LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM- levoleucovorin injection injection, solution
LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Hainan Poly Pharm. Co., Ltd.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use LEVOLEUCOVORIN INJECTION safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for LEVOLEUCOVORIN INJECTION.
Levoleucovorin injection, for intravenous use
Initial U.S. Approval: 1952 ( d,l-leucovorin)RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Levoleucovorin injection is a folate analog indicated for:
- Rescue after high-dose methotrexate therapy in adult and pediatric patients with osteosarcoma. ( 1)
- Diminishing the toxicity associated with overdosage of folic acid antagonists or impaired methotrexate elimination in adult and pediatric patients. ( 1)
- Treatment of adults with metastatic colorectal cancer in combination with fluorouracil. ( 1)
Limitations of Use:
Levoleucovorin injection is not indicated for the treatment of pernicious anemia and megaloblastic anemia secondary to lack of vitamin B 12, because of the risk of progression of neurologic manifestations despite hematologic remission. ( 1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
For intravenous administration only. Do not administer intrathecally. ( 2.1)
Rescue After High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
- Rescue recommendations are based on methotrexate dose of 12 grams/m 2 administered by intravenous infusion over 4 hours. Initiate rescue at a dose of 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m 2) every 6 hours, 24 hours after the beginning of methotrexate infusion. ( 2.3)
- Continue until the methotrexate level is below 5 x 10 -8 M (0.05 micromolar). Adjust dose if necessary based on methotrexate elimination; refer to Full Prescribing Information. ( 2.3)
Overdosage of Folic Acid Antagonists or Impaired Methotrexate Elimination
- Start as soon as possible after methotrexate overdosage or within 24 hours of delayed methotrexate elimination. ( 2.4)
- Administer levoleucovorin injection 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m 2) intravenously every 6 hours until methotrexate level is less than 5 x 10 -8 M (0.05 micromolar). ( 2.4)
Metastatic Colorectal Cancer in Combination with Fluorouracil- The following regimens have been used for the treatment of colorectal cancer:
- Levoleucovorin injection 100 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection over a minimum of 3 minutes, followed by fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 once daily for 5 consecutive days. ( 2.5)
- Levoleucovorin injection 10 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection followed by fluorouracil 425 mg/m 2 once daily for 5 consecutive days. ( 2.5)
- Administer Fluorouracil and levoleucovorin injection separately to avoid the formation of precipitate.
- The above five-day courses may be repeated every 4 weeks for 2 courses, then every 4 to 5 weeks, if the patient has recovered from toxicity from the prior course.
- Do not adjust levoleucovorin injection dosage for toxicity. ( 2.5)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
- Injection: 175 mg per 17.5 mL (10 mg per mL) or 250 mg per 25 mL (10 mg per mL) in a single-dose vial ( 3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Patients who have had severe hypersensitivity reactions to leucovorin products, folic acid or folinic acid. ( 4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Hypercalcemia: Due to calcium content, inject no more than 16 mL (160 mg) of levoleucovorin solution intravenously per minute. ( 5.1)
- Increased Gastrointestinal Toxicities with Fluorouracil: Do not initiate or continue therapy with levoleucovorin and fluorouracil in patients with symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity until symptoms have resolved. Monitor patients with diarrhea until it has resolved as rapid deterioration leading to death can occur. ( 5.2, 7)
- Drug Interaction with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole: Increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity with concomitant use of d,l-leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV. ( 5.3)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
- The most common adverse reactions (≥20%) in patients receiving high-dose methotrexate therapy with levoleucovorin rescue are stomatitis and vomiting. ( 6.1)
- The most common adverse reactions (>50%) in patients receiving levoleucovorin in combination with fluorouracil for metastatic colorectal cancer are stomatitis, diarrhea, and nausea. ( 6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Hainan Poly Pharm. Co., Ltd. at 1-800-571-8369 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Revised: 5/2023
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Use Information
2.2 Co-administration of Levoleucovorin Injection with Other Agents
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Rescue After High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Overdosage of Folic Acid Antagonists or Impaired Methotrexate Elimination
2.5 Dosage in Combination with Fluorouracil for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
2.6 Preparation for Administration
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypercalcemia
5.2 Increased Gastrointestinal Toxicities with Fluorouracil
5.3 Drug Interaction with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Leucovorin Products on Other Drugs
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Rescue after High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy in Patients with Osteosarcoma
14.2 Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Levoleucovorin injection is indicated for:
- rescue after high-dose methotrexate therapy in adult and pediatric patients with osteosarcoma.
