Cefdinir by Proficient Rx LP CEFDINIR capsule
Cefdinir by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Cefdinir by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Proficient Rx LP. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefdinir and other antibacterial drugs, cefdinir should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by bacteria.
-
DESCRIPTION
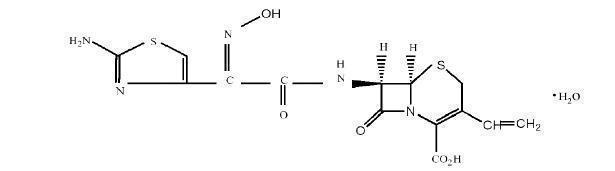
Cefdinir capsules USP contain the active ingredient cefdinir monohydrate, an extended-spectrum, semisynthetic cephalosporin, for oral administration. Chemically, cefdinir USP is [6R-[6α, 7β (Z)]]-7-[[(2-amino-4-thiazolyl)-(hydroxyimino)acetyl]amino]-3-ethenyl-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid. Cefdinir monohydrate is a white to slightly brownish-yellow solid. It is slightly soluble in dilute hydrochloric acid and sparingly soluble in 0.1M pH 7 phosphate buffer. The empirical formula is C14H13N5O5S2.H2O and the molecular weight is 413.47. Cefdinir monohydrate has the structural formula shown below:
Cefdinir Capsules USP contain cefdinir USP equivalent to anhydrous cefdinir 300 mg and the following inactive ingredients: carboxymethylcellulose calcium; croscarmellose sodium; polyoxyl 40 stearate; colloidal silicon dioxide and magnesium stearate. The capsule shells contain FD&C Blue #1, FD&C Green #3, FD&C Red #40, D&C Red #28, D&C Red #33, titanium dioxide and gelatin. Ink constituents are: shellac, dehydrated alcohol, isopropyl alcohol, butyl alcohol, propylene glycol, strong ammonia solution, potassium hydroxide and black iron oxide.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacokinetics and Drug Metabolism
Absorption
Oral Bioavailability:
Maximal plasma cefdinir concentrations occur 2 to 4 hours postdose following capsule or suspension administration. Plasma cefdinir concentrations increase with dose, but the increases are less than dose-proportional from 300 mg (7 mg/kg) to 600 mg (14 mg/kg). Following administration of suspension to healthy adults, cefdinir bioavailability is 120% relative to capsules. Estimated bioavailability of cefdinir capsules is 21% following administration of a 300 mg capsule dose, and 16% following administration of a 600 mg capsule dose. Estimated absolute bioavailability of cefdinir suspension is 25%. Cefdinir oral suspension of 250 mg/5 mL strength was shown to be bioequivalent to the 125 mg/5 mL strength in healthy adults under fasting conditions.
Effect of Food:
The Cmax and AUC of cefdinir from the capsules are reduced by 16% and 10%, respectively, when given with a high-fat meal. In adults given the 250 mg/5 mL oral suspension with a high-fat meal, the Cmax and AUC of cefdinir are reduced by 44% and 33%, respectively. The magnitude of these reductions is not likely to be clinically significant because the safety and efficacy studies of oral suspension in pediatric patients were conducted without regard to food intake. Therefore, cefdinir may be taken without regard to food.
Cefdinir Capsules: Cefdinir plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameter values following administration of single 300 and 600 mg oral doses of cefdinir to adult subjects are presented in the following table:
Mean (±SD) Plasma Cefdinir Pharmacokinetic Parameter Values Following Administration of Capsules to Adult Subjects Dose Cmax
(mcg/mL)tmax
(hr)AUC
(mcghr/mL)300 mg
1.6
(0.55)2.9
(0.89)7.05
(2.17)600 mg
2.87
(1.01)3
(0.66)11.1
(3.87)Cefdinir Suspension: Cefdinir plasma concentrations and pharmacokinetic parameter values following administration of single 7 and 14 mg/kg oral doses of cefdinir to pediatric subjects (age 6 months 12 years) are presented in the following table:
Mean (±SD) Plasma Cefdinir Pharmacokinetic Parameter Values Following Administration of Suspension to Pediatric Subjects Dose Cmax
(mcg/mL)tmax
(hr)AUC
(mcghr/mL)7 mg/kg
2.3
(0.65)2.2
(0.6)8.31
(2.5)14 mg/kg
3.86
(0.62)1.8
(0.4)13.4
(2.64)Distribution:
The mean volume of distribution (Vdarea) of cefdinir in adult subjects is 0.35 L/kg (±0.29); in pediatric subjects (age 6 months to 12 years), cefdinir Vdarea is 0.67 L/kg (±0.38). Cefdinir is 60% to 70% bound to plasma proteins in both adult and pediatric subjects; binding is independent of concentration.
Skin Blister:
In adult subjects, median (range) maximal blister fluid cefdinir concentrations of 0.65 (0.33 to 1.1) and 1.1 (0.49 to 1.9) mcg/mL were observed 4 to 5 hours following administration of 300 and 600 mg doses, respectively. Mean (±SD) blister Cmax and AUC(0 to ∞) values were 48% (±13) and 91% (±18) of corresponding plasma values.
