Sulfasalazine by REMEDYREPACK INC. SULFASALAZINE tablet
Sulfasalazine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Sulfasalazine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by REMEDYREPACK INC.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
Sulfasalazine tablets contain sulfasalazine, 500 mg, for oral administration.
Therapeutic Classification: Anti-inflammatory agent.
Chemical Designation: 5-([p-(2-pyridylsulfamoyl)phenyl]azo) salicylic acid.
Chemical Structure:
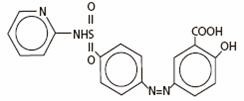
Molecular Formula: C 18H 14N 4O 5S
Inactive Ingredients: magnesium stearate, povidone, silica (colloidal anhydrous), starch (pregelatinized).
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Pharmacodynamics
The mode of action of sulfasalazine (SSZ) or its metabolites, 5-aminosalicylic acid (5-ASA) and sulfapyridine (SP), is still under investigation, but may be related to the anti-inflammatory and/or immunomodulatory properties that have been observed in animal and in vitro models, to its affinity for connective tissue, and/or to the relatively high concentration it reaches in serous fluids, the liver and intestinal walls, as demonstrated in autoradiographic studies in animals. In ulcerative colitis, clinical studies utilizing rectal administration of SSZ, SP, and 5-ASA have indicated that the major therapeutic action may reside in the 5-ASA moiety.
Pharmacokinetics
In vivo studies have indicated that the absolute bioavailability of orally administered SSZ is less than 15% for parent drug. In the intestine, SSZ is metabolized by intestinal bacteria to SP and 5-ASA. Of the two species, SP is relatively well absorbed from the intestine and highly metabolized, while 5-ASA is much less well absorbed.
Absorption
Following oral administration of 1 g of SSZ to 9 healthy males, less than 15% of a dose of SSZ is absorbed as parent drug. Detectable serum concentrations of SSZ have been found in healthy subjects within 90 minutes after the ingestion. Maximum concentrations of SSZ occur between 3 and 12 hours post-ingestion, with the mean peak concentration (6 μg/mL) occurring at 6 hours.
In comparison, peak plasma levels of both SP and 5-ASA occur approximately 10 hours after dosing. This longer time to peak is indicative of gastrointestinal transit to the lower intestine where bacteria mediated metabolism occurs. SP apparently is well absorbed from the colon with an estimated bioavailability of 60%. In this same study, 5-ASA is much less well absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with an estimated bioavailability of from 10 to 30%.
Distribution
Following intravenous injection, the calculated volume of distribution (Vdss) for SSZ was 7.5 ± 1.6 L. SSZ is highly bound to albumin (>99.3%) while SP is only about 70% bound to albumin. Acetylsulfapyridine (AcSP), the principal metabolite of SP, is approximately 90% bound to plasma proteins.
Metabolism
As mentioned above, SSZ is metabolized by intestinal bacteria to SP and 5-ASA. Approximately 15% of a dose of SSZ is absorbed as parent and is metabolized to some extent in the liver to the same two species. The observed plasma half-life for intravenous sulfasalazine is 7.6 ± 3.4 hours. The primary route of metabolism of SP is via acetylation to form AcSP. The rate of metabolism of SP to AcSP is dependent upon acetylator phenotype. In fast acetylators, the mean plasma half-life of SP is 10.4 hours while in slow acetylators, it is 14.8 hours. SP can also be metabolized to 5-hydroxy-sulfapyridine (SPOH) and N-acetyl-5-hydroxy-sulfapyridine. 5-ASA is primarily metabolized in both the liver and intestine to N-acetyl-5-aminosalicylic acid via a non-acetylation phenotype dependent route. Due to low plasma levels produced by 5-ASA after oral administration, reliable estimates of plasma half-life are not possible.