- diminishing the toxicity associated with overdosage of folic acid antagonists or impaired methotrexate elimination in adult and pediatric patients.
- the treatment of adults with metastatic colorectal cancer in combination with fluorouracil.
Limitations of Use:
Levoleucovorin injection is not indicated for pernicious anemia and megaloblastic anemia secondary to the lack of vitamin B 12, because of the risk of progression of neurologic manifestations despite hematologic remission.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Important Use Information
Levoleucovorin injection is indicated for intravenous administration only . Do not administer intrathecally.
2.2 Co-administration of Levoleucovorin Injection with Other Agents
Due to the risk of precipitation, do not co-administer levoleucovorin injection with other agents in the same admixture.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Rescue After High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
The recommended dosage for levoleucovorin injection is based on a methotrexate dose of 12 grams/m 2 administered by intravenous infusion over 4 hours. Twenty-four hours after starting the methotrexate infusion, initiate levoleucovorin injection at a dose of 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m 2) as an intravenous infusion every 6 hours.
Monitor serum creatinine and methotrexate levels at least once daily. Continue levoleucovorin injection administration, hydration, and urinary alkalinization (pH of 7 or greater) until the methotrexate level is below 5 x 10 -8 M (0.05 micromolar). Adjust the levoleucovorin injection dose or extend the duration as recommended in Table 1.
Table 1: Recommended Dosage for Levoleucovorin Injection based on Serum Methotrexate and Creatinine Levels Clinical Situation Laboratory Findings Recommendation Normal
Methotrexate
EliminationSerum methotrexate level approximately 10 micromolar at 24 hours after administration, 1 micromolar at 48 hours, and less than 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours Administer 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 6 hours for 60 hours (10 doses starting at 24 hours after start of methotrexate infusion). Delayed Late
Methotrexate
EliminationSerum methotrexate level remaining above 0.2 micromolar at 72 hours, and more than 0.05 micromolar at 96 hours after administration. Continue 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 6 hours until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. Delayed Early
Methotrexate
Elimination and/or
Evidence of Acute
Renal Injury*Serum methotrexate level of 50 micromolar or more at 24 hours, or 5 micromolar or more at 48 hours after administration
OR
100% or greater increase in serum creatinine level at 24 hours after methotrexate administration (e.g., an increase from 0.5 mg/dL to a level of 1 mg/dL or more).Administer 75 mg by intravenous infusion every 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 1 micromolar; then 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 3 hours until methotrexate level is less than 0.05 micromolar. * These patients are likely to develop reversible renal failure. In addition to appropriate levoleucovorin injection therapy, continue hydration and urinary alkalinization and monitor fluid and electrolyte status, until the serum methotrexate level has fallen to below 0.05 micromolar and the renal failure has resolved.
Impaired Methotrexate Elimination or Renal Impairment
Decreased methotrexate elimination or renal impairment which are clinically important but less severe than the abnormalities described in Table 1 can occur following methotrexate administration. If toxicity associated with methotrexate is observed, in subsequent courses extend levoleucovorin injection rescue for an additional 24 hours (total of 14 doses over 84 hours).
Third-Space Fluid Collection and Other Causes of Delayed Methotrexate Elimination
Accumulation in a third space fluid collection (i.e., ascites, pleural effusion), renal insufficiency, or inadequate hydration can delay methotrexate elimination. Under such circumstances, higher doses of levoleucovorin injection or prolonged administration may be indicated.
2.4 Recommended Dosage for Overdosage of Folic Acid Antagonists or Impaired Methotrexate Elimination
Start levoleucovorin injection as soon as possible after an overdosage of methotrexate or within 24 hours of methotrexate administration when methotrexate elimination is impaired. As the time interval between methotrexate administration and levoleucovorin injection increases, the effectiveness of levoleucovorin injection to diminish methotrexate toxicity may decrease. Administer levoleucovorin injection 7.5 mg (approximately 5 mg/m 2 ) by intravenous infusion every 6 hours until the serum methotrexate level is less than 5 x 10 -8 M (0.05 micromolar).
