ACTOPLUS MET XR- pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended release
Actoplus Met by
Drug Labeling and Warnings
Actoplus Met by is a Prescription medication manufactured, distributed, or labeled by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.. Drug facts, warnings, and ingredients follow.
Drug Details [pdf]
-
HIGHLIGHTS OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION
These highlights do not include all the information needed to use ACTOPLUS MET XR safely and effectively. See full prescribing information for ACTOPLUS MET XR.
ACTOPLUS MET XR (pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) tablets for oral use
Initial U.S. Approval: 2009WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE AND LACTIC ACIDOSIS
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning
Congestive Heart Failure
- Thiazolidinediones, including pioglitazone, which is a component of ACTOPLUS MET XR, cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure in some patients. (5.1)
- After initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR, and after dose increases, monitor patients carefully for signs and symptoms of heart failure (e.g., excessive, rapid weight gain, dyspnea, and/or edema). If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOPLUS MET XR must be considered. (5.1)
- ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure. (5.1)
- Initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR in patients with established New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure is contraindicated. (4, 5.1)
Lactic Acidosis
- Post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. Symptoms included malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Laboratory abnormalities included elevated blood lactate levels, anion gap acidosis, increased lactate/pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally greater than 5 mcg/mL. (5.2)
- Risk factors include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs, age ≥65 years old, radiological studies with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states, excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment. Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the Full Prescribing Information. (5.2)
- If lactic acidosis is suspected, discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended. (5.2)
RECENT MAJOR CHANGES
Warnings and Precautions Urinary Bladder Tumors (5.6) 12/2016 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ACTOPLUS MET XR is a thiazolidinedione and biguanide combination product indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus when treatment with both pioglitazone and metformin is appropriate. (1)
Important Limitations of Use:
- Not for treatment of type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis. (1)
DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
- Individualize the starting dose based on the patient's current regimen and adjust the dosing based on effectiveness and tolerability while not exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of pioglitazone 45 mg and extended-release metformin 2000 mg. (2.1)
- Give in divided daily doses with meals to reduce gastrointestinal effects. (2.1)
- Monitor patients for adverse events related to fluid retention after initiation and dose increases. (2.1)
- Obtain liver tests before initiation. If abnormal, use caution when treating with ACTOPLUS MET XR, investigate the probable cause, treat (if possible) and follow appropriately. (2.1, 5.4)
-
Prior to initiation, assess renal function with estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) (2.2)
- Do not use in patients with eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Initiation is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 - 45 mL/min/1.73 m2
- Assess risk/benefit of continuing if eGFR falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2
- discontinue if eGFR falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2
- ACTOPLUS MET XR may need to be discontinued at time of, or prior to, iodinated contrast imaging procedures (2.4)
DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Initiation in patients with established New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure [see Boxed Warning]. (4)
- Severe renal impairment (eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2). (4)
- Use in patients with known hypersensitivity to pioglitazone, metformin or any other component of ACTOPLUS MET XR. (4)
- Metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis. (4, 5.2)
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
- Congestive heart failure: Fluid retention may occur and can exacerbate or lead to congestive heart failure. Combination use with insulin and use in congestive heart failure NYHA Class I and II may increase risk. Monitor patients for signs and symptoms. (5.1)
- Lactic acidosis: See boxed warning. (5.2)
- Edema: Dose-related edema may occur. (5.3)
- Hypoglycemia: When used with insulin or an insulin secretagogue, a lower dose of the insulin or insulin secretagogue may be needed to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia. (5.4)
- Hepatic effects: Postmarketing reports of hepatic failure, sometimes fatal. Causality cannot be excluded. If liver injury is detected, promptly interrupt ACTOPLUS MET XR and assess patient for probable cause, then treat cause if possible, to resolution or stabilization. Do not restart ACTOPLUS MET XR if liver injury is confirmed and no alternate etiology can be found. (5.5)
- Bladder cancer: May increase the risk of bladder cancer. Do not use in patients with active bladder cancer. Use caution when using in patients with a prior history of bladder cancer. (5.6)
- Fractures: Increased incidence in female patients. Apply current standards of care for assessing and maintaining bone health. (5.7)
- Macular edema: Postmarketing reports. Recommend regular eye exams in all patients with diabetes according to current standards of care with prompt evaluation for acute visual changes. (5.8)
- Vitamin B12 deficiency: Metformin may lower vitamin B12 levels. Monitor hematologic parameters annually. (5.9)
- Macrovascular outcomes: There have been no clinical studies establishing conclusive evidence of macrovascular risk reduction with ACTOPLUS MET XR. (5.10)
ADVERSE REACTIONS
Most common adverse reactions (>5%) are upper respiratory tract infection, edema, diarrhea, headache and weight gain. (6.1)
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact Takeda Pharmaceuticals at 1-877-825-3327 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
DRUG INTERACTIONS
- Strong CYP2C8 inhibitors (e.g., gemfibrozil) increase pioglitazone concentrations. Limit ACTOPLUS MET XR dose to 15 mg/1000 mg daily. (2.3, 7.1)
- CYP2C8 inducers (e.g., rifampin) may decrease pioglitazone concentrations. (7.2)
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may increase risk of lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring. (7.3)
- Drugs that reduce metformin clearance (such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine), may increase the accumulation of metformin. Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use. (7.4)
- Alcohol can potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake. (7.5)
- Use of insulin secretagogues or insulin use may increase the risk for hypoglycemia and may require dose reduction. (7.6)
- Topiramate may decrease pioglitazone concentrations. (7.8)
USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
- Females and Males of Reproductive Potential: Advise premenopausal females of the potential for an unintended pregnancy. (8.3)
- Pediatrics: Not recommended for use in pediatric patients.(8.4)
- Geriatric Use: Assess renal function more frequently. (8.5)
- Hepatic impairment: Avoid use in patients with hepatic impairment. (8.7)
See 17 for PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION and Medication Guide.
Revised: 12/2017
-
Table of Contents
FULL PRESCRIBING INFORMATION: CONTENTS*
WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE AND LACTIC ACIDOSIS
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations for All Patients
2.2 Recommendations for Use in Renal Impairment
2.3 Concomitant Use with Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
2.4 Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Congestive Heart Failure
5.2 Lactic Acidosis
5.3 Edema
5.4 Hypoglycemia
5.5 Hepatic Effects
5.6 Urinary Bladder Tumors
5.7 Fractures
5.8 Macular Edema
5.9 Vitamin B12 Levels
5.10 Macrovascular Outcomes
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
7.2 CYP2C8 Inducers
7.3 Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
7.4 Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance
7.5 Alcohol
7.6 Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin
7.7 Drugs Affecting Glycemic Control
7.8 Topiramate
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
8.2 Lactation
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
8.4 Pediatric Use
8.5 Geriatric Use
8.6 Renal Impairment
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
10 OVERDOSAGE
11 DESCRIPTION
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
- * Sections or subsections omitted from the full prescribing information are not listed.
-
BOXED WARNING
(What is this?)
WARNING: CONGESTIVE HEART FAILURE AND LACTIC ACIDOSIS
Congestive Heart Failure
- Thiazolidinediones, including pioglitazone, which is a component of ACTOPLUS MET XR, cause or exacerbate congestive heart failure in some patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- After initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR, and after dose increases, monitor patients carefully for signs and symptoms of heart failure (e.g., excessive, rapid weight gain, dyspnea, and/or edema). If heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOPLUS MET XR must be considered [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended in patients with symptomatic heart failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
- Initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR in patients with established New York Heart Association (NYHA) Class III or IV heart failure is contraindicated [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
Lactic Acidosis
- Post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis have resulted in death, hypothermia, hypotension, and resistant bradyarrhythmias. The onset of metformin-associated lactic acidosis is often subtle, accompanied only by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, respiratory distress, somnolence, and abdominal pain. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate levels (greater than 5 mmol/L), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), an increased lactate:pyruvate ratio; and metformin plasma levels generally greater than 5 mcg/mL [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis include renal impairment, concomitant use of certain drugs (e.g., carbonic anhydrase inhibitors such as topiramate), age 65 years old or greater, having a radiological study with contrast, surgery and other procedures, hypoxic states (e.g., acute congestive heart failure), excessive alcohol intake, and hepatic impairment.
- Steps to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis in these high risk groups are provided in the Full Prescribing Information [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2), Drug Interactions (7), and Use in Specific Populations (8.6, 8.7)].
- If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, immediately discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR and institute general supportive measures in a hospital setting. Prompt hemodialysis is recommended [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
1 INDICATIONS AND USAGE
ACTOPLUS MET XR is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus when treatment with both pioglitazone and metformin is appropriate [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Important Limitations of Use
Pioglitazone exerts its antihyperglycemic effect only in the presence of endogenous insulin. ACTOPLUS MET XR should not be used to treat type 1 diabetes or diabetic ketoacidosis, as it would not be effective in these settings.
Use caution in patients with liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
-
2 DOSAGE AND ADMINISTRATION
2.1 Recommendations for All Patients
ACTOPLUS MET XR should be taken with meals to reduce the gastrointestinal side effects associated with metformin.
If therapy with a combination tablet containing pioglitazone and extended-release metformin is considered appropriate the recommended starting dose is:
- 15 mg/1000 mg or 30 mg/1000 mg once daily and gradually titrated as needed, after assessing adequacy of therapeutic response and tolerability,
- for patients with NYHA Class I or Class II congestive heart failure: 15 mg/1000 mg or 30 mg/1000 mg once daily and gradually titrated as needed, after assessing adequacy of therapeutic response and tolerability.
- for patients inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy: 15 mg/1000 mg twice daily or 30 mg/1000 mg once daily (depending on the dose of metformin already being taken) and gradually titrated, as needed, after assessing adequacy of therapeutic response and tolerability,
- for patients inadequately controlled on pioglitazone monotherapy: 15 mg/1000 mg twice daily or 30 mg/1000 mg once daily and gradually titrated, as needed, after assessing adequacy of therapeutic response and tolerability.
- for patients who are changing from combination therapy of pioglitazone plus metformin as separate tablets: ACTOPLUS MET XR should be taken at doses that are as close as possible to the dose of pioglitazone and metformin already being taken.
ACTOPLUS MET XR may be titrated up to a maximum daily dose of 45 mg/2000 mg of pioglitazone/extended-release metformin.
Metformin doses above 2000 mg may be better tolerated given three times a day.
Patients should be informed that ACTOPLUS MET XR must be swallowed whole and not chewed, cut, or crushed, and that the inactive ingredients may occasionally be eliminated in the feces as a soft mass that may resemble the original tablet.
After initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR or with dose increase, monitor patients carefully for adverse reactions related to fluid retention such as weight gain, edema, and signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]. Liver tests (serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferases, alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) should be obtained prior to initiating ACTOPLUS MET XR. Routine periodic monitoring of liver tests during treatment with ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended in patients without liver disease. Patients who have liver test abnormalities prior to initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR or who are found to have abnormal liver tests while taking ACTOPLUS MET XR should be managed as described under Warnings and Precautions [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.2 Recommendations for Use in Renal Impairment
Assess renal function prior to initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR and periodically thereafter.
ACTOPLUS MET XR is contraindicated in patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2.
Initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR in patients with an eGFR between 30 – 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 is not recommended.
In patients taking ACTOPLUS MET XR whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, assess the benefit risk of continuing therapy.
Discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR if the patient's eGFR later falls below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.12)].
2.3 Concomitant Use with Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
Coadministration of pioglitazone (one of the ingredients in ACTOPLUS MET XR) and gemfibrozil, a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor, increases pioglitazone exposure by approximately 3-fold. Therefore, the maximum recommended dose of ACTOPLUS MET XR is 15 mg/1000 mg daily when used in combination with gemfibrozil or other strong CYP2C8 inhibitors [see Drug Interactions (7.1) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
2.4 Discontinuation for Iodinated Contrast Imaging Procedures
Discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; in patients with a history of liver disease, alcoholism or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure; restart ACTOPLUS MET XR if renal function is stable [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- 3 DOSAGE FORMS AND STRENGTHS
-
4 CONTRAINDICATIONS
- Initiation in patients with established NYHA Class III or IV heart failure [see Boxed Warning].
- Severe renal impairment ( eGFR below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
- Use in patients with known hypersensitivity to pioglitazone, metformin or any other component of ACTOPLUS MET XR.
- Metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin.
-
5 WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
5.1 Congestive Heart Failure
Pioglitazone
Pioglitazone, like other thiazolidinediones, can cause dose-related fluid retention when used alone or in combination with other antidiabetic medications and is most common when pioglitazone is used in combination with insulin. Fluid retention may lead to or exacerbate congestive heart failure. Patients treated with ACTOPLUS MET XR should be observed for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure. If congestive heart failure develops, it should be managed according to current standards of care and discontinuation or dose reduction of ACTOPLUS MET XR must be considered [see Boxed Warning, Contraindications (4), and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.2 Lactic Acidosis
Metformin hydrochloride
Lactic Acidosis
There have been post-marketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis, including fatal cases. These cases had a subtle onset and were accompanied by nonspecific symptoms such as malaise, myalgias, abdominal pain, respiratory distress, or increased somnolence; however, hypothermia, hypotension and resistant bradyarrhythmias have occurred with severe acidosis. Metformin-associated lactic acidosis was characterized by elevated blood lactate concentrations (greater than 5 mmol/Liter), anion gap acidosis (without evidence of ketonuria or ketonemia), and an increased lactate:pyruvate ratio; metformin plasma levels generally greater than 5 mcg/mL. Metformin decreases liver uptake of lactate increasing lactate blood levels which may increase the risk of lactic acidosis, especially in patients at risk.
If metformin-associated lactic acidosis is suspected, general supportive measures should be instituted promptly in a hospital setting, along with immediate discontinuation of ACTOPLUS MET XR. Patients treated with ACTOPLUS MET XR with a diagnosis or strong suspicion of lactic acidosis, prompt hemodialysis is recommended to correct the acidosis and remove accumulated metformin (metformin hydrochloride is dialyzable, with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions). Hemodialysis has often resulted in reversal of symptoms and recovery.
Educate patients and their families about the symptoms of lactic acidosis and if these symptoms occur instruct them to discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR and report these symptoms to their healthcare provider.
For each of the known and possible risk factors for metformin-associated lactic acidosis, recommendations to reduce the risk of and manage metformin-associated lactic acidosis are provided below:
Renal Impairment
The postmarketing metformin-associated lactic acidosis cases primarily occurred in patients with significant renal impairment. The risk of metformin accumulation and metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the severity of renal impairment because metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney. Clinical recommendations based upon the patient's renal function include [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
- Before initiating ACTOPLUS MET XR, obtain an eGFR.
- ACTOPLUS MET XR is contraindicated in patients with an eGFR less than 30 mL/min/1.73 m2. Initiation of ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended in patients with eGFR between 30 – 45 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Contraindications (4)].
- Obtain an eGFR at least annually in all patients taking ACTOPLUS MET XR. In patients at increased risk for the development of renal impairment (e.g., the elderly), renal function should be assessed more frequently.
- In patients taking ACTOPLUS MET XR whose eGFR later falls below 45 mL/min/1.73 m2, assess the benefit and risk of continuing therapy.
Drug Interactions
The concomitant use of ACTOPLUS MET XR with specific drugs may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis: those that impair renal function, result in significant hemodynamic change, interfere with acid-base balance or increase metformin accumulation (e.g., cationic drugs) [see Drug Interactions (7)]. Therefore, consider more frequent monitoring of patients.
Age 65 or Greater
The risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis increases with the patient's age because elderly patients have a greater likelihood of having hepatic, renal, or cardiac impairment than younger patients. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.5)].
Radiological Studies with Contrast
Administration of intravascular iodinated contrast agents in patients treated with metformin has led to an acute decrease in renal function and the occurrence of lactic acidosis. Stop ACTOPLUS MET XR at the time of, or prior to, an iodinated contrast imaging procedure in patients with an eGFR between 30 and 60 mL/min/1.73 m2; in patients with a history of hepatic impairment, alcoholism, or heart failure; or in patients who will be administered intra-arterial iodinated contrast. Re-evaluate eGFR 48 hours after the imaging procedure, and restart ACTOPLUS MET XR if renal function is stable.
Surgery and Other Procedures
Withholding of food and fluids during surgical or other procedures may increase the risk for volume depletion, hypotension and renal impairment. ACTOPLUS MET XR should be temporarily discontinued while patients have restricted food and fluid intake.
Hypoxic States
Several of the postmarketing cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis occurred in the setting of acute congestive heart failure (particularly when accompanied by hypoperfusion and hypoxemia). Cardiovascular collapse (shock), acute myocardial infarction, sepsis, and other conditions associated with hypoxemia have been associated with lactic acidosis and may also cause prerenal azotemia. When such events occur, discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR.
Excessive Alcohol Intake
Alcohol potentiates the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism and this may increase the risk of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR.
Hepatic Impairment
Patients with hepatic impairment have developed with cases of metformin-associated lactic acidosis. This may be due to impaired lactate clearance resulting in higher lactate blood levels. Therefore, avoid use of ACTOPLUS MET XR in patients with clinical or laboratory evidence of hepatic disease.
5.3 Edema
In controlled clinical trials with pioglitazone, edema was reported more frequently in patients treated with pioglitazone than in patients treated with placebo and is dose related [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)]. In postmarketing experience, reports of new onset or worsening of edema have been received. ACTOPLUS MET XR should be used with caution in patients with edema. Because thiazolidinediones, including pioglitazone, can cause fluid retention, which can exacerbate or lead to congestive heart failure, ACTOPLUS MET XR should be used with caution in patients at risk for congestive heart failure. Patients treated with ACTOPLUS MET XR should be monitored for signs and symptoms of congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning, Warnings and Precautions (5.1), and Patient Counseling Information (17)].
5.4 Hypoglycemia
Patients receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR in combination with insulin or other anti-diabetic medications (particularly insulin secretagogues such as sulfonylureas) may be at risk for hypoglycemia. A reduction in the dose of the concomitant anti-diabetic medication may be necessary to reduce the risk of hypoglycemia [see Drug Interactions (7.7)]. Hypoglycemia can also occur when caloric intake is deficient or when strenuous exercise is not compensated by caloric supplement. Elderly, debilitated, or malnourished patients and those with adrenal or pituitary insufficiency or alcohol intoxication are particularly susceptible to hypoglycemic effects. Hypoglycemia may be difficult to recognize in the elderly, and in people who are taking beta-adrenergic blocking drugs.
5.5 Hepatic Effects
There have been postmarketing reports of fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure in patients taking pioglitazone, although the reports contain insufficient information necessary to establish the probable cause. There has been no evidence of drug-induced hepatotoxicity in the pioglitazone controlled clinical trial database to date [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
Patients with type 2 diabetes may have fatty liver disease or cardiac disease with episodic congestive heart failure, both of which may cause liver test abnormalities, and they may also have other forms of liver disease, many of which can be treated or managed. Therefore, obtaining a liver test panel (serum alanine aminotransferase [ALT], aspartate aminotransferase [AST], alkaline phosphatase, and total bilirubin) and assessing the patient is recommended before initiating ACTOPLUS MET XR therapy.
In patients with abnormal liver tests, ACTOPLUS MET XR should be initiated with caution.
Measure liver tests promptly in patients who report symptoms that may indicate liver injury, including fatigue, anorexia, right upper abdominal discomfort, dark urine or jaundice. In this clinical context, if the patient is found to have abnormal liver tests (ALT greater than three times the upper limit of the reference range), ACTOPLUS MET XR treatment should be interrupted and investigation done to establish the probable cause. ACTOPLUS MET XR should not be restarted in these patients without another explanation for the liver test abnormalities.
Patients who have serum ALT greater than three times the reference range with serum total bilirubin greater than two times the reference range without alternative etiologies are at risk for severe drug-induced liver injury, and should not be restarted on ACTOPLUS MET XR. For patients with lesser elevations of serum ALT or bilirubin and with an alternate probable cause, treatment with ACTOPLUS MET XR can be used with caution.
5.6 Urinary Bladder Tumors
Tumors were observed in the urinary bladder of male rats in the two-year carcinogenicity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. In addition, during the three year PROactive clinical trial, 14 patients out of 2605 (0.54%) randomized to pioglitazone and 5 out of 2633 (0.19%) randomized to placebo were diagnosed with bladder cancer. After excluding patients in whom exposure to study drug was less than one year at the time of diagnosis of bladder cancer, there were 6 (0.23%) cases on pioglitazone and two (0.08%) cases on placebo. After completion of the trial, a large subset of patients was observed for up to 10 additional years, with little additional exposure to pioglitazone. During the 13 years of both PROactive and observational follow-up, the occurrence of bladder cancer did not differ between patients randomized to pioglitazone or placebo (HR =1.00; [95% CI: 0.59–1.72]).