Tonsil Tissue:
In adult patients undergoing elective tonsillectomy, respective median tonsil tissue cefdinir concentrations 4 hours after administration of single 300 and 600 mg doses were 0.25 (0.22 to 0.46) and 0.36 (0.22 to 0.8) mcg/g. Mean tonsil tissue concentrations were 24% (±8) of corresponding plasma concentrations.
Sinus Tissue:
In adult patients undergoing elective maxillary and ethmoid sinus surgery, respective median sinus tissue cefdinir concentrations 4 hours after administration of single 300 and 600 mg doses were <0.12 (<0.12 to 0.46) and 0.21 (<0.12 to 2) mcg/g. Mean sinus tissue concentrations were 16% (±20) of corresponding plasma concentrations.
Lung Tissue:
In adult patients undergoing diagnostic bronchoscopy, respective median bronchial mucosa cefdinir concentrations 4 hours after administration of single 300 and 600 mg doses were 0.78 (<0.06 to 1.33) and 1.14 (<0.06 to 1.92) mcg/mL, and were 31% (±18) of corresponding plasma concentrations. Respective median epithelial lining fluid concentrations were 0.29 (<0.3 to 4.73) and 0.49 (<0.3 to 0.59) mcg/mL, and were 35% (±83) of corresponding plasma concentrations.
Middle Ear Fluid:
In 14 pediatric patients with acute bacterial otitis media, respective median middle ear fluid cefdinir concentrations 3 hours after administration of single 7 and 14 mg/kg doses were 0.21 (<0.09 to 0.94) and 0.72 (0.14 to 1.42) mcg/mL. Mean middle ear fluid concentrations were 15% (±15) of corresponding plasma concentrations.
Metabolism and Excretion:
Cefdinir is not appreciably metabolized. Activity is primarily due to parent drug. Cefdinir is eliminated principally via renal excretion with a mean plasma elimination half-life (t½) of 1.7 (±0.6) hours. In healthy subjects with normal renal function, renal clearance is 2 (±1) mL/min/kg, and apparent oral clearance is 11.6 (±6) and 15.5 (±5.4) mL/min/kg following doses of 300 and 600 mg, respectively. Mean percent of dose recovered unchanged in the urine following 300- and 600 mg doses is 18.4% (±6.4) and 11.6% (±4.6), respectively. Cefdinir clearance is reduced in patients with renal dysfunction (see Special Populations: Patients with Renal Insufficiency).
Because renal excretion is the predominant pathway of elimination, dosage should be adjusted in patients with markedly compromised renal function or who are undergoing hemodialysis (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Special Populations:
Patients with Renal Insufficiency:
Cefdinir pharmacokinetics were investigated in 21 adult subjects with varying degrees of renal function. Decreases in cefdinir elimination rate, apparent oral clearance (CL/F), and renal clearance were approximately proportional to the reduction in creatinine clearance (CLcr). As a result, plasma cefdinir concentrations were higher and persisted longer in subjects with renal impairment than in those without renal impairment. In subjects with CLcr between 30 and 60 mL/min, Cmax and t½ increased by approximately 2 fold and AUC by approximately 3 fold. In subjects with CLcr <30 mL/min, Cmax increased by approximately 2 fold, t½ by approximately 5 fold, and AUC by approximately 6 fold. Dosage adjustment is recommended in patients with markedly compromised renal function (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min; see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hemodialysis:
Cefdinir pharmacokinetics were studied in 8 adult subjects undergoing hemodialysis. Dialysis (4 hours duration) removed 63% of cefdinir from the body and reduced apparent elimination t½ from 16 (±3.5) to 3.2 (±1.2) hours. Dosage adjustment is recommended in this patient population (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Hepatic Disease:
Because cefdinir is predominantly renally eliminated and not appreciably metabolized, studies in patients with hepatic impairment were not conducted. It is not expected that dosage adjustment will be required in this population.
Geriatric Patients:
The effect of age on cefdinir pharmacokinetics after a single 300 mg dose was evaluated in 32 subjects 19 to 91 years of age. Systemic exposure to cefdinir was substantially increased in older subjects (N=16), Cmax by 44% and AUC by 86%. This increase was due to a reduction in cefdinir clearance. The apparent volume of distribution was also reduced, thus no appreciable alterations in apparent elimination t½ were observed (elderly: 2.2 ± 0.6 hours vs young: 1.8 ± 0.4 hours). Since cefdinir clearance has been shown to be primarily related to changes in renal function rather than age, elderly patients do not require dosage adjustment unless they have markedly compromised renal function (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, see Patients with Renal Insufficiency, above).
Microbiology
As with other cephalosporins, bactericidal activity of cefdinir results from inhibition of cell wall synthesis. Cefdinir is stable in the presence of some, but not all, β-lactamase enzymes. As a result, many organisms resistant to penicillins and some cephalosporins are susceptible to cefdinir.
Cefdinir has been shown to be active against most strains of the following microorganisms, both in vitro and in clinical infections as described in INDICATIONS AND USAGE.
Aerobic Gram-Positive Microorganisms
Staphylococcus aureus (including β-lactamase producing strains)
NOTE: Cefdinir is inactive against methicillin-resistant staphylococci.
Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only)
Streptococcus pyogenes
Aerobic Gram-Negative Microorganisms
Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains)
Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains)
Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase producing strains)
The following in vitro data are available, but their clinical significance is unknown.
Cefdinir exhibits in vitro minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) of 1 mcg/mL or less against (≥90%) strains of the following microorganisms; however, the safety and effectiveness of cefdinir in treating clinical infections due to these microorganisms have not been established in adequate and well-controlled clinical trials.
Susceptibility Tests
Dilution Techniques
Quantitative methods are used to determine antimicrobial minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs). These MICs provide estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. The MICs should be determined using a standardized procedure. Standardized procedures are based on a dilution method1 (broth or agar) or equivalent with standardized inoculum concentrations and standardized concentrations of cefdinir powder. The MIC values should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For organisms other than Haemophilus spp. and Streptococcus spp:
MIC (mcg/mL) Interpretation ≤1
Susceptible (S)
2
Intermediate (I)
≥4
Resistant (R)
For Haemophilus spp2:
MIC (mcg/mL)
Interpretation
≤ 1
Susceptible (S)
*The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than Susceptible. Strains yielding MIC results suggestive of a nonsusceptible category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing.
For Streptococcus spp:
Streptococcus pneumoniae that are susceptible to penicillin (MIC 0.06 mcg/mL), or streptococci other than S. pneumoniae that are susceptible to penicillin (MIC 0.12 mcg/mL), can be considered susceptible to cefdinir. Testing of cefdinir against penicillin-intermediate or penicillin-resistant isolates is not recommended. Reliable interpretive criteria for cefdinir are not available.
A report of Susceptible indicates that the pathogen is likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentration usually achievable. A report of Intermediate indicates that the result should be considered equivocal, and, if the microorganism is not fully susceptible to alternative, clinically feasible drugs, the test should be repeated. This category implies possible clinical applicability in body sites where the drug is physiologically concentrated or in situations where high dosage of drug can be used. This category also provides a buffer zone which prevents small uncontrolled technical factors from causing major discrepancies in interpretation. A report of Resistant indicates that the pathogen is not likely to be inhibited if the antimicrobial compound in the blood reaches the concentrations usually achievable; other therapy should be selected.
Standardized susceptibility test procedures require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of laboratory procedures. Standard cefdinir powder should provide the following MIC values:
Microorganism
MIC Range (mcg/mL)
Escherichia coli
ATCC 25922
0.12 to 0.5
Haemophilus influenzae
ATCC 49766*
0.12 to 0.5
Staphylococcus aureus
ATCC 29213
0.12 to 0.5
*This quality control range is applicable only to H. influenzae ATCC 49766 tested by a broth microdilution procedure using HTM.
- 1 National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 4th ed. Approved Standard, NCCLS Document M7-A4, Vol 17(2). NCCLS, Villanova, PA, Jan 1997.
- 2 These interpretive standards are applicable only to broth microdilution susceptibility tests with Haemophilus spp. using Haemophilus Test Medium (HTM). (see reference 1)
Diffusion Techniques
Quantitative methods that require measurement of zone diameters also provide reproducible estimates of the susceptibility of bacteria to antimicrobial compounds. One such standardized procedure3 requires the use of standardized inoculum concentrations. This procedure uses paper disks impregnated with 5 mcg cefdinir to test the susceptibility of microorganisms to cefdinir.
Reports from the laboratory providing results of the standard single-disk susceptibility test with a 5 mcg cefdinir disk should be interpreted according to the following criteria:
For organisms other than Haemophilus spp. and Streptococcus spp4:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation ≥20
Susceptible (S)
17-19
Intermediate (I)
≤16
Resistant (R)
For Haemophilus spp5:
Zone Diameter (mm) Interpretation* - * The current absence of data on resistant strains precludes defining any results other than “Susceptible.” Strains yielding MIC results suggestive of a “nonsusceptible” category should be submitted to a reference laboratory for further testing.
≥20
Susceptible (S)
For Streptococcus spp:
Isolates of Streptococcus pneumoniae should be tested against a 1 mcg oxacillin disk. Isolates with oxacillin zone sizes ≥20 mm are susceptible to penicillin and can be considered susceptible to cefdinir. Streptococci other than S. pneumoniae should be tested with a 10-unit penicillin disk. Isolates with penicillin zone sizes ≥28 mm are susceptible to penicillin and can be considered susceptible to cefdinir.
As with standardized dilution techniques, diffusion methods require the use of laboratory control microorganisms to control the technical aspects of laboratory procedures. For the diffusion technique, the 5-mcg cefdinir disk should provide the following zone diameters in these laboratory quality control strains:
Organism Zone Diameter (mm) - * This quality control range is applicable only to testing of H. influenzae ATCC 49766 using HTM.
Escherichia coli
ATCC 25922
24-28
Haemophilus influenzae
ATCC 49766*
24-31
Staphylococcus aureus
ATCC 25923
25-32
- 3 National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 6th ed. Approved Standard, NCCLS Document M2-A6, Vol 17(1). NCCLS, Villanova, PA, Jan 1997.
- 4 Because certain strains of Citrobacter, Providencia, and Enterobacter spp. have been reported to give false susceptible results with the cefdinir disk, strains of these genera should not be tested and reported with this disk.