Monitor serum creatinine and methotrexate levels at least every 24 hours. Increase the dosage of levoleucovorin injection to 50 mg/m 2 intravenously every 3 hours and continue levoleucovorin injection at this dosage until the methotrexate level is less than 5 x 10 -8 M for the following:
- if serum creatinine at 24-hours increases 50% or more compared to baseline
- if the methotrexate level at 24-hours is greater than 5 x 10 -6 M
- if the methotrexate level at 48-hours is greater than 9 x 10 -7 M,
Continue concomitant hydration (3 L per day) and urinary alkalinization with sodium bicarbonate. Adjust the sodium bicarbonate dose to maintain urine pH at 7 or greater.
2.5 Dosage in Combination with Fluorouracil for Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
The following regimens have been used for the treatment of colorectal cancer:
- Levoleucovorin injection 100 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection over a minimum of 3 minutes, followed by fluorouracil at 370 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection, once daily for 5 consecutive days.
- Levoleucovorin injection 10 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection, followed by fluorouracil 425 mg/m 2 by intravenous injection, once daily for 5 consecutive days.
Administer fluorouracil and levoleucovorin injection separately to avoid the formation of a precipitate.
This five-day course may be repeated every 4 weeks for 2 courses, then every 4 to 5 weeks, if the patient has recovered from the toxicity from the prior course. Do not adjust levoleucovorin injection dosage for toxicity.
Refer to fluorouracil prescribing information for information on fluorouracil dosage and dosage modifications for adverse reactions.
2.6 Preparation for Administration
- Levoleucovorin contains no preservative. Observe strict aseptic technique during reconstitution of the drug product. Discard unused portion.
- Levoleucovorin solutions may be further diluted to concentrations of 0.5 mg per mL in 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP. Do not store the product diluted using 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, USP or 5% Dextrose Injection, USP for more than 4 hours at room temperature.
- Visually inspect the diluted solution for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration. Do not use if cloudiness or precipitate is observed.
- Inject no more than 16 mL of levoleucovorin injection (160 mg of levoleucovorin) intravenously per minute, because of the calcium content of the levoleucovorin solution.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Levoleucovorin is contraindicated in patients who have had severe hypersensitivity to leucovorin products, folic acid or folinic acid [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.2)] .
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypercalcemia
Because of the calcium content of the levoleucovorin solution, inject no more than 16 mL (160 mg of levoleucovorin) intravenously per minute.
5.2 Increased Gastrointestinal Toxicities with Fluorouracil
Leucovorin products increase the toxicities of fluorouracil [see Drug Interactions ( 7)] . Gastrointestinal toxicities, including stomatitis and diarrhea, occur more commonly and may be of greater severity and of prolonged duration. Deaths from severe enterocolitis, diarrhea, and dehydration have occurred in elderly patients receiving weekly d,l-leucovorin and fluorouracil.
Monitor patients for gastrointestinal toxicities. Do not initiate or continue therapy with levoleucovorin and fluorouracil in patients with symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity until those symptoms have resolved. Monitor patients with diarrhea until resolved, as rapid deterioration leading to death can occur.
5.3 Drug Interaction with Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
The concomitant use of d,l-leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity [see Drug Interactions ( 7)] .
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following clinically significant adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
- Hypercalcemia [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.1)]
- Increased gastrointestinal toxicities with fluorouracil [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
Table 2 presents the frequency of adverse reactions which occurred during the administration of 58 courses of high-dose methotrexate 12 grams/m 2 followed by levoleucovorin rescue for osteosarcoma in 16 patients aged 6 to 21 years. Most patients received levoleucovorin 7.5 mg every 6 hours for 60 hours or longer, beginning 24 hours after completion of methotrexate administration.
