Fluconazole by Avera McKennan Hospital FLUCONAZOLE tablet
Fluconazole by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Fluconazole by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Avera McKennan Hospital. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Fluconazole, the first of a new subclass of synthetic triazole antifungal agents, is available as tablets for oral administration and as a powder for oral suspension.
Fluconazole is designated chemically as 2,4-difluoro-α,α1-bis(1H-1,2,4-triazol-1-ylmethyl) benzyl alcohol with an empirical formula of C13H12F2N6O and molecular weight of 306.3. The structural formula is:
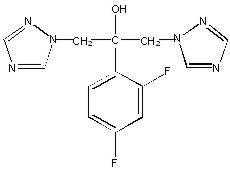
Fluconazole is a white crystalline solid which is slightly soluble in water and saline.
Fluconazole Tablets contain 50, 100, 150, or 200 mg of fluconazole and the following inactive ingredients: microcrystalline cellulose, dibasic calcium phosphate anhydrous, povidone, croscarmellose sodium, FD&C Red No. 40 aluminum lake dye, and magnesium stearate.
Fluconazole for Oral Suspension contains 350 mg or 1400 mg of fluconazole and the following inactive ingredients: sucrose, sodium citrate dihydrate, citric acid anhydrous, sodium benzoate, titanium dioxide, colloidal silicon dioxide, xanthan gum, and natural orange flavor. After reconstitution with 24 mL of distilled water or Purified Water (USP), each mL of reconstituted suspension contains 10 mg or 40 mg of fluconazole.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
The pharmacokinetic properties of fluconazole are similar following administration by the intravenous or oral routes. In normal volunteers, the bioavailability of orally administered fluconazole is over 90% compared with intravenous administration. Bioequivalence was established between the 100 mg tablet and both suspension strengths when administered as a single 200 mg dose.
Peak plasma concentrations (Cmax) in fasted normal volunteers occur between 1 and 2 hours with a terminal plasma elimination half-life of approximately 30 hours (range: 20–50 hours) after oral administration.
In fasted normal volunteers, administration of a single oral 400 mg dose of fluconazole leads to a mean Cmax of 6.72 µg/mL (range: 4.12 to 8.08 µg/mL) and after single oral doses of 50–400 mg, fluconazole plasma concentrations and AUC (area under the plasma concentration-time curve) are dose proportional.
The Cmax and AUC data from a food-effect study involving administration of fluconazole tablets to healthy volunteers under fasting conditions and with a high-fat meal indicated that exposure to the drug is not affected by food. Therefore, fluconazole may be taken without regard to meals. (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
Administration of a single oral 150 mg tablet of fluconazole to ten lactating women resulted in a mean Cmax of 2.61 µg/mL (range: 1.57 to 3.65 µg/mL).
Steady-state concentrations are reached within 5–10 days following oral doses of 50–400 mg given once daily. Administration of a loading dose (on day 1) of twice the usual daily dose results in plasma concentrations close to steady-state by the second day. The apparent volume of distribution of fluconazole approximates that of total body water. Plasma protein binding is low (11–12%). Following either single- or multiple oral doses for up to 14 days, fluconazole penetrates into all body fluids studied (see table below). In normal volunteers, saliva concentrations of fluconazole were equal to or slightly greater than plasma concentrations regardless of dose, route, or duration of dosing. In patients with bronchiectasis, sputum concentrations of fluconazole following a single 150 mg oral dose were equal to plasma concentrations at both 4 and 24 hours post dose. In patients with fungal meningitis, fluconazole concentrations in the CSF are approximately 80% of the corresponding plasma concentrations.
A single oral 150 mg dose of fluconazole administered to 27 patients penetrated into vaginal tissue, resulting in tissue:plasma ratios ranging from 0.94 to 1.14 over the first 48 hours following dosing.
A single oral 150 mg dose of fluconazole administered to 14 patients penetrated into vaginal fluid, resulting in fluid:plasma ratios ranging from 0.36 to 0.71 over the first 72 hours following dosing.
Tissue or Fluid Ratio of Fluconazole
Tissue (Fluid)/Plasma
Concentration*- * Relative to concurrent concentrations in plasma in subjects with normal renal function.
- † Independent of degree of meningeal inflammation.
Cerebrospinal fluid† 0.5–0.9 Saliva 1 Sputum 1 Blister fluid 1 Urine 10 Normal skin 10 Nails 1 Blister skin 2 Vaginal tissue 1 Vaginal fluid 0.4–0.7 In normal volunteers, fluconazole is cleared primarily by renal excretion, with approximately 80% of the administered dose appearing in the urine as unchanged drug. About 11% of the dose is excreted in the urine as metabolites.
The pharmacokinetics of fluconazole are markedly affected by reduction in renal function. There is an inverse relationship between the elimination half-life and creatinine clearance. The dose of fluconazole may need to be reduced in patients with impaired renal function. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.) A 3-hour hemodialysis session decreases plasma concentrations by approximately 50%.
In normal volunteers, fluconazole administration (doses ranging from 200 mg to 400 mg once daily for up to 14 days) was associated with small and inconsistent effects on testosterone concentrations, endogenous corticosteroid concentrations, and the ACTH-stimulated cortisol response.
Pharmacokinetics in Children
In children, the following pharmacokinetic data {Mean (%cv)} have been reported:
Age
StudiedDose
(mg/kg)Clearance
(mL/min/kg)Half-life
(Hours)Cmax
(µg/mL)Vdss
(L/kg)9 Months–
13 yearsSingle-Oral
2 mg/kg0.40 (38%)
N=1425.0 2.9 (22%)
N=16— 9 Months–
13 yearsSingle-Oral
8 mg/kg0.51 (60%)
N=1519.5 9.8 (20%)
N=15— 5–15 years Multiple IV
2 mg/kg0.49 (40%)
N=417.4 5.5 (25%)
N=50.722 (36%)
N=45–15 years Multiple IV
4 mg/kg0.59 (64%)
N=515.2 11.4 (44%)
N=60.729 (33%)
N=55–15 years Multiple IV
8 mg/kg0.66 (31%)
N=717.6 14.1 (22%)
N=81.069 (37%)
N=7Clearance corrected for body weight was not affected by age in these studies. Mean body clearance in adults is reported to be 0.23 (17%) mL/min/kg.
In premature newborns (gestational age 26 to 29 weeks), the mean (%cv) clearance within 36 hours of birth was 0.180 (35%, N=7) mL/min/kg, which increased with time to a mean of 0.218 (31%, N=9) mL/min/kg six days later and 0.333 (56%, N=4) mL/min/kg 12 days later. Similarly, the half-life was 73.6 hours, which decreased with time to a mean of 53.2 hours six days later and 46.6 hours 12 days later.
Pharmacokinetics in Elderly
A pharmacokinetic study was conducted in 22 subjects, 65 years of age or older receiving a single 50 mg oral dose of fluconazole. Ten of these patients were concomitantly receiving diuretics. The Cmax was 1.54 mcg/mL and occurred at 1.3 hours post dose. The mean AUC was 76.4 ± 20.3 mcg∙h/mL, and the mean terminal half-life was 46.2 hours. These pharmacokinetic parameter values are higher than analogous values reported for normal young male volunteers. Coadministration of diuretics did not significantly alter AUC or Cmax. In addition, creatinine clearance (74 mL/min), the percent of drug recovered unchanged in urine (0–24 hr, 22%), and the fluconazole renal clearance estimates (0.124 mL/min/kg) for the elderly were generally lower than those of younger volunteers. Thus, the alteration of fluconazole disposition in the elderly appears to be related to reduced renal function characteristic of this group. A plot of each subject's terminal elimination half-life versus creatinine clearance compared with the predicted half-life – creatinine clearance curve derived from normal subjects and subjects with varying degrees of renal insufficiency indicated that 21 of 22 subjects fell within the 95% confidence limit of the predicted half-life – creatinine clearance curves. These results are consistent with the hypothesis that higher values for the pharmacokinetic parameters observed in the elderly subjects compared with normal young male volunteers are due to the decreased kidney function that is expected in the elderly.
Drug Interaction Studies
Oral contraceptives
Oral contraceptives were administered as a single dose both before and after the oral administration of fluconazole 50 mg once daily for 10 days in 10 healthy women. There was no significant difference in ethinyl estradiol or levonorgestrel AUC after the administration of 50 mg of fluconazole. The mean increase in ethinyl estradiol AUC was 6% (range: −47 to 108%) and levonorgestrel AUC increased 17% (range: −33 to 141%).
In a second study, twenty-five normal females received daily doses of both 200 mg fluconazole tablets or placebo for two, ten-day periods. The treatment cycles were one month apart with all subjects receiving fluconazole during one cycle and placebo during the other. The order of study treatment was random. Single doses of an oral contraceptive tablet containing levonorgestrel and ethinyl estradiol were administered on the final treatment day (day 10) of both cycles. Following administration of 200 mg of fluconazole, the mean percentage increase of AUC for levonorgestrel compared to placebo was 25% (range: –12 to 82%) and the mean percentage increase for ethinyl estradiol compared to placebo was 38% (range: –11 to 101%). Both of these increases were statistically significantly different from placebo.
A third study evaluated the potential interaction of once weekly dosing of fluconazole 300 mg to 21 normal females taking an oral contraceptive containing ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone. In this placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized, two-way crossover study carried out over three cycles of oral contraceptive treatment, fluconazole dosing resulted in small increases in the mean AUCs of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone compared to similar placebo dosing. The mean AUCs of ethinyl estradiol and norethindrone increased by 24% (95% C.I. range: 18–31%) and 13% (95% C.I. range: 8–18%), respectively, relative to placebo. Fluconazole treatment did not cause a decrease in the ethinyl estradiol AUC of any individual subject in this study compared to placebo dosing. The individual AUC values of norethindrone decreased very slightly (<5%) in 3 of the 21 subjects after fluconazole treatment.