- 5 These zone diameter standards are applicable only to tests with Haemophilus spp. using HTM. (see reference 2)
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
To reduce the development of drug-resistant bacteria and maintain the effectiveness of cefdinir and other antibacterial drugs, cefdinir should be used only to treat or prevent infections that are proven or strongly suspected to be caused by susceptible bacteria. When culture and susceptibility information are available, they should be considered in selecting or modifying antibacterial therapy. In the absence of such data, local epidemiology and susceptibility patterns may contribute to the empiric selection of therapy.
Cefdinir capsules are indicated for the treatment of patients with mild to moderate infections caused by susceptible strains of the designated microorganisms in the conditions listed below.
Adults and Adolescents
Community-Acquired Pneumonia caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase producing strains) (see CLINICAL STUDIES).
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Haemophilus parainfluenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase producing strains).
Acute Maxillary Sinusitis caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase producing strains).
NOTE: For information on use in pediatric patients, see Pediatric Use and DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION.
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (see CLINICAL STUDIES).
NOTE: Cefdinir capsules are effective in the eradication of S. pyogenes from the oropharynx. Cefdinir has not, however, been studied for the prevention of rheumatic fever following S. pyogenes pharyngitis/tonsillitis. Only intramuscular penicillin has been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of rheumatic fever.
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including β-lactamase producing strains) and Streptococcus pyogenes.
Pediatric Patients
Acute Bacterial Otitis Media caused by Haemophilus influenzae (including β-lactamase producing strains), Streptococcus pneumoniae (penicillin-susceptible strains only), and Moraxella catarrhalis (including β-lactamase producing strains).
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis caused by Streptococcus pyogenes (see CLINICAL STUDIES).
NOTE: Cefdinir capsules are effective in the eradication of S. pyogenes from the oropharynx. Cefdinir capsules has not, however, been studied for the prevention of rheumatic fever following S. pyogenes pharyngitis/tonsillitis. Only intramuscular penicillin has been demonstrated to be effective for the prevention of rheumatic fever.
Uncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections caused by Staphylococcus aureus (including β-lactamase producing strains) and Streptococcus pyogenes.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
BEFORE THERAPY WITH CEFDINIR IS INSTITUTED, CAREFUL INQUIRY SHOULD BE MADE TO DETERMINE WHETHER THE PATIENT HAS HAD PREVIOUS HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS TO CEFDINIR, OTHER CEPHALOSPORINS, PENICILLINS, OR OTHER DRUGS. IF CEFDINIR IS TO BE GIVEN TO PENICILLIN-SENSITIVE PATIENTS, CAUTION SHOULD BE EXERCISED BECAUSE CROSS-HYPERSENSITIVITY AMONG β-LACTAM ANTIBIOTICS HAS BEEN CLEARLY DOCUMENTED AND MAY OCCUR IN UP TO 10% OF PATIENTS WITH A HISTORY OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. IF AN ALLERGIC REACTION TO CEFDINIR OCCURS, THE DRUG SHOULD BE DISCONTINUED. SERIOUS ACUTE HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS MAY REQUIRE TREATMENT WITH EPINEPHRINE AND OTHER EMERGENCY MEASURES, INCLUDING OXYGEN, INTRAVENOUS FLUIDS, INTRAVENOUS ANTIHISTAMINES, CORTICOSTEROIDS, PRESSOR AMINES, AND AIRWAY MANAGEMENT, AS CLINICALLY INDICATED.
Clostridium difficile associated diarrhea (CDAD) has been reported with use of nearly all antibacterial agents, including cefdinir, and may range in severity from mild diarrhea to fatal colitis. Treatment with antibacterial agents alters the normal flora of the colon leading to overgrowth of C. difficile.
C. difficile produces toxins A and B which contribute to the development of CDAD. Hypertoxin producing strains of C. difficile cause increased morbidity and mortality, as these infections can be refractory to antimicrobial therapy and may require colectomy. CDAD must be considered in all patients who present with diarrhea following antibiotic use. Careful medical history is necessary since CDAD has been reported to occur over two months after the administration of antibacterial agents.
If CDAD is suspected or confirmed, ongoing antibiotic use not directed against C. difficile may need to be discontinued. Appropriate fluid and electrolyte management, protein supplementation, antibiotic treatment of C. difficile, and surgical evaluation should be instituted as clinically indicated.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Prescribing cefdinir in the absence of a proven or strongly suspected bacterial infection or a prophylactic indication is unlikely to provide benefit to the patient and increases the risk of the development of drug-resistant bacteria.
As with other broad-spectrum antibiotics, prolonged treatment may result in the possible emergence and overgrowth of resistant organisms. Careful observation of the patient is essential. If superinfection occurs during therapy, appropriate alternative therapy should be administered.
Cefdinir, as with other broad-spectrum antimicrobials (antibiotics), should be prescribed with caution in individuals with a history of colitis.