Table 2 Adverse Reactions with High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy Adverse Reactions Levoleucovorin
n = 16All Grades (%) Grades 3-4 (%) Gastrointestinal Stomatitis 38 6 Vomiting 38 0 Nausea 19 0 Diarrhea 6 0 Dyspepsia 6 0 Typhlitis 6 6 Respiratory Dyspnea 6 0 Skin and Appendages Dermatitis 6 0 Other Confusion 6 0 Neuropathy 6 0 Renal function abnormal 6 0 Taste perversion 6 0 Combination with Fluorouracil in Colorectal Cancer
Table 3 presents the frequency of adverse reaction which occurred in 2 arms of a randomized controlled trial conducted by the North Central Cancer Treatment Group (NCCTG) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. The trial failed to show superior overall survival with fluorouracil + levoleucovorin compared to fluorouracil + d,l-leucovorin. Patients were randomized to fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 intravenously and levoleucovorin 100 mg/m 2 intravenously, both daily for 5 days, or to fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 intravenously and d,l-leucovorin 200 mg/m 2 intravenously, both daily for 5 days. Treatment was repeated week 4 and week 8, and then every 5 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Table 3 Adverse Reactions Occurring in ≥ 10% of Patients in Either Arm 1Includes abdominal pain, upper abdominal pain, lower abdominal pain, and abdominal tenderness
Adverse Reaction Levoleucovorin/fluorouracil
n=318d,l-Leucovorin/fluorouracil
n=307Grades 1-4
(%)Grades 3-4
(%)Grades 1-4
(%)Grades 3-4
(%)Gastrointestinal Disorders Stomatitis 72 12 72 14 Diarrhea 70 19 65 17 Nausea 62 8 61 8 Vomiting 40 5 37 6 Abdominal Pain 1 14 3 19 3 General Disorders Asthenia/Fatigue/Malaise 29 5 32 11 Skin Disorders Dermatitis 29 1 28 1 Alopecia 26 0.3 28 1 Metabolism and Nutrition Anorexia/Decreased Appetite 24 4 25 2 6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reaction have been identified during postapproval use of levoleucovorin products. Because these reactions are reported from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Dermatologic: pruritus, rash
Respiratory: dyspnea
Other: temperature change, rigors, allergic reactions
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Effects of Leucovorin Products on Other Drugs
Antiepileptic Drugs
Folic acid in large amounts may counteract the antiepileptic effect of phenobarbital, phenytoin and primidone and increase the frequency of seizures in susceptible children. It is not known whether folinic acid has the same effects; however, both folic and folinic acids share some common metabolic pathways. Monitor patients taking folinic acid in combination with antiepileptic drugs.
Fluorouracil
Leucovorin products increase the toxicity of fluorouracil. Do not initiate or continue therapy with levoleucovorin and fluorouracil in patients with symptoms of gastrointestinal toxicity until those symptoms have resolved. Monitor patients with diarrhea until the diarrhea has resolved, as rapid deterioration leading to death can occur [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.2)].
Trimethoprim-Sulfamethoxazole
The concomitant use of d,l-leucovorin with trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole for the acute treatment of Pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia in patients with HIV infection was associated with increased rates of treatment failure and morbidity in a placebo-controlled study [see Warnings and Precautions ( 5.3)] .
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
There are limited data with levoleucovorin use in pregnant women. Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with levoleucovorin.
Levoleucovorin is administered in combination with methotrexate or fluorouracil, which can cause embryo-fetal harm. Refer to methotrexate and fluorouracil prescribing information for additional information.
In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2% to 4% and 15% to 20%, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There are no data on the presence of levoleucovorin in human milk or its effects on the breastfed infant or on milk production.
Levoleucovorin is administered in combination with methotrexate or fluorouracil. Refer to methotrexate and fluorouracil prescribing information for additional information.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of levoleucovorin have been established in pediatric patients for rescue after high-dose methotrexate therapy in osteosarcoma and diminishing the toxicity associated with overdosage of folic acid antagonists or impaired methotrexate elimination. Use of levoleucovorin in pediatric patients is supported by open-label clinical trial data in 16 pediatric patients 6 years of age and older, with additional supporting evidence from literature [see Clinical Studies ( 14.1)].
The safety and effectiveness of levoleucovorin have not been established for the treatment of pediatric patients with advanced metastatic colorectal cancer.
8.5 Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of levoleucovorin in the treatment of osteosarcoma did not include patients aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients.
