WESNATE DHA- ascorbic acid, cholecalciferol, .alpha.-tocopherol, d-, thiamine mononitrate, riboflavin, pyridoxine hydrochloride, folic acid, cyanocobalamin, ferrous fumarate, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, cupric sulfate, and omega-3 fatty acids capsule, gelatin coated
WesNate DHA by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
WesNate DHA by is a Other medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- HEALTH CLAIM
- DESCRIPTION
- DIRECTIONS FOR USE
-
STATEMENT OF IDENTITY
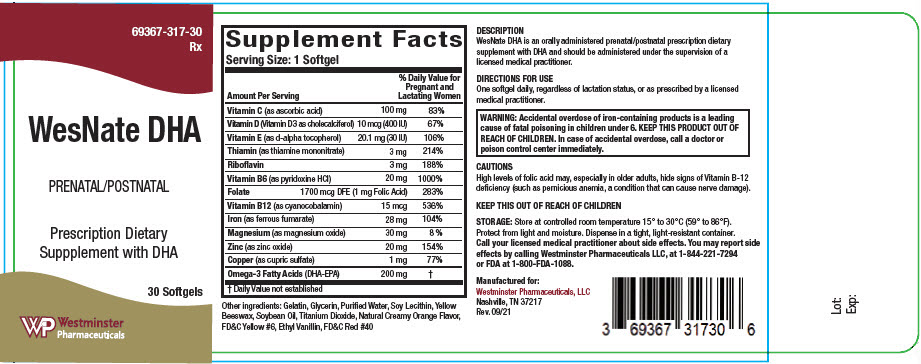
Supplement Facts Serving Size: 1 Softgel Amount Per Serving % Daily Value for Pregnant and Lactating Women - * Daily Value not established
Vitamin C (as ascorbic acid) 100 mg 83% Vitamin D (Vitamin D3 as cholecalciferol) 10 mcg (400 IU) 67% Vitamin E (as d-alpha tocopherol) 20.1 mg (30 IU) 106% Thiamin (as thiamine mononitrate) 3 mg 214% Riboflavin 3 mg 188% Vitamin B6 (as pyridoxine HCl) 20 mg 1000% Folate 1700 mcg DFE (1 mg Folic Acid) 283% Vitamin B12 (as cyanocobalamin) 15 mcg 536% Iron (as ferrous fumarate) 28 mg 104% Magnesium (as magnesium oxide) 30 mg 8 % Zinc (as zinc oxide) 20 mg 154% Copper (as cupric sulfate) 1 mg 77% Omega-3 Fatty Acids (DHA-EPA) 200 mg * Other ingredients: Gelatin, Soybean Oil, Glycerin, Purified Water, Yellow Beeswax, Soy Lecithin, Titanium Dioxide, Ethyl Vanillin, FD&C Yellow #6, FD&C Red #40.
Contains: Fish and Soy
KEEP THIS OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN
-
CONTRAINDICTIONS
WesNate DHA should not be used by patients with known history of hypersensitivity to any of its ingredients.
WARNING: Accidental overdose of iron-containing products is a leading cause of fatal poisoning in children under 6. KEEP THIS PRODUCT OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN. In case of accidental overdose, call a doctor or poison control center immediately. -
CAUTIONS
High levels of folic acid may, especially in older adults, hide signs of Vitamin B-12 deficiency (such as pernicious anemia, a condition that can cause nerve damage).
Concurrent use of folic acid has been associated with enhanced phenytoin metabolism, lowering the level of the AED in the blood and allowing breakthrough seizures to occur. Caution should be used when prescribing this product among patients who are receiving treatment with phenytoin or other anticonvulsants.
Exercise caution with the concomitant use of folinic acid and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis carinii pneumonia in patients with HIV infection as it is associated with increased rates of treatment failure and mortality in a placebo controlled study.
The action of levodopa is antagonized by pyridoxine.
Products containing iron should not be used during dimercaprol therapy. Dimercaprol can bind to iron and cause kidney damage.
Avoid administering omega-3 fatty acids to patients with inherited or acquired predisposition toward bleeding, including patients taking anticoagulants. Exercise caution with these patients to ensure that the prescribed dosage of DHA does not exceed 1 gram (1000 mg) per day.
-
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Folic Acid
Concurrent use of folic acid has been associated with enhanced phenytoin metabolism, lowering the level of the AED in the blood and allowing breakthrough seizures to occur.
Folinic acid may enhance the toxicity of fluorouracil.
High levels of folic acid may result in decreased serum levels of pyrimethamine.
Concurrent administration of chloramphenicol and folinic acid in folate-deficient patients may result in antagonism of the hematopoietic response to folate.
Antiepileptic drugs (including, but not limited to, phenytoin, carbamazepine, primidone, valproic acid, fosphenytoin, valproate, phenobarbital and lamotrigine) have been shown to impair folate absorption and increase the metabolism of circulating folate.
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine exerts a noncompetitive inhibition of the 5-methyltetrahydrofolate active transport system in the intestine.
Decreased folic acid levels have been reported to be associated with the administration of Cholestyramine, Colestipol, Cycloserine, Dihydrofolate Reductase Inhibitors (aminopterin, methotrexate, pyrimethamine, triamterene, and trimethoprim), L-dopa, colchicine, oral contraceptives, methylprednisolone, pancreatic extracts (pancreatin, pancrelipase), prolonged intravenous pentamidine, smoking and alcohol consumption, sulfasalazine, metformin, heme iron, isotretinoin, and after a 6-month course of therapy, warfarin can produce a significant impairment of folate status.