In patients with transient or persistent renal insufficiency (creatinine clearance <30 mL/min), the total daily dose of cefdinir should be reduced because high and prolonged plasma concentrations of cefdinir can result following recommended doses (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
Information for Patients
Patients should be counseled that antibacterial drugs including cefdinir should only be used to treat bacterial infections. They do not treat viral infections (e.g., the common cold). When cefdinir is prescribed to treat a bacterial infection, patients should be told that although it is common to feel better early in the course of therapy, the medication should be taken exactly as directed. Skipping doses or not completing the full course of therapy may (1) decrease the effectiveness of the immediate treatment and (2) increase the likelihood that bacteria will develop resistance and will not be treatable by cefdinir or other antibacterial drugs in the future.
Antacids containing magnesium or aluminum interfere with the absorption of cefdinir. If this type of antacid is required during cefdinir therapy, cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the antacid.
Iron supplements, including multivitamins that contain iron, interfere with the absorption of cefdinir. If iron supplements are required during cefdinir therapy, cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the supplement.
Iron-fortified infant formula does not significantly interfere with the absorption of cefdinir.
Diarrhea is a common problem caused by antibiotics which usually ends when the antibiotic is discontinued. Sometimes after starting treatment with antibiotics, patients can develop watery and bloody stools (with or without stomach cramps and fever) even as late as two or more months after having taken the last dose of the antibiotic. If this occurs, patients should contact their physician as soon as possible.
Drug Interactions
Antacids:
(aluminum- or magnesium-containing): Concomitant administration of 300 mg cefdinir capsules with 30 mL Maalox® TC suspension reduces the rate (Cmax) and extent (AUC) of absorption by approximately 40%. Time to reach Cmax is also prolonged by 1 hour. There are no significant effects on cefdinir pharmacokinetics if the antacid is administered 2 hours before or 2 hours after cefdinir. If antacids are required during cefdinir therapy, cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the antacid.
Probenecid:
As with other β-lactam antibiotics, probenecid inhibits the renal excretion of cefdinir, resulting in an approximate doubling in AUC, a 54% increase in peak cefdinir plasma levels, and a 50% prolongation in the apparent elimination t½.
Iron Supplements and Foods Fortified With Iron:
Concomitant administration of cefdinir with a therapeutic iron supplement containing 60 mg of elemental iron (as FeSO4) or vitamins supplemented with 10 mg of elemental iron reduced extent of absorption by 80% and 31%, respectively. If iron supplements are required during cefdinir therapy, cefdinir should be taken at least 2 hours before or after the supplement.
The effect of foods highly fortified with elemental iron (primarily iron-fortified breakfast cereals) on cefdinir absorption has not been studied.
Concomitantly administered iron-fortified infant formula (2.2 mg elemental iron/6 oz) has no significant effect on cefdinir pharmacokinetics.
There have been reports of reddish stools in patients receiving cefdinir. In many cases, patients were also receiving iron-containing products. The reddish color is due to the formation of a nonabsorbable complex between cefdinir or its breakdown products and iron in the gastrointestinal tract.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
A false-positive reaction for ketones in the urine may occur with tests using nitroprusside, but not with those using nitroferricyanide. The administration of cefdinir may result in a false-positive reaction for glucose in urine using Clinitest®, Benedict’s solution, or Fehling's solution. It is recommended that glucose tests based on enzymatic glucose oxidase reactions (such as Clinistix® or Tes-Tape®) be used. Cephalosporins are known to occasionally induce a positive direct Coombs’ test.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
The carcinogenic potential of cefdinir has not been evaluated. No mutagenic effects were seen in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames) or point mutation assay at the hypoxanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase locus (HGPRT) in V79 Chinese hamster lung cells. No clastogenic effects were observed in vitro in the structural chromosome aberration assay in V79 Chinese hamster lung cells or in vivo in the micronucleus assay in mouse bone marrow. In rats, fertility and reproductive performance were not affected by cefdinir at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (70 times the human dose based on mg/kg/day, 11 times based on mg/m2/day).
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category B:
Cefdinir was not teratogenic in rats at oral doses up to 1000 mg/kg/day (70 times the human dose based on mg/kg/day, 11 times based on mg/m2/day) or in rabbits at oral doses up to 10 mg/kg/day (0.7 times the human dose based on mg/kg/day, 0.23 times based on mg/m2/day). Maternal toxicity (decreased body weight gain) was observed in rabbits at the maximum tolerated dose of 10 mg/kg/day without adverse effects on offspring. Decreased body weight occurred in rat fetuses at ≥100 mg/kg/day, and in rat offspring at ≥32 mg/kg/day. No effects were observed on maternal reproductive parameters or offspring survival, development, behavior, or reproductive function.
There are, however, no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
Nursing Mothers
Following administration of single 600 mg doses, cefdinir was not detected in human breast milk.
Pediatric Use
Safety and efficacy in neonates and infants less than 6 months of age have not been established. Use of cefdinir for the treatment of acute maxillary sinusitis in pediatric patients (age 6 months through 12 years) is supported by evidence from adequate and well-controlled studies in adults and adolescents, the similar pathophysiology of acute sinusitis in adult and pediatric patients, and comparative pharmacokinetic data in the pediatric population.
Geriatric Use
Efficacy is comparable in geriatric patients and younger adults. While cefdinir has been well-tolerated in all age groups, in clinical trials geriatric patients experienced a lower rate of adverse events, including diarrhea, than younger adults. Dose adjustment in elderly patients is not necessary unless renal function is markedly compromised (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION).
