JYLAMVO- methotrexate solution
JYLAMVO by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
JYLAMVO by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by SHORLA ONCOLOGY INC., SHORLA PHARMA LTD., SGS Quay Pharmaceuticals Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use JYLAMVO® safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for JYLAMVO®.
JYLAMVO®(methotrexate) oral solution
Initial U.S. Approval: 1953WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS, AND SEVERE ADVERSE REACTIONS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
- Methotrexate can cause embryo-fetal toxicity, including fetal death. For non-neoplastic diseases, Jylamvo is contraindicated in pregnancy. For neoplastic diseases, advise patients of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to use effective contraception during and after treatment with Jylamvo (4, 5.1, 8.1, 8.3).
- Jylamvo is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to methotrexate, including anaphylaxis (4, 5.2).
- Serious adverse reactions, including death, have been reported with methotrexate. Closely monitor for infections and adverse reactions of the bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract, liver, lungs, skin, and kidneys. Withhold or discontinue Jylamvo as appropriate (5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 5.11).
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
JYLAMVO is a folate analog metabolic inhibitor indicated for the:
- Treatment of adults and pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) as part of a combination chemotherapy maintenance regimen (1.1)
- Treatment of adults with mycosis fungoides (1.1)
- Treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma as part of a metronomic combination regimen (1.1)
- Treatment of adults with rheumatoid arthritis (1.2)
- Treatment of pediatric patients with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA) (1.3)
- Treatment of adults with severe psoriasis (1.4)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential before starting JYLAMVO. (2.1, 4, 5.1)
- Instruct patients and caregivers to take the recommended dosage as directed, because medication errors have led to deaths. (2.1, 5.9)
- ALL: The recommended dosage is 20 mg/m2 orally once weekly as a part of a combination chemotherapy maintenance regimen. (2.2)
- Mycosis fungoides: The recommended dosage is 25 mg to 75 mg orally once weekly as monotherapy; 10 mg/m2 orally twice weekly as part of combination chemotherapy. (2.2)
- Relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphoma: The recommended dosage is 2.5 mg orally two to four times per week as part of metronomic combination chemotherapy. (2.2)
- Rheumatoid Arthritis: The recommended starting dosage is 7.5 mg orally once weekly; adjust dose to achieve an optimal response. (2.3)
- pJIA: The recommended starting dosage is 10 mg/m2 orally once weekly; adjust dose to achieve an optimal response. (2.4)
- Psoriasis: The recommended dosage is 10 mg to 25 mg orally once weekly until adequate response is achieved. (2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Oral solution: 2 mg/mL (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Serious Infections: Monitor patients for infection during and after treatment with JYLAMVO. Withhold or discontinue methotrexate for serious infections as appropriate. (5.11)
- Neurotoxicity: Monitor patients for neurotoxicity and withhold or discontinue methotrexate as appropriate. (5.12)
- Secondary Malignancies: Can occur with methotrexate. (5.13)
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome: Institute appropriate prophylactic measures in patients at risk for tumor lysis syndrome prior to initiation of JYLAMVO. (5.14)
- Immunizations and Risks Associated with Live Vaccines: Immunizations with live vaccines is not recommended. Follow current vaccination practice guidelines. (5.15)
- Infertility: Can cause impairment of fertility, oligospermia, and menstrual dysfunction. (5.16, 8.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Common adverse reactions include ulcerative stomatitis, leukopenia, nausea, abdominal distress. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Shorla Oncology at 844-9-SHORLA or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Refer to the full prescribing information for drug interactions with JYLAMVO. (7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 10/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS AND SEVERE ADVERSE REACTIONS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Neoplastic Diseases
1.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
1.3 Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
1.4 Psoriasis
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Safety Information
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Neoplastic Diseases
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Rheumatoid Arthritis
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Psoriasis
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.3 Myelosuppression
5.4 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
5.6 Pulmonary Toxicity
5.7 Dermatologic Reactions
5.8 Renal Toxicity
5.9 Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions with Medication Error
5.10 Folic Acid Supplementation
5.11 Serious Infections
5.12 Neurotoxicity
5.13 Secondary Malignancies
5.14 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
5.15 Immunization and Risks Associated with Live Vaccines
5.16 Infertility
5.17 Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions Due to Third-Space Accumulation
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Methotrexate
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
15 REFERENCES
16 HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: EMBRYO-FETAL TOXICITY, HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS AND SEVERE ADVERSE REACTIONS
- Methotrexate can cause embryo-fetal toxicity, including fetal death. For non-neoplastic diseases, Jylamvo is contraindicated in pregnancy. For neoplastic diseases, advise females and males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during and after treatment with Jylamvo [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Jylamvo is contraindicated in patients with a history of severe hypersensitivity reactions to methotrexate, including anaphylaxis [Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Serious adverse reactions, including death, have been reported with methotrexate. Closely monitor for infections and adverse reactions of the bone marrow, gastrointestinal tract, liver, lungs, skin, and kidneys. Withhold or discontinue Jylamvo as appropriate [Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.4, 5.5, 5.6, 5.7, 5.8, 5.11)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Neoplastic Diseases
JYLAMVO is indicated for the:
- treatment of adults and pediatric patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) as part of a combination chemotherapy maintenance regimen.
- treatment of adults with mycosis fungoides (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma) as a single agent or as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen.
- treatment of adults with relapsed or refractory non-Hodgkin lymphomas as part of a metronomic combination chemotherapy regimen.
1.2 Rheumatoid Arthritis
JYLAMVO is indicated for the treatment of adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Dosage and Safety Information
Verify pregnancy status in females of reproductive potential before starting JYLAMVO [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Instruct patients and caregivers on how to measure and administer the recommended dosage using the copackaged syringe and bottle adaptor as directed, because medication errors have led to deaths [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Ensure patients and caregivers understand the instructions provided in the Patient Information on proper dosing of JYLAMVO based on volume (mL) utilizing the copackaged syringe before use.
Advise patients and caregivers to only use the copackaged syringe to measure JYLAMVO and that a teaspoon is not an appropriate measuring device. The dosing syringe utilizes mL as the unit of measure; ensure that the correct dose expressed in volume (mL) is prescribed. JYLAMVO contains 2 mg of methotrexate in each mL of solution.
JYLAMVO is intended for oral use only. When switching the patient’s dosing regimen from a methotrexate product for oral administration to a methotrexate product for intravenous, intramuscular, or subcutaneous administration, an alternative dosing regimen may be necessary due to potential differences in bioavailability.
