BRINSUPRI- brensocatib tablet
Brinsupri by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Brinsupri by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Insmed Incorporated, Patheon Inc., Esteve Huayi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Esteve Quimica, SA. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use BRINSUPRI safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for BRINSUPRI.
BRINSUPRI™ (brensocatib) tablets, for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2025INDICATIONS AND USAGE
BRINSUPRI is a dipeptidyl peptidase 1 (DPP1) inhibitor indicated for the treatment of non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis in adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Recommended dosage: 10 mg or 25 mg orally once daily with or without food. (2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Tablets: 10 mg and 25 mg (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions: Monitor for new rash or skin conditions and refer to dermatology for evaluation. (5.1)
Gingival and Periodontal Adverse Reactions: Gingival and periodontal adverse reactions can occur with BRINSUPRI use. Refer to the dental care services for regular dental checkups and advise patients to perform routine dental hygiene. (5.2)
Live Attenuated Vaccines: It is unknown whether administration of live attenuated vaccines during BRINSUPRI treatment will affect the safety or effectiveness of the vaccines. Avoid use of live attenuated vaccines. (5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%): upper respiratory tract infection, headache, rash, dry skin, hyperkeratosis, hypertension. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Insmed Incorporated at 1-844-4-INSMED or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or https://www.fda.gov/medwatch.
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and FDA-approved patient labeling.
Revised: 8/2025
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
5.2 Gingival and Periodontal Adverse Reactions
5.3 Live Attenuated Vaccines
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
- 2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Treatment with BRINSUPRI is associated with an increase in dermatologic adverse reactions, including rash, dry skin, and hyperkeratosis [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Monitor patients for development of new rashes or skin conditions and refer patients to a dermatologist for evaluation of new dermatologic findings.
5.2 Gingival and Periodontal Adverse Reactions
Treatment with BRINSUPRI is associated with an increase in gingival and periodontal adverse reactions [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. Refer patients to dental care services for regular dental checkups while taking BRINSUPRI. Advise patients to perform routine dental hygiene.
5.3 Live Attenuated Vaccines
The concomitant use of BRINSUPRI and live attenuated vaccines has not been evaluated. It is unknown whether administration of live attenuated vaccines during BRINSUPRI treatment will affect the safety or effectiveness of these vaccines. The use of live attenuated vaccines should be avoided in patients receiving BRINSUPRI.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Dermatologic Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Gingival and Periodontal Adverse Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
The safety data below reflect the safety of BRINSUPRI in adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older with non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (NCFB). A total of 1721 patients with NCFB were randomized in a double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial of 52 weeks duration (ASPEN) [see Clinical Studies (14)]. The safety of BRINSUPRI was based on data from 1719 adult and pediatric patients aged 12 years and older who received at least one dose of BRINSUPRI or placebo. A total of 1156 patients received at least one dose of BRINSUPRI 10 mg or 25 mg orally once daily.
Table 1 shows the adverse reactions occurring at an incidence of ≥2% and higher in BRINSUPRI-treated patients compared to placebo in the safety population from ASPEN.
Table 1 Adverse Reactions with BRINSUPRI with an Incidence of ≥2% and More Common than Placebo in ASPEN Adverse Reaction Placebo
(N=563)
n (%)BRINSUPRI
10 mg QD
(N=582)
n (%)BRINSUPRI
25 mg QD
(N=574)
n (%)- * Upper respiratory tract infection includes coronavirus infection, COVID-19, influenza, upper respiratory tract infection, viral infection, and viral upper respiratory tract infection.
- † Rash includes rash, rash maculo-papular, rash pruritic, rash erythematous, dermatitis, and erythema.
- ‡ Dry skin includes dry skin, chapped lips, cheilitis, lip dry, skin exfoliation, skin fissures, xeroderma, and xerosis.
- § Hyperkeratosis includes hyperkeratosis, palmoplantar keratoderma, and skin hypertrophy.
