PHYTONADIONE injection, emulsion
Phytonadione by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Phytonadione by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by International Medication Systems, Limited , International Medication Systems, Limited. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use PHYTONADIONE INJECTABLE EMULSION, USP safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for PHYTONADIONE INJECTABLE EMULSION, USP.
PHYTONADIONE Injection, for intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous use.Initial U.S. Approval: 1960WARNING – HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS WITH INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR USE
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.Fatal hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred during and immediately after INTRAVENOUS and INTRAMUSCULAR injection of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP. Reactions have occurred despite dilution to avoid rapid infusion and upon first and subsequent doses. Avoid the intravenous and intramuscular routes of administration unless the subcutaneous route is not feasible and the serious risk is justified (5.1)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions, Cutaneous Reactions (5.3) 04/2018
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is a vitamin K replacement indicated for the treatment of the following coagulation disorders which are due to faulty formation of factors II, VII, IX and X when caused by vitamin K deficiency or interference with vitamin K activity.
Anticoagulant-induced hypoprothrombinemia deficiency caused by coumarin or indane-
dione derivatives; (1.1)Hypoprothrombinemia due to antibacterial therapy; (1.1)
Hypoprothrombinemia secondary to factors limiting absorption or synthesis of vitamin
K, e.g., obstructive jaundice, biliary fistula, sprue, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease,
intestinal resection, cystic fibrosis of the pancreas, and regional enteritis; (1.1)Other drug-induced hypoprothrombinemia where is it definitely shown that the result is
due to interference with vitamin K metabolism, e.g., salicylates. (1.1)Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is indicated for prophylaxis and treatment of vitamin K-deficiency bleeding in neonates. (1.2)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
Injection: 1 mg/0.5 mL single-dose vial and a SAF-T-Jet® vial injector. (3)
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to any component of this medication. (4)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions are cyanosis, diaphoresis, dizziness, dysgeusia, dyspnea, flushing, hypotension and tachycardia. (6)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Amphastar Pharmaceuticals, Inc. at 1-800-423-4136, or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
Anticoagulants: May induce temporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants. (7)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
Pregnancy: If available, use the preservative-free formulation in pregnant women. (8.1)
Lactation: If available, use the preservative-free formulation in lactating women. (8.2)
Pediatric Use: The safety and effectiveness of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP
in pediatric patients from 6 months to 17 years have not been established. (8.4)See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION.
Revised: 4/2019
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING – HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS WITH INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR USE
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Vitamin K Deficiency or Interference
1.2 Prophylaxis and Treatment of Vitamin K-Deficiency Bleeding in Neonates
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Considerations
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Coagulation Disorders from Vitamin K Deficiency of Interference
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding in Neonates
2.4 Directions for Dilution
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
5.2 Risk of Serious Adverse Reaction in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative
5.3 Cutaneous Reactions
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.3 Clinical Trials and Post-Marketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.4 Pediatric Use
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING – HYPERSENSITIVITY REACTIONS WITH INTRAVENOUS AND INTRAMUSCULAR USE
Fatal hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred during and immediately after intravenous and intramuscular injection of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP. Reactions have occurred despite dilution to avoid rapid intravenous infusion and upon first dose. Avoid the intravenous and intramuscular routes of administration unless the subcutaneous route is not feasible and the serious risk is justified [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
1.1 Treatment of Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Vitamin K Deficiency or Interference
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is indicated for the treatment of the following coagulation disorders which are due to faulty formation of factors II, VII, IX and X when caused by vitamin K deficiency or interference with vitamin K activity:
anticoagulant-induced hypoprothrombinemia caused by coumarin or indanedione derivatives;
hypoprothrombinemia due to antibacterial therapy;
hypoprothrombinemia secondary to factors limiting absorption or synthesis of vitamin K, e.g., obstructive jaundice, biliary fistula, sprue, ulcerative colitis, celiac disease, intestinal resection, cystic fibrosis of the pancreas, and regional enteritis;
other drug-induced hypoprothrombinemia where it is definitely shown that the result is due to interference with vitamin K metabolism, e.g., salicylates.
