. Oral contraceptives and non-fatal vascular disease—recent experience. Obstet Gynecol 1982; 59 (3):299–302. 25. Vessey M, Doll R, Peto R, Johnson B, Wiggins P. A long-term follow-up study of women using different methods of contraception: an interim report. Biosocial Sci 1976; 8:375–427. 26. Royal College of General Practitioners: Oral contraceptives, venous thrombosis, and varicose veins. J Royal Coll Gen Pract 1978; 28:393–399. 27. Collaborative Group for the Study of Stroke in Young Women: Oral contraception and increased risk of cerebral ischemia or thrombosis. N Engl J Med 1973; 288:871–878. 28. Petitti DB, Wingerd J. Use of oral contraceptives, cigarette smoking, and risk of subarachnoid hemorrhage. Lancet 1978; 2:234–236. 29. Inman WH. Oral contraceptives and fatal subarachnoid hemorrhage. Br Med J 1979; 2 (6203):1468–70. 30. Collaborative Group for the Study of Stroke in Young Women: Oral contraceptives and stroke in young women: associated risk factors. JAMA 1975; 231:718–722. 31. Inman WH, Vessey MP, Westerholm B, Engelund A. Thromboembolic disease and the steroidal content of oral contraceptives. A report to the Committee on Safety of Drugs. Br Med J 1970; 2:203–209. 32. Meade TW, Greenberg G, Thompson SG. Progestogens and cardiovascular reactions associated with oral contraceptives and a comparison of the safety of 50- and 35-mcg oestrogen preparations. Br Med J 1980; 280 (6224):1157–1161. 33. Kay CR. Progestogens and arterial disease—evidence from the Royal College of General Practitioners’ Study. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1982; 142:762–765. 34. Royal College of General Practitioners: Incidence of arterial disease among oral contraceptive users. J Royal Coll Gen Pract 1983; 33:75–82. 35. Ory HW. Mortality associated with fertility and fertility control: 1983. Family Planning Perspectives 1983; 15:50–56. 36. The Cancer and Steroid Hormone Study of the Centers for Disease Control and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Oral-contraceptive use and the risk of breast cancer. N Engl J Med 1986; 315:405–411. 37. Pike MC, Henderson BE, Krailo MD, Duke A, Roy S. Breast cancer risk in young women and use of oral contraceptives: possible modifying effect of formulation and age at use. Lancet 1983; 2:926–929. 38. Paul C, Skegg DG, Spears GFS, Kaldor JM. Oral contraceptives and breast cancer: A national study. Br Med J 1986; 293:723–725. 39. Miller DR, Rosenberg L, Kaufman DW, Schottenfeld D, Stolley PD, Shapiro S. Breast cancer risk in relation to early oral contraceptive use. Obstet Gynecol 1986; 68:863–868. 40. Olson H, Olson KL, Moller TR, Ranstam J, Holm P. Oral contraceptive use and breast cancer in young women in Sweden (letter). Lancet 1985; 2:748–749. 41. McPherson K, Vessey M, Neil A, Doll R, Jones L, Roberts M. Early contraceptive use and breast cancer: Results of another case-control study. Br J Cancer 1987; 56:653–660. 42. Huggins GR, Zucker PF. Oral contraceptives and neoplasia: 1987 update. Fertil Steril 1987; 47:733–761. 43. McPherson K, Drife JO. The pill and breast cancer: why the uncertainty? Br Med J 1986; 293:709–710. 44. Shapiro S. Oral contraceptives—time to take stock. N Engl J Med 1987; 315:450–451. 45. Ory H, Naib Z, Conger SB, Hatcher RA, Tyler CW. Contraceptive choice and prevalence of cervical dysplasia and carcinoma in situ. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976; 124:573–577. 46. Vessey MP, Lawless M, McPherson K, Yeates D. Neoplasia of the cervix uteri and contraception: a possible adverse effect of the pill. Lancet 1983; 2:930. 47. Brinton LA, Huggins GR, Lehman HF, Malli K, Savitz DA, Trapido E, Rosenthal J, Hoover R. Long-term use of oral contraceptives and risk of invasive cervical cancer. Int J Cancer 1986; 38:339–344. 48. WHO Collaborative Study of Neoplasia and Steroid Contraceptives: Invasive cervical cancer and combined oral contraceptives. Br Med J 1985; 209:961–965. 49. Rooks JB, Ory HW, Ishak KG, Strauss LT, Greenspan JR, Hill AP, Tyler CW. Epidemiology of hepatocellular adenoma: the role of oral contraceptive use. JAMA 1979; 242:644–648. 50. Bein NN, Goldsmith HS. Recurrent massive hemorrhage from benign hepatic tumors secondary to oral contraceptives. Br J Surg 1977; 64:433–435. 51. Klatskin G. Hepatic tumors: possible relationship to use of oral contraceptives. Gastroenterology 1977; 73:386–394. 52. Henderson BE, Preston-Martin S, Edmondson HA, Peters RL, Pike MC. Hepatocellular carcinoma and oral contraceptives. Br J Cancer 1983; 48:437–440. 53. Neuberger J, Forman D, Doll R, Williams R. Oral contraceptives and hepatocellular carcinoma. Br Med J 1986; 292:1355–1357. 54. Forman D, Vincent TJ, Doll R. Cancer of the liver and oral contraceptives. Br Med J 1986; 292:1357–1361. 55. Harlap S, Eldor J. Births following oral contraceptive failures. Obstet Gynecol 1980; 55:447–452. 56. Savolainen E, Saksela E, Saxen L. Teratogenic hazards of oral contraceptives analyzed in a national malformation register. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1981; 140:521–524. 57. Janerich DT, Piper JM, Glebatis DM. Oral contraceptives and birth defects. Am J Epidemiol 1980; 112:73–79. 58. Ferencz C, Matanoski GM, Wilson PD, Rubin JD, Neill CA, Gutberlet R. Maternal hormone therapy and congenital heart disease. Teratology 1980; 21:225–239. 