Cimetidine
Fluconazole 100 mg was administered as a single oral dose alone and two hours after a single dose of cimetidine 400 mg to six healthy male volunteers. After the administration of cimetidine, there was a significant decrease in fluconazole AUC and Cmax. There was a mean ± SD decrease in fluconazole AUC of 13% ± 11% (range: −3.4 to −31%) and Cmax decreased 19% ± 14% (range: −5 to −40%). However, the administration of cimetidine 600 mg to 900 mg intravenously over a four-hour period (from one hour before to 3 hours after a single oral dose of fluconazole 200 mg) did not affect the bioavailability or pharmacokinetics of fluconazole in 24 healthy male volunteers.
Antacid
Administration of Maalox® (20 mL) to 14 normal male volunteers immediately prior to a single dose of fluconazole 100 mg had no effect on the absorption or elimination of fluconazole.
Hydrochlorothiazide
Concomitant oral administration of 100 mg fluconazole and 50 mg hydrochlorothiazide for 10 days in 13 normal volunteers resulted in a significant increase in fluconazole AUC and Cmax compared to fluconazole given alone. There was a mean ± SD increase in fluconazole AUC and Cmax of 45% ± 31% (range: 19 to 114%) and 43% ± 31% (range: 19 to 122%), respectively. These changes are attributed to a mean ± SD reduction in renal clearance of 30% ± 12% (range: −10 to −50%).
Rifampin
Administration of a single oral 200 mg dose of fluconazole after 15 days of rifampin administered as 600 mg daily in eight healthy male volunteers resulted in a significant decrease in fluconazole AUC and a significant increase in apparent oral clearance of fluconazole. There was a mean ± SD reduction in fluconazole AUC of 23% ± 9% (range: −13 to −42%). Apparent oral clearance of fluconazole increased 32% ± 17% (range: 16 to 72%). Fluconazole half-life decreased from 33.4 ± 4.4 hours to 26.8 ± 3.9 hours. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Warfarin
There was a significant increase in prothrombin time response (area under the prothrombin time-time curve) following a single dose of warfarin (15 mg) administered to 13 normal male volunteers following oral fluconazole 200 mg administered daily for 14 days as compared to the administration of warfarin alone. There was a mean ± SD increase in the prothrombin time response (area under the prothrombin time-time curve) of 7% ± 4% (range: −2 to 13%). (See PRECAUTIONS.) Mean is based on data from 12 subjects as one of 13 subjects experienced a 2-fold increase in his prothrombin time response.
Phenytoin
Phenytoin AUC was determined after 4 days of phenytoin dosing (200 mg daily, orally for 3 days followed by 250 mg intravenously for one dose) both with and without the administration of fluconazole (oral fluconazole 200 mg daily for 16 days) in 10 normal male volunteers. There was a significant increase in phenytoin AUC. The mean ± SD increase in phenytoin AUC was 88% ± 68% (range: 16 to 247%). The absolute magnitude of this interaction is unknown because of the intrinsically nonlinear disposition of phenytoin. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Cyclosporine
Cyclosporine AUC and Cmax were determined before and after the administration of fluconazole 200 mg daily for 14 days in eight renal transplant patients who had been on cyclosporine therapy for at least 6 months and on a stable cyclosporine dose for at least 6 weeks. There was a significant increase in cyclosporine AUC, Cmax, Cmin (24-hour concentration), and a significant reduction in apparent oral clearance following the administration of fluconazole. The mean ± SD increase in AUC was 92% ± 43% (range: 18 to 147%). The Cmax increased 60% ± 48% (range: −5 to 133%). The Cmin increased 157% ± 96% (range: 33 to 360%). The apparent oral clearance decreased 45% ± 15% (range: −15 to −60%). (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Zidovudine
Plasma zidovudine concentrations were determined on two occasions (before and following fluconazole 200 mg daily for 15 days) in 13 volunteers with AIDS or ARC who were on a stable zidovudine dose for at least two weeks. There was a significant increase in zidovudine AUC following the administration of fluconazole. The mean ± SD increase in AUC was 20% ± 32% (range: −27 to 104%). The metabolite, GZDV, to parent drug ratio significantly decreased after the administration of fluconazole, from 7.6 ± 3.6 to 5.7 ± 2.2.
Theophylline
The pharmacokinetics of theophylline were determined from a single intravenous dose of aminophylline (6 mg/kg) before and after the oral administration of fluconazole 200 mg daily for 14 days in 16 normal male volunteers. There were significant increases in theophylline AUC, Cmax, and half-life with a corresponding decrease in clearance. The mean ± SD theophylline AUC increased 21% ± 16% (range: −5 to 48%). The Cmax increased 13% ± 17% (range: −13 to 40%). Theophylline clearance decreased 16% ± 11% (range: −32 to 5%). The half-life of theophylline increased from 6.6 ± 1.7 hours to 7.9 ± 1.5 hours. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Terfenadine
Six healthy volunteers received terfenadine 60 mg BID for 15 days. Fluconazole 200 mg was administered daily from days 9 through 15. Fluconazole did not affect terfenadine plasma concentrations. Terfenadine acid metabolite AUC increased 36% ± 36% (range: 7 to 102%) from day 8 to day 15 with the concomitant administration of fluconazole. There was no change in cardiac repolarization as measured by Holter QTc intervals. Another study at a 400 mg and 800 mg daily dose of fluconazole demonstrated that fluconazole taken in doses of 400 mg per day or greater significantly increases plasma levels of terfenadine when taken concomitantly. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Quinidine
Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of fluconazole with quinidine may result in inhibition of quinidine metabolism. Use of quinidine has been associated with QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole and quinidine is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Oral hypoglycemics
The effects of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of the sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agents tolbutamide, glipizide, and glyburide were evaluated in three placebo-controlled studies in normal volunteers. All subjects received the sulfonylurea alone as a single dose and again as a single dose following the administration of fluconazole 100 mg daily for 7 days. In these three studies, 22/46 (47.8%) of fluconazole treated patients and 9/22 (40.1%) of placebo-treated patients experienced symptoms consistent with hypoglycemia. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Tolbutamide
In 13 normal male volunteers, there was significant increase in tolbutamide (500 mg single dose) AUC and Cmax following the administration of fluconazole. There was a mean ± SD increase in tolbutamide AUC of 26% ± 9% (range: 12 to 39%). Tolbutamide Cmax increased 11% ± 9% (range: –6 to 27%). (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Glipizide
The AUC and Cmax of glipizide (2.5 mg single dose) were significantly increased following the administration of fluconazole in 13 normal male volunteers. There was a mean ± SD increase in AUC of 49% ± 13% (range: 27 to 73%) and an increase in Cmax of 19% ± 23% (range: −11 to 79%). (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Glyburide
The AUC and Cmax of glyburide (5 mg single dose) were significantly increased following the administration of fluconazole in 20 normal male volunteers. There was a mean ± SD increase in AUC of 44% ± 29% (range: –13 to 115%) and Cmax increased 19% ± 19% (range: −23 to 62%). Five subjects required oral glucose following the ingestion of glyburide after 7 days of fluconazole administration. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Rifabutin
There have been published reports that an interaction exists when fluconazole is administered concomitantly with rifabutin, leading to increased serum levels of rifabutin. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Tacrolimus
There have been published reports that an interaction exists when fluconazole is administered concomitantly with tacrolimus, leading to increased serum levels of tacrolimus. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Cisapride
A placebo-controlled, randomized, multiple-dose study examined the potential interaction of fluconazole with cisapride. Two groups of 10 normal subjects were administered fluconazole 200 mg daily or placebo. Cisapride 20 mg four times daily was started after 7 days of fluconazole or placebo dosing. Following a single dose of fluconazole, there was a 101% increase in the cisapride AUC and a 91% increase in the cisapride Cmax. Following multiple doses of fluconazole, there was a 192% increase in the cisapride AUC and a 154% increase in the cisapride Cmax . Fluconazole significantly increased the QTc interval in subjects receiving cisapride 20 mg four times daily for 5 days. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and PRECAUTIONS.)
Midazolam
The effect of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of midazolam was examined in a randomized, cross-over study in 12 volunteers. In the study, subjects ingested placebo or 400 mg fluconazole on Day 1 followed by 200 mg daily from Day 2 to Day 6. In addition, a 7.5 mg dose of midazolam was orally ingested on the first day, 0.05 mg/kg was administered intravenously on the fourth day, and 7.5 mg orally on the sixth day. Fluconazole reduced the clearance of IV midazolam by 51%. On the first day of dosing, fluconazole increased the midazolam AUC and Cmax by 259% and 150%, respectively. On the sixth day of dosing, fluconazole increased the midazolam AUC and Cmax by 259% and 74%, respectively. The psychomotor effects of midazolam were significantly increased after oral administration of midazolam but not significantly affected following intravenous midazolam.
A second randomized, double-dummy, placebo-controlled, cross-over study in three phases was performed to determine the effect of route of administration of fluconazole on the interaction between fluconazole and midazolam. In each phase the subjects were given oral fluconazole 400 mg and intravenous saline; oral placebo and intravenous fluconazole 400 mg; and oral placebo and IV saline. An oral dose of 7.5 mg of midazolam was ingested after fluconazole/placebo. The AUC and Cmax of midazolam were significantly higher after oral than IV administration of fluconazole. Oral fluconazole increased the midazolam AUC and Cmax by 272% and 129%, respectively. IV fluconazole increased the midazolam AUC and Cmax by 244% and 79%, respectively. Both oral and IV fluconazole increased the pharmacodynamic effects of midazolam. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Azithromycin
An open-label, randomized, three-way crossover study in 18 healthy subjects assessed the effect of a single 800 mg oral dose of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of a single 1200 mg oral dose of azithromycin as well as the effects of azithromycin on the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole. There was no significant pharmacokinetic interaction between fluconazole and azithromycin.