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Dosing Considerations
Whenever possible, administer Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP by the subcutaneous route [see Boxed Warning]. When intravenous administration is unavoidable, inject the drug very slowly, not exceeding 1 mg per minute [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Monitor international normalized ratio (INR) regularly and as clinical conditions indicate. Use the lowest effective dose of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP.
The coagulant effects of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP are not immediate; improvement of INR may take 1-8 hours. Interim use of whole blood or component therapy may also be necessary if bleeding is severe.
Whenever possible, administer benzyl alcohol-free formulations in pediatric patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
When Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is used to correct excessive anticoagulant-induced hypoprothrombinemia, anticoagulant therapy still being indicated, the patient is again faced with the clotting hazards existing prior to starting the anticoagulant therapy. Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is not a clotting agent, but overzealous therapy with Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP may restore conditions which originally permitted thromboembolic phenomena. Dosage should be kept as low as possible, and INR should be checked regularly as clinical conditions indicate.
2.2 Recommended Dosage for Coagulation Disorders from Vitamin K Deficiency of Interference
The recommended dosage of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is based on whether the hypoprothrombinemia is anticoagulant-induced (e.g., due to coumarin or indanedione derivatives) or non-anticoagulant-induced (e.g., due to antibiotics; salicylates or other drugs; factors limiting absorption or synthesis) as follows:
Anticoagulant-Induced Hypoprothrombinemia: Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP 2.5 mg to 10 mg or more subcutaneously, intramuscularly, or intravenously. Up to 25 mg to 50 mg may be administered as a single dose.
Repeated large doses of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP are not warranted in liver disease if the initial response is unsatisfactory. Failure to respond to Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP may indicate that the condition being treated is inherently unresponsive to Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP.
Hypoprothrombinemia Due to Other Causes (Non-Anticoagulation-Induced Hypoprothrombinemia): Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP 2.5 mg to 25 mg or
more intravenously, intramuscularly, or subcutaneously. Up to 50 mg may be administered as a single dose.Evaluate INR after 6-8 hours, and repeat dose if INR remains prolonged. Modify subsequent dosage (amount and frequency) based on the INR or clinical condition.
2.3 Recommended Dosage for Prophylaxis and Treatment of Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding in Neonates
Prophylaxis of Vitamin K-Deficiency Bleeding in Neonates
The recommended dosage of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is 0.5 mg to 1 mg within one hour of birth for a single dose.Treatment of Vitamin K Deficiency Bleeding in Neonates
The recommended dosage of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is 1 mg given either subcutaneously or intramuscularly.
Consider higher doses if the mother has been receiving oral anticoagulants.A failure to respond (shortening of the INR in 2 to 4 hours) may indicate another diagnosis or coagulation disorder.
2.4 Directions for Dilution
Dilute Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP with 0.9% Sodium Chloride Injection, 5% Dextrose Injection, or 5% Dextrose and Sodium Chloride Injection. Avoid use of other diluents that may contain benzyl alcohol, which can cause serious toxicity in newborns or low birth weight infants [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
When diluted, start administration of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP immediately after dilution.
Discard unused portions of diluted solution as well as unused contents of the vial.
Protect Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP from light at all times.
Parenteral drug products should be inspected visually for particulate matter and discoloration prior to administration, whenever solution and container permit.
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
Hypersensitivity to phytonadione or any other component of this medication [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Hypersensitivity Reactions
Fatal and severe hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylaxis, have occurred with intravenous or intramuscular administration of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP. Reactions have occurred despite dilution to avoid rapid intravenous infusion and upon first dose. These reactions have included shock, cardiorespiratory arrest, flushing, diaphoresis, chest pain, tachycardia, cyanosis, weakness, and dyspnea. Administer Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP subcutaneously whenever feasible. Avoid the intravenous and intramuscular routes of administration unless the subcutaneous route is not feasible and the serious risk is justified [see Dosage and Administration (2.1)].