59. Rothman KJ, Fyler DC, Goldblatt A, Kreidberg MB. Exogenous hormones and other drug exposures of children with congenital heart disease. Am J Epidemiol 1979; 109:433–439. 60. Boston Collaborative Drug Surveillance Program: Oral contraceptives and venous thromboembolic disease, surgically confirmed gallbladder disease, and breast tumors. Lancet 1973; 1:1399–1404. 61. Royal College of General Practitioners: Oral contraceptives and health. New York, Pittman, 1974. 62. Layde PM, Vessey MP, Yeates D. Risk of gallbladder disease: a cohort study of young women attending family planning clinics. J Epidemiol Community Health 1982; 36:274–278. 63. Rome Group for the Epidemiology and Prevention of Cholelithiasis (GREPCO): Prevalence of gallstone disease in an Italian adult female population. Am J Epidemiol 1984; 119:796–805. 64. Strom BL, Tamragouri RT, Morse ML, Lazar EL, West SL, Stolley PD, Jones JK. Oral contraceptives and other risk factors for gallbladder disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther 1986; 39:335–341. 65. Wynn V, Adams PW, Godsland IF, Melrose J, Niththyananthan R, Oakley NW, Seedj A. Comparison of effects of different combined oral-contraceptive formulations on carbohydrate and lipid metabolism. Lancet 1979; 1:1045–1049. 66. Wynn V. Effect of progesterone and progestins on carbohydrate metabolism. In Progesterone and Progestin. Edited by Bardin CW, Milgrom E, Mauvis-Jarvis P. New York, Raven Press, 1983 pp. 395–410. 67. Perlman JA, Roussell-Briefel RG, Ezzati TM, Lieberknecht G. Oral glucose tolerance and the potency of oral contraceptive progestogens. J Chronic Dis 1985; 38:857–864. 68. Royal College of General Practitioners’ Oral Contraception Study: Effect on hypertension and benign breast disease of progestogen component in combined oral contraceptives. Lancet 1977; 1:624. 69. Fisch IR, Frank J. Oral contraceptives and blood pressure. JAMA 1977; 237:2499–2503. 70. Laragh AJ. Oral contraceptive induced hypertension—nine years later. Am J Obstet Gynecol 1976; 126:141–147. 71. Ramcharan S, Peritz E, Pellegrin FA, Williams WT. Incidence of hypertension in the Walnut Creek Contraceptive Drug Study cohort. In Pharmacology of Steroid Contraceptive Drugs. Garattini S, Berendes HW. Eds. New York, Raven Press, 1977 pp. 277–288. (Monographs of the Mario Negri Institute for Pharmacological Research, Milan). 72. Stockley I. Interactions with oral contraceptives. J Pharm 1976; 216:140–143. 73. The Cancer and Steroid Hormone Study of the Centers for Disease Control and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Oral contraceptive use and the risk of ovarian cancer. JAMA 1983; 249:1596–1599. 74. The Cancer and Steroid Hormone Study of the Centers for Disease Control and the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development: Combination oral contraceptive use and the risk of endometrial cancer. JAMA 1987; 257:796–800. 75. Ory HW. Functional ovarian cysts and oral contraceptives: negative association confirmed surgically. JAMA 1974; 228:68–69. 76. Ory HW, Cole P, Macmahon B, Hoover R. Oral contraceptives and reduced risk of benign breast disease. N Engl J Med 1976; 294:419–422. 77. Ory HW. The noncontraceptive health benefits from oral contraceptive use. Fam Plann Perspect 1982; 14:182–184. 78. Ory HW, Forrest JD, Lincoln R. Making Choices: Evaluating the health risks and benefits of birth control methods. New York, The Alan Guttmacher Institute, 1983; p. 1. 79. Schlesselman J, Stadel BV, Murray P, Lai S. Breast Cancer in relation to early use of oral contraceptives 1988; 259:1828–1833. 80. Hennekens CH, Speizer FE, Lipnick RJ, Rosner B, Bain C, Belanger C, Stampfer MJ, Willett W, Peto R. A case-controlled study of oral contraceptive use and breast cancer. JNCI 1984; 72:39–42. 81. LaVecchia C, Decarli A, Fasoli M, Franceschi S, Gentile A, Negri E, Parazzini F, Tognoni G. Oral contraceptives and cancers of the breast and of the female genital tract. Interim results from a case-control study. Br. J. Cancer 1986; 54:311–317. 82. Meirik O, Lund E, Adami H, Bergstrom R, Christoffersen T, Bergsjo P. Oral contraceptive use in breast cancer in young women. A Joint National Case-control study in Sweden and Norway. Lancet 1986; 11:650–654. 83. Kay CR, Hannaford PC. Breast cancer and the pill—A further report from the Royal College of General Practitioners’ oral contraception study. Br. J. Cancer 1988; 58:675–680. 84. Stadel BV, Lai S, Schlesselman JJ, Murray P. Oral contraceptives and premenopausal breast cancer in nulliparous women. Contraception 1988; 38:287–299. 85. Miller DR, Rosenberg L, Kaufman DW, Stolley P, Warshauer ME, Shapiro S. Breast cancer before age 45 and oral contraceptive use: New Findings. Am. J. Epidemiol 1989; 129:269–280. 86. The UK National Case-Control Study Group, Oral contraceptive use and breast cancer risk in young women. Lancet 1989; 1:973–982. 87. Schlesselman JJ. Cancer of the breast and reproductive tract in relation to use of oral contraceptives. Contraception 1989; 40:1–38. 88. Vessey MP, McPherson K, Villard-Mackintosh L, Yeates D. Oral contraceptives and breast cancer: latest findings in a large cohort study. Br. J. Cancer 1989; 59:613–617. 89. Jick SS, Walker AM, Stergachis A, Jick H. Oral contraceptives and breast cancer. Br. J. Cancer 1989; 59:618–621. 