In the NCCTG clinical trial of levoleucovorin in combination with fluorouracil for the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer, no overall differences in safety or effectiveness were observed between patients age 65 years and older and younger patients.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
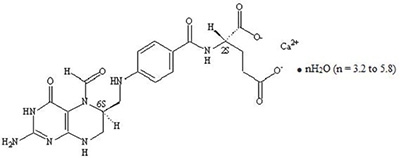
Levoleucovorin is a folate analog and the pharmacologically active levo-isomer of d,l-leucovorin. The chemical name of levoleucovorin calcium is calcium (6S)-N-{4-[[(2-amino-5-formyl-1,4,5,6,7,8-hexahydro-4-oxo-6-pteridinyl)methyl] amino]benzoyl}-L-glutamate mixed hydrates. The molecular formula is C 20H 21CaN 7O 7●nH 2O (n = 3.2 to 5.8) and the molecular weight is 569.1 to 616.0. The molecular structure is:
Levoleucovorin injection, for intravenous use is supplied as a colorless to faint yellow solution of either 175 mg levoleucovorin in 17.5 mL or 250 mg levoleucovorin in 25 mL per single-dose vial. Each mL contains 10 mg levoleucovorin (equivalent to 10.8 mg levoleucovorin calcium (as mixed hydrates)) and 8.3 mg sodium chloride. Sodium hydroxide is used for pH adjustment to pH 8.2 (6.5 to 8.5).
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy
Levoleucovorin is the pharmacologically active isomer of 5-formyl tetrahydrofolic acid. Levoleucovorin does not require reduction by the enzyme dihydrofolate reductase in order to participate in reactions utilizing folates as a source of “one-carbon” moieties. Administration of levoleucovorin counteracts the therapeutic and toxic effects of folic acid antagonists such as methotrexate, which act by inhibiting dihydrofolate reductase.
Combination with Fluorouracil in Colorectal Cancer
Levoleucovorin enhances the therapeutic and toxic effects of fluorouracil. Fluorouracil is metabolized to 5-fluoro-2'-deoxyuridine-5'-monophosphate (FdUMP), which binds to and inhibits thymidylate synthase (an enzyme important in DNA repair and replication). Levoleucovorin is converted to another reduced folate, 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate, which acts to stabilize the binding of FdUMP to thymidylate synthase and thereby enhancing the inhibition of thymidylate synthase.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
The pharmacokinetics of levoleucovorin after intravenous administration of a 15 mg dose was studied in healthy subjects. The mean maximum serum total tetrahydrofolate (total-THF) concentrations was 1722 ng/mL (CV 39%) and the mean maximum serum (6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate concentrations was 275 ng/mL (CV 18%) observed around 0.9 hours post injection.
Distribution
Exploratory studies show that small quantities of systemically administered leucovorin enter the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), primarily as its major metabolite 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-MTHFA). In humans, the CSF levels of 5-MTHFA remain 1-3 orders of magnitude lower than the usual methotrexate concentrations following intrathecal administration.
Elimination
The mean terminal half-life was 5.1 hours for total-THF and 6.8 hours for (6S)-5-methyl-5,6,7,8-tetrahydrofolate.
Drug Interaction Studies
The mean dose-normalized steady-state plasma concentrations for both levoleucovorin and 5-methyl-THF were comparable whether fluorouracil (370 mg/m 2/day as an intravenous bolus) was given in combination with levoleucovorin (250 mg/m 2 and 1000 mg/m 2 as a continuous intravenous infusion for 5.5 days) or with d,l-leucovorin (500 mg/m 2 as a continuous intravenous infusion for 5.5 days).
- 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
14.1 Rescue after High-Dose Methotrexate Therapy in Patients with Osteosarcoma
The efficacy of levoleucovorin rescue following high-dose methotrexate was evaluated in 16 patients aged 6 to 21 years who received 58 courses of therapy for osteogenic sarcoma. High-dose methotrexate was one component of several different combination chemotherapy regimens evaluated across several trials. Methotrexate 12 grams/m 2 as an intravenous infusion over 4 hours was administered to 13 patients, who received levoleucovorin 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 6 hours for 60 hours or longer beginning 24 hours after completion of methotrexate. Three patients received methotrexate 12.5 grams/m 2 intravenously over 6 hours, followed by levoleucovorin 7.5 mg by intravenous infusion every 3 hours for 18 doses beginning 12 hours after completion of methotrexate. The mean number of levoleucovorin doses per course was 18.2 and the mean total dose per course was 350 mg. The efficacy of levoleucovorin rescue following high-dose methotrexate was based on the adverse reaction profile [see Adverse Reactions ( 6.1)].
