PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE capsule, extended release
Propranolol Hydrochloride by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Propranolol Hydrochloride by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Golden State Medical Supply, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
- SPL UNCLASSIFIED SECTION
-
DESCRIPTION
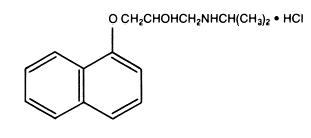
Propranolol hydrochloride, USP is a synthetic beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent chemically described as 2-Propanol, 1-[(1-methylethyl)amino]-3-(1-naphthalenyloxy)-, hydrochloride,(±)-. Its molecular and structural formulae are:
C 16H 21NO 2·HCl
Propranolol hydrochloride is a stable, white, crystalline solid which is readily soluble in water and ethanol. Its molecular weight is 295.80.
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are formulated to provide a sustained release of propranolol hydrochloride. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are available as 60 mg, 80 mg, 120 mg, and 160 mg capsules for oral administration.
The inactive ingredients contained in propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are: ethylcellulose, gelatin, hydroxypropyl cellulose, povidone, sugar spheres, talc, titanium dioxide. In addition, the 60 mg and 80 mg capsule shells contain yellow iron oxide. The 120 mg capsule shells contain black iron oxide and yellow iron oxide. The 160 mg capsule shells contain black iron oxide. The ink ingredients are common for all strengths: Opacode S-1-8114 or Opacode
S-1-8115 black contains: D&C Yellow #10 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #1 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Blue #2 Aluminum Lake, FD&C Red #40 Aluminum Lake, pharmaceutical glaze, propylene glycol, and synthetic black iron oxide.This drug product complies with USP Drug Release Test 1.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
General
Propranolol is a nonselective, beta-adrenergic receptor-blocking agent possessing no other autonomic nervous system activity. It specifically competes with beta-adrenergic receptor-stimulating agents for available receptor sites. When access to beta-receptor sites is blocked by propranolol, the chronotropic, inotropic, and vasodilator responses to beta-adrenergic stimulation are decreased proportionately. At dosages greater than required for beta blockade, propranolol also exerts a quinidine-like or anesthetic-like membrane action, which affects the cardiac action potential. The significance of the membrane action in the treatment of arrhythmias is uncertain.
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules should not be considered a simple mg-for-mg substitute for conventional propranolol and the blood levels achieved do not match (are lower than) those of two to four times daily dosing with the same dose (see DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION). When changing to propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules from conventional propranolol, a possible need for retitration upwards should be considered, especially to maintain effectiveness at the end of the dosing interval. In most clinical settings, however, such as hypertension or angina where there is little correlation between plasma levels and clinical effect, propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules have been therapeutically equivalent to the same mg dose of conventional propranolol hydrochloride as assessed by 24-hour effects on blood pressure and on 24-hour exercise responses of heart rate, systolic pressure, and rate pressure product.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism of the antihypertensive effect of propranolol has not been established. Among the factors that may be involved in contributing to the antihypertensive action include: (1) decreased cardiac output, (2) inhibition of renin release by the kidneys, and (3) diminution of tonic sympathetic nerve outflow from vasomotor centers in the brain. Although total peripheral resistance may increase initially, it readjusts to or below the pretreatment level with chronic use of propranolol. Effects of propranolol on plasma volume appear to be minor and somewhat variable.
In angina pectoris, propranolol generally reduces the oxygen requirement of the heart at any given level of effort by blocking the catecholamine-induced increases in the heart rate, systolic blood pressure, and the velocity and extent of myocardial contraction. Propranolol may increase oxygen requirements by increasing left ventricular fiber length, end diastolic pressure, and systolic ejection period. The net physiologic effect of beta-adrenergic blockade is usually advantageous and is manifested during exercise by delayed onset of pain and increased work capacity.
Propranolol exerts its antiarrhythmic effects in concentrations associated with beta-adrenergic blockade, and this appears to be its principal antiarrhythmic mechanism of action. In dosages greater than required for beta blockade, propranolol also exerts a quinidine-like or anesthetic-like membrane action which affects the cardiac action potential. The significance of the membrane action in the treatment of arrhythmias is uncertain.
The mechanism of the anti-migraine effect of propranolol has not been established. Beta-adrenergic receptors have been demonstrated in the pial vessels of the brain.
PHARMACOKINETICS AND DRUG METABOLISM
Absorption
Propranolol is highly lipophilic and almost completely absorbed after oral administration. However, it undergoes high first pass metabolism by the liver and on average, only about 25% of propranolol reaches the systemic circulation. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules (60, 80, 120, and 160 mg) release propranolol hydrochloride at a controlled and predictable rate. Peak blood levels following dosing with propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules occur at about 6 hours.
The effect of food on propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules bioavailability has not been investigated.
Distribution
Approximately 90% of circulating propranolol is bound to plasma proteins (albumin and alpha-1-acid glycoprotein). The binding is enantiomer-selective. The S(–)-enantiomer is preferentially bound to alpha-1-glycoprotein and the R(+)-enantiomer preferentially bound to albumin. The volume of distribution of propranolol is approximately 4 liters/kg.
