TRIFERIC- ferric pyrophosphate solution TRIFERIC- ferric pyrophosphate citrate powder
Triferic by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Triferic by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Rockwell Medical, Inc. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use TRIFERIC safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for TRIFERIC.
TRIFERIC ® (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) solution, for hemodialysis use
TRIFERIC ® (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) for solution, for hemodialysis use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2015INDICATIONS AND USAGE
TRIFERIC is an iron replacement product indicated for the replacement of iron to maintain hemoglobin in adult patients with hemodialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease (HDD-CKD). ( 1)
Limitation of Use
Triferic is not intended for use in patients receiving peritoneal dialysis. ( 1.1)
Triferic has not been studied in patients receiving home hemodialysis. ( 1.1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Add one 5 mL ampule of Triferic solution to each 2.5 gallons of bicarbonate concentrate to achieve a concentration of iron (III) in the final hemodialysate of 2 micromolar (110 mcg/L). ( 2.1)
- Add one 50 mL ampule of Triferic solution to each 25 gallons of bicarbonate concentrate to achieve a concentration of iron (III) in the final hemodialysate of 2 micromolar (110 mcg/L). ( 2.1)
- Add one packet of Triferic powder to each 25 gallons of bicarbonate concentrate to achieve a concentration of iron (III) in the final hemodialysate of 2 micromolar (110 mcg/L). ( 2.1)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
None (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Hypersensitivity Reactions: Observe for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after hemodialysis and until clinically stable. ( 5.1)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions in controlled clinical studies include: headache, peripheral edema, asthenia, AV fistula thrombosis, urinary tract infection, AV fistula site hemorrhage, pyrexia, fatigue, procedural hypotension, muscle spasms, pain in extremity, back pain, and dyspnea. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Rockwell Medical at 1-855-333-4315 or 1-248-960-9009 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch. (6)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2016
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Limitation of Use
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Iron Laboratory Testing
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
16.2 Storage
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
- 1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommended Dosage
Inspect Triferic solution in ampules for signs of precipitation prior to mixing with the bicarbonate concentrate. Triferic solution should appear slightly yellow-green in color.
Triferic solution or powder should only be added to the bicarbonate concentrate and should NOT be added to acid concentrate mixtures.
Add Triferic solution or powder to bicarbonate concentrate used for the generation of hemodialysate. The concentration of iron (III) in the final hemodialysate is 2 micromolar (110 mcg/L).
- Add one 5 mL ampule of Triferic solution to 2.5 gallons (9.46 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate. Multiple 5 mL ampules can be added to the master bicarbonate mix at each center at a ratio of one 5 mL ampule for each 2.5 gallons (9.46 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate.
- Add one 50 mL ampule of Triferic solution to 25 gallons (94.6 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate. Multiple 50 mL ampules can be added to the master bicarbonate mix at each center at a ratio of one 50 mL ampule for each 25 gallons (94.6 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate.
- Add one packet of Triferic powder to 25 gallons (94.6 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate. Multiple packets can be added to the master bicarbonate mix at each center at a ratio of one packet for each 25 gallons (94.6 liters) of bicarbonate concentrate.
Product comparison table with dilution instructions for the 5 mL ampule of Triferic solution, the 50 mL ampule of Triferic Solution, and the packet of Triferic Powder are provided in the Table below.
Triferic Dosage Form Triferic Solution Triferic Powder 5 mL Ampule 50 mL Ampule Packet Iron content per Ampule or Packet 27.2 mg 272 mg 272 mg Number of Ampules or Packets to be added to each unit of bicarbonate concentrate 1 1 1 Per unit of bicarbonate concentrate (volume) 2.5 gallons
(9.46 Liters)25 gallons
(94.6 Liters)25 gallons
(94.6 Liters)Final iron concentration in dialysate 110 mcg/L 110 mcg/L 110 mcg/L Administer Triferic to patients at each dialysis procedure for as long as patients are receiving maintenance hemodialysis therapy for CKD.
Dosage of Triferic is expressed as mg of iron (III).
Hemodialysis solutions should be used within 24 hours of the preparation of the bicarbonate concentrate mixture.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- 4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Serious hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic-type reactions, some of which have been life-threatening and fatal, have been reported in patients receiving parenteral iron products. Patients may present with shock, clinically significant hypotension, loss of consciousness, and/or collapse. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity during and after hemodialysis until clinically stable. Personnel and therapies should be immediately available for the treatment of serious hypersensitivity reactions [ see Adverse Reactions (6)].
