BUTALBITAL, ACETAMINOPHEN, CAFFEINE AND CODEINE PHOSPHATE capsule
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Codeine Phosphate by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Codeine Phosphate by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Dispensing Solutions, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate is supplied in capsule form for oral administration.
Each capsule contains the following active ingredients:
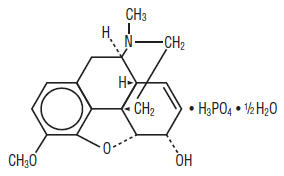
Codeine Phosphate, USP ........................................ 30 mg Butalbital, USP ........................................................ 50 mg Caffeine, USP ......................................................... 40 mg Acetaminophen, USP .............................................. 325 mg Codeine phosphate [7,8-didehydro-4,5α-epoxy-3-methoxy-17-methylmorphinan-6α-ol phosphate (1:1) (salt) hemihydrate, C18H24N07P, anhydrous mw 397.37], is a narcotic analgesic and antitussive. The structural formula of codeine phosphate is:
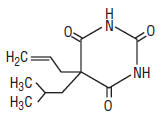
Butalbital (5-allyl-5-isobutylbarbituric acid, C11H16N203, mw 224.26), is a short-to intermediate- acting barbiturate. The structural formula of butalbital is:
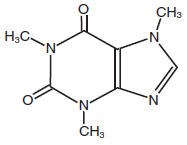
Caffeine (1,3,7-trimethylxanthine, C8H10N4O2, mw 194.19), is a central nervous system stimulant. The structural formula of caffeine is:
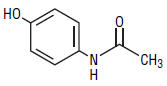
Acetaminophen (4'-hydroxyacetanilide, C8H9NO2, mw 151.16), is a non-opiate, non-salicylate analgesic and antipyretic. The structural formula of acetaminophen is:
Active Ingredients: Codeine Phosphate, USP, Butalbital, USP, Caffeine, USP, and Acetaminophen, USP. Inactive Ingredients: FD&C Blue No. 1, FD&C Red No. 3, FD&C Red No. 40, *FD&C Yellow No.5 (see PRECAUTIONS), Gelatin, Microcrystalline Cellulose, Sodium Lauryl Sulfate, Stearic Acid, Talc, Titanium Dioxide.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules is a combination drug product intended as a treatment for tension headache. Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Codeine Phosphate Capsules consists of a fixed combination of butalbital 50 mg, acetaminophen 325 mg and caffeine 40 mg. The role each component plays in the relief of the complex of symptoms known as tension headache is incompletely understood.
Pharmacokinetics
The behavior of the individual components is described below.
Codeine
Codeine is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. It is rapidly distributed from the intravascular spaces to the various body tissues, with preferential uptake by parenchymatous organs such as the liver, spleen and kidney. Codeine crosses the blood-brain barrier, and is found in fetal tissue and breast milk. The plasma concentration does not correlate with brain concentration or relief of pain; however, codeine is not bound to plasma proteins and does not accumulate in body tissues. The plasma half-life is about 2.9 hours. The elimination of codeine is primarily via the kidneys, and about 90% of an oral dose is excreted by the kidneys within 24 hours of dosing. The urinary secretion products consist of free and glucuronide conjugated codeine (about 70%), free and conjugated norcodeine (about 10%), free and conjugated morphine (about 10%), normorphine (about 4%), and hydrocodone (1%). The remainder of the dose is excreted in the feces.
At therapeutic doses, the analgesic effect reaches a peak within 2 hours and persists between 4 and 6 hours. See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Butalbital
Butalbital is well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is expected to distribute to most tissues in the body. Barbiturates in general may appear in breast milk and readily cross the placental barrier. They are bound to plasma and tissue proteins to a varying degree and binding increases directly as a function of lipid solubility.
Elimination of butalbital is primarily via the kidney (59% to 88% of the dose) as unchanged drug or metabolites. The plasma half-life is about 35 hours. Urinary excretion products include parent drug (about 3.6% of the dose), 5-isobutyl-5-(2,3-dihydroxypropyl) barbituric acid (about 24% of the dose), 5-allyl-5(3-hydroxy-2-methyl-1-propyl) barbituric acid (about 4.8% of the dose), products with the barbituric acid ring hydrolyzed with excretion of urea (about 14% of the dose), as well as unidentified materials. Of the material excreted in the urine, 32% is conjugated.