Propranolol crosses the blood-brain barrier and the placenta, and is distributed into breast milk.
Metabolism and Elimination
Propranolol is extensively metabolized with most metabolites appearing in the urine. Propranolol is metabolized through three primary routes: aromatic hydroxylation (mainly 4-hydroxylation), N-dealkylation followed by further side-chain oxidation, and direct glucuronidation. It has been estimated that the percentage contributions of these routes to total metabolism are 42%, 41% and 17%, respectively, but with considerable variability between individuals. The four major metabolites are propranolol glucuronide, naphthyloxylactic acid and glucuronic acid, and sulfate conjugates of 4-hydroxy propranolol.
In-vitro studies have indicated that the aromatic hydroxylation of propranolol is catalyzed mainly by polymorphic CYP2D6. Side-chain oxidation is mediated mainly by CYP1A2 and to some extent by CYP2D6. 4-hydroxy propranolol is a weak inhibitor of CYP2D6.
Propranolol is also a substrate of CYP2C19 and a substrate for the intestinal efflux transporter, p-glycoprotein (p-gp). Studies suggest however that p-gp is not dose-limiting for intestinal absorption of propranolol in the usual therapeutic dose range.
In healthy subjects, no difference was observed between CYP2D6 extensive metabolizers (EMs) and poor metabolizers (PMs) with respect to oral clearance or elimination half-life. Partial clearance of 4-hydroxy propranolol was significantly higher and naphthyloxyactic acid was significantly lower in EMs than PMs.
When measured at steady state over a 24-hour period the areas under the propranolol plasma concentration-time curve (AUCs) for the propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are approximately 60% to 65% of the AUCs for a comparable divided daily dose of propranolol hydrochloride tablets. The lower AUCs for the propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are due to greater hepatic metabolism of propranolol, resulting from the slower rate of absorption of propranolol. Over a twenty-four (24) hour period, blood levels are fairly constant for about twelve (12) hours, then decline exponentially. The apparent plasma half-life is about 10 hours.
Enantiomers
Propranolol is a racemic mixture of two enantiomers, R(+) and S(–). The S(–)-enantiomer is approximately 100 times as potent as the R(+)-enantiomer in blocking beta adrenergic receptors. In normal subjects receiving oral doses of racemic propranolol, S(–)-enantiomer concentrations exceeded those of the R(+)-enantiomer by 40-90% as a result of stereoselective hepatic metabolism. Clearance of the pharmacologically active S(–)-propranolol is lower than
R(+)-propranolol after intravenous and oral doses.Special Population
Geriatric
The pharmacokinetics of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules have not been investigated in patients over 65 years of age. In a study of 12 elderly (62 to 79 years old) and 12 young (25 to 33 years old) healthy subjects, the clearance of S-enantiomer of propranolol was decreased in the elderly. Additionally, the half-life of both the R- and S-propranolol were prolonged in the elderly compared with the young (11 hours vs. 5 hours).
Clearance of propranolol is reduced with aging due to decline in oxidation capacity (ring oxidation and side chain oxidation). Conjugation capacity remains unchanged. In a study of 32 patients age 30 to 84 years given a single 20-mg dose of propranolol, an inverse correlation was found between age and the partial metabolic clearances to 4-hydroxypropranolol (40HP ring oxidation) and to naphthoxylactic acid (NLA-side chain oxidation). No correlation was found between age and the partial metabolic clearance to propranolol glucuronide (PPLG conjugation).
Gender
In a study of 9 healthy women and 12 healthy men, neither the administration of testosterone nor the regular course of the menstrual cycle affected the plasma binding of the propranolol enantiomers. In contrast, there was a significant, although non-enantioselective diminution of the binding of propranolol after treatment with ethinyl estradiol. These findings are inconsistent with another study, in which administration of testosterone cypionate confirmed the stimulatory role of this hormone on propranolol metabolism and concluded that the clearance of propranolol in men is dependent on circulating concentrations of testosterone. In women, none of the metabolic clearances for propranolol showed any significant association with either estradiol or testosterone.
Race
A study conducted in 12 Caucasian and 13 African-American male subjects taking propranolol, showed that at steady state, the clearance of R(+)- and S(–)-propranolol were about 76% and 53% higher in African-Americans than in Caucasians, respectively.
Chinese subjects had a greater proportion (18% to 45% higher) of unbound propranolol in plasma compared to Caucasians, which was associated with a lower plasma concentration of alpha-1-acid glycoprotein.
Renal Insufficiency
The pharmacokinetics of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules have not been investigated in patients with renal insufficiency.
In a study conducted in 5 patients with chronic renal failure, 6 patients on regular dialysis, and 5 healthy subjects, who received a single oral dose of 40 mg of propranolol, the peak plasma concentrations (C max) of propranolol in the chronic renal failure group were 2 to 3-fold higher (161±41 ng/mL) than those observed in the dialysis patients (47±9 ng/mL) and in the healthy subjects (26±1 ng/mL). Propranolol plasma clearance was also reduced in the patients with chronic renal failure.
