EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN tablet
ezetimibe and simvastatin by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
ezetimibe and simvastatin by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by NORTHSTAR RX LLC, Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN TABLETS safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN TABLETS.
EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2004RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, which contains a cholesterol absorption inhibitor and an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor (statin), is indicated as adjunctive therapy to diet to:
- reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and to increase HDL-C in patients with primary (heterozygous familial and non-familial) hyperlipidemia or mixed hyperlipidemia. (1.1)
- reduce elevated total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HoFH), as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments. (1.2)
Limitations of Use (1.3)
- No incremental benefit of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for simvastatin has been established.
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have not been studied in Fredrickson Type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias.
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Dose range is 10/10 mg/day to 10/40 mg/day. (2.1)
- Recommended usual starting dose is 10/10 or 10/20 mg/day. (2.1)
- Due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, use of the 10/80 mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be restricted to patients who have been taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80 mg chronically (e.g., for 12 months or more) without evidence of muscle toxicity. (2.2)
- Patients who are currently tolerating the 10/80 mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets who need to be initiated on an interacting drug that is contraindicated or is associated with a dose cap for simvastatin should be switched to an alternative statin or statin-based regimen with less potential for the drug-drug interaction. (2.2)
- Due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, associated with the 10/80 mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, patients unable to achieve their LDL-C goal utilizing the 10/40 mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should not be titrated to the 10/80 mg dose, but should be placed on alternative LDL-C-lowering treatment(s) that provides greater LDL-C lowering. (2.2)
- Dosing of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should occur either ≥2 hours before or ≥4 hours after administration of a bile acid sequestrant. (2.3, 7.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Tablets (ezetimibe mg/simvastatin mg): 10/10, 10/20, 10/40, 10/80 (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors. (4, 5.1)
- Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol. (4, 5.1)
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication (4, 6.2)
- Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations of hepatic transaminase levels (4, 5.2)
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant (4, 8.1)
- Nursing mothers (4, 8.3)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Patients should be advised of the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, with the 10/80 mg dose. (5.1)
- Patients should be advised to report promptly any unexplained and/or persistent muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. (5.1)
- Skeletal muscle effects (e.g., myopathy and rhabdomyolysis): Risks increase with higher doses and concomitant use of certain medicines. Predisposing factors include advanced age (≥65), female gender, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and renal impairment. Rare cases of rhabdomyolysis with acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria have been reported. (4, 5.1, 8.5, 8.6)
- Liver enzyme abnormalities: Persistent elevations in hepatic transaminases can occur. Check liver enzyme tests before initiating therapy and as clinically indicated thereafter. (5.2)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Common (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) adverse reactions in clinical trials: headache, increased ALT, myalgia, upper respiratory tract infection, and diarrhea. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact NorthStar RxLLC at 1-800-206-7821 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Drug Interactions Associated with Increased Risk of Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis (2.3, 2.4, 4, 5.1, 7.1, 7.2, 7.3, 7.8, 12.3)
Interacting Agents Prescribing
RecommendationsStrong CYP3A4 Inhibitors,
(e.g., itraconazole,
ketoconazole,
posaconazole,
voriconazole,
erythromycin,
clarithromycin,
telithromycin, HIV protease
inhibitors, boceprevir,
telaprevir, nefazodone,
cobicistat-containing
products), gemfibrozil,
cyclosporine, danazol
Contraindicated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
Niacin (≥1 g/day)
For Chinese patients, not recommended with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
Verapamil, diltiazem,
dronedarone
Do not exceed 10/10 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily
Amiodarone, amlodipine,
ranolazine
Do not exceed 10/20 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily
Lomitapide
For patients with HoFH, do not exceed 10/20 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily*
Daptomycin
Temporarily suspend ezetimibe and simvastatin
Grapefruit juice
Avoid grapefruit juice
* For patients with HoFH who have been taking 80 mg simvastatin chronically (e.g., for 12 months or more) without evidence of muscle toxicity, do not exceed 10/40 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets when taking lomitapide.
- Coumarin anticoagulants: simvastatin prolongs INR. Achieve stable INR prior to starting ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Monitor INR frequently until stable upon initiation or alteration of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets therapy. (7.8)
- Cholestyramine: Combination decreases exposure of ezetimibe. (2.3, 7.5)
- Other Lipid-lowering Medications: Use with fenofibrates increases the risk of adverse skeletal muscle effects. Caution should be used when prescribing with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. (5.1, 7.2)
- Fenofibrates: Combination increases exposure of ezetimibe. If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving ezetimibe and a fenofibrate, gallbladder studies are indicated and alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered. (7.2, 7.7, 12.3)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 11/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
1.2 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
1.3 Limitations of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
2.2 Restricted Dosing for 10/80 mg
2.3 Coadministration with Other Drugs
2.4 Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
2.5 Patients with Renal Impairment/Chronic Kidney Disease
2.6 Geriatric Patients
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
5.2 Liver Enzymes
5.3 Endocrine Function
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors, Cyclosporine, or Danazol
7.2 Lipid-Lowering Drugs That Can Cause Myopathy When Given Alone
7.3 Amiodarone, Dronedarone, Ranolazine, or Calcium Channel Blockers
7.4 Niacin
7.5 Cholestyramine
7.6 Digoxin
7.7 Fenofibrates (e.g., fenofibrate and fenofibric acid)
7.8 Coumarin Anticoagulants
7.9 Colchicine
7.10 Daptomycin
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.3 Nursing Mothers
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
8.8 Chinese Patients
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
14.2 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
14.3 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
17.1 Muscle Pain
17.2 Liver Enzymes
17.3 Pregnancy
17.4 Breastfeeding
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- Therapy with lipid-altering agents should be only one component of multiple risk factor intervention in individuals at significantly increased risk for atherosclerotic vascular disease due to hypercholesterolemia. Drug therapy is indicated as an adjunct to diet when the response to a diet restricted in saturated fat and cholesterol and other nonpharmacologic measures alone has been inadequate.
1.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are indicated for the reduction of elevated total cholesterol (total-C), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), apolipoprotein B (Apo B), triglycerides (TG), and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (non-HDL-C), and to increase high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) in patients with primary (heterozygous familial and non-familial) hyperlipidemia or mixed hyperlipidemia.
1.2 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are indicated for the reduction of elevated total-C and LDL-C in patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia, as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) or if such treatments are unavailable.
1.3 Limitations of Use
- No incremental benefit of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for simvastatin has been established.
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have not been studied in Fredrickson type I, III, IV, and V dyslipidemias.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosing
- The usual dosage range is 10/10 mg/day to 10/40 mg/day. The recommended usual starting dose is 10/10 mg/day or 10/20 mg/day. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be taken as a single daily dose in the evening, with or without food. Patients who require a larger reduction in LDL-C (greater than 55%) may be started at 10/40 mg/day in the absence of moderate to severe renal impairment (estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2). After initiation or titration of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, lipid levels may be analyzed after 2 or more weeks and dosage adjusted, if needed.
2.2 Restricted Dosing for 10/80 mg
- Due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, particularly during the first year of treatment, use of the 10/80-mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be restricted to patients who have been taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80 mg chronically (e.g., for 12 months or more) without evidence of muscle toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Patients who are currently tolerating the 10/80-mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets who need to be initiated on an interacting drug that is contraindicated or is associated with a dose cap for simvastatin should be switched to an alternative statin or statin-based regimen with less potential for the drug-drug interaction.
- Due to the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, associated with the 10/80-mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, patients unable to achieve their LDL-C goal utilizing the 10/40-mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should not be titrated to the 10/80-mg dose, but should be placed on alternative LDL-C-lowering treatment(s) that provides greater LDL-C lowering.
2.3 Coadministration with Other Drugs
Patients taking Verapamil, Diltiazem, or Dronedarone
- The dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should not exceed 10/10 mg/day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Patients taking Amiodarone, Amlodipine or Ranolazine
- The dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should not exceed 10/20 mg/day [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.3), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Patients taking Bile Acid Sequestrants
- Dosing of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should occur either greater than or equal to 2 hours before or greater than or equal to 4 hours after administration of a bile acid sequestrant [see Drug Interactions (7.5)].
2.4 Patients with Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia
- The recommended dosage for patients with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia is ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/40 mg/day in the evening [see Dosage and Administration, Restricted Dosing for 10/80 mg (2.2)]. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be used as an adjunct to other lipid-lowering treatments (e.g., LDL apheresis) in these patients or if such treatments are unavailable.
- Simvastatin exposure is approximately doubled with concomitant use of lomitapide; therefore, the dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be reduced by 50% if initiating lomitapide. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets dosage should not exceed 10/20 mg/day (or 10/40 mg/day for patients who have previously taken simvastatin 80 mg/day chronically, e.g., for 12 months or more, without evidence of muscle toxicity) while taking lomitapide.
2.5 Patients with Renal Impairment/Chronic Kidney Disease
- In patients with mild renal impairment (estimated GFR greater than or equal to 60 mL/min/1.73 m2), no dosage adjustment is necessary. In patients with chronic kidney disease and estimated glomerular filtration rate less than 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, the dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets is 10/20 mg/day in the evening. In such patients, higher doses should be used with caution and close monitoring [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1); Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.6 Geriatric Patients
- No dosage adjustment is necessary in geriatric patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
-
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/10 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘321’ on the other side.
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/20 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets
- debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘322’ on the other side.
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/40 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘323’ on the other side.
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/80 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘324’ on the other side.
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are contraindicated in the following conditions:
- Concomitant administration of strong CYP3A4 inhibitors (e.g., itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, HIV protease inhibitors, boceprevir, telaprevir, erythromycin, clarithromycin, telithromycin, nefazodone, and cobicistat-containing products) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Concomitant administration of gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
- Active liver disease or unexplained persistent elevations in hepatic transaminase levels [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Women who are pregnant or may become pregnant. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Because HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins), such as simvastatin, decrease cholesterol synthesis and possibly the synthesis of other biologically active substances derived from cholesterol, ezetimibe and simvastatin may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process and the discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on the outcome of long-term therapy of primary hypercholesterolemia. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ezetimibe and simvastatin use during pregnancy; however, in rare reports congenital anomalies were observed following intrauterine exposure to statins. In rat and rabbit animal reproduction studies, simvastatin revealed no evidence of teratogenicity. Ezetimibe and simvastatin should be administered to women of childbearing age only when such patients are highly unlikely to conceive. If the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, ezetimibe and simvastatin should be discontinued immediately and the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Nursing mothers. It is not known whether simvastatin is excreted into human milk; however, a small amount of another drug in this class does pass into breast milk. Because statins have the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who require ezetimibe and simvastatin treatment should not breastfeed their infants [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis
- Simvastatin occasionally causes myopathy manifested as muscle pain, tenderness or weakness with creatine kinase above ten times the upper limit of normal (ULN). Myopathy sometimes takes the form of rhabdomyolysis with or without acute renal failure secondary to myoglobinuria, and rare fatalities have occurred. The risk of myopathy is increased by elevated plasma levels of simvastatin and simvastatin acid. Predisposing factors for myopathy include advanced age (≥65 years), female gender, uncontrolled hypothyroidism, and renal impairment. Chinese patients may be at increased risk for myopathy[see Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
- The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, is dose related. In a clinical trial database in which 41,413 patients were treated with simvastatin, 24,747 (approximately 60%) of whom were enrolled in studies with a median follow-up of at least 4 years, the incidence of myopathy was approximately 0.03% and 0.08% at 20 and 40 mg/day, respectively. The incidence of myopathy with 80 mg (0.61%) was disproportionately higher than that observed at the lower doses. In these trials, patients were carefully monitored and some interacting medicinal products were excluded.
- In a clinical trial in which 12,064 patients with a history of myocardial infarction were treated with simvastatin (mean follow-up 6.7 years), the incidence of myopathy (defined as unexplained muscle weakness or pain with a serum creatine kinase [CK] >10 times upper limit of normal [ULN]) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.9% compared with 0.02% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of rhabdomyolysis (defined as myopathy with a CK >40 times ULN) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.4% compared with 0% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, was highest during the first year and then notably decreased during the subsequent years of treatment. In this trial, patients were carefully monitored and some interacting medicinal products were excluded.
