DASH CHLORHEXIDINE GLUCONATE 0.12% ORAL RINSE- chlorhexidine gluconate 0.12% oral rinse liquid
DASH Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.12% Oral Rinse by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
DASH Chlorhexidine Gluconate 0.12% Oral Rinse by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Cardinal Health 107, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
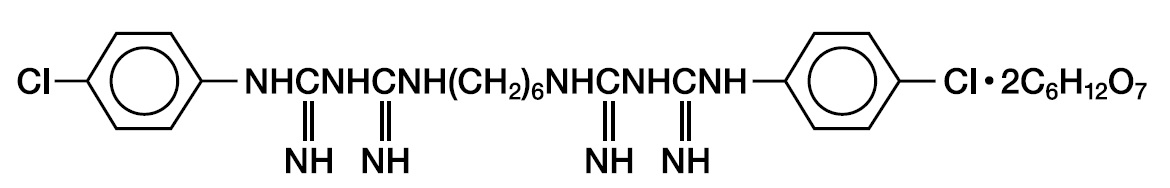
This product is an oral rinse containing 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate (1,1'-hexamethylene bis [5-(p-chlorophenyl) biguanide]di-0-gluconate) in a base containing water, 11.6% alcohol, glycerin, PEG-40 sorbitan diisostearate, peppermint oil, saccharin sodium, and FD&C Blue #1. The pH may be adjusted with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide. The solution is near-neutral (pH range 5-7). Chlorhexidine gluconate is a salt of chlorhexidine and gluconic acid. Its molecular formula is C22H30Cl2N10 2C6H1207, molecular weight 897.77 and its structural formula is:
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Chlorhexidine gluconate provides antimicrobial activity during oral rinsing. The clinical significance of chlorhexidine gluconate's antimicrobial activities is not clear. Microbiological sampling of plaque has shown a general reduction of counts of certain assayed bacteria, both aerobic and anaerobic, ranging from 54-97% through six months' use.
Use of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse in a six-month clinical study did not result in any significant changes in bacterial resistance, overgrowth of potentially opportunistic organisms or other adverse changes in the oral microbial ecosystem. Three months after chlorhexidine gluconate use was discontinued, the number of bacteria in plaque had returned to baseline levels and resistance of plaque bacteria to chlorhexidine gluconate was equal to that at baseline.
-
PHARMACOKINETICS
Pharmacokinetics: Pharmacokinetic studies with 0.12% chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse indicate approximately 30% of the active ingredient, chlorhexidine gluconate, is retained in the oral cavity following rinsing. This retained drug is slowly released into the oral fluids. Studies conducted on human subjects and animals demonstrate chlorhexidine gluconate is poorly absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract. The mean plasma level of chlorhexidine gluconate reached a peak of 0.206 mcg/g in humans 30 minutes after they ingested a 300-mg dose of the drug. Detectable levels of chlorhexidine gluconate were not present in the plasma of these subjects 12 hours after the compound was administered. Excretion of chlorhexidine gluconate occurred primarily through the feces (~90%). Less than 1% of the chlorhexidine gluconate ingested by these subjects was excreted in the urine.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse is indicated for use between dental visits as part of a professional program for the treatment of gingivitis as characterized by redness and swelling of the gingivae, including gingival bleeding upon probing. Chlorhexidine gluconate has not been tested among patients with acute necrotizing ulcerative gingivitis (ANUG). For patients having coexisting gingivitis and periodontitis, see
PRECAUTIONS. - CONTRAINDICATIONS:
-
WARNINGS
The effect of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse on periodontitis has not been determined. An increase in supragingival calculus was noted in clinical testing in chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse users compared with control users. It is not known if chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse use results in an increase in subgingival calculus. Calculus deposits should be removed by a dental prophylaxis at intervals not greater than six months. Anaphylaxis, as well as serious allergic reactions, have been reported during postmarketing use with dental products containing chlorhexidine.