Studies have reported a delayed absorption rate and a reduced half-life of propranolol in patients with renal failure of varying severity. Despite this shorter plasma half-life, propranolol peak plasma levels were 3 to 4 times higher and total plasma levels of metabolites were up to 3 times higher in these patients than in subjects with normal renal function.
Chronic renal failure has been associated with a decrease in drug metabolism via down regulation of hepatic cytochrome P450 activity resulting in a lower “first-pass” clearance.
Propranolol is not significantly dialyzable.
Hepatic Insufficiency
The pharmacokinetics of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules have not been investigated in patients with hepatic insufficiency.
Propranolol is extensively metabolized by the liver. In a study conducted in 6 patients with cirrhosis and 7 healthy subjects receiving 160 mg of a long-acting preparation of propranolol once a day for 7 days, the steady-state propranolol concentration in patients with cirrhosis was increased 2.5-fold in comparison to controls. In the patients with cirrhosis, the half-life obtained after a single intravenous dose of 10 mg propranolol increased to 7.2 hours compared to 2.9 hours in control (see PRECAUTIONS).
Drug Interactions
All drug interaction studies were conducted with propranolol. There are no data on drug interactions with propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules.
Interactions with Substrates, Inhibitors or Inducers of Cytochrome P-450 Enzymes
Because propranolol’s metabolism involves multiple pathways in the Cytochrome P-450 system (CYP2D6, 1A2, 2C19), co-administration with drugs that are metabolized by, or affect the activity (induction or inhibition) of one or more of these pathways may lead to clinically relevant drug interactions (see Drug Interactions under PRECAUTIONS).
Substrates or Inhibitors of CYP2D6
Blood levels and/or toxicity of propranolol may be increased by co-administration with substrates or inhibitors of CYP2D6, such as amiodarone, cimetidine, delavudin, fluoxetine, paroxetine, quinidine, and ritonavir. No interactions were observed with either ranitidine or lansoprazole.
Substrates or Inhibitors of CYP1A2
Blood levels and/or toxicity of propranolol may be increased by co-administration with substrates or inhibitors of CYP1A2, such as imipramine, cimetidine, ciprofloxacin, fluvoxamine, isoniazid, ritonavir, theophylline, zileuton, zolmitriptan, and rizatriptan.
Substrates or Inhibitors of CYP2C19
Blood levels and/or toxicity of propranolol may be increased by co-administration with substrates or inhibitors of CYP2C19, such as fluconazole, cimetidine, fluoxetine, fluvoxamine, tenioposide, and tolbutamide. No interaction was observed with omeprazole.
Inducers of Hepatic Drug Metabolism
Blood levels of propranolol may be decreased by co-administration with inducers such as rifampin, ethanol, phenytoin, and phenobarbital. Cigarette smoking also induces hepatic metabolism and has been shown to increase up to 77% the clearance of propranolol, resulting in decreased plasma concentrations.
Cardiovascular Drugs
Antiarrhythmics
The AUC of propafenone is increased by more than 200% by co-administration of propranolol.
The metabolism of propranolol is reduced by co-administration of quinidine, leading to a two to three fold increased blood concentration and greater degrees of clinical beta-blockade.
The metabolism of lidocaine is inhibited by co-administration of propranolol, resulting in a 25% increase in lidocaine concentrations.
Calcium Channel Blockers
The mean C max and AUC of propranolol are increased respectively, by 50% and 30% by
co-administration of nisoldipine and by 80% and 47%, by co-administration of nicardipine.The mean C max and AUC of nifedipine are increased by 64% and 79%, respectively, by
co-administration of propranolol.Propranolol does not affect the pharmacokinetics of verapamil and norverapamil. Verapamil does not affect the pharmacokinetics of propranolol.
Non-Cardiovascular Drugs
Migraine Drugs
Administration of zolmitriptan or rizatriptan with propranolol resulted in increased concentrations of zolmitriptan (AUC increased by 56% and C max by 37%) or rizatriptan (the AUC and C max were increased by 67% and 75%, respectively).
Theophylline
Co-administration of theophylline with propranolol decreases theophylline oral clearance by 30% to 52%.
Benzodiazepines
Propranolol can inhibit the metabolism of diazepam, resulting in increased concentrations of diazepam and its metabolites. Diazepam does not alter the pharmacokinetics of propranolol.
The pharmacokinetics of oxazepam, triazolam, lorazepam, and alprazolam are not affected by co-administration of propranolol.
Neuroleptic Drugs
Co-administration of long-acting propranolol at doses greater than or equal to 160 mg/day resulted in increased thioridazine plasma concentrations ranging from 55% to 369% and increased thioridazine metabolite (mesoridazine) concentrations ranging from 33% to 209%.
Co-administration of chlorpromazine with propranolol resulted in a 70% increase in propranolol plasma level.