Hypersensitivity reactions have been reported in 1 (0.3%) of 292 patients receiving Triferic in two randomized clinical trials.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse reactions are described below and elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypersensitivity reactions [ see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
In two randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trials, a total of 292 patients were administered Triferic for periods of up to 1 year [ see Clinical Studies (14)]. The mean total exposure in the randomized treatment period was 5 months. A total of 296 patients received placebo treatment for a similar time period. In the two studies, 64% were male and 54% were Caucasian. The median age of patients was 60 years (range, 20 to 89 years).
Adverse events occurring in 3% or greater of patients treated with Triferic in the randomized clinical trials are listed in Table 1.
Table 1: Adverse Reactions Reported in Two Clinical Trials in at Least 3% of Patients Receiving Triferic and at an Incidence at Least 1% Greater than Placebo System Organ Class
Preferred TermTriferic
N=292
n (%)Placebo
N=296
n (%)Number of patients with at least one adverse reaction 229 (78.4) 223 (75.3) General Disorders and Administration Site Conditions Peripheral edema 20 (6.8) 11 (3.7) Pyrexia 13 (4.5) 9 (3.0) Asthenia 12 (4.1) 9 (3.0) Fatigue 11 (3.8) 6 (2.0) Infections and Infestations Urinary tract infection 13 (4.5) 4 (1.4) Injury, Poisoning, and Procedural Complications Procedural hypotension 63 (21.6) 57 (19.3) Arteriovenous fistula thrombosis 10 (3.4) 6 (2.0) Arteriovenous fistula site hemorrhage 10 (3.4) 5 (1.7) Musculoskeletal and Connective Tissue Disorders Muscle spasms 28 (9.6) 24 (8.1) Pain in extremity 20 (6.8) 17 (5.7) Back pain 13 (4.5) 10 (3.4) Nervous System Disorders Headache 27 (9.2) 16 (5.4) Respiratory, Thoracic and Mediastinal Disorders Dyspnea 17 (5.8) 13 (4.4) Adverse Reactions Leading to Treatment Discontinuation
In clinical trials, adverse reactions leading to treatment discontinuation included headache, asthenia, dizziness, constipation, nausea, hypersensitivity reactions, intradialytic hypotension, pruritus, and pyrexia.
Adverse reactions reported in the treatment extension period were similar to those observed in the randomized clinical studies.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are no data with Triferic use in pregnant women to inform a drug-associated risk. No teratogenicity was observed in animal reproduction studies with administration of ferric pyrophosphate citrate to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at doses 96 and 128 times, respectively, the maximum recommended human dose (MRHD) of 27.2 mg per dialysis [see Data].
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2%–4% and 15%–20%, respectively.
Data
Animal Data
In a fertility and early embryonic development study in female rats, the maternally toxic ferric pyrophosphate citrate dose of 40 mg/kg administered three times per week by intravenous (IV) infusion was not toxic to the developing embryo.
In embryo-fetal developmental toxicity studies, ferric pyrophosphate citrate was administered during the period of organogenesis as a one-hour IV infusion to pregnant rats and rabbits. No maternal or developmental toxicity was observed at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day in rats and 20 mg/kg/day in rabbits. Maternally toxic doses affected embryo-fetal development, resulting in post-implantation loss due to early resorptions, abnormal placentae, decreased fetal body weight and fetal head and vertebral malformations at 90 mg/kg/day in rats and vertebral malformations at 40 mg/kg/day in rabbits.
A pre-and post-natal development study was conducted in pregnant rats with intravenous doses of ferric pyrophosphate citrate up to 90 mg/kg/day. The maternally toxic dose of 90 mg/kg/day resulted in reductions in the number of live offspring and lower offspring body weights. There were no adverse effects on survival of offspring at doses up to 30 mg/kg/day, or on behavior, sexual maturation or reproductive parameters of offspring at any dose level.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of Triferic in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for Triferic and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from Triferic or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Triferic may cause fetal harm when administered to pregnant women. Advise females of reproductive potential to use effective contraception measures to prevent pregnancy during treatment with Triferic and for at least 2 weeks following completion of therapy.
8.5 Geriatric Use
In controlled clinical trials, 99 (28.6%) patients ≥ 65 years of age were treated with Triferic. No overall differences in safety and efficacy were observed between older and younger patients in these trials [ see Clinical Studies (14)].
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Triferic (ferric pyrophosphate citrate) is a mixed-ligand iron complex in which iron (III) is bound to pyrophosphate and citrate. It has a molecular formula of Fe 4(C 6H 4O 7) 3(H 2P 2O 7) 2(P 2O 7) and a relative molecular weight of approximately 1313 daltons. Triferic contains iron (7.5-9.0% w/w), citrate (15-22% w/w), pyrophosphate (15-22% w/w), phosphate (< 2% w/w), sodium (18-25% w/w) and sulfate (20-35%). Ferric pyrophosphate citrate has the following molecular structure:
Triferic solution:
A clear, slightly yellow-green color, sterile solution containing 27.2 mg of iron (III) per 5 mL filled into a 5 mL low density polyethylene ampule or 272 mg of iron (III) per 50 mL filled into a 50 mL low density polyethylene ampule.