The in vitro plasma protein binding of butalbital is 45% over the concentration range of 0.5 to 20 mcg/mL. This falls within the range of plasma protein binding (20% to 45%) reported with other barbiturates such as phenobarbital, pentobarbital, and secobarbital sodium. The plasma-to-blood concentration ratio was almost unity indicating that there is no preferential distribution of butalbital into either plasma or blood cells. See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Caffeine
Like most xanthines, caffeine is rapidly absorbed and distributed in all body tissues and fluids, including the CNS, fetal tissues, and breast milk. Caffeine is cleared through metabolism and excretion in the urine. The plasma half-life is about 3 hours. Hepatic biotransformation prior to excretion results in about equal amounts of 1-methylxanthine and 1-methyluric acid. Of the 70% of the dose that is recovered in the urine, only 3% is unchanged drug. See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is rapidly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and is distributed throughout most body tissues. The plasma half-life is 1.25 to 3 hours, but may be increased by liver damage and following overdosage. Elimination of acetaminophen is principally by liver metabolism (conjugation) and subsequent renal excretion of metabolites. Approximately 85% of an oral dose appears in the urine within 24 hours of administration, most as the glucuronide conjugate, with small amounts of other conjugates and unchanged drug. See OVERDOSAGE for toxicity information.
-
INDICATIONS
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules are indicated for the relief of the symptom complex of tension (or muscle contraction) headache. Evidence supporting the efficacy and safety of Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules in the treatment of multiple recurrent headaches is unavailable. Caution in this regard is required because codeine and butalbital are habit-forming and potentially abusable.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
In the presence of head injury or other intracranial lesions, the respiratory depressant effects of codeine and other narcotics may be markedly enhanced, as well as their capacity for elevating cerebrospinal fluid pressure. Narcotics also produce other CNS depressant effects, such as drowsiness, that may further obscure the clinical course of the patients with head injuries.
Codeine or other narcotics may obscure signs on which to judge the diagnosis or clinical course of patients with acute abdominal conditions. Butalbital and codeine are both habit-forming and potentially abusable.
Consequently, the extended use of this combination product is not recommended.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules should be prescribed with caution in certain special-risk patients such as the elderly or debilitated, and those with severe impairment of renal or hepatic function, head injuries, elevated intracranial pressure, acute abdominal conditions, hypothyroidism, urethral stricture, Addison's disease, or prostatic hypertrophy.
Ultra-rapid Metabolizers of Codeine
Some individuals may be ultra-rapid metabolizers due to a specific CYP2D6*2x2 genotype. These individuals convert codeine into its active metabolite, morphine, more rapidly and completely than other people. This rapid conversion results in higher than expected serum morphine levels. Even at labeled dosage regimens, individuals who are ultra-rapid metabolizers may experience overdose symptoms such as extreme sleepiness, confusion or shallow breathing.
The prevalence of this CYP2D6 phenotype varies widely and has been estimated at 0.5 to 1% in Chinese and Japanese, 0.5 to 1% in Hispanics, 1-10% in Caucasians, 3% in African Americans, and 16-28% in North Africans, Ethiopians and Arabs. Data is not available for other ethnic groups.
When physicians prescribe codeine-containing drugs, they should choose the lowest effective dose for the shortest period of time and should inform their patients about these risks and the signs of morphine overdose. (See PRECAUTIONS, Nursing Mothers)
FD&C Yellow No. 5 (Tartrazine)
This product contains FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) which may cause allergic type reactions (including bronchial asthma) in certain susceptible persons. Although the overall incidence of FD&C Yellow No. 5 (tartrazine) sensitivity in the general population is low, it is frequently seen in patients who also have aspirin hypersensitivity.
Information for Patients
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules may impair mental and/or physical abilities required for the performance of potentially hazardous tasks such as driving a car or operating machinery. Such tasks should be avoided while taking this combination product. Alcohol and other CNS depressants may produce an additive CNS depression when taken with this combination product and should be avoided. Codeine and butalbital may be habit-forming. Patients should take the drug only for as long as it is prescribed, in the amounts prescribed, and no more frequently than prescribed. For information on use in geriatric patients, see PRECAUTIONS/Geriatric Use.
Caution patients that some people have a variation in a liver enzyme and change codeine into morphine more rapidly and completely than other people. These people are ultra-rapid metabolizers and are more likely to have higher-than-normal levels of morphine in their blood after taking codeine which can result in overdose symptoms such as extreme sleepiness, confusion, or shallow breathing. In most cases, it is unknown if someone is an ultra-rapid codeine metabolizer.