Anti-Ulcer Drugs
Co-administration of propranolol with cimetidine, a non-specific CYP450 inhibitor, increased propranolol AUC and C max by 46% and 35%, respectively. Co-administration with aluminum hydroxide gel (1200 mg) may result in a decrease in propranolol concentrations.
Co-administration of metoclopramide with the long-acting propranolol did not have a significant effect on propranolol’s pharmacokinetics.
Lipid Lowering Drugs
Co-administration of cholestyramine or colestipol with propranolol resulted in up to 50% decrease in propranolol concentrations.
Co-administration of propranolol with lovastatin or pravastatin, decreased 18% to 23% the AUC of both, but did not alter their pharmacodynamics. Propranolol did not have an effect on the pharmacokinetics of fluvastatin.
Warfarin
Concomitant administration of propranolol and warfarin has been shown to increase warfarin bioavailability and increase prothrombin time.
PHARMACODYNAMICS AND CLINICAL EFFECTS
Hypertension
In a retrospective, uncontrolled study, 107 patients with diastolic blood pressure 110 to 150 mmHg received propranolol 120 mg t.i.d. for at least 6 months, in addition to diuretics and potassium, but with no other hypertensive agent. Propranolol contributed to control of diastolic blood pressure, but the magnitude of the effect of propranolol on blood pressure cannot be ascertained.
Four double-blind, randomized, crossover studies were conducted in a total of 74 patients with mild or moderately severe hypertension treated with propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules 160 mg once daily or propranolol 160 mg given either once daily or in two 80 mg doses. Three of these studies were conducted over a 4-week treatment period. One study was assessed after a 24-hour period. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules were as effective as propranolol in controlling hypertension (pulse rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure) in each of these trials.
Angina Pectoris
In a double-blind, placebo-controlled study of 32 patients of both sexes, aged 32 to 69 years, with stable angina, propranolol 100 mg t.i.d. was administered for 4 weeks and shown to be more effective than placebo in reducing the rate of angina episodes and in prolonging total exercise time.
Twelve male patients with moderately severe angina pectoris were studied in a double-blind, crossover study. Patients were randomized to either propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules 160 mg daily or conventional propranolol 40 mg four times a day for 2 weeks. Nitroglycerine tablets were allowed during the study. Blood pressure, heart rate and ECG's were recorded during serial exercise treadmill testing. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules were as effective as conventional propranolol for exercise heart rate, systolic and diastolic blood pressure, duration of anginal pain and ST-segment depression before or after exercise, exercise duration, angina attack rate and nitroglycerine consumption.
In another double-blind, randomized, crossover trial, the effectiveness of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules 160 mg daily and conventional propranolol 40 mg four times a day were evaluated in 13 patients with angina. ECG's were recorded while patients exercised until angina developed. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules were as effective as conventional propranolol for amount of exercise performed, ST-segment depression, number of anginal attacks, amount of nitroglycerine consumed, systolic and diastolic blood pressures and heart rate at rest and after exercise.
Migraine
In a 34-week, placebo-controlled, 4-period, dose-finding crossover study with a double-blind randomized treatment sequence, 62 patients with migraine received propranolol 20 to 80 mg 3 or 4 times daily. The headache unit index, a composite of the number of days with headache and the associated severity of the headache, was significantly reduced for patients receiving propranolol as compared to those on placebo.
Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis
In an uncontrolled series of 13 patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class 2 or 3 symptoms and hypertrophic subaortic stenosis diagnosed at cardiac catheterization, oral propranolol 40 to 80 mg t.i.d. was administered and patients were followed for up to 17 months.
Propranolol was associated with improved NYHA class for most patients.
-
INDICATIONS AND USAGE
Hypertension
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are indicated in the management of hypertension. It may be used alone or used in combination with other antihypertensive agents, particularly a thiazide diuretic. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are not indicated in the management of hypertensive emergencies.
Angina Pectoris Due to Coronary Atherosclerosis
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are indicated to decrease angina frequency and increase exercise tolerance in patients with angina pectoris.
- CONTRAINDICATIONS
-
WARNINGS
Angina Pectoris
There have been reports of exacerbation of angina and, in some cases, myocardial infarction, following abrupt discontinuance of propranolol therapy. Therefore, when discontinuance of propranolol is planned, the dosage should be gradually reduced over at least a few weeks, and the patient should be cautioned against interruption or cessation of therapy without the physician's advice. If propranolol therapy is interrupted and exacerbation of angina occurs, it usually is advisable to reinstitute propranolol therapy and take other measures appropriate for the management of unstable angina pectoris. Since coronary artery disease may be unrecognized, it may be prudent to follow the above advice in patients considered at risk of having occult atherosclerotic heart disease who are given propranolol for other indications.
Hypersensitivity and Skin Reactions
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions, have been associated with the administration of propranolol (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Cutaneous reactions, including Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, and urticaria, have been reported with use of propranolol (see ADVERSE REACTIONS).
Cardiac Failure
Sympathetic stimulation may be a vital component supporting circulatory function in patients with congestive heart failure, and its inhibition by beta blockade may precipitate more severe failure. Although beta blockers should be avoided in overt congestive heart failure, some have been shown to be highly beneficial when used with close follow-up in patients with a history of failure who are well compensated and are receiving diuretics as needed. Beta-adrenergic blocking agents do not abolish the inotropic action of digitalis on heart muscle.