Excretion
Absorbed SP and 5-ASA and their metabolites are primarily eliminated in the urine either as free metabolites or as glucuronide conjugates. The majority of 5-ASA stays within the colonic lumen and is excreted as 5-ASA and acetyl-5-ASA with the feces. The calculated clearance of SSZ following intravenous administration was 1 L/hr. Renal clearance was estimated to account for 37% of total clearance.
Special Populations
Elderly
Elderly patients with rheumatoid arthritis showed a prolonged plasma half-life for SSZ, SP, and their metabolites. The clinical impact of this is unknown.
Pediatric
Small studies have been reported in the literature in children down to the age of 4 years with ulcerative colitis and inflammatory bowel disease. In these populations, relative to adults, the pharmacokinetics of SSZ and SP correlated poorly with either age or dose.
Acetylator Status
The metabolism of SP to AcSP is mediated by polymorphic enzymes such that two distinct populations of slow and fast metabolizers exist. Approximately 60% of the Caucasian population can be classified as belonging to the slow acetylator phenotype. These subjects will display a prolonged plasma half-life for SP (14.8 hours vs. 10.4 hours) and an accumulation of higher plasma levels of SP than fast acetylators. The clinical implication of this is unclear; however, in a small pharmacokinetic trial where acetylator status was determined, subjects who were slow acetylators of SP showed a higher incidence of adverse events.
- INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Only after critical appraisal should Sulfasalazine tablets be given to patients with hepatic or renal damage or blood dyscrasias. Deaths associated with the administration of sulfasalazine have been reported from hypersensitivity reactions, agranulocytosis, aplastic anemia, other blood dyscrasias, renal and liver damage, irreversible neuromuscular and central nervous system changes, and fibrosing alveolitis. The presence of clinical signs such as sore throat, fever, pallor, purpura, or jaundice may be indications of serious blood disorders or hepatotoxicity. Complete blood counts, as well as urinalysis with careful microscopic examination, should be done frequently in patients receiving sulfasalazine (see PRECAUTIONS Laboratory Tests). Discontinue treatment with sulfasalazine while awaiting the results of blood tests. Oligospermia and infertility have been observed in men treated with sulfasalazine; however, withdrawal of the drug appears to reverse these effects.
Serious infections, including fatal sepsis and pneumonia, have been reported. Some infections were associated with agranulocytosis, neutropenia, or myelosuppression. Discontinue sulfasalazine if a patient develops a serious infection. Closely monitor patients for the development of signs and symptoms of infection during and after treatment with sulfasalazine. For a patient who develops a new infection during treatment with sulfasalazine, perform a prompt and complete diagnostic workup for infection and myelosuppression. Caution should be exercised when considering the use of sulfasalazine in patients with a history of recurring or chronic infections or with underlying conditions or concomitant drugs which may predispose patients to infections.
Severe hypersensitivity reactions may include internal organ involvement, such as hepatitis, nephritis, myocarditis, mononucleosis-like syndrome (i.e., pseudomononucleosis), hematological abnormalities (including hematophagic histiocytosis), and/or pneumonitis including eosinophilic infiltration.
Serious skin reactions, some of them fatal, including exfoliative dermatitis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, and toxic epidermal necrolysis, have been reported in association with the use of sulfasalazine. Patients are at highest risk for these events early in therapy, with most events occurring within the first month of treatment. Sulfasalazine should be discontinued at the first appearance of skin rash, mucosal lesions, or any other sign of hypersensitivity.
Severe, life-threatening, systemic hypersensitivity reactions such as drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms have been reported in patients taking sulfasalazine. Early manifestations of hypersensitivity, such as fever or lymphadenopathy, may be present even though rash is not evident. If such signs or symptoms are present, the patient should be evaluated immediately. Sulfasalazine should be discontinued if an alternative etiology for the signs or symptoms cannot be established.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Sulfasalazine tablets should be given with caution to patients with severe allergy or bronchial asthma. Adequate fluid intake must be maintained in order to prevent crystalluria and stone formation. Patients with glucose-6 phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency should be observed closely for signs of hemolytic anemia. This reaction is frequently dose related. If toxic or hypersensitivity reactions occur, the drug should be discontinued immediately.
