NIFEDIPINE tablet, film coated, extended release
Nifedipine by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Nifedipine by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
DESCRIPTION
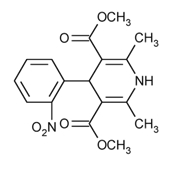
Nifedipine extended-release tablets are an extended release tablet dosage form of the calcium channel blocker nifedipine. Nifedipine is dimethyl 1,4-dihydro-2,6-dimethyl-4-(o-nitrophenyl)-3,5-pyridinedicarboxylate, C17H18N2O6, and has the structural formula:
Nifedipine, USP is a yellow powder, practically insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol. It has a molecular weight of 346.33. Nifedipine extended-release tablets consist of an external coat and an internal core. Both contain nifedipine, the coat as a slow release formulation and the core as a fast release formulation. Nifedipine extended-release tablets, USP contain either 30 mg, 60 mg or 90 mg of nifedipine for once-a-day oral administration.
Inert ingredients in the formulation are: colloidal silicon dioxide, hydroxypropyl cellulose, hypromellose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, polydextrose, polyethylene glycol, titanium dioxide and triacetin. The 60 mg tablets also contain FD&C Yellow No. 6 Aluminum Lake and the 90 mg tablets also contain D&C Red No. 27, FD&C Blue No. 2 and FD&C Red No. 40.
USP Dissolution Test Pending.
-
CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
Nifedipine is a calcium ion influx inhibitor (slow-channel blocker or calcium ion antagonist) which inhibits the transmembrane influx of calcium ions into vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle. The contractile processes of vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle are dependent upon the movement of extracellular calcium ions into these cells through specific ion channels. Nifedipine selectively inhibits calcium ion influx across the cell membrane of vascular smooth muscle and cardiac muscle without altering serum calcium concentrations.
Mechanism of Action
The mechanism by which nifedipine reduces arterial blood pressure involves peripheral arterial vasodilatation and, consequently, a reduction in peripheral vascular resistance. The increased peripheral vascular resistance, an underlying cause of hypertension, results from an increase in active tension in the vascular smooth muscle. Studies have demonstrated that the increase in active tension reflects an increase in cytosolic free calcium.
Nifedipine is a peripheral arterial vasodilator which acts directly on vascular smooth muscle. The binding of nifedipine to voltage-dependent and possibly receptor-operated channels in vascular smooth muscle results in an inhibition of calcium influx through these channels. Stores of intracellular calcium in vascular smooth muscle are limited and thus dependent upon the influx of extracellular calcium for contraction to occur. The reduction in calcium influx by nifedipine causes arterial vasodilation and decreased peripheral vascular resistance which results in reduced arterial blood pressure.
Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism
Nifedipine is completely absorbed after oral administration. The bioavailability of nifedipine as nifedipine extended-release tablets relative to immediate release nifedipine is in the range of 84% to 89%. After ingestion of nifedipine extended-release tablets under fasting conditions, plasma concentrations peak at about 2.5 to 5 hours with a second small peak or shoulder evident at approximately 6 to 12 hours post dose. The elimination half-life of nifedipine administered as nifedipine extended-release tablets is approximately 7 hours in contrast to the known 2 hour elimination half-life of nifedipine administered as an immediate release capsule.
When nifedipine extended-release tablets are administered as multiples of 30 mg tablets over a dose range of 30 mg to 90 mg, the area under the curve (AUC) is dose proportional; however, the peak plasma concentration for the 90 mg dose given as three 30 mg tablets is 29% greater than predicted from the 30 mg and 60 mg doses.
Two 30 mg nifedipine extended-release tablets may be interchanged with a 60 mg nifedipine extended-release tablet. Three 30 mg nifedipine extended-release tablets, however, result in substantially higher Cmax values than those after a single 90 mg nifedipine extended-release tablet. Three 30 mg tablets should, therefore, not be considered interchangeable with a 90 mg tablet.
Once daily dosing of nifedipine extended-release tablets under fasting conditions results in decreased fluctuations in the plasma concentration of nifedipine when compared to t.i.d. dosing with immediate release nifedipine capsules. The mean peak plasma concentration of nifedipine following a 90 mg nifedipine extended-release tablet, administered under fasting conditions, is approximately 115 ng/mL. When nifedipine extended-release tablets are given immediately after a high fat meal in healthy volunteers, there is an average increase of 60% in the peak plasma nifedipine concentration, a prolongation in the time to peak concentration, but no significant change in the AUC. Plasma concentrations of nifedipine when nifedipine extended-release tablets are taken after a fatty meal result in slightly lower peaks compared to the same daily dose of the immediate release formulation administered in three divided doses. This may be, in part, because nifedipine extended-release tablets are less bioavailable than the immediate release formulation.
Nifedipine is extensively metabolized to highly water soluble, inactive metabolites accounting for 60% to 80% of the dose excreted in the urine. Only traces (less than 0.1% of the dose) of the unchanged form can be detected in the urine. The remainder is excreted in the feces in metabolized form, most likely as a result of biliary excretion.
Nifedipine is metabolized via the cytochrome P450 3A4 system. Drugs that are known to either inhibit or induce this enzyme system may alter the first pass or clearance of nifedipine.