In Patients without a History of Heart Failure, continued use of beta blockers can, in some cases, lead to cardiac failure.
Nonallergic Bronchospasm (e.g., Chronic Bronchitis, Emphysema)
In general, patients with bronchospastic lung disease should not receive beta-blockers. Propranolol should be administered with caution in this setting since it may provoke a bronchial asthmatic attack by blocking bronchodilation produced by endogenous and exogenous catecholamine stimulation of beta-receptors.
Major Surgery
Chronically administered beta-blocking therapy should not be routinely withdrawn prior to major surgery, however the impaired ability of the heart to respond to reflex adrenergic stimuli may augment the risks of general anesthesia and surgical procedures.
Diabetes and Hypoglycemia
Beta-adrenergic blockade may prevent the appearance of certain premonitory signs and symptoms (pulse rate and pressure changes) of acute hypoglycemia, especially in labile insulin-dependent diabetics. In these patients, it may be more difficult to adjust the dosage of insulin.
Propranolol therapy, particularly when given to infants and children, diabetic or not, has been associated with hypoglycemia especially during fasting as in preparation for surgery.
Hypoglycemia has been reported in patients taking propranolol after prolonged physical exertion and in patients with renal insufficiency.
Thyrotoxicosis
Beta-adrenergic blockade may mask certain clinical signs of hyperthyroidism. Therefore, abrupt withdrawal of propranolol may be followed by an exacerbation of symptoms of hyperthyroidism, including thyroid storm. Propranolol may change thyroid-function tests, increasing T 4 and reverse T 3, and decreasing T 3.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Propranolol should be used with caution in patients with impaired hepatic or renal function. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are not indicated for the treatment of hypertensive emergencies.
Beta-adrenergic receptor blockade can cause reduction of intraocular pressure. Patients should be told that propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules may interfere with the glaucoma screening test. Withdrawal may lead to a return of increased intraocular pressure.
While taking beta-blockers, patients with a history of severe anaphylactic reaction to a variety of allergens may be more reactive to repeated challenge, either accidental, diagnostic, or therapeutic. Such patients may be unresponsive to the usual doses of epinephrine used to treat allergic reaction.
Clinical Laboratory Tests
In patients with hypertension, use of propranolol has been associated with elevated levels of serum potassium, serum transaminases, and alkaline phosphatase. In severe heart failure, the use of propranolol has been associated with increases in Blood Urea Nitrogen.
Drug Interactions
Caution should be exercised when propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are administered with drugs that have an affect on CYP2D6, 1A2, or 2C19 metabolic pathways. Co-administration of such drugs with propranolol may lead to clinically relevant drug interactions and changes on its efficacy and/or toxicity (see Drug Interactions in PHARMACOKINETICS AND DRUG METABOLISM).
Alcohol when used concomitantly with propranolol, may increase plasma levels of propranolol.
Cardiovascular Drugs
Antiarrhythmics
Propafenone has negative inotropic and beta-blocking properties that can be additive to those of propranolol.
Quinidine increases the concentration of propranolol and produces greater degrees of clinical beta-blockade and may cause postural hypotension.
Amiodarone is an antiarrhythmic agent with negative chronotropic properties that may be additive to those seen with β-blockers such as propranolol.
The clearance of lidocaine is reduced with administration of propranolol. Lidocaine toxicity has been reported following co-administration with propranolol.
Caution should be exercised when administering propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules with drugs that slow A-V nodal conduction, e.g., lidocaine and calcium channel blockers.
Digitalis Glycosides
Both digitalis glycosides and beta-blockers slow atrioventricular conduction and decrease heart rate. Concomitant use can increase the risk of bradycardia.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Caution should be exercised when patients receiving a beta-blocker are administered a calcium-channel-blocking drug with negative inotropic and/or chronotropic effects. Both agents may depress myocardial contractility or atrioventricular conduction.
There have been reports of significant bradycardia, heart failure, and cardiovascular collapse with concurrent use of verapamil and beta-blockers.
Co-administration of propranolol and diltiazem in patients with cardiac disease has been associated with bradycardia, hypotension, high degree heart block, and heart failure.
ACE Inhibitors
When combined with beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors can cause hypotension, particularly in the setting of acute myocardial infarction.
The antihypertensive effects of clonidine may be antagonized by beta-blockers. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be administered cautiously to patients withdrawing from clonidine.
Alpha Blockers
Prazosin has been associated with prolongation of first dose hypotension in the presence of beta-blockers.
Postural hypotension has been reported in patients taking both beta-blockers and terazosin or doxazosin.
Reserpine
Patients receiving catecholamine-depleting drugs, such as reserpine should be closely observed for excessive reduction of resting sympathetic nervous activity, which may result in hypotension, marked bradycardia, vertigo, syncopal attacks, or orthostatic hypotension.
