BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, AND DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE syrup
BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, AND DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, AND DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Par Pharmaceutical, Sovereign Pharmaceuticals, LLC, Vintage Pharmaceuticals, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup is a clear, sweet, unflavored, pink syrup.
Each 5 mL (1 teaspoonful) contains:
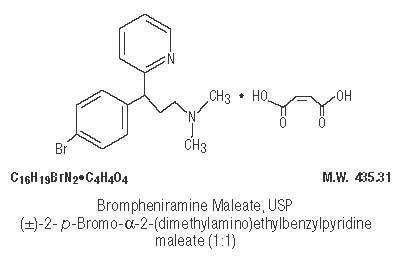
Brompheniramine Maleate, USP ................................... 2 mg
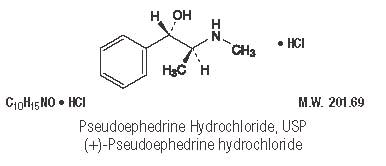
Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, USP ........................ 30 mg
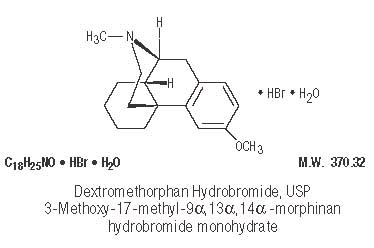
Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide, USP ..................... 10 mgInactive Ingredients: citric acid anhydrous, FD&C Red #40, glycerin, methylparaben, purified water, sodium benzoate, sodium citrate dihydrate, and sucrose.
Antihistamine/Nasal Decongestant/Antitussive syrup for oral administration.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Brompheniramine maleate is a histamine antagonist, specifically an H1-receptor-blocking agent belonging to the alkylamine class of antihistamines. Antihistamines appear to compete with histamine for receptor sites on effector cells. Brompheniramine also has anticholinergic (drying) and sedative effects. Among the antihistaminic effects, it antagonizes the allergic response (vasodilation, increased vascular permeability, increased mucus secretion) of nasal tissue. Brompheniramine is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentration after single, oral dose of 4 mg reached in 5 hours; urinary excretion is the major route of elimination, mostly as products of biodegradation; the liver is assumed to be the main site of metabolic transformation.
Pseudoephedrine acts on sympathetic nerve endings and also on smooth muscle, making it useful as a nasal decongestant. The nasal decongestant effect is mediated by the action of pseudoephedrine on α-sympathetic receptors, producing vasoconstriction of the dilated nasal arterioles. Following oral administration, effects are noted within 30 minutes with peak activity occurring at approximately one hour.
Dextromethorphan acts centrally to elevate the threshold for coughing. It has no analgesic or addictive properties. The onset of antitussive action occurs in 15 to 30 minutes after administration and is of long duration.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to any of the ingredients. Do not use in the newborn, in premature infants, in nursing mothers, or in patients with severe hypertension or severe coronary artery disease. Do not use dextromethorphan in patients receiving monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI) (see PRECAUTIONS - Drug Interactions).
Antihistamines should not be used to treat lower respiratory tract conditions including asthma.
- WARNINGS
-
PRECAUTIONS
General:
Because of its antihistamine component, brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup should be used with caution in patients with a history of bronchial asthma, narrow angle glaucoma, gastrointestinal obstruction, or urinary bladder neck obstruction. Because of its sympathomimetic component, brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup should be used with caution in patients with diabetes, hypertension, heart disease, or thyroid disease.
Information for Patients:
Patients should be warned about engaging in activities requiring mental alertness, such as driving a car or operating dangerous machinery.
Drug Interactions:
Monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOI)-Hyperpyrexia, hypotension, and death have been reported coincident with the coadministration of MAOI and products containing dextromethorphan. In addition, MAOI prolong and intensify the anticholinergic (drying) effects of antihistamines and may enhance the effect of pseudoephedrine. Concomitant administration of brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup and MAOI should be avoided (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Central nervous system (CNS) depressants-Antihistamines have additive effects with alcohol and other CNS depressants (hypnotics, sedatives, tranquilizers, antianxiety agents, etc.).
Antihypertensive drugs-Sympathomimetic may reduce the effects of antihypertensive drugs.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility:
Animal studies of brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup to assess the carcinogenic and mutagenic potential or the effect on fertility have not been performed.
Pregnancy:
Teratogenic Effects –
Pregnancy Category C: Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup. It is also not known whether brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. It should be given to a pregnant woman only if clearly needed.
Reproduction studies of brompheniramine maleate (a component of brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup) in rats and mice at doses up to 16 times the maximum human doses have revealed no evidence of impaired fertility or harm to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers:
Because of the higher risk of intolerance of antihistamines in small infants generally, and in newborns and prematures in particular, brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup is contraindicated in nursing mothers.