No studies have been performed with nifedipine extended-release tablets in patients with renal failure; however, significant alterations in the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine immediate release capsules have not been reported in patients undergoing hemodialysis or chronic ambulatory peritoneal dialysis. Since the absorption of nifedipine from nifedipine extended-release tablets could be modified by renal disease, caution should be exercised in treating such patients.
Because nifedipine is metabolized via the cytochrome P450 3A4 system, its pharmacokinetics may be altered in patients with chronic liver disease. Nifedipine extended-release tablets have not been studied in patients with hepatic disease; however, in patients with hepatic impairment (liver cirrhosis) nifedipine has a longer elimination half-life and higher bioavailability than in healthy volunteers.
The degree of protein binding of nifedipine is high (92% to 98%). Protein binding may be greatly reduced in patients with renal or hepatic impairment.
After administration of nifedipine extended-release tablets to healthy elderly men and women (age > 60 years), the mean Cmax is 36% higher and the average plasma concentration is 70% greater than in younger patients.
In healthy subjects, the elimination half-life of a different sustained release nifedipine formulation was longer in elderly subjects (6.7 h) compared to young subjects (3.8 h) following oral administration. A decreased clearance was also observed in the elderly (348 mL/min) compared to young subjects (519 mL/min) following intravenous administration.
Coadministration of nifedipine with grapefruit juice results in up to a 2-fold increase in AUC and Cmax, due to inhibition of CYP3A related first-pass metabolism. Ingestion of grapefruit and grapefruit juice should be avoided while taking nifedipine.
Clinical Studies
Nifedipine extended-release tablets produced dose related decreases in systolic and diastolic blood pressure as demonstrated in two double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trials in which over 350 patients were treated with nifedipine extended-release tablets 30 mg, 60 mg or 90 mg once daily for 6 weeks. In the first study, nifedipine extended-release tablets was given as monotherapy and in the second study, nifedipine extended-release tablets was added to a beta-blocker in patients not controlled on a beta-blocker alone. The mean trough (24 hours post-dose) blood pressure results from these studies are shown below:
Mean Reductions in Trough Supine Blood Pressure (mmHg) Systolic/Diastolic - * Placebo response subtracted.
Study 1
Nifedipine Extended-release
Tablets DoseN
Mean Trough Reduction*
30 mg
60
5.3/2.9
60 mg
57
8/4.1
90 mg
55
12.5/8.1
Study 2
Nifedipine Extended-release
Tablets DoseN
Mean Trough Reduction*
30 mg
58
7.6/3.8
60 mg
63
10.1/5.3
90 mg
62
10.2/5.8
The trough/peak ratios estimated from 24 hour blood pressure monitoring ranged from 41% to 78% for diastolic and 46% to 91% for systolic blood pressure.
Hemodynamics
Like other slow-channel blockers, nifedipine exerts a negative inotropic effect on isolated myocardial tissue. This is rarely, if ever, seen in intact animals or man, probably because of reflex responses to its vasodilating effects. In man, nifedipine decreases peripheral vascular resistance which leads to a fall in systolic and diastolic pressures, usually minimal in normotensive volunteers (less than 5 to 10 mm Hg systolic), but sometimes larger. With nifedipine extended-release tablets, these decreases in blood pressure are not accompanied by any significant change in heart rate. Hemodynamic studies of the immediate release nifedipine formulation in patients with normal ventricular function have generally found a small increase in cardiac index without major effects on ejection fraction, left ventricular end-diastolic pressure (LVEDP) or volume (LVEDV). In patients with impaired ventricular function, most acute studies have shown some increase in ejection fraction and reduction in left ventricular filling pressure.
Electrophysiologic Effects
Although, like other members of its class, nifedipine causes a slight depression of sinoatrial node function and atrioventricular conduction in isolated myocardial preparations, such effects have not been seen in studies in intact animals or in man. In formal electrophysiologic studies, predominantly in patients with normal conduction systems, nifedipine administered as the immediate release capsule has had no tendency to prolong atrioventricular conduction or sinus node recovery time, or to slow sinus rate.
- INDICATION AND USAGE
-
CONTRAINDICATIONS
Concomitant administration with strong P450 inducers, such as rifampin, are contraindicated since the efficacy of nifedipine tablets could be significantly reduced. (See PRECAUTIONS: Drug Interactions.)
Nifedipine must not be used in cases of cardiogenic shock.
Known hypersensitivity to nifedipine.
-
WARNINGS
Excessive Hypotension
Although in most patients the hypotensive effect of nifedipine is modest and well tolerated, occasional patients have had excessive and poorly tolerated hypotension. These responses have usually occurred during initial titration or at the time of subsequent upward dosage adjustment, and may be more likely in patients using concomitant beta-blockers.