Triferic powder:
A slightly yellow-green powder packaged in paper, polyethylene and aluminum foil packets, each containing 272.0 mg of iron (III).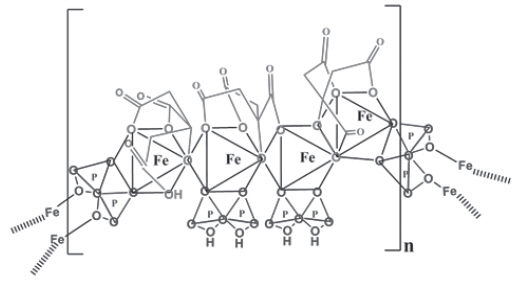
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Triferic contains iron in the form of ferric pyrophosphate citrate and is added to hemodialysate solution to be administered to patients by transfer across the dialyzer membrane. Iron delivered into the circulation binds to transferrin for transport to erythroid precursor cells to be incorporated into hemoglobin.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of serum iron was investigated in healthy volunteers administered 2.5, 5, 7.5 and 10 mg Triferic intravenously over 4 hours, or 15 mg and 20 mg Triferic intravenously over 12 hours. After correcting for the basal iron levels, the AUC and C max of baseline-corrected serum iron increased in a dose-proportional manner. The half-life of serum iron was approximately 1.48 hours, the mean clearance (CL) ranged from 0.406 to 0.556 L/hour, the mean apparent volume of distribution (Vz) ranged from 0.765 to 0.859 L after a 4-hour intravenous administration of Triferic. Compared to the 4-hour infusion of Triferic, higher mean CL and Vz were observed following the administration of Triferic 15 mg (CL = 0.672 L/hour and Vz = 1.66 L) and Triferic 20 mg (CL = 0.661 L/hour, Vz = 2.08L) infused over 12 hours. In a study that assessed the impact of different dialysis conditions on iron delivery in patients administered Triferic via hemodialysis, a reduction of the blood and dialysate flow rates (Qb/Qd of 200/400 mL/min vs. ≥ 350/ ≥ 600 mL/min) resulted in a 33% decrease in the median cumulative iron delivered.
-
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Studies examining the carcinogenic potential of ferric pyrophosphate citrate have not been conducted.
Ferric pyrophosphate citrate was clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cells in the presence of metabolic activation. Ferric pyrophosphate citrate was not mutagenic in the in vitro bacterial reverse mutation (Ames) test or clastogenic in the in vitro chromosomal aberration assay in CHO cells in the absence of metabolic activation or in the in vivo mouse micronucleus assay.
In a combined male and female fertility study in rats, ferric pyrophosphate citrate was administered intravenously over one hour three times per week at doses of up to 40 mg/kg. No adverse effects on fertility or reproduction were noted.
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
The safety and efficacy of Triferic in patients with HDD-CKD was assessed in two randomized, single blind, placebo-controlled clinical trials. Patients with hemoglobin of 9 g/dL to 12 g/dL with TSAT > 20% and serum ferritin concentrations > 200 mcg/L were enrolled. Patients were to remain in randomized treatment until pre-specified hemoglobin or ferritin criteria were met, indicating the need for a change in anemia management, or if they completed 48 weeks. Triferic was added to the bicarbonate concentrate with a final concentration of 110 mcg iron/L in the dialysate and was administered 3 or 4 times per week during hemodialysis. Most patients were receiving a stable dose of erythropoiesis stimulating agents (ESAs) at baseline. After randomization, patients' ESA doses were not to be changed.
In Study 1, the mean age of patients was 58 years (range 23 to 89); 32% were female, 55% were Caucasian, 32% were African American, and 13% were other races.
In Study 2, the mean age of patients was 58 years (range 20 to 89); 41% were female, 54% were Caucasian, 40% were African American, and 6% were other races.
The primary endpoint of the studies was the mean change in hemoglobin from baseline to the end-of-treatment period (average hemoglobin of the last one-sixth (1/6th) of the time in the randomized treatment period). About 18% of patients completed the planned 48-week treatment duration.
Table 2 shows the mean changes in hemoglobin (Hgb) and iron parameters in each treatment group from baseline to the end-of-treatment period for the ITT population.