-
ADVERSE EVENTS
Clinical Trials - Cefdinir Capsules (Adult and Adolescent Patients)
In clinical trials, 5093 adult and adolescent patients (3841 U.S. and 1252 non-U.S.) were treated with the recommended dose of cefdinir capsules (600 mg/day). Most adverse events were mild and self-limiting. No deaths or permanent disabilities were attributed to cefdinir. One hundred forty-seven of 5093 (3%) patients discontinued medication due to adverse events thought by the investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely associated with cefdinir therapy. The discontinuations were primarily for gastrointestinal disturbances, usually diarrhea or nausea. Nineteen of 5093 (0.4%) patients were discontinued due to rash thought related to cefdinir administration.
In the U.S., the following adverse events were thought by investigators to be possibly, probably, or definitely related to cefdinir capsules in multiple-dose clinical trials (N = 3841 cefdinir-treated patients):
ADVERSE EVENTS ASSOCIATED WITH CEFDINIR CAPSULES U.S. TRIALS IN ADULT AND ADOLESCENT PATIENTS (N=3841)* Incidence 1%
Diarrhea
15%
Vaginal moniliasis
4% of women
Nausea
3%
Headache
2%
Abdominal pain1%
1%
Vaginitis
1% of women
Incidence <1% but >0.1%
Rash
0.9%
Dyspepsia
0.7%
Flatulence
0.7%
Vomiting
0.7%
Abnormal stools
0.3%
Anorexia
0.3%
Constipation
0.3%
Dizziness
0.3%
Dry mouth
0.3%
Asthenia
0.2%
Insomnia
0.2%
Leukorrhea
0.2% of women
Moniliasis
0.2%
Pruritus
0.2%
Somnolence
0.2%
*1733 males, 2108 females
The following laboratory value changes of possible clinical significance, irrespective of relationship to therapy with cefdinir, were seen during clinical trials conducted in the U.S.:
LABORATORY VALUE CHANGES OBSERVED WITH CEFDINIR CAPSULES U.S. TRIALS IN ADULT AND ADOLESCENT PATIENTS (N=3841) Incidence 1%
Urine leukocytes
2%
Urine protein
2%
Gamma-glutamyltransferase*
1%
Lymphocytes, Lymphocytes
1%, 0.2%
Microhematuria
1%
Incidence <1% but >0.1%
Glucose*
0.9%
Urine glucose
0.9%
White blood cells, White blood cells
0.9%, 0.7%
Alanine aminotransferase (ALT)
0.7%
Eosinophils
0.7%
Urine specific gravity, Urine specific gravity*
0.6%, 0.2%
Bicarbonate*
0.6%
Phosphorus, Phosphorus*
0.6%, 0.3%
Aspartate aminotransferase (AST)
0.4%
Alkaline phosphatase
0.3%
Blood urea nitrogen (BUN)
0.3%
Hemoglobin
0.3%
Polymorphonuclear neutrophils (PMNs),PMNs
0.3%, 0.2%
Bilirubin
0.2%
Lactate dehydrogenase*
0.2%
Platelets
0.2%
Potassium*
0.2%
Urine pH*
0.2%
*N<3841 for these parameters
Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse experiences and altered laboratory tests, regardless of their relationship to cefdinir, have been reported during extensive postmarketing experience, beginning with approval in Japan in 1991: shock, anaphylaxis with rare cases of fatality, facial and laryngeal edema, feeling of suffocation, serum sickness-like reactions, conjunctivitis, stomatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, erythema nodosum, acute hepatitis, cholestasis, fulminant hepatitis, hepatic failure, jaundice, increased amylase, acute enterocolitis, bloody diarrhea, hemorrhagic colitis, melena, pseudomembranous colitis, pancytopenia, granulocytopenia, leucopenia, thrombocytopenia, idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura, hemolytic anemia, acute respiratory failure, asthmatic attack, drug-induced pneumonia, eosinophilic pneumonia, idiopathic interstitial pneumonia, fever, acute renal failure, nephropathy, bleeding tendency, coagulation disorder, disseminated intravascular coagulation, upper GI bleed, peptic ulcer, ileus, loss of consciousness, allergic vasculitis, possible cefdinir-diclofenac interaction, cardiac failure, chest pain, myocardial infarction, hypertension, involuntary movements, and rhabdomyolysis.
Cephalosporin Class Adverse Events
The following adverse events and altered laboratory tests have been reported for cephalosporin-class antibiotics in general:
Allergic reactions, anaphylaxis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis, renal dysfunction, toxic nephropathy, hepatic dysfunction including cholestasis, aplastic anemia, hemolytic anemia, hemorrhage, false-positive test for urinary glucose, neutropenia, pancytopenia, and agranulocytosis. Pseudomembranous colitis symptoms may begin during or after antibiotic treatment (see WARNINGS).