Severe hypotension and/or increased fluid volume requirements have been reported in patients who received immediate release capsules together with a beta-blocking agent and who underwent coronary artery bypass surgery using high dose fentanyl anesthesia. The interaction with high dose fentanyl appears to be due to the combination of nifedipine and a beta-blocker, but the possibility that it may occur with nifedipine alone, with low doses of fentanyl, in other surgical procedures, or with other narcotic analgesics cannot be ruled out. In nifedipine-treated patients where surgery using high dose fentanyl anesthesia is contemplated, the physician should be aware of these potential problems and, if the patient’s condition permits, sufficient time (at least 36 hours) should be allowed for nifedipine to be washed out of the body prior to surgery.
Increased Angina and/or Myocardial Infarction
Rarely, patients, particularly those who have severe obstructive coronary artery disease, have developed well-documented increased frequency, duration and/or severity of angina or acute myocardial infarction upon starting nifedipine or at the time of dosage increase. The mechanism of this effect is not established.
Beta-Blocker Withdrawal
When discontinuing a beta-blocker it is important to taper its dose, if possible, rather than stopping abruptly before beginning nifedipine. Patients recently withdrawn from beta blockers may develop a withdrawal syndrome with increased angina, probably related to increased sensitivity to catecholamines. Initiation of nifedipine treatment will not prevent this occurrence and on occasion has been reported to increase it.
Congestive Heart Failure
Rarely, patients (usually while receiving a beta-blocker) have developed heart failure after beginning nifedipine. Patients with tight aortic stenosis may be at greater risk for such an event, as the unloading effect of nifedipine would be expected to be of less benefit to these patients, owing to their fixed impedance to flow across the aortic valve.
-
PRECAUTIONS
General
Hypotension
Because nifedipine decreases peripheral vascular resistance, careful monitoring of blood pressure during the initial administration and titration of nifedipine extended-release tablets is suggested. Close observation is especially recommended for patients already taking medications that are known to lower blood pressure (see WARNINGS).
Peripheral Edema
Mild to moderate peripheral edema occurs in a dose-dependent manner with nifedipine extended-release tablets. The placebo subtracted rate is approximately 8% at 30 mg, 12% at 60 mg and 19% at 90 mg daily. This edema is a localized phenomenon, thought to be associated with vasodilation of dependent arterioles and small blood vessels and not due to left ventricular dysfunction or generalized fluid retention. With patients whose hypertension is complicated by congestive heart failure, care should be taken to differentiate this peripheral edema from the effects of increasing left ventricular dysfunction.
Use in Cirrhotic Patients
Clearance of nifedipine is reduced and systemic exposure increased in patients with cirrhosis. It is unknown how systemic exposure may be altered in patients with moderate or severe liver impairment. Careful monitoring and dose reduction may be necessary; consider initiating therapy with the lowest dose available.
Information for Patients
Nifedipine extended-release tablets are extended release tablets and should be swallowed whole and taken on an empty stomach. They should not be administered with food. Do not chew, divide or crush tablets.
Laboratory Tests
Rare, usually transient, but occasionally significant elevations of enzymes such as alkaline phosphatase, CPK, LDH, SGOT, and SGPT have been noted. The relationship to nifedipine therapy is uncertain in most cases, but probable in some. These laboratory abnormalities have rarely been associated with clinical symptoms; however, cholestasis with or without jaundice has been reported. A small increase (< 5%) in mean alkaline phosphatase was noted in patients treated with nifedipine extended-release tablets. This was an isolated finding and it rarely resulted in values which fell outside the normal range. Rare instances of allergic hepatitis have been reported with nifedipine treatment. In controlled studies, nifedipine extended-release tablets did not adversely affect serum uric acid, glucose, cholesterol or potassium.
Nifedipine, like other calcium channel blockers, decreases platelet aggregation in vitro. Limited clinical studies have demonstrated a moderate but statistically significant decrease in platelet aggregation and increase in bleeding time in some nifedipine patients. This is thought to be a function of inhibition of calcium transport across the platelet membrane. No clinical significance for these findings has been demonstrated.
Positive direct Coombs’ test with or without hemolytic anemia has been reported but a causal relationship between nifedipine administration and positivity of this laboratory test, including hemolysis, could not be determined.
Although nifedipine has been used safely in patients with renal dysfunction and has been reported to exert a beneficial effect in certain cases, rare reversible elevations in BUN and serum creatinine have been reported in patients with preexisting chronic renal insufficiency. The relationship to nifedipine therapy is uncertain in most cases but probable in some.
Drug Interactions
Nifedipine is mainly eliminated by metabolism and is a substrate of CYP3A. Inhibitors and inducers of CYP3A can impact the exposure to nifedipine and consequently its desirable and undesirable effects. In vitro and in vivo data indicate that nifedipine can inhibit the metabolism of drugs that are substrates of CYP3A, thereby increasing the exposure to other drugs. Nifedipine is a vasodilator, and coadministration of other drugs affecting blood pressure may result in pharmacodynamic interactions.
CYP3A Inhibitors
CYP3A inhibitors such as ketoconazole, fluconazole, itraconazole, clarithromycin, erythromycin, grapefruit, nefazodone, saquinavir, indinavir, nelfinavir, and ritonavir may result in increased exposure to nifedipine when coadministered. Careful monitoring and dose adjustment may be necessary; consider initiating nifedipine at the lowest dose available if given concomitantly with these medications.