Table 2: Changes from Baseline to End-of-Treatment in Hemoglobin, Ferritin, Reticulocyte Hgb (CHr), and Transferrin Saturation (TSAT) Study 1 Study 2 Triferic
n=152Placebo
n=153Triferic
n=147Placebo
n=147- * p < 0.05 for primary efficacy endpoint
Baseline Hemoglobin
Mean ± (SD), g/dL10.96
(0.592)10.91
(0.632)10.96
(0.605)10.94
(0.622)Hemoglobin, Change from Baseline to End-of-Treatment
Mean ± (SD), g/dL-0.03
(1.147) *-0.38
(1.240)-0.08
(1.152) *-0.44
(1.157)Baseline Ferritin
Mean (SD), mcg/L508.2
(193.55)509.3
(209.06)519.0
(201.56)478.4
(200.59)Ferritin, Change from Baseline to End-of-Treatment
Mean (SD), mcg/L-70.8
(132.41)-141.2
(187.74)-65.3
(162.45)-120.9
(268.19)Baseline Reticulocyte Hemoglobin (CHr)
Mean (SD), pg32.37
(1.967)32.53
(1.965)32.56
(2.210)32.57
(1.932)CHr, Change from Baseline to End-of-Treatment
Mean (SD), pg-0.22
(1.191)-0.90
(1.407)-0.55
(1.441)-0.85
(1.474)Baseline TSAT
Mean (SD), %28.2
(8.23)27.1
(7.76)28.0
(8.15)28.2
(8.52)TSAT, Change from Baseline to End-of-Treatment)
Mean (SD), %-1.0
(9.07)-2.9
(7.65)-0.9
(7.54)-3.6
(7.29) -
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
16.1 How Supplied
Triferic is available in ampules or packets in the following package sizes:
NDC Code Package Description Amount/Total Volume in Ampule 5 mL Ampule 27.2 mg iron (III)/ 5mL as Triferic solution (5.44 mg of iron (III) per mL) NDC: 57278-314-01 5 Ampules per Pouch NDC: 57278-314-02 8 Pouches per Carton NDC: 57278-316-01 50 mL Ampule 272 mg iron (III)/ 50 mL as Triferic solution (5.44 mg of iron (III) per mL) NDC: 57278-316-02 4 Ampules per Pouch NDC: 57278-316-03 6 Pouches per Carton NDC Code Package Description Amount/Packet NDC: 57278-315-01 Packet 272 mg iron (III)/ packet as Triferic powder NDC: 57278-315-02 100 Packets per Carton 16.2 Storage
Store ampules protected from light in the aluminum pouch at controlled room temperature (20° to 25°C [68° to 77°F]); excursions permitted to 15°to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Store packets at controlled room temperature (20° to 25°C [68° to 77°F]); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Prior to the administration of Triferic:
- Question patients regarding any prior history of reactions to parenteral iron products.
- Advise patients of the risks associated with Triferic.
- Advise patient to report any signs and symptoms of hypersensitivity that may develop during and after the dialysis session, such as rash, itching, dizziness, lightheadedness, swelling and breathing problems [ see Warnings and Precautions (5)].
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 40 Ampule Carton
NDC: 57278-314-01
40 AmpulesRx Only
TRIFERIC™
ferric pyrophosphate citrate27.2 mg Fe/5 mL
(5.44 mg Fe/mL)ROCKWELL
MEDICALProtect from light
Keep ampules in pouch until time of use
For dialysis use only
Must be diluted
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 100 Packet Carton
NDC: 57278-315-02
Rx only
100 PacketsTRIFERIC™
ferric pyrophosphate citratePowder
PacketMust be diluted in 25 gallons (94.6 liters) of
bicarbonate concentrate prior to use.Dialysis use only
Do not freeze272 mg Fe
PER PACKET
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
TRIFERIC
ferric pyrophosphate solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 57278-314 Route of Administration PARENTERAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FERRIC PYROPHOSPHATE CITRATE (UNII: UBY79OCO9G) (FERRIC CATION - UNII:91O4LML611) FERRIC CATION 5.44 mg in 1 mL Product Characteristics Color green (Greenish-yellow) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 57278-314-01 8 in 1 CARTON 02/06/2015 1 5 in 1 POUCH 1 5 mL in 1 AMPULE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 2 NDC: 57278-314-02 6 in 1 CARTON 02/06/2015 2 4 in 1 POUCH 2 50 mL in 1 AMPULE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA206317 02/06/2015 TRIFERIC
ferric pyrophosphate citrate powderProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 57278-315 Route of Administration PARENTERAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength FERRIC PYROPHOSPHATE CITRATE (UNII: UBY79OCO9G) (FERRIC CATION - UNII:91O4LML611) FERRIC CATION 272 mg Product Characteristics Color green (Slightly yellow-green) Score Shape Size Flavor Imprint Code Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 57278-315-02 100 in 1 CARTON 04/25/2016 1 1 in 1 PACKET; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA208551 04/25/2016 Labeler - Rockwell Medical, Inc (933721433)
Trademark Results [Triferic]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 TRIFERIC 86036014 4837260 Live/Registered |
ROCKWELL MEDICAL, INC. 2013-08-13 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.