Inotropic Agents
Patients on long-term therapy with propranolol may experience uncontrolled hypertension if administered epinephrine as a consequence of unopposed alpha-receptor stimulation. Epinephrine is therefore not indicated in the treatment of propranolol overdose (see OVERDOSAGE).
Isoproterenol and Dobutamine
Propranolol is a competitive inhibitor of beta-receptor agonists, and its effects can be reversed by administration of such agents, e.g., dobutamine or isoproterenol. Also, propranolol may reduce sensitivity to dobutamine stress echocardiography in patients undergoing evaluation for myocardial ischemia.
Non-Cardiovascular Drugs
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) have been reported to blunt the antihypertensive effect of beta-adrenoreceptor blocking agents.
Administration of indomethacin with propranolol may reduce the efficacy of propranolol in reducing blood pressure and heart rate.
Antidepressants
The hypotensive effects of MAO inhibitors or tricyclic antidepressants may be exacerbated when administered with beta-blockers by interfering with the beta blocking activity of propranolol.
Anesthetic Agents
Methoxyflurane and trichloroethylene may depress myocardial contractility when administered with propranolol.
Warfarin
Propranolol when administered with warfarin increases the concentration of warfarin. Prothrombin time, therefore, should be monitored.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
In dietary administration studies in which mice and rats were treated with propranolol hydrochloride for up to 18 months at doses of up to 150 mg/kg/day, there was no evidence of drug-related tumorigenesis. On a body surface area basis, this dose in the mouse and rat is, respectively, about equal to and about twice the maximum recommended human oral daily dose (MRHD) of 640 mg propranolol hydrochloride. In a study in which both male and female rats were exposed to propranolol hydrochloride in their diets at concentrations of up to 0.05% (about 50 mg/kg body weight and less than the MRHD), from 60 days prior to mating and throughout pregnancy and lactation for two generations, there were no effects on fertility. Based on differing results from Ames Tests performed by different laboratories, there is equivocal evidence for a genotoxic effect of propranolol in bacteria ( S. typhimurium strain TA 1538).
Pregnancy:
Pregnancy Category C
In a series of reproductive and developmental toxicology studies, propranolol was given to rats by gavage or in the diet throughout pregnancy and lactation. At doses of 150 mg/kg/day, but not at doses of 80 mg/kg/day (equivalent to the MRHD on a body surface area basis), treatment was associated with embryotoxicity (reduced litter size and increased resorption rates) as well as neonatal toxicity (deaths). Propranolol hydrochloride also was administered (in the feed) to rabbits (throughout pregnancy and lactation) at doses as high as 150 mg/kg/day (about 5 times the maximum recommended human oral daily dose). No evidence of embryo or neonatal toxicity was noted.
There are no adequate and well-controlled studies in pregnant women. Intrauterine growth retardation, small placentas, and congenital abnormalities have been reported in neonates whose mothers received propranolol during pregnancy. Neonates whose mothers are receiving propranolol at parturition have exhibited bradycardia, hypoglycemia and/or respiratory depression. Adequate facilities for monitoring such infants at birth should be available. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules should be used during pregnancy only if the potential benefit justifies the potential risk to the fetus.
Nursing Mothers
Propranolol is excreted in human milk. Caution should be exercised when propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules are administered to a nursing woman.
Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of propranolol in pediatric patients have not been established.
Bronchospasm and congestive heart failure have been reported coincident with the administration of propranolol therapy in pediatric patients.
Geriatric Use
Clinical studies of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of the decreased hepatic, renal or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following adverse events were observed and have been reported in patients using propranolol.
Cardiovascular:
Bradycardia; congestive heart failure; intensification of AV block; hypotension; paresthesia of hands; thrombocytopenic purpura; arterial insufficiency, usually of the Raynaud type.
Central Nervous System:
Light-headedness; mental depression manifested by insomnia, lassitude, weakness, fatigue; catatonia; visual disturbances; hallucinations; vivid dreams; an acute reversible syndrome characterized by disorientation for time and place, short-term memory loss, emotional lability, slightly clouded sensorium, and decreased performance on neuropsychometrics. For immediate release formulations, fatigue, lethargy, and vivid dreams appear dose related.
Gastrointestinal:
Nausea, vomiting, epigastric distress, abdominal cramping, diarrhea, constipation, mesenteric arterial thrombosis, ischemic colitis.
Allergic:
Hypersensitivity reactions, including anaphylactic/anaphylactoid reactions; pharyngitis and agranulocytosis; erythematous rash; fever combined with aching and sore throat; laryngospasm; respiratory distress.
Skin and mucous membranes:
Stevens-Johnson Syndrome, toxic epidermal necrolysis, dry eyes, exfoliative dermatitis, erythema multiforme, urticaria, alopecia, SLE-like reactions, and psoriasiform rashes. Oculomucocutaneous syndrome involving the skin, serous membranes, and conjunctivae reported for a beta-blocker (practolol) have not been associated with propranolol.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Propranolol is not significantly dialyzable. In the event of overdosage or exaggerated response, the following measures should be employed:
General:
If ingestion is or may have been recent, evacuate gastric contents, taking care to prevent pulmonary aspiration.