JYLAMVO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures1.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Neoplastic Diseases
Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia
The recommended starting dosage of JYLAMVO is 20 mg/m2 orally once weekly, as part of a combination chemotherapy maintenance regimen. After initiating JYLAMVO, periodically monitor absolute neutrophil count (ANC) and platelet count and adjust the dose to maintain ANC at a desirable level and for excessive myelosuppression.
Mycosis Fungoides
The recommended dosage of JYLAMVO is 25 mg to 75 mg orally once weekly when administered as a single agent or 10 mg/m2 orally twice weekly as part of a combination chemotherapy regimen.
Relapsed or Refractory Non-Hodgkin Lymphomas
The recommended dosage of JYLAMVO is 2.5 mg orally 2 to 4 times per week (maximum 10 mg per week) as part of a metronomic combination chemotherapy regimen.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Rheumatoid Arthritis
The recommended starting dosage of JYLAMVO is 7.5 mg orally once weekly with escalation to achieve optimal response. Dosages of more than 20 mg once weekly result in an increased risk of serious adverse reactions, including myelosuppression. When responses are observed, the majority occur between 3 and 6 weeks from initiation of treatment; however, responses have occurred up to 12 weeks after treatment initiation.
Administer folic acid or folinic acid to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
The recommended starting dose of JYLAMVO is 10 mg/m2 orally once weekly with escalation to achieve optimal response. Dosages of more than 30 mg/m2 once weekly result in an increased risk of serious adverse reactions, including myelosuppression. When responses are observed, the majority occurred between 3 and 6 weeks from initiation of treatment; however, responses have occurred up to 12 weeks after treatment initiation.
Administer folic acid or folinic acid to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
2.5 Recommended Dosage for Psoriasis
The recommended dosage of JYLAMVO is 10 mg to 25 mg orally once weekly until an adequate response is achieved. Adjust the dose gradually to achieve optimal clinical response; do not exceed a dose of 30 mg per week. Once optimal clinical response has been achieved, reduce the dosage to the lowest possible dosing regimen.
Administer folic acid or folinic acid supplementation to reduce the risk of methotrexate adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
2.6 Dosage Modifications for Adverse Reactions
Discontinue JYLAMVO for:
- Anaphylaxis or other severe hypersensitivity reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Lymphoproliferative disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
Withhold, dose reduce or discontinue JYLAMVO as appropriate for:
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
Withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO as appropriate for:
- Severe gastrointestinal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Pulmonary toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Severe dermatologic reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Severe renal toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Serious infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Neurotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
JYLAMVO is contraindicated in:
- Pregnant women for treatment of non-neoplastic diseases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
- Patients with a history of a severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, to methotrexate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
Based on published reports and its mechanism of action, methotrexate can cause fetal harm, including fetal death, when administered to a pregnant woman. JYLAMVO is contraindicated for use in pregnant women receiving JYLAMVO for the treatment of non-malignant diseases. Advise pregnant women with neoplastic diseases of the potential risk to a fetus. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JYLAMVO and for 6 months after the final dose. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during JYLAMVO treatment and for at least 3 months after the final dose [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.3)].
5.2 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, can occur with methotrexate [see Contraindications (4), Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
If anaphylaxis or other serious hypersensitivity reaction occurs, immediately and permanently discontinue JYLAMVO [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.3 Myelosuppression
Methotrexate suppresses hematopoiesis and can cause severe and life-threatening pancytopenia, anemia, leukopenia, neutropenia, and thrombocytopenia [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Obtain blood counts at baseline, periodically during treatment, and as clinically indicated. Monitor patients for clinical complications of myelosuppression. Withhold, dose reduce, or discontinue JYLAMVO taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.4 Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and stomatitis occurred in up to 10% of patients receiving methotrexate for treatment of non-neoplastic diseases. Hemorrhagic enteritis and fatal intestinal perforation have been reported [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)]. Patients with peptic ulcer disease or ulcerative colitis are at a greater risk of developing severe gastrointestinal adverse reactions [see Drug Interactions (7.1)].
Withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO for severe gastrointestinal toxicity taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.5 Hepatotoxicity
Methotrexate can cause severe and potentially irreversible hepatotoxicity, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and fatal liver failure [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. The safety of JYLAMVO in patients with hepatic disease is unknown.
The risk of hepatotoxicity is increased with heavy alcohol consumption. In patients with psoriasis, fibrosis or cirrhosis may occur in the absence of symptoms or abnormal liver tests; the risk of hepatotoxicity appears to increase with total cumulative dose and generally occurs after receipt of a total cumulative dose of 1.5 g or more.
Monitor liver tests at baseline, periodically during treatment and as clinically indicated. Withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.6 Pulmonary Toxicity
Pulmonary toxicity, including acute or chronic interstitial pneumonitis and irreversible or fatal cases, can occur with methotrexate [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
Monitor patients for pulmonary toxicity and withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.7 Dermatologic Reactions
Severe, including fatal dermatologic reactions, such as toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, skin necrosis, and erythema multiforme, can occur with methotrexate [see Adverse Reactions (6.1, 6.2)].
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation while taking methotrexate may aggravate psoriasis.
Methotrexate can cause radiation recall dermatitis and photodermatitis (sunburn) reactivation.
Monitor patients for dermatologic toxicity and withhold or permanently discontinue JYLAMVO for severe dermatologic reactions taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)]. Advise patients to avoid excessive sun exposure and use sun protection measures.
5.8 Renal Toxicity
Methotrexate can cause renal toxicity, including irreversible acute renal failure [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Monitor renal function at baseline, periodically during treatment and as clinically indicated. Withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO for severe renal toxicity taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
Administer glucarpidase in patients with toxic plasma methotrexate concentrations (> 1 micromole per liter) and delayed methotrexate clearance due to impaired renal function. Refer to the glucarpidase prescribing information for additional information.
5.9 Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions with Medication Error
Deaths occurred in patients as a result of medication errors. Most commonly, these errors occurred in patients who were taking methotrexate daily when a weekly dosing regimen was prescribed.
For patients prescribed a once weekly dosing regimen, instruct patients and caregivers to take the recommended dosage as directed, because medication errors have led to death.
Instruct patients and caregivers on how to measure, dose, and administer the recommended dosage as directed [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
5.10 Folic Acid Supplementation
Neoplastic Diseases
Products containing folic acid or its derivatives may decrease the clinical effectiveness of methotrexate. Therefore, instruct patients not to take products containing folic acid or folinic acid unless directed to do so by their healthcare provider.
Non-neoplastic Diseases
Folate deficiency may increase methotrexate adverse reactions. Administer folic acid or folinic acid for patients with rheumatoid arthritis, pJIA, and psoriasis [see Dosage and Administration (2.3, 2.4, 2.5)].