Voriconazole
Voriconazole is a substrate for both CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 isoenzymes. Concurrent administration of oral Voriconazole (400 mg Q12h for 1 day, then 200 mg Q12h for 2.5 days) and oral fluconazole (400 mg on day 1, then 200 mg Q24h for 4 days) to 6 healthy male subjects resulted in an increase in Cmax and AUCτ of voriconazole by an average of 57% (90% CI: 20%, 107%) and 79% (90% CI: 40%, 128%), respectively. In a follow-on clinical study involving 8 healthy male subjects, reduced dosing and/or frequency of voriconazole and fluconazole did not eliminate or diminish this effect. Concomitant administration of voriconazole and fluconazole at any dose is not recommended. Close monitoring for adverse events related to voriconazole is recommended if voriconazole is used sequentially after fluconazole, especially within 24 h of the last dose of fluconazole. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Tofacitinib
Co-administration of fluconazole (400 mg on Day 1 and 200 mg once daily for 6 days [Days 2-7]) and tofacitinib (30 mg single dose on Day 5) in healthy subjects resulted in increased mean tofacitinib AUC and Cmax values of approximately 79% (90% CI: 64% – 96%) and 27% (90% CI: 12% – 44%), respectively, compared to administration of tofacitinib alone. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Microbiology
Mechanism of Action
Fluconazole is a highly selective inhibitor of fungal cytochrome P450 dependent enzyme lanosterol 14-α-demethylase. This enzyme functions to convert lanosterol to ergosterol. The subsequent loss of normal sterols correlates with the accumulation of 14-α-methyl sterols in fungi and may be responsible for the fungistatic activity of fluconazole. Mammalian cell demethylation is much less sensitive to fluconazole inhibition.
Drug Resistance
Fluconazole resistance may arise from a modification in the quality or quantity of the target enzyme (lanosterol 14-α-demethylase), reduced access to the drug target, or some combination of these mechanisms.
Point mutations in the gene (ERG11) encoding for the target enzyme lead to an altered target with decreased affinity for azoles. Overexpression of ERG11 results in the production of high concentrations of the target enzyme, creating the need for higher intracellular drug concentrations to inhibit all of the enzyme molecules in the cell.
The second major mechanism of drug resistance involves active efflux of fluconazole out of the cell through the activation of two types of multidrug efflux transporters; the major facilitators (encoded by MDR genes) and those of the ATP-binding cassette superfamily (encoded by CDR genes). Upregulation of the MDR gene leads to fluconazole resistance, whereas, upregulation of CDR genes may lead to resistance to multiple azoles.
Resistance in Candida glabrata usually includes upregulation of CDR genes resulting in resistance to multiple azoles. For an isolate where the MIC is categorized as Intermediate (16 to 32 µg/mL), the highest fluconazole dose is recommended.
Candida krusei should be considered to be resistant to fluconazole. Resistance in C. krusei appears to be mediated by reduced sensitivity of the target enzyme to inhibition by the agent.
There have been reports of cases of superinfection with Candida species other than C. albicans, which are often inherently not susceptible to fluconazole (e.g., Candida krusei). Such cases may require alternative antifungal therapy.
Activity In Vitro and In Clinical Infections
Fluconazole has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms both in vitro and in clinical infections.
Candida albicans
Candida glabrata (Many strains are intermediately susceptible)1
Candida parapsilosis
Candida tropicalis
Cryptococcus neoformansThe following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown.
Fluconazole exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MIC values) of 8 µg/mL or less against most (≥90%) strains of the following microorganisms, however, the safety and effectiveness of fluconazole in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled trials.
Candida dubliniensis
Candida guilliermondii
Candida kefyr
Candida lusitaniaeCandida krusei should be considered to be resistant to fluconazole. Resistance in C. krusei appears to be mediated by reduced sensitivity of the target enzyme to inhibition by the agent.
There have been reports of cases of superinfection with Candida species other than C. albicans, which are often inherently not susceptible to fluconazole (e.g., Candida krusei). Such cases may require alternative antifungal therapy.
- 1 In a majority of the studies, fluconazole MIC90 values against C. glabrata were above the susceptible breakpoint (≥16 µg/mL). Resistance in Candida glabrata usually includes upregulation of CDR genes resulting in resistance to multiple azoles. For an isolate where the MIC is categorized as intermediate (16 to 32 µg/mL, see Table 1), the highest dose is recommended (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). For resistant isolates, alternative therapy is recommended.
Susceptibility Testing Methods
Cryptococcus neoformans and filamentous fungi
No interpretive criteria have been established for Cryptococcus neoformans and filamentous fungi.
Candida species
Broth Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antifungal minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of Candida spp. to antifungal agents. MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method (broth)1 with standardized inoculum concentrations of fluconazole powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the criteria provided in Table 1.
Diffusion Techniques
Qualitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of Candida spp. to an antifungal agent. One such standardized procedure2 requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 25 µg of fluconazole to test the susceptibility of yeasts to fluconazole. Disk diffusion interpretive criteria are also provided in Table 1.
Table 1: Susceptibility Interpretive Criteria for Fluconazole against Candida species Broth Dilution at 48 hours
(MIC in µg/mL)Disk Diffusion at 24 hours
(Zone Diameters in mm)Antifungal agent Susceptible
(S)Intermediate
(I)*Resistant
(R)Susceptible
(S)Intermediate
(I)*Resistant
(R)- * The intermediate category is sometimes called Susceptible-Dose Dependent (SDD) and both categories are equivalent for fluconazole.
- † Isolates of C. krusei are assumed to be intrinsically resistant to fluconazole and their MICs and/or zone diameters should not be interpreted using this scale.
Fluconazole† ≤ 8.0 16–32 ≥64 ≥19 15–18 ≤14 A report of Susceptible (S) indicates that the antimicrobial drug is likely to inhibit growth of the microorganism if the antimicrobial drug reaches the concentration usually achievable at the site of infection.
A report of Intermediate (I) indicates that an infection due to the isolate may be appropriately treated in body sites where the drugs are physiologically concentrated or when a high dosage of drug is used.
A report of Resistant (R) indicates that the antimicrobial is not likely to inhibit growth of the pathogen if the antimicrobial drug reaches the concentrations usually achievable at the infection site; other therapy should be selected.
Quality Control
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of quality control organisms to control the technical aspects of the test procedures. Standardized fluconazole powder and 25 µg disks should provide the following range of values noted in Table 2. NOTE: Quality control microorganisms are specific strains of organisms with intrinsic biological properties relating to resistance mechanisms and their genetic expression within fungi; the specific strains used for microbiological control are not clinically significant.
Table 2: Acceptable Quality Control Ranges for Fluconazole to be Used in Validation of Susceptibility Test Results QC Strain Macrodilution
(MIC in µg/mL)
@ 48 hoursMicrodilution
(MIC in µg/mL)
@ 48 hoursDisk Diffusion
(Zone Diameter in mm)
@ 24 hours- * Quality control ranges have not been established for this strain/antifungal agent combination due to their extensive interlaboratory variation during initial quality control studies.
Candida parapsilosis ATCC 22019 2.0–8.0 1.0–4.0 22–33 Candida krusei ATCC 6258 16–64 16–128 ---* Candida albicans ATCC 90028 ---* ---* 28–39 Candida tropicalis ATCC 750 ---* ---* 26–37 -
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Fluconazole is indicated for the treatment of:
- Vaginal candidiasis (vaginal yeast infections due to Candida).
- Oropharyngeal and esophageal candidiasis. In open noncomparative studies of relatively small numbers of patients, fluconazole was also effective for the treatment of Candida urinary tract infections, peritonitis, and systemic Candida infections including candidemia, disseminated candidiasis, and pneumonia.
- Cryptococcal meningitis. Before prescribing fluconazole for AIDS patients with cryptococcal meningitis, please see CLINICAL STUDIES section. Studies comparing fluconazole to amphotericin B in non-HIV infected patients have not been conducted.
Prophylaxis
Fluconazole is also indicated to decrease the incidence of candidiasis in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation who receive cytotoxic chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy.
Specimens for fungal culture and other relevant laboratory studies (serology, histopathology) should be obtained prior to therapy to isolate and identify causative organisms. Therapy may be instituted before the results of the cultures and other laboratory studies are known; however, once these results become available, anti-infective therapy should be adjusted accordingly.
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
Cryptococcal meningitis
In a multicenter study comparing fluconazole (200 mg/day) to amphotericin B (0.3 mg/kg/day) for treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS, a multivariate analysis revealed three pretreatment factors that predicted death during the course of therapy: abnormal mental status, cerebrospinal fluid cryptococcal antigen titer greater than 1:1024, and cerebrospinal fluid white blood cell count of less than 20 cells/mm3. Mortality among high risk patients was 33% and 40% for amphotericin B and fluconazole patients, respectively (p=0.58), with overall deaths 14% (9 of 63 subjects) and 18% (24 of 131 subjects) for the 2 arms of the study (p=0.48). Optimal doses and regimens for patients with acute cryptococcal meningitis and at high risk for treatment failure remain to be determined. (Saag, et al. N Engl J Med 1992; 326:83–9.)
Vaginal candidiasis
Two adequate and well-controlled studies were conducted in the U.S. using the 150 mg tablet. In both, the results of the fluconazole regimen were comparable to the control regimen (clotrimazole or miconazole intravaginally for 7 days) both clinically and statistically at the one month post-treatment evaluation.
The therapeutic cure rate, defined as a complete resolution of signs and symptoms of vaginal candidiasis (clinical cure), along with a negative KOH examination and negative culture for Candida (microbiologic eradication), was 55% in both the fluconazole group and the vaginal products group.