Supportive Therapy:
Hypotension and bradycardia have been reported following propranolol overdose and should be treated appropriately. Glucagon can exert potent inotropic and chronotropic effects and may be particularly useful for the treatment of hypotension or depressed myocardial function after a propranolol overdose. Glucagon should be administered as 50 to 150 mcg/kg intravenously followed by continuous drip of 1 to 5 mg/hour for positive chronotropic effect. Isoproterenol, dopamine or phosphodiesterase inhibitors may also be useful. Epinephrine, however, may provoke uncontrolled hypertension. Bradycardia can be treated with atropine or isoproterenol. Serious bradycardia may require temporary cardiac pacing.
The electrocardiogram, pulse, blood pressure, neurobehavioral status and intake and output balance must be monitored. Isoproterenol and aminophylline may be used for bronchospasm.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
General
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules provide propranolol hydrochloride in a sustained-release capsule for administration once daily. If patients are switched from propranolol hydrochloride tablets to propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules, care should be
taken to assure that the desired therapeutic effect is maintained. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules should not be considered a simple mg-for-mg substitute for propranolol hydrochloride tablets. Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules have different kinetics and produces lower blood levels. Retitration may be necessary, especially to maintain effectiveness at the end of the 24-hour dosing interval.
Hypertension
The usual initial dosage is 80 mg propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules once daily, whether used alone or added to a diuretic. The dosage may be increased to 120 mg once daily or higher until adequate blood pressure control is achieved. The usual maintenance dosage is 120 to 160 mg once daily. In some instances a dosage of 640 mg may be required. The time needed for full hypertensive response to a given dosage is variable and may range from a few days to several weeks.
Angina Pectoris
Starting with 80 mg propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules once daily, dosage should be gradually increased at three- to seven-day intervals until optimal response is obtained. Although individual patients may respond at any dosage level, the average optimal dosage appears to be 160 mg once daily. In angina pectoris, the value and safety of dosage exceeding 320 mg per day have not been established.
If treatment is to be discontinued, reduce dosage gradually over a period of a few weeks (see “ WARNINGS”).
Migraine
The initial oral dose is 80 mg propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules once daily. The usual effective dose range is 160 to 240 mg once daily. The dosage may be increased gradually to achieve optimal migraine prophylaxis. If a satisfactory response is not obtained within four to six weeks after reaching the maximal dose, propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsule therapy should be discontinued. It may be advisable to withdraw the drug gradually over a period of several weeks depending on the patient's age, comorbidity, and dose of propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules.
-
HOW SUPPLIED:
Propranolol hydrochloride extended-release capsules, USP are available as follows:
60 mg – Each #3 capsule with white opaque cap and yellow opaque body printed with
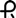 and 2778 on the cap and body in black ink contains 60 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-126-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-126-05).
and 2778 on the cap and body in black ink contains 60 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-126-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-126-05).
80 mg – Each #3 capsule with yellow opaque cap and yellow opaque body printed with
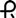 and 2779 on the cap and body in black ink contains 80 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-127-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-127-05).
and 2779 on the cap and body in black ink contains 80 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-127-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-127-05).
120 mg – Each #2 capsule with gray opaque cap and yellow opaque body printed with
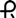 and 2780 on the cap and body in black ink contains 120 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-128-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-128-05).
and 2780 on the cap and body in black ink contains 120 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-128-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-128-05).
160 mg – Each #1 capsule with gray opaque cap and gray opaque body printed with
 and 2781 on the cap and body in black ink contains 160 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-129-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-129-05).
and 2781 on the cap and body in black ink contains 160 mg of propranolol hydrochloride, USP. Capsules are supplied in bottles of 100 (NDC: 60429-129-01) and 500 (NDC: 60429-129-05).
Store at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F) [See USP Controlled Room Temperature].
Protect from light, moisture, freezing, and excessive heat.
Dispense in a tight, light-resistant container as defined in the USP.
Manufactured by:
Actavis Elizabeth LLC
Elizabeth, NJ 07207 USADistributed by:
Actavis Pharma, Inc.