Several cephalosporins have been implicated in triggering seizures, particularly in patients with renal impairment when the dosage was not reduced (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION and OVERDOSAGE). If seizures associated with drug therapy occur, the drug should be discontinued. Anticonvulsant therapy can be given if clinically indicated.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Information on cefdinir overdosage in humans is not available. In acute rodent toxicity studies, a single oral 5600 mg/kg dose produced no adverse effects. Toxic signs and symptoms following overdosage with other β-lactam antibiotics have included nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, diarrhea, and convulsions. Hemodialysis removes cefdinir from the body. This may be useful in the event of a serious toxic reaction from overdosage, particularly if renal function is compromised.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
(see INDICATIONS AND USAGE for Indicated Pathogens)
The recommended dosage and duration of treatment for infections in adults and adolescents are described in the following chart; the total daily dose for all infections is 600 mg. Once-daily dosing for 10 days is as effective as BID dosing. Once-daily dosing has not been studied in pneumonia or skin infections; therefore, Cefdinir Capsules should be administered twice daily in these infections. Cefdinir Capsules may be taken without regard to meals.
Adults and Adolescents (Age 13 Years and Older) Type of Infection
Dosage
Duration
Community-Acquired Pneumonia
300 mg q12h
10 days
Acute Exacerbations of Chronic Bronchitis
300 mg q12h
or
600 mg q24h5 to 10 days
10 daysAcute Maxillary Sinusitis
300 mg q12h
or
600 mg q24h10 days
10 daysPharyngitis/Tonsillitis
300 mg q12h
or
600 mg q24h5 to 10 days
10 daysUncomplicated Skin and Skin Structure Infections
300 mg q12h
10 days
Patients With Renal Insufficiency
For adult patients with creatinine clearance <30 mL/min, the dose of cefdinir should be 300 mg given once daily.
Creatinine clearance is difficult to measure in outpatients. However, the following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance (CLcr) in adult patients. For estimates to be valid, serum creatinine levels should reflect steady-state levels of renal function.
Males: CLcr = (weight) (140 – age)
(72) (serum creatinine)
Females: CLcr = 0.85 x above value
where creatinine clearance is in mL/min, age is in years, weight is in kilograms, and serum creatinine is in mg/dL6.
The following formula may be used to estimate creatinine clearance in pediatric patients:
CLcr = K x body length or height
serum creatinine
where K = 0.55 for pediatric patients older than 1 year7 and 0.45 for infants (up to 1 year)8.
In the above equation, creatinine clearance is in mL/min/1.73 m2, body length or height is in centimeters, and serum creatinine is in mg/dL.
For pediatric patients with a creatinine clearance of <30 mL/min/1.73 m2, the dose of cefdinir should be 7 mg/kg (up to 300 mg) given once daily.
- 6 Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976; 16:31-41.
- 7 Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM, Spitzer A. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 1976; 58:259-63.
- 8 Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatrics 1984; 104:849-54.
Patients on Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis removes cefdinir from the body. In patients maintained on chronic hemodialysis, the recommended initial dosage regimen is a 300 mg or 7 mg/kg dose every other day. At the conclusion of each hemodialysis session, 300 mg (or 7 mg/kg) should be given. Subsequent doses (300 mg or 7 mg/kg) are then administered every other day.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Cefdinir Capsules USP, 300 mg: Purple Opaque Cap / Teal Opaque body, size “0” hard gelatin capsules imprinted “C” on cap & “300” on body with black ink, filled with off-white to yellow granular powder.
They are supplied as follows:
Bottles of 20 NDC: 63187-593-20
Bottles of 28 NDC: 63187-593-28
Bottles of 30 NDC: 63187-593-30
Bottles of 40 NDC: 63187-593-40
Bottles of 60 NDC: 63187-593-60
Store the capsules at 20 to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
CLINICAL STUDIES
Community-Acquired Bacterial Pneumonia
In a controlled, double-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted in the U.S., cefdinir BID was compared with cefaclor 500 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
U.S. Community-Acquired Pneumonia Study Cefdinir vs Cefaclor Cefdinir BID Cefaclor TID Outcome Clinical Cure Rates
150/187 (80%)
147/186 (79%)
Cefdinir equivalent
to controlEradication Rates
Overall177/195 (91%)
184/200 (92%)
Cefdinir equivalent
to controlS. pneumoniae
31/31 (100%)
35/35 (100%)
H. influenzae
55/65 (85%)
60/72 (83%)
M. catarrhalis
10/10 (100%)
11/11 (100%)
H. parainfluenzae
81/89 (91%)
78/82 (95%)
In a second controlled, investigator-blind study in adults and adolescents conducted primarily in Europe, cefdinir BID was compared with amoxicillin/clavulanate 500/125 mg TID. Using strict evaluability and clinical response criteria 6 to 14 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, presumptive microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
European Community-Acquired Pneumonia Study Cefdinir vs Amoxicillin/Clavulanate Cefdinir BID Amoxicillin/
Clavulanate TIDOutcome Clinical Cure Rates
83/104 (80%)
86/97 (89%)
Cefdinir not equivalent
to controlEradication Rates
Overall85/96 (89%)
84/90 (93%)