Pediatric Use:
Safety and effectiveness in pediatric patients below the age of 6 months have not been established (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Geriatric Use:
Clinical studies of brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. However, antihistamines are more likely to cause dizziness, sedation, and hypotension in elderly patients. The elderly are also more likely to experience adverse reactions to sympathomimetics.
In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most frequent adverse reactions to brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrup are: sedation; dryness of mouth, nose and throat; thickening of bronchial secretions; dizziness. Other adverse reactions may include:
Dermatologic: Urticaria, drug rash, photosensitivity, pruritus.
Cardiovascular System: Hypotension, hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias, palpitation.
CNS: Disturbed coordination, tremor, irritability, insomnia, visual disturbances, weakness, nervousness, convulsions, headache, euphoria, and dysphoria.
G.U. System: Urinary frequency, difficult urination.
G.I. System: Epigastric discomfort, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, constipation.
Respiratory System: Tightness of chest and wheezing, shortness of breath.
Hematologic System: Hemolytic anemia, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Signs and Symptoms: Central nervous system effects from overdosage of brompheniramine may vary from depression to stimulation, especially in children. Anticholinergic effects may be noted. Toxic doses of pseudoephedrine may result in CNS stimulation, tachycardia, hypertension, and cardiac arrhythmias; signs of CNS depression may occasionally be seen. Dextromethorphan in toxic doses will cause drowsiness, ataxia, nystagmus, opisthotonos, and convulsive seizures.
Toxic Doses: Data suggest that individuals may respond in an unexpected manner to apparently small amounts of a particular drug. A 2½-year-old child survived the ingestion of 21 mg/kg of dextromethorphan exhibiting only ataxia, drowsiness, and fever, but seizures have been reported in 2 children following the ingestion of 13-17 mg/kg. Another 2½-year-old child survived a dose of 300-900 mg of brompheniramine. The toxic dose of pseudoephedrine should be less than that of ephedrine, which is estimated to be 50 mg/kg.
Treatment: Induce emesis if patient is alert and is seen prior to 6 hours following ingestion. Precautions against aspiration must be taken, especially in infants and small children. Gastric lavage may be carried out, although in some instances tracheostomy may be necessary prior to lavage. Naloxone hydrochloride 0.005 mg/kg intravenously may be of value in reversing the CNS depression that may occur from an overdose of dextromethorphan. CNS stimulants may counter CNS depression. Should CNS hyperactivity or convulsive seizures occur, intravenous short-acting barbiturates may be indicated. Hypertensive responses and/or tachycardia should be treated appropriately. Oxygen, intravenous fluids, and other supportive measures should be employed as indicated.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Adults and pediatric patients 12 years of age and over: 10 mL (2 teaspoonfuls) every 4 hours. Children 6 to under 12 years of age: 5 mL (1 teaspoonful) every 4 hours. Children 2 to under 6 years of age: 2.5 mL (½ teaspoonful) every 4 hours. Infants 6 months to under 2 years of age: Dosage to be established by a physician.
Do not exceed 6 doses during a 24-hour period.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Brompheniramine Maleate, Pseudoephedrine Hydrochloride, and Dextromethorphan Hydrobromide Syrup is a clear, sweet, unflavored, pink syrup containing in each 5 mL (1 teaspoonful) brompheniramine maleate 2 mg, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride 30 mg and dextromethorphan hydrobromide 10 mg, available in bottles of 4 fluid ounces (118 mL), NDC: 64376-657-40, and in bottles of 16 fluid ounces (473 mL), NDC: 64376-657-16.
- STORAGE AND HANDLING
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE, PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE, AND DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE
brompheniramine maleate, pseudoephedrine hydrochloride, and dextromethorphan hydrobromide syrupProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 64376-657 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE (UNII: IXA7C9ZN03) (BROMPHENIRAMINE - UNII:H57G17P2FN) BROMPHENIRAMINE MALEATE 2 mg in 5 mL DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE (UNII: 9D2RTI9KYH) (DEXTROMETHORPHAN - UNII:7355X3ROTS) DEXTROMETHORPHAN HYDROBROMIDE 10 mg in 5 mL PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 6V9V2RYJ8N) (PSEUDOEPHEDRINE - UNII:7CUC9DDI9F) PSEUDOEPHEDRINE HYDROCHLORIDE 30 mg in 5 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) METHYLPARABEN (UNII: A2I8C7HI9T) ANHYDROUS CITRIC ACID (UNII: XF417D3PSL) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SODIUM BENZOATE (UNII: OJ245FE5EU) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) TRISODIUM CITRATE DIHYDRATE (UNII: B22547B95K) Product Characteristics Color PINK (Clear) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 64376-657-16 473 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/21/2014 08/30/2020 2 NDC: 64376-657-40 118 mL in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/21/2014 10/31/2020 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA202940 07/21/2014 10/31/2020 Labeler - Par Pharmaceutical (170266089) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Sovereign Pharmaceuticals, LLC 623168267 MANUFACTURE(64376-657) , PACK(64376-657)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