- The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, is greater in patients on simvastatin 80 mg compared with other statin therapies with similar or greater LDL-C-lowering efficacy and compared with lower doses of simvastatin. Therefore, the 10/80 mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be used only in patients who have been taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80 mg chronically (e.g., for 12 months or more) without evidence of muscle toxicity [see Dosage and Administration, Restricted Dosing for 10/80 mg (2.2)]. If, however, a patient who is currently tolerating the 10/80-mg dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets needs to be initiated on an interacting drug that is contraindicated or is associated with a dose cap for simvastatin, that patient should be switched to an alternative statin or statin-based regimen with less potential for the drug-drug interaction. Patients should be advised of the increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, and to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness. If symptoms occur, treatment should be discontinued immediately [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- In the Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP), 9270 patients with chronic kidney disease were allocated to receive ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 mg daily (n=4650) or placebo (n=4620). During a median follow-up period of 4.9 years, the incidence of myopathy (defined as unexplained muscle weakness or pain with a serum creatine kinase [CK] >10 times upper limit of normal [ULN]) was 0.2% for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 0.1% for placebo: the incidence of rhabdomyolysis (defined as myopathy with a CK > 40 times ULN) was 0.09% for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 0.02% for placebo.
- In postmarketing experience with ezetimibe, cases of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis have been reported. Most patients who developed rhabdomyolysis were taking a statin prior to initiating ezetimibe. However, rhabdomyolysis has been reported with ezetimibe monotherapy and with the addition of ezetimibe to agents known to be associated with increased risk of rhabdomyolysis, such as fibric acid derivatives. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and a fenofibrate, if taking concomitantly, should both be immediately discontinued if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected.
- There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy (IMNM), an autoimmune myopathy, associated with statin use. IMNM is characterized by: proximal muscle weakness and elevated serum creatine kinase, which persist despite discontinuation of statin treatment; muscle biopsy showing necrotizing myopathy without significant inflammation; improvement with immunosuppressive agents.
- All patients starting therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or whose dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are being increased should be advised of the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, and told to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if muscle signs and symptoms persist after discontinuing ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets therapy should be discontinued immediately if myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. In most cases, muscle symptoms and CK increases resolved when simvastatin treatment was promptly discontinued. Periodic CK determinations may be considered in patients starting therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or whose dose is being increased, but there is no assurance that such monitoring will prevent myopathy.
- Many of the patients who have developed rhabdomyolysis on therapy with simvastatin have had complicated medical histories, including renal insufficiency usually as a consequence of long-standing diabetes mellitus. Such patients taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets merit closer monitoring.
-
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets therapy should be discontinued if markedly elevated CPK levels occur or myopathy is diagnosed or suspected. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets therapy should also be temporarily withheld in any patient experiencing an acute or serious condition predisposing to the development of renal failure secondary to rhabdomyolysis, e.g., sepsis; hypotension; major surgery; trauma; severe metabolic, endocrine, or electrolyte disorders; or uncontrolled epilepsy.
- Drug Interactions
- The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis is increased by elevated plasma levels of simvastatin and simvastatin acid. Simvastatin is metabolized by the cytochrome P450 isoform 3A4. Certain drugs that inhibit this metabolic pathway can raise the plasma levels of simvastatin and may increase the risk of myopathy. These include itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, and voriconazole, the macrolide antibiotics erythromycin and clarithromycin, and the ketolide antibiotic telithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, boceprevir, telaprevir, the antidepressant nefazodone, cobicistat-containing products, or grapefruit juice [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Combination of these drugs with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are contraindicated. If short-term treatment with strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is unavoidable, therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets must be suspended during the course of treatment [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7)].
- The combined use of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with gemfibrozil, cyclosporine, or danazol is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Drug Interactions (7.1 and 7.2)].
- Caution should be used when prescribing fenofibrates with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, as these agents can cause myopathy when given alone and the risk is increased when they are coadministered [see Drug Interactions (7.2, 7.7)].
-
Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been reported with simvastatin coadministered with colchicine, and caution should be exercised when prescribing ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with colchicine [see Drug Interactions (7.9)].
The benefits of the combined use of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with the following drugs should be carefully weighed against the potential risks of combinations: other lipid-lowering drugs (fenofibrates or, for patients with HoFH, lomitapide), amiodarone, dronedarone, verapamil, diltiazem, amlodipine, or ranolazine [see Dosage and Administration (2.4), Drug Interactions (7.3)]. - Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been observed with simvastatin coadministered with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day niacin) of niacin-containing products[see Drug Interactions (7.4)].
Cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported with ezetimibe and simvastatin administered with daptomycin. Temporarily suspend ezetimibe and simvastatin in patients taking daptomycin[see Drug Interactions (7.10)].
- Prescribing recommendations for interacting agents are summarized in Table 1 [see also Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4), Drug Interactions (7), and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Table 1: Drug Interactions Associated with Increased Risk of Myopathy/Rhabdomyolysis Interacting Agents
Prescribing Recommendations
- Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors, e.g.:
- Itraconazole
- Ketoconazole
- Posaconazole
- Voriconazole
- Erythromycin
- Clarithromycin
- Telithromycin
- HIV protease inhibitors
- Boceprevir
- Telaprevir
- Nefazodone
- Cobicistat-containing products
Gemfibrozil
Cyclosporine
Danazol
Contraindicated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
Niacin (≥1 g/day)
For Chinese patients, not recommended with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
Verapamil
Diltiazem
Dronedarone
Do not exceed 10/10 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily
Amiodarone
Amlodipine
Ranolazine
Do not exceed 10/20 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily
Lomitapide
For patients with HoFH, do not exceed 10/20 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets daily*
Daptomycin
Temporarily suspend ezetimibe and simvastatin
Grapefruit juice
Avoid grapefruit juice
* For patients with HoFH who have been taking 80 mg simvastatin chronically (e.g., for 12 months or more) without evidence of muscle toxicity, do not exceed 10/40 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets when taking lomitapide.
5.2 Liver Enzymes
- In three placebo-controlled, 12-week trials, the incidence of consecutive elevations (≥3 X ULN) in serum transaminases was 1.7% overall for patients treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and appeared to be dose-related with an incidence of 2.6% for patients treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80. In controlled long-term (48-week) extensions, which included both newly-treated and previously-treated patients, the incidence of consecutive elevations (≥3 X ULN) in serum transaminases was 1.8% overall and 3.6% for patients treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80. These elevations in transaminases were generally asymptomatic, not associated with cholestasis, and returned to baseline after discontinuation of therapy or with continued treatment.
- In SHARP, 9270 patients with chronic kidney disease were allocated to receive ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 mg daily (n=4650), or placebo (n=4620). During a median follow-up period of 4.9 years, the incidence of consecutive elevations of transaminases (>3 X ULN) was 0.7% for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 0.6% for placebo.
- It is recommended that liver function tests be performed before the initiation of treatment with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, and thereafter when clinically indicated. There have been rare postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking statins, including simvastatin. If serious liver injury with clinical symptoms and/or hyperbilirubinemia or jaundice occurs during treatment with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, promptly interrupt therapy. If an alternate etiology is not found do not restart ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Note that ALT may emanate from muscle, therefore ALT rising with CK may indicate myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be used with caution in patients who consume substantial quantities of alcohol and/or have a past history of liver disease. Active liver diseases or unexplained persistent transaminase elevations are contraindications to the use of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed in greater detail in other sections of the label:
- Rhabdomyolysis and myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Liver enzyme abnormalities [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
- Because clinical studies are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical studies of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical studies of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
- In the ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets placebo-controlled clinical trials database of 1420 patients (age range 20 to 83 years, 52% women, 87% Caucasians, 3% Blacks, 5% Hispanics, 3% Asians) with a median treatment duration of 27 weeks, 5% of patients on ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 2.2% of patients on placebo discontinued due to adverse reactions.
- The most common adverse reactions in the group treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets that led to treatment discontinuation and occurred at a rate greater than placebo were:
- Increased ALT (0.9%)
- Myalgia (0.6%)
- Increased AST (0.4%)
- Back pain (0.4%)
- The most commonly reported adverse reactions (incidence ≥2% and greater than placebo) in controlled clinical trials were: headache (5.8%), increased ALT (3.7%), myalgia (3.6%), upper respiratory tract infection (3.6%), and diarrhea (2.8%).
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have been evaluated for safety in more than 10,189 patients in clinical trials.
- Table 2 summarizes the frequency of clinical adverse reactions reported in ≥2% of patients treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (n=1420) and at an incidence greater than placebo, regardless of causality assessment, from four placebo-controlled trials.
Table 2: Clinical Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥2% of Patients Treated with Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets and at an Incidence Greater than Placebo, Regardless of Causality Body System/Organ Class
Adverse Reaction
Placebo
(%)
n=371
Ezetimibe
10 mg
(%)
n=302
Simvastatin†
(%)
n=1234
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets†
(%)
n=1420
Body as a whole – general disorders
Headache
5.4
6
5.9
5.8
Gastrointestinal system disorders
Diarrhea
2.2
5
3.7
2.8
Infections and infestations
Influenza
0.8
1
1.9
2.3
Upper respiratory tract infection
2.7
5
5
3.6
Musculoskeletal and connective tissue disorders
Myalgia
2.4
2.3
2.6
3.6
Pain in extremity
1.3
3
2
2.3
* Includes two placebo-controlled combination studies in which the active ingredients equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets were coadministered and two placebo-controlled studies in which ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets was administered.
† All doses.
Study of Heart and Renal Protection
- In SHARP, 9270 patients were allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 mg daily (n=4650) or placebo (n=4620) for a median follow-up period of 4.9 years. The proportion of patients who permanently discontinued study treatment as a result of either an adverse event or abnormal safety blood result was 10.4% vs. 9.8% among patients allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and placebo, respectively. Comparing those allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets vs. placebo, the incidence of myopathy (defined as unexplained muscle weakness or pain with a serum CK >10 times ULN) was 0.2% vs. 0.1% and the incidence of rhabdomyolysis (defined as myopathy with a CK >40 times ULN) was 0.09% vs. 0.02%, respectively. Consecutive elevations of transaminases (>3 X ULN) occurred in 0.7% vs. 0.6%, respectively. Patients were asked about the occurrence of unexplained muscle pain or weakness at each study visit: 21.5% vs. 20.9% patients ever reported muscle symptoms in the ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and placebo groups, respectively. Cancer was diagnosed during the trial in 9.4% vs. 9.5% of patients assigned to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and placebo, respectively.
Ezetimibe
- Other adverse reactions reported with ezetimibe in placebo-controlled studies, regardless of causality assessment: Musculoskeletal system disorders: arthralgia; Infections and infestations: sinusitis; Body as a whole – general disorders: fatigue.
Simvastatin
- In a clinical trial in which 12,064 patients with a history of myocardial infarction were treated with simvastatin (mean follow-up 6.7 years), the incidence of myopathy (defined as unexplained muscle weakness or pain with a serum creatine kinase [CK] >10 times upper limit of normal [ULN]) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.9% compared with 0.02% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of rhabdomyolysis (defined as myopathy with a CK >40 times ULN) in patients on 80 mg/day was approximately 0.4% compared with 0% for patients on 20 mg/day. The incidence of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, was highest during the first year and then notably decreased during the subsequent years of treatment. In this trial, patients were carefully monitored and some interacting medicinal products were excluded.
- Other adverse reactions reported with simvastatin in placebo-controlled clinical studies, regardless of causality assessment: Cardiac disorders: atrial fibrillation; Ear and labyrinth disorders: vertigo; Gastrointestinal disorders: abdominal pain, constipation, dyspepsia, flatulence, gastritis; Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: eczema, rash; Endocrine disorders: diabetes mellitus; Infections and infestations: bronchitis, sinusitis, urinary tract infections; Body as a whole – general disorders: asthenia, edema/swelling; Psychiatric disorders: insomnia.
Laboratory Tests
Marked persistent increases of hepatic serum transaminases have been noted [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Elevated alkaline phosphatase and γ-glutamyl transpeptidase have been reported. About 5% of patients taking simvastatin had elevations of CK levels of 3 or more times the normal value on one or more occasions. This was attributable to the noncardiac fraction of CK [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
- Because the below reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
- The following adverse reactions have been reported in postmarketing experience for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or ezetimibe or simvastatin: pruritus; alopecia; erythema multiforme; a variety of skin changes (e.g., nodules, discoloration, dryness of skin/mucous membranes, changes to hair/nails); dizziness; muscle cramps; myalgia; arthralgia; pancreatitis; paresthesia; peripheral neuropathy; vomiting; nausea; anemia; erectile dysfunction; interstitial lung disease; myopathy/rhabdomyolysis [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]; hepatitis/jaundice; fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure; depression; cholelithiasis; cholecystitis; thrombocytopenia; elevations in liver transaminases; elevated creatine phosphokinase.