Cefdinir equivalent
to controlS. pneumoniae
42/44 (95%)
43/44 (98%)
H. influenzae
26/35 (74%)
21/26 (81%)
M. catarrhalis
6/6 (100%)
8/8 (100%)
H. parainfluenzae
11/11 (100%)
12/12 (100%)
Streptococcal Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis
In four controlled studies conducted in the United States, cefdinir was compared with 10 days of penicillin in adult, adolescent, and pediatric patients. Two studies (one in adults and adolescents, the other in pediatric patients) compared 10 days of cefdinir QD or BID to penicillin 250 mg or 10 mg/kg QID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 5 to 10 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis Studies
Cefdinir (10 days) vs Penicillin (10 days)Study
Efficacy Parameter
Cefdinir QD
Cefdinir BID
Penicillin QID
Outcome
Adults/
AdolescentsEradication of
S. pyogenes192/210
(91%)199/217
(92%)181/217
(83%)Cefdinir
superior
to controlClinical Cure Rates
199/210
(95%)209/217
(96%)193/217
(89%)Cefdinir
superior
to controlPediatric
PatientsEradication of
S. pyogenes215/228
(94%)214/227
(94%)159/227
(70%)Cefdinir
superior
to controlClinical Cure
Rates222/228
(97%)218/227
(96%)196/227
(86%)Cefdinir
superior
to controlTwo studies (one in adults and adolescents, the other in pediatric patients) compared 5 days of cefdinir BID to 10 days of penicillin 250 mg or 10 mg/kg QID. Using strict evaluability and microbiologic/clinical response criteria 4 to 10 days posttherapy, the following clinical cure rates, microbiologic eradication rates, and statistical outcomes were obtained:
Pharyngitis/Tonsillitis Studies
Cefdinir (5 days) vs Penicillin (10 days)Study
Efficacy
ParameterCefdinir
BIDPenicillin
QIDOutcome
Adults/
AdolescentsEradication of
S. pyogenes193/218
(89%)176/214
(82%)Cefdinir equivalent
to controlClinical Cure
Rates194/218
(89%)181/214
(85%)Cefdinir equivalent
to controlPediatric Patients
Eradication of
S. pyogenes176/196
(90%)135/193
(70%)Cefdinir superior
to controlClinical Cure
Rates179/196
(91%)173/193
(90%)Cefdinir equivalent
to control -
REFERENCES
- 1. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically, 4th ed. Approved Standard, NCCLS Document M7-A4, Vol 17(2). NCCLS, Villanova, PA, Jan 1997.
- 2. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards. Performance Standards for Antimicrobial Disk Susceptibility Tests, 6th ed. Approved Standard, NCCLS Document M2-A6, Vol 17(1). NCCLS, Villanova, PA, Jan 1997.
- 3. Cockcroft DW, Gault MH. Prediction of creatinine clearance from serum creatinine. Nephron 1976; 16:31-41.
- 4. Schwartz GJ, Haycock GB, Edelmann CM, Spitzer A. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in children derived from body length and plasma creatinine. Pediatrics 1976; 58:259-63.
- 5. Schwartz GJ, Feld LG, Langford DJ. A simple estimate of glomerular filtration rate in full-term infants during the first year of life. J Pediatrics 1984; 104:849-54.
Maalox® is a registered trademark of Rhone-Poulenc Rorer.
Clinistix® and Clinitest® are registered trademarks of Miles Diagnostics.
Tes-Tape® is a registered trademark of Lilly.
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for : OrchidPharma, Inc.
Princeton, NJ 08540, USAManufactured by : Hospira Healthcare India Pvt.Ltd.,
At Irungattukottai – 602 105, IndiaOn behalf of : Orchid Healthcare
(A Division of Orchid Chemicals & Pharmaceuticals Ltd.)
At Irungattukottai – 602 105, IndiaRelabeled by:
Proficient Rx LP
Thousand Oaks, CA 91320
I06/13
949999291
- PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
CEFDINIR
cefdinir capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 63187-593(NDC: 42043-250) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CEFDINIR MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 6E7SN358SE) (CEFDINIR - UNII:CI0FAO63WC) CEFDINIR 300 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength CARBOXYMETHYLCELLULOSE CALCIUM (UNII: UTY7PDF93L) CROSCARMELLOSE SODIUM (UNII: M28OL1HH48) POLYOXYL 40 STEARATE (UNII: 13A4J4NH9I) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C GREEN NO. 3 (UNII: 3P3ONR6O1S) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) D&C RED NO. 28 (UNII: 767IP0Y5NH) D&C RED NO. 33 (UNII: 9DBA0SBB0L) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) SHELLAC (UNII: 46N107B71O) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) ISOPROPYL ALCOHOL (UNII: ND2M416302) BUTYL ALCOHOL (UNII: 8PJ61P6TS3) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) AMMONIA (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: WZH3C48M4T) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) Product Characteristics Color purple (purple opaque) , blue (teal opaque) Score no score Shape capsule Size 21mm Flavor Imprint Code C;300 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 63187-593-14 14 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/01/2016 2 NDC: 63187-593-20 20 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/01/2015 3 NDC: 63187-593-28 28 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/01/2015 4 NDC: 63187-593-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/01/2015 5 NDC: 63187-593-40 40 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/01/2015 6 NDC: 63187-593-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 12/01/2015 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA065418 07/04/2014 Labeler - Proficient Rx LP (079196022) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Proficient Rx LP 079502574 REPACK(63187-593) , RELABEL(63187-593)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.