90. Godsland, I et al. The effects of different formulations of oral contraceptive agents on lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. N Engl J Med 1990; 323:1375–81. 91. Kloosterboer, HJ et al. Selectivity in progesterone and androgen receptor binding of progestogens used in oral contraception. Contraception, 1988; 38:325–32. 92. Van der Vies, J and de Visser, J. Endocrinological studies with desogestrel. Arzneim. Forsch./Drug Res., 1983; 33(l),2:231–6. 93. Data on file, Organon Inc. 94. Fotherby, K. Oral contraceptives, lipids and cardiovascular diseases. Contraception, 1985; Vol. 31; 4:367–94. 95. Lawrence, DM et al. Reduced sex hormone binding globulin and derived free testosterone levels in women with severe acne. Clinical Endocrinology, 1981; 15:87–91. 96. Cullberg, G et al. Effects of a low-dose desogestrel-ethinyl estradiol combination on hirsutism, androgens and sex hormone binding globulin in women with a polycystic ovary syndrome. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand, 1985; 64:195–202. 97. Jung-Hoffmann, C and Kuhl, H. Divergent effects of two low-dose oral contraceptives on sex hormone-binding globulin and free testosterone. AJOG, 1987; 156:199–203. 98. Hammond, G et al. Serum steroid binding protein concentrations, distribution of progestogens, and bioavailability of testosterone during treatment with contraceptives containing desogestrel or levonorgestrel. Fertil. Steril., 1984; 42:44–51. 99. Palatsi, R et al. Serum total and unbound testosterone and sex hormone-binding globulin (SHBG) in female acne patients treated with two different oral contraceptives. Acta Derm Venereol, 1984; 64:517–23. 100. Porter JB, Hunter J, Jick H et al. Oral contraceptives and nonfatal vascular disease. Obstet Gynecol 1985; 66:1–4. 101. Porter JB, Jick H, Walker AM. Mortality among oral contraceptive users. Obstet Gynecol 1987; 7029–32. 102. Jick H, Jick SS, Gurewich V, Myers MW, Vasilakis C. Risk of idiopathic cardiovascular death and non-fatal venous thromboembolism in women using oral contraceptives with differing progestagen components. Lancet, 1995; 346:1589–93. 103. World Health Organization Collaborative Study of Cardiovascular Disease and Steroid Hormone Contraception. Effect of different progestagens in low oestrogen oral contraceptives on venous thromboembolic disease. Lancet, 1995; 346:1582–88. 104. Spitzer WO, Lewis MA, Heinemann LAJ, Thorogood M, MacRae KD on behalf of Transnational Research Group on Oral Contraceptives and Health of Young Women. Third generation oral contraceptives and risk of venous thromboembolic disorders: An international case-control study. Br Med J, 1996; 312:83–88.
Manufactured by:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.North Wales, PA 19454
Distributed by:
Mayne Pharma
Greenville, NC 27834Rev. B 8/2017
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
DETAILED PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Caziant®
(desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets USP - triphasic regimen)28 Day Regimen
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not protect against HIV infection (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases.
PLEASE NOTE: This labeling is revised from time to time as important new medical information becomes available. Therefore, please review this labeling carefully.
DESCRIPTION
Caziant tablets are a triphasic oral contraceptive product, containing a combination of a progestin and estrogen, the two kinds of female hormones.
Each beige tablet contains 0.1 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol; each orange tablet contains 0.125 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol; and each pink tablet contains 0.15 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol. Each white tablet contains inert ingredients.
INTRODUCTION
Any woman who considers using oral contraceptives (the birth control pill or the pill) should understand the benefits and risks of using this form of birth control. This leaflet will give you much of the information you will need to make this decision and will also help you determine if you are at risk of developing any of the serious side effects of the pill. It will tell you how to use the pill properly so that it will be as effective as possible. However, this leaflet is not a replacement for a careful discussion between you and your doctor or healthcare provider. You should discuss the information provided in this leaflet with him or her, both when you first start taking the pill and during your revisits. You should also follow your doctor’s or healthcare provider’s advice with regard to regular check-ups while you are on the pill.
EFFECTIVENESS OF ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Oral contraceptives or “birth control pills” or “the pill” are used to prevent pregnancy and are more effective than other non-surgical methods of birth control. When they are taken correctly, the chance of becoming pregnant is less than 1% (1 pregnancy per 100 women per year of use), when used perfectly, without missing any pills. Typical failure rates are actually 5% (5 pregnancies per 100 women per year of use). The chance of becoming pregnant increases with each missed pill during a menstrual cycle.