Strong CYP3A Inducers
Strong CYP3A inducers, such as rifampin, rifabutin, phenobarbital, phenytoin, carbamazepine, and St. John’s Wort reduce the bioavailability and efficacy of nifedipine; therefore nifedipine should not be used in combination with strong CYP3A inducers such as rifampin (see CONTRAINDICATIONS).
Cardiovascular Drugs
Antiarrhythmics
Quinidine
Quinidine is a substrate of CYP3A and has been shown to inhibit CYP3A in vitro. Coadministration of multiple doses of quinidine sulfate, 200 mg t.i.d., and nifedipine, 20 mg t.i.d., increased Cmax and AUC of nifedipine in healthy volunteers by factors of 2.30 and 1.37, respectively. The heart rate in the initial interval after drug administration was increased by up to 17.9 beats/minute. The exposure to quinidine was not importantly changed in the presence of nifedipine. Monitoring of heart rate and adjustment of the nifedipine dose, if necessary, are recommended when quinidine is added to a treatment with nifedipine.
Calcium Channel Blockers
Diltiazem
Pre-treatment of healthy volunteers with 30 mg or 90 mg t.i.d. diltiazem p.o. increased the AUC of nifedipine after a single dose of 20 mg nifedipine by factors of 2.2 and 3.1, respectively. The corresponding Cmax values of nifedipine increased by factors of 2 and 1.7, respectively. Caution should be exercised when coadministering diltiazem and nifedipine and a reduction of the dose of nifedipine should be considered.
ACE Inhibitors
Benazepril
In healthy volunteers receiving single dose of 20 mg nifedipine extended-release and benazepril 10 mg, the plasma concentrations of benazeprilat and nifedipine in the presence and absence of each other were not statistically significantly different. A hypotensive effect was only seen after coadministration of the two drugs. The tachycardic effect of nifedipine was attenuated in the presence of benazepril.
Angiotensin-II Blockers
Irbesartan
In vitro studies show significant inhibition of the formation of oxidized irbesartan metabolites by nifedipine. However, in clinical studies, concomitant nifedipine had no effect on irbesartan pharmacokinetics.
Candesartan
No significant drug interaction has been reported in studies with candesartan cilexitil given together with nifedipine. Because candesartan is not significantly metabolized by the cytochrome P450 system and at therapeutic concentrations has no effect on cytochrome P450 enzymes, interactions with drugs that inhibit or are metabolized by those enzymes would not be expected.
Beta-Blockers
Nifedipine extended-release tablets were well tolerated when administered in combination with beta-blockers in 187 hypertensive patients in a placebo-controlled clinical trial. However, there have been occasional literature reports suggesting that the combination nifedipine and beta-adrenergic blocking drugs may increase the likelihood of congestive heart failure, severe hypotension or exacerbation of angina in patients with cardiovascular disease. Clinical monitoring is recommended and a dose adjustment of nifedipine should be considered.
Central Alpha1-Blockers
Doxazosin
Healthy volunteers participating in a multiple dose doxazosin-nifedipine interaction study received 2 mg doxazosin q.d. alone or combined with 20 mg nifedipine extended-release b.i.d. Coadministration of nifedipine resulted in a decrease in AUC and Cmax of doxazosin to 83% and 86% of the values in the absence of nifedipine, respectively. In the presence of doxazosin, AUC and Cmax of nifedipine were increased by factors of 1.13 and 1.23, respectively. Compared to nifedipine monotherapy, blood pressure was lower in the presence of doxazosin. Blood pressure should be monitored when doxazosin is coadministered with nifedipine, and dose reduction of nifedipine considered.
Digitalis
Digoxin
The simultaneous administration of nifedipine and digoxin may lead to reduced clearance resulting in an increase in plasma concentrations of digoxin. Since there have been isolated reports of patients with elevated digoxin levels, and there is a possible interaction between digoxin and nifedipine extended-release tablets, it is recommended that digoxin levels be monitored when initiating, adjusting and discontinuing nifedipine extended-release tablets to avoid possible over- or under-digitalization.
Non-Cardiovascular Drugs
Antifungal Drugs
Ketoconazole, itraconazole and fluconazole are CYP3A inhibitors and can inhibit the metabolism of nifedipine and increase the exposure to nifedipine during concomitant therapy. Blood pressure should be monitored and a dose reduction of nifedipine considered.
Antisecretory Drugs
Omeprazole
In healthy volunteers receiving a single dose of 10 mg nifedipine, AUC and Cmax of nifedipine after pretreatment with omeprazole 20 mg q.d. for 8 days were 1.26 and 0.87 times those after pre-treatment with placebo. Pretreatment with or coadministration of omeprazole did not impact the effect of nifedipine on blood pressure or heart rate. The impact of omeprazole on nifedipine is not likely to be of clinical relevance.
Pantoprazole
In healthy volunteers the exposure to neither drug was changed significantly in the presence of the other drug.
Ranitidine
Five studies in healthy volunteers investigated the impact of multiple ranitidine doses on the single or multiple dose pharmacokinetics of nifedipine. Two studies investigated the impact of coadministered ranitidine on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects on nifedipine. Coadministration of ranitidine did not have relevant effects on the exposure to nifedipine that affected the blood pressure or heart rate in normotensive or hypertensive subjects.