Information for Patients
Patients should be informed of the possibility of adverse reactions and of the need for careful medical supervision. The occurrence of sore throat, fever, pallor, purpura, or jaundice may indicate a serious blood disorder. Should any of these occur, the patient should seek medical advice. They should also be made aware that ulcerative colitis rarely remits completely, and that the risk of relapse can be reduced by continued administration of sulfasalazine at a maintenance dosage. Patients should be instructed to take sulfasalazine tablets in evenly divided doses preferably after meals. Additionally, patients should be advised that sulfasalazine may produce an orange-yellow discoloration of the urine or skin.
Laboratory Tests
Complete blood counts, including differential white cell count and liver function tests, should be performed before starting sulfasalazine and every second week during the first three months of therapy. During the second three months, the same tests should be done once monthly and thereafter once every three months, and as clinically indicated. Urinalysis and an assessment of renal function should also be done periodically during treatment with sulfasalazine.
The determination of serum sulfapyridine levels may be useful since concentrations greater than 50 μg/mL appear to be associated with an increased incidence of adverse reactions.
Drug Interactions
Reduced absorption of folic acid and digoxin have been reported when those agents were administered concomitantly with sulfasalazine.
Drug/Laboratory Test Interactions
Several reports of possible interference with measurements, by liquid chromatography, of urinary normetanephrine causing a false-positive test result have been observed in patients exposed to sulfasalazine or its metabolite, mesalamine/mesalazine.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Two-year oral carcinogenicity studies were conducted in male and female F344/N rats and B6C3F1 mice. Sulfasalazine was tested at 84 (496 mg/m 2), 168 (991 mg/m 2), and 337.5 (1991 mg/m 2) mg/kg/day doses in rats. A statistically significant increase in the incidence of urinary bladder transitional cell papillomas was observed in male rats. In female rats, two (4%) of the 337.5 mg/kg rats had transitional cell papilloma of the kidney. The increased incidence of neoplasms in the urinary bladder and kidney of rats was also associated with an increase in the renal calculi formation and hyperplasia of transitional cell epithelium. For the mouse study, sulfasalazine was tested at 675 (2025 mg/m 2), 1350 (4050 mg/m 2), and 2700 (8100 mg/m 2) mg/kg/day. The incidence of hepatocellular adenoma or carcinoma in male and female mice was significantly greater than the control at all doses tested.
Sulfasalazine did not show mutagenicity in the bacterial reverse mutation assay (Ames test) and in L51784 mouse lymphoma cell assay at the HGPRT gene. However, sulfasalazine showed equivocal mutagenic response in the micronucleus assay of mouse and rat bone marrow and mouse peripheral RBC and in the sister chromatid exchange, chromosomal aberration, and micronucleus assays in lymphocytes obtained from humans.
Impairment of male fertility was observed in reproductive studies performed in rats at a dose of 800 mg/kg/day (4800 mg/m 2). Oligospermia and infertility have been described in men treated with sulfasalazine. Withdrawal of the drug appears to reverse these effects.
Pregnancy
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies of sulfasalazine in pregnant women. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at doses up to 6 times the human maintenance dose of 2 g/day based on body surface area and have revealed no evidence of impaired female fertility or harm to the fetus due to sulfasalazine. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
There have been case reports of neural tube defects (NTDs) in infants born to mothers who were exposed to sulfasalazine during pregnancy, but the role of sulfasalazine in these defects has not been established. However, oral sulfasalazine inhibits the absorption and metabolism of folic acid which may interfere with folic acid supplementation (see Drug Interactions) and diminish the effect of periconceptional folic acid supplementation that has been shown to decrease the risk of NTDs.