Findings regarding the risk of bladder cancer in patients exposed to pioglitazone vary among observational studies; some did not find an increased risk of bladder cancer associated with pioglitazone, while others did.
A large prospective 10-year observational cohort study conducted in the United States found no statistically significant increase in the risk of bladder cancer in diabetic patients ever exposed to pioglitazone, compared to those never exposed to pioglitazone (HR =1.06 [95% CI 0.89–1.26]).
A retrospective cohort study conducted with data from the United Kingdom found a statistically significant association between ever exposure to pioglitazone and bladder cancer (HR: 1.63; [95% CI: 1.22–2.19]).
Associations between cumulative dose or cumulative duration of exposure to pioglitazone and bladder cancer were not detected in some studies including the 10-year observational study in the U.S., but were in others. Inconsistent findings and limitations inherent in these and other studies preclude conclusive interpretations of the observational data.
Pioglitazone may be associated with an increase in the risk of urinary bladder tumors. There are insufficient data to determine whether pioglitazone is a tumor promoter for urinary bladder tumors.
Consequently, ACTOPLUS MET XR should not be used in patients with active bladder cancer and the benefits of glycemic control versus unknown risks for cancer recurrence with ACTOPLUS MET XR should be considered in patients with a prior history of bladder cancer.
5.7 Fractures
In PROactive (the Prospective Pioglitazone Clinical Trial in Macrovascular Events), 5238 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of macrovascular disease were randomized to pioglitazone (N=2605), force–titrated up to 45 mg daily or placebo (N=2633) in addition to standard of care. During a mean follow-up of 34.5 months, the incidence of bone fracture in females was 5.1% (44/870) for pioglitazone versus 2.5% (23/905) for placebo. This difference was noted after the first year of treatment and persisted during the course of the study. The majority of fractures observed in female patients were nonvertebral fractures including lower limb and distal upper limb. No increase in the incidence of fracture was observed in men treated with pioglitazone (1.7%) versus placebo (2.1%). The risk of fracture should be considered in the care of patients, especially female patients, treated with ACTOPLUS MET XR and attention should be given to assessing and maintaining bone health according to current standards of care.
5.8 Macular Edema
Macular edema has been reported in postmarketing experience in diabetic patients who were taking pioglitazone or another thiazolidinedione. Some patients presented with blurred vision or decreased visual acuity, but others were diagnosed on routine ophthalmologic examination.
Most patients had peripheral edema at the time macular edema was diagnosed. Some patients had improvement in their macular edema after discontinuation of the thiazolidinedione.
Patients with diabetes should have regular eye exams by an ophthalmologist according to current standards of care. Patients with diabetes who report any visual symptoms should be promptly referred to an ophthalmologist, regardless of the patient's underlying medications or other physical findings [see Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
5.9 Vitamin B12 Levels
In controlled clinical trials of metformin of 29 weeks duration, a decrease to subnormal levels of previously normal serum vitamin B12 levels, without clinical manifestations, was observed in approximately 7% of patients. Such decrease, possibly due to interference with B12 absorption from the B12 -intrinsic factor complex, is, however, very rarely associated with anemia and appears to be rapidly reversible with discontinuation of metformin or vitamin B12 supplementation. Measurement of hematologic parameters on an annual basis is advised in patients on ACTOPLUS MET XR and any apparent abnormalities should be appropriately investigated and managed. Certain individuals (those with inadequate vitamin B12 or calcium intake or absorption) appear to be predisposed to developing subnormal vitamin B12 levels. In these patients, routine serum vitamin B12 measurements at two- to three-year intervals may be useful.
-
6 ADVERSE REACTIONS
The following serious adverse reactions are discussed elsewhere in the labeling:
- Congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)]
- Lactic acidosis [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]
- Edema [see Warnings and Precautions (5.3)]
- Fractures [see Warnings and Precautions (5.7)]
6.1 Clinical Trials Experience
Because clinical trials are conducted under widely varying conditions, adverse reaction rates observed in the clinical trials of a drug cannot be directly compared to rates in the clinical trials of another drug and may not reflect the rates observed in practice.
Pioglitazone
Over 8500 patients with type 2 diabetes have been treated with pioglitazone in randomized, double-blind, controlled clinical trials, including 2605 patients with type 2 diabetes and macrovascular disease treated with pioglitazone from the PROactive clinical trial. In these trials, over 6000 patients have been treated with pioglitazone for 6 months or longer, over 4500 patients have been treated with pioglitazone for one year or longer, and over 3000 patients have been treated with pioglitazone for at least two years.
In six pooled 16- to 26-week placebo-controlled monotherapy and 16- to 24-week add-on combination therapy trials, the incidence of withdrawals due to adverse events was 4.5% for patients treated with pioglitazone and 5.8% for patients treated with comparator. The most common adverse events leading to withdrawal were related to inadequate glycemic control, although the incidence of these events was lower (1.5%) with pioglitazone than with placebo (3.0%).
In the PROactive trial, the incidence of withdrawals due to adverse events was 9.0% for patients treated with pioglitazone and 7.7% for patients treated with placebo. Congestive heart failure was the most common serious adverse event leading to withdrawal occurring in 1.3% of patients treated with pioglitazone and 0.6% of patients treated with placebo.
Common Adverse Events: 16- to 26-Week Monotherapy Trials
A summary of the incidence and type of common adverse events reported in three pooled 16- to 26-week placebo-controlled monotherapy trials of pioglitazone is provided in Table 1. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly in patients treated with pioglitazone than in patients who received placebo. None of these adverse events were related to the pioglitazone dose.
-
Table 1. Three Pooled 16- to 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Clinical Trials of Pioglitazone Monotherapy: Adverse Events Reported at an Incidence >5% and More Commonly in Patients Treated with Pioglitazone than in Patients Treated with Placebo
% of Patients
Placebo
N=259Pioglitazone
N=606Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
8.5
13.2
Headache
6.9
9.1
Sinusitis
4.6
6.3
Myalgia
2.7
5.4
Pharyngitis
0.8
5.1
Common Adverse Events: 16- to 24-Week Add-on Combination Therapy Trials
A summary of the overall incidence and types of common adverse events reported in trials of pioglitazone add-on to metformin is provided in Table 2. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly with the highest tested dose of pioglitazone.
-
Table 2. 16- to 24-Week Clinical Trials of Pioglitazone Add-on to Metformin
16-Week Placebo-Controlled Trial
Adverse Events Reported in >5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with Pioglitazone + Metformin than in Patients Treated with Placebo + Metformin% of Patients
Placebo
+ Metformin
N=160Pioglitazone 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=168Edema
2.5
6.0
Headache
1.9
6.0
24-Week Non-Controlled Double-Blind Trial Adverse Events Reported in >5% of Patients and More Commonly in Patients Treated with Pioglitazone 45 mg + Metformin than in Patients Treated with Pioglitazone 30 mg + Metformin
% of Patients
Pioglitazone 30 mg
+ Metformin
N=411Pioglitazone 45 mg
+ Metformin
N=416Upper Respiratory Tract Infection
12.4
13.5
Edema
5.8
13.9
Headache
5.4
5.8
Weight Increased
2.9
6.7
Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema."
Common Adverse Events: PROactive Trial
A summary of the overall incidence and types of common adverse events reported in the PROactive trial is provided in Table 3. Terms that are reported represent those that occurred at an incidence of >5% and more commonly in patients treated with pioglitazone than in patients who received placebo.
- Table 3. PROactive Trial: Incidence and Types of Adverse Events Reported in >5% of Patients Treated with Pioglitazone and More Commonly than Placebo
% of Patients
Placebo
N=2633
Pioglitazone
N=2605
Hypoglycemia
18.8
27.3
Edema
15.3
26.7
Cardiac Failure
6.1
8.1
Pain in Extremity
5.7
6.4
Back Pain
5.1
5.5
Chest Pain
5.0
5.1
Mean duration of patient follow-up was 34.5 months.
Congestive Heart Failure
A summary of the incidence of adverse events related to congestive heart failure is provided in Table 4 for the 16- to 24-week add-on to metformin trials. None of the events were fatal.
-
Table 4. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) Patients Treated with Pioglitazone or Placebo Added on to Metformin
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled
Double Blind Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Metformin
N=160Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Metformin
N=168Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Metformin
N=411Pioglitazone
45 mg
+ Metformin
N=416At least one congestive heart failure event
0
1 (0.6%)
0
1 (0.2%)
Hospitalized
0
1 (0.6%)
0
1 (0.2%)
Table 5. Treatment–Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF)Patients Treated with Pioglitazone or Placebo Added on to a Sulfonylurea
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled Double Blind
Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Sulfonylurea
N=187Pioglitazone
15 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=184Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=189Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351Pioglitazone
45 mg
+ Sulfonylurea
N=351At least one congestive
heart failure event2 (1.1%)
0
0
1 (0.3%)
6 (1.7%)
Hospitalized
2 (1.1%)
0
0
0
2 (0.6%)
Patients Treated with Pioglitazone or Placebo Added on to Insulin
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled Double Blind
Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Insulin
N=187Pioglitazone
15 mg
+ Insulin
N=191Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Insulin
N=188Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Insulin
N=345Pioglitazone
45 mg
+ Insulin
N=345At least one congestive
heart failure event0
2 (1.0%)
2 (1.1%)
3 (0.9%)
5 (1.4%)
Hospitalized
0
2 (1.0%)
1 (0.5%)
1 (0.3%)
3 (0.9%)
Patients Treated with Pioglitazone or Placebo Added on to Metformin
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo-Controlled Trial
(16 weeks)Non-Controlled Double Blind
Trial
(24 weeks)Placebo
+ Metformin
N=160Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Metformin
N=168Pioglitazone
30 mg
+ Metformin
N=411Pioglitazone
45 mg
+ Metformin
N=416At least one congestive
heart failure event0
1 (0.6%)
0
1 (0.2%)
Hospitalized
0
1 (0.6%)
0
1 (0.2%)
-
Table 6. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) in Patients with NYHA Class II or III Congestive Heart Failure Treated with Pioglitazone or Glyburide
Number (%) of Subjects
Pioglitazone
N=262Glyburide
N=256Death due to cardiovascular causes (adjudicated)
5 (1.9%)
6 (2.3%)
Overnight hospitalization for worsening CHF (adjudicated)
26 (9.9%)
12 (4.7%)
Emergency room visit for CHF (adjudicated)
4 (1.5%)
3 (1.2%)
Patients experiencing CHF progression during study
35 (13.4%)
21 (8.2%)
Congestive heart failure events leading to hospitalization that occurred during the PROactive trial are summarized in Table 7.