Thiamin (Vitamin B1)
Furosemide, a loop diuretic, can decrease thiamin levels.
There have been case reports that fluorouracil may increase thiamin metabolism.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6 should not be given to patients receiving the drug levodopa because the action of levodopa is antagonized by Vitamin B6. However, Vitamin B6 may be used concurrently in patients receiving a preparation containing both carbidopa and levodopa.
Isoniazid can produce a Vitamin B6 deficiency.
Vitamin B12
Antibiotics, cholestyramine, colchicine, colestipol, metformin, para-aminosalicylic acid, and potassium chloride may decrease the absorption of vitamin B12 , and nitrous oxide can produce a functional vitamin B12 deficiency.
Vitamin D3
Some thiazide diuretics, such as hydrochlorothiazide, as well as antacids, bile acid sequestrants (such as cholestyramine), mineral oil, orlistat, olestra, cimetidine, and anticonvulsant medications may reduce the absorption or increase the catabolism of Vitamin D.
Vitamin D supplementation should not be given with calcium to patients with hypercalcemia or conditions that may lead to hypercalcemia such as hyperparathyroidism or those who form calcium-containing kidney stones.
Iron
Iron supplements might reduce the amounts of levodopa available to the body and diminish its clinical effectiveness.
Levothyroxine ingested simultaneously with iron can result in clinically significant reductions in levothyroxine efficacy.
Proton pump inhibitors reduce the acidity of stomach contents and can reduce iron absorption.
Cupric oxide
Concomitant use of penicillamine and copper can cause decreased absorption of both substances.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Ingestion of more than 3 grams per day of omega-3 fatty acids (ALA, EPA, and DHA) may have potential antithrombotic effects, and may increase bleeding times.
Avoid administering omega-3 fatty acids to patients with inherited or acquired predisposition toward bleeding, including patients taking anticoagulants. Exercise caution with these patients to ensure that the prescribed dosage of DHA does not exceed 1 gram (1000 mg) per day.
- PREGNANT AND NURSING MOTHERS
- HEALTH CLAIM
- HOW SUPPLIED
- STORAGE
- HEALTH CLAIM
- HEALTH CLAIM
- HEALTH CLAIM
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 Softgel Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
WESNATE DHA
ascorbic acid, cholecalciferol, .alpha.-tocopherol, d-, thiamine mononitrate, riboflavin, pyridoxine hydrochloride, folic acid, cyanocobalamin, ferrous fumarate, magnesium oxide, zinc oxide, cupric sulfate, and omega-3 fatty acids capsule, gelatin coatedProduct Information Product Type DIETARY SUPPLEMENT Item Code (Source) NHRIC:69367-317 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength ASCORBIC ACID (UNII: PQ6CK8PD0R) (ASCORBIC ACID - UNII:PQ6CK8PD0R) ASCORBIC ACID 100 mg CHOLECALCIFEROL (UNII: 1C6V77QF41) (CHOLECALCIFEROL - UNII:1C6V77QF41) CHOLECALCIFEROL 400 [iU] .ALPHA.-TOCOPHEROL, D- (UNII: N9PR3490H9) (.ALPHA.-TOCOPHEROL, D- - UNII:N9PR3490H9) .ALPHA.-TOCOPHEROL, D- 30 [iU] THIAMINE MONONITRATE (UNII: 8K0I04919X) (THIAMINE ION - UNII:4ABT0J945J) THIAMINE 3 mg RIBOFLAVIN (UNII: TLM2976OFR) (RIBOFLAVIN - UNII:TLM2976OFR) RIBOFLAVIN 3 mg PYRIDOXINE HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: 68Y4CF58BV) (PYRIDOXINE - UNII:KV2JZ1BI6Z) PYRIDOXINE 20 mg FOLIC ACID (UNII: 935E97BOY8) (FOLIC ACID - UNII:935E97BOY8) FOLIC ACID 1 mg CYANOCOBALAMIN (UNII: P6YC3EG204) (CYANOCOBALAMIN - UNII:P6YC3EG204) CYANOCOBALAMIN 15 ug FERROUS FUMARATE (UNII: R5L488RY0Q) (FERROUS CATION - UNII:GW89581OWR) FERROUS CATION 28 mg MAGNESIUM OXIDE (UNII: 3A3U0GI71G) (MAGNESIUM CATION - UNII:T6V3LHY838) MAGNESIUM CATION 30 mg ZINC OXIDE (UNII: SOI2LOH54Z) (ZINC CATION - UNII:13S1S8SF37) ZINC CATION 20 mg CUPRIC SULFATE (UNII: LRX7AJ16DT) (CUPRIC CATION - UNII:8CBV67279L) CUPRIC CATION 1 mg OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS (UNII: 71M78END5S) (OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS - UNII:71M78END5S) OMEGA-3 FATTY ACIDS 200 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 2G86QN327L) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SOYBEAN OIL (UNII: 241ATL177A) YELLOW WAX (UNII: 2ZA36H0S2V) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) SOYBEAN LECITHIN (UNII: 1DI56QDM62) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) ETHYL VANILLIN (UNII: YC9ST449YJ) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NHRIC:69367-317-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date DIETARY SUPPLEMENT 12/14/2021 Supplement Facts Serving Size : Serving per Container : Amount Per Serving % Daily Value color scoring 1 shape size (solid drugs) 13 mm imprint Labeler - Westminster Pharmaceuticals, LLC (079516651)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.