Cimetidine
Five studies in healthy volunteers investigated the impact of multiple cimetidine doses on the single or multiple dose pharmacokinetics of nifedipine. Two studies investigated the impact of coadministered cimetidine on blood pressure in hypertensive subjects on nifedipine. In normotensive subjects receiving single doses of 10 mg or multiple doses of up to 20 mg nifedipine t.i.d. alone or together with cimetidine up to 1000 mg/day, the AUC values of nifedipine in the presence of cimetidine were between 1.52 and 2.01 times those in the absence of cimetidine. The Cmax values of nifedipine in the presence of cimetidine were increased by factors ranging between 1.60 and 2.02. The increase in exposure to nifedipine by cimetidine was accompanied by relevant changes in blood pressure or heart rate in normotensive subjects. Hypertensive subjects receiving 10 mg q.d. nifedipine alone or in combination with cimetidine 1000 mg q.d. also experienced relevant changes in blood pressure when cimetidine was added to nifedipine. The interaction between cimetidine and nifedipine is of clinical relevance and blood pressure should be monitored and a reduction of the dose of nifedipine considered.
Antibacterial Drugs
Quinupristin/Dalfopristin
In vitro drug interaction studies have demonstrated that quinupristin/dalfopristin significantly inhibits the CYP3A metabolism of nifedipine. Concomitant administration of quinupristin/dalfopristin and nifedipine (repeated oral dose) in healthy volunteers increased AUC and Cmax for nifedipine by factors of 1.44 and 1.18, respectively, compared to nifedipine monotherapy. Upon coadministration of quinupristin/dalfopristin with nifedipine, blood pressure should be monitored and a reduction of the dose of nifedipine considered.
Antitubercular Drugs
Rifampin
Strong CYP3A inducers, such as rifampin, rifapentin, and rifabutin reduce the bioavailability of nifedipine which may reduce the efficacy of nifedipine; therefore, nifedipine should not be used in combination with strong CYP3A inducers such as rifampin (see CONTRAINDICATIONS). The impact of multiple oral doses of 600 mg rifampin on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine after a single oral dose of 20 mg nifedipine capsule was evaluated in a clinical study. Twelve healthy male volunteers received a single oral dose of 20 mg nifedipine capsule on study Day 1. Starting on study Day 2, the subjects received 600 mg rifampin once daily for 14 days. On study Day 15, a second single oral dose of 20 mg nifedipine capsule was administered together with the last dose of rifampin. Compared to study Day 1, 14 days pretreatment with rifampin reduced Cmax and AUC of concomitantly administered nifedipine on average by 95% and 97%, respectively.
Antiviral Drugs
Amprenavir, atanazavir, delavirine, fosamprinavir, indinavir, nelfinavir and ritonavir, as CYP3A inhibitors, can inhibit the metabolism of nifedipine and increase the exposure to nifedipine. Caution is warranted and clinical monitoring of patients recommended.
CNS Drugs
Nefazodone
Nefazodone, a CYP3A inhibitor, can inhibit the metabolism of nifedipine and increase the exposure to nifedipine during concomitant therapy. Blood pressure should be monitored and a reduction of the dose of nifedipine considered.
Fluoxetine
Fluoxetine, a CYP3A inhibitor, can inhibit the metabolism of nifedipine and increase the exposure to nifedipine during concomitant therapy. Blood pressure should be monitored and a reduction of the dose of nifedipine considered.
Valproic Acid
Valproic acid may increase the exposure to nifedipine during concomitant therapy. Blood pressure should be monitored and a dose reduction of nifedipine considered.
Phenytoin, Phenobarbital and Carbamazepine
Nifedipine is metabolized by CYP3A. Coadministration of nifedipine 10 mg capsule and 60 mg nifedipine coat-core tablet with phenytoin, an inducer of CYP3A, lowered the AUC and Cmax of nifedipine by approximately 70%. Phenobarbital and carbamazepine are also inducers of CYP3A. Alternative antihypertensive therapy should be considered in patients taking phenytoin, phenobarbital, and carbamazepine.
Immunosuppressive Drugs
Tacrolimus
Tacrolimus has been shown to be metabolized via the CYP3A system. Nifedipine has been shown to inhibit the metabolism of tacrolimus in vitro. Transplant patients on tacrolimus and nifedipine required from 26% to 38% smaller doses than patients not receiving nifedipine. Nifedipine can increase the exposure to tacrolimus. When nifedipine is coadministered with tacrolimus the blood concentrations of tacrolimus should be monitored and a reduction of the dose of tacrolimus considered.
Glucose Lowering Drugs
Pioglitazone
Coadministration of pioglitazone for 7 days with 30 mg nifedipine extended-release administered orally q.d. for 4 days to male and female volunteers resulted in least square mean (90% CI) values for unchanged nifedipine of 0.83 (0.73 to 0.95) for Cmax and 0.88 (0.80 to 0.96) for AUC relative to nifedipine monotherapy. In view of the high variability of nifedipine pharmacokinetics, the clinical significance of this finding is unknown.