Nursing mothers taking codeine can also have higher morphine levels in their breast milk if they are ultra-rapid metabolizers. These higher levels of morphine in breast milk may lead to life-threatening or fatal side effects in nursing babies. Instruct nursing mothers to watch for signs of morphine toxicity in their infants including increased sleepiness (more than usual), difficulty breastfeeding, breathing difficulties, or limpness. Instruct nursing mothers to talk to the baby's doctor immediately if they notice these signs and, if they cannot reach the doctor right away, to take the baby to an emergency room or call 911 (or local emergency services).
Laboratory Tests
In patients with severe hepatic or renal disease, effects of therapy should be monitored with serial liver and/or renal function tests.
Drug Interactions
The CNS effects of butalbital may be enhanced by monoamine oxidase (MAO) inhibitors. Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules may enhance the effects of:
- Other narcotic analgesics, alcohol, general anesthetics, tranquilizers such as chlordiazepoxide, sedative-hypnotics, or other CNS depressants, causing increased CNS depression.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether acetaminophen, codeine and butalbital have a potential for carcinogenesis or mutagenesis. No adequate studies have been conducted in animals to determine whether acetaminophen and butalbital have a potential for impairment of fertility.
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy Category C
Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules. It is also not known whether Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman or can affect reproduction capacity. This combination product should be given to a pregnant woman only when clearly needed.
Nonteratogenic Effects
Withdrawal seizures were reported in a two-day-old male infant whose mother had taken a butalbital-containing drug during the last 2 months of pregnancy. Butalbital was found in the infant's serum. The infant was given phenobarbital 5 mg/kg, which was tapered without further seizure or other withdrawal symptoms.
Nursing Mothers
Caffeine, barbiturates, acetaminophen and codeine are excreted in breast milk in small amounts, but the significance of their effects on nursing infants is not known. Because of potential for serious adverse reactions in nursing infants from Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Codeine Phosphate Capsules, a decision should be made whether to discontinue nursing or to discontinue the drug, taking into account the importance of the drug to the mother.
Codeine is secreted into human milk. In women with normal codeine metabolism (normal CYP2D6 activity), the amount of codeine secreted into human milk is low and dose-dependent. Despite the common use of codeine products to manage postpartum pain, reports of adverse events in infants are rare. However, some women are ultra-rapid metabolizers of codeine. These women achieve higher-than-expected serum levels of codeine's active metabolite, morphine, leading to higher-than-expected levels of morphine in breast milk and potentially dangerously high serum morphine levels in their breastfed infants. Therefore, maternal use of codeine can potentially lead to serious adverse reactions, including death, in nursing infants.
The prevalence of this CYP2D6 phenotype varies widely and has been estimated at 0.5 to 1% in Chinese and Japanese, 0.5 to 1% in Hispanics, 1-10% in Caucasians, 3% in African Americans, and 16-28% in North Africans, Ethiopians and Arabs. Data is not available for other ethnic groups.
The risk of infant exposure to codeine and morphine through breast milk should be weighed against the benefits of breastfeeding for both the mother and baby. Caution should be exercised when codeine is administered to a nursing woman. If a codeine containing product is selected, the lowest dose should be prescribed for the shortest period of time to achieve the desired clinical effect. Mothers using codeine should be informed about when to seek immediate medical care and how to identify the signs and symptoms of neonatal toxicity, such as drowsiness or sedation, difficulty breastfeeding, breathing difficulties, and decreased tone, in their baby. Nursing mothers who are ultra-rapid metabolizers may also experience overdose symptoms such as extreme sleepiness, confusion or shallow breathing. Prescribers should closely monitor mother-infant pairs and notify treating pediatricians about the use of codeine during breastfeeding. (See PRECAUTIONS, General, Ultra-rapid Metabolizers of Codeine)
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy. Butalbital is known to be substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of toxic reactions to this drug may be greater in patients with impaired renal function. Because elderly patients are more likely to have decreased renal function, care should be taken in dose selection, and it may be useful to monitor renal function.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Frequently Observed: The most frequently reported adverse reactions are drowsiness, lightheadedness, dizziness, sedation, shortness of breath, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and intoxicated feeling.
Infrequently Observed: All adverse events tabulated below are classified as infrequent.
Central Nervous: headache, shaky feeling, tingling, agitation, fainting, fatigue, heavy eyelids, high energy, hot spells, numbness, sluggishness, seizure. Mental confusion, excitement or depression can also occur due to intolerance, particularly in elderly or debilitated patients, or due to overdosage of butalbital.
Autonomic Nervous: dry mouth, hyperhidrosis.
Gastrointestinal: difficulty swallowing, heartburn, flatulence, constipation.