5.2 Risk of Serious Adverse Reaction in Infants due to Benzyl Alcohol Preservative
Use benzyl alcohol-free formulations in neonates and infants, if available. Serious and fatal adverse reactions including “gasping syndrome” can occur in neonates and infants treated with benzyl alcohol-preserved drugs, including Phytonadione. The “gasping syndrome” is characterized by central nervous system depression, metabolic acidosis, and gasping respirations.
When prescribing Phytonadione in infants, consider the combined daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources including Phytonadione and other drugs containing benzyl alcohol. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which serious adverse reactions may occur is not known [see Use in Specific Populations (8.1, 8.2 and 8.4)].5.3 Cutaneous Reactions
Parenteral administration of vitamin K replacements (including Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP) may cause cutaneous reactions. Reactions have included eczematous reactions, scleroderma-like patches, urticaria, and delayed-type hypersensitivity reactions. Time of onset ranged from 1 day to a year after parenteral administration. Discontinue Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP for skin reactions and institute medical management.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are described elsewhere in the labeling:
Hypersensitivity Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
Cutaneous Reactions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]6.3 Clinical Trials and Post-Marketing Experience
The following adverse reactions associated with the use of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP were identified in clinical studies or postmarketing reports. Because some of these reactions were reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is not always possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Cardiac Disorders: Tachycardia, hypotension.
General disorders and administration site conditions: Generalized flushing; pain, swelling, and tenderness at injection site.
Hepatobiliary Disorders: Hyperbilirubinemia
Immune System Disorders: Fatal hypersensitivity reactions, anaphylactic reactions.
Neurologic: Dysgeusia, dizziness.
Pulmonary: Dyspnea.
Skin and Subcutaneous Tissue Disorders: Erythema, pruritic plaques, scleroderma-like lesions, erythema perstans.
Vascular: Cyanosis. -
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
Anticoagulants
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP may induce temporary resistance to prothrombin-depressing anticoagulants, especially when larger doses of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP are used. Should this occur, higher doses of anticoagulant therapy may be needed when resuming anticoagulant therapy, or a change in therapy to a different class of anticoagulant may be necessary (i.e., heparin sodium).Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP does not affect the anticoagulant action of heparin.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
The preservative benzyl alcohol can cause serious adverse events and death when administered intravenously to neonates and infants. If Phytonadione is needed during pregnancy, consider using a benzyl alcohol-free formulation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].Published studies with the use of phytonadione during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with phytonadione and adverse developmental outcomes (see Data). There are maternal and fetal risks associated with vitamin K deficiency during pregnancy (see Clinical Considerations). Animal reproduction studies have not been conducted with phytonadione.
The estimated background risk for the indicated population is unknown. All pregnancies have a background risk of birth defect, loss, or other adverse outcomes. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Pregnant women with vitamin K deficiency hypoprothrombinemia may be at an increased risk for bleeding diatheses during pregnancy and hemorrhagic events at delivery. Subclinical maternal vitamin K deficiency during pregnancy has been implicated in rare cases of fetal intracranial hemorrhage.
Data
Human Data
Phytonadione has been measured in cord blood of infants whose mothers were treated with phytonadione during pregnancy in concentrations lower than seen in maternal plasma. Administration of vitamin K1 to pregnant women shortly before delivery increased both maternal and cord blood concentrations. Published data do not report a clear association with phytonadione and adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitively establish the absence of any risk because of methodologic limitations including small sample size and lack of blinding.