Upper respiratory tract infection* 141 (25) 157 (27) 169 (29) Headache 39 (7) 39 (7) 49 (9) Rash† 22 (4) 25 (4) 35 (6) Dry skin‡ 8 (1) 17 (3) 25 (4) Hyperkeratosis§ 5 (1) 8 (1) 16 (3) Hypertension 17 (3) 28 (5) 13 (2) Adverse Reactions in WILLOW
A total of 256 adult patients with NCFB were randomized in the 24-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial (WILLOW). Of those randomized, 255 adult patients received BRINSUPRI 10 mg, BRINSUPRI 25 mg, or placebo, which consisted of 170 adults treated with at least one dose of BRINSUPRI 10 mg or 25 mg orally once daily. The safety profile for adult patients with NCFB in WILLOW was generally similar to ASPEN, with the exception of a higher incidence of gingival and periodontal adverse reactions. The incidence of gingival and periodontal adverse reactions in WILLOW among patients treated with BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg were 9.9% and 10.1%, respectively, compared to 2.4% in placebo-treated patients.
Less Common Adverse Reactions
Liver Function Test Elevations
In ASPEN, there was an increase from baseline in average ALT, AST, and alkaline phosphatase levels at all time points from Week 4 through Week 56 in both BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg arms compared to placebo. The incidence of ALT >3× upper limit of normal (ULN) was 0%, 1.2%, and 0.9%, in patients treated with placebo and BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg, respectively. The incidence of AST >3× ULN was 0.2%, 0.3%, and 0.5% in patients treated with placebo and BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg, respectively. The incidence of alkaline phosphatase >1.5× ULN was 2.5%, 4.1%, and 4.0% in patients treated with placebo and BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg, respectively.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no available data on BRINSUPRI use in pregnant women to evaluate for a drug-associated risk of major birth defects, miscarriage, or other adverse maternal or fetal outcomes.
In animal embryo fetal development (EFD) studies, oral administration of brensocatib to pregnant rats during organogenesis at maternal exposures 128 times the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) on an AUC basis was associated with malformations. Oral administration of brensocatib to pregnant rabbits during organogenesis demonstrated no adverse developmental effects at doses that produced maternal exposures up to 20 times the MRHD. No adverse development effects were observed after oral administration of brensocatib to pregnant rats from the period of organogenesis through lactation at doses that produced maternal exposures 17 times the MRHD on an AUC basis (see Data).
The estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a rat fertility and EFD study, brensocatib was administered at oral doses of 3, 20, and 100 mg/kg/day to female rats 2 weeks prior to mating, during mating, and through organogenesis until gestation Day 16. The malformation of bent scapula was observed at a maternal dose of 100 mg/kg/day (128 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). There were no adverse findings at maternal oral doses of 20 mg/kg/day (42 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). In a rabbit EFD study, brensocatib was administered at oral doses of 5, 15, or 50 mg/kg/day from gestation Days 7 to 19, a period that covers implantation and major organogenesis. Brensocatib was not associated with adverse effects on the fetus at maternal exposures up to 20 times the MRHD on an AUC basis. Maternal toxicity as indicated by reductions in body weight gain and food consumption was noted at maternal doses of 15 mg/kg/day and greater (greater than 5 times the MRHD on an AUC basis). In a pre- and postnatal development study, oral administration of brensocatib to pregnant rats at doses of 3, 9, or 20 mg/kg/day from gestation Day 6 through lactation Day 20 resulted in no adverse developmental effects in pups at maternal doses up to 20 mg/kg/day (17 times the MRHD on an AUC basis).
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of brensocatib and/or its metabolite(s) in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production.
The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for BRINSUPRI and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from BRINSUPRI or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of BRINSUPRI for the treatment of NCFB have been established in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older. Use of BRINSUPRI for this indication is supported by evidence from an adequate and well-controlled trial (ASPEN), which enrolled 41 pediatric patients aged 12 years and older, and additional pharmacokinetic data in pediatric patients aged 12 to 17 years [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3) and Clinical Studies (14)].