- There have been rare reports of immune-mediated necrotizing myopathy associated with statin use [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, angioedema, rash, and urticaria have been reported.
- In addition, an apparent hypersensitivity syndrome has been reported rarely that has included one or more of the following features: anaphylaxis, angioedema, lupus erythematous-like syndrome, polymyalgia rheumatica, dermatomyositis, vasculitis, purpura, thrombocytopenia, leukopenia, hemolytic anemia, positive ANA, ESR increase, eosinophilia, arthritis, arthralgia, urticaria, asthenia, photosensitivity, fever, chills, flushing, malaise, dyspnea, toxic epidermal necrolysis, erythema multiforme, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome.
There have been rare postmarketing reports of cognitive impairment (e.g., memory loss, forgetfulness, amnesia, memory impairment, confusion) associated with statin use. These cognitive issues have been reported for all statins. The reports are generally nonserious, and reversible upon statin discontinuation, with variable times to symptom onset (1 day to years) and symptom resolution (median of 3 weeks).
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
[See Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
7.1 Strong CYP3A4 Inhibitors, Cyclosporine, or Danazol
- Strong CYP3A4 inhibitors: The risk of myopathy is increased by reducing the elimination of the simvastatin component of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Hence when ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are used with an inhibitor of CYP3A4 (e.g., as listed below), elevated plasma levels of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity increases the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis, particularly with higher doses of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Concomitant use of drugs labeled as having a strong inhibitory effect on CYP3A4 is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4)]. If treatment with itraconazole, ketoconazole, posaconazole, voriconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin or telithromycin is unavoidable, therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets must be suspended during the course of treatment.
Cyclosporine or Danazol: The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis is increased by concomitant administration of cyclosporine or danazol. Therefore, concomitant use of these drugs is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 Lipid-Lowering Drugs That Can Cause Myopathy When Given Alone
- Gemfibrozil: Contraindicated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Fenofibrates (e.g., fenofibrate and fenofibric acid): Caution should be used when prescribing with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.7)].
7.3 Amiodarone, Dronedarone, Ranolazine, or Calcium Channel Blockers
The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, is increased by concomitant administration of amiodarone, dronedarone, ranolazine, or calcium channel blockers such as verapamil, diltiazem or amlodipine [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Table 6 in Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.4 Niacin
Cases of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis have been observed with simvastatin coadministered with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day niacin) of niacin-containing products. The risk of myopathy is greater in Chinese patients. In a clinical trial (median follow-up 3.9 years) involving patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease and with well-controlled LDL-C levels on simvastatin 40 mg/day with or without ezetimibe 10 mg/day, there was no incremental benefit on cardiovascular outcomes with the addition of lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day) of niacin. Coadministration of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day) of niacin is not recommended in Chinese patients. It is unknown if this risk applies to other Asian patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Use in Specific Populations (8.8)].
7.5 Cholestyramine
Concomitant cholestyramine administration decreased the mean AUC of total ezetimibe approximately 55%. The incremental LDL-C reduction due to adding ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets to cholestyramine may be reduced by this interaction.
7.6 Digoxin
In one study, concomitant administration of digoxin with simvastatin resulted in a slight elevation in plasma digoxin concentrations. Patients taking digoxin should be monitored appropriately when ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are initiated.
7.7 Fenofibrates (e.g., fenofibrate and fenofibric acid)
- The safety and effectiveness of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets administered with fibrates have not been established. Because it is known that the risk of myopathy during treatment with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors is increased with concurrent administration of fenofibrates, Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be administered with caution when used concomitantly with a fenofibrate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Fenofibrates may increase cholesterol excretion into the bile, leading to cholelithiasis. In a preclinical study in dogs, ezetimibe increased cholesterol in the gallbladder bile [see Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology (13.2)]. If cholelithiasis is suspected in a patient receiving ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and a fenofibrate, gallbladder studies are indicated and alternative lipid-lowering therapy should be considered [see the product labeling for fenofibrate and fenofibric acid].
7.8 Coumarin Anticoagulants
- Simvastatin 20 to 40 mg/day modestly potentiated the effect of coumarin anticoagulants: the prothrombin time, reported as International Normalized Ratio (INR), increased from a baseline of 1.7 to 1.8 and from 2.6 to 3.4 in a normal volunteer study and in a hypercholesterolemic patient study, respectively. With other statins, clinically evident bleeding and/or increased prothrombin time has been reported in a few patients taking coumarin anticoagulants concomitantly. In such patients, prothrombin time should be determined before starting ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and frequently enough during early therapy to ensure that no significant alteration of prothrombin time occurs. Once a stable prothrombin time has been documented, prothrombin times can be monitored at the intervals usually recommended for patients on coumarin anticoagulants. If the dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets is changed or discontinued, the same procedure should be repeated. Simvastatin therapy has not been associated with bleeding or with changes in prothrombin time in patients not taking anticoagulants.
-
Concomitant administration of ezetimibe (10 mg once daily) had no significant effect on bioavailability of warfarin and prothrombin time in a study of twelve healthy adult males. There have been postmarketing reports of increased INR in patients who had ezetimibe added to warfarin. Most of these patients were also on other medications.
The effect of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on the prothrombin time has not been studied.
7.9 Colchicine
Cases of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, have been reported with simvastatin coadministered with colchicine, and caution should be exercised when prescribing ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with colchicine.
7.10 Daptomycin
Cases of rhabdomyolysis have been reported with ezetimibe and simvastatin administered with daptomycin. Both ezetimibe and simvastatin and daptomycin can cause myopathy and rhabdomyolysis when given alone and the risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis may be increased by coadministration. Temporarily suspend ezetimibe and simvastatin in patients taking daptomycin [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category X.
- [See Contraindications (4)].
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are contraindicated in women who are or may become pregnant. Lipid-lowering drugs offer no benefit during pregnancy, because cholesterol and cholesterol derivatives are needed for normal fetal development. Atherosclerosis is a chronic process, and discontinuation of lipid-lowering drugs during pregnancy should have little impact on long-term outcomes of primary hypercholesterolemia therapy. There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets use during pregnancy; however, there are rare reports of congenital anomalies in infants exposed to statins in utero. Animal reproduction studies of simvastatin in rats and rabbits showed no evidence of teratogenicity. Serum cholesterol and triglycerides increase during normal pregnancy, and cholesterol or cholesterol derivatives are essential for fetal development. Because statins, such as simvastatin, decrease cholesterol synthesis and possibly the synthesis of other biologically active substances derived from cholesterol, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets may cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman. If ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking this drug, the patient should be apprised of the potential hazard to the fetus.
- Women of childbearing potential, who require ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets treatment for a lipid disorder, should be advised to use effective contraception. For women trying to conceive, discontinuation of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be considered. If pregnancy occurs, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be immediately discontinued.
Ezetimibe
- In oral (gavage) embryo-fetal development studies of ezetimibe conducted in rats and rabbits during organogenesis, there was no evidence of embryolethal effects at the doses tested (250, 500, 1000 mg/kg/day). In rats, increased incidences of common fetal skeletal findings (extra pair of thoracic ribs, unossified cervical vertebral centra, shortened ribs) were observed at 1000 mg/kg/day (~10 times the human exposure at 10 mg daily based on AUC0-24hr for total ezetimibe). In rabbits treated with ezetimibe, an increased incidence of extra thoracic ribs was observed at 1000 mg/kg/day (150 times the human exposure at 10 mg daily based on AUC0-24hr for total ezetimibe). Ezetimibe crossed the placenta when pregnant rats and rabbits were given multiple oral doses.
- Multiple-dose studies of ezetimibe coadministered with statins in rats and rabbits during organogenesis result in higher ezetimibe and statin exposures. Reproductive findings occur at lower doses in coadministration therapy compared to monotherapy.
Simvastatin
- Simvastatin was not teratogenic in rats or rabbits at doses (25, 10 mg/kg/day, respectively) that resulted in 3 times the human exposure based on mg/m2 surface area. However, in studies with another structurally-related statin, skeletal malformations were observed in rats and mice.
- There are rare reports of congenital anomalies following intrauterine exposure to statins. In a review1 of approximately 100 prospectively followed pregnancies in women exposed to simvastatin or another structurally-related statin, the incidences of congenital anomalies, spontaneous abortions and fetal deaths/stillbirths did not exceed what would be expected in the general population. The number of cases is adequate only to exclude a 3- to 4-fold increase in congenital anomalies over the background incidence. In 89% of the prospectively followed pregnancies, drug treatment was initiated prior to pregnancy and was discontinued at some point in the first trimester when pregnancy was identified.
- 1Manson, J.M., Freyssinges, C., Ducrocq, M.B., Stephenson, W.P., Postmarketing Surveillance of Lovastatin and Simvastatin Exposure During Pregnancy, Reproductive Toxicology, 10(6):439-446, 1996.
8.3 Nursing Mothers
- It is not known whether simvastatin is excreted in human milk. Because a small amount of another drug in this class is excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women taking simvastatin should not nurse their infants. A decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or discontinue drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother [see Contraindications (4)].
- In rat studies, exposure to ezetimibe in nursing pups was up to half of that observed in maternal plasma. It is not known whether ezetimibe or simvastatin are excreted into human breast milk. Because a small amount of another drug in the same class as simvastatin is excreted in human milk and because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants, women who are nursing should not take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets [see Contraindications (4)].
8.4 Pediatric Use
The effects of ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin (n=126) compared to simvastatin monotherapy (n=122) have been evaluated in adolescent boys and girls with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia (HeFH). In a multicenter, double-blind, controlled study followed by an open-label phase, 142 boys and 106 postmenarchal girls, 10 to 17 years of age (mean age 14.2 years, 43% females, 82% Caucasians, 4% Asian, 2% Blacks, 13% multiracial) with HeFH were randomized to receive either ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin or simvastatin monotherapy. Inclusion in the study required 1) a baseline LDL-C level between 160 and 400 mg/dL and 2) a medical history and clinical presentation consistent with HeFH. The mean baseline LDL-C value was 225 mg/dL (range: 161 to 351 mg/dL) in the ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin group compared to 219 mg/dL (range: 149 to 336 mg/dL) in the simvastatin monotherapy group. The patients received coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg) or simvastatin monotherapy (10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg) for 6 weeks, coadministered ezetimibe and 40 mg simvastatin or 40 mg simvastatin monotherapy for the next 27 weeks, and open-label coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg) for 20 weeks thereafter.
The results of the study at Week 6 are summarized in Table 3. Results at Week 33 were consistent with those at Week 6.
Table 3: Mean Percent Difference at Week 6 Between the Pooled Ezetimibe Coadministered with Simvastatin Group and the Pooled Simvastatin Monotherapy Group in Adolescent Patients with Heterozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia Total-C LDL-C Apo B Non-HDL-C TG* HDL-C Mean percent difference between treatment groups
-12%
-15%
-12%
-14%
-2%
+0.1%
95% Confidence Interval
(-15%, -9%)
(-18%, -12%)
(-15%, -9%)
(-17%, -11%)
(-9, +4)
(-3, +3)
* For triglycerides, median % change from baseline.
From the start of the trial to the end of Week 33, discontinuations due to an adverse reaction occurred in 7 (6%) patients in the ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin group and in 2 (2%) patients in the simvastatin monotherapy group.
During the trial, hepatic transaminase elevations (two consecutive measurements for ALT and/or AST ≥3 X ULN) occurred in four (3%) individuals in the ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin group and in two (2%) individuals in the simvastatin monotherapy group. Elevations of CPK (≥10 X ULN) occurred in two (2%) individuals in the ezetimibe coadministered with simvastatin group and in zero individuals in the simvastatin monotherapy group.
In this limited controlled study, there was no significant effect on growth or sexual maturation in the adolescent boys or girls, or on menstrual cycle length in girls.
Coadministration of ezetimibe with simvastatin at doses greater than 40 mg/day has not been studied in adolescents. Also, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have not been studied in patients younger than 10 years of age or in pre-menarchal girls.
EzetimibeBased on total ezetimibe (ezetimibe + ezetimibe-glucuronide) there are no pharmacokinetic differences between adolescents and adults. Pharmacokinetic data in the pediatric population <10 years of age are not available.
Simvastatin
The pharmacokinetics of simvastatin has not been studied in the pediatric population.