5.11 Serious Infections
Patients treated with methotrexate are at increased risk for developing life-threatening or fatal bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, including opportunistic infections such as Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive fungal infections, hepatitis B reactivation, tuberculosis primary infection or reactivation, and disseminated Herpes zoster and cytomegalovirus infections [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)].
Monitor patients for infection during and after treatment with JYLAMVO. Withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO for serious infections taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.12 Neurotoxicity
Methotrexate can cause severe acute and chronic neurotoxicity, which can be progressive, irreversible, and fatal [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. The risk of leukoencephalopathy is increased in patients who received prior cranial radiation.
Monitor patients for neurotoxicity and withhold or discontinue JYLAMVO taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.13 Secondary Malignancies
Secondary malignancies can occur with methotrexate [see Adverse Reactions (6.2)]. The risk of cutaneous malignancies is further increased when cyclosporine is administered to patients with psoriasis who received prior methotrexate.
In some cases, lymphoproliferative disease occurring during therapy with low-dose methotrexate regressed completely following withdrawal of methotrexate. If lymphoproliferative disease occurs, discontinue JYLAMVO [see Dosage and Administration (2.6)].
5.14 Tumor Lysis Syndrome
Methotrexate can induce tumor lysis syndrome in patients with rapidly growing tumors. Institute appropriate prophylactic measures in patients at risk for tumor lysis syndrome prior to initiation of JYLAMVO.
5.15 Immunization and Risks Associated with Live Vaccines
Disseminated infections following administration of live vaccines have been reported. Immunization with live vaccines is not recommended during treatment. Follow current vaccination practice guidelines for administration of immunizations in patients receiving JYLAMVO.
Update immunizations according to immunization guidelines prior to initiating JYLAMVO. The interval between live vaccinations and initiation of methotrexate should be in accordance with current vaccination guidelines for patients on immunosuppressive agents.
5.16 Infertility
Based on published reports, methotrexate can cause impairment of fertility, oligospermia, and menstrual dysfunction. It is not known if the infertility may be reversible. Discuss the risk of infertility with females and males of reproductive potential [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
5.17 Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions Due to Third-Space Accumulation
Methotrexate accumulates in third-spaces (e.g., pleural effusions or ascites), which results in prolonged elimination and increases the risk of adverse reactions. Evacuate significant third-space accumulations prior to JYLAMVO administration taking into account the importance of JYLAMVO treatment in the context of the severity of the disease being treated, the severity of the adverse drug reaction, and availability of alternative therapy.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Myelosuppression [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Gastrointestinal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)]
- Hepatotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)]
- Pulmonary Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)]
- Dermatologic Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
- Renal Toxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)]
- Serious Infections [see Warnings and Precautions (5.11)]
- Neurotoxicity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)]
- Secondary Malignancies [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)]
- Tumor Lysis Syndrome [see Warnings and Precautions (5.14)]
- Increased Risk of Adverse Reactions Due to Third-Space Accumulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.17)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Common adverse reactions were: ulcerative stomatitis, leukopenia, nausea, and abdominal distress. Other clinically relevant adverse reactions were infection, malaise, fatigue, chills, fever, and dizziness.
Rheumatoid Arthritis
The most common adverse reactions of methotrexate that exceeded the rate of placebo in 12- to 18-week double-blind studies in patients (n=128) with rheumatoid arthritis are listed below. Patients received methotrexate 7.5 mg to 15 mg orally once weekly. Most patients received concomitant nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and some also received corticosteroids. Hepatic histology was not examined in these short-term studies.
Incidence ≥10%: Elevated liver tests 15%, nausea/vomiting 10%
Incidence 3% to <10%: Stomatitis, thrombocytopenia (platelet count < 100,000/mm3)
Incidence 1% to <3%: Rash/pruritus/dermatitis, diarrhea, alopecia, leukopenia (white blood cell count < 3000/mm3), pancytopenia, dizziness
Two other controlled trials of patients (n=680) with rheumatoid arthritis who received methotrexate 7.5 mg to 15 mg orally once weekly showed the following serious adverse reaction:
Incidence 1%: Interstitial pneumonitis
Other less common adverse reactions were: anemia, headache, upper respiratory infection, anorexia, arthralgias, chest pain, coughing, dysuria, eye discomfort, epistaxis, fever, infection, sweating, tinnitus, vaginal discharge.
Polyarticular Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis (pJIA)
The most common adverse reactions reported in patients 2 to 18 years of age with pJIA treated with methotrexate 5 mg/m2 to 20 mg/m2 orally once weekly or 0.1 mg/kg to 0.65 mg/kg orally once weekly were as follows: elevated liver tests 14%; gastrointestinal reactions (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea) 11%; stomatitis 2%; leukopenia 2%; headache 1.2%; alopecia 0.5%; dizziness 0.2%; rash 0.2%. Most patients received concomitant NSAIDs and some also received corticosteroids.
Psoriasis
In two published series of adults with psoriasis (n=204, 248) who received methotrexate up to 25 mg per week for up to 4 years, adverse reaction rates were similar to those in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, except for alopecia, photosensitivity, and “burning of skin lesions” (3% to 10% each). Painful plaque erosions have been reported.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during postapproval use of methotrexate. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiovascular: Thromboembolic events (including arterial thrombosis, cerebral thrombosis, deep vein thrombosis, retinal vein thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, and pulmonary embolus), pericarditis, pericardial effusion, hypotension, sudden death
Endocrine: Diabetes
Eye: Optic neuropathy, blurred vision, ocular pain, conjunctivitis, xerophthalmia
Gastrointestinal: Hemorrhagic enteritis, intestinal perforation, gingivitis, pancreatitis, pharyngitis, hematemesis, melena, gastrointestinal ulceration
Hematology: Aplastic anemia, lymphadenopathy, hypogammaglobulinemia
Hepatobiliary: Acute hepatitis, decreased serum albumin, fibrosis, cirrhosis
Immune system: Anaphylaxis, anaphylactoid reactions, vasculitis
Metabolism: Hyperglycemia
Musculoskeletal: Stress fracture, soft tissue and bone necrosis, arthralgia, myalgia, osteoporosis
Nervous system: Headaches, drowsiness, blurred vision, speech impairment (including dysarthria and aphasia), transient cognitive dysfunction, mood alteration, unusual cranial sensations, paresis, encephalopathy, and convulsions.