Fluconazole PO 150 mg tablet Vaginal Product qhs × 7 days Enrolled 448 422 Evaluable at Late Follow-up 347 (77%) 327 (77%) Clinical cure 239/347 (69%) 235/327 (72%) Mycologic eradication 213/347 (61%) 196/327 (60%) Therapeutic cure 190/347 (55%) 179/327 (55%) Approximately three-fourths of the enrolled patients had acute vaginitis (<4 episodes/12 months) and achieved 80% clinical cure, 67% mycologic eradication, and 59% therapeutic cure when treated with a 150 mg fluconazole tablet administered orally. These rates were comparable to control products. The remaining one-fourth of enrolled patients had recurrent vaginitis (≥4 episodes/12 months) and achieved 57% clinical cure, 47% mycologic eradication, and 40% therapeutic cure. The numbers are too small to make meaningful clinical or statistical comparisons with vaginal products in the treatment of patients with recurrent vaginitis.
Substantially more gastrointestinal events were reported in the fluconazole group compared to the vaginal product group. Most of the events were mild to moderate. Because fluconazole was given as a single dose, no discontinuations occurred.
Parameter Fluconazole PO Vaginal Products Evaluable patients 448 422 With any adverse event 141 (31%) 112 (27%) Nervous System 90 (20%) 69 (16%) Gastrointestinal 73 (16%) 18 (4%) With drug-related event 117 (26%) 67 (16%) Nervous System 61 (14%) 29 (7%) Headache 58 (13%) 28 (7%) Gastrointestinal 68 (15%) 13 (3%) Abdominal pain 25 (6%) 7 (2%) Nausea 30 (7%) 3 (1%) Diarrhea 12 (3%) 2 (<1%) Application site event 0 (0%) 19 (5%) Taste Perversion 6 (1%) 0 (0%) Pediatric Studies
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
An open-label, comparative study of the efficacy and safety of fluconazole (2–3 mg/kg/day) and oral nystatin (400,000 I.U. 4 times daily) in immunocompromised children with oropharyngeal candidiasis was conducted. Clinical and mycological response rates were higher in the children treated with fluconazole.
Clinical cure at the end of treatment was reported for 86% of fluconazole treated patients compared to 46% of nystatin treated patients. Mycologically, 76% of fluconazole treated patients had the infecting organism eradicated compared to 11% for nystatin treated patients.
Fluconazole Nystatin - * Subjects without follow-up cultures for any reason were considered nonevaluable for mycological response.
Enrolled 96 90 Clinical Cure 76/88 (86%) 36/78 (46%) Mycological eradication* 55/72 (76%) 6/54 (11%) The proportion of patients with clinical relapse 2 weeks after the end of treatment was 14% for subjects receiving fluconazole and 16% for subjects receiving nystatin. At 4 weeks after the end of treatment, the percentages of patients with clinical relapse were 22% for fluconazole and 23% for nystatin.
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Fluconazole is contraindicated in patients who have shown hypersensitivity to fluconazole or to any of its excipients. There is no information regarding cross-hypersensitivity between fluconazole and other azole antifungal agents. Caution should be used in prescribing fluconazole to patients with hypersensitivity to other azoles. Coadministration of terfenadine is contraindicated in patients receiving fluconazole at multiple doses of 400 mg or higher based upon results of a multiple dose interaction study. Coadministration of other drugs known to prolong the QT interval and which are metabolized via the enzyme CYP3A4 such as cisapride, astemizole, erythromycin, pimozide, and quinidine are contraindicated in patients receiving fluconazole. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies and PRECAUTIONS.)
-
WARNINGS
(1) Hepatic injury
Fluconazole should be administered with caution to patients with liver dysfunction. Fluconazole has been associated with rare cases of serious hepatic toxicity, including fatalities primarily in patients with serious underlying medical conditions. In cases of fluconazole associated hepatotoxicity, no obvious relationship to total daily dose, duration of therapy, sex, or age of the patient has been observed. Fluconazole hepatotoxicity has usually, but not always, been reversible on discontinuation of therapy. Patients who develop abnormal liver function tests during fluconazole therapy should be monitored for the development of more severe hepatic injury. Fluconazole should be discontinued if clinical signs and symptoms consistent with liver disease develop that may be attributable to fluconazole.
(3) Dermatologic
Exfoliative skin disorders during treatment with fluconazole have been reported. Fatal outcomes have been reported in patients with serious underlying diseases. Patients with deep seated fungal infections who develop rashes during treatment with fluconazole should be monitored closely and the drug discontinued if lesions progress. Fluconazole should be discontinued in patients treated for superficial fungal infection who develop a rash that may be attributed to fluconazole.
(4) Use in Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of fluconazole in pregnant women. Available human data do not suggest an increased risk of congenital anomalies following a single maternal dose of 150 mg. A few published case reports describe a rare pattern of distinct congenital anomalies in infants exposed in utero to high dose maternal fluconazole (400–800 mg/day) during most or all of the first trimester. These reported anomalies are similar to those seen in animal studies. If this drug is used during pregnancy or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be informed of the potential hazard to the fetus (See PRECAUTIONS, Pregnancy.)
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Some azoles, including fluconazole, have been associated with prolongation of the QT interval on the electrocardiogram. During post-marketing surveillance, there have been rare cases of QT prolongation and torsade de pointes in patients taking fluconazole. Most of these reports involved seriously ill patients with multiple confounding risk factors, such as structural heart disease, electrolyte abnormalities, and concomitant medications that may have been contributory.
Fluconazole should be administered with caution to patients with these potentially proarrhythmic conditions.
Concomitant use of fluconazole and erythromycin has the potential to increase the risk of cardiotoxicity (prolonged QT interval, torsade de pointes) and consequently sudden heart death. This combination should be avoided.
Fluconazole should be administered with caution to patients with renal dysfunction.
Fluconazole is a potent CYP2C9 inhibitor and a moderate CYP3A4 inhibitor. Fluconazole treated patients who are concomitantly treated with drugs with a narrow therapeutic window metabolized through CYP2C9 and CYP3A4 should be monitored.
Fluconazole Powder for Oral Suspension contains sucrose and should not be used in patients with hereditary fructose, glucose/galactose malabsorption, and sucrase-isomaltase deficiency.
When driving vehicles or operating machines, it should be taken into account that occasionally dizziness or seizures may occur.
Single Dose
The convenience and efficacy of the single dose oral tablet of fluconazole regimen for the treatment of vaginal yeast infections should be weighed against the acceptability of a higher incidence of drug related adverse events with fluconazole (26%) versus intravaginal agents (16%) in U.S. comparative clinical studies. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS and CLINICAL STUDIES.)
Drug Interactions
(See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies and CONTRAINDICATIONS.) Fluconazole is a potent inhibitor of cytochrome P450 (CYP) isoenzyme 2C9 and 2C19, and a moderate inhibitor of CYP3A4. In addition to the observed /documented interactions mentioned below, there is a risk of increased plasma concentration of other compounds metabolized by CYP2C9, CYP2C19 and CYP3A4 coadministered with fluconazole. Therefore, caution should be exercised when using these combinations and the patients should be carefully monitored. The enzyme inhibiting effect of fluconazole persists 4–5 days after discontinuation of fluconazole treatment due to the long half-life of fluconazole. Clinically or potentially significant drug interactions between fluconazole and the following agents/classes have been observed. These are described in greater detail below:
Oral hypoglycemics
Coumarin-type anticoagulants
Phenytoin
Cyclosporine
Rifampin
Theophylline
Terfenadine
Cisapride
Astemizole
Rifabutin
Voriconazole
Tacrolimus
Short-acting benzodiazepines
Tofacitinib
Triazolam
Oral Contraceptives
Pimozide
Quinidine
Hydrochlorothiazide
Alfentanil
Amitriptyline, nortriptyline
Amphotericin B
Azithromycin
Carbamazepine
Calcium Channel Blockers
Celecoxib
Cyclophosphamide
Fentanyl
Halofantrine
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
Losartan
Methadone
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Prednisone
Saquinavir
Sirolimus
Vinca Alkaloids
Vitamin A
ZidovudineOral hypoglycemics
Clinically significant hypoglycemia may be precipitated by the use of fluconazole with oral hypoglycemic agents; one fatality has been reported from hypoglycemia in association with combined fluconazole and glyburide use. Fluconazole reduces the metabolism of tolbutamide, glyburide, and glipizide and increases the plasma concentration of these agents. When fluconazole is used concomitantly with these or other sulfonylurea oral hypoglycemic agents, blood glucose concentrations should be carefully monitored and the dose of the sulfonylurea should be adjusted as necessary. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Coumarin-type anticoagulants
Prothrombin time may be increased in patients receiving concomitant fluconazole and coumarin-type anticoagulants. In post-marketing experience, as with other azole antifungals, bleeding events (bruising, epistaxis, gastrointestinal bleeding, hematuria, and melena) have been reported in association with increases in prothrombin time in patients receiving fluconazole concurrently with warfarin. Careful monitoring of prothrombin time in patients receiving fluconazole and coumarin-type anticoagulants is recommended. Dose adjustment of warfarin may be necessary. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Phenytoin
Fluconazole increases the plasma concentrations of phenytoin. Careful monitoring of phenytoin concentrations in patients receiving fluconazole and phenytoin is recommended. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Cyclosporine
Fluconazole significantly increases cyclosporine levels in renal transplant patients with or without renal impairment. Careful monitoring of cyclosporine concentrations and serum creatinine is recommended in patients receiving fluconazole and cyclosporine. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies). This combination may be used by reducing the dosage of cyclosporine depending on cyclosporine concentration.