8.5 Geriatric Use
- Of the 10,189 patients who received ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets in clinical studies, 3242 (32%) were 65 and older (this included 844 (8%) who were 75 and older). No overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between these subjects and younger subjects, and other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients but greater sensitivity of some older individuals cannot be ruled out. Since advanced age (≥65 years) is a predisposing factor for myopathy, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be prescribed with caution in the elderly [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Because advanced age (≥65 years) is a predisposing factor for myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be prescribed with caution in the elderly. In a clinical trial of patients treated with simvastatin 80 mg/day, patients ≥65 years of age had an increased risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, compared to patients <65 years of age [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
- In the SHARP trial of 9270 patients with moderate to severe renal impairment (6247 non-dialysis patients with median serum creatinine 2.5 mg/dL and median estimated glomerular filtration rate 25.6 mL/min/1.73 m2, and 3023 dialysis patients), the incidence of serious adverse events, adverse events leading to discontinuation of study treatment, or adverse events of special interest (musculoskeletal adverse events, liver enzyme abnormalities, incident cancer) was similar between patients ever assigned to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 mg (n=4650) or placebo (n=4620) during a median follow-up of 4.9 years. However, because renal impairment is a risk factor for statin-associated myopathy, doses of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets exceeding 10/20 mg should be used with caution and close monitoring in patients with moderate to severe renal impairment [see Dosage and Administration (2.5), Adverse Reactions (6.1), and Clinical Studies (14.3)].
8.8 Chinese Patients
In a clinical trial in which patients at high risk of cardiovascular disease were treated with simvastatin 40 mg/day (median follow-up 3.9 years), the incidence of myopathy was approximately 0.05% for non- Chinese patients (n=7367) compared with 0.24% for Chinese patients (n=5468). The incidence of myopathy for Chinese patients on simvastatin 40 mg/day or ezetimibe and simvastatin 10/40 mg/day coadministered with extended-release niacin 2 g/day was 1.24%.
Chinese patients may be at higher risk for myopathy, monitor patients appropriately. Coadministration of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day niacin) of niacin-containing products is not recommended in Chinese patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Drug Interactions (7.4)]. -
10 OVERDOSAGE
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
- No specific treatment of overdosage with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets can be recommended. In the event of an overdose, symptomatic and supportive measures should be employed.
Ezetimibe
- In clinical studies, administration of ezetimibe, 50 mg/day to 15 healthy subjects for up to 14 days, or 40 mg/day to 18 patients with primary hyperlipidemia for up to 56 days, was generally well tolerated.
- A few cases of overdosage have been reported; most have not been associated with adverse experiences. Reported adverse experiences have not been serious.
Simvastatin
- Significant lethality was observed in mice after a single oral dose of 9 g/m2. No evidence of lethality was observed in rats or dogs treated with doses of 30 and 100 g/m2, respectively. No specific diagnostic signs were observed in rodents. At these doses the only signs seen in dogs were emesis and mucoid stools.
- A few cases of overdosage with simvastatin have been reported; the maximum dose taken was 3.6 g. All patients recovered without sequelae.
- The dialyzability of simvastatin and its metabolites in man is not known at present.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets contain ezetimibe, a selective inhibitor of intestinal cholesterol and related phytosterol absorption, and simvastatin, an HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor.
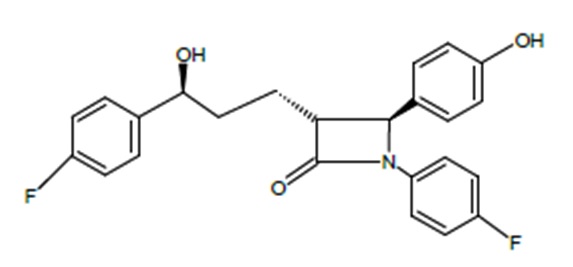
The chemical name of ezetimibe is 1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(R)-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-3(S)-hydroxypropyl]-4(S)-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-azetidinone. The molecular formula is C24H21F2NO3 and its molecular weight is 409.44 g/mol.
Ezetimibe is a white, crystalline powder that is freely soluble in ethanol, methanol and acetone and practically insoluble in water. Its structural formula is:
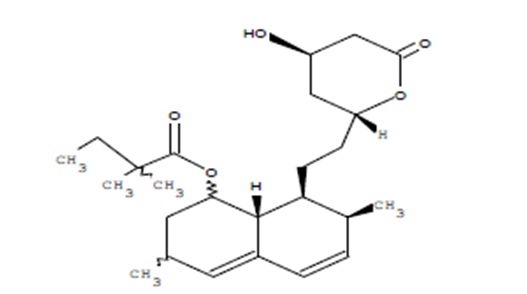
Simvastatin, an inactive lactone, is hydrolyzed to the corresponding β-hydroxyacid form, which is an inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Simvastatin is butanoic acid, 2,2-dimethyl-,1,2,3,7,8,8a-hexahydro-3,7-dimethyl-8-[2-(tetrahydro-4-hydroxy-6-oxo-2H-pyran-2-yl)-ethyl]-1-naphthalenyl ester, [1S-[1α,3α,7α,8α(2S*,4S*),-8aβ]]. The molecular formula of simvastatin is C25H38O5 and its molecular weight is 418.57 g/mol.
Simvastatin is a white to off-white, nonhygroscopic powder that is freely soluble in chloroform, methanol and alcohol, sparingly soluble in propylene glycol, very slightly soluble in hexane and practically insoluble in water. Its structural formula is:
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets are available for oral use as tablets containing 10 mg of ezetimibe, and either 10 mg of simvastatin (Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/10 mg), 20 mg of simvastatin (Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/20 mg), 40 mg of simvastatin (Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/40 mg), or 80 mg of simvastatin (Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/80 mg). Each tablet contains the following inactive ingredients: butylated hydroxyanisole, citric acid monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, propyl gallate, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
- Plasma cholesterol is derived from intestinal absorption and endogenous synthesis. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets contain ezetimibe and simvastatin, two lipid-lowering compounds with complementary mechanisms of action. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets reduce elevated total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and increases HDL-C through dual inhibition of cholesterol absorption and synthesis.
Ezetimibe
- Ezetimibe reduces blood cholesterol by inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol by the small intestine. The molecular target of ezetimibe has been shown to be the sterol transporter, Niemann-Pick C1-Like 1 (NPC1L1), which is involved in the intestinal uptake of cholesterol and phytosterols. In a 2-week clinical study in 18 hypercholesterolemic patients, ezetimibe inhibited intestinal cholesterol absorption by 54%, compared with placebo. Ezetimibe had no clinically meaningful effect on the plasma concentrations of the fat-soluble vitamins A, D, and E and did not impair adrenocortical steroid hormone production.
-
Ezetimibe localizes at the brush border of the small intestine and inhibits the absorption of cholesterol, leading to a decrease in the delivery of intestinal cholesterol to the liver. This causes a reduction of hepatic cholesterol stores and an increase in clearance of cholesterol from the blood; this distinct mechanism is complementary to that of statins [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Simvastatin - Simvastatin is a prodrug and is hydrolyzed to its active β-hydroxyacid form, simvastatin acid, after administration. Simvastatin is a specific inhibitor of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A (HMG-CoA) reductase, the enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of HMG-CoA to mevalonate, an early and rate limiting step in the biosynthetic pathway for cholesterol. In addition, simvastatin reduces very-low-density lipoproteins (VLDL) and TG and increases HDL-C.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
- Clinical studies have demonstrated that elevated levels of total-C, LDL-C and Apo B, the major protein constituent of LDL, promote human atherosclerosis. In addition, decreased levels of HDL-C are associated with the development of atherosclerosis. Epidemiologic studies have established that cardiovascular morbidity and mortality vary directly with the level of total-C and LDL-C and inversely with the level of HDL-C. Like LDL, cholesterol-enriched triglyceride-rich lipoproteins, including VLDL, intermediate-density lipoproteins (IDL), and remnants, can also promote atherosclerosis. The independent effect of raising HDL-C or lowering TG on the risk of coronary and cardiovascular morbidity and mortality has not been determined.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
- The results of a bioequivalence study in healthy subjects demonstrated that the ezetimibe and simvastatin 10 mg/10 mg to 10 mg/80 mg combination tablets are bioequivalent to coadministration of corresponding doses of ezetimibe (ZETIA®) and simvastatin (ZOCOR®) as individual tablets.
Absorption
Ezetimibe
- After oral administration, ezetimibe is absorbed and extensively conjugated to a pharmacologically active phenolic glucuronide (ezetimibe-glucuronide).
Simvastatin- The availability of the β-hydroxyacid to the systemic circulation following an oral dose of simvastatin was found to be less than 5% of the dose, consistent with extensive hepatic first-pass extraction.
Effect of Food on Oral Absorption
Ezetimibe
-
Concomitant food administration (high-fat or non-fat meals) had no effect on the extent of absorption of ezetimibe when administered as 10-mg tablets. The Cmax value of ezetimibe was increased by 38% with consumption of high-fat meals.
Simvastatin - Relative to the fasting state, the plasma profiles of both active and total inhibitors of HMG-CoA reductase were not affected when simvastatin was administered immediately before an American Heart Association recommended low-fat meal.
Distribution
Ezetimibe
- Ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are highly bound (>90%) to human plasma proteins.
Simvastatin
- Both simvastatin and its β-hydroxyacid metabolite are highly bound (approximately 95%) to human plasma proteins. When radiolabeled simvastatin was administered to rats, simvastatin-derived radioactivity crossed the blood-brain barrier.
Metabolism and Excretion
Ezetimibe
- Ezetimibe is primarily metabolized in the small intestine and liver via glucuronide conjugation with subsequent biliary and renal excretion. Minimal oxidative metabolism has been observed in all species evaluated.
- In humans, ezetimibe is rapidly metabolized to ezetimibe-glucuronide. Ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are the major drug-derived compounds detected in plasma, constituting approximately 10 to 20% and 80 to 90% of the total drug in plasma, respectively. Both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide are eliminated from plasma with a half-life of approximately 22 hours for both ezetimibe and ezetimibe-glucuronide. Plasma concentration-time profiles exhibit multiple peaks, suggesting enterohepatic recycling.
- Following oral administration of 14C-ezetimibe (20 mg) to human subjects, total ezetimibe (ezetimibe + ezetimibe-glucuronide) accounted for approximately 93% of the total radioactivity in plasma. After 48 hours, there were no detectable levels of radioactivity in the plasma.
- Approximately 78% and 11% of the administered radioactivity were recovered in the feces and urine, respectively, over a 10-day collection period. Ezetimibe was the major component in feces and accounted for 69% of the administered dose, while ezetimibe-glucuronide was the major component in urine and accounted for 9% of the administered dose.
Simvastatin
- Simvastatin is a lactone that is readily hydrolyzed in vivo to the corresponding β-hydroxyacid, a potent inhibitor of HMG-CoA reductase. Inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase is a basis for an assay in pharmacokinetic studies of the β-hydroxyacid metabolites (active inhibitors) and, following base hydrolysis, active plus latent inhibitors (total inhibitors) in plasma following administration of simvastatin. The major active metabolites of simvastatin present in human plasma are the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin and its 6'-hydroxy, 6'-hydroxymethyl, and 6'-exomethylene derivatives.
- Following an oral dose of 14C-labeled simvastatin in man, 13% of the dose was excreted in urine and 60% in feces. Plasma concentrations of total radioactivity (simvastatin plus 14C-metabolites) peaked at 4 hours and declined rapidly to about 10% of peak by 12 hours postdose.
Specific Populations
Geriatric Patients
Ezetimibe
-
In a multiple-dose study with ezetimibe given 10 mg once daily for 10 days, plasma concentrations for total ezetimibe were about 2-fold higher in older (≥65 years) healthy subjects compared to younger subjects.
Simvastatin - In a study including 16 elderly patients between 70 and 78 years of age who received simvastatin 40 mg/day, the mean plasma level of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity was increased approximately 45% compared with 18 patients between 18 to 30 years of age.
Pediatric Patients: [See Pediatric Use (8.4).]
Gender
Ezetimibe
- In a multiple-dose study with ezetimibe given 10 mg once daily for 10 days, plasma concentrations for total ezetimibe were slightly higher (<20%) in women than in men.
Race
Ezetimibe
- Based on a meta-analysis of multiple-dose pharmacokinetic studies, there were no pharmacokinetic differences between Black and Caucasian subjects. Studies in Asian subjects indicated that the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe was similar to those seen in Caucasian subjects.