Cardiovascular: tachycardia.
Musculoskeletal: leg pain, muscle fatigue.
Genitourinary: diuresis.
Miscellaneous: pruritus, fever, earache, nasal congestion, tinnitus, euphoria, allergic reactions.
The following adverse reactions have been voluntarily reported as temporally associated with Fiorinal®1 with Codeine, a related product containing aspirin, butalbital, caffeine, and codeine phosphate.
Central Nervous: abuse, addiction, anxiety, disorientation, hallucination, hyperactivity, insomnia, libido decrease, nervousness, neuropathy, psychosis, sexual activity increase, slurred speech, twitching, unconsciousness, vertigo.
Autonomic Nervous: epistaxis, flushing, miosis, salivation.
Gastrointestinal: anorexia, appetite increased, diarrhea, esophagitis, gastroenteritis, gastrointestinal spasms, hiccup, mouth burning, pyloric ulcer.
Cardiovascular: chest pain, hypotensive reaction, palpitations, syncope.
Skin: erythema, erythema multiforme, exfoliative dermatitis, hives, rash, toxic epidermal necrolysis.
Urinary: kidney impairment, urinary difficulty.
Miscellaneous: allergic reaction, anaphylactic shock, cholangiocarcinoma, drug interaction with erythromycin (stomach upset), edema.
The following adverse drug events may be borne in mind as potential effects of the components of Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules. Potential effects of high dosage are listed in the OVERDOSAGE section.
Acetaminophen: allergic reactions, rash, thrombocytopenia, agranulocytosis.
Caffeine: cardiac stimulation, irritability, tremor, dependence, nephrotoxicity, hyperglycemia.
Codeine: nausea, vomiting, drowsiness, lightheadedness, constipation, pruritus. Several cases of dermatological reactions, including toxic epidermal necrolysis and erythema multiforme, have been reported for Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine and Codeine Phosphate Capsules, USP.
- 1 Fiorinal® is a registered trademark of Watson Pharmaceuticals, Inc.
-
DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
Controlled Substance
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules is controlled by the Drug Enforcement Administration and is classified under Schedule III.
Abuse and Dependence
Codeine
Codeine can produce drug dependence of the morphine type and, therefore, has the potential for being abused. Psychological dependence, physical dependence, and tolerance may develop upon repeated administration and it should be prescribed and administered with the same degree of caution appropriate to the use of other oral narcotic medications.
Butalbital
Barbiturates may be habit-forming
Tolerance, psychological dependence, and physical dependence may occur especially following prolonged use of high doses of barbiturates. The average daily dose for the barbiturate addict is usually about 1,500 mg. As tolerance to barbiturates develops, the amount needed to maintain the same level of intoxication increases; tolerance to a fatal dosage, however, does not increase more than two-fold. As this occurs, the margin between an intoxication dosage and fatal dosage becomes smaller. The lethal dose of a barbiturate is far less if alcohol is also ingested. Major withdrawal symptoms (convulsions and delirium) may occur within 16 hours and last up to 5 days after abrupt cessation of these drugs. Intensity of withdrawal symptoms gradually declines over a period of approximately 15 days. Treatment of barbiturate dependence consists of cautious and gradual withdrawal of the drug.
Barbiturate-dependent patients can be withdrawn by using a number of different withdrawal regimens. One method involves initiating treatment at the patient's regular dosage level and gradually decreasing the daily dosage as tolerated by the patient.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Following an acute overdosage of Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules, toxicity may result from the barbiturate, the codeine, or the acetaminophen. Toxicity due to the caffeine is less likely, due to the relatively small amounts in this formulation.
Signs and Symptoms
Toxicity from barbiturate poisoning includes drowsiness, confusion, and coma; respiratory depression; hypotension; and hypovolemic shock. Toxicity from codeine poisoning includes the opioid triad of: pinpoint pupils, depression of respiration, and loss of consciousness. Convulsions may occur. In acetaminophen overdosage : dose-dependent, potentially fatal hepatic necrosis is the most serious adverse effect. Renal tubular necroses, hypoglycemic coma, and thrombocytopenia may also occur. Early symptoms following a potentially hepatotoxic overdose may include: nausea, vomiting, diaphoresis, and general malaise. Clinical and laboratory evidence of hepatic toxicity may not be apparent until 48 to 72 hours post-ingestion. In adults hepatic toxicity has rarely been reported with acute overdoses of less than 10 grams, or fatalities with less than 15 grams. Acute caffeine poisoning may cause insomnia, restlessness, tremor, and delirium, tachycardia, and extrasystoles.