See CONTRAINDICATIONS.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General:
1. For patients having coexisting gingivitis and periodontitis, the presence or absence of gingival inflammation following treatment with chlorhexidine gluconate should not be used as a major indicator of underlying periodontitis.
2. Chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse can cause staining of oral surfaces, such as tooth surfaces, restorations, and the dorsum of the tongue. Not all patients will experience a visually significant increase in toothstaining. In clinical testing, 56% of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse users exhibited a measurable increase in facial anterior stain, compared to 35% of control users after six months; 15% of chlorhexidine gluconate users developed what was judged to be heavy stain, compared to 1% of control users after six months. Stain will be more pronounced in patients who have heavier accumulations of unremoved plaque. Stain resulting from use of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse does not adversely affect health of the gingivae or other oral tissues. Stain can be removed from most tooth surfaces by conventional professional prophylactic techniques. Additional time may be required to complete the prophylaxis.
Discretion should be used when prescribing to patients with anterior facial restorations with rough surfaces or margins. If natural stain cannot be removed from these surfaces by a dental prophylaxis, patients should be excluded from chlorhexidine gluconate treatment if permanent discoloration is unacceptable. Stain in these areas may be difficult to remove by dental prophylaxis and on rare occasions may necessitate replacement of these restorations.
3. Some patients may experience an alteration in taste perception while undergoing treatment with chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse. Rare instances of permanent taste alteration following use of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse have been reported via postmarketing product surveillance.
-
Pregnancy
Teratogenic Effects
Pregnancy category B. Reproduction studies have been performed in rats and rabbits at chlorhexidine gluconate doses up to 300 mg/kg/day and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively, and have not revealed evidence of harm to the fetus. However, adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women have not been done. Because animal reproduction studies are not always predictive of human response, this drug should be used during pregnancy only if clearly needed.
-
Nursing Mothers
It is not known whether this drug is excreted in human milk. Because many drugs are excreted in human milk, caution should be exercised when chlorhexidine gluconate is administered to a nursing woman. In parturition and lactation studies with rats, no evidence of impaired parturition or of toxic effects to suckling pups was observed when chlorhexidine gluconate was administered to dams at doses that were over 100 times greater than that which would result from a person's ingesting 30ml (2 capfuls) of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse per day.
- Pediatric Use
-
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In a drinking water study in rats, carcinogenic effects were not observed at doses up to 38 mg/kg/day. Mutagenic effects were not observed in two mammalian in vivo mutagenesis studies with chlorhexidine gluconate. The highest doses of chlorhexidine used in a mouse dominant-lethal assay and a hamster cytogenetics test were 1000 mg/kg/day and 250 mg/kg/day, respectively. No evidence of impaired fertility was observed in rats at doses up to 100 mg/kg/day.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common side effects associated with chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinses are (1) an increase in staining of teeth and other oral surfaces, (2) an increase in calculus formation, and (3) an alteration in taste perception; see WARNINGS and PRECAUTIONS. Oral irritation and local allergy-type symptoms have been spontaneously reported as side effects associated with the use of chlorhexidine gluconate rinse. The following oral mucosal side effects were reported during placebo-controlled adult clinical trials: aphthous ulcer, grossly obvious gingivitis, trauma,
ulceration, erythema, desquamation, coated tongue, keratinization, geographic tongue, mucocele, and short frenum. Each occurred at a frequency of less than 1.0%.Among postmarketing reports, the most frequently reported oral mucosal symptoms associated with chlorhexidine gluconate are stomatitis, gingivitis, glossitis, ulcer, dry mouth, hypesthesia, glossal edema, and paresthesia.
Minor irritation and superficial desquamation of the oral mucosa have been noted in patients using chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse.