- Table 7. Treatment-Emergent Adverse Events of Congestive Heart Failure (CHF) in PROactive Trial
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo
N=2633Pioglitazone
N=2605- At least one hospitalized congestive heart failure event
108 (4.1%)
149 (5.7%)
- Fatal
22 (0.8%)
25 (1%)
- Hospitalized, non-fatal
86 (3.3%)
124 (4.7%)
Cardiovascular Safety
In the PROactive trial, 5238 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of macrovascular disease were randomized to pioglitazone (N=2605), force-titrated up to 45 mg daily or placebo (N=2633) in addition to standard of care. Almost all patients (95%) were receiving cardiovascular medications (beta blockers, ACE inhibitors, angiotensin II receptor blockers, calcium channel blockers, nitrates, diuretics, aspirin, statins and fibrates). At baseline, patients had a mean age of 62 years, mean duration of diabetes of 9.5 years, and mean HbA1c of 8.1%. Mean duration of follow-up was 34.5 months.
The primary objective of this trial was to examine the effect of pioglitazone on mortality and macrovascular morbidity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus who were at high risk for macrovascular events. The primary efficacy variable was the time to the first occurrence of any event in a cardiovascular composite endpoint that included all-cause mortality, non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI) including silent MI, stroke, acute coronary syndrome, cardiac intervention including coronary artery bypass grafting or percutaneous intervention, major leg amputation above the ankle, and bypass surgery or revascularization in the leg. A total of 514 (19.7%) patients treated with pioglitazone and 572 (21.7%) patients treated with placebo experienced at least one event from the primary composite endpoint (hazard ratio 0.90; 95% Confidence Interval: 0.80, 1.02; p=0.10).
Although there was no statistically significant difference between pioglitazone and placebo for the 3-year incidence of a first event within this composite, there was no increase in mortality or in total macrovascular events with pioglitazone. The number of first occurrences and total individual events contributing to the primary composite endpoint is shown in Table 8.
Table 8. PROactive: Number of First and Total Events for Each Component within the Cardiovascular Composite Endpoint
Cardiovascular Events
Placebo
N=2633Pioglitazone
N=2605First Events
n (%)Total Events
nFirst Events
n (%)Total Events
nAny event
572 (21.7)
900
514 (19.7)
803
- All-cause mortality
122 (4.6)
186
110 (4.2)
177
- Non-fatal myocardial infarction (MI)
118 (4.5)
157
105 (4.0)
131
- Stroke
96 (3.6)
119
76 (2.9)
92
- Acute coronary syndrome
63 (2.4)
78
42 (1.6)
65
- Cardiac intervention (CABG/PCI)
101 (3.8)
240
101 (3.9)
195
- Major leg amputation
15 (0.6)
28
9 (0.3)
28
- Leg revascularization
57 (2.2)
92
71 (2.7)
115
CABG = coronary artery bypass grafting; PCI = percutaneous intervention
Weight Gain
Dose-related weight gain occurs when pioglitazone is used alone or in combination with other anti-diabetic medications. The mechanism of weight gain is unclear but probably involves a combination of fluid retention and fat accumulation.
Tables 9 and 10 summarize the changes in body weight with pioglitazone and placebo in the 16- to 26-week randomized, double-blind monotherapy and 16- to 24-week combination add-on therapy trials and in the PROactive trial.
Table 9. Weight Changes (kg) from Baseline during Randomized, Double-Blind Clinical TrialsControl
Group
(Placebo)Pioglitazone
15 mgPioglitazone
30 mgPioglitazone
45 mgMedian
(25th/75th
percentile)Median
(25th/75th
percentile)Median
(25th/75th
percentile)Median
(25th/75th
percentile)Monotherapy (16 to 26 weeks)
-1.4 (-2.7, 0.0)
N=2560.9 (-0.5, 3.4)
N=791.0 (-0.9, 3.4)
N=188-
2.6 (0.2, 5.4)
N=79
Combination
Therapy
(16 to 24 weeks)Sulfonylurea
-0.5 (-1.8, 0.7)
N=1872.0 (0.2, 3.2)
N=1833.1 (1.1, 5.4)
N=528-
4.1 (1.8, 7.3)
N=333
Metformin
-1.4 (-3.2, 0.3)
N=160N/A
0.9 (-1.3, 3.2)
N=567-
1.8 (-0.9, 5.0)
N=407
Insulin
0.2 (-1.4, 1.4)
N=1822.3 (0.5, 4.3)
N=1903.3 (0.9, 6.3)
N=522-
4.1 (1.4, 6.8)
N=338
- Table 10. Median Change in Body Weight in Patients Treated with Pioglitazone Versus Patients Treated with Placebo During the Double-Blind Treatment Period in the PROactive Trial
Placebo
Pioglitazone
Median
(25th, 75th
percentile)Median
(25th, 75th
percentile)Change from Baseline to Final Visit (kg)
-0.5 (-3.3, 2.0)
N=2581+3.6 (0.0, 7.5)
N=2560Note: Median exposure for both Pioglitazone and Placebo was 2.7 years.
Edema
Edema induced from taking pioglitazone is reversible when pioglitazone is discontinued. The edema usually does not require hospitalization unless there is coexisting congestive heart failure. A summary of the frequency and types of edema adverse events occurring in clinical investigations of pioglitazone is provided in Table 11.
Table 11. Adverse Events of Edema in Patients Treated with PioglitazoneNumber (%) of Patients
Placebo
Pioglitazone
15 mgPioglitazone
30 mgPioglitazone
45 mg- Monotherapy (16 to 26 weeks)
3 (1.2%)
N=2592 (2.5%)
N=8113 (4.7%)
N=27511 (6.5%)
N=169Combined
Therapy
(16 to 24 weeks)Sulfonylurea
4 (2.1%)
N=1873 (1.6%)
N=18461 (11.3%)
N=54081 (23.1%)
N=351Metformin
4 (2.5%)
N=160N/A
34 (5.9%)
N=57958 (13.9%)
N=416Insulin
13 (7.0%)
N=18724 (12.6%)
N=191109 (20.5%)
N=53390 (26.1%)
N=345- Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema."
- Table 12. Adverse Events of Edema in Patients in the PROactive Trial
Number (%) of Patients
Placebo
N=2633Pioglitazone
N=2605419 (15.9%)
712 (27.3%)
Note: The preferred terms of edema peripheral, generalized edema, pitting edema and fluid retention were combined to form the aggregate term of "edema."
Hepatic Effects
There has been no evidence of pioglitazone-induced hepatotoxicity in the pioglitazone controlled clinical trial database to date. One randomized, double-blind, 3-year trial comparing pioglitazone to glyburide as add-on to metformin and insulin therapy was specifically designed to evaluate the incidence of serum ALT elevation to greater than three times the upper limit of the reference range, measured every 8 weeks for the first 48 weeks of the trial then every 12 weeks thereafter. A total of 3/1051 (0.3%) patients treated with pioglitazone and 9/1046 (0.9%) patients treated with glyburide developed ALT values >three times the upper limit of the reference range. None of the patients treated with pioglitazone in the pioglitazone controlled clinical trial database to date have had a serum ALT >three times the upper limit of the reference range and a corresponding total bilirubin >two times the upper limit of the reference range, a combination predictive of the potential for severe drug-induced liver injury.
Hypoglycemia
In the pioglitazone clinical trials, adverse events of hypoglycemia were reported based on clinical judgment of the investigators and did not require confirmation with fingerstick glucose testing.
In the 16-week add-on to sulfonylurea trial, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 3.7% with pioglitazone 30 mg and 0.5% with placebo. In the 16-week add-on to insulin trial, the incidence of reported hypoglycemia was 7.9% with pioglitazone 15 mg, 15.4% with pioglitazone 30 mg, and 4.8% with placebo.
The incidence of reported hypoglycemia was higher with pioglitazone 45 mg compared to pioglitazone 30 mg in both the 24-week add-on to sulfonylurea trial (15.7% vs. 13.4%) and in the 24-week add-on to insulin trial (47.8% vs. 43.5%).
Three patients in these four trials were hospitalized due to hypoglycemia. All three patients were receiving pioglitazone 30 mg (0.9%) in the 24-week add-on to insulin trial. An additional 14 patients reported severe hypoglycemia (defined as causing considerable interference with patient's usual activities) that did not require hospitalization. These patients were receiving pioglitazone 45 mg in combination with sulfonylurea (n=2) or pioglitazone 30 mg or 45 mg in combination with insulin (n=12).
Urinary Bladder Tumors
Tumors were observed in the urinary bladder of male rats in the two-year carcinogenicity study [see Nonclinical Toxicology (13.1)]. During the three year PROactive clinical trial, 14 patients out of 2605 (0.54%) randomized to pioglitazone and 5 out of 2633 (0.19%) randomized to placebo were diagnosed with bladder cancer. After excluding patients in whom exposure to study drug was less than one year at the time of diagnosis of bladder cancer, there were 6 (0.23%) cases on pioglitazone and two (0.08%) cases on placebo. After completion of the trial, a large subset of patients was observed for up to 10 additional years, with little additional exposure to pioglitazone. During the 13 years of both PROactive and observational follow-up, the occurrence of bladder cancer did not differ between patients randomized to pioglitazone or placebo (HR =1.00; 95% CI: 0.59-1.72) [see Warnings and Precautions (5.6)].
Metformin hydrochloride
In a double-blind clinical study of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes, a total of 141 patients received metformin therapy (up to 2550 mg per day) and 145 patients received placebo. Adverse reactions reported in greater than 5% of the metformin patients, and that were more common in metformin than patients treated with placebo, are listed in Table 13. In this trial, diarrhea led to discontinuation of study medication in 6% of patients treated with metformin.
- * Reactions that were more common in metformin than patients treated with placebo.
- Table 13. Most Common Adverse Reactions (>5.0%) in a Placebo-Controlled Clinical Study of Metformin Monotherapy*
Adverse Reaction
Metformin Monotherapy
(n=141)Placebo
(n=145)% of Patients
Diarrhea
53.2
11.7
Nausea/Vomiting
25.5
8.3
Flatulence
12.1
5.5
Asthenia
9.2
5.5
Indigestion
7.1
4.1
Abdominal Discomfort
6.4
4.8
Headache
5.7
4.8
Laboratory Abnormalities
Hematologic Effects
Pioglitazone may cause decreases in hemoglobin and hematocrit. In placebo-controlled monotherapy trials, mean hemoglobin values declined by 2% to 4% in patients treated with pioglitazone compared with a mean change in hemoglobin of -1% to +1% in patients treated with placebo. These changes primarily occurred within the first four to 12 weeks of therapy and remained relatively constant thereafter. These changes may be related to increased plasma volume associated with pioglitazone therapy and are not likely to be associated with any clinically significant hematologic effects.