Parsippany, NJ 07054 USAMarketed/Packaged by GSMS, Incorporated, Camarillo, CA 93012
40-9180
Revised - December 2015
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 60429-126-05
60 mg
Propranolol Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP
500 Capsules
Rx Only
GSMS, Incorporated

-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
NDC: 60429-127-05
80 mg
Propranolol Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP
500 Capsules
Rx Only
GSMS, Incorporated

-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
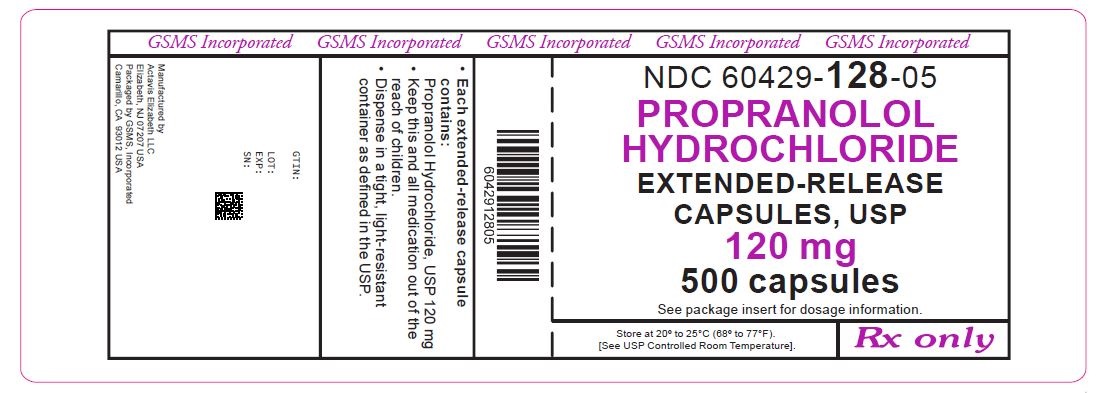
NDC: 60429-128-05
120 mg
Propranolol Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP
500 Capsules
Rx Only
GSMS, Incorporated
-
PACKAGE LABEL.PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
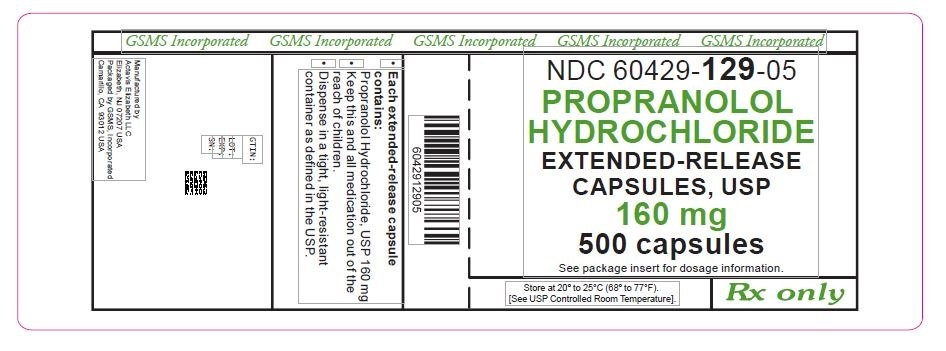
NDC: 60429-129-05
160 mg
Propranolol Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules, USP
500 Capsules
Rx Only
GSMS, Incorporated
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE
propranolol hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60429-126(NDC:0228-2778) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F8A3652H1V) (PROPRANOLOL - UNII:9Y8NXQ24VQ) PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE 60 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) POVIDONE K29/32 (UNII: 390RMW2PEQ) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color yellow, white Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code R;2778 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60429-126-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 2 NDC: 60429-126-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078494 07/15/2014 PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE
propranolol hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60429-127(NDC:0228-2779) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F8A3652H1V) (PROPRANOLOL - UNII:9Y8NXQ24VQ) PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE 80 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) POVIDONE K29/32 (UNII: 390RMW2PEQ) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color yellow Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 16mm Flavor Imprint Code R;2779 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60429-127-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 2 NDC: 60429-127-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078494 07/15/2014 PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE
propranolol hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60429-128(NDC:0228-2780) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F8A3652H1V) (PROPRANOLOL - UNII:9Y8NXQ24VQ) PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE 120 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) POVIDONE K29/32 (UNII: 390RMW2PEQ) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) FERRIC OXIDE YELLOW (UNII: EX438O2MRT) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color yellow, gray Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 18mm Flavor Imprint Code R;2780 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60429-128-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 2 NDC: 60429-128-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078494 07/15/2014 PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE
propranolol hydrochloride capsule, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 60429-129(NDC:0228-2781) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE (UNII: F8A3652H1V) (PROPRANOLOL - UNII:9Y8NXQ24VQ) PROPRANOLOL HYDROCHLORIDE 160 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength GELATIN (UNII: 2G86QN327L) POVIDONE K29/32 (UNII: 390RMW2PEQ) TALC (UNII: 7SEV7J4R1U) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) D&C YELLOW NO. 10 (UNII: 35SW5USQ3G) FD&C BLUE NO. 1 (UNII: H3R47K3TBD) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) PROPYLENE GLYCOL (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) FERROSOFERRIC OXIDE (UNII: XM0M87F357) ETHYLCELLULOSES (UNII: 7Z8S9VYZ4B) SUCROSE (UNII: C151H8M554) STARCH, CORN (UNII: O8232NY3SJ) Product Characteristics Color gray Score no score Shape CAPSULE Size 19mm Flavor Imprint Code R;2781 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 60429-129-01 100 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 2 NDC: 60429-129-05 500 in 1 BOTTLE; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/15/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA078494 07/15/2014 Labeler - Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. (603184490) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Golden State Medical Supply, Inc. 603184490 repack(60429-126, 60429-127, 60429-128, 60429-129) , relabel(60429-126, 60429-127, 60429-128, 60429-129)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.