There have been cases of parotid gland swelling and inflammation of the salivary glands (sialadenitis) reported in patients using chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Ingestion of 1 or 2 ounces of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse by a small child (~10 kg body weight) might result in gastric distress, including nausea, or signs of alcohol intoxication. Medical attention should be sought if more than 4 ounces of chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse is ingested by a small child or if signs of alcohol intoxication develop.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse therapy should be initiated directly following a dental prophylaxis. Patients using chlorhexidine gluconate should be reevaluated and given a thorough prophylaxis at intervals no longer than six months.
Recommended use is twice daily oral rinsing for 30 seconds, morning and evening after toothbrushing. Usual dosage is 15ml (marked in cap) of undiluted chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse. Patients should be instructed to not rinse with water, or other mouthwashes, brush teeth, or eat immediately after using chlorhexidine gluconate oral rinse. Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse is not intended for ingestion and should be expectorated after rinsing.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse USP 0.12% is supplied as a blue liquid in the following sizes:
Overbagged with 5 x 15 mL amber plastic unit-dose cups in each bag, NDC: 55154-1981-5
WARNING: This Unit Dose package is not child resistant and is Intended for Institutional Use Only. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Store at 20°-25°C (68°-77°F); excursions permitted to 15°-30°C (59°-86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Dispense in original container or in amber glass bottles.
-
What to expect when using Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse
Your dentist has prescribed Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse to treat your gingivitis, to help reduce the redness and swelling of your gums, and also to help you control any gum bleeding. Use Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse regularly, as directed by your dentist, in addition to daily brushing. Spit out after use. Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse should not be swallowed.
If you develop allergic symptoms such as skin rash, itch, generalized swelling, breathing difficulties, light headedness, rapid heart rate, upset stomach or diarrhea, seek medical attention immediately. Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse should not be used by persons who have a sensitivity to it or its components.
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse may cause some tooth discoloration, or increases in tartar (calculus) formation, particularly in areas where stain and tartar usually form. It is important to see your dentist for removal of any stain or tartar at least every six months, or more frequently if your dentist advises.
Both stain and tartar can be removed by your dentist or hygienist. Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse may cause permanent discoloration of some front-tooth fillings.
To minimize discoloration, you should brush and floss daily, emphasizing areas which begin to discolor.
Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse may taste bitter to some patients and can affect how foods and beverages taste. This will become less noticeable in most cases with continued use of Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse.
To avoid taste interference, rinse with Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse after meals. Do not rinse with water or other mouthwashes immediately after rinsing with Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse.
If you have any questions or comments about Chlorhexidine Gluconate Oral Rinse, contact your dentist or pharmacist.
Call your health care provider for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Manufactured for:
DASH Pharmaceuticals LLC
Upper Saddle River, NJ 07458Manufactured by:
Lyne Laboratories, Inc.
Brockton, MA 02301Distributed By:
Cardinal Health
Dublin, OH 43017
L56460620124
R0-09/17
- Package/Label Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
DASH CHLORHEXIDINE GLUCONATE 0.12% ORAL RINSE
chlorhexidine gluconate 0.12% oral rinse liquidProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 55154-1981(NDC:69339-138) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength CHLORHEXIDINE GLUCONATE (UNII: MOR84MUD8E) (CHLORHEXIDINE - UNII:R4KO0DY52L) CHLORHEXIDINE GLUCONATE 1.2 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) ALCOHOL (UNII: 3K9958V90M) GLYCERIN (UNII: PDC6A3C0OX) PEG-40 SORBITAN DIISOSTEARATE (UNII: JL4CCU7I1G) PEPPERMINT OIL (UNII: AV092KU4JH) SACCHARIN SODIUM (UNII: SB8ZUX40TY) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) Other Ingredients Ingredient Kind Ingredient Name Quantity May contain HYDROCHLORIC ACID (UNII: QTT17582CB) May contain SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Product Characteristics Color blue Score Shape Size Flavor MINT Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 55154-1981-5 5 in 1 BAG 04/25/2018 1 15 mL in 1 CUP, UNIT-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA074291 04/25/2018 Labeler - Cardinal Health 107, LLC (118546603)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.