Hepatic Impairment
Ezetimibe
- After a single 10-mg dose of ezetimibe, the mean exposure (based on area under the curve [AUC]) to total ezetimibe was increased approximately 1.7-fold in patients with mild hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 5 to 6), compared to healthy subjects. The mean AUC values for total ezetimibe and ezetimibe increased approximately 3- to 4-fold and 5- to 6-fold, respectively, in patients with moderate (Child-Pugh score 7 to 9) or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh score 10 to 15). In a 14-day, multiple-dose study (10 mg daily) in patients with moderate hepatic impairment, the mean AUC for total ezetimibe and ezetimibe increased approximately 4-fold compared to healthy subjects.
Renal Impairment
Ezetimibe
-
After a single 10-mg dose of ezetimibe in patients with severe renal disease (n=8; mean CrCl ≤30 mL/min/1.73 m2), the mean AUC for total ezetimibe and ezetimibe increased approximately 1.5-fold, compared to healthy subjects (n=9).
Simvastatin - Pharmacokinetic studies with another statin having a similar principal route of elimination to that of simvastatin have suggested that for a given dose level higher systemic exposure may be achieved in patients with severe renal impairment (as measured by creatinine clearance).
Drug Interactions [See also Drug Interactions (7).]
- No clinically significant pharmacokinetic interaction was seen when ezetimibe was coadministered with simvastatin. No specific pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have been conducted other than the following study with NIASPAN (Niacin extended-release tablets).
- Niacin: The effect of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/20 mg daily for 7 days) on the pharmacokinetics of NIASPAN extended-release tablets (1000 mg for 2 days and 2000 mg for 5 days following a low-fat breakfast) was studied in healthy subjects. The mean Cmax and AUC of niacin increased 9% and 22%, respectively. The mean Cmax and AUC of nicotinuric acid increased 10% and 19%, respectively (N=13). In the same study, the effect of NIASPAN on the pharmacokinetics of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets was evaluated (N=15). While concomitant NIASPAN decreased the mean Cmax of total ezetimibe (1%), and simvastatin (2%), it increased the mean Cmax of simvastatin acid (18%). In addition, concomitant NIASPAN increased the mean AUC of total ezetimibe (26%), simvastatin (20%), and simvastatin acid (35%).
- Cases of myopathy/rhabdomyolysis have been observed with simvastatin coadministered with lipid-modifying doses (≥1 g/day niacin) of niacin-containing products [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1) and Drug Interactions (7.4)].
- Cytochrome P450: Ezetimibe had no significant effect on a series of probe drugs (caffeine, dextromethorphan, tolbutamide, and IV midazolam) known to be metabolized by cytochrome P450 (1A2, 2D6, 2C8/9 and 3A4) in a "cocktail" study of twelve healthy adult males. This indicates that ezetimibe is neither an inhibitor nor an inducer of these cytochrome P450 isozymes, and it is unlikely that ezetimibe will affect the metabolism of drugs that are metabolized by these enzymes.
- In a study of 12 healthy volunteers, simvastatin at the 80-mg dose had no effect on the metabolism of the probe cytochrome P450 isoform 3A4 (CYP3A4) substrates midazolam and erythromycin. This indicates that simvastatin is not an inhibitor of CYP3A4 and, therefore, is not expected to affect the plasma levels of other drugs metabolized by CYP3A4.
- Simvastatin acid is a substrate of the transport protein OATP1B1. Concomitant administration of medicinal products that are inhibitors of the transport protein OATP1B1 may lead to increased plasma concentrations of simvastatin acid and an increased risk of myopathy. For example, cyclosporine has been shown to increase the AUC of statins; although the mechanism is not fully understood, the increase in AUC for simvastatin acid is presumably due, in part, to inhibition of CYP3A4 and/or OATP1B1.
-
Simvastatin is a substrate for CYP3A4. Inhibitors of CYP3A4 can raise the plasma levels of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitory activity and increase the risk of myopathy [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1); Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Ezetimibe
Table 4: Effect of Coadministered Drugs on Total Ezetimibe
Coadministered Drug and Dosing Regimen
Total Ezetimibe*
Change in AUC
Change in Cmax
Cyclosporine-stable dose required (75 to 150 mg BID)†,‡
↑240%
↑290%
Fenofibrate, 200 mg QD, 14 days‡
↑48%
↑64%
Gemfibrozil, 600 mg BID, 7 days‡
↑64%
↑91%
Cholestyramine, 4 g BID, 14 days‡
↓55%
↓4%
Aluminum & magnesium hydroxide combination antacid, single dose§
↓4%
↓30%
Cimetidine, 400 mg BID, 7 days
↑6%
↑22%
Glipizide, 10 mg, single dose
↑4%
↓8%
Statins
- Lovastatin 20 mg QD, 7 days
↑9%
↑3%
- Pravastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days
↑7%
↑23%
- Atorvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days
↓2%
↑12%
- Rosuvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days
↑13%
↑18%
- Fluvastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days
↓19%
↑7%
- * Based on 10 mg-dose of ezetimibe.
- † Post-renal transplant patients with mild impaired or normal renal function. In a different study, a renal transplant patient with severe renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance of 13.2 mL/min/1.73 m2) who was receiving multiple medications, including cyclosporine, demonstrated a 12-fold greater exposure to total ezetimibe compared to healthy subjects.
- ‡ See 7. Drug Interactions.
- § Supralox, 20 mL.
Table 5: Effect of Ezetimibe Coadministration on Systemic Exposure to Other Drugs Coadministered Drug and its Dosage Regimen Ezetimibe Dosage Regimen Change in AUC
of Coadministered DrugChange in Cmax of Coadministered Drug Warfarin, 25 mg single dose on Day 7
10 mg QD, 11 days
↓2% (R-warfarin)
↓4% (S-warfarin)
↑3% (R-warfarin)
↑1% (S-warfarin)
Digoxin, 0.5 mg single dose
10 mg QD, 8 days
↑2%
↓7%
Gemfibrozil, 600 mg BID, 7 days*
10 mg QD, 7 days
↓1%
↓11%
Ethinyl estradiol & Levonorgestrel, QD, 21 days
10 mg QD, Days 8 to 14 of 21 day oral contraceptive cycle
Ethinyl estradiol
0%
Levonorgestrel
0%
Ethinyl estradiol
↓9%
Levonorgestrel
↓5%
Glipizide, 10 mg on Days 1 and 9
10 mg QD, Days 2 to 9
↓3%
↓5%
Fenofibrate, 200 mg QD, 14 days*
10 mg QD, 14 days
↑11%
↑7%
Cyclosporine, 100 mg single dose Day 7*
20 mg QD, 8 days
↑15%
↑10%
Statins
- Lovastatin 20 mg QD, 7 days
10 mg QD, 7 days
↑19%
↑3%
- Pravastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days
10 mg QD, 14 days
↓20%
↓24%
- Atorvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days
10 mg QD, 14 days
↓4%
↑7%
- Rosuvastatin 10 mg QD, 14 days
10 mg QD, 14 days
↑19%
↑17%
- Fluvastatin 20 mg QD, 14 days
10 mg QD, 14 days
↓39%
↓27%
* See 7. Drug Interactions.
Simvastatin
Table 6: Effect of Coadministered Drugs or Grapefruit Juice on Simvastatin Systemic Exposure Coadministered Drug or Grapefruit Juice Dosing of Coadministered Drug or Grapefruit Juice Dosing of Simvastatin Geometric Mean Ratio
(Ratio* with / without
coadministered drug)
No Effect = 1AUC Cmax Contraindicated with Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Telithromycin†
200 mg QD for 4 days
80 mg
simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin
12
8.9
15
5.3
Nelfinavir†
1250 mg BID for 14 days
20 mg QD for 28 days
simvastatin acid‡
simvastatin
6
6.2Itraconazole†
200 mg QD for 4 days
80 mg
simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin
13.1
13.1
Posaconazole
100 mg (oral suspension) QD for 13 days
200 mg (oral suspension) QD for 13 days40 mg
40 mgsimvastatin acid‡ simvastatin
simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin7.3
10.3
8.5
10.6
9.2
9.4
9.5
11.4
Gemfibrozil
600 mg BID for 3 days
40 mg
simvastatin acid‡ simvastatin
2.85
1.35
2.18
0.91
Avoid grapefruit juice with Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Grapefruit Juice§ (high dose)
200 mL of double-strength TID¶
60 mg single dose
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
7
16
Grapefruit Juice§ (low dose)
8 oz (about 237 mL) of single-strength#
20 mg single dose
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
1.3
1.9
Avoid taking with >10/10 mg Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets, based on clinical and/or postmarketing simvastatin experience [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Verapamil SR
240 mg QD Days 1 to 7 then 240 mg BID on Days 8 to 10
80 mg on Day 10
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
2.3
2.5
2.4
2.1
Diltiazem
120 mg BID for 10 days
80 mg on Day 10
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
2.69
3.10
2.69
2.88
Diltiazem
120 mg BID for 14 days
20 mg on Day 14
simvastatin
4.6
3.6
Dronedarone
400 mg BID for 14 days
40 mg QD for 14 days
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
1.96
3.90
2.14
3.75
Avoid taking with >10/20 mg Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets, based on clinical and/or postmarketing simvastatin experience [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Amiodarone
400 mg QD for 3 days
40 mg on Day 3
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
1.75
1.76
1.72
1.79
Amlodipine
10 mg QD for 10 days
80 mg on Day 10
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
1.58
1.77
1.56
1.47
Ranolazine SR
1000 mg BID for 7 days
80 mg on Day 1 and Days 6 to 9
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
2.26
1.86
2.28
1.75
Avoid taking with >10/20 mg Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets (or 10/40 mg for patients who have previously taken 80 mg simvastatin chronically, e.g., for 12 months or more, without evidence of muscle toxicity), based on clinical experience
Lomitapide
60 mg QD for 7 days
40 mg single dose
simvastatin acid
1.7
1.6
simvastatin
2
2
Lomitapide
10 mg QD for 7 days
20 mg single dose
simvastatin acid
1.4
1.4
simvastatin
1.6
1.7
No dosing adjustments required for the following:
Fenofibrate
160 mg QD for 14 days
80 mg QD on Days 8 to 14
simvastatin acid
simvastatin
0.64
0.89
0.89
0.83
Propranolol
80 mg single dose
80 mg single dose
total inhibitor
active inhibitor0.79
0.79↓ from 33.6 to 21.1 ng∙eq/mL
↓ from 7 to 4.7 ng∙eq/mL-
* Results based on a chemical assay except results with propranolol as indicated.
† Results could be representative of the following CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and nefazodone.
‡ Simvastatin acid refers to the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin.
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
† Results could be representative of the following CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and nefazodone.
‡ Simvastatin acid refers to the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin.
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
† Results could be representative of the following CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and nefazodone.
-
† Results could be representative of the following CYP3A4 inhibitors: ketoconazole, erythromycin, clarithromycin, HIV protease inhibitors, and nefazodone.
‡ Simvastatin acid refers to the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin.
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
‡ Simvastatin acid refers to the β-hydroxyacid of simvastatin.
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
- # Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
-
§ The effect of amounts of grapefruit juice between those used in these two studies on simvastatin pharmacokinetics has not been studied.
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
¶ Double-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with one can of water. Grapefruit juice was administered TID for 2 days, and 200 mL together with single dose simvastatin and 30 and 90 minutes following single dose simvastatin on Day 3.
# Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
- # Single-strength: one can of frozen concentrate diluted with 3 cans of water. Grapefruit juice was administered with breakfast for 3 days, and simvastatin was administered in the evening on Day 3.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
- No animal carcinogenicity or fertility studies have been conducted with the combination of ezetimibe and simvastatin. The combination of ezetimibe with simvastatin did not show evidence of mutagenicity in vitro in a microbial mutagenicity (Ames) test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli with or without metabolic activation. No evidence of clastogenicity was observed in vitro in a chromosomal aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes with ezetimibe and simvastatin with or without metabolic activation. There was no evidence of genotoxicity at doses up to 600 mg/kg with the combination of ezetimibe and simvastatin (1:1) in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
- Ezetimibe
- A 104-week dietary carcinogenicity study with ezetimibe was conducted in rats at doses up to 1500 mg/kg/day (males) and 500 mg/kg/day (females) (~20 times the human exposure at 10 mg daily based on AUC0-24hr for total ezetimibe). A 104-week dietary carcinogenicity study with ezetimibe was also conducted in mice at doses up to 500 mg/kg/day (>150 times the human exposure at 10 mg daily based on AUC0-24hr for total ezetimibe). There were no statistically significant increases in tumor incidences in drug-treated rats or mice.