A national survey evaluated the outcome of pregnancies associated with inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). In a group of 186 women treated with sulfasalazine alone or sulfasalazine and concomitant steroid therapy, the incidence of fetal morbidity and mortality was comparable to that for 245 untreated IBD pregnancies as well as to pregnancies in the general population. 1 A study of 1,455 pregnancies associated with exposure to sulfonamides indicated that this group of drugs, including sulfasalazine, did not appear to be associated with fetal malformation. 2 A review of the medical literature covering 1,155 pregnancies in women with ulcerative colitis suggested that the outcome was similar to that expected in the general population. 3
No clinical studies have been performed to evaluate the effect of sulfasalazine on the growth development and functional maturation of children whose mothers received the drug during pregnancy.
Clinical Considerations
Sulfasalazine and its metabolite, sulfapyridine, pass through the placenta. Sulfasalazine and its metabolite are also present in human milk. In the newborn, sulfonamides compete with bilirubin for binding sites on the plasma proteins and may cause kernicterus. Although sulfapyridine has been shown to have a poor bilirubin-displacing capacity, monitor the newborn for the potential for kernicterus.
A case of agranulocytosis has been reported in an infant whose mother was taking both sulfasalazine and prednisone throughout pregnancy.
Nursing Mothers
Sulfonamides, including sulfasalazine, are present in human milk (see Pregnancy, Clinical Considerations). Insignificant amounts of sulfasalazine have been found in milk, whereas levels of the active metabolite sulfapyridine in milk are about 30 to 60 percent of those in the maternal serum. Caution should be exercised when sulfasalazine is administered to a nursing mother.
There are reports with limited data of bloody stools or diarrhea in human milk fed infants of mothers taking sulfasalazine. In cases where the outcome was reported, bloody stools or diarrhea resolved in the infant after discontinuation of sulfasalazine in the mother or discontinuation of breastfeeding. Due to limited data, a causal relationship between sulfasalazine exposure and bloody stools or diarrhea cannot be confirmed or denied. Monitor human milk fed infants of mothers taking sulfasalazine for signs and symptoms of diarrhea and/or bloody stools.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions associated with sulfasalazine are anorexia, headache, nausea, vomiting, gastric distress, and apparently reversible oligospermia. These occur in about one-third of the patients. Less frequent adverse reactions are skin rash, pruritus, urticaria, fever, Heinz body anemia, hemolytic anemia, and cyanosis, which may occur at a frequency of one in every thirty patients or less. Experience suggests that with a daily dosage of 4 g or more, or total serum sulfapyridine levels above 50 μg/mL, the incidence of adverse reactions tends to increase.
Although the listing which follows includes a few adverse reactions which have not been reported with this specific drug, the pharmacological similarities among the sulfonamides require that each of these reactions be considered when sulfasalazine tablets are administered. Less common or rare adverse reactions include:
Blood dyscrasias: aplastic anemia, agranulocytosis, leukopenia, megaloblastic (macrocytic) anemia, purpura, thrombocytopenia, hypoprothrombinemia, methemoglobinemia, congenital neutropenia, and myelodysplastic syndrome.
Hypersensitivity reactions: erythema multiforme (Stevens-Johnson syndrome), exfoliative dermatitis, epidermal necrolysis (Lyell's syndrome) with corneal damage, drug rash with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms (DRESS), anaphylaxis, serum sickness syndrome, interstitial lung disease, pneumonitis with or without eosinophilia, vasculitis, fibrosing alveolitis, pleuritis, pericarditis with or without tamponade, allergic myocarditis, polyarteritis nodosa, lupus erythematosus-like syndrome, hepatitis and hepatic necrosis with or without immune complexes, fulminant hepatitis, sometimes leading to liver transplantation, parapsoriasis varioliformis acuta (Mucha-Haberman syndrome), rhabdomyolysis, photosensitization, arthralgia, periorbital edema, conjunctival and scleral injection, and alopecia.