In comparison, typical failure rates for other methods of birth control during the first year of use are as follows:
No methods: 85%
Spermicides alone: 26%
Periodic abstinence: 25%
Condom alone (female): 21%
Cervical Cap with spermicides: 20 to 40%
Vaginal sponge: 20 to 40%
Diaphragm with spermicides: 20%
Withdrawal: 19%
Condom alone (male): 14%
IUD: less than 1 to 2%
Implants: less than 1%
Injectable progestogen: less than 1%
Male sterilization: less than 1%
Female sterilization: less than 1%
WHO SHOULD NOT TAKE ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of serious cardiovascular side effects from oral contraceptive use. This risk increases with age and with heavy smoking (15 or more cigarettes per day) and is quite marked in women over 35 years of age. Women who use oral contraceptives are strongly advised not to smoke. Some women should not use the pill. For example, you should not take the pill if you are pregnant or think you may be pregnant. You should also not use the pill if you have any of the following conditions:
- A history of heart attack or stroke
- A history of blood clots in the legs (thrombophlebitis), lungs (pulmonary embolism), or eyes
- A history of blood clots in the deep veins of your legs
- Chest pain (angina pectoris)
- Severe high blood pressure
- Diabetes with complications of the kidneys, eyes, nerves, or blood vessels
- Headache with neurological symptoms
- Known or suspected breast cancer or cancer of the lining of the uterus, cervix, or vagina (now or in the past)
- Unexplained vaginal bleeding (until a diagnosis is reached by your healthcare provider)
- Yellowing of the whites of the eyes or of the skin (jaundice) during pregnancy or during previous use of hormonal birth control of any kind (the pill, patch, vaginal ring, injection, or implant)
- Liver tumor (benign or cancerous)
- Heart valve or heart rhythm disorders that may be associated with formation of blood clots
- Need for a long period of bed rest following major surgery
- Known or suspected pregnancy
- Active liver disease with abnormal liver function tests
- Take any Hepatitis C drug combination containing ombitasvir/paritaprevir/ritonavir, with or without dasabuvir. This may increase levels of the liver enzyme "alanine aminotransferase" (ALT) in the blood
- An allergy or hypersensitivity to any of the components of Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets)
Tell your doctor or healthcare provider if you have ever had any of the above conditions. Your doctor or healthcare provider can recommend another method of birth control.
OTHER CONSIDERATIONS BEFORE TAKING ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
Tell your doctor or healthcare provider if you have:
- Breast nodules, fibrocystic disease of the breast, an abnormal breast x-ray or mammogram
- Diabetes
- Elevated cholesterol or triglycerides
- High blood pressure
- Migraine or other headaches or epilepsy
- Depression
- Gallbladder, liver, heart, or kidney disease
- Scanty or irregular menstrual periods
Women with any of these conditions should be checked often by their doctor or healthcare provider if they choose to use oral contraceptives.
Talk to your healthcare provider about using Caziant if you:
- Smoke
- Recently had a baby
- Recently had a miscarriage or abortion
- Are breastfeeding
- Are taking any other medications
RISKS OF TAKING ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
1. Risk of Developing Blood Clots
Blood clots and blockage of blood vessels are one of the most serious side effects of taking oral contraceptives and can cause death or serious disability. In particular, a clot in the leg can cause thrombophlebitis and a clot that travels to the lungs can cause a sudden blockage of a vessel carrying blood to the lungs. The risks of these side effects may be greater with desogestrel-containing oral contraceptives, such as Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) than with certain other low-dose pills. Rarely, clots occur in the blood vessels of the eye and may cause blindness, double vision, or impaired vision.
If you take oral contraceptives and need elective surgery, need to stay in bed for a prolonged illness or have recently delivered a baby, you may be at risk of developing blood clots. You should consult your doctor or healthcare provider about stopping oral contraceptives three to four weeks before surgery and not taking oral contraceptives for two weeks after surgery or during bed rest. You should also not take oral contraceptives soon after delivery of a baby. It is advisable to wait for at least four weeks after delivery if you are not breastfeeding. If you are breastfeeding, you should wait until you have weaned your child before using the pill (see GENERAL PRECAUTIONS, While Breastfeeding).
The risk of circulatory disease in oral contraceptive users may be higher in users of high-dose pills and may be greater with longer duration of oral contraceptive use. In addition, some of these increased risks may continue for a number of years after stopping oral contraceptives. The risk of venous thromboembolic disease associated with oral contraceptives does not increase with length of use and disappears after pill use is stopped. The risk of abnormal blood clotting increases with age in both users and non-users of oral contraceptives, but the increased risk from the oral contraceptive appears to be present at all ages. For women aged 20 to 44 it is estimated that about 1 in 2000 using oral contraceptives will be hospitalized each year because of abnormal clotting. Among non-users in the same age group, about 1 in 20,000 would be hospitalized each year. For oral contraceptive users in general, it has been estimated that in women between the ages of 15 and 34 the risk of death due to a circulatory disorder is about 1 in 12,000 per year, whereas for non-users the rate is about 1 in 50,000 per year. In the age group 35 to 44, the risk is estimated to be about 1 in 2500 per year for oral contraceptive users and about 1 in 10,000 per year for non-users.
2. Heart Attacks and Strokes
Oral contraceptives may increase the tendency to develop strokes (blockage or rupture of blood vessels in the brain), angina pectoris (chest pain), and heart attacks (blockage of blood vessels in the heart). Any of these conditions can cause death or serious disability.
Smoking greatly increases the possibility of suffering heart attacks and strokes. Furthermore, smoking and the use of oral contraceptives greatly increase the chances of developing and dying of heart disease.
Women with migraine (especially migraine with aura) who take oral contraceptives also may be at a higher risk of stroke.
3. Gallbladder Disease
Oral contraceptive users probably have a greater risk than non-users of having gallbladder disease, although this risk may be related to pills containing high doses of estrogens.
4. Liver Tumors
In rare cases, oral contraceptives can cause benign but dangerous liver tumors. These benign liver tumors can rupture and cause fatal internal bleeding. In addition, a possible, but not definite, association has been found with the pill and liver cancers in two studies, in which a few women who developed these very rare cancers were found to have used oral contraceptives for long periods. However, liver cancers are extremely rare. The chance of developing liver cancer from using the pill is thus even rarer.
5. Cancer of the Reproductive Organs and Breasts
Breast cancer has been diagnosed slightly more often in women who use the pill than in women of the same age who do not use the pill. This small increase in the number of breast cancer diagnoses gradually disappears during the 10 years after stopping use of the pill. It is not known whether the difference is caused by the pill. It may be that women taking the pill are examined more often, so that breast cancer is more likely to be detected. You should have regular breast examinations by a healthcare provider and examine your own breasts monthly. Tell your healthcare provider if you have a family history of breast cancer or if you have had breast nodules or an abnormal mammogram.