Animal Data
In pregnant rats receiving vitamin K1 orally, fetal plasma and liver concentrations increased following administration, supporting placental transfer.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
If available, preservative-free Phytonadione is recommended when Phytonadione is needed during lactation [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].Phytonadione is present in breastmilk. There are no data on the effects of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP on the breastfed child or on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the clinical need for Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed child from Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP or from the underlying maternal condition.
8.4 Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP for prophylaxis and treatment of vitamin K deficiency have been established in neonates. Use of phytonadione injection for prophylaxis and treatment of vitamin K deficiency is based on published clinical studies.
Serious adverse reactions including fatal reactions and the “gasping syndrome” occurred in premature neonates and infants in the intensive care unit who received drugs containing benzyl alcohol as a preservative. In these cases, benzyl alcohol dosages of 99 to 234 mg/kg/day produced high levels of benzyl alcohol and its metabolites in the blood and urine (blood levels of benzyl alcohol were 0.61 to 1.378 mmol/L). Additional adverse reactions included gradual neurological deterioration, seizures, intracranial hemorrhage, hematologic abnormalities, skin breakdown, hepatic and renal failure, hypotension, bradycardia, and cardiovascular collapse. Preterm, low-birth weight infants may be more likely to develop these reactions because they may be less able to metabolize benzyl alcohol.
When prescribing Phytonadione in infants consider the combined daily metabolic load of benzyl alcohol from all sources including Phytonadione and other drugs containing benzyl alcohol. The minimum amount of benzyl alcohol at which serious adverse reactions may occur is not known [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Whenever possible, use preservative-free phytonadione formulations in neonates. The preservative benzyl alcohol has been associated with serious adverse events and death in pediatric patients. Premature and low-birth weight infants may be more likely to develop toxicity.
- 10 OVERDOSAGE
-
11 DESCRIPTION
Phytonadione is a vitamin K replacement, which is a clear, yellow to amber, viscous, odorless or nearly odorless liquid. It is insoluble in water, soluble in chloroform and slightly soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 450.70.
Phytonadione is 2-methyl-3-phytyl-1, 4-naphthoquinone. Its empirical formula is C31H46O2 and its molecular structure is:
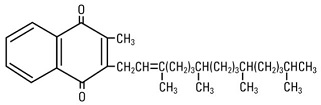
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP injection is a yellow, sterile, aqueous colloidal solution of vitamin K1, with a pH of 3.5 to 7.0, available for injection by the intravenous, intramuscular, and subcutaneous routes. Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is available in 1 mg (1 mg/0.5 mL) single-dose vials. Each 0.5 mL of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP contains the following inactive ingredients: 10 mg polysorbate 80, 10.4 mg propylene glycol, 0.17 mg sodium acetate anhydrous, and 0.00002 mL glacial acetic acid. Additional glacial acetic acid or sodium acetate anhydrous may have been added to adjust pH to meet USP limits of 3.5 to 7.0. The air above the liquid in the individual containers has been displaced by flushing with nitrogen during the filling operation.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP aqueous colloidal solution of vitamin K1 for parenteral injection, possesses the same type and degree of activity as does naturally-occurring vitamin K, which is necessary for the production via the liver of active prothrombin (factor II), proconvertin (factor VII), plasma thromboplastin component (factor IX), and Stuart factor (factor X). Vitamin K is an essential cofactor for a microsomal enzyme that catalyzes the posttranslational carboxylation of multiple, specific, peptide-bound glutamic acid residues in inactive hepatic precursors of factors II, VII, IX, and X. The resulting gamma-carboxy-glutamic acid residues convert the precursors into active coagulation factors that are subsequently secreted by liver cells into the blood.