Gastrointestinal reactions: hepatitis, hepatic failure, pancreatitis, bloody diarrhea, impaired folic acid absorption, impaired digoxin absorption, stomatitis, diarrhea, abdominal pains, and neutropenic enterocolitis.
Central nervous system reactions: transverse myelitis, convulsions, meningitis, transient lesions of the posterior spinal column, cauda equina syndrome, Guillian-Barre syndrome, peripheral neuropathy, mental depression, vertigo, hearing loss, insomnia, ataxia, hallucinations, tinnitus, and drowsiness.
Renal reactions: toxic nephrosis with oliguria and anuria, nephritis, nephrotic syndrome, urinary tract infections, hematuria, crystalluria, proteinuria, and hemolytic-uremic syndrome.
Other reactions: urine discoloration and skin discoloration.
The sulfonamides bear certain chemical similarities to some goitrogens, diuretics (acetazolamide and the thiazides), and oral hypoglycemic agents. Goiter production, diuresis and hypoglycemia have occurred rarely in patients receiving sulfonamides. Cross-sensitivity may exist with these agents. Rats appear to be especially susceptible to the goitrogenic effects of sulfonamides and long-term administration has produced thyroid malignancies in this species.
Postmarketing Reports
The following events have been identified during post-approval use of products which contain (or are metabolized to) mesalamine in clinical practice. Because they are reported voluntarily from a population of unknown size, estimates of frequency cannot be made. These events have been chosen for inclusion due to a combination of seriousness, frequency of reporting, or potential causal connection to mesalamine:
Blood dyscrasias: pseudomononucleosis
Cardiac disorders: myocarditis
Hepatobiliary disorders: reports of hepatotoxicity, including elevated liver function tests (SGOT/AST, SGPT/ALT, GGT, LDH, alkaline phosphatase, bilirubin), jaundice, cholestatic jaundice, cirrhosis, hepatitis cholestatic, cholestasis and possible hepatocellular damage including liver necrosis and liver failure. Some of these cases were fatal. One case of Kawasaki-like syndrome, which included hepatic function changes, was also reported.
Immune system disorders: anaphylaxis
Metabolism and nutrition system disorders: folate deficiency
Renal and urinary disorders: nephrolithiasis
Respiratory, thoracic and mediastinal disorders: oropharyngeal pain
Skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders: angioedema, purpura
Vascular disorders: pallor
- DRUG ABUSE AND DEPENDENCE
-
OVERDOSAGE
There is evidence that the incidence and severity of toxicity following overdosage are directly related to the total serum sulfapyridine concentration. Symptoms of overdosage may include nausea, vomiting, gastric distress, and abdominal pains. In more advanced cases, central nervous system symptoms such as drowsiness, convulsions, etc., may be observed. Serum sulfapyridine concentrations may be used to monitor the progress of recovery from overdosage.
There are no documented reports of deaths due to ingestion of large single doses of sulfasalazine. Doses of Azulfidine tablets of 16 g per day have been given to patients without mortality. A single oral dose of 12 g/kg was not lethal to mice.
Instructions for Overdosage
Gastric lavage or emesis plus catharsis as indicated. Alkalinize urine. If kidney function is normal, force fluids. If anuria is present, restrict fluids and salt, and treat appropriately. Catheterization of the ureters may be indicated for complete renal blockage by crystals. The low molecular weight of sulfasalazine and its metabolites may facilitate their removal by dialysis.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
The dosage of sulfasalazine tablets should be adjusted to each individual's response and tolerance.
Initial Therapy
Adults: 3 to 4 g daily in evenly divided doses with dosage intervals not exceeding eight hours. In some cases, it is advisable to initiate therapy with a smaller dosage, e.g., 1 to 2 g daily, to reduce possible gastrointestinal intolerance. If daily doses exceeding 4 g are required to achieve desired effects, the increased risk of toxicity should be kept in mind.
Children, six years of age and older: 40 to 60 mg/kg body weight in each 24-hour period, divided into 3 to 6 doses.