Rifampin
Rifampin enhances the metabolism of concurrently administered fluconazole. Depending on clinical circumstances, consideration should be given to increasing the dose of fluconazole when it is administered with rifampin. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Theophylline
Fluconazole increases the serum concentrations of theophylline. Careful monitoring of serum theophylline concentrations in patients receiving fluconazole and theophylline is recommended. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Terfenadine
Because of the occurrence of serious cardiac dysrhythmias secondary to prolongation of the QTc interval in patients receiving azole antifungals in conjunction with terfenadine, interaction studies have been performed. One study at a 200 mg daily dose of fluconazole failed to demonstrate a prolongation in QTc interval. Another study at a 400 mg and 800 mg daily dose of fluconazole demonstrated that fluconazole taken in doses of 400 mg per day or greater significantly increases plasma levels of terfenadine when taken concomitantly. The combined use of fluconazole at doses of 400 mg or greater with terfenadine is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.) The coadministration of fluconazole at doses lower than 400 mg/day with terfenadine should be carefully monitored.
Cisapride
There have been reports of cardiac events, including torsade de pointes, in patients to whom fluconazole and cisapride were coadministered. A controlled study found that concomitant fluconazole 200 mg once daily and cisapride 20 mg four times a day yielded a significant increase in cisapride plasma levels and prolongation of QTc interval. The combined use of fluconazole with cisapride is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS and CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Astemizole
Concomitant administration of fluconazole with astemizole may decrease the clearance of astemizole. Resulting increased plasma concentrations of astemizole can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsade de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole and astemizole is contraindicated.
Rifabutin
There have been reports that an interaction exists when fluconazole is administered concomitantly with rifabutin, leading to increased serum levels of rifabutin up to 80%. There have been reports of uveitis in patients to whom fluconazole and rifabutin were coadministered. Patients receiving rifabutin and fluconazole concomitantly should be carefully monitored. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Voriconazole
Avoid concomitant administration of voriconazole and fluconazole. Monitoring for adverse events and toxicity related to voriconazole is recommended; especially, if voriconazole is started within 24 h after the last dose of fluconazole. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Tacrolimus
Fluconazole may increase the serum concentrations of orally administered tacrolimus up to 5 times due to inhibition of tacrolimus metabolism through CYP3A4 in the intestines. No significant pharmacokinetic changes have been observed when tacrolimus is given intravenously. Increased tacrolimus levels have been associated with nephrotoxicity. Dosage of orally administered tacrolimus should be decreased depending on tacrolimus concentration. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Short-acting Benzodiazepines
Following oral administration of midazolam, fluconazole resulted in substantial increases in midazolam concentrations and psychomotor effects. This effect on midazolam appears to be more pronounced following oral administration of fluconazole than with fluconazole administered intravenously. If short-acting benzodiazepines, which are metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system, are concomitantly administered with fluconazole, consideration should be given to decreasing the benzodiazepine dosage, and the patients should be appropriately monitored. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Tofacitinib
Systemic exposure to tofacitinib is increased when tofacitinib is coadministered with fluconazole, a combined moderate CYP3A4 and potent CYP2C19 inhibitor. Reduce the dose of tofacitinib when given concomitantly with fluconazole (i.e., from 5 mg twice daily to 5 mg once daily as instructed in the XELJANZ® [tofacitinib] label). (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Drug Interaction Studies.)
Triazolam
Fluconazole increases the AUC of triazolam (single dose) by approximately 50%, Cmax by 20–32%, and increases t½ by 25–50 % due to the inhibition of metabolism of triazolam. Dosage adjustments of triazolam may be necessary.
Oral Contraceptives
Two pharmacokinetic studies with a combined oral contraceptive have been performed using multiple doses of fluconazole. There were no relevant effects on hormone level in the 50 mg fluconazole study, while at 200 mg daily, the AUCs of ethinyl estradiol and levonorgestrel were increased 40% and 24%, respectively. Thus, multiple dose use of fluconazole at these doses is unlikely to have an effect on the efficacy of the combined oral contraceptive.
Pimozide
Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of fluconazole with pimozide may result in inhibition of pimozide metabolism. Increased pimozide plasma concentrations can lead to QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsade de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole and pimozide is contraindicated.
Quinidine
Although not studied in vitro or in vivo, concomitant administration of fluconazole with quinidine may result in inhibition of quinidine metabolism. Use of quinidine has been associated with QT prolongation and rare occurrences of torsades de pointes. Coadministration of fluconazole and quinidine is contraindicated. (See CONTRAINDICATIONS.)
Hydrochlorothiazide
In a pharmacokinetic interaction study, coadministration of multiple dose hydrochlorothiazide to healthy volunteers receiving fluconazole increased plasma concentrations of fluconazole by 40%. An effect of this magnitude should not necessitate a change in the fluconazole dose regimen in subjects receiving concomitant diuretics.
Alfentanil
A study observed a reduction in clearance and distribution volume as well as prolongation of T½ of alfentanil following concomitant treatment with fluconazole. A possible mechanism of action is fluconazole's inhibition of CYP3A4. Dosage adjustment of alfentanil may be necessary.
Amitriptyline, nortriptyline
Fluconazole increases the effect of amitriptyline and nortriptyline. 5-nortriptyline and/or S-amitriptyline may be measured at initiation of the combination therapy and after one week. Dosage of amitriptyline/nortriptyline should be adjusted, if necessary.
Amphotericin B
Concurrent administration of fluconazole and amphotericin B in infected normal and immunosuppressed mice showed the following results: a small additive antifungal effect in systemic infection with C. albicans, no interaction in intracranial infection with Cryptococcus neoformans, and antagonism of the two drugs in systemic infection with A. fumigatus. The clinical significance of results obtained in these studies is unknown.
Azithromycin
An open-label, randomized, three-way crossover study in 18 healthy subjects assessed the effect of a single 1200 mg oral dose of azithromycin on the pharmacokinetics of a single 800 mg oral dose of fluconazole as well as the effects of fluconazole on the pharmacokinetics of azithromycin. There was no significant pharmacokinetic interaction between fluconazole and azithromycin.
Carbamazepine
Fluconazole inhibits the metabolism of carbamazepine and an increase in serum carbamazepine of 30% has been observed. There is a risk of developing carbamazepine toxicity. Dosage adjustment of carbamazepine may be necessary depending on concentration measurements/effect.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Certain calcium channel antagonists (nifedipine, isradipine, amlodipine, verapamil, and felodipine) are metabolized by CYP3A4. Fluconazole has the potential to increase the systemic exposure of the calcium channel antagonists. Frequent monitoring for adverse events is recommended.
Celecoxib
During concomitant treatment with fluconazole (200 mg daily) and celecoxib (200 mg), the celecoxib Cmax and AUC increased by 68% and 134%, respectively. Half of the celecoxib dose may be necessary when combined with fluconazole.
Cyclophosphamide
Combination therapy with cyclophosphamide and fluconazole results in an increase in serum bilirubin and serum creatinine. The combination may be used while taking increased consideration to the risk of increased serum bilirubin and serum creatinine.
Fentanyl
One fatal case of possible fentanyl fluconazole interaction was reported. The author judged that the patient died from fentanyl intoxication. Furthermore, in a randomized crossover study with 12 healthy volunteers it was shown that fluconazole delayed the elimination of fentanyl significantly. Elevated fentanyl concentration may lead to respiratory depression.
Halofantrine
Fluconazole can increase halofantrine plasma concentration due to an inhibitory effect on CYP3A4.
HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors
The risk of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis increases when fluconazole is coadministered with HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors metabolized through CYP3A4, such as atorvastatin and simvastatin, or through CYP2C9, such as fluvastatin. If concomitant therapy is necessary, the patient should be observed for symptoms of myopathy and rhabdomyolysis and creatinine kinase should be monitored. HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors should be discontinued if a marked increase in creatinine kinase is observed or myopathy/rhabdomyolysis is diagnosed or suspected.
Losartan
Fluconazole inhibits the metabolism of losartan to its active metabolite (E-31 74) which is responsible for most of the angiotensin II-receptor antagonism which occurs during treatment with losartan. Patients should have their blood pressure monitored continuously.
Methadone
Fluconazole may enhance the serum concentration of methadone. Dosage adjustment of methadone may be necessary.
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The Cmax and AUC of flurbiprofen were increased by 23% and 81%, respectively, when coadministered with fluconazole compared to administration of flurbiprofen alone. Similarly, the Cmax and AUC of the pharmacologically active isomer [S-(+)-ibuprofen] were increased by 15% and 82%, respectively, when fluconazole was coadministered with racemic ibuprofen (400 mg) compared to administration of racemic ibuprofen alone.
Although not specifically studied, fluconazole has the potential to increase the systemic exposure of other NSAIDs that are metabolized by CYP2C9 (e.g., naproxen, lornoxicam, meloxicam, diclofenac). Frequent monitoring for adverse events and toxicity related to NSAIDs is recommended. Adjustment of dosage of NSAIDs may be needed.
Prednisone
There was a case report that a liver-transplanted patient treated with prednisone developed acute adrenal cortex insufficiency when a three month therapy with fluconazole was discontinued. The discontinuation of fluconazole presumably caused an enhanced CYP3A4 activity which led to increased metabolism of prednisone. Patients on long-term treatment with fluconazole and prednisone should be carefully monitored for adrenal cortex insufficiency when fluconazole is discontinued.
Saquinavir
Fluconazole increases the AUC of saquinavir by approximately 50%, Cmax by approximately 55%, and decreases clearance of saquinavir by approximately 50% due to inhibition of saquinavir's hepatic metabolism by CYP3A4 and inhibition of P-glycoprotein. Dosage adjustment of saquinavir may be necessary.
Sirolimus
Fluconazole increases plasma concentrations of sirolimus presumably by inhibiting the metabolism of sirolimus via CYP3A4 and P-glycoprotein. This combination may be used with a dosage adjustment of sirolimus depending on the effect/concentration measurements.