Treatment
A single or multiple overdose with Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules is a potentially lethal polydrug overdose, and consultation with a regional poison control center is recommended. Immediate treatment includes support of cardiorespiratory function and measures to reduce drug absorption. Vomiting should be induced mechanically, or with syrup of ipecac, if the patient is alert (adequate pharyngeal and laryngeal reflexes). Oral activated charcoal (1 g/kg) should follow gastric emptying. The first dose should be accompanied by an appropriate cathartic. If repeated doses are used, the cathartic might be included with alternate doses as required. Hypotension is usually hypovolemic and should respond to fluids. The value of vasopressor agents such as norepinephrine or phenylephrine hydrochloride in treating hypotension is questionable since they increase vasoconstriction and decrease blood flow. However, if prolonged support of blood pressure is required, norepinephrine bitartrate (Levophed®)2 may be given I.V. with the usual precautions and serial blood pressure monitoring. A cuffed endotracheal tube should be inserted before gastric lavage of the unconscious patient and, when necessary, to provide assisted respiration. If renal function is normal, forced diuresis may aid in the elimination of the barbiturate. Alkalinization of the urine increases renal excretion of some barbiturates, especially phenobarbital.
Meticulous attention should be given to maintaining adequate pulmonary ventilation. In severe cases of intoxication, peritoneal dialysis, or preferably hemodialysis may be considered. If hypoprothrombinemia occurs due to acetaminophen overdose, vitamin K should be administered intravenously.
Naloxone, a narcotic antagonist, can reverse respiratory depression and coma associated with opioid overdose. Naloxone 0.4 to 2 mg is given parenterally. Since the duration of action of codeine may exceed that of the naloxone, the patient should be kept under continuous surveillance and repeated doses of the antagonist should be administered as needed to maintain adequate respiration. A narcotic antagonist should not be administered in the absence of clinically significant respiratory or cardiovascular depression.
If the dose of acetaminophen may have exceeded 140 mg/kg, N-acetyl-cysteine should be administered as early as possible. Serum acetaminophen levels should be obtained, since levels 4 or more hours following ingestion help predict acetaminophen toxicity. Do not await acetaminophen assay results before initiating treatment. Hepatic enzymes should be obtained initially, and repeated at 24-hour intervals. Methemoglobinemia over 30% should be treated with methylene blue by slow intravenous administration.
- 2 Levophed® is a registered Trademark of Hospira, Inc.
- DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules: Dark blue, opaque cap with a gray, opaque body, and body is imprinted with "B 073" in black ink.
Bottles of 100's (NDC: 51991-073-01)
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 Capsule Bottle

NDC: 68258-2012-XX
NDC: 68258-2012-09Butalbital, Acetaminophen, Caffeine, and Codeine Phosphate Capsules
CIIICodeine Phosphate, USP ........................................ 30 mg Butalbital, USP ........................................................ 50 mg Caffeine, USP ......................................................... 40 mg Acetaminophen, USP .............................................. 325 mg Rx Only
90 Capsules -
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BUTALBITAL, ACETAMINOPHEN, CAFFEINE AND CODEINE PHOSPHATE
butalbital, acetaminophen, caffeine and codeine phosphate capsuleProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 68258-2012(NDC:51991-073) Route of Administration ORAL DEA Schedule CIII Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Butalbital (UNII: KHS0AZ4JVK) (Butalbital - UNII:KHS0AZ4JVK) Butalbital 50 mg Acetaminophen (UNII: 362O9ITL9D) (Acetaminophen - UNII:362O9ITL9D) Acetaminophen 325 mg Caffeine (UNII: 3G6A5W338E) (Caffeine - UNII:3G6A5W338E) Caffeine 40 mg Codeine Phosphate (UNII: GSL05Y1MN6) (Codeine - UNII:Q830PW7520) Codeine 30 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength FD&C Blue No. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C Red No. 3 (UNII: PN2ZH5LOQY) FD&C Red No. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) FD&C Yellow No. 5 (UNII: I753WB2F1M) Gelatin (UNII: 2G86QN327L) Cellulose, Microcrystalline (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Sodium Lauryl Sulfate (UNII: 368GB5141J) Stearic Acid (UNII: 4ELV7Z65AP) Talc (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) Titanium Dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) Product Characteristics Color blue, gray Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 22mm Flavor Imprint Code B073 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 68258-2012-9 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA076560 07/01/2004 Labeler - Dispensing Solutions, Inc. (066070785) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Dispensing Solutions, Inc. 066070785 relabel, repack
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.