Women who currently have or have had breast cancer should not use oral contraceptives because breast cancer is usually a hormone-sensitive tumor.
Some studies have found an increase in the incidence of cancer of the cervix in women who use oral contraceptives. However, this finding may be related to factors other than the use of oral contraceptives. There is insufficient evidence to rule out the possibility that pills may cause such cancers.
6. Lipid Metabolism and Inflammation of the Pancreas
In patients with inherited defects of lipid metabolism, there have been reports of significant elevations of plasma triglycerides during estrogen therapy. This has led to pancreatitis in some cases.
ESTIMATED RISK OF DEATH FROM A BIRTH CONTROL METHOD OR PREGNANCY
All methods of birth control and pregnancy are associated with a risk of developing certain diseases which may lead to disability or death. An estimate of the number of deaths associated with different methods of birth control and pregnancy has been calculated and is shown in the following table.
ANNUAL NUMBER OF BIRTH-RELATED OR METHOD-RELATED DEATHS ASSOCIATED WITH CONTROL OF FERTILITY PER 100,000 NON-STERILE WOMEN, BY FERTILITY CONTROL METHOD ACCORDING TO AGE
Method of control and outcome
15 to 19
20 to 24
25 to 29
30 to 34
35 to 39
40 to 44
No fertility control methods1
7
7.4
9.1
14.8
25.7
28.2
Oral contraceptives non-smoker2
0.3
0.5
0.9
1.9
13.8
31.6
Oral contraceptives smoker2
2.2
3.4
6.6
13.5
51.1
117.2
IUD2
0.8
0.8
1
1
1.4
1.4
Condom1
1.1
1.6
0.7
0.2
0.3
0.4
Diaphragm/spermicide1
1.9
1.2
1.2
1.3
2.2
2.8
Periodic abstinence1
2.5
1.6
1.6
1.7
2.9
3.6
- Deaths are birth related
- Deaths are method related
In the above table, the risk of death from any birth control method is less than the risk of childbirth, except for oral contraceptive users over the age of 35 who smoke and pill users over the age of 40 even if they do not smoke. It can be seen in the table that for women aged 15 to 39, the risk of death was highest with pregnancy (7 to 26 deaths per 100,000 women, depending on age). Among pill users who do not smoke, the risk of death is always lower than that associated with pregnancy for any age group, although over the age of 40, the risk increases to 32 deaths per 100,000 women, compared to 28 associated with pregnancy at that age. However, for pill users who smoke and are over the age of 35, the estimated number of deaths exceeds those for other methods of birth control. If a woman is over the age of 40 and smokes, her estimated risk of death is four times higher (117 per 100,000 women) than the estimated risk associated with pregnancy (28 per 100,000 women) in that age group.
The suggestion that women over 40 who do not smoke should not take oral contraceptives is based on information from older, high-dose pills and on less selective use of pills than is practiced today. An Advisory Committee of the FDA discussed this issue in 1989 and recommended that the benefits of oral contraceptive use by healthy, non-smoking women over 40 years of age may outweigh the possible risks. However, all women, especially older women, are cautioned to use the lowest dose pill that is effective.
WARNING SIGNALS
If any of these adverse effects occur while you are taking oral contraceptives, call your doctor or healthcare provider immediately:
- Sharp chest pain, coughing of blood, or sudden shortness of breath (indicating a possible clot in the lung)
- Pain in the calf (indicating a possible clot in the leg)
- Crushing chest pain or heaviness in the chest (indicating a possible heart attack)
- Sudden severe headache or vomiting, dizziness or fainting, disturbances of vision or speech, weakness, or numbness in an arm or leg (indicating a possible stroke)
- Sudden partial or complete loss of vision (indicating a possible clot in the eye)
- Breast lumps (indicating possible breast cancer or fibrocystic disease of the breast; ask your doctor or healthcare provider to show you how to examine your breasts)
- Severe pain or tenderness in the stomach area (indicating a possibly ruptured liver tumor)
- Difficulty in sleeping, weakness, lack of energy, fatigue, or change in mood (possibly indicating severe depression)
- Jaundice or a yellowing of the skin or eyeballs, accompanied frequently by fever, fatigue, loss of appetite, dark colored urine, or light colored bowel movements (indicating possible liver problems)
SIDE EFFECTS OF ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
In addition to the risks and more serious side effects discussed above (see RISKS OF TAKING ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES, ESTIMATED RISK OF DEATH FROM A BIRTH CONTROL METHOD OR PREGNANCY and WARNING SIGNALS sections), the following may also occur:
1. Irregular Vaginal Bleeding
Irregular vaginal bleeding or spotting may occur while you are taking the pills. Irregular bleeding may vary from slight staining between menstrual periods to breakthrough bleeding, which is a flow much like a regular period. Irregular bleeding occurs most often during the first few months of oral contraceptive use, but may also occur after you have been taking the pill for some time. Such bleeding may be temporary and usually does not indicate any serious problems. It is important to continue taking your pills on schedule. If the bleeding occurs in more than one cycle or lasts for more than a few days, talk to your doctor or healthcare provider.
2. Contact Lenses
If you wear contact lenses and notice a change in vision or an inability to wear your lenses, contact your doctor or healthcare provider.
3. Fluid Retention or Raised Blood Pressure
Oral contraceptives may cause edema (fluid retention) with swelling of the fingers or ankles and may raise your blood pressure. If you experience fluid retention, contact your doctor or healthcare provider.
4. Melasma
A spotty darkening of the skin is possible, particularly of the face.
5. Other Side Effects
Other side effects may include nausea and vomiting, change in appetite, headache, nervousness, depression, dizziness, loss of scalp hair, rash, and vaginal infections.
If any of these side effects bother you, call your doctor or healthcare provider.