Common adverse reactions in pediatric patients aged 12 years and older enrolled in ASPEN were consistent with those in adults [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of BRINSUPRI have not been established in pediatric patients younger than 12 years of age.
8.5 Geriatric Use
There were 988 patients 65 years of age and older in the clinical studies for non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis [see Clinical Studies (14)]. Of the total number of BRINSUPRI-treated patients in these studies, 676 (51%) were 65 years of age and older while 201 (15%) were 75 years of age and older. No observed differences in safety and/or effectiveness in geriatric patients compared to younger adult patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
BRINSUPRI (brensocatib) is a dipeptidyl peptidase 1 (DPP1) inhibitor.
The chemical name for the active ingredient brensocatib monohydrate is (2S)-N-{(1S)-1-cyano-2-[4-(3-methyl-2-oxo-2,3-dihydro-1,3-benzoxazol-5-yl)phenyl]ethyl}-1,4-oxazepane-2-carboxamide monohydrate with a chemical formula of C23H24N4O4 ∙ H2O which corresponds to a molecular weight of 438.48 g/mol. Its structural formula is:
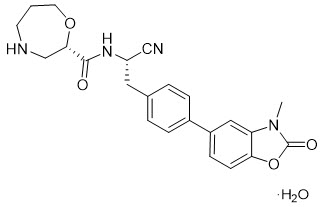
Brensocatib monohydrate drug substance is a white to off-white solid powder. It is slightly soluble at pH 1.2, freely soluble at pH 4.5, and very slightly soluble at pH 6.8 of aqueous media. It is also soluble in acetonitrile and sparingly soluble in ethanol.
BRINSUPRI tablets are available for oral administration in strengths of 10 mg and 25 mg brensocatib with the following inactive ingredients: dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate, glyceryl dibehenate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, and sodium starch glycolate. The film coating contains ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide, iron oxide yellow, and iron oxide red (10 mg) or ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide (25 mg), macrogol/PEG, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxide.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Brensocatib is a competitive, reversible inhibitor of dipeptidyl peptidase 1 (DPP1). DPP1 activates pro-inflammatory neutrophil serine proteases (NSPs) during neutrophil maturation in the bone marrow. Activated NSPs are implicated in the pathogenesis of neutrophil-mediated NCFB inflammation. In cell-based assays, DPP1 inhibition by brensocatib reduces the activity of NSPs including neutrophil elastase, cathepsin G, and proteinase 3.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Brensocatib prevents the activation of NSPs via DPP1 inhibition resulting in decreases in NSP activity in patients. In exploratory assays, brensocatib was associated with dose-dependent reductions in NSP activity in patients with NCFB.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Following once daily administration of brensocatib 10 mg, the estimated geometric mean (CV%) Cmax is 85.4 ng/mL (33%) and AUCtau is 1360 ng*h/mL (41%). Following once daily administration of brensocatib 25 mg, the estimated geometric mean (CV%) Cmax is 259 ng/mL (31%) and AUCtau is 4060 ng*h/mL (39%).
Brensocatib Cmax and AUCtau increase in a greater than dose proportional manner between doses of 10 mg and 1.6 times the highest recommended dose. Between doses of 10 mg and 1.6 times the highest recommended dose brensocatib once daily, brensocatib geometric mean steady state Cmax increased by 5.1-fold and AUCtau increased by 5.3-fold. In healthy subjects, at steady state, Cmax increased by about 1.5-fold and AUCtau increased by about 2-fold when compared to those observed following a single dose.
No clinically relevant differences in brensocatib pharmacokinetics were observed between healthy subjects and patients with NCFB.
Absorption
The absolute oral bioavailability of brensocatib has not been studied in humans. Based on data from a mass balance study in healthy subjects, the oral absorption of brensocatib in humans is greater than 80%. Following a single dose of 10 mg or 25 mg brensocatib, the median (min, max) time to maximum plasma concentration (Tmax) is 1.0-1.4 hours (0.5, 3.0 hours).