- No evidence of mutagenicity was observed in vitro in a microbial mutagenicity (Ames) test with Salmonella typhimurium and Escherichia coli with or without metabolic activation. No evidence of clastogenicity was observed in vitro in a chromosomal aberration assay in human peripheral blood lymphocytes with or without metabolic activation. In addition, there was no evidence of genotoxicity in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test.
- In oral (gavage) fertility studies of ezetimibe conducted in rats, there was no evidence of reproductive toxicity at doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day in male or female rats (~7 times the human exposure at 10 mg daily based on AUC0-24hr for total ezetimibe).
- Simvastatin
- In a 72-week carcinogenicity study, mice were administered daily doses of simvastatin of 25, 100, and 400 mg/kg body weight, which resulted in mean plasma drug levels approximately 1, 4, and 8 times higher than the mean human plasma drug level, respectively, (as total inhibitory activity based on AUC) after an 80-mg oral dose. Liver carcinomas were significantly increased in high-dose females and mid- and high-dose males with a maximum incidence of 90% in males. The incidence of adenomas of the liver was significantly increased in mid- and high-dose females. Drug treatment also significantly increased the incidence of lung adenomas in mid- and high-dose males and females. Adenomas of the Harderian gland (a gland of the eye of rodents) were significantly higher in high-dose mice than in controls. No evidence of a tumorigenic effect was observed at 25 mg/kg/day.
- In a separate 92-week carcinogenicity study in mice at doses up to 25 mg/kg/day, no evidence of a tumorigenic effect was observed (mean plasma drug levels were 1 times higher than humans given 80 mg simvastatin as measured by AUC).
- In a two-year study in rats at 25 mg/kg/day, there was a statistically significant increase in the incidence of thyroid follicular adenomas in female rats exposed to approximately 11 times higher levels of simvastatin than in humans given 80 mg simvastatin (as measured by AUC).
- A second two-year rat carcinogenicity study with doses of 50 and 100 mg/kg/day produced hepatocellular adenomas and carcinomas (in female rats at both doses and in males at 100 mg/kg/day). Thyroid follicular cell adenomas were increased in males and females at both doses; thyroid follicular cell carcinomas were increased in females at 100 mg/kg/day. The increased incidence of thyroid neoplasms appears to be consistent with findings from other statins. These treatment levels represented plasma drug levels (AUC) of approximately 7 and 15 times (males) and 22 and 25 times (females) the mean human plasma drug exposure after an 80-mg daily dose.
- No evidence of mutagenicity was observed in a microbial mutagenicity (Ames) test with or without rat or mouse liver metabolic activation. In addition, no evidence of damage to genetic material was noted in an in vitro alkaline elution assay using rat hepatocytes, a V-79 mammalian cell forward mutation study, an in vitro chromosome aberration study in CHO cells, or an in vivo chromosomal aberration assay in mouse bone marrow.
- There was decreased fertility in male rats treated with simvastatin for 34 weeks at 25 mg/kg body weight (4 times the maximum human exposure level, based on AUC, in patients receiving 80 mg/day); however, this effect was not observed during a subsequent fertility study in which simvastatin was administered at this same dose level to male rats for 11 weeks (the entire cycle of spermatogenesis including epididymal maturation). No microscopic changes were observed in the testes of rats from either study. At 180 mg/kg/day (which produces exposure levels 22 times higher than those in humans taking 80 mg/day based on surface area, mg/m2), seminiferous tubule degeneration (necrosis and loss of spermatogenic epithelium) was observed. In dogs, there was drug-related testicular atrophy, decreased spermatogenesis, spermatocytic degeneration and giant cell formation at 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 2 times the human exposure, based on AUC, at 80 mg/day). The clinical significance of these findings is unclear.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
CNS Toxicity
- Optic nerve degeneration was seen in clinically normal dogs treated with simvastatin for 14 weeks at 180 mg/kg/day, a dose that produced mean plasma drug levels about 12 times higher than the mean plasma drug level in humans taking 80 mg/day.
- A chemically similar drug in this class also produced optic nerve degeneration (Wallerian degeneration of retinogeniculate fibers) in clinically normal dogs in a dose-dependent fashion starting at 60 mg/kg/day, a dose that produced mean plasma drug levels about 30 times higher than the mean plasma drug level in humans taking the highest recommended dose (as measured by total enzyme inhibitory activity). This same drug also produced vestibulocochlear Wallerian-like degeneration and retinal ganglion cell chromatolysis in dogs treated for 14 weeks at 180 mg/kg/day, a dose that resulted in a mean plasma drug level similar to that seen with the 60 mg/kg/day dose.
- CNS vascular lesions, characterized by perivascular hemorrhage and edema, mononuclear cell infiltration of perivascular spaces, perivascular fibrin deposits and necrosis of small vessels, were seen in dogs treated with simvastatin at a dose of 360 mg/kg/day, a dose that produced mean plasma drug levels that were about 14 times higher than the mean plasma drug levels in humans taking 80 mg/day. Similar CNS vascular lesions have been observed with several other drugs of this class.
- There were cataracts in female rats after two years of treatment with 50 and 100 mg/kg/day (22 and 25 times the human AUC at 80 mg/day, respectively) and in dogs after three months at 90 mg/kg/day (19 times) and at two years at 50 mg/kg/day (5 times).
- Ezetimibe
- The hypocholesterolemic effect of ezetimibe was evaluated in cholesterol-fed Rhesus monkeys, dogs, rats, and mouse models of human cholesterol metabolism. Ezetimibe was found to have an ED50 value of 0.5 mcg/kg/day for inhibiting the rise in plasma cholesterol levels in monkeys. The ED50 values in dogs, rats, and mice were 7, 30, and 700 mcg/kg/day, respectively. These results are consistent with ezetimibe being a potent cholesterol absorption inhibitor.
- In a rat model, where the glucuronide metabolite of ezetimibe (ezetimibe-glucuronide) was administered intraduodenally, the metabolite was as potent as ezetimibe in inhibiting the absorption of cholesterol, suggesting that the glucuronide metabolite had activity similar to the parent drug.
- In 1-month studies in dogs given ezetimibe (0.03 to 300 mg/kg/day), the concentration of cholesterol in gallbladder bile increased ~2- to 4-fold. However, a dose of 300 mg/kg/day administered to dogs for one year did not result in gallstone formation or any other adverse hepatobiliary effects. In a 14-day study in mice given ezetimibe (0.3 to 5 mg/kg/day) and fed a low-fat or cholesterol-rich diet, the concentration of cholesterol in gallbladder bile was either unaffected or reduced to normal levels, respectively.
- A series of acute preclinical studies was performed to determine the selectivity of ezetimibe for inhibiting cholesterol absorption. Ezetimibe inhibited the absorption of 14C-cholesterol with no effect on the absorption of triglycerides, fatty acids, bile acids, progesterone, ethinyl estradiol, or the fat-soluble vitamins A and D.
- In 4- to 12-week toxicity studies in mice, ezetimibe did not induce cytochrome P450 drug-metabolizing enzymes. In toxicity studies, a pharmacokinetic interaction of ezetimibe with statins (parents or their active hydroxy acid metabolites) was seen in rats, dogs, and rabbits.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Primary Hyperlipidemia
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets reduces total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C, and increases HDL-C in patients with hyperlipidemia. Maximal to near maximal response is generally achieved within 2 weeks and maintained during chronic therapy.
- Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are effective in men and women with hyperlipidemia. Experience in non-Caucasians is limited and does not permit a precise estimate of the magnitude of the effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
- Five multicenter, double-blind studies conducted with either ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets in patients with primary hyperlipidemia are reported: two were comparisons with simvastatin, two were comparisons with atorvastatin, and one was a comparison with rosuvastatin.
- In a multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12-week trial, 1528 hyperlipidemic patients were randomized to one of ten treatment groups: placebo, ezetimibe (10 mg), simvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg), or ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/10, 10/20, 10/40, or 10/80).
- When patients receiving ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets were compared to those receiving all doses of simvastatin, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets significantly lowered total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C. The effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on HDL-C were similar to the effects seen with simvastatin. Further analysis showed ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets significantly increased HDL-C compared with placebo. (See Table 7.) The lipid response to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets was similar in patients with TG levels greater than or less than 200 mg/dL.
Table 7: Response to Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets in Patients with Primary Hyperlipidemia (Mean* % Change from Untreated Baseline†)
Treatment
(Daily Dose)N Total-C LDL-C Apo B HDL-C TG* Non-HDL-C Pooled data (All Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets doses)‡
609
-38
-53
-42
+7
-24
-49
Pooled data (All simvastatin doses)‡
622
-28
-39
-32
+7
-21
-36
Ezetimibe 10 mg
149
-13
-19
-15
+5
-11
-18
Placebo
148
-1
-2
0
0
-2
-2
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets by dose
10/10
152
-31
-45
-35
+8
-23
-41
10/20
156
-36
-52
-41
+10
-24
-47
10/40
147
-39
-55
-44
+6
-23
-51
10/80
154
-43
-60
-49
+6
-31
-56
Simvastatin by dose
10 mg
158
-23
-33
-26
+5
-17
-30
20 mg
150
-24
-34
-28
+7
-18
-32
40 mg
156
-29
-41
-33
+8
-21
-38
80 mg
158
-35
-49
-39
+7
-27
-45
* For triglycerides, median % change from baseline.
† Baseline - on no lipid-lowering drug.
‡ Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets doses pooled (10/10 to 10/80) significantly reduced total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, and non-HDL-C compared to simvastatin and significantly increased HDL-C compared to placebo.
In a multicenter, double-blind, controlled, 23-week study, 710 patients with known CHD or CHD risk equivalents, as defined by the NCEP ATP III guidelines, and an LDL-C ≥130 mg/dL were randomized to one of four treatment groups: coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/10, 10/20, and 10/40) or simvastatin 20 mg. Patients not reaching an LDL-C <100 mg/dL had their simvastatin dose titrated at 6-week intervals to a maximal dose of 80 mg.
At Week 5, the LDL-C reductions with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/10, 10/20, or 10/40 were significantly larger
than with simvastatin 20 mg (see Table 8).
Table 8: Response to Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets after 5 Weeks in Patients with CHD or CHD Risk Equivalents and an LDL-C ≥130 mg/dL Simvastatin
20 mgEzetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
10/10Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
10/20Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
10/40N
253
251
109
97
Mean baseline
LDL-C
174
165
167
171
Percent
change LDL-C
-38
-47
-53
-59
- In a multicenter, double-blind, 6-week study, 1902 patients with primary hyperlipidemia, who had not met their NCEP ATP III target LDL-C goal, were randomized to one of eight treatment groups: ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/10, 10/20, 10/40, or 10/80) or atorvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, 40 mg, or 80 mg).
- Across the dosage range, when patients receiving ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets were compared to those receiving milligram-equivalent statin doses of atorvastatin, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets lowered total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, and non-HDL-C significantly more than atorvastatin. Only the 10/40 mg and 10/80 mg ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets doses increased HDL-C significantly more than the corresponding milligram-equivalent statin dose of atorvastatin. The effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on TG were similar to the effects seen with atorvastatin (see Table 9).
Table 9: Response to Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets and Atorvastatin in Patients with Primary Hyperlipidemia (Mean* % Change from Untreated Baseline†)
Treatment
(Daily Dose)N Total-C‡ LDL-C‡ Apo B‡ HDL-C TG* Non-HDL-C‡ Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets by dose
10/10
230
-34§
-47§
-37§
+8
-26
-43§
10/20
233
-37§
-51§
-40§
+7
-25
-46§
10/40
236
-41§
-57§
-46§
+9§
-27
-52§
10/80
224
-43§
-59§
-48§
+8§
-31
-54§
Atorvastatin by dose
10 mg
235
-27
-36
-31
+7
-21
-34
20 mg
230
-32
-44
-37
+5
-25
-41
40 mg
232
-36
-48
-40
+4
-24
-45
80 mg
230
-40
-53
-44
+1
-32
-50
* For triglycerides, median % change from baseline.
† Baseline - on no lipid-lowering drug.
‡ Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets doses pooled (10/10 to 10/80) provided significantly greater reductions in total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, and non-HDL-C compared to atorvastatin doses pooled (10 to 80).
§ p<0.05 for difference with atorvastatin at equal mg doses of the simvastatin component.
In a multicenter, double-blind, 24-week, forced-titration study, 788 patients with primary hyperlipidemia, who had not met their NCEP ATP III target LDL-C goal, were randomized to receive coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/10 and 10/20) or atorvastatin 10 mg. For all three treatment groups, the dose of the statin was titrated at 6-week intervals to 80 mg. At each pre-specified dose comparison, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets lowered LDL-C to a greater degree than atorvastatin (see Table 10).