GENERAL PRECAUTIONS
1. Missed Periods and Use of Oral Contraceptives Before or During Early Pregnancy
There may be times when you may not menstruate regularly after you have completed taking a cycle of pills. If you have taken your pills regularly and miss one menstrual period, continue taking your pills for the next cycle but be sure to inform your doctor or healthcare provider before doing so. If you have not taken the pills daily as instructed and missed a menstrual period, or if you missed two consecutive menstrual periods, you may be pregnant. Check with your doctor or healthcare provider immediately to determine whether you are pregnant. Stop taking Caziant (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets) if you are pregnant.
There is no conclusive evidence that oral contraceptive use is associated with an increase in birth defects, when taken inadvertently during early pregnancy. Previously, a few studies had reported that oral contraceptives might be associated with birth defects, but these studies have not been confirmed. Nevertheless, oral contraceptives or any other drugs should not be used during pregnancy unless clearly necessary and prescribed by your doctor or healthcare provider. You should check with your doctor or healthcare provider about risks to your unborn child of any medication taken during pregnancy.
2. While Breastfeeding
If you are breastfeeding, consult your doctor or healthcare provider before starting oral contraceptives. Some of the drug will be passed on to the child in the milk. A few adverse effects on the child have been reported, including yellowing of the skin (jaundice) and breast enlargement. In addition, oral contraceptives may decrease the amount and quality of your milk. If possible, do not use oral contraceptives while breastfeeding. You should use another method of contraception since breastfeeding provides only partial protection from becoming pregnant and this partial protection decreases significantly as you breastfeed for longer periods of time. You should consider starting oral contraceptives only after you have weaned your child completely.
3. Laboratory Tests
If you are scheduled for any laboratory tests, tell your doctor or healthcare provider you are taking birth control pills. Certain blood tests may be affected by birth control pills.
4. Drug Interactions
Certain drugs may interact with birth control pills to make them less effective in preventing pregnancy or cause an increase in breakthrough bleeding. Such drugs include rifampin, drugs used for epilepsy such as barbiturates (for example, phenobarbital), phenytoin (Dilantin® is one brand of this drug), phenylbutazone (Butazolidin® is one brand), herbal products containing St. John’s Wort (hypericum perforatum), and possibly certain antibiotics. You may need to use additional contraception when you take drugs which can make oral contraceptives less effective. Be sure to tell your healthcare provider if you are taking or start taking any medications while taking birth control pills.
5. Sexually Transmitted Diseases
This product (like all oral contraceptives) is intended to prevent pregnancy. It does not protect against transmission of HIV (AIDS) and other sexually transmitted diseases such as chlamydia, genital herpes, genital warts, gonorrhea, hepatitis B, and syphilis.
HOW TO TAKE CAZIANT
IMPORTANT POINTS TO REMEMBER
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS:
1. BE SURE TO READ THESE DIRECTIONS:
- Before you start taking your pills
- Anytime you are not sure what to do
2. THE RIGHT WAY TO TAKE THE PILL IS TO TAKE ONE PILL EVERY DAY AT THE SAME TIME. If you miss pills you could get pregnant. This includes starting the pack late. The more pills you miss, the more likely you are to get pregnant.
3. MANY WOMEN HAVE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, OR MAY FEEL SICK TO THEIR STOMACH DURING THE FIRST 1 TO 3 PACKS OF PILLS. If you have spotting or light bleeding or feel sick to your stomach, do not stop taking the pill. The problem will usually go away. If it doesn't go away, check with your doctor or healthcare provider.
4. MISSING PILLS CAN ALSO CAUSE SPOTTING OR LIGHT BLEEDING, even when you make up these missed pills. On the days you take 2 pills to make up for missed pills, you could also feel a little sick to your stomach.
5. IF YOU HAVE VOMITING OR DIARRHEA, for any reason, or IF YOU TAKE CERTAIN MEDICINES, including some antibiotics or the herbal supplement St. John’s Wort, your pills may not work as well. Use a back-up method (such as condoms, spermicides, or diaphragm) until you check with your doctor or healthcare provider.
6. IF YOU HAVE TROUBLE REMEMBERING TO TAKE THE PILL, talk to your doctor or healthcare provider about how to make pill-taking easier or about using another method of birth control.
7. IF YOU HAVE ANY QUESTIONS OR ARE UNSURE ABOUT THE INFORMATION IN THIS LEAFLET, call your doctor or healthcare provider.
BEFORE YOU START TAKING YOUR PILLS
1. DECIDE WHAT TIME OF DAY YOU WANT TO TAKE YOUR PILL.
It is important to take it at about the same time every day.
2. LOOK AT YOUR PILL PACK: IT WILL HAVE 28 PILLS:
This 28 pill pack has 21 “active” [beige, orange, and pink] pills (with hormones) for Weeks 1, 2, 3 and 7 “inactive” [white] pills (without hormones) for Week 4.
3. ALSO FIND:
- where on the pack to start taking the pills,
- in what order to take the pills (follow the arrows), and
- the week numbers as shown in the picture below.
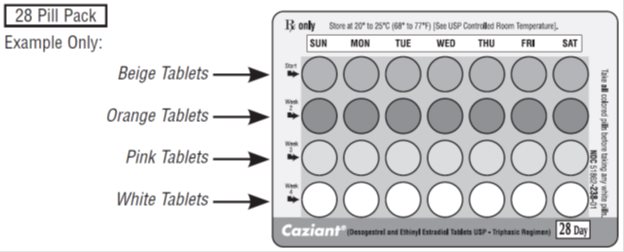
4. BE SURE YOU HAVE READY AT ALL TIMES:
- ANOTHER KIND OF BIRTH CONTROL (such as condoms, spermicides, or diaphragm) to use as a back-up in case you miss pills.