Maintenance Therapy
Adults: 2 g daily.
Children, six years of age and older: 30 mg/kg body weight in each 24-hour period, divided into 4 doses.
The response of acute ulcerative colitis to sulfasalazine tablets can be evaluated by clinical criteria, including the presence of fever, weight changes, and degree and frequency of diarrhea and bleeding, as well as by sigmoidoscopy and the evaluation of biopsy samples. It is often necessary to continue medication even when clinical symptoms, including diarrhea, have been controlled. When endoscopic examination confirms satisfactory improvement, the dosage of sulfasalazine should be reduced to a maintenance level. If diarrhea recurs, the dosage should be increased to previously effective levels. If symptoms of gastric intolerance (anorexia, nausea, vomiting, etc.) occur after the first few doses of sulfasalazine, they are probably due to increased serum levels of total sulfapyridine and may be alleviated by halving the daily dose of sulfasalazine and subsequently increasing it gradually over several days. If gastric intolerance continues, the drug should be stopped for 5 to 7 days, then reintroduced at a lower daily dose.
Some patients may be sensitive to treatment with sulfasalazine. Various desensitization-like regimens have been reported to be effective in 34 of 53 patients, 4 7 of 8 patients, 5 and 19 of 20 patients. 6 These regimens suggest starting with a total daily dose of 50 to 250 mg sulfasalazine initially, and doubling it every 4 to 7 days until the desired therapeutic level is achieved. If the symptoms of sensitivity recur, sulfasalazine should be discontinued. Desensitization should not be attempted in patients who have a history of agranulocytosis, or who have experienced an anaphylactoid reaction while previously receiving sulfasalazine.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Sulfasalazine tablets, 500 mg, are round, gold-colored, scored tablets, monogrammed "G500". They are available in the following package sizes:
Bottles of 100 NDC: 59762-5000-1
Bottles of 300 NDC: 59762-5000-2
-
REFERENCES
- Mogadam M, et al. Pregnancy in inflammatory bowel disease: effect of sulfasalazine and corticosteroids on fetal outcome. Gastroenterology 1981;80:72–6.
- Kaufman DW, editor. Birth defects and drugs during pregnancy. Littleton, MA: Publishing Sciences Group, Inc, 1977: 296–313.
- Jarnerot G. Fertility, sterility and pregnancy in chronic inflammatory bowel disease. Scand J Gastroenterol 1982;17:1–4.
- Korelitz B, et al. Desensitization to sulfasalazine in allergic patients with IBD: an important therapeutic modality. Gastroenterology 1982;82:1104.
- Holdworth CG. Sulphasalazine desensitization. Br Med J 1981;282:110.
- Taffet SL, Das KM. Desensitization of patients with inflammatory bowel disease to sulfasalazine. Am J Med 1982;73:520–4.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
DRUG: Sulfasalazine
GENERIC: Sulfasalazine
DOSAGE: TABLET
ADMINSTRATION: ORAL
NDC: 70518-1829-0
COLOR: yellow
SHAPE: ROUND
SCORE: Two even pieces
SIZE: 14 mm
IMPRINT: G500
PACKAGING: 270 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC
ACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- SULFASALAZINE 500mg in 1
INACTIVE INGREDIENT(S):
- MAGNESIUM STEARATE
- SILICON DIOXIDE
- POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED
- STARCH, CORN

-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
SULFASALAZINE
sulfasalazine tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 70518-1829(NDC:59762-5000) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength SULFASALAZINE (UNII: 3XC8GUZ6CB) (SULFASALAZINE - UNII:3XC8GUZ6CB) SULFASALAZINE 500 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color yellow (Gold) Score 2 pieces Shape ROUND Size 14mm Flavor Imprint Code G500 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 70518-1829-0 270 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 01/28/2019 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA authorized generic NDA007073 01/28/2019 Labeler - REMEDYREPACK INC. (829572556)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.