Table 10: Response to Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets and Atorvastatin in Patients with Primary Hyperlipidemia (Mean* % Change from Untreated Baseline†)
Treatment N Total-C LDL-C Apo B HDL-C TG* Non-HDL-C Week 6
Atorvastatin 10 mg‡
262
-28
-37
-32
+5
-23
-35
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/10§
263
-34¶
-46¶
-38¶
+8¶
-26
-43¶
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/20#
263
-36¶
-50¶
-41¶
+10¶
-25
-46¶
Week 12
Atorvastatin 20 mg
246
-33
-44
-38
+7
-28
-42
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/20
250
-37¶
-50¶
-41¶
+9
-28
-46¶
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/40
252
-39¶
-54¶
-45¶
+12¶
-31
-50¶
Week 18
Atorvastatin 40 mg
237
-37
-49
-42
+8
-31
-47
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/40Þ
482
-40¶
-56¶
-45¶
+11¶
-32
-52¶
Week 24
Atorvastatin 80 mg
228
-40
-53
-45
+6
-35
-50
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10/80Þ
459
-43¶
-59¶
-49¶
+12¶
-35
-55¶
* For triglycerides, median % change from baseline.
† Baseline -on no lipid-lowering drug.
‡ Atorvastatin: 10 mg start dose titrated to 20 mg, 40 mg, and 80 mg through Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24.
§ Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets: 10/10 start dose titrated to 10/20, 10/40, and 10/80 through Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24.
¶ p≤0.05 for difference with atorvastatin in the specified week.
# Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets: 10/20 start dose titrated to 10/40, 10/40, and 10/80 through Weeks 6, 12, 18, and 24.
Ϸ Data pooled for common doses of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets at Weeks 18 and 24.
In a multicenter, double-blind, 6-week study, 2959 patients with primary hyperlipidemia, who had not met their NCEP ATP III target LDL-C goal, were randomized to one of six treatment groups: Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/20, 10/40, or 10/80) or rosuvastatin (10 mg, 20 mg, or 40 mg).
The effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and rosuvastatin on total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, TG, non-HDL-C and HDL-C are shown in Table 11.
Table 11: Response to Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets and Rosuvastatin in Patients with Primary Hyperlipidemia (Mean* % Change from Untreated Baseline†)
Treatment (Daily Dose) N Total-C‡ LDL-C‡ Apo B‡ HDL-C TG* Non-HDL-C‡ Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets by dose
10/20
476
-37§
-52§
-42§
+7
-23§
-47§
10/40
477
-39¶
-55¶
-44¶
+8
-27
-50¶
10/80
474
-44#
-61#
-50#
+8
-30#
-56#
Rosuvastatin by dose
10 mg
475
-32
-46
-37
+7
-20
-42
20 mg
478
-37
-52
-43
+8
-26
-48
40 mg
475
-41
-57
-47
+8
-28
-52
* For triglycerides, median % change from baseline.
† Baseline - on no lipid-lowering drug.
‡ Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets doses pooled (10/20 to 10/80) provided significantly greater reductions in total-C, LDL-C, Apo B, and non-HDL-C compared to rosuvastatin doses pooled (10 to 40 mg).
§ p<0.05 vs. rosuvastatin 10 mg.
¶ p<0.05 vs. rosuvastatin 20 mg.
# p<0.05 vs. rosuvastatin 40 mg.
In a multicenter, double-blind, 24-week trial, 214 patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus treated with thiazolidinediones (rosiglitazone or pioglitazone) for a minimum of 3 months and simvastatin 20 mg for a minimum of 6 weeks were randomized to receive either simvastatin 40 mg or the coadministered active ingredients equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20. The median LDL-C and HbA1c levels at baseline were 89 mg/dL and 7.1%, respectively.
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 was significantly more effective than doubling the dose of simvastatin to 40 mg. The median percent changes from baseline for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets vs. simvastatin were: LDL-C
-25% and -5%; total-C -16% and -5%; Apo B -19% and -5%; and non-HDL-C -23% and -5%. Results for HDL-C and TG between the two treatment groups were not significantly different.
Ezetimibe
In two multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, 12-week studies in 1719 patients with primary hyperlipidemia, ezetimibe significantly lowered total-C (-13%), LDL-C (-19%), Apo B (-14%), and TG (-8%), and increased HDL-C (+3%) compared to placebo. Reduction in LDL-C was consistent across age, sex, and baseline LDL-C.
Simvastatin
In two large, placebo-controlled clinical trials, the Scandinavian Simvastatin Survival Study (N=4,444 patients) and the Heart Protection Study (N=20,536 patients), the effects of treatment with simvastatin were assessed in patients at high risk of coronary events because of existing coronary heart disease, diabetes, peripheral vessel disease, history of stroke or other cerebrovascular disease. Simvastatin was proven to reduce: the risk of total mortality by reducing CHD deaths; the risk of non-fatal myocardial infarction and stroke; and the need for coronary and non-coronary revascularization procedures.
No incremental benefit of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on cardiovascular morbidity and mortality over and above that demonstrated for simvastatin has been established.
14.2 Homozygous Familial Hypercholesterolemia (HoFH)
- A double-blind, randomized, 12-week study was performed in patients with a clinical and/or genotypic diagnosis of HoFH. Data were analyzed from a subgroup of patients (n=14) receiving simvastatin 40 mg at baseline. Increasing the dose of simvastatin from 40 to 80 mg (n=5) produced a reduction of LDL-C of 13% from baseline on simvastatin 40 mg. Coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/40 and 10/80 pooled, n=9), produced a reduction of LDL-C of 23% from baseline on simvastatin 40 mg. In those patients coadministered ezetimibe and simvastatin equivalent to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets (10/80, n=5), a reduction of LDL-C of 29% from baseline on simvastatin 40 mg was produced.
14.3 Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
The Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP) was a multinational, randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind trial that investigated the effect of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on the time to a first major vascular event (MVE) among 9438 patients with moderate to severe chronic kidney disease (approximately one-third on dialysis at baseline) who did not have a history of myocardial infarction or coronary revascularization. An MVE was defined as nonfatal MI, cardiac death, stroke, or any revascularization procedure. Patients were allocated to treatment using a method that took into account the distribution of 8 important baseline characteristics of patients already enrolled and minimized the imbalance of those characteristics across the groups.
For the first year, 9438 patients were allocated 4:4:1, to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20, placebo, or simvastatin 20 mg daily, respectively. The 1-year simvastatin arm enabled the comparison of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets to simvastatin with regard to safety and effect on lipid levels. At 1 year the simvastatin-only arm was re-allocated 1:1 to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 or placebo. A total of 9270 patients were ever allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 (n=4650) or placebo (n=4620) during the trial. The median follow-up duration was 4.9 years. Patients had a mean age of 61 years; 63% were male, 72% were Caucasian, and 23% were diabetic; and, for those not on dialysis at baseline, the median serum creatinine was 2.5 mg/dL and the median estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was 25.6 mL/min/1.73 m2, with 94% of patients having an eGFR < 45 mL/min/1.73 m2. Eligibility did not depend on lipid levels. Mean LDL-C at baseline was 108 mg/dL. At 1 year, the mean LDL-C was 26% lower in the simvastatin arm and 38% lower in the ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets arm relative to placebo. At the midpoint of the study (2.5 years), the mean LDL-C was 32% lower for ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets relative to placebo. Patients no longer taking study medication were included in all lipid measurements.
In the primary intent-to-treat analysis, 639 (15.2%) of 4193 patients initially allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 749 (17.9%) of 4191 patients initially allocated to placebo experienced an MVE. This corresponded to a relative risk reduction of 16% (p=0.001) (see Figure 1). Similarly, 526 (11.3%) of 4650 patients ever allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and 619 (13.4%) of 4620 patients ever allocated to placebo experienced a major atherosclerotic event (MAE; a subset of the MVE composite that excluded non-coronary cardiac deaths and hemorrhagic stroke), corresponding to a relative risk reduction of 17% (p=0.002). The trial demonstrated that treatment with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/20 mg versus placebo reduced the risk for MVE and MAE in this CKD population. The study design precluded drawing conclusions regarding the independent contribution of either ezetimibe or simvastatin to the observed effect.
The treatment effect of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets on MVE was attenuated among patients on dialysis at baseline compared with those not on dialysis at baseline. Among 3023 patients on dialysis at baseline, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets reduced the risk of MVE by 6% (RR 0.94: 95% CI 0.80 to 1.09) compared with 22% (RR 0.78: 95% CI 0.69 to 0.89) among 6247 patients not on dialysis at baseline (interaction P=0.08).
Figure 1: Effect of Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets on the Primary Endpoint of Risk of Major Vascular Events
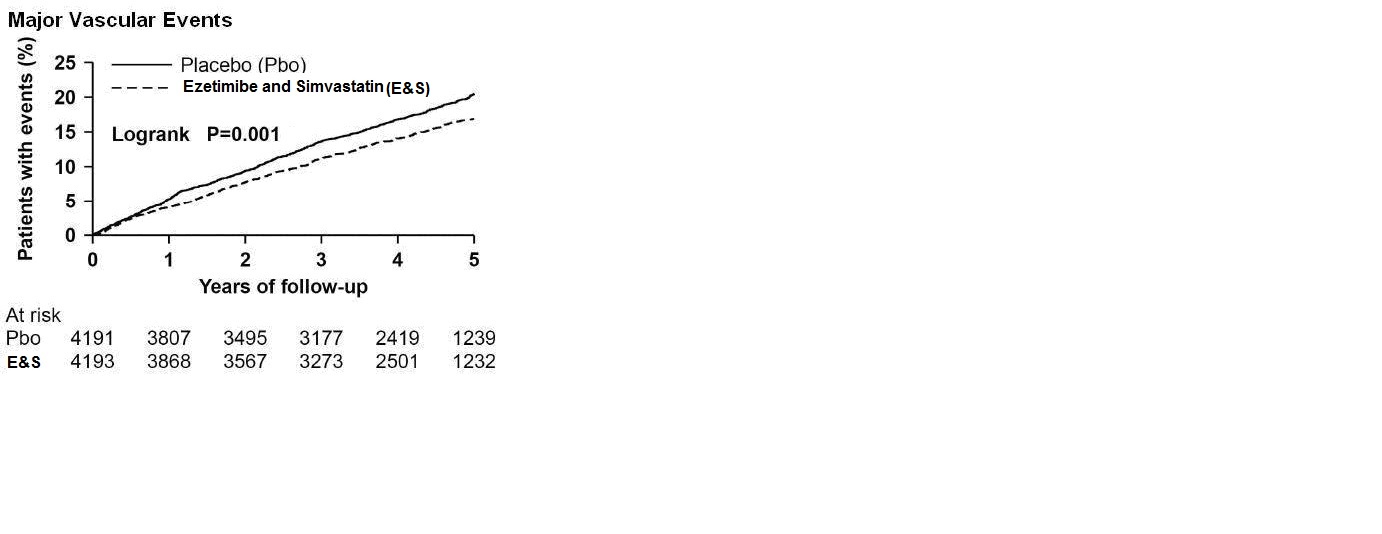
The individual components of MVE in all patients ever allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or placebo are presented in Table 12.
Table 12: Number of First Events for Each Component of the Major Vascular Event Composite Endpoint in SHARP*
Outcome
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets
10/20 (N=4650)
Placebo (N=4620)
Risk Ratio (95% CI)
P-value
Major Vascular Events
701 (15.1%)
814 (17.6%)
0.85 (0.77 to 0.94)
0.001
Nonfatal MI
134 (2.9%)
159 (3.4%)
0.84 (0.66 to 1.05)
0.12
Cardiac Death
253 (5.4%)
272 (5.9%)
0.93 (0.78 to 1.10)
0.38
Any Stroke
171 (3.7%)
210 (4.5%)
0.81 (0.66 to 0.99)
0.038
- Non-hemorrhagic Stroke
131 (2.8%)
174 (3.8%)
0.75 (0.60 to 0.94)
0.011
- Hemorrhagic Stroke
45 (1%)
37 (0.8%)
1.21 (0.78 to 1.86)
0.4
Any Revascularization
284 (6.1%)
352 (7.6%)
0.79 (0.68 to 0.93)
0.004
*Intention-to-treat analysis on all SHARP patients ever allocated to ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or placebo.