Distribution
Following once daily administration of 10 mg or 25 mg brensocatib in patients with NCFB, the estimated volume of distribution at steady state ranged from 126 to 138 L. The protein binding of brensocatib in human plasma was 87.2%.
Elimination
Following a single oral administration of brensocatib at 10 mg or 25 mg in healthy subjects, the elimination half-life ranged from 25 to 39 hours and the apparent oral clearance ranged from 6.4 to 10.7 L/hour.
Metabolism
Brensocatib is primarily metabolized by CYP3A and to a lesser extent by CYP2C8 and CYP2D6. Brensocatib accounted for 16.2% of the total radioactivity in plasma. One major circulating metabolite, thiocyanate, was identified in plasma and accounted for 51% of the total radioactivity AUC following administration of a radio-labeled brensocatib dose. In patients with NCFB at recommended doses of brensocatib, no clinically meaningful changes of plasma thiocyanate from baseline were observed.
Specific Populations
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of brensocatib were observed based on age (12 to 85 years), sex, race (72% White, 6% Black, and 12% Asian), or body weight (32 to 155 kg).
No clinically significant differences in the pharmacokinetics of brensocatib were observed based on mild, moderate, or severe renal impairment (eGFR 15-89 mL/min/1.73 m2); or mild, moderate, or severe hepatic impairment (Child-Pugh Class A, B, or C).
Drug Interaction Studies
Clinical Studies and Model-Informed Approaches
Strong CYP3A4 and P-gp Inhibitors: Brensocatib Cmax increased by 68% and AUC increased by 55% following concomitant administration with clarithromycin (a strong CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitor) 500 mg twice daily for 6 days.
Moderate CYP3A4 and P-gp Inhibitors: Brensocatib Cmax increased by 53% and AUC increased by 32% following concomitant administration with verapamil (a moderate CYP3A4 and P-gp inhibitor) 240 mg once daily for 5 days.
Strong CYP3A4 Inducers: Brensocatib Cmax decreased by 15% and AUC decreased by 33% following concomitant administration with rifampin (a strong CYP3A4 inducer) 600 mg once daily for 9 days.
In Vitro Studies
CYP450 Enzymes: Brensocatib is a substrate of CYP3A. Brensocatib does not inhibit CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, or CYP3A. Brensocatib is a weak CYP3A inducer, but not an inducer of CYP1A2, CYP2B6, CYP2C8, CYP2C9, or CYP2C19.
Transporter Systems: Brensocatib is a substrate of P-glycoprotein (P-gp) and breast cancer resistance protein (BCRP), but is not a substrate of MATE1, MATE2-K, OAT1, OAT3, OATP1B1, OATP1B3, OCT1, and OCT2. Brensocatib is an inhibitor of BCRP, OATP1B, MATE1, and MATE2-K, but is not an inhibitor of P-gp, OAT1, OCT2, OAT3, or OATP1B3.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
A two-year study in Han Wistar rats and a 6-month study in Tg.rasH2 transgenic mice were conducted to assess the carcinogenic potential of brensocatib. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male or female rats at an exposure approximately 56 times the MRHD on an AUC basis. No evidence of tumorigenicity was observed in male and female Tg.rasH2 mice at oral doses up to 50 mg/kg/day, the highest dose tested. Brensocatib was negative for genotoxicity in the following assays: in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) assay, in vitro mouse lymphoma mutation assay, and in vivo micronucleus assay in rats.
Oral administration of brensocatib to male and female rats at up to 50 and 100 mg/kg/day, respectively, had no adverse effects on fertility and reproductive performance indices (150 and 231 times the MRHD on an AUC basis, respectively).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The efficacy of BRINSUPRI was evaluated in two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, multicenter, multinational clinical trials (ASPEN [NCT04594369] and WILLOW [NCT03218917]).