Vitamin B12 concentrations
Metformin may lower serum vitamin B12 concentrations. Measurement of hematologic parameters on an annual basis is advised in patients on ACTOPLUS MET XR and any apparent abnormalities should be appropriately investigated and managed [see Warnings and Precautions (5.9)].
Creatine Phosphokinase
During protocol-specified measurement of serum creatine phosphokinase (CPK) in pioglitazone clinical trials, an isolated elevation in CPK to greater than 10 times the upper limit of the reference range was noted in 9 (0.2%) patients treated with pioglitazone (values of 2150 to 11400 IU/L) and in no patients treated with comparator. Six of these nine patients continued to receive pioglitazone, two patients were noted to have the CPK elevation on the last day of dosing, and one patient discontinued pioglitazone due to the elevation. These elevations resolved without any apparent clinical sequelae. The relationship of these events to pioglitazone therapy is unknown.
6.2 Postmarketing Experience
The following adverse reactions have been identified during post-approval use of pioglitazone. Because these reactions are reported voluntarily from a population of uncertain size, it is generally not possible to reliably estimate their frequency or establish a causal relationship to drug exposure.
Pioglitazone
- New onset or worsening diabetic macular edema with decreased visual acuity [see Warnings and Precautions (5.8)].
- Fatal and non-fatal hepatic failure [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Postmarketing reports of congestive heart failure have been reported in patients treated with pioglitazone, both with and without previously known heart disease and both with and without concomitant insulin administration.
In postmarketing experience, there have been reports of unusually rapid increases in weight and increases in excess of that generally observed in clinical trials. Patients who experience such increases should be assessed for fluid accumulation and volume-related events such as excessive edema and congestive heart failure [see Boxed Warning and Warnings and Precautions (5.1)].
-
7 DRUG INTERACTIONS
7.1 Strong CYP2C8 Inhibitors
An inhibitor of CYP2C8 (e.g., gemfibrozil) significantly increases the exposure (area under the serum concentration-time curve or AUC) and half-life (t½) of pioglitazone. Therefore, the maximum recommended dose of pioglitazone is 15 mg daily if used in combination with gemfibrozil or other strong CYP2C8 inhibitors [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.2 CYP2C8 Inducers
An inducer of CYP2C8 (e.g., rifampin) may significantly decrease the exposure (AUC) of pioglitazone. Therefore, if an inducer of CYP2C8 is started or stopped during treatment with pioglitazone, changes in diabetes treatment may be needed based on clinical response without exceeding the maximum recommended daily dose of 45 mg for pioglitazone [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
7.3 Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors
Topiramate or other carbonic anhydrase inhibitors (e.g., zonisamide, acetazolamide or dichlorphenamide) frequently causes a decrease in serum bicarbonate and induce non-anion gap, hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis. Concomitant use of these drugs with ACTOPLUS MET XR may increase the risk for lactic acidosis. Consider more frequent monitoring of these patients.
7.4 Drugs that Reduce Metformin Clearance
Concomitant use of drugs that interfere with common renal tubular transport systems involved in the renal elimination of metformin (e.g., organic cationic transporter-2 [OCT2]/multidrug and toxin extrusion [MATE] inhibitors such as ranolazine, vandetanib, dolutegravir, and cimetidine) could increase systemic exposure to metformin and may increase the risk for lactic acidosis [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. Consider the benefits and risks of concomitant use.
7.5 Alcohol
Alcohol is known to potentiate the effect of metformin on lactate metabolism. Warn patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR.
7.6 Insulin Secretagogues or Insulin
If hypoglycemia occurs in a patient coadministered ACTOPLUS MET XR and an insulin secretagogue (e.g., sulfonylurea), the dose of the insulin secretagogue should be reduced.
If hypoglycemia occurs in a patient coadministered ACTOPLUS MET XR and insulin, the dose of insulin should be decreased by 10% to 25%. Further adjustments to the insulin dose should be individualized based on glycemic response.
7.7 Drugs Affecting Glycemic Control
Certain drugs tend to produce hyperglycemia and may lead to loss of glycemic control. These drugs include the thiazides and other diuretics, corticosteroids, phenothiazines, thyroid products, estrogens, oral contraceptives, phenytoin, nicotinic acid, sympathomimetics, calcium channel blockers, and isoniazid. When such drugs are administered to a patient receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR, the patient should be closely observed for loss of blood glucose control. When such drugs are withdrawn from a patient receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR, the patient should be observed closely for hypoglycemia.
7.8 Topiramate
A decrease in the exposure of pioglitazone and its active metabolites were noted with concomitant administration of pioglitazone and topiramate [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)]. The clinical relevance of this decrease is unknown; however, when ACTOPLUS MET XR and topiramate are used concomitantly, monitor patients for adequate glycemic control.
-
8 USE IN SPECIFIC POPULATIONS
8.1 Pregnancy
Risk Summary
Limited data with ACTOPLUS MET XR or pioglitazone in pregnant women are not sufficient to determine a drug-associated risk for major birth defects or miscarriage. Published studies with metformin use during pregnancy have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defect or miscarriage risk [see Data]. There are risks to the mother and fetus associated with poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy [see Clinical Considerations].
In animal reproduction studies, no adverse developmental effects were observed when pioglitazone was administered to pregnant rats and rabbits during organogenesis at exposures up to 5- and 35-times the 45 mg clinical dose, respectively, based on body surface area. No adverse developmental effects were observed when metformin was administered to pregnant Sprague Dawley rats and rabbits during the period of organogenesis at doses up to 2- to 6-times, respectively, a 2000 mg clinical dose, based on body surface area [see Data].
The estimated background risk of major birth defects is 6-10% in women with pre-gestational diabetes with a HbA1c >7 and has been reported to be as high as 20-25% in women with a HbA1c >10. The estimated background risk of miscarriage for the indicated population is unknown. In the U.S. general population, the estimated background risk of major birth defects and miscarriage in clinically recognized pregnancies is 2-4% and 15-20%, respectively.
Clinical Considerations
Disease-associated maternal and/or embryo/fetal risk
Poorly controlled diabetes in pregnancy increases the maternal risk for diabetic ketoacidosis, pre-eclampsia, spontaneous abortions, preterm delivery, still birth and delivery complications. Poorly controlled diabetes increases the fetal risk for major birth defects, still birth, and macrosomia related morbidity.
Data
Human Data
Published data from post-marketing studies have not reported a clear association with metformin and major birth defects, miscarriage, or adverse maternal or fetal outcomes when metformin was used during pregnancy. However, these studies cannot definitely establish the absence of any metformin-associated risk because of methodological limitations, including small sample size and inconsistent comparator groups.
Animal Data
Pioglitazone and Metformin hydrochloride
Animal reproduction studies were not conducted with the combined products in ACTOPLUS MET XR. The following data are based on studies conducted with the individual components of ACTOPLUS MET XR.
Pioglitazone
Pioglitazone administered to pregnant rats during organogenesis did not cause adverse developmental effects at a dose of 20 mg/kg (~5-times the 45 mg clinical dose), but delayed parturition and reduced embryofetal viability at 40 and 80 mg/kg, or ≥9-times the 45 mg clinical dose, by body surface area. In pregnant rabbits administered pioglitazone during organogenesis, no adverse developmental effects were observed at 80 mg/kg (~35-times the 45 mg clinical dose), but reduced embryofetal viability at 160 mg/kg, or ~69-times the 45 mg clinical dose, by body surface area. When pregnant rats received pioglitazone during late gestation and lactation, delayed postnatal development, attributed to decreased body weight occurred in offspring at maternal doses of 10 mg/kg and above or ≥2-times the 45 mg clinical dose, by body surface area.
Metformin hydrochloride
Metformin hydrochloride did not cause adverse developmental effects when administered to pregnant Sprague Dawley rats and rabbits up to 600 mg/kg/day during the period of organogenesis. This represents an exposure of about 2- to 6-times a 2000 mg clinical dose based on body surface area (mg/m2) for rats and rabbits, respectively.
8.2 Lactation
Risk Summary
There is no information regarding the presence of ACTOPLUS MET XR or pioglitazone in human milk, the effects on the breastfed infant, or the effects on milk production. Pioglitazone is present in rat milk; however, due to species-specific differences in lactation physiology, animal data may not reliably predict drug levels in human milk. Limited published studies report that metformin is present in human milk [see Data]. However, there is insufficient information on the effects of metformin on the breastfed infant and no available information on the effects of metformin on milk production. The developmental and health benefits of breastfeeding should be considered along with the mother's clinical need for ACTOPLUS MET XR and any potential adverse effects on the breastfed infant from ACTOPLUS MET XR or from the underlying maternal condition.
Data
Published clinical lactation studies report that metformin is present in human milk which resulted in infant doses approximately 0.11% to 1% of the maternal weight-adjusted dosage and a milk/plasma ratio ranging between 0.13 and 1. However, the studies were not designed to definitely establish the risk of use of metformin during lactation because of small sample size and limited adverse event data collected in infants.
8.3 Females and Males of Reproductive Potential
Discuss the potential for unintended pregnancy with premenopausal women as therapy with ACTOPLUS MET XR may result in ovulation in some premenopausal anovulatory women.
8.4 Pediatric Use
Safety and effectiveness of ACTOPLUS MET XR in pediatric patients have not been established.
ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended for use in pediatric patients based on adverse effects observed in adults, including fluid retention and congestive heart failure, fractures, and urinary bladder tumors [see Warnings and Precautions (5.1, 5.3, 5.6, 5.7)].
8.5 Geriatric Use
Pioglitazone
A total of 92 patients (15.2%) treated with pioglitazone in the three pooled 16- to 26-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, monotherapy trials were ≥65 years old and two patients (0.3%) were ≥75 years old. In the two pooled 16- to 24-week add-on to sulfonylurea trials, 201 patients (18.7%) treated with pioglitazone were ≥65 years old and 19 (1.8%) were ≥75 years old. In the two pooled 16- to 24-week add-on to metformin trials, 155 patients (15.5%) treated with pioglitazone were ≥65 years old and 19 (1.9%) were ≥75 years old. In the two pooled 16- to 24-week add-on to insulin trials, 272 patients (25.4%) treated with pioglitazone were ≥65 years old and 22 (2.1%) were ≥75 years old.
In PROactive, 1068 patients (41.0%) treated with pioglitazone were ≥65 years old and 42 (1.6%) were ≥75 years old.