Rosiglitazone
Coadministration of rosiglitazone (4 mg b.i.d.) was shown to have no clinically relevant effect on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine.
Metformin
A single dose metformin-nifedipine interaction study in normal healthy volunteers demonstrated that coadministration of nifedipine increased plasma metformin Cmax and AUC by 20% and 9%, respectively, and increased the amount of metformin excreted in urine. Tmax and half-life were unaffected. Nifedipine appears to enhance the absorption of metformin.
Miglitol
No effect of miglitol was observed on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of nifedipine.
Dietary Supplements
Grapefruit Juice
In healthy volunteers, a single dose coadministration of 250 mL double strength grapefruit juice with 10 mg nifedipine increased AUC and Cmax by factors of 1.35 and 1.13, respectively. Ingestion of repeated doses of grapefruit juice (5 x 200 mL in 12 hours) after administration of 20 mg nifedipine extended-release increased AUC and Cmax of nifedipine by a factor of 2. Grapefruit juice should be avoided by patients on nifedipine. The intake of grapefruit juice should be stopped at least 3 days prior to initiating patients on nifedipine.
CYP2D6 Probe Drug
Debrisoquine
In healthy volunteers, pretreatment with nifedipine 20 mg t.i.d. for 5 days did not change the metabolic ratio of hydroxydebrisoquine to debrisoquine measured in urine after a single dose of 10 mg debrisoquine. Thus, it is improbable that nifedipine inhibits in vivo the metabolism of other drugs that are substrates of CYP2D6.
Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
Nifedipine was administered orally to rats for 2 years and was not shown to be carcinogenic. When given to rats prior to mating, nifedipine caused reduced fertility at a dose approximately 30 times the maximum recommended human dose. There is a literature report of reversible reduction in the ability of human sperm obtained from a limited number of infertile men taking recommended doses of nifedipine to bind to and fertilize an ovum in vitro. In vivo mutagenicity studies were negative.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy Category C
In rodents, rabbits and monkeys, nifedipine has been shown to have a variety of embryotoxic, placentotoxic, teratogenic and fetotoxic effects, including stunted fetuses (rats, mice and rabbits), digital anomalies (rats and rabbits), rib deformities (mice), cleft palate (mice), small placentas and underdeveloped chorionic villi (monkeys), embryonic and fetal deaths (rats, mice and rabbits), prolonged pregnancy (rats; not evaluated in other species), and decreased neonatal survival (rats; not evaluated in other species). On a mg/kg or mg/m2 basis, some of the doses associated with these various effects are higher than the maximum recommended human dose and some are lower, but all are within an order of magnitude of it.
The digital anomalies seen in nifedipine-exposed rabbit pups are strikingly similar to those seen in pups exposed to phenytoin, and these are in turn similar to the phalangeal deformities that are the most common malformation seen in human children with in utero exposure to phenytoin.
From the clinical evidence available, a specific prenatal risk has not been identified. However, an increase in perinatal asphyxia, caesarean delivery, prematurity and intrauterine growth retardation have been reported.
Careful monitoring of blood pressure must be exercised in pregnant women, when administering nifedipine in combination with IV magnesium sulfate due to the possibility of an excessive fall in blood pressure which could harm the mother and fetus.
There are no adequate and well controlled studies in pregnant women.
Nursing Mothers
Nifedipine is excreted in human milk. Nursing mothers are advised not to breast-feed their babies when taking the drug.
Pediatric Use
The safety and effectiveness of nifedipine extended-release tablets in pediatric patients have not been established.
Geriatric Use
Although small pharmacokinetic studies have identified an increased half-life and increased Cmax and AUC (See CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY: Pharmacokinetics and Metabolism), clinical studies of nifedipine did not include sufficient numbers of subjects aged 65 and over to determine whether they respond differently from younger subjects. Other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and younger patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy.
-
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The incidence of adverse events during treatment with nifedipine extended-release tablets in doses up to 90 mg daily were derived from multicenter placebo-controlled clinical trials in 370 hypertensive patients. Atenolol 50 mg once daily was used concomitantly in 187 of the 370 patients on nifedipine extended-release tablets and in 64 of the 126 patients on placebo. All adverse events reported during nifedipine extended-release tablets therapy were tabulated independently of their causal relationship to medication.
The most common adverse event reported with nifedipine extended-release tablets was peripheral edema. This was dose related and the frequency was 18% on nifedipine extended-release tablets 30 mg daily, 22% on nifedipine extended-release tablets 60 mg daily and 29% on nifedipine extended-release tablets 90 mg daily versus 10% on placebo.
Other common adverse events reported in the above placebo-controlled trials include:
Nifedipine Extended-release Tablets (%)
(n = 370)Placebo (%)
(n = 126)Adverse Event
Headache
19
13
Flushing/heat sensation
4
0
Dizziness
4
2
Fatigue/asthenia
4
4
Nausea
2
1
Constipation
1
0
Where the frequency of adverse events with nifedipine extended-release tablets and placebo is similar, causal relationship cannot be established.