Among patients not on dialysis at baseline, ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets did not reduce the risk of progressing to end-stage renal disease compared with placebo (RR 0.97: 95% CI 0.89 to 1.05).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/10 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘321’ on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
- Bottles of 30 NDC: 16714-778-01
- Bottles of 90 NDC: 16714-778-02
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/20 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘322’ on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
- Bottles of 30 NDC: 16714-779-01
- Bottles of 90 NDC: 16714-779-02
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/40 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘323’ on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
- Bottles of 30 NDC: 16714-780-01
- Bottles of 90 NDC: 16714-780-02
- Ezetimibe and Simvastatin Tablets 10 mg/80 mg are white to off-white, capsule shaped, uncoated tablets debossed with ‘G’ on one side and ‘324’ on the other side. They are supplied as follows:
- Bottles of 30 NDC: 16714-781-01
- Bottles of 90 NDC: 16714-781-02
Storage
- Store at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
- Patients should be advised to adhere to their National Cholesterol Education Program (NCEP)-recommended diet, a regular exercise program, and periodic testing of a fasting lipid panel.
- Patients should be advised about substances they should not take concomitantly with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Patients should also be advised to inform other healthcare professionals prescribing a new medication or increasing the dose of an existing medication that they are taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
17.1 Muscle Pain
- All patients starting therapy with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be advised of the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, and told to report promptly any unexplained muscle pain, tenderness or weakness particularly if accompanied by malaise or fever or if these muscle signs or symptoms persist after discontinuing ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Patients using the 10/80-mg dose should be informed that the risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, is increased with the use of the 10/80-mg dose. The risk of myopathy, including rhabdomyolysis, occurring with use of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets is increased when taking certain types of medication or consuming grapefruit juice. Patients should discuss all medication, both prescription and over the counter, with their healthcare professional.
17.2 Liver Enzymes
- It is recommended that liver function tests be performed before the initiation of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, and thereafter when clinically indicated. All patients treated with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets should be advised to report promptly any symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice.
17.3 Pregnancy
- Women of childbearing age should be advised to use an effective method of birth control to prevent pregnancy while using ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Discuss future pregnancy plans with your patients, and discuss when to stop taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets if they are trying to conceive. Patients should be advised that if they become pregnant they should stop taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and call their healthcare professional.
17.4 Breastfeeding
- Women who are breastfeeding should be advised to not use ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Patients who have a lipid disorder and are breastfeeding should be advised to discuss the options with their healthcare professional.
*Trademarks are the properties of their respective owners.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
Ezetimibe and Simvastatin
(e zet' i mibe and sim" va stat' in)
Tablets
Read this Patient Information carefully before you start taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. If you have any questions about ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, ask your doctor. Only your doctor can determine if ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are right for you.
What are ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are a prescription medicine that contains 2 cholesterol lowering medicines, ezetimibe and simvastatin. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are used along with diet to:
- lower the level of your "bad" cholesterol (LDL)
- increase the level of your "good" cholesterol (HDL)
- lower the level of fat in your blood (triglycerides)
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are for patients who cannot control their cholesterol levels by diet and exercise alone.
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets have not been shown to reduce heart attacks or strokes more than simvastatin alone.
It is not known if ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets are safe and effective in children under 10 years of age or in girls who have not started their period (menses).
The usual dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets is 10/10 mg to 10/40 mg 1 time each day.
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80 mg increases your chance of developing muscle damage. The 10/80 mg dose should only be used by people who:
- have been taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/80 mg chronically (such as 12 months or more) without having muscle damage.
- do not need to take certain other medicines with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets that would increase your chance of getting muscle damage.
If you are unable to reach your LDL-cholesterol goal using ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 10/40 mg, your doctor should switch you to another cholesterol-lowering medicine.
Who should not take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
Do not take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets if you take:
-
Certain anti-fungal medicines including:
- o itraconazole
- o ketoconazole
- o posaconazole
- o voriconazole
- HIV protease inhibitors (indinavir, nelfinavir, ritonavir, saquinavir, tipranavir, or atazanavir)
- Certain hepatitis C virus protease inhibitors (such as boceprevir or telaprevir)
-
Certain antibiotics, including:
- o erythromycin
- o clarithromycin
- o telithromycin
- nefazodone
- medicines containing cobicistat
- A fibric acid medicine for lowering cholesterol called gemfibrozil
- cyclosporine
- danazol
Ask your doctor or pharmacist for a list of these medicines if you are not sure.
Also do not take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets if you:
- are allergic to ezetimibe or simvastatin or any of the ingredients in ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. See the end of this leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
- have liver problems.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets may harm your unborn baby. If you are a woman of childbearing age, you should use an effective method of birth control to prevent pregnancy while using ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. If you become pregnant while taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, stop taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and call your doctor.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if ezetimibe and simvastatin passes into your breast milk. You and your doctor should decide the best way to feed your baby if you take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
What should I tell my doctor before and while taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
Tell your doctor if you:
- have unexplained muscle aches or weakness
- have kidney problems
- have or have had liver problems or drink more than 2 glasses of alcohol daily
- have thyroid problems
- are 65 years of age or older
- are Chinese
Also see "What are the possible side effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?"
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
Tell your doctor who prescribes ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets if another doctor increases the dose of another medicine you are taking.
Talk to your doctor before you start taking any new medicines.
Taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with certain other medicines may affect each other causing side effects. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets may affect the way other medicines work, and other medicines may affect how ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets works.
Taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with certain substances can increase the risk of muscle problems. It is especially important to tell your doctor if you take:
- fibric acid derivatives (such as fenofibrate)
- amiodarone or dronedarone (drugs used to treat an irregular heartbeat)
- verapamil, diltiazem, amlodipine, or ranolazine (drugs used to treat high blood pressure, chest pain associated with heart disease, or other heart conditions)
- grapefruit juice (which should be avoided while taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets)
- colchicine (a medicine used to treat gout)
- lomitapide (a medicine used to treat a serious and rare genetic cholesterol condition)
- daptomycin (a drug used to treat complicated skin and bloodstream infections)
- large doses of niacin or nicotinic acid
Tell your doctor if you are taking niacin or a niacin-containing product, as this may increase your risk of muscle problems, especially if you are Chinese.
It is also important to tell your doctor if you are taking coumarin anticoagulants (drugs that prevent blood clots, such as warfarin).
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take, including any prescription and nonprescription medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
How should I take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
- Take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets exactly as your doctor tells you to take it.
- Do not change your dose or stop taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets without talking to your doctor.
- Take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets 1 time each day in the evening.
- Take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets with or without food.
- While taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, continue to follow your cholesterol-lowering diet and to exercise as your doctor told you to.
- If you miss a dose, do not take an extra dose. Just resume your usual schedule.
- Your doctor should do fasting blood tests to check your cholesterol while you take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Your doctor may change your dose of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets if needed.
- If you take too much ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, call your doctor or Poison Control Center at 1-800-222-1222 or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away.
What are the possible side effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets may cause serious side effects, including:
- Muscle pain, tenderness and weakness (myopathy). Muscle problems, including muscle breakdown, can be serious in some people and rarely cause kidney damage that can lead to death.
- Tell your doctor right away if:
- o you have unexplained muscle pain, tenderness, or weakness, especially if you have a fever or feel more tired than usual, while you take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
- o you have muscle problems that do not go away even after your doctor has advised you to stop taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Your doctor may do further tests to diagnose the cause of your muscle problems.
- Your chances of getting muscle problems are higher if you:
- o are taking certain other medicines while you take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets
- o are 65 years of age or older
- o are female
- o have thyroid problems (hypothyroidism) that are not controlled
- o have kidney problems
- o are taking higher doses of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets, particularly the 10/80 mg dose
- o are Chinese
-
Liver problems. Your doctor should do blood tests to check your liver before you start taking ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and if you have any symptoms of liver problems while you take ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. Call your doctor right away if you have the following symptoms of liver problems:
- o loss of appetite
- o upper belly pain
- o dark urine
- o yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
- o feel tired or weak
The most common side effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets include:
- headache
- increased liver enzyme levels
- muscle pain
- upper respiratory infection
- diarrhea
Additional side effects that have been reported in general use with ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets or with ezetimibe or simvastatin tablets (tablets that contain the active ingredients of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets) include:
- allergic reactions including swelling of the face, lips, tongue, and/or throat that may cause difficulty in breathing or swallowing (which may require treatment right away), rash, hives; joint pain; inflammation of the pancreas; nausea; dizziness; tingling sensation; depression; gallstones; trouble sleeping; poor memory; memory loss; confusion; erectile dysfunction; breathing problems including persistent cough and/or shortness of breath or fever.
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or does not go away.
These are not all the possible side effects of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor about medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
- Store ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets at room temperature between 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F).
- Keep ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets in its original container until you use it.
- Keep ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets in a tightly closed container, and keep ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets out of light.
Keep ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Information about the safe and effective use of ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets.
Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets work to reduce your cholesterol in two ways. It reduces the cholesterol absorbed in your digestive tract, as well as the cholesterol your body makes by itself. Ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets do not help you lose weight.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets to other people, even if they have the same condition that you have. It may harm them.
This Patient Information summarizes the most important information about ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets that is written for health professionals.
For more information, please call 1-800-206-7821.
What are the ingredients in ezetimibe and simvastatin tablets?
Active Ingredients: ezetimibe and simvastatin
- Inactive Ingredients: butylated hydroxyanisole, citric acid monohydrate, croscarmellose sodium, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, microcrystalline cellulose, propyl gallate, and sodium lauryl sulfate.
This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Manufactured for:
Northstar Rx LLC
Memphis, TN 38141.
Manufactured by:
Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Ltd.Plot No. 2, Phase-2, Pharma Zone SEZ, Pithampur,
Dist-Dhar, Madhya Pradesh 454775, India
November 2019
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/20 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/40 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg/80 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN
ezetimibe and simvastatin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16714-778 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ezetimibe (UNII: EOR26LQQ24) (ezetimibe - UNII:EOR26LQQ24) ezetimibe 10 mg simvastatin (UNII: AGG2FN16EV) (simvastatin - UNII:AGG2FN16EV) simvastatin 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxyanisole (UNII: REK4960K2U) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) propyl gallate (UNII: 8D4SNN7V92) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (capsule-shaped) Size 8mm Flavor Imprint Code G321 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16714-778-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 2 NDC: 16714-778-02 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208699 08/19/2019 EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN
ezetimibe and simvastatin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16714-779 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ezetimibe (UNII: EOR26LQQ24) (ezetimibe - UNII:EOR26LQQ24) ezetimibe 10 mg simvastatin (UNII: AGG2FN16EV) (simvastatin - UNII:AGG2FN16EV) simvastatin 20 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxyanisole (UNII: REK4960K2U) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) propyl gallate (UNII: 8D4SNN7V92) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (capsule-shaped) Size 11mm Flavor Imprint Code G322 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16714-779-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 2 NDC: 16714-779-02 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208699 08/19/2019 EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN
ezetimibe and simvastatin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16714-780 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ezetimibe (UNII: EOR26LQQ24) (ezetimibe - UNII:EOR26LQQ24) ezetimibe 10 mg simvastatin (UNII: AGG2FN16EV) (simvastatin - UNII:AGG2FN16EV) simvastatin 40 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxyanisole (UNII: REK4960K2U) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) propyl gallate (UNII: 8D4SNN7V92) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (capsule-shaped) Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code G323 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16714-780-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 2 NDC: 16714-780-02 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208699 08/19/2019 EZETIMIBE AND SIMVASTATIN
ezetimibe and simvastatin tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 16714-781 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ezetimibe (UNII: EOR26LQQ24) (ezetimibe - UNII:EOR26LQQ24) ezetimibe 10 mg simvastatin (UNII: AGG2FN16EV) (simvastatin - UNII:AGG2FN16EV) simvastatin 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength butylated hydroxyanisole (UNII: REK4960K2U) citric acid monohydrate (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) croscarmellose sodium (UNII: M28OL1HH48) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) propyl gallate (UNII: 8D4SNN7V92) MICROCRYSTALLINE CELLULOSE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) SODIUM LAURYL SULFATE (UNII: 368GB5141J) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape CAPSULE (capsule-shaped) Size 17mm Flavor Imprint Code G324 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 16714-781-01 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 2 NDC: 16714-781-02 90 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/19/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA208699 08/19/2019 Labeler - NORTHSTAR RX LLC (830546433) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Glenmark Pharmaceuticals Limited 862603186 MANUFACTURE(16714-778, 16714-779, 16714-781, 16714-781) , ANALYSIS(16714-778, 16714-779, 16714-780, 16714-781)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.