ASPEN was a 52-week trial that included 1721 adult and pediatric patients 12 years of age and older with NCFB (1680 adults and 41 pediatric patients 12 years of age to less than 18 years of age) who were randomized to BRINSUPRI 10 mg (n=583), BRINSUPRI 25 mg (n=575), or placebo (n=563) administered orally once daily.
WILLOW was a 24-week trial that included 256 adult patients with NCFB who were randomized to BRINSUPRI 10 mg (n=82), BRINSUPRI 25 mg (n=87), or placebo (n=87) administered orally once daily.
In both ASPEN and WILLOW, all adult patients had a history of confirmed NCFB by chest computed tomography with at least 2 documented pulmonary exacerbations (PEx) prior to screening in the past 12 months. In ASPEN, pediatric patients 12 years of age and older had at least one PEx in the prior 12 months.
Demographics and baseline characteristics of patients in ASPEN and WILLOW are provided in Table 2.
Table 2 Demographics and Baseline Characteristics of Patients in ASPEN and WILLOW ASPEN
(N=1721)WILLOW
(N=256)Abbreviations: N, number of patients in the intent-to-treat analysis set; n, number of patients; PEx, pulmonary exacerbations; pp, percent predicted; FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; SD, standard deviation Age (years), mean (SD) 60 (16) 64 (12) Female n (%) 1107 (64) 174 (68) White n (%) 1266 (74) 225 (88) Black or African American n (%) 10 (1) 4 (2) Asian n (%) 191 (11) 23 (9) Hispanic or Latino n (%) 511 (30) 6 (2) ≥3 PEx in prior 12 months n (%) 502 (29) 84 (33) Former smoker n (%) 510 (30) 86 (34) ppFEV1 post-bronchodilator, mean (SD) 74 (23) 68 (24) Sputum positive for Pseudomonas aeruginosa n (%) 607 (35) 89 (35) Chronic macrolide therapy n (%) 329 (19) 40 (16) ASPEN
The primary efficacy endpoint in ASPEN was the annualized rate of PEx over the 52-week treatment period.
Pulmonary exacerbations were defined as worsening of 3 or more of the following major symptoms over 48 hours: increased cough, increased sputum volume or change in sputum consistency, increased sputum purulence, increased breathlessness, decreased exercise tolerance, fatigue and/or malaise, and hemoptysis, resulting in a healthcare provider's decision to prescribe systemic antibiotics. Pulmonary exacerbations were considered severe if requiring treatment with intravenous antibacterial drugs and/or resulted in hospitalization.
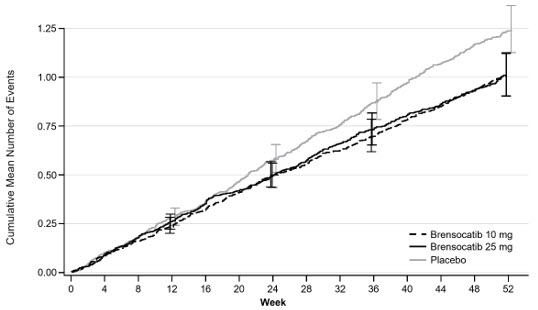
Treatment with BRINSUPRI 10 mg or 25 mg in patients with NCFB demonstrated reductions in the mean rate of PEx over 52 weeks compared with placebo (Figure 1). Table 3 provides the results of the annualized rate of PEx, and the results of the key secondary endpoints in ASPEN of time to first PEx, proportion of patients remaining exacerbation free throughout the 52-week treatment period, annualized rate of severe PEx, and the change from baseline in post-bronchodilator FEV1.