Vinca Alkaloids
Although not studied, fluconazole may increase the plasma levels of the vinca alkaloids (e.g., vincristine and vinblastine) and lead to neurotoxicity, which is possibly due to an inhibitory effect on CYP3A4.
Vitamin A
Based on a case report in one patient receiving combination therapy with all-trans-retinoid acid (an acid form of vitamin A) and fluconazole, CNS related undesirable effects have developed in the form of pseudotumour cerebri, which disappeared after discontinuation of fluconazole treatment. This combination may be used but the incidence of CNS related undesirable effects should be borne in mind.
Zidovudine
Fluconazole increases Cmax and AUC of zidovudine by 84% and 74%, respectively, due to an approximately 45% decrease in oral zidovudine clearance. The half-life of zidovudine was likewise prolonged by approximately 128% following combination therapy with fluconazole. Patients receiving this combination should be monitored for the development of zidovudine-related adverse reactions. Dosage reduction of zidovudine may be considered.
Physicians should be aware that interaction studies with medications other than those listed in the CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY section have not been conducted, but such interactions may occur.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, and Impairment of Fertility
Fluconazole showed no evidence of carcinogenic potential in mice and rats treated orally for 24 months at doses of 2.5, 5, or 10 mg/kg/day (approximately 2–7× the recommended human dose). Male rats treated with 5 and 10 mg/kg/day had an increased incidence of hepatocellular adenomas.
Fluconazole, with or without metabolic activation, was negative in tests for mutagenicity in 4 strains of S. typhimurium, and in the mouse lymphoma L5178Y system. Cytogenetic studies in vivo (murine bone marrow cells, following oral administration of fluconazole) and in vitro (human lymphocytes exposed to fluconazole at 1000 µg/mL) showed no evidence of chromosomal mutations.
Fluconazole did not affect the fertility of male or female rats treated orally with daily doses of 5, 10, or 20 mg/kg or with parenteral doses of 5, 25, or 75 mg/kg, although the onset of parturition was slightly delayed at 20 mg/kg PO. In an intravenous perinatal study in rats at 5, 20, and 40 mg/kg, dystocia and prolongation of parturition were observed in a few dams at 20 mg/kg (approximately 5–15× the recommended human dose) and 40 mg/kg, but not at 5 mg/kg. The disturbances in parturition were reflected by a slight increase in the number of stillborn pups and decrease of neonatal survival at these dose levels. The effects on parturition in rats are consistent with the species specific estrogen-lowering property produced by high doses of fluconazole. Such a hormone change has not been observed in women treated with fluconazole. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.)
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category D
All other indications
A few published case reports describe a rare pattern of distinct congenital anomalies in infants exposed in utero to high dose maternal fluconazole (400–800 mg/day) during most or all of the first trimester. These reported anomalies are similar to those seen in animal studies. If this drug is used during pregnancy, or if the patient becomes pregnant while taking the drug, the patient should be informed of the potential hazard to the fetus. (See WARNINGS, Use in Pregnancy.)
Human Data
Several published epidemiologic studies do not suggest an increased risk of congenital anomalies associated with low dose exposure to fluconazole in pregnancy (most subjects received a single oral dose of 150 mg). A few published case reports describe a distinctive and rare pattern of birth defects among infants whose mothers received high-dose (400–800 mg/day) fluconazole during most or all of the first trimester of pregnancy. The features seen in these infants include: brachycephaly, abnormal facies, abnormal calvarial development, cleft palate, femoral bowing, thin ribs and long bones, arthrogryposis, and congenital heart disease. These effects are similar to those seen in animal studies.
Animal Data
Fluconazole was administered orally to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis in two studies at doses of 5, 10, and 20 mg/kg and at 5, 25, and 75 mg/kg, respectively. Maternal weight gain was impaired at all dose levels (approximately 0.25 to 4 times the 400 mg clinical dose based on BSA), and abortions occurred at 75 mg/kg (approximately 4 times the 400 mg clinical dose based on BSA); no adverse fetal effects were observed.
In several studies in which pregnant rats received fluconazole orally during organogenesis, maternal weight gain was impaired and placental weights were increased at 25 mg/kg. There were no fetal effects at 5 or 10 mg/kg; increases in fetal anatomical variants (supernumerary ribs, renal pelvis dilation) and delays in ossification were observed at 25 and 50 mg/kg and higher doses. At doses ranging from 80 to 320 mg/kg (approximately 2 to 8 times the 400 mg clinical dose based on BSA), embryolethality in rats was increased and fetal abnormalities included wavy ribs, cleft palate, and abnormal cranio-facial ossification. These effects are consistent with the inhibition of estrogen synthesis in rats and may be a result of known effects of lowered estrogen on pregnancy, organogenesis, and parturition.
Nursing Mothers
Fluconazole is secreted in human milk at concentrations similar to maternal plasma concentrations. Caution should be exercised when fluconazole is administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
An open-label, randomized, controlled trial has shown fluconazole to be effective in the treatment of oropharyngeal candidiasis in children 6 months to 13 years of age. (See CLINICAL STUDIES.)
The use of fluconazole in children with cryptococcal meningitis, Candida esophagitis, or systemic Candida infections is supported by the efficacy shown for these indications in adults and by the results from several small noncomparative pediatric clinical studies. In addition, pharmacokinetic studies in children (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY) have established a dose proportionality between children and adults. (See DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
In a noncomparative study of children with serious systemic fungal infections, most of which were candidemia, the effectiveness of fluconazole was similar to that reported for the treatment of candidemia in adults. Of 17 subjects with culture-confirmed candidemia, 11 of 14 (79%) with baseline symptoms (3 were asymptomatic) had a clinical cure; 13/15 (87%) of evaluable patients had a mycologic cure at the end of treatment but two of these patients relapsed at 10 and 18 days, respectively, following cessation of therapy.
The efficacy of fluconazole for the suppression of cryptococcal meningitis was successful in 4 of 5 children treated in a compassionate-use study of fluconazole for the treatment of life-threatening or serious mycosis. There is no information regarding the efficacy of fluconazole for primary treatment of cryptococcal meningitis in children.
The safety profile of fluconazole in children has been studied in 577 children ages 1 day to 17 years who received doses ranging from 1 to 15 mg/kg/day for 1 to 1,616 days. (See ADVERSE REACTIONS.)
Efficacy of fluconazole has not been established in infants less than 6 months of age. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.) A small number of patients (29) ranging in age from 1 day to 6 months have been treated safely with fluconazole.
Geriatric Use
In non-AIDS patients, side effects possibly related to fluconazole treatment were reported in fewer patients aged 65 and older (9%, n =339) than for younger patients (14%, n=2240). However, there was no consistent difference between the older and younger patients with respect to individual side effects. Of the most frequently reported (>1%) side effects, rash, vomiting, and diarrhea occurred in greater proportions of older patients. Similar proportions of older patients (2.4%) and younger patients (1.5%) discontinued fluconazole therapy because of side effects. In post-marketing experience, spontaneous reports of anemia and acute renal failure were more frequent among patients 65 years of age or older than in those between 12 and 65 years of age. Because of the voluntary nature of the reports and the natural increase in the incidence of anemia and renal failure in the elderly, it is however not possible to establish a casual relationship to drug exposure.
Controlled clinical trials of fluconazole did not include sufficient numbers of patients aged 65 and older to evaluate whether they respond differently from younger patients in each indication. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients.
Fluconazole is primarily cleared by renal excretion as unchanged drug. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken to adjust dose based on creatinine clearance. It may be useful to monitor renal function. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.)
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Fluconazole is generally well tolerated.
In some patients, particularly those with serious underlying diseases such as AIDS and cancer, changes in renal and hematological function test results and hepatic abnormalities have been observed during treatment with fluconazole and comparative agents, but the clinical significance and relationship to treatment is uncertain.
In Patients Receiving a Single Dose for Vaginal Candidiasis
During comparative clinical studies conducted in the United States, 448 patients with vaginal candidiasis were treated with fluconazole, 150 mg single dose. The overall incidence of side effects possibly related to fluconazole was 26%. In 422 patients receiving active comparative agents, the incidence was 16%. The most common treatment-related adverse events reported in the patients who received 150 mg single dose fluconazole for vaginitis were headache (13%), nausea (7%), and abdominal pain (6%). Other side effects reported with an incidence equal to or greater than 1% included diarrhea (3%), dyspepsia (1%), dizziness (1%), and taste perversion (1%). Most of the reported side effects were mild to moderate in severity. Rarely, angioedema and anaphylactic reaction have been reported in marketing experience.
In Patients Receiving Multiple Doses for Other Infections
Sixteen percent of over 4000 patients treated with fluconazole in clinical trials of 7 days or more experienced adverse events. Treatment was discontinued in 1.5% of patients due to adverse clinical events and in 1.3% of patients due to laboratory test abnormalities.
Clinical adverse events were reported more frequently in HIV infected patients (21%) than in non-HIV infected patients (13%); however, the patterns in HIV infected and non-HIV infected patients were similar. The proportions of patients discontinuing therapy due to clinical adverse events were similar in the two groups (1.5%).
The following treatment-related clinical adverse events occurred at an incidence of 1% or greater in 4048 patients receiving fluconazole for 7 or more days in clinical trials: nausea 3.7%, headache 1.9%, skin rash 1.8%, vomiting 1.7%, abdominal pain 1.7%, and diarrhea 1.5%.
Hepatobiliary
In combined clinical trials and marketing experience, there have been rare cases of serious hepatic reactions during treatment with fluconazole. (See WARNINGS.) The spectrum of these hepatic reactions has ranged from mild transient elevations in transaminases to clinical hepatitis, cholestasis and fulminant hepatic failure, including fatalities. Instances of fatal hepatic reactions were noted to occur primarily in patients with serious underlying medical conditions (predominantly AIDS or malignancy) and often while taking multiple concomitant medications. Transient hepatic reactions, including hepatitis and jaundice, have occurred among patients with no other identifiable risk factors. In each of these cases, liver function returned to baseline on discontinuation of fluconazole.