- AN EXTRA, FULL PILL PACK OF CAZIANT (desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablets).
WHEN TO START THE FIRST PACK OF PILLS
You have a choice of which day to start taking your first pack of pills. Decide with your doctor or healthcare provider which is the best day for you. Pick a time of day which will be easy to remember.
DAY 1 START:
1. Pick the day label strip that starts with the first day of your period (this is the day you start bleeding or spotting, even if it is almost midnight when the bleeding begins).
2. Place this day label strip on the blister card above the first row of tablets.
Pick correct day label.
Example Only:
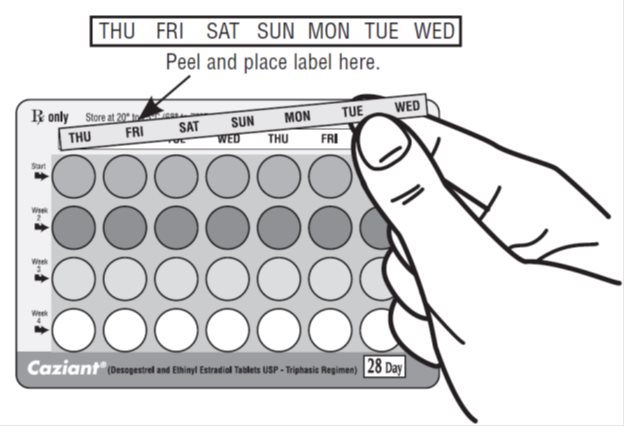
3. Take the first “active” [beige] pill of the first pack during the first 24 hours of your period.
4. You will not need to use a back-up method of birth control, since you are starting the pill at the beginning of your period.
SUNDAY START:
1. Take the first “active” [beige] pill of the first pack on the first Sunday after your period starts, even if you are still bleeding. If your period begins on Sunday, start the pack that same day.
2. Use another method of birth control as a back-up method if you have sex anytime from the Sunday you start your first pack until the next Sunday (7 days). Condoms, spermicides, or a diaphragm are good back-up methods of birth control.
WHAT TO DO DURING THE MONTH
1. TAKE ONE PILL AT THE SAME TIME EVERY DAY UNTIL THE PACK IS EMPTY.
Do not skip pills even if you are spotting or bleeding between monthly periods or feel sick to your stomach (nausea).
Do not skip pills even if you do not have sex very often.
2. WHEN YOU FINISH A PACK OR SWITCH YOUR BRAND OF PILLS:
Start the next pack on the day after your last pill. Do not wait any days between packs.
WHAT TO DO IF YOU MISS PILLS
If you MISS 1 “active” [beige, orange, or pink] pill:
1. Take it as soon as you remember. Take the next pill at your regular time. This means you may take 2 pills in 1 day.
2. You do not need to use a back-up birth control method if you have sex.
If you MISS 2 “active” [beige or orange] pills in a row in WEEK 1 OR WEEK 2 of your pack:
1. Take 2 pills on the day you remember and 2 pills the next day.
2. Then take 1 pill a day until you finish the pack.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use another birth control method (such as condoms, spermicides, or diaphragm) as a back-up method for those 7 days.
If you MISS 2 “active” [pink] pills in a row in WEEK 3:
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month, but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your doctor or healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex in the 7 days after you restart your pills. You MUST use another birth control method (such as condoms, spermicides, or diaphragm) as a back-up method for those 7 days.
If you MISS 3 OR MORE “active” [beige, orange, or pink] pills in a row (during the first 3 weeks):
1. If you are a Day 1 Starter:
THROW OUT the rest of the pill pack and start a new pack that same day.
If you are a Sunday Starter:
Keep taking 1 pill every day until Sunday.
On Sunday, THROW OUT the rest of the pack and start a new pack of pills that same day.
2. You may not have your period this month, but this is expected. However, if you miss your period 2 months in a row, call your doctor or healthcare provider because you might be pregnant.
3. You COULD BECOME PREGNANT if you have sex on the days when you missed pills or during the first 7 days after restarting your pills. You MUST use another birth control method (such as condoms, spermicides, or diaphragm) as a back-up method the next time you have sex and for the first 7 days after you restart your pills.
IF YOU FORGET ANY OF THE 7 “INACTIVE” [WHITE] PILLS IN WEEK 4:
- THROW AWAY the pills you missed.
- Keep taking 1 pill each day until the pack is empty.
- You do not need to use a back-up method of birth control.
FINALLY, IF YOU ARE STILL NOT SURE WHAT TO DO ABOUT THE PILLS YOU HAVE MISSED:
- Use a BACK-UP METHOD of birth control anytime you have sex.
- KEEP TAKING ONE “ACTIVE” [BEIGE, ORANGE, OR PINK] PILL EACH DAY until you can reach your doctor or healthcare provider.
ADDITIONAL INFORMATION
1. PREGNANCY DUE TO PILL FAILURE
The incidence of pill failure resulting in pregnancy is approximately one percent (i.e., one pregnancy per 100 women per year of use) if taken every day as directed, but more typical failure rates are about 5% (5 pregnancies per 100 women per year of use). If failure does occur, the risk to the fetus is minimal.
2. PREGNANCY AFTER STOPPING THE PILL
There may be some delay in becoming pregnant after you stop using oral contraceptives, especially if you had irregular menstrual cycles before you used oral contraceptives. It may be advisable to postpone conception until you begin menstruating regularly once you have stopped taking the pill and desire pregnancy.
There does not appear to be any increase in birth defects in newborn babies when pregnancy occurs soon after stopping the pill.
3. OVERDOSAGE
Serious ill effects have not been reported following ingestion of large doses of oral contraceptives by young children. Overdosage may cause nausea and withdrawal bleeding in females. In case of overdosage, contact your doctor, healthcare provider, or pharmacist.