Renal: Azotemia, hematuria, proteinuria, cystitis
Reproductive: Defective oogenesis or spermatogenesis, loss of libido, impotence, gynecomastia, menstrual dysfunction
Respiratory: Pulmonary fibrosis, respiratory failure, chronic interstitial obstructive pulmonary disease, pleuritic pain and thickening, alveolitis
Skin: Toxic epidermal necrolysis, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, exfoliative dermatitis, skin necrosis, and erythema multiforme, erythematous rashes, pruritus, alopecia, skin ulceration, accelerated nodulosis, urticaria, pigmentary changes, ecchymosis, telangiectasia, photosensitivity, acne, furunculosis
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Other Drugs on Methotrexate
Drugs that Increase Methotrexate Exposure
Coadministration of methotrexate with the following products may increase methotrexate plasma concentrations, which may increase the risk of methotrexate severe adverse reactions. In some cases, the coadministration of methotrexate with these products may also subsequently reduce active metabolite formation, which may decrease the clinical effectiveness of methotrexate. Increased organ specific adverse reactions may also occur when methotrexate is coadministered with hepatotoxic or nephrotoxic products.
If coadministration cannot be avoided, monitor closely for methotrexate adverse reactions when coadministered with:
- Oral antibiotics (including neomycin)
- Oral or intravenous penicillin or sulfonamide antibiotics
- Antifolate drugs (e.g., dapsone, pemetrexed, pyrimethamine and sulfonamides)
- Aspirin and other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
- Hepatotoxic products
- Highly protein-bound drugs (e.g., oral anticoagulants, phenytoin, salicylates, sulfonamides, sulfonylureas, and tetracyclines)
- Probenecid
- Proton pump inhibitors
- Weak acids (e.g., salicylates)
- Nephrotoxic products
Nitrous Oxide
Coadministration of methotrexate with nitrous oxide anesthesia potentiates the effect of methotrexate on folate-dependent metabolic pathways, which may increase the risk of severe methotrexate adverse reactions. Avoid nitrous oxide anesthesia in patients receiving methotrexate. Consider alternative therapies in patients who have received prior nitrous oxide anesthesia.
Folic Acid
Coadministration of methotrexate with folic acid or its derivatives decreases the clinical effectiveness of methotrexate in patients with neoplastic diseases. Methotrexate competes with reduced folates for active transport across cell membranes. Instruct patients to take folic or folinic acid only as directed by their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10)].
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Based on published reports and methotrexate’s mechanism of action, methotrexate can cause embryo-fetal toxicity and fetal death when administered to a pregnant woman [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.1)]. There are no animal data that meet current standards for nonclinical developmental toxicity studies. In pregnant women with non-malignant disease, JYLAMVO is contraindicated. Consider the benefits and risks of JYLAMVO and risks to the fetus when prescribing JYLAMVO to a pregnant patient with a neoplastic disease.
The background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated populations are unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Human Data
Published data from case reports, literature reviews, and observational studies report that methotrexate exposure during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of embryo-fetal toxicity and fetal death. Methotrexate exposure during the first trimester of pregnancy is associated with an increased incidence of spontaneous abortions and multiple adverse developmental outcomes, including skull anomalies, facial dysmorphism, central nervous system abnormalities, limb abnormalities, and sometimes cardiac anomalies and intellectual impairment. Adverse outcomes associated with exposure during second and third trimesters of pregnancy include intrauterine growth restriction and functional abnormalities. Because methotrexate is widely distributed and persists in the body for a prolonged period, there is a potential risk to the fetus from preconception methotrexate exposure.
A prospective multicenter study evaluated pregnancy outcomes in women taking methotrexate less than or equal to 30 mg/week after conception. The rate of spontaneous abortion and miscarriage in pregnant women exposed to methotrexate was 42% (95% confidence interval [95% CI] 29, 59), which was higher than in unexposed patients with autoimmune disease (22%; 95% CI: 17, 30) and unexposed patients with nonautoimmune disease (17%; 95% CI: 13, 23). Of the live births, the rate of major birth defects in pregnant women exposed to methotrexate after conception was higher than in unexposed patients with autoimmune disease (adjusted odds ratio (OR) 1.8 [95% CI: 0.6, 6]) and unexposed patients with non-autoimmune disease (adjusted OR 3.1 [95% CI: 1, 10]) (2.9%). Major birth defects associated with pregnancies exposed to methotrexate after conception were not always consistent with methotrexate-associated adverse developmental outcomes.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
Limited published literature report the presence of methotrexate in human milk in low amounts, with the highest breast milk to plasma concentration ratio reported to be 0.08:1. There are no data on the effects of methotrexate or its metabolites on the breastfed child or their effects on milk production. Because of the potential for serious adverse reactions in a breastfed child, including myelosuppression, advise women not to breastfeed during treatment with JYLAMVO and for 1 week after the final dose.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Methotrexate can cause malformations and fetal death at doses less than or equal to the recommended clinical doses [Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Pregnancy Testing
Verify the pregnancy status of females of reproductive potential prior to initiating JYLAMVO [see Contraindications (4), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
Contraception
Females
JYLAMVO can cause fetal harm when administered to a pregnant woman [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1)]. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JYLAMVO and for 6 months after the final dose of JYLAMVO.
Males
Methotrexate can cause chromosomal damage to sperm cells. Advise males with female partners of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JYLAMVO and for at least 3 months after the final dose of JYLAMVO.
Infertility
Females
Based on published reports of female infertility after treatment with methotrexate, advise females of reproductive potential that methotrexate can cause impairment of fertility and menstrual dysfunction during treatment with JYLAMVO and after the final dose. It is not known if the infertility may be reversed in all affected females.
Males
Based on published reports of male infertility after treatment with methotrexate, advise males of reproductive potential that methotrexate can cause oligospermia or infertility during treatment with JYLAMVO and after the final dose. It is not known if the infertility may be reversed in all affected males.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of JYLAMVO in pediatric patients have been established for the treatment of ALL as part of the combination chemotherapy maintenance regimen and the treatment of pJIA [see Indications and Usage (1), Dosage and Administration (2), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of JYLAMVO have not been established in pediatric patients for the other indications [see Indications and Usage (1)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of methotrexate did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects.
8.6 Renal Impairment
Methotrexate elimination is reduced in patients with renal impairment [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Patients with renal impairment are at increased risk for methotrexate adverse reactions. Closely monitor patients with renal impairment [creatinine clearance (CLcr) less than 90 mL/min, Cockcroft-Gault] for adverse reactions. Reduce the dosage or discontinue JYLAMVO as appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
The pharmacokinetics and safety of methotrexate in patients with hepatic impairment is unknown. Patients with hepatic impairment may be at increased risk for methotrexate adverse reactions based on the elimination characteristics of methotrexate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Closely monitor patients with hepatic impairment for adverse reactions. Reduce the dosage or discontinue JYLAMVO as appropriate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Overdosage, including fatal overdosage, has occurred with methotrexate [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Manifestations
Manifestations of methotrexate overdosage include adverse reactions reported at pharmacologic doses, particularly hematologic and gastrointestinal reactions (e.g., leukopenia, thrombocytopenia, anemia, pancytopenia, myelosuppression, mucositis, stomatitis, oral ulceration, nausea, vomiting, gastrointestinal ulceration, or gastrointestinal bleeding). In some cases, no symptoms were reported; however, sepsis or septic shock, renal failure, and aplastic anemia were also reported.