In normal animals and humans, phytonadione is virtually devoid of activity. However, in animals and humans deficient in vitamin K, the pharmacological action of vitamin K is related to its normal physiological function, that is, to promote the hepatic biosynthesis of vitamin K dependent clotting factors.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
The action of the aqueous dispersion, when administered intravenously, is generally detectable within an hour or two and hemorrhage is usually controlled within 3 to 6 hours. A normal INR may often be obtained in 12 to 14 hours.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption:
Phytonadione is readily absorbed following intramuscular administration.Distribution:
After absorption, phytonadione is initially concentrated in the liver, but the concentration declines rapidly. Very little vitamin K accumulates in tissues.Elimination:
Little is known about the metabolic fate of vitamin K. Almost no free unmetabolized vitamin K appears in bile or urine. - 13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY SECTION
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP is a yellow, sterile, aqueous colloidal solution and is supplied in unit use packages containing one single-dose vial and a SAF-T-Jet® vial injector, 27 G. x ½” needle.
Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion USP, 1 mg in 0.5 mL
Stock No. 1240 NDC: 76329-1240-110 individual cartons shrink wrapped as a group of 10 cartons.
Syringe Assembly Directions:
See User Guide
USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not remove from carton or assemble until ready to use.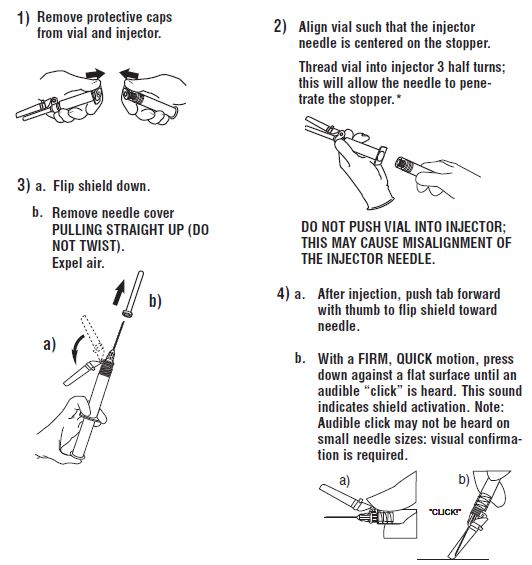
*CAUTION: IMPROPER ENGAGING MAY CAUSE GLASS BREAKAGE AND SUBSEQUENT INJURY.
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP from light. Store container in closed original carton until contents have been used.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
Inform the patient of the following important risks of Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP:
Serious Hypersensitivity Reactions
Advise the patient and caregivers to immediately report signs of hypersensitivity after receiving Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].Risk of Gasping Syndrome Due to Benzyl Alcohol
Advise the patient and caregivers of the risk of gasping syndrome associated with the use of products that contain benzyl alcohol (including Phytonadione) in neonates, infants, and pregnant women [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].Cutaneous Reactions
Advise the patient and caregivers to report the occurrence of new rashes after receiving Phytonadione Injectable Emulsion, USP. These reactions may be delayed for up to a year after treatment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]. - SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
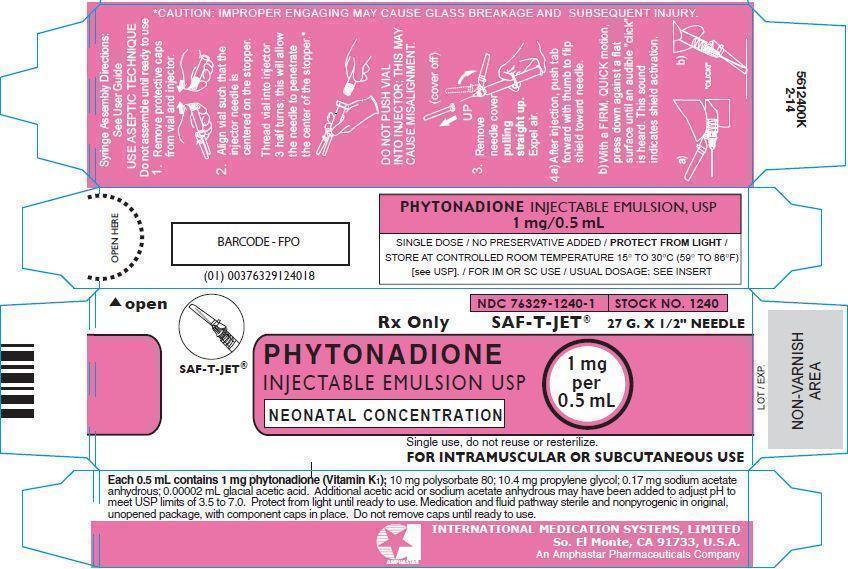
PRINCIPLE DISPLAY PANEL: Carton
SAF-T-JET®
NDC: 76329-1240-1
STOCK NO. 1240
Rx Only
SAF-T-JET®
27 G. X 1/2" NEEDLE
PHYTONADIONE INJECTABLE EMULSION USP
NEONATAL CONCENTRATION
1 mg per 0.5 mL
Single use, do not reuse or resterilize.