The following adverse events were reported with an incidence of 3% or less in daily doses up to 90 mg:
Body as a Whole/Systemic: chest pain, leg pain
Central Nervous System: paresthesia, vertigo
Dermatologic: rash
Gastrointestinal: constipation
Musculoskeletal: leg cramps
Respiratory: epistaxis, rhinitis
Urogenital: impotence, urinary frequency
Other adverse events reported with an incidence of less than 1% were:
Body as a Whole/Systemic: allergic reaction, asthenia, cellulitis, substernal chest pain, chills, facial edema, lab test abnormal, malaise, neck pain, pelvic pain, pain, photosensitivity reaction
Cardiovascular: atrial fibrillation, bradycardia, cardiac arrest, extrasystole, hypotension, migraine, palpitations, phlebitis, postural hypotension, tachycardia, cutaneous angiectases
Central Nervous System: anxiety, confusion, decreased libido, depression, hypertonia, hypesthesia, insomnia, somnolence
Dermatologic: angioedema, petechial rash, pruritus, sweating
Gastrointestinal: abdominal pain, diarrhea, dry mouth, dysphagia, dyspepsia, eructation, esophagitis, flatulence, gastrointestinal disorder, gastrointestinal hemorrhage, GGT increased, gum disorder, gum hemorrhage, vomiting
Hematologic: eosinophilia, lymphadenopathy
Metabolic: gout, weight loss
Musculoskeletal: arthralgia, arthritis, joint disorder, myalgia, myasthenia
Respiratory: dyspnea, increased cough, rales, pharyngitis, stridor
Special Senses: abnormal vision, amblyopia, conjunctivitis, diplopia, eye disorder, eye hemorrhage, tinnitus
Urogenital/Reproductive: dysuria, kidney calculus, nocturia, breast engorgement, polyuria, urogenital disorder
The following adverse events have been reported rarely in patients given nifedipine in coat core or other formulations: allergenic hepatitis, alopecia, anaphylactic reaction, anemia, arthritis with ANA (+), depression, erythromelalgia, exfoliative dermatitis, fever, gingival hyperplasia, gynecomastia, hyperglycemia, jaundice, leukopenia, mood changes, muscle cramps, nervousness, paranoid syndrome, purpura, shakiness, sleep disturbances, Stevens-Johnson syndrome, syncope, taste perversion, thrombocytopenia, toxic epidermal necrolysis, transient blindness at the peak of plasma level, tremor and urticaria.
-
OVERDOSAGE
Experience with nifedipine overdosage is limited. Symptoms associated with severe nifedipine overdosage include loss of consciousness, drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm disturbances, metabolic acidosis, hypoxia, cardiogenic shock with pulmonary edema. Generally, overdosage with nifedipine leading to pronounced hypotension calls for active cardiovascular support including monitoring of cardiovascular and respiratory function, elevation of extremities, judicious use of calcium infusion, pressor agents and fluids. After oral ingestion, thorough gastric lavage is indicated, if necessary in combination with irrigation of the small intestine. In cases involving overdosage of a slow-release product like nifedipine, elimination must be as complete as possible, including from the small intestine, to prevent the subsequent absorption of the active substance. Additional liquid or volume must be administered with caution because of the risk of fluid overload.
Clearance of nifedipine would be expected to be prolonged in patients with impaired liver function. Since nifedipine is highly protein bound, dialysis is not likely to be of any benefit; however, plasmapheresis may be beneficial.
There has been one reported case of massive overdosage with tablets of another extended release formulation of nifedipine. The main effects of ingestion of approximately 4800 mg of nifedipine in a young man attempting suicide as a result of cocaine-induced depression was initial dizziness, palpitations, flushing, and nervousness. Within several hours of ingestion, nausea, vomiting, and generalized edema developed. No significant hypotension was apparent at presentation, 18 hours post ingestion. Blood chemistry abnormalities consisted of a mild, transient elevation of serum creatinine, and modest elevations of LDH and CPK, but normal SGOT. Vital signs remained stable, no electrocardiographic abnormalities were noted and renal function returned to normal within 24 to 48 hours with routine supportive measures alone. No prolonged sequelae were observed.
The effect of a single 900 mg ingestion of nifedipine capsules in a depressed anginal patient on tricyclic antidepressants was loss of consciousness within 30 minutes of ingestion, and profound hypotension, which responded to calcium infusion, pressor agents, and fluid replacement. A variety of ECG abnormalities were seen in this patient with a history of bundle branch block, including sinus bradycardia and varying degrees of AV block. These dictated the prophylactic placement of a temporary ventricular pacemaker, but otherwise resolved spontaneously. Significant hyperglycemia was seen initially in this patient, but plasma glucose levels rapidly normalized without further treatment.
A young hypertensive patient with advanced renal failure ingested 280 mg of nifedipine capsules at one time, with resulting marked hypotension responding to calcium infusion and fluids. No AV conduction abnormalities, arrhythmias, or pronounced changes in heart rate were noted, nor was there any further deterioration in renal function.