Table 3 Primary and Key Secondary Efficacy Analyses of Pulmonary Exacerbations and FEV1 Over 52 Weeks in ASPEN Placebo
(N=563)BRINSUPRI
10 mg
(N=583)BRINSUPRI
25 mg
(N=575)Abbreviations: FEV1, forced expiratory volume in 1 second; LS, least squares; PEx, pulmonary exacerbation Annualized Rate of PEx 1.29 1.02 1.04 Rate Ratio (95% CI) -- 0.79 (0.68, 0.92) 0.81 (0.69, 0.94) Median Time to First PEx (weeks) 36.71 49.00 50.71 Hazard Ratio (95% CI) -- 0.81 (0.70, 0.95) 0.83 (0.70, 0.97) Proportion of Patients that were PEx Free at Week 52 (%) 40.3 48.5 48.5 Odds Ratio (95% CI) -- 1.41 (1.11, 1.81) 1.40 (1.10, 1.79) Annualized Rate of Severe PEx 0.19 0.14 0.14 Rate Ratio (95% CI) -- 0.74 (0.51, 1.09) 0.74 (0.52, 1.06) LS Mean Change from Baseline in Post-Bronchodilator FEV1 (mL) at Week 52 -62 -50 -24 Difference vs Placebo (95% CI) -- 11 (-14, 37) 38 (11, 65) Figure 1 Cumulative Mean Number of Pulmonary Exacerbations through Week 52
WILLOW
The primary efficacy endpoint in WILLOW was the time to first PEx over the 24-week treatment period. The time to first PEx was longer for patients receiving BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg compared to placebo (hazard ratio BRINSUPRI 10 mg and 25 mg versus placebo; 0.58 and 0.62, respectively; 95% CI: 0.35 to 0.95 and 0.38 to 0.99, respectively).
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
BRINSUPRI (brensocatib) tablets are supplied as described in Table 4:
Table 4 BRINSUPRI Tablets and Package Configuration Strength Tablet Description Package Configuration NDC 10 mg brown, round, film-coated tablets debossed with "10" on one side and "BRE" on the other bottles of 30 tablets 71558-001-30 25 mg gray, round, film-coated tablets debossed with "25" on one side and "BRE" on the other bottles of 30 tablets 71558-002-30 -
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Advise the patient to read the FDA-approved patient labeling (Patient Information).
Dermatologic Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that BRINSUPRI is associated with a risk of adverse skin reactions including rash, dry skin, and hyperkeratosis. Advise patients to monitor their skin and report any new rash or skin condition [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Gingival and Periodontal Adverse Reactions
Inform patients that BRINSUPRI is associated with a risk of gingival and periodontal adverse reactions. Advise patients to have regular dental checkups while taking BRINSUPRI. Advise patients to perform routine dental hygiene [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Live Attenuated Vaccines
Instruct patients to inform the healthcare provider that they are taking BRINSUPRI prior to a potential vaccination [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)].
-
SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
Manufactured for:
Insmed Incorporated
Bridgewater, NJ 08807© Insmed Incorporated 2025
BRINSUPRI and Insmed are trademarks of Insmed Incorporated.
For patent information: https://insmed.com/program-patents/
For more information, go to www.BRINSUPRI.com or call 1-844-4-INSMED (1-844-446-7633). -
PATIENT PACKAGE INSERT
Patient Information
BRINSUPRI (brin-SOO-pree)
(brensocatib)
tablets, for oral useThis Patient Information has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration Issued: 08/2025 What is BRINSUPRI?
BRINSUPRI is a prescription medicine used to treat non-cystic fibrosis bronchiectasis (NCFB) in adults and children 12 years of age and older. It is not known if BRINSUPRI is safe and effective in children under 12 years of age.Before taking BRINSUPRI, tell your healthcare provider about all of your medical conditions, including if you: - have recently received or are scheduled to receive any live attenuated vaccinations.
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if BRINSUPRI will harm your unborn baby.
- are breastfeeding or plan to breastfeed. It is not known if BRINSUPRI passes into your breast milk. Talk to your healthcare provider about the best way to feed your baby during this time.
How should I take BRINSUPRI? - Take BRINSUPRI exactly as your healthcare provider tells you to take it.
- Take 1 BRINSUPRI tablet by mouth daily with or without food.
- If you forget to take a dose of BRINSUPRI, take your next dose at your regular time the next day.
- Do not double the dose to make up for the missed dose.