Management
Leucovorin and levoleucovorin are indicated for diminishing the methotrexate adverse reactions of methotrexate overdosage. Administer leucovorin or levoleucovorin as soon as possible after methotrexate overdosage. Monitor serum creatinine and methotrexate levels to guide leucovorin or levoleucovorin therapy. Refer to the leucovorin or levoleucovorin prescribing information for additional dosage information.
Glucarpidase is indicated for the treatment of toxic plasma methotrexate concentrations (>1 micromole per liter) in patients with delayed methotrexate clearance due to impaired renal function. Refer to the glucarpidase prescribing information for additional dosage information.
Administer concomitant hydration and urinary alkalinization.
Neither hemodialysis nor peritoneal dialysis has been shown to improve methotrexate elimination; however, methotrexate has been effectively cleared with acute, intermittent hemodialysis using a high-flux dialyzer.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Methotrexate is a folate analog metabolic inhibitor with the chemical name of N-[4-[[(2,4 diamino-6-pteridinyl) methyl]methylamino]benzoyl]-L glutamic acid. The molecular formula is C20H22N8O5 and the molecular weight is 454.4 g/mol. The structural formula is:
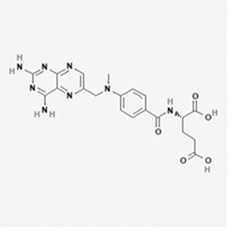
JYLAMVO (methotrexate) oral solution is a clear yellow solution that contains methotrexate, 2 mg/mL. Inactive ingredients include citric acid, ethylparaben, glycerin, methylparaben sodium, orange flavoring powder, polyethylene glycol, purified water, sodium citrate and sucralose. The target pH of the oral solution is 6.8.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Methotrexate inhibits dihydrofolic acid reductase. Dihydrofolates must be reduced to tetrahydrofolates by this enzyme before they can be utilized as carriers of one-carbon groups in the synthesis of purine nucleotides and thymidylate. Therefore, methotrexate interferes with DNA synthesis, repair, and cellular replication. Actively proliferating tissues such as malignant cells, bone marrow, fetal cells, buccal and intestinal mucosa, and cells of the urinary bladder are in general more sensitive to this effect of methotrexate.
The mechanism of action in rheumatoid arthritis and in psoriasis is unknown.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
At doses of 30 mg/m2 or less, the mean bioavailability is approximately 60%. Peak plasma concentrations are reached within 0.75 to 6 hours following oral administration. Methotrexate may undergo enterohepatic recirculation; however, this pathway has not been fully characterized.
Effect of Food
Food has been shown to delay absorption and reduce peak concentration.
Distribution
Methotrexate in serum is approximately 50% protein bound.
Methotrexate does not penetrate the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier at concentrations achieved with the recommended dosages.
Elimination
The elimination half-life of methotrexate is approximately 3 to 10 hours.
Small amounts of methotrexate polyglutamates may remain in tissues for extended periods. The retention and prolonged drug action of these active metabolites vary among different cells, tissues, and tumors.
Nonlinear elimination due to saturation of renal tubular reabsorption has been observed in studies of patients with psoriasis receiving methotrexate doses between 7.5 mg and 30 mg.
Metabolism
Methotrexate is partially metabolized by intestinal flora after oral administration.
Methotrexate primarily undergoes hepatic and intracellular metabolism to active polyglutamated forms which can be converted back to methotrexate by hydrolase enzymes. Methotrexate also undergoes minor metabolism to active 7-hydroxymethotrexate.
Excretion
Methotrexate primarily undergoes renal excretion by glomerular filtration and active tubular secretion that is dependent upon dosage and route of administration.
Biliary excretion accounts for ≤10% of the methotrexate dose.
Specific Populations
The effect of hepatic impairment on the pharmacokinetics of methotrexate is unknown.
Pediatric Patients
In pediatric patients with leukemia, oral absorption (23% to 95%) of methotrexate is variable and dose-dependent. The difference between highest and lowest peak methotrexate concentrations (Cmax 0.11 to 2.3 micromolar after a 20 mg/m2 dose) was 20-fold. The time to peak concentration (Tmax 0.67 to 4 hours after a 15 mg/m2 dose) and fraction of dose absorbed is variable. The absorption of doses greater than 40 mg/m2 is significantly less than that of lower doses.
In pediatric patients with pJIA, plasma concentrations of methotrexate are variable. Following oral administration of methotrexate 6.4 mg/m2/week to 11.2 mg/m2/week, mean serum concentrations were 0.59 micromolar (0.03 to 1.40) at 1 hour, 0.44 micromolar (0.01 to 1.00) at 2 hours, and 0.29 micromolar (0.06 to 0.58) at 3 hours.
In pediatric patients receiving methotrexate for acute lymphoblastic leukemia (6.3 mg/m2 to 30 mg/m2) or for JIA (3.75 mg/m2 to 26.2 mg/m2), the terminal half-life has been reported to range from 0.7 to 5.8 hours or from 0.9 to 2.3 hours, respectively.
Patients with Renal Impairment
The elimination half-life of methotrexate is variable and increases with the severity of renal impairment.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Methotrexate has been evaluated in a number of animal studies for carcinogenic potential with inconclusive results. Although there is evidence that methotrexate causes chromosomal damage to animal somatic cells and human bone marrow cells, the clinical significance remains uncertain.
- 15 REFERENCES
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED / STORAGE AND HANDLING
JYLAMVO is supplied as a clear yellow oral solution that contains 2 mg of methotrexate per mL. It is packaged in an amber type III glass bottle with tamper evident child-resistant closure (polypropylene with expanded polyethylene liner) containing 60 mL of oral solution.
Each pack contains one bottle, a low-density polyethylene (LDPE) bottle adaptor and a 10 mL white polypropylene dosing syringe (with major graduations at every 1 mL and minor graduations at every 0.25 mL) (NDC: 81927-204-01).
Store JYLAMVO at 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F) excursions permitted to 15°C to 30°C (59°F to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
In Use storage conditions: Store JYLAMVO at room temperature 20°C to 25°C (68°F to 77°F). Keep the bottle tightly closed. After first opening, discard any unused medicine after 3 months.
JYLAMVO is a hazardous drug. Follow applicable special handling and disposal procedures.1
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Embryo-Fetal Toxicity
- Advise females of reproductive potential of the potential risk to a fetus and to inform their healthcare provider of a known or suspected pregnancy [see Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.1), Use in Specific Populations (8.1)].
- Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JYLAMVO and for 6 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Advise males of reproductive potential to use effective contraception during treatment with JYLAMVO and for at least 3 months after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise patients and their caregivers of the potential risk of hypersensitivity and that JYLAMVO is contraindicated in patients with a history of hypersensitivity reactions to methotrexate. Instruct patients to seek immediate medical attention for signs of a hypersensitivity reaction [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Myelosuppression and Serious Infections
Inform patients and their caregivers that JYLAMVO can cause myelosuppression and the need for frequent monitoring of blood cell counts. Advise patients and their caregivers to immediately report new onset fever, symptoms of infection, easy bruising or persistent bleeding to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3, 5.11)].
Gastrointestinal Toxicity
Advise patients and their caregivers to report new or worsening diarrhea, vomiting, or stomatitis to their healthcare provider. Advise patients to immediately contact their healthcare provider for high fever, rigors, persistent or severe abdominal pain, severe constipation, hematemesis, or melena [see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)].
Hepatotoxicity
Advise patients and their caregivers to report signs or symptoms of hepatic toxicity to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Pulmonary Toxicity
Advise patients and their caregivers to report new or worsening cough, fever, or dyspnea to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Dermatologic Reactions
Advise patients and their caregivers that JYLAMVO can cause serious skin rash and to immediately contact their healthcare provider for new or worsening skin rash. Advise patients and their caregivers to avoid excessive sun exposure and use sun protection measures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)].
Renal Toxicity
Advise patients and their caregivers to immediately contact their healthcare provider for signs or symptoms of renal toxicity, such as marked increases or decreases in urinary output [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
Risk of Serious Adverse Reactions with Medication Error
For patients who are prescribed a once weekly dosing regimen, advise patients and caregivers that the recommended dosage is to be taken once weekly as a single dose and that mistakenly taking the recommended weekly dosage once daily has led to fatal adverse reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Importance of Proper Dosage and Administration
Before use, instruct patients and caregivers on how to measure and administer the recommended dosage, utilizing the copackaged syringe and bottle adaptor and that a teaspoon is not an appropriate measuring device. Advise patients and caregivers to only use the copackaged syringe and that a household spoon is not an accurate measuring device [see Dosage and Administration (2)].
Neurotoxicity
Advise patients and their caregivers to report new neurological signs or symptoms to their healthcare provider [see Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
Secondary Malignancies
Advise patients on the risk of second primary malignancies during treatment with JYLAMVO [see Warnings and Precautions (5.13)].
Ineffective Immunization and Risks Associated with Live Vaccines
Advise patients to avoid receiving vaccines during treatment with JYLAMVO because they may not be effective and live virus vaccines may cause infections [see Warnings and Precautions(5.15)].
Lactation
Instruct women not to breastfeed during treatment with JYLAMVO and for 1 week after the final dose [see Use in Specific Populations (8.2)].
Infertility
Advise females and males of reproductive potential that methotrexate may impair fertility [see Warnings and Precautions (5.16), Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
Drug Interactions
Advise patients and caregivers to inform their healthcare provider of all concomitant medications, including prescription medicines, over-the-counter drugs, vitamins, and herbal products [see Drug Interactions (7)].
Proper Storage and Disposal
Advise patients to store JYLAMVO at room temperature (20°C to 25°C/ 68°F to 77°F). Once the bottle has been opened, any remaining medication must be disposed of after 90 days. Inform patients and caregivers of the need for proper disposal of the medication, bottle, and syringe [see References (15)]. This medicine should not be disposed of in wastewater or household waste.
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
JYLAMVO® (Jye lam voe)
(methotrexate)oral solution
What is the most important information I should know about JYLAMVO®?
JYLAMVO can cause serious side effects that may be severe and lead to death, including:
Harm to an unborn baby, including birth defects or death of an unborn baby.
Females who can become pregnant:
- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start taking JYLAMVO to see if you are pregnant.
- If you are being treated for a medical condition other than cancer, do not take JYLAMVO if you are pregnant. See “Who should not take JYLAMVO?”
- If you are taking JYLAMVO to treat your cancer, you and your healthcare provider will decide if you will take JYLAMVO if you are pregnant.
- Use effective birth control (contraception) during treatment and for 6 months after your final dose of JYLAMVO. Ask your healthcare provider what forms of birth control you can use during this time.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you become pregnant or think you are pregnant during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Males with female partners who are able to become pregnant:
- Use effective birth control during treatment and for at least 3 months after your final dose of JYLAMVO.
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if your female partner becomes pregnant during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Severe allergic reactions. Severe allergic reactions can happen with JYLAMVO. Signs and symptoms of a severe allergic reaction may include:
- skin rash, itching and hives
- swelling of the face, lips, tongue, or throat
- dizziness
- trouble breathing
- wheezing
- fast heart rate
- feeling faint
- stomach-area pain
- vomiting or diarrhea
Do not take JYLAMVO if you have had a severe allergic reaction to methotrexate in the past.
Get medical help right away if you develop any of the signs or symptoms of a severe allergic reaction listed above.
Decreased blood cell counts. JYLAMVO can affect your bone marrow and cause decreases in red blood counts, white blood cell counts, and platelets that can be severe and life-threatening.
- Your healthcare provider will check your blood cell counts when you start and during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Call your healthcare provider right away if you develop any of the following:
- a new fever
- symptoms of infection
- easy bruising or bleeding that will not stop (persistent bleeding)
Severe stomach and intestine problems (gastrointestinal) problems.
- Diarrhea, vomiting, nausea, and mouth sores can happen in people who take JYLAMVO.
- Inflammation of the intestine with severe bleeding and a tear in the intestinal wall (perforation) have happened with methotrexate and cause death.
- People who have stomach ulcers (peptic ulcer disease) or ulcerative colitis (UC) have a greater risk of developing severe stomach or intestine problems with JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider if you develop new or worsening diarrhea, vomiting, or mouth sores during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop high fever, shaking chills (rigors), pain in your stomach-area (abdomen) that will not go away or is severe, severe constipation, if you are vomiting blood or have blood in your stools.
Liver problems. JYLAMVO can cause severe liver problems including liver scarring (fibrosis), cirrhosis, and liver failure that may not get better (possibly irreversible) and can cause death.
- In people with psoriasis who take JYLAMVO, liver fibrosis or cirrhosis may happen without any symptoms or abnormal liver tests. The risk for liver problems in people with psoriasis increases with the amount of JYLAMVO taken over time.