In pharmacokinetic studies with pioglitazone, no significant differences were observed in pharmacokinetic parameters between elderly and younger patients [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Although clinical experiences have not identified differences in effectiveness and safety between the elderly (≥65 years) and younger patients, these conclusions are limited by small sample sizes for patients ≥75 years old.
Metformin hydrochloride
Controlled clinical studies of metformin did not include sufficient numbers of elderly patients to determine whether they respond differently from younger patients, although other reported clinical experience has not identified differences in responses between the elderly and young patients. In general, dose selection for an elderly patient should be cautious, usually starting at the low end of the dosing range, reflecting the greater frequency of decreased hepatic, renal, or cardiac function, and of concomitant disease or other drug therapy and the higher risk of lactic acidosis. Assess renal function more frequently in elderly patients [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Dosage and Administration (2.2)].
8.6 Renal Impairment
Metformin is substantially excreted by the kidney, and the risk of metformin accumulation and lactic acidosis increases with the degree of renal impairment. ACTOPLUS MET XR is contraindicated in severe renal impairment, patients with an estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) below 30 mL/min/1.73 m2 [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4), Warnings and Precautions (5.2) and Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
8.7 Hepatic Impairment
Use of metformin in patients with hepatic impairment has been associated with some cases of lactic acidosis. ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended in patients with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
-
10 OVERDOSAGE
Pioglitazone
During controlled clinical trials, one case of overdose with pioglitazone was reported. A male patient took 120 mg per day for four days, then 180 mg per day for seven days. The patient denied any clinical symptoms during this period.
In the event of overdosage, appropriate supportive treatment should be initiated according to the patient's clinical signs and symptoms.
Metformin hydrochloride
Overdose of metformin hydrochloride has occurred, including ingestion of amounts greater than 50 grams. Hypoglycemia was reported in approximately 10% of cases, but no causal association with metformin hydrochloride has been established. Lactic acidosis has been reported in approximately 32% of metformin overdose cases [see Warnings and Precautions (5.2)]. Metformin is dialyzable with a clearance of up to 170 mL/min under good hemodynamic conditions. Therefore, hemodialysis may be useful for removal of accumulated metformin from patients in whom metformin overdosage is suspected.
-
11 DESCRIPTION
ACTOPLUS MET XR tablets are a thiazolidinedione and biguanide combination product that contains two oral anti-diabetic medications: pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride (extended-release).
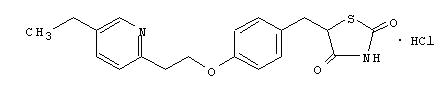
Pioglitazone [(±)-5-[[4-[2-(5-ethyl-2-pyridinyl)ethoxy]phenyl]methyl]-2,4-] thiazolidinedione monohydrochloride contains one asymmetric carbon, and the compound is synthesized and used as the racemic mixture. The two enantiomers of pioglitazone interconvert in vivo. No differences were found in the pharmacologic activity between the two enantiomers. The structural formula is as shown:
Pioglitazone hydrochloride is an odorless white crystalline powder that has a molecular formula of C19H20N2O3SHCl and a molecular weight of 392.90 daltons. It is soluble in N,N-dimethylformamide, slightly soluble in anhydrous ethanol, very slightly soluble in acetone and acetonitrile, practically insoluble in water, and insoluble in ether.
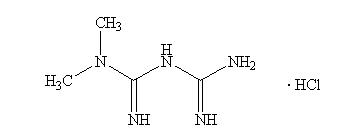
Metformin hydrochloride (N,N-dimethylimidodicarbonimidic diamide hydrochloride) is a white crystalline powder with a molecular formula of C4H11N5HCl and a molecular weight of 165.62. Metformin hydrochloride is freely soluble in water and is practically insoluble in acetone, ether, and chloroform. The pKa of metformin is 12.4. The pH of a 1% aqueous solution of metformin hydrochloride is 6.68. The structural formula is as shown:
ACTOPLUS MET XR is available as a tablet for oral administration containing 15 mg pioglitazone (as the base) and 1000 mg metformin hydrochloride (15 mg/1000 mg) or 30 mg pioglitazone (as the base) and 1000 mg metformin hydrochloride (30 mg/1000 mg) formulated with the following excipients: candelilla wax, cellulose acetate, povidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycols (PEG 400, PEG 8000), sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Tablets are imprinted with ink containing shellac, iron oxide red (15 mg/1000 mg strength only), FD&C Blue No. 2 Lake (30 mg/1000 mg strength only), propylene glycol, and ammonium hydroxide.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS AND PERFORMANCE
ACTOPLUS MET XR consists of an extended-release metformin core coated tablet with an immediate-release pioglitazone layer. The tablet is similar in appearance to other film-coated orally administered tablets but it consists of an osmotically active core formulation that is surrounded by a semipermeable membrane and coated with a pioglitazone drug layer. Two laser drilled exit ports exist in the membrane, one on either side of the tablet. The core formulation is composed primarily of drug with small concentrations of excipients. The semipermeable membrane is permeable to water but not to higher molecular weight components of biological fluids. Upon ingestion, the pioglitazone layer is dissolved; water is then taken up through the membrane, which in turn dissolves the metformin and excipients in the core formulation. The dissolved metformin and excipients exit through the laser drilled ports in the membrane. The rate of drug delivery is constant and dependent upon the maintenance of a constant osmotic gradient across the membrane. This situation exists so long as there is undissolved metformin present in the core tablet. Following the dissolution of the core materials, the rate of drug delivery slowly decreases until the osmotic gradient across the membrane falls to zero at which time delivery ceases. The membrane coating remains intact during the transit of the dosage form through the gastrointestinal tract and is excreted in the feces.
-
12 CLINICAL PHARMACOLOGY
12.1 Mechanism of Action
ACTOPLUS MET XR
ACTOPLUS MET XR combines two anti-diabetic medications with different mechanisms of action to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes: pioglitazone, a thiazolidinedione, and metformin hydrochloride, a biguanide. Thiazolidinediones are insulin-sensitizing agents that act primarily by enhancing peripheral glucose utilization, whereas biguanides act primarily by decreasing endogenous hepatic glucose production.
Pioglitazone
Pioglitazone is a thiazolidinedione that depends on the presence of insulin for its mechanism of action. Pioglitazone decreases insulin resistance in the periphery and in the liver resulting in increased insulin-dependent glucose disposal and decreased hepatic glucose output. Pioglitazone is not an insulin secretagogue. Pioglitazone is an agonist for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma (PPARγ). PPAR receptors are found in tissues important for insulin action such as adipose tissue, skeletal muscle, and liver. Activation of PPARγ nuclear receptors modulates the transcription of a number of insulin responsive genes involved in the control of glucose and lipid metabolism.
In animal models of diabetes, pioglitazone reduces the hyperglycemia, hyperinsulinemia, and hypertriglyceridemia characteristic of insulin-resistant states such as type 2 diabetes. The metabolic changes produced by pioglitazone result in increased responsiveness of insulin-dependent tissues and are observed in numerous animal models of insulin resistance.
Because pioglitazone enhances the effects of circulating insulin (by decreasing insulin resistance), it does not lower blood glucose in animal models that lack endogenous insulin.
Metformin hydrochloride
Metformin hydrochloride improves glucose tolerance in patients with type 2 diabetes, lowering both basal and postprandial plasma glucose. Metformin decreases hepatic glucose production, decreases intestinal absorption of glucose and improves insulin sensitivity by increasing peripheral glucose uptake and utilization. Metformin does not produce hypoglycemia in either patients with type 2 diabetes or healthy subjects [except in specific circumstances, see Warnings and Precautions (5.4)] and does not cause hyperinsulinemia. With metformin therapy, insulin secretion remains unchanged while fasting insulin levels and day-long plasma insulin response may actually decrease.
12.2 Pharmacodynamics
Pioglitazone
Clinical studies demonstrate that pioglitazone improves insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant patients. Pioglitazone enhances cellular responsiveness to insulin, increases insulin-dependent glucose disposal and improves hepatic sensitivity to insulin. In patients with type 2 diabetes, the decreased insulin resistance produced by pioglitazone results in lower plasma glucose concentrations, lower plasma insulin concentrations, and lower HbA1c values. In controlled clinical trials, pioglitazone had an additive effect on glycemic control when used in combination with a sulfonylurea, metformin, or insulin [see Clinical Studies (14)].
Patients with lipid abnormalities were included in clinical trials with pioglitazone. Overall, patients treated with pioglitazone had mean decreases in serum triglycerides, mean increases in HDL cholesterol, and no consistent mean changes in LDL and total cholesterol. There is no conclusive evidence of macrovascular benefit with pioglitazone [see Warnings and Precautions (5.10) and Adverse Reactions (6.1)].
In a 26-week, placebo-controlled, dose-ranging monotherapy study, mean serum triglycerides decreased in the 15 mg, 30 mg, and 45 mg pioglitazone dose groups compared to a mean increase in the placebo group. Mean HDL cholesterol increased to a greater extent in patients treated with pioglitazone than in the patients treated with placebo. There were no consistent differences for LDL and total cholesterol in patients treated with pioglitazone compared to placebo (Table 14).
Table 14. Lipids in a 26-Week Placebo-Controlled Monotherapy Dose-Ranging Study
Placebo
Pioglitazone
15 mg
Once
DailyPioglitazone
30 mg
Once
DailyPioglitazone
45 mg
Once
DailyTriglycerides (mg/dL)
N=79
N=79
N=84
N=77
Baseline (mean)
263
284
261
260
Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
4.8%
-9.0%†
-9.6%†
-9.3%†
HDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)
N=79
N=79
N=83
N=77
Baseline (mean)
42
40
41
41
Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
8.1%
14.1%†
12.2%
19.1%†
LDL Cholesterol (mg/dL)
N=65
N=63
N=74
N=62
Baseline (mean)
139
132
136
127
Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
4.8%
7.2%
5.2%
6.0%
Total Cholesterol (mg/dL)
N=79
N=79
N=84
N=77
Baseline (mean)
225
220
223
214
Percent change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
4.4%
4.6%
3.3%
6.4%
*Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
†p <0.05 versus placeboIn the two other monotherapy studies (16 weeks and 24 weeks) and in combination therapy studies with metformin (16 weeks and 24 weeks), the results were generally consistent with the data above.
12.3 Pharmacokinetics
Absorption
ACTOPLUS MET XR
In bioequivalence studies of ACTOPLUS MET XR 15 mg/1000 mg and 30 mg/1000 mg, the AUC and maximum concentration (Cmax) of both the pioglitazone and the extended-release metformin components following a single dose of the combination tablet were bioequivalent to ACTOS 15 mg and 30 mg concomitantly administered with extended-release metformin hydrochloride (FORTAMET) 1000 mg tablets under fed conditions in healthy subjects.