What are the possible side effects of BRINSUPRI?
BRINSUPRI may cause serious side effects including:- Skin problems. Tell your healthcare provider about any new skin symptoms. Your healthcare provider may send you to a dermatologist for an examination if needed.
- Dental problems. Get regular dental checkups while taking BRINSUPRI. Brush and clean your teeth as recommended by your dentist. Tell your healthcare provider and contact your dentist if you experience new gum (gingival) or teeth (dental) symptoms.
- upper respiratory tract infection
- headache
- rash
- dry skin
- small areas of skin thickening (hyperkeratosis)
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
Less common side effects include abnormal liver blood test, hair loss (alopecia), and skin cancers.
These are not all of the possible side effects of BRINSUPRI.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may also report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.How should I store BRINSUPRI? - Store BRINSUPRI at room temperature between 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C).
- Keep BRINSUPRI in its original bottle.
General information about the safe and effective use of BRINSUPRI
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Patient Information leaflet. Do not use BRINSUPRI for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give BRINSUPRI to other people, even if they have the same symptoms that you have. It may harm them. You can ask your pharmacist or healthcare provider for information about BRINSUPRI that is written for health professionals.What are the ingredients in BRINSUPRI?
Active ingredient: brensocatib monohydrate
Inactive ingredients: dibasic calcium phosphate dihydrate, glyceryl dibehenate, microcrystalline cellulose, silicon dioxide, and sodium starch glycolate
Film coating: ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide, iron oxide yellow, and iron oxide red or ferrosoferric oxide/black iron oxide, macrogol/PEG, polyvinyl alcohol-partially hydrolyzed, talc, and titanium dioxideManufactured for: Insmed Incorporated, Bridgewater, NJ 08807
© Insmed Incorporated 2025
BRINSUPRI and Insmed are trademarks of Insmed Incorporated.
For patent information:https://insmed.com/program-patents/
For more information, go to www.BRINSUPRI.com or call 1-844-4-INSMED (1-844-446-7633). - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 25 mg Tablet Bottle Label
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 10 mg Tablet Bottle Label
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
BRINSUPRI
brensocatib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71558-002 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Brensocatib (UNII: 25CG88L0BB) (Brensocatib - UNII:25CG88L0BB) Brensocatib 25 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate (UNII: O7TSZ97GEP) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A (UNII: H8AV0SQX4D) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Glyceryl Dibehenate (UNII: R8WTH25YS2) Product Characteristics Color GRAY Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 25;BRE Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71558-002-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/12/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA217673 08/12/2025 BRINSUPRI
brensocatib tabletProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 71558-001 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Brensocatib (UNII: 25CG88L0BB) (Brensocatib - UNII:25CG88L0BB) Brensocatib 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength Microcrystalline Cellulose (UNII: OP1R32D61U) Dibasic Calcium Phosphate Dihydrate (UNII: O7TSZ97GEP) SODIUM STARCH GLYCOLATE TYPE A (UNII: H8AV0SQX4D) Silicon Dioxide (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) Glyceryl Dibehenate (UNII: R8WTH25YS2) Product Characteristics Color BROWN Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code 10;BRE Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 71558-001-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 08/12/2025 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA217673 08/12/2025 Labeler - Insmed Incorporated (183470066) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Patheon Inc. 205475333 MANUFACTURE(71558-002, 71558-001) , PACK(71558-002, 71558-001) , ANALYSIS(71558-002, 71558-001) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Esteve Huayi Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. 528179890 API MANUFACTURE(71558-002, 71558-001) , ANALYSIS(71558-002, 71558-001) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Esteve Quimica, SA 633485529 API MANUFACTURE(71558-002, 71558-001) , ANALYSIS(71558-002, 71558-001)
Trademark Results [Brinsupri]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 BRINSUPRI 98107946 not registered Live/Pending |
Insmed Incorporated 2023-07-29 |
 BRINSUPRI 97883411 not registered Live/Pending |
Insmed Incorporated 2023-04-11 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.