- Your healthcare provider will do tests to monitor your liver function before you start and during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider if you have any signs or symptoms of liver problems during treatment with JYLAMVO, including:
- tiredness
- easy bleeding or bruising
- loss of appetite
- nausea
- difficulty thinking clearly
- swelling in your legs, feet or ankles
- weight loss
- itchy skin
- yellowing of your skin or the white part of your eyes
- weakness
Lung problems. Lung problems can happen suddenly (acute) with JYLAMVO or they can develop over a long period-of-time (chronic). Lung problems may not get better (possibly irreversible) and can cause death. Tell your healthcare provider if you have any new or worsening symptoms including: cough (especially a dry cough), fever, or trouble breathing.
Severe skin reactions. Severe skin reactions can happen with JYLAMVO and can lead to death.
- In people with psoriasis: Your psoriasis may get worse if you are exposed to sunlight or other types of ultraviolet light.
- JYLAMVO can cause reactivation of skin reactions that can happen after radiation therapy (radiation recall dermatitis) and cause sunburn to come back (photodermatitis).
Limit sunlight exposure during treatment with JYLAMVO. Use sunscreen and wear protective clothing when you will be exposed to sunlight during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider right away about any new or worsening skin rash during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Kidney problems. Kidney problems can happen with JYLAMVO, including kidney failure which can happen suddenly (acute) and may not go away (irreversible).
Your healthcare provider will check your kidney function before you start and during treatment with JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider right away if you have any signs or symptoms of kidney problems, including:
- a big change (either increase or decrease)
in the amount of urine you produce - swelling in your legs, ankles or feet
- shortness of breath
- tiredness
- weight gain
See “What are the possible side effects of JYLAMVO” for more information about side effects.
What is JYLAMVO?
JYLAMVO is a prescription medicine used:
- in combination with other chemotherapy medicines in adults and children, for maintenance treatment of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL)
- to treat adults with mycosis fungoides (cutaneous T-cell lymphoma)
- in combination with other therapies to treat adults with non-Hodgkin lymphoma that has come back (relapsed) or did not respond to previous treatment (refractory)
- to treat adults with rheumatoid arthritis
- to treat children with polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (pJIA)
- to treat adults with severe psoriasis
It is not known if JYLAMVO is safe in people with liver problems.
Do not take JYLAMVO if you:
- are pregnant and are being treated or will be treated with JYLAMVO for rheumatoid arthritis, pJIA, severe psoriasis or for any medical condition other than cancer. JYLAMVO can cause harm to an unborn baby, including birth defects or death of an unborn baby. See “What is the most important information I should know about JYLAMVO?”
- have or had a severe allergic reaction to JYLAMVO or any other medicine containing methotrexate. See “What is the most important information I should know about JYLAMVO?” See the end of this Patient Information leaflet for a complete list of ingredients in JYLAMVO.
Before taking JYLAMVO tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have kidney problems or are receiving dialysis treatments.
- have liver problems.
- drink alcohol-containing beverages and, during treatment with JYLAMVO, if there are any changes in the amount of alcoholic beverages you drink.
- have fluid in your stomach-area (ascites).
- have lung problems or fluid in your lungs (pleural effusion).
- plan to have any surgeries with general anesthesia, including dental surgery.
- have stomach ulcers (peptic ulcer disease).
- have ulcerative colitis.
- have recently received or are scheduled to receive a vaccine. You should not receive live vaccines during treatment with JYLAMVO. These vaccines may not be safe or may not work as well during treatment with JYLAMVO.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. JYLAMVO may pass into your breast milk. Do not breastfeed during treatment and for 1 week after your last dose of JYLAMVO.
Tell your healthcare provider about all the medicines you take, including prescription and over-the-counter medicines, vitamins and herbal supplements. JYLAMVO and certain other medicines can affect each other and cause serious side effects. Do not start or change any medicines unless you have talked to your healthcare provider and your healthcare provider has told you it is safe. Know all the medicines that you take and keep a list of them with you at all times to show healthcare providers and pharmacists.
How should I take JYLAMVO?
- JYLAMVO is for use by mouth only (oral use).
- Take JYLAMVO exactly as prescribed by your healthcare provider. Your dose of JYLAMVO and when you take it will depend on the condition that is being treated.
- Do not take more JYLAMVO than prescribed. Do not change your dose of JYLAMVO unless your healthcare provider tells you to.
- Taking more JYLAMVO than prescribed or taking JYLAMVO more often than prescribed, can lead to severe side effects and cause death.
- If you take too much JYLAMVO call your healthcare provider or go to your nearest hospital emergency room right away. You will need to receive a medicine as soon as possible to help reduce side effects that could be severe and could cause death.
- If you miss taking a dose of JYLAMVO, call your healthcare provider for instructions about when to take your next dose of JYLAMVO.
If you are taking JYLAMVO for treatment of severe psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis or polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis:
- Take your JYLAMVO dose 1 time each week, not every day. Severe side effects and death have happened in people who mistakenly have taken JYLAMVO every day instead of 1 time each week.
- Take a folic acid or folinic acid supplement every day during treatment with JYLAMVO, as instructed by your healthcare provider, to help reduce the chance of developing certain side effects, such as mouth sores.
If you are taking JYLAMVO to treat your cancer:
- Follow your healthcare provider’s instructions about how much JYLAMVO to take and when to take it.
- Do not take folic acid or folinic acid during treatment with JYLAMVO unless your healthcare provider tells you to. Taking folic acid or folinic acid with JYLAMVO may make your JYLAMVO treatment less effective.
Instructions for Using JYLAMVO
Each pack of JYLAMVO contains a bottle of medicine with a cap, a bottle neck adaptor, and a white dosing syringe. Always use the dosing syringe provided in the pack to take JYLAMVO. A household teaspoon is not an accurate measuring device.
Note: the dosing syringe measures the amount of oral solution in mL and JYLAMVO contains 2 mg of methotrexate in 1 mL of solution.
Read and carefully follow the instructions below:
- Put on disposable gloves before handling JYLAMVO.
- Shake the bottle.
- Remove the bottle cap and push the adaptor firmly into the top of the bottle.
- Push the tip of the dosing syringe into the hole in the adaptor.
- Turn the bottle upside down.
- Pull the syringe plunger back slowly so that the medicine is drawn from the bottle into the syringe until the widest part of the white syringe plunger is lined up to the black syringe marking of the prescribed dose. Do not measure to the narrow tip of the plunger. If there are air bubbles in the syringe, use the syringe plunger to push the medicine back into the bottle then draw the medicine into the syringe again until there are no more air bubbles.
- Turn the bottle back upright and carefully remove the syringe from the adaptor, holding the syringe by the barrel rather than the plunger.
- Check that the dose in the syringe is correct.