Administration of ACTOPLUS MET XR 30 mg/1000 mg with food resulted in no change in total (AUC) exposure of pioglitazone; however, a decrease in Cmax by approximately 18% was observed. With the extended-release metformin component, there was an increase in Cmax by approximately 98% and AUC exposure by approximately 85% when administered with food. These levels are comparable to exposures obtained with extended release metformin when administered with food. Time to peak serum concentration (Tmax) was prolonged by approximately three and two hours for pioglitazone and extended-release metformin respectively, under fed conditions.
Pioglitazone
Following once daily administration of pioglitazone, steady-state serum concentrations of both pioglitazone and its major active metabolites, M-III (keto derivative of pioglitazone) and M-IV (hydroxyl derivative of pioglitazone), are achieved within 7 days. At steady-state, M-III and M-IV reach serum concentrations equal to or greater than that of pioglitazone. At steady-state, in both healthy volunteers and patients with type 2 diabetes, pioglitazone comprises approximately 30% to 50% of the peak total pioglitazone serum concentrations (pioglitazone plus active metabolites) and 20% to 25% of the total AUC.
Cmax, AUC, and trough serum concentrations (Cmin) for pioglitazone and M-III and M-IV, increased proportionally with administered doses of 15 mg and 30 mg per day.
Following oral administration of pioglitazone, Tmax of pioglitazone was within two hours. Food delays the Tmax to three to four hours, but does not alter the extent of absorption (AUC).
Metformin hydrochloride
The absolute bioavailability of a 500 mg metformin tablet given under fasting conditions is approximately 50% - 60%. Studies using single oral doses of metformin tablets of 500 mg to 1500 mg, and 850 mg to 2550 mg, indicate that there is a lack of dose proportionality with increasing doses, which is due to decreased absorption rather than an alteration in elimination. At usual clinical doses and dosing schedules of metformin, steady-state plasma concentrations of metformin are reached within 24 - 48 hours and are generally <1 mcg/mL. During controlled clinical trials, maximum metformin plasma levels did not exceed 5 mcg/mL, even at maximum doses.
Food decreases the rate and extent of metformin absorption, as shown by approximately a 40% lower mean Cmax, a 25% lower AUC, and a 35-minute prolongation of Tmax following administration of a single 850 mg tablet of metformin with food, compared to the same tablet strength administered fasting. The clinical relevance of these decreases is unknown.
Distribution
Pioglitazone
The mean apparent volume of distribution (Vd/F) of pioglitazone following single-dose administration is 0.63 ± 0.41 (mean ± SD) L/kg of body weight. Pioglitazone is extensively protein bound (>99%) in human serum, principally to serum albumin. Pioglitazone also binds to other serum proteins, but with lower affinity. M-III and M-IV are also extensively bound (>98%) to serum albumin.
Metformin hydrochloride
The Vd/F of metformin following single oral doses of 850 mg immediate-release metformin averaged 654 ± 358 L. Metformin is negligibly bound to plasma proteins. Metformin partitions into erythrocytes, most likely as a function of time.
Metabolism
Pioglitazone
Pioglitazone is extensively metabolized by hydroxylation and oxidation; the metabolites also partly convert to glucuronide or sulfate conjugates. Metabolites M‑III and M‑IV are the major circulating active metabolites in humans.
In vitro data demonstrate that multiple CYP isoforms are involved in the metabolism of pioglitazone which include CYP2C8 and, to a lesser degree, CYP3A4 with additional contributions from a variety of other isoforms including the mainly extrahepatic CYP1A1. In vivo study of pioglitazone in combination with gemfibrozil, a strong CYP2C8 inhibitor, showed that pioglitazone is a CYP2C8 substrate [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]. Urinary 6ß-hydroxycortisol/cortisol ratios measured in patients treated with pioglitazone showed that pioglitazone is not a strong CYP3A4 enzyme inducer.
Metformin hydrochloride
Intravenous single-dose studies in healthy subjects demonstrate that metformin is excreted unchanged in the urine and does not undergo hepatic metabolism (no metabolites have been identified in humans) nor biliary excretion.
Excretion and Elimination
Pioglitazone
Following oral administration, approximately 15% to 30% of the pioglitazone dose is recovered in the urine. Renal elimination of pioglitazone is negligible and the drug is excreted primarily as metabolites and their conjugates. It is presumed that most of the oral dose is excreted into the bile either unchanged or as metabolites and eliminated in the feces.
The mean serum half-life (t1/2) of pioglitazone and its metabolites (M-III and M-IV) range from three to seven hours and 16 to 24 hours, respectively. Pioglitazone has an apparent clearance (CL/F) calculated to be five to seven L/hr.
Metformin hydrochloride
Renal clearance is approximately 3.5 times greater than creatinine clearance (CLcr) which indicates that tubular secretion is the major route of metformin elimination. Following oral administration, approximately 90% of the absorbed drug is eliminated via the renal route within the first 24 hours, with a plasma t1/2 of approximately 6.2 hours. In blood, the t1/2 is approximately 17.6 hours, suggesting that the erythrocyte mass may be a compartment of distribution.
Specific Populations
Renal Impairment
Pioglitazone
The serum t1/2 of pioglitazone, M-III and M-IV remains unchanged in patients with moderate (CLcr 30 to 50 mL/min) and severe (CLcr <30 mL/min) renal impairment when compared to subjects with normal renal function. Therefore, no dose adjustment in patients with renal impairment is required.
Metformin hydrochloride
In patients with decreased renal function, the plasma and blood t1/2 of metformin is prolonged and the renal clearance is decreased [see Dosage and Administration (2.2), Contraindications (4) and Warnings and Precautions (5.2)].
Hepatic Impairment
Pioglitazone
Compared with healthy controls, subjects with impaired hepatic function (Child-Turcotte-Pugh Grade B/C) have an approximate 45% reduction in pioglitazone and total pioglitazone (pioglitazone, M-III and M-IV) mean Cmax but no change in the mean AUC values. Therefore, no dose adjustment in patients with hepatic impairment is required.
There are postmarketing reports of liver failure with pioglitazone and clinical trials have generally excluded patients with serum ALT >2.5 times the upper limit of the reference range. Use ACTOPLUS MET XR with caution in patients with liver disease [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Metformin hydrochloride
No pharmacokinetic studies of metformin have been conducted in subjects with hepatic impairment [see Warnings and Precautions (5.5)].
Geriatric Patients
Pioglitazone
In healthy elderly subjects, Cmax of pioglitazone was not significantly different, but AUC values were approximately 21% higher than those achieved in younger subjects. The mean t1/2 of pioglitazone was also prolonged in elderly subjects (about ten hours) as compared to younger subjects (about seven hours). These changes were not of a magnitude that would be considered clinically relevant.
Metformin hydrochloride
Limited data from controlled pharmacokinetic studies of metformin in healthy elderly subjects suggest that total plasma CL/F is decreased, the t1/2 is prolonged, and Cmax is increased, compared to healthy young subjects. From these data, it appears that the change in metformin pharmacokinetics with aging is primarily accounted for by a change in renal function.
Pediatrics
Pioglitazone
Safety and efficacy of pioglitazone in pediatric patients have not been established. ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended for use in pediatric patients [see Use in Specific Populations (8.4)].
Metformin hydrochloride
After administration of a single oral metformin 500 mg tablet with food, geometric mean metformin Cmax and AUC differed less than 5% between pediatric type 2 diabetic patients (12 to 16 years of age) and gender- and weight-matched healthy adults (20 to 45 years of age), all with normal renal function.
Gender
Pioglitazone
The mean Cmax and AUC values of pioglitazone were increased 20% to 60% in women compared to men. In controlled clinical trials, HbA1c decreases from baseline were generally greater for females than for males (average mean difference in HbA1c 0.5%). Because therapy should be individualized for each patient to achieve glycemic control, no dose adjustment is recommended based on gender alone.
Metformin hydrochloride
Metformin pharmacokinetic parameters did not differ significantly between normal subjects and patients with type 2 diabetes when analyzed according to gender (males=19, females=16). Similarly, in controlled clinical studies in patients with type 2 diabetes, the antihyperglycemic effect of metformin was comparable in males and females.
Ethnicity
Pioglitazone
Pharmacokinetic data among various ethnic groups are not available.
Metformin hydrochloride
No studies of metformin pharmacokinetic parameters according to race have been performed. In controlled clinical studies of metformin in patients with type 2 diabetes, the antihyperglycemic effect was comparable in whites (n=249), blacks (n=51), and Hispanics (n=24).
Drug-Drug Interactions
Specific pharmacokinetic drug interaction studies with ACTOPLUS MET XR have not been performed, although such studies have been conducted with the individual pioglitazone and metformin components.
Pioglitazone
Table 15. Effect of Pioglitazone Coadministration on Systemic Exposure of Other Drugs
Coadministered Drug
Pioglitazone
Dosage
Regimen (mg)*Name and Dose Regimens
Change
in AUC†Change
in Cmax†45 mg
(N = 12)Warfarin‡
Daily loading then maintenance doses
based PT and INR values
Quick's Value = 35 ± 5%R-Warfarin - ↓3%
R-Warfarin
↓2%
S-Warfarin
↓1%
S-Warfarin
↑1%
45 mg
(N = 12)Digoxin
0.200 mg twice daily (loading dose) then
0.250 mg daily (maintenance dose, 7 days)↑15%
↑17%
45 mg daily
for 21 days
(N = 35)Oral Contraceptive
[Ethinyl Estradiol (EE) 0.035 mg plus
Norethindrone (NE) 1 mg] for 21 daysEE
↓11%
EE
↓13%
NE
↑3%
NE
↓7%
45 mg
(N = 23)Fexofenadine
60 mg twice daily for 7 days
↑30%
↑37%
45 mg
(N = 14)Glipizide
5 mg daily for 7 days
↓3%
↓8%
45 mg daily
for 8 days
(N = 16)Metformin
1000 mg single dose on Day 8
↓3%
↓5%
45 mg
(N = 21)Midazolam
7.5 mg single dose on Day 15
↓26%
↓26%
45 mg
(N = 24)Ranitidine
150 mg twice daily for 7 days
↑1%
↓1%
45 mg daily
for 4 days
(N = 24)Nifedipine ER
30 mg daily for 4 days
↓13%
↓17%
45 mg
(N = 25)Atorvastatin Ca
80 mg daily for 7 days
↓14%
↓23%
45 mg
(N = 22)Theophylline
400 mg twice daily for 7 days
↑2%
↑5%
*Daily for 7 days unless otherwise noted
†% change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively
‡Pioglitazone had no clinically significant effect on prothrombin time- Table 16. Effect of Coadministered Drugs on Pioglitazone Systemic Exposure
Coadministered Drug and
Dosage RegimenPioglitazone
Dose
Regimen
(mg)*Change
in AUC†Change
in Cmax†Gemfibrozil 600 mg
twice daily for 2 days
(N = 12)15 mg
single dose↑3.2-fold‡
↑6%
Ketoconazole 200 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 28)45 mg
↑34%
↑14%
Rifampin 600 mg
daily for 5 days
(N = 10)30 mg
single dose↓54%
↓5%
Fexofenadine 60 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 23)45 mg
↑1%
0%
Ranitidine 150 mg
twice daily for 4 days
(N = 23)45 mg
↓13%
↓16%
Nifedipine ER 30 mg
daily for 7 days
(N = 23)45 mg
↑5%
↑4%
Atorvastatin Ca 80 mg
daily for 7 days
(N = 24)45 mg
↓24%
↓31%
Theophylline 400 mg
twice daily for 7 days
(N = 22)45 mg
↓4%
↓2%
Topiramate 96 mg
twice daily for 7 days§30 mg§
↓15%¶
0%
(N = 26)
*Daily for 7 days unless otherwise noted
†Mean ratio (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 1-fold) % change (with/without coadministered drug and no change = 0%); symbols of ↑ and ↓ indicate the exposure increase and decrease, respectively.