14.2 Metastatic Colorectal Cancer
In a randomized clinical study conducted by Mayo Clinic and North Central Cancer Treatment Group (NCCTG) in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer comparing d,l-leucovorin 200 mg/m 2 and fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 versus d,l-leucovorin 20 mg/m 2 and fluorouracil 425 mg/m 2 versus fluorouracil 500 mg/m 2, with all drugs administered by intravenous infusion daily for 5 days every 28 to 35 days, response rates were 26% (p=0.04 versus fluorouracil alone), 43% (p=0.001 versus fluorouracil alone) and 10%, respectively. Respective median survival times were 12.2 months (p=0.037), 12 months (p=0.050), and 7.7 months. The low dose d,l-leucovorin regimen was associated with a statistically significant improvement in weight gain of more than 5%, relief of symptoms, and improvement in performance status. The high dose d,l-leucovorin regimen was associated with a statistically significant improvement in performance status and trended toward improvement in weight gain and in relief of symptoms but these were not statistically significant.
In a second randomized clinical study conducted by Mayo Clinic and NCCTG, the fluorouracil alone arm was replaced by a regimen of sequentially administered methotrexate, fluorouracil, and d,l-leucovorin. Response rates with d,l-leucovorin 200 mg/m 2 and fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 versus d,l-leucovorin 20 mg/m 2 and fluorouracil 425 mg/m 2 versus sequential methotrexate and fluorouracil and d,l-leucovorin were respectively 31% (p≤0.01), 42% (p≤0.01), and 14%. Respective median survival times were 12.7 months (p≤0.04), 12.7 months (p≤0.01), and 8.4 months. There was no statistically significant difference in weight gain of more than 5% or in improvement in performance status was seen between the treatment arms.
A randomized controlled trial conducted by NCCTG in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer failed to show superiority of a regimen of fluorouracil + levoleucovorin to fluorouracil + d,l-leucovorin in overall survival. Patients were randomized to fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 intravenously and levoleucovorin 100 mg/m 2 intravenously, both daily for 5 days, or to fluorouracil 370 mg/m 2 intravenously and d,l-leucovorin 200 mg/m 2 intravenously, both daily for 5 days. Treatment was repeated week 4 and week 8, and then every 5 weeks until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Levoleucovorin injection is a sterile colorless to faint yellow solution in a single-dose vial available as:
175 mg/17.5 mL (10 mg/mL) solution – NDC: 14335-340-01
250 mg/25 mL (10 mg/mL) solution – NDC: 14335-341-01
Store in refrigerator at 2°C to 8°C (36°F to 46°F). Protect from light. Store in carton until contents are used.Manufactured by:
Hainan Poly Pharm. Co., Ltd.
Guilinyang Economic Development Zone, Haikou, Hainan, China, 571127 - 18 Principal Display Panel
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM
levoleucovorin injection injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 14335-340 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM (UNII: 778XL6VBS8) (LEVOLEUCOVORIN - UNII:990S25980Y) LEVOLEUCOVORIN 10 mg in 1 mL Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) 1 mL in 1 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 8.3 mg in 1 mL SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 14335-340-01 1 in 1 CARTON 05/31/2023 1 17.5 mL in 1 VIAL, SINGLE-DOSE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA217314 05/31/2023 LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM
levoleucovorin injection injection, solutionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 14335-341 Route of Administration INTRAVENOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength LEVOLEUCOVORIN CALCIUM (UNII: 778XL6VBS8) (LEVOLEUCOVORIN - UNII:990S25980Y) LEVOLEUCOVORIN 10 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength WATER (UNII: 059QF0KO0R) 1 mL SODIUM CHLORIDE (UNII: 451W47IQ8X) 8.3 mg SODIUM HYDROXIDE (UNII: 55X04QC32I) Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 14335-341-01 1 in 1 CARTON 05/31/2023 1 25 in 1 VIAL; Type 0: Not a Combination Product Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA217314 05/31/2023 Labeler - Hainan Poly Pharm. Co., Ltd. (654561638) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Hainan Poly Pharm. Co., Ltd. 654561638 manufacture(14335-340, 14335-341) , analysis(14335-340, 14335-341)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.