FOR INTRAMUSCULAR OR SUBCUTANEOUS USE
-
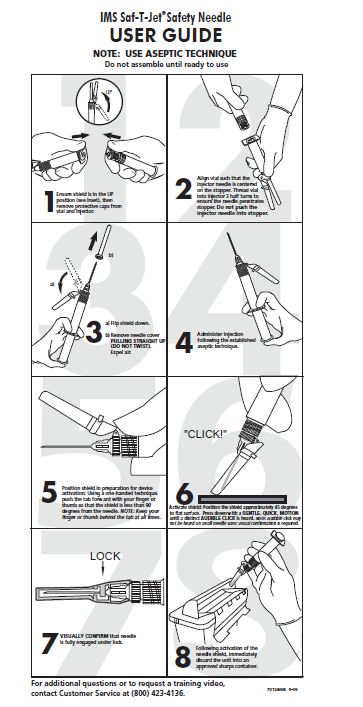
PRINCIPLE DISPLAY PANEL: User Guide
IMS Saf-T-Jet® Safety Needle
USER GUIDE
NOTE: USE ASEPTIC TECHNIQUE
Do not assemble until ready to use
1 Ensure shield is in the UP position (see inset), then remove protective caps from vial and injector.
2 Align vial such that the injector needle is centered on the stopper. Thread vial into injection 3 half turns to ensure the needle penetrates stopper. Do not push the injector needle into stopper.
3 a) Flip shield down.
b) Remove needle cover PULLING STRAIGHT UP (DO NOT TWIST). Expel air.
4 Administer injection following the established aseptic technique.
5 Position shield in preparation for device activation: Using a one-handed technique, push the tab forward with your finger or thumb so that the shield is less than 90 degrees from the needle. NOTE: Keep your finger or thumb behind the tab at all times.
6 Activate shield: Position the shield approximately 45 degrees to flat surface. Press down with a GENTLE, QUICK MOTION until a distinct AUDIBLE CLICK is heard. Note: Audible click may not be heard on small needle sizes: visual confirmation is required.
7VISUALLY CONFIRM that needle is fully engaged under lock.
8 Following activation of the needle shield, immediately discard the unit into an approved sharps container.
For additional questions or to request a traning video, contact Customer Service at (800) 423-4136.
7012400E 9-09
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PHYTONADIONE
phytonadione injection, emulsionProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 76329-1240 Route of Administration INTRAMUSCULAR, INTRAVENOUS, SUBCUTANEOUS Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength Phytonadione (UNII: A034SE7857) (Phytonadione - UNII:A034SE7857) Phytonadione 1 mg in 0.5 mL Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 76329-1240-1 1 in 1 CARTON 04/18/2003 1 0.5 mL in 1 SYRINGE; Type 2: Prefilled Drug Delivery Device/System (syringe, patch, etc.) Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA083722 04/18/2003 Labeler - International Medication Systems, Limited (055750020) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations International Medication Systems, Limited 055750020 analysis(76329-1240) , manufacture(76329-1240) , label(76329-1240)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.