In two comparative trials evaluating the efficacy of fluconazole for the suppression of relapse of cryptococcal meningitis, a statistically significant increase was observed in median AST (SGOT) levels from a baseline value of 30 IU/L to 41 IU/L in one trial and 34 IU/L to 66 IU/L in the other. The overall rate of serum transaminase elevations of more than 8 times the upper limit of normal was approximately 1% in fluconazole-treated patients in clinical trials. These elevations occurred in patients with severe underlying disease, predominantly AIDS or malignancies, most of whom were receiving multiple concomitant medications, including many known to be hepatotoxic. The incidence of abnormally elevated serum transaminases was greater in patients taking fluconazole concomitantly with one or more of the following medications: rifampin, phenytoin, isoniazid, valproic acid, or oral sulfonylurea hypoglycemic agents.
Post-Marketing Experience
In addition, the following adverse events have occurred during post-marketing experience.
Immunologic: In rare cases, anaphylaxis (including angioedema, face edema, and pruritus) has been reported.
Body as a Whole: Asthenia, fatigue, fever, malaise.
Cardiovascular: QT prolongation, torsade de pointes. (See PRECAUTIONS.)
Central Nervous System: Seizures, dizziness.
Hematopoietic and Lymphatic: Leukopenia, including neutropenia and agranulocytosis, thrombocytopenia.
Metabolic: Hypercholesterolemia, hypertriglyceridemia, hypokalemia.
Gastrointestinal: Cholestasis, dry mouth, hepatocellular damage, dyspepsia, vomiting.
Other Senses: Taste perversion.
Musculoskeletal System: myalgia.
Nervous System: Insomnia, paresthesia, somnolence, tremor, vertigo.
Skin and Appendages: Acute generalized exanthematous-pustulosis, drug eruption, increased sweating, exfoliative skin disorders including Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis (see WARNINGS), alopecia.
Adverse Reactions in Children
The pattern and incidence of adverse events and laboratory abnormalities recorded during pediatric clinical trials are comparable to those seen in adults.
In Phase II/III clinical trials conducted in the United States and in Europe, 577 pediatric patients, ages 1 day to 17 years were treated with fluconazole at doses up to 15 mg/kg/day for up to 1,616 days. Thirteen percent of children experienced treatment-related adverse events. The most commonly reported events were vomiting (5%), abdominal pain (3%), nausea (2%), and diarrhea (2%). Treatment was discontinued in 2.3% of patients due to adverse clinical events and in 1.4% of patients due to laboratory test abnormalities. The majority of treatment-related laboratory abnormalities were elevations of transaminases or alkaline phosphatase.
Percentage of Patients With Treatment-Related Side Effects Fluconazole Comparative Agents (N=577) (N=451) With any side effect 13.0 9.3 Vomiting 5.4 5.1 Abdominal pain 2.8 1.6 Nausea 2.3 1.6 Diarrhea 2.1 2.2 -
OVERDOSAGE
There have been reports of overdose with fluconazole accompanied by hallucination and paranoid behavior.
In the event of overdose, symptomatic treatment (with supportive measures and gastric lavage if clinically indicated) should be instituted.
Fluconazole is largely excreted in urine. A three-hour hemodialysis session decreases plasma levels by approximately 50%.
In mice and rats receiving very high doses of fluconazole, clinical effects in both species included decreased motility and respiration, ptosis, lacrimation, salivation, urinary incontinence, loss of righting reflex, and cyanosis; death was sometimes preceded by clonic convulsions.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage and Administration in Adults
Multiple Dose
SINCE ORAL ABSORPTION IS RAPID AND ALMOST COMPLETE, THE DAILY DOSE OF FLUCONAZOLE IS THE SAME FOR ORAL (TABLETS AND SUSPENSION) AND INTRAVENOUS ADMINISTRATION. In general, a loading dose of twice the daily dose is recommended on the first day of therapy to result in plasma concentrations close to steady-state by the second day of therapy.
The daily dose of fluconazole for the treatment of infections other than vaginal candidiasis should be based on the infecting organism and the patient's response to therapy. Treatment should be continued until clinical parameters or laboratory tests indicate that active fungal infection has subsided. An inadequate period of treatment may lead to recurrence of active infection. Patients with AIDS and cryptococcal meningitis or recurrent oropharyngeal candidiasis usually require maintenance therapy to prevent relapse.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
The recommended dosage of fluconazole for oropharyngeal candidiasis is 200 mg on the first day, followed by 100 mg once daily. Clinical evidence of oropharyngeal candidiasis generally resolves within several days, but treatment should be continued for at least 2 weeks to decrease the likelihood of relapse.
Esophageal candidiasis
The recommended dosage of fluconazole for esophageal candidiasis is 200 mg on the first day, followed by 100 mg once daily. Doses up to 400 mg/day may be used, based on medical judgment of the patient's response to therapy. Patients with esophageal candidiasis should be treated for a minimum of three weeks and for at least two weeks following resolution of symptoms.
Systemic Candida infections
For systemic Candida infections including candidemia, disseminated candidiasis, and pneumonia, optimal therapeutic dosage and duration of therapy have not been established. In open, noncomparative studies of small numbers of patients, doses of up to 400 mg daily have been used.
Urinary tract infections and peritonitis
For the treatment of Candida urinary tract infections and peritonitis, daily doses of 50–200 mg have been used in open, noncomparative studies of small numbers of patients.
Cryptococcal meningitis
The recommended dosage for treatment of acute cryptococcal meningitis is 400 mg on the first day, followed by 200 mg once daily. A dosage of 400 mg once daily may be used, based on medical judgment of the patient's response to therapy. The recommended duration of treatment for initial therapy of cryptococcal meningitis is 10–12 weeks after the cerebrospinal fluid becomes culture negative. The recommended dosage of fluconazole for suppression of relapse of cryptococcal meningitis in patients with AIDS is 200 mg once daily.
Prophylaxis in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation
The recommended fluconazole daily dosage for the prevention of candidiasis in patients undergoing bone marrow transplantation is 400 mg, once daily. Patients who are anticipated to have severe granulocytopenia (less than 500 neutrophils per cu mm) should start fluconazole prophylaxis several days before the anticipated onset of neutropenia, and continue for 7 days after the neutrophil count rises above 1000 cells per cu mm.
Dosage and Administration in Children
The following dose equivalency scheme should generally provide equivalent exposure in pediatric and adult patients:
Pediatric Patients Adults - * Some older children may have clearances similar to that of adults. Absolute doses exceeding 600 mg/day are not recommended.
3 mg/kg 100 mg 6 mg/kg 200 mg 12* mg/kg 400 mg Experience with fluconazole in neonates is limited to pharmacokinetic studies in premature newborns. (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY.) Based on the prolonged half-life seen in premature newborns (gestational age 26 to 29 weeks), these children, in the first two weeks of life, should receive the same dosage (mg/kg) as in older children, but administered every 72 hours. After the first two weeks, these children should be dosed once daily. No information regarding fluconazole pharmacokinetics in full-term newborns is available.
Oropharyngeal candidiasis
The recommended dosage of fluconazole for oropharyngeal candidiasis in children is 6 mg/kg on the first day, followed by 3 mg/kg once daily. Treatment should be administered for at least 2 weeks to decrease the likelihood of relapse.
Esophageal candidiasis
For the treatment of esophageal candidiasis, the recommended dosage of fluconazole in children is 6 mg/kg on the first day, followed by 3 mg/kg once daily. Doses up to 12 mg/kg/day may be used, based on medical judgment of the patient's response to therapy. Patients with esophageal candidiasis should be treated for a minimum of three weeks and for at least 2 weeks following the resolution of symptoms.
Systemic Candida infections
For the treatment of candidemia and disseminated Candida infections, daily doses of 6–12 mg/kg/day have been used in an open, noncomparative study of a small number of children.
Cryptococcal meningitis
For the treatment of acute cryptococcal meningitis, the recommended dosage is 12 mg/kg on the first day, followed by 6 mg/kg once daily. A dosage of 12 mg/kg once daily may be used, based on medical judgment of the patient's response to therapy. The recommended duration of treatment for initial therapy of cryptococcal meningitis is 10–12 weeks after the cerebrospinal fluid becomes culture negative. For suppression of relapse of cryptococcal meningitis in children with AIDS, the recommended dose of fluconazole is 6 mg/kg once daily.
Dosage In Patients With Impaired Renal Function
Fluconazole is cleared primarily by renal excretion as unchanged drug. There is no need to adjust single dose therapy for vaginal candidiasis because of impaired renal function. In patients with impaired renal function who will receive multiple doses of fluconazole, an initial loading dose of 50 to 400 mg should be given. After the loading dose, the daily dose (according to indication) should be based on the following table:
Creatinine Clearance (mL/min) Percent of Recommended Dose >50 100% ≤50 (no dialysis) 50% Regular dialysis 100% after each dialysis Patients on regular dialysis should receive 100% of the recommended dose after each dialysis; on non-dialysis days, patients should receive a reduced dose according to their creatinine clearance.
These are suggested dose adjustments based on pharmacokinetics following administration of multiple doses. Further adjustment may be needed depending upon clinical condition.
When serum creatinine is the only measure of renal function available, the following formula (based on sex, weight, and age of the patient) should be used to estimate the creatinine clearance in adults:
Males: Weight (kg) × (140 – age)
72 × serum creatinine (mg/100 mL)Females: 0.85 × above value
Although the pharmacokinetics of fluconazole has not been studied in children with renal insufficiency, dosage reduction in children with renal insufficiency should parallel that recommended for adults. The following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance in children:
K × linear length or height (cm)
serum creatinine (mg/100 mL)(Where K=0.55 for children older than 1 year and 0.45 for infants.)