- Make sure that you are sitting up or standing before taking the medicine.
- Gently place the tip of the syringe in your mouth and direct it to the inside of your cheek.
- Slowly and gently push the plunger down to gently squirt the medicine into the inside of your cheek. Do not pushdown on the plunger too hard or squirt the medicine to the back of the mouth or throat as this may cause choking. The plunger should be pushed down gently and completely until it clicks into place.
- Remove the syringe from your mouth.
- Swallow the medicine and then drink some water, making sure no medicine is left in the mouth.
- Put the cap back on the bottle with the adaptor left in place. Make sure that the cap is tightly closed.
- Wash the syringe immediately after use with warm, soapy water and rinse well. The syringe should be held underwater and the plunger drawn in and out several times until all of the medicine is removed from inside the syringe including the tip. Remove the plunger from the syringe barrel and wash both parts well in the warm, soapy water. Each part should then be rinsed well under cold water and any extra water shaken off before wiping dry with a clean paper towel. The plunger and barrel should be stored in a clean dry container with the medicine. All parts of the syringe should be completely dry before putting the plunger back into the syringe and using it for the next dose.
What are the possible side effects of JYLAMVO?
JYLAMVO can cause serious side effects that may be severe and lead to death including:
- See “What is the most important information I should know about JYLAMVO?”
- Serious infections. People who take methotrexate have an increased risk of developing infections that can be life-threatening or cause death. These infections may include: bacterial, fungal, or viral infections, including Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia, invasive fungal infections, hepatitis B infection that comes back (reactivation), tuberculosis infection that may be new or reactivation, and Herpes zoster or cytomegalovirus (CMV) that spreads throughout the body (disseminated).
- Tell your healthcare provider right away if you develop a new fever or if you have any symptoms of infection during treatment with JYLAMVO.
-
Brain and spinal cord (nervous system) problems. Methotrexate can cause nervous system problems that can be severe and last for a short time or last for a long time. These nervous system problems can get progressively worse, may not get better (irreversible), and can cause death. The risk for a certain nervous system problem called leukoencephalopathy is increased in people who have had radiation treatment to their head (cranial radiation) in the past.
Tell your healthcare provider about any new nervous system symptoms that you develop during treatment with JYLAMVO. -
New (secondary) cancers. New (secondary) cancers can happen in people who take JYLAMVO.
- In people with psoriasis, the risk of new skin cancers is increased with JYLAMVO and further increased if you take the medicine cyclosporine after receiving treatment with JYLAMVO.
- Certain blood cancers can happen during treatment with JYLAMVO. In some cases, these blood cancers may completely go away (regress completely) after JYLAMVO is stopped.
- Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS). TLS is caused by the fast breakdown of cancer cells. TLS can cause kidney failure and the need for dialysis treatment, abnormal heart rhythm, seizure, and sometimes death. Your healthcare provider may do blood tests to check you for TLS if you are receiving JYLAMVO as a cancer treatment.
- Possible fertility problems (infertility) in males and females. JYLAMVO can cause fertility problems in males and females, and can cause sperm production to stop in males, and menstrual problems in females. Males may not be able to father a child. Females may not be able to become pregnant. It is not known if your fertility may return. Talk with your healthcare provider about your risk for infertility if this is a concern for you.
The most common side effects of JYLAMVO include:
- mouth sores
- low white blood cells. See“What is the most important information I should know about JYLAMVO?”
- nausea, upset stomach
These are not all the possible side effects of JYLAMVO. Ask your healthcare provider or pharmacist for more information. Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800- FDA-1088.
How should I store JYLAMVO?
- Store the JYLAMVO bottle at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep JYLAMVO tightly closed with the cap on the bottle.
- Store the dosing syringe in a clean, dry place when not in use.
- Use JYLAMVO within 3 months of first opening the bottle. After 3 months throw away (dispose of) any remaining medicine. Ask the pharmacist how to throw away (dispose of) unused medicine, the bottle and the dosing syringe. This medicine should not be disposed of in wastewater or household waste.
Keep JYLAMVO and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of JYLAMVO.
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use JYLAMVO for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give JYLAMVO to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. This Patient Information leaflet summarizes the most important information about JYLAMVO. If you would like more information, talk with your healthcare provider. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about JYLAMVO that is written for health professionals.
What are the ingredients in JYLAMVO?
Active Ingredient: methotrexate
Inactive Ingredients: citric acid, ethylparaben, glycerin, methylparaben sodium, orange flavoring powder, polyethylene glycol, purified water, sodium citrate and sucralose.
Manufactured By:
SGS Quay Pharmaceuticals Ltd., Deeside, UKDistributed By:
Shorla Oncology Inc., Cambridge, MA 02142, USA Version: JYLPL007This Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Revised: 10/2025
- Your healthcare provider should do a pregnancy test before you start taking JYLAMVO to see if you are pregnant.
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
WARNING: Hazardous drug
NDC: 81927-204-01
Jylamvo®
(methotrexate)
Oral Solution
2 mg/mL
For Oral Use Only
Attention Pharmacist:
Dispense the accompanying Patient
Information to each patient.60 mL
Rx Only

WARNING: hazardous drug
NDC: 81927-204-01
Jylamvo®
(methotrexate)
Oral Solution
2 mg/mL
For Oral Use Only
Attention Pharmacist:
Dispense the accompanying Patient
Information to each patient.60 mL
Rx Only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
JYLAMVO
methotrexate solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 81927-204 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength METHOTREXATE (UNII: YL5FZ2Y5U1) (METHOTREXATE - UNII:YL5FZ2Y5U1) METHOTREXATE 2 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) SUCRALOSE (UNII: 96K6UQ3ZD4) ETHYLPARABEN (UNII: 14255EXE39) METHYLPARABEN SODIUM (UNII: CR6K9C2NHK) CITRIC ACID MONOHYDRATE (UNII: 2968PHW8QP) SODIUM CITRATE (UNII: 1Q73Q2JULR) WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) Product Characteristics Color Score Shape Size Flavor ORANGE Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 81927-204-01 1 in 1 CARTON 12/15/2023 1 60 mL in 1 BOTTLE, GLASS; Type 1: Convenience Kit of Co-Package Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA212479 12/15/2023 Labeler - SHORLA ONCOLOGY INC. (118055608) Registrant - SHORLA PHARMA LTD. (985706879) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations SGS United Kingdom Limited 234085922 manufacture(81927-204) , analysis(81927-204)
Trademark Results [JYLAMVO]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 JYLAMVO 98183585 not registered Live/Pending |
Shorla Pharma Limited 2023-09-17 |
 JYLAMVO 98183580 not registered Live/Pending |
Shorla Pharma Limited 2023-09-17 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.