-
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
Dosage should be adjusted according to each patient’s needs. It is recommended that nifedipine extended-release tablets be administered orally once daily on an empty stomach. Nifedipine extended-release tablets are an extended release dosage form and tablets should be swallowed whole, not bitten or divided. In general, titration should proceed over a 7 to 14 day period starting with 30 mg once daily. Upward titration should be based on therapeutic efficacy and safety. The usual maintenance dose is 30 mg to 60 mg once daily. Titration to doses above 90 mg daily is not recommended.
If discontinuation of nifedipine extended-release tablets is necessary, sound clinical practice suggests that the dosage should be decreased gradually with close physician supervision.
Coadministration of nifedipine with grapefruit juice is to be avoided (see CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY and PRECAUTIONS).
Care should be taken when dispensing nifedipine extended-release tablets to assure that the extended release dosage form has been prescribed.
-
HOW SUPPLIED
Repackaged by Aphena Pharma Solutions - TN.
See Repackaging Information for available configurations.
Nifedipine Extended-release Tablets, USP are available containing 30 mg, 60 mg or 90 mg of nifedipine, USP.
The 30 mg tablets are supplied as white, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and NE over 30 on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-0353-93
bottles of 30 tabletsNDC: 0378-0353-01
bottles of 100 tabletsNDC: 0378-0353-10
bottles of 1000 tabletsThe 60 mg tablets are supplied as orange, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and NE over 60 on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-0360-93
bottles of 30 tabletsNDC: 0378-0360-01
bottles of 100 tabletsNDC: 0378-0360-10
bottles of 1000 tabletsThe 90 mg tablets are supplied as pink, film-coated, round, unscored tablets debossed with M on one side of the tablet and NE over 90 on the other side. They are available as follows:
NDC: 0378-0390-93
bottles of 30 tabletsNDC: 0378-0390-01
bottles of 100 tabletsNDC: 0378-0390-10
bottles of 1000 tabletsStore at 20° to 25°C (68° to 77°F). [See USP Controlled Room Temperature.]
Protect from light and moisture.
Dispense in a tight light-resistant container as defined in the USP using a child-resistant closure.
Mylan Pharmaceuticals Inc.
Morgantown, WV 26505MAY 2010
NIFECC:R1 -
Repackaging Information
Please reference the How Supplied section listed above for a description of individual tablets or capsules. This drug product has been received by Aphena Pharma - TN in a manufacturer or distributor packaged configuration and repackaged in full compliance with all applicable cGMP regulations. The package configurations available from Aphena are listed below:
Count 60mg 90mg 30 43353-836-30 - 90 43353-836-60 43353-750-60 180 43353-836-80 - 800 - 43353-750-81 6000 - 43353-750-16 9000 43353-836-09 - Store between 20°-25°C (68°-77°F). See USP Controlled Room Temperature. Dispense in a tight light-resistant container as defined by USP. Keep this and all drugs out of the reach of children.
Repackaged by:

Cookeville, TN 38506
20140403SC - PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 60mg
- PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 90mg
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
NIFEDIPINE
nifedipine tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 43353-836(NDC:0378-0360) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NIFEDIPINE (UNII: I9ZF7L6G2L) (NIFEDIPINE - UNII:I9ZF7L6G2L) NIFEDIPINE 60 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 9XZ8H6N6OH) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYDEXTROSE (UNII: VH2XOU12IE) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) TRIACETIN (UNII: XHX3C3X673) FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 (UNII: H77VEI93A8) Product Characteristics Color ORANGE Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code M;NE;60 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 43353-836-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/13/2013 2 NDC: 43353-836-60 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/22/2013 3 NDC: 43353-836-80 180 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/23/2013 4 NDC: 43353-836-09 9000 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 03/01/2014 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA201071 07/23/2012 NIFEDIPINE
nifedipine tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 43353-750(NDC:0378-0390) Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength NIFEDIPINE (UNII: I9ZF7L6G2L) (NIFEDIPINE - UNII:I9ZF7L6G2L) NIFEDIPINE 90 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength SILICON DIOXIDE (UNII: ETJ7Z6XBU4) D&C RED NO. 27 (UNII: 2LRS185U6K) FD&C BLUE NO. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (1600000 WAMW) (UNII: RFW2ET671P) HYPROMELLOSES (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) LACTOSE MONOHYDRATE (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) MAGNESIUM STEARATE (UNII: 70097M6I30) POLYDEXTROSE (UNII: VH2XOU12IE) POLYETHYLENE GLYCOL, Unspecified (UNII: 3WJQ0SDW1A) TITANIUM DIOXIDE (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) TRIACETIN (UNII: XHX3C3X673) FD&C RED NO. 40 (UNII: WZB9127XOA) Product Characteristics Color PINK Score no score Shape ROUND Size 9mm Flavor Imprint Code M;NE;90 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 43353-750-60 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/25/2012 2 NDC: 43353-750-81 800 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 07/27/2012 3 NDC: 43353-750-16 6000 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 05/08/2017 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date ANDA ANDA201071 07/23/2012 Labeler - Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC (128385585) Establishment Name Address ID/FEI Business Operations Aphena Pharma Solutions - Tennessee, LLC 128385585 Repack(43353-836, 43353-750)
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.