4. OTHER INFORMATION
Your doctor or healthcare provider will take a medical and family history and may examine you before prescribing an oral contraceptive. The physical examination may be delayed to another time if you request it and your doctor or the healthcare provider believes that it is a good medical practice to postpone it. You should be reexamined at least once a year. Be sure to inform your doctor or healthcare provider if there is a family history of any of the conditions listed previously in this leaflet. Be sure to keep all appointments with your doctor or healthcare provider, because this is a time to determine if there are early signs of side effects of oral contraceptive use.
Do not use the drug for any condition other than the one for which it was prescribed. This drug has been prescribed specifically for you; do not give it to others who may want birth control pills.
HEALTH BENEFITS FROM ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES
In addition to preventing pregnancy, use of combination oral contraceptives may provide certain benefits. They are:
- menstrual cycles may become more regular
- blood flow during menstruation may be lighter and less iron may be lost. Therefore, anemia due to iron deficiency is less likely to occur
- pain or other symptoms during menstruation may be encountered less frequently
- ectopic (tubal) pregnancy may occur less frequently
- non-cancerous cysts or lumps in the breast may occur less frequently
- acute pelvic inflammatory disease may occur less frequently
- oral contraceptive use may provide some protection against developing two forms of cancer: cancer of the ovaries and cancer of the lining of the uterus
If you want more information about birth control pills, ask your doctor, healthcare provider, or pharmacist. They have a more technical leaflet called the Prescribing Information, which you may wish to read.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
KEEP THIS AND ALL MEDICATIONS OUT OF THE REACH OF CHILDREN.
All brand names listed are the registered trademarks of their respective owners and are not trademarks of Teva Pharmaceuticals USA.
Manufactured by:
Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc.North Wales, PA 19454
Distributed by:
Mayne Pharma
Greenville, NC 27834Rev. B 8/2017
- Package/Label Display Panel, Part 1 of 2
-
Package/Label Display Panel, Part 2 of 2

NDC: 51862-238-03 3 Blister Card Dispensers, 28 Tablets Each
CAZIANT®
Desogestrel and Ethinyl Estradiol Tablets USP
(Triphasic Regimen)
Rx only
THIS PRODUCT (LIKE ALL ORAL CONTRACEPTIVES) IS INTENDED TO PREVENT
PREGNANCY. IT DOES NOT PROTECT AGAINST HIV INFECTIONS (AIDS) AND OTHER
SEXUALLY TRANSMITTED DISEASES.
Each beige tablet contains 0.1 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol; each
orange tablet contains 0.125 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol; and each
pink tablet contains 0.15 mg desogestrel and 0.025 mg ethinyl estradiol. Each white
tablet contains inert ingredients.
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CAZIANT TRIPHASIC REGIMEN
desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol kitProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 51862-238 Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 51862-238-03 3 in 1 CARTON 08/03/2016 1 NDC: 51862-238-01 1 in 1 POUCH 1 1 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Quantity of Parts Part # Package Quantity Total Product Quantity Part 1 7 Part 2 7 Part 3 7 Part 4 7 Part 1 of 4 DESOGESTREL AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL
desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablet, film coatedProduct Information Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DESOGESTREL (UNII: 81K9V7M3A3) (DESOGESTREL - UNII:81K9V7M3A3) DESOGESTREL 0.1 mg ETHINYL ESTRADIOL (UNII: 423D2T571U) (ETHINYL ESTRADIOL - UNII:423D2T571U) ETHINYL ESTRADIOL 0.025 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (3 MPA.S) (UNII: 0VUT3PMY82) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) ALPHA-TOCOPHEROL (UNII: H4N855PNZ1) FERRIC OXIDE RED (UNII: 1K09F3G675) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) Product Characteristics Color BROWN (beige) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code b;333 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076455 08/03/2016 Part 2 of 4 DESOGESTREL AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL
desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablet, film coatedProduct Information Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DESOGESTREL (UNII: 81K9V7M3A3) (DESOGESTREL - UNII:81K9V7M3A3) DESOGESTREL 0.125 mg ETHINYL ESTRADIOL (UNII: 423D2T571U) (ETHINYL ESTRADIOL - UNII:423D2T571U) ETHINYL ESTRADIOL 0.025 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (3 MPA.S) (UNII: 0VUT3PMY82) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) ALPHA-TOCOPHEROL (UNII: H4N855PNZ1) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code b;332 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076455 08/03/2016 Part 3 of 4 DESOGESTREL AND ETHINYL ESTRADIOL
desogestrel and ethinyl estradiol tablet, film coatedProduct Information Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength DESOGESTREL (UNII: 81K9V7M3A3) (DESOGESTREL - UNII:81K9V7M3A3) DESOGESTREL 0.15 mg ETHINYL ESTRADIOL (UNII: 423D2T571U) (ETHINYL ESTRADIOL - UNII:423D2T571U) ETHINYL ESTRADIOL 0.025 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (6 MPA.S) (UNII: 0WZ8WG20P6) HYPROMELLOSE 2910 (3 MPA.S) (UNII: 0VUT3PMY82) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) POLYSORBATE 80 (UNII: 6OZP39ZG8H) POVIDONE K30 (UNII: U725QWY32X) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) STEARIC ACID (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) ALPHA-TOCOPHEROL (UNII: H4N855PNZ1) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code b;335 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076455 08/03/2016 Part 4 of 4 INERT
inert tabletProduct Information Route of Administration ORAL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength ANHYDROUS LACTOSE (UNII: 3SY5LH9PMK) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color WHITE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 6mm Flavor Imprint Code b;334 Contains Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076455 08/03/2016 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076455 08/03/2016 Labeler - Mayne Pharma Inc. (867220261)
Trademark Results [Caziant]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 CAZIANT 78612508 3652644 Live/Registered |
MAYNE PHARMA LLC 2005-04-20 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