Directions for Mixing the Oral Suspension
Prepare a suspension at time of dispensing as follows: tap bottle until all the powder flows freely. To reconstitute, add 24 mL of distilled water or Purified Water (USP) to fluconazole bottle and shake vigorously to suspend powder. Each bottle will deliver 35 mL of suspension. The concentrations of the reconstituted suspensions are as follows:
Fluconazole Content per Bottle Concentration of Reconstituted Suspension 350 mg 10 mg/mL 1400 mg 40 mg/mL Note: Shake oral suspension well before using. Store reconstituted suspension between 86°F (30°C) and 41°F (5°C) and discard unused portion after 2 weeks. Protect from freezing.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Fluconazole Tablets
Pink trapezoidal tablets containing 100 mg of fluconazole are packaged in bottles or unit dose blisters.
Fluconazole 100 mg Tablets: Embossed with "FLZ 100" on one side with no markings on the other side.
NDC: 59762-5016-1 Bottles of 30
NDC 69189-5016-1 single dose pack with 1 tablet as repackaged by Avera McKennan Hospital
Storage: Store tablets below 86°F (30°C).
Fluconazole for Oral Suspension
Fluconazole for Oral Suspension is supplied as an orange-flavored powder to provide 35 mL per bottle as follows:
NDC: 59762-5029-1 Fluconazole 350 mg per bottle
NDC: 59762-5030-1 Fluconazole 1400 mg per bottleStorage: Store dry powder below 86°F (30°C). Store reconstituted suspension between 86°F (30°C) and 41°F (5°C) and discard unused portion after 2 weeks. Protect from freezing.
-
REFERENCES
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Reference Method for Broth Dilution Antifungal Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Standard-Third Edition. CLSI Document M27-A3, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, PA, 19087, USA, 2008.
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Antifungal Disk Diffusion Susceptibility Testing of Yeasts; Approved Guideline-Second Edition. CLSI Document M44-A2, Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute, 940 West Valley Road, Suite 1400, Wayne, PA, 19087, USA, 2009.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT INFORMATIONFluconazole (fluconazole tablets)
This leaflet contains important information about FLUCONAZOLE (FLEW-kan-a-zol). It is not meant to take the place of your doctor's instructions. Read this information carefully before you take FLUCONAZOLE. Ask your doctor or pharmacist if you do not understand any of this information or if you want to know more about FLUCONAZOLE.
What Is FLUCONAZOLE?
FLUCONAZOLE is a tablet you swallow to treat vaginal yeast infections caused by a yeast called Candida. FLUCONAZOLE helps stop too much yeast from growing in the vagina so the yeast infection goes away.
FLUCONAZOLE is different from other treatments for vaginal yeast infections because it is a tablet taken by mouth. FLUCONAZOLE is also used for other conditions. However, this leaflet is only about using FLUCONAZOLE for vaginal yeast infections. For information about using FLUCONAZOLE for other reasons, ask your doctor or pharmacist. See the section of this leaflet for information about vaginal yeast infections.
What Is a Vaginal Yeast Infection?
It is normal for a certain amount of yeast to be found in the vagina. Sometimes too much yeast starts to grow in the vagina and this can cause a yeast infection. Vaginal yeast infections are common. About three out of every four adult women will have at least one vaginal yeast infection during their life.
Some medicines and medical conditions can increase your chance of getting a yeast infection. If you are pregnant, have diabetes, use birth control pills, or take antibiotics you may get yeast infections more often than other women. Personal hygiene and certain types of clothing may increase your chances of getting a yeast infection. Ask your doctor for tips on what you can do to help prevent vaginal yeast infections.
If you get a vaginal yeast infection, you may have any of the following symptoms:
- itching
- a burning feeling when you urinate
- redness
- soreness
- a thick white vaginal discharge that looks like cottage cheese
What To Tell Your Doctor Before You Start FLUCONAZOLE?
Do not take FLUCONAZOLE if you take certain medicines. They can cause serious problems. Therefore, tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including:
- diabetes medicines such as glyburide, tolbutamide, glipizide
- blood pressure medicines like hydrochlorothiazide, losartan, amlodipine, nifedipine or felodipine
- blood thinners such as warfarin
- cyclosporine, tacrolimus or sirolimus (used to prevent rejection of organ transplants)
- rifampin or rifabutin for tuberculosis
- astemizole for allergies
- phenytoin or carbamazepine to control seizures
- theophylline to control asthma
- cisapride for heartburn
- quinidine (used to correct disturbances in heart rhythm)
- amitriptyline or nortriptyline for depression
- pimozide for psychiatric illness
- amphotericin B or voriconazole for fungal infections
- erythromycin for bacterial infections
- cyclophosphamide or vinca alkaloids such as vincristine or vinblastine for treatment of cancer
- fentanyl, afentanil or methadone for chronic pain
- halofantrine for malaria
- lipid lowering drugs such as atorvastatin, simvastatin, and fluvastatin
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs including celecoxib, ibuprofen, and naproxen
- prednisone, a steroid used to treat skin, gastrointestinal, hematological or respiratory disorders
- antiviral medications used to treat HIV like saquinavir or zidovudine
- tofacitinib for rheumatoid arthritis
- vitamin A nutritional supplement
Since there are many brand names for these medicines, check with your doctor or pharmacist if you have any questions.
- are taking any over-the-counter medicines you can buy without a prescription, including natural or herbal remedies
- have any liver problems.
- have any other medical conditions
- are pregnant, plan to become pregnant, or think you might be pregnant. Your doctor will discuss whether FLUCONAZOLE is right for you.
- are breast-feeding. FLUCONAZOLE can pass through breast milk to the baby.
- are allergic to any other medicines including those used to treat yeast and other fungal infections.
- are allergic to any of the ingredients in FLUCONAZOLE. The main ingredient of FLUCONAZOLE is fluconazole. If you need to know the inactive ingredients, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Who Should Not Take FLUCONAZOLE?
To avoid a possible serious reaction, do NOT take FLUCONAZOLE if you are taking erythromycin, astemizole, pimozide, quinidine, and cisapride (Propulsid®) since it can cause changes in heartbeat in some people if taken with FLUCONAZOLE.
How Should I Take FLUCONAZOLE?
Take FLUCONAZOLE by mouth with or without food. You can take FLUCONAZOLE at any time of the day.
FLUCONAZOLE keeps working for several days to treat the infection. Generally the symptoms start to go away after 24 hours. However, it may take several days for your symptoms to go away completely. If there is no change in your symptoms after a few days, call your doctor.
Just swallow 1 FLUCONAZOLE tablet to treat your vaginal yeast infection.
What Should I Avoid while Taking FLUCONAZOLE?
Some medicines can affect how well FLUCONAZOLE works. Check with your doctor before starting any new medicines within seven days of taking FLUCONAZOLE.
What Are the Possible Side Effects of FLUCONAZOLE?
Like all medicines, FLUCONAZOLE may cause some side effects that are usually mild to moderate.
The most common side effects of FLUCONAZOLE are:
- headache
- diarrhea
- nausea or upset stomach
- dizziness
- stomach pain
- changes in the way food tastes
Allergic reactions to FLUCONAZOLE are rare, but they can be very serious if not treated right away by a doctor. If you cannot reach your doctor, go to the nearest hospital emergency room. Signs of an allergic reaction can include shortness of breath; coughing; wheezing; fever; chills; throbbing of the heart or ears; swelling of the eyelids, face, mouth, neck, or any other part of the body; or skin rash, hives, blisters or skin peeling.
FLUCONAZOLE has been linked to rare cases of serious liver damage, including deaths, mostly in patients with serious medical problems. Call your doctor if your skin or eyes become yellow, your urine turns a darker color, your stools (bowel movements) are light-colored, or if you vomit or feel like vomiting or if you have severe skin itching.
In patients with serious conditions such as AIDS or cancer, rare cases of severe rashes with skin peeling have been reported. Tell your doctor right away if you get a rash while taking FLUCONAZOLE.
FLUCONAZOLE may cause other less common side effects besides those listed here. If you develop any side effects that concern you, call your doctor. For a list of all side effects, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What to Do For an Overdose?
In case of an accidental overdose, call your doctor right away or go to the nearest emergency room.
How to Store FLUCONAZOLE?
Keep FLUCONAZOLE and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General Advice about Prescription Medicines
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for conditions that are mentioned in patient information leaflets. Do not use FLUCONAZOLE for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give FLUCONAZOLE to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This leaflet summarizes the most important information about FLUCONAZOLE. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your pharmacist or doctor for information about FLUCONAZOLE that is written for health professionals.
This product's label may have been updated. For current full prescribing information, please visit www.greenstonellc.com

LAB-0367-9.0
December 2014 - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
FLUCONAZOLE
fluconazole tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 69189-5016(NDC:59762-5016) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FLUCONAZOLE (UNII: 8VZV102JFY) (FLUCONAZOLE - UNII:8VZV102JFY) FLUCONAZOLE 100 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CELLULOSE, MICROCRYSTALLINE (UNII: OP1R32D61U) ANHYDROUS DIBASIC CALCIUM PHOSPHATE (UNII: L11K75P92J) POVIDONES (UNII: FZ989GH94E) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) ALUMINUM OXIDE (UNII: LMI26O6933) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape TRAPEZOID Size 10mm Flavor Imprint Code FLZ;100 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 69189-5016-1 1 in 1 DOSE PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 02/04/2016 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA AUTHORIZED GENERIC NDA019949 02/04/2016 Labeler - Avera McKennan Hospital (068647668) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Avera McKennan Hospital 068647668 relabel(69189-5016) , repack(69189-5016)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