‡The half-life of pioglitazone increased from 8.3 hours to 22.7 hours in the presence of gemfibrozil [see Dosage and Administration (2.3) and Drug Interactions (7.1)]
§Indicates duration of concomitant administration with highest twice-daily dose of topiramate from Day 14 onwards over the 22 days of study
¶Additional decrease in active metabolites; 60% for M-III and 16% for M-IVMetformin hydrochloride
Table 17. Effect of Coadministered Drug on Plasma Metformin Systemic Exposure
Coadministered
DrugDose of
Coadministered
Drug*Dose of
Metformin*Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without
coadministered drug) No effect = 1.00AUC†
Cmax
No dosing adjustments required for the following:
Glyburide
5 mg
500 mg§
0.98‡
0.99‡
Furosemide
40 mg
850 mg
1.09‡
1.22‡
Nifedipine
10 mg
850 mg
1.16
1.21
Propranolol
40 mg
850 mg
0.90
0.94
Ibuprofen
400 mg
850 mg
1.05‡
1.07‡
Drugs that are eliminated by renal tubular secretion may increase the accumulation of metformin [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Cimetidine
400 mg
850 mg
1.40
1.61
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors may cause metabolic acidosis [see Warnings and Precautions (5) and Drug Interactions (7)].
Topiramate
100 mg¶
500 mg¶
1.25¶
1.17
*All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses
†AUC = AUC0–∞
‡Ratio of arithmetic means
§Metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets, 500 mg
¶At steady state with topiramate 100 mg every 12 hours and metformin 500 mg every 12 hours; AUC = AUC0-12hTable 18. Effect of Metformin on Coadministered Drug Systemic Exposure
Coadministered
DrugDose of
Coadministered
Drug*Dose of
Metformin*Geometric Mean Ratio (ratio with/without
coadministered drug) No effect = 1.00AUC†
Cmax
No dosing adjustments required for the following:
Glyburide
5 mg
500 mg§
0.78‡
0.63‡
Furosemide
40 mg
850 mg
0.87‡
0.69‡
Nifedipine
10 mg
850 mg
1.10§
1.08
Propranolol
40 mg
850 mg
1.01§
0.94
Ibuprofen
400 mg
850 mg
0.97¶
1.01¶
Cimetidine
400 mg
850 mg
0.95§
1.01
*All metformin and coadministered drugs were given as single doses
†AUC = AUC0–∞
‡Ratio of arithmetic means, p-value of difference <0.05
§AUC0-24 hr reported
¶Ratio of arithmetic means -
13 NONCLINICAL TOXICOLOGY
13.1 Carcinogenesis, Mutagenesis, Impairment of Fertility
ACTOPLUS MET XR
No animal studies have been conducted with ACTOPLUS MET XR. The following data are based on findings in studies performed with pioglitazone or metformin individually.
Pioglitazone
A two-year carcinogenicity study was conducted in male and female rats at oral doses up to 63 mg/kg (approximately 14 times the maximum recommended human oral dose of 45 mg based on mg/m2). Drug-induced tumors were not observed in any organ except for the urinary bladder of male rats. Benign and/or malignant transitional cell neoplasms were observed in male rats at 4 mg/kg/day and above (approximately equal to the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). Urinary calculi with subsequent irritation and hyperplasia were postulated as the mechanism for bladder tumors observed in male rats. A two-year mechanistic study in male rats utilizing dietary acidification to reduce calculi formation was completed in 2009. Dietary acidification decreased but did not abolish the hyperplastic changes in the bladder. The presence of calculi exacerbated the hyperplastic response to pioglitazone but was not considered the primary cause of the hyperplastic changes.
The relevance to humans of the bladder findings in the male rat cannot be excluded.
A two-year carcinogenicity study was also conducted in male and female mice at oral doses up to 100 mg/kg/day (approximately 11 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). No drug-induced tumors were observed in any organ.
Pioglitazone hydrochloride was not mutagenic in a battery of genetic toxicology studies, including the Ames bacterial assay, a mammalian cell forward gene mutation assay (CHO/HPRT and AS52/XPRT), an in vitro cytogenetics assay using CHL cells, an unscheduled DNA synthesis assay, and an in vivo micronucleus assay.
No adverse effects upon fertility were observed in male and female rats at oral doses up to 40 mg/kg pioglitazone hydrochloride daily prior to and throughout mating and gestation (approximately nine times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2).
Metformin hydrochloride
Long-term carcinogenicity studies have been performed in rats (dosing duration of 104 weeks) and mice (dosing duration of 91 weeks) at doses up to and including 900 mg/kg/day and 1500 mg/kg/day, respectively. These doses are both approximately four times a human daily dose of 2000 mg of the metformin component of ACTOPLUS MET XR based on body surface area comparisons. No evidence of carcinogenicity with metformin was found in either male or female mice. Similarly, there was no tumorigenic potential observed with metformin in male rats. There was, however, an increased incidence of benign stromal uterine polyps in female rats treated with 900 mg/kg/day.
There was no evidence of mutagenic potential of metformin in the following in vitro tests: Ames test (S. typhimurium), gene mutation test (mouse lymphoma cells), or chromosomal aberrations test (human lymphocytes). Results in the in vivo mouse micronucleus test were also negative.
Fertility of male or female rats was unaffected by metformin when administered at doses as high as 600 mg/kg/day, which is approximately three times the maximum recommended human daily dose of the metformin component of ACTOPLUS MET XR based on body surface area comparisons.
13.2 Animal Toxicology and/or Pharmacology
Heart enlargement has been observed in mice (100 mg/kg), rats (4 mg/kg and above) and dogs (3 mg/kg) treated orally with pioglitazone hydrochloride (approximately 11, 1, and 2 times the maximum recommended human oral dose for mice, rats, and dogs, respectively, based on mg/m2). In a one-year rat study, drug-related early death due to apparent heart dysfunction occurred at an oral dose of 160 mg/kg/day (approximately 35 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2). Heart enlargement was seen in a 13-week study in monkeys at oral doses of 8.9 mg/kg and above (approximately 4 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2), but not in a 52-week study at oral doses up to 32 mg/kg (approximately 13 times the maximum recommended human oral dose based on mg/m2).
-
14 CLINICAL STUDIES
There have been no clinical efficacy studies conducted with ACTOPLUS MET XR. However, the efficacy and safety of the separate components have been previously established and the coadministration of the separate components has been evaluated for efficacy and safety in two clinical studies. These clinical studies established an added benefit of pioglitazone in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes while on metformin therapy. Bioequivalence of ACTOPLUS MET XR with coadministered pioglitazone and extended-release metformin tablets was demonstrated for both tablet strengths of ACTOPLUS MET XR [see Clinical Pharmacology (12.3)].
Two clinical trials were conducted with pioglitazone in combination with metformin. Both trials included patients with type 2 diabetes on any dose of metformin, either alone or in combination with another antidiabetic agent. All other antidiabetic agents were withdrawn at least 3 weeks prior to starting study treatment.
In the first trial, 328 patients were randomized to receive either 30 mg of pioglitazone or placebo once daily for 16 weeks in addition to their current metformin regimen. Treatment with pioglitazone as add-on to metformin produced statistically significant improvements in HbA1c and FPG at endpoint compared to placebo add-on to metformin (see Table 19).
Table 19. Glycemic Parameters in a 16 Week Placebo-Controlled, Add-on to Metformin Trial
Placebo
+ MetforminPioglitazone 30 mg
+ MetforminTotal Population
HbA1c (%)
N=153
N=161
Baseline (mean)
9.8
9.9
Change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
0.2
-0.6
Difference from placebo + metformin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-0.8†
(-1.2, -0.5)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL)
N=157
N=165
Baseline (mean)
260
254
Change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
-5
-43
Difference from placebo + metformin (adjusted mean*)
95% Confidence Interval-38†
(-49, -26)*Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
†p≤0.05 versus placebo + metforminIn the second trial, 827 patients were randomized to receive either 30 mg or 45 mg of pioglitazone once daily for 24 weeks in addition to their current metformin regimen. The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in HbA1c was 0.8% for the 30 mg dose and 1.0% for the 45 mg dose (see Table 20). The mean reduction from baseline at Week 24 in FPG was 38 mg/dL for the 30 mg dose and 51 mg/dL for the 45 mg dose.
Table 20. Glycemic Parameters in a 24 Week Add-on to Metformin Study
Pioglitazone 30 mg +
MetforminPioglitazone 45 mg +
MetforminTotal Population
HbA1c (%)
N=400
N=398
Baseline (mean)
9.9
9.8
Change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
-0.8
-1.0
Difference from 30 mg daily Pioglitazone
+ Metformin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI)-0.2
(-0.5, 0.1)Fasting Plasma Glucose (mg/dL)
N=398
N=399
Baseline (mean)
233
232
Change from baseline (adjusted mean*)
-38
-51
Difference from 30 mg daily Pioglitazone
+ Metformin (adjusted mean*) (95% CI)-12†
(-21, -4)95% CI = 95% confidence interval
*Adjusted for baseline, pooled center, and pooled center by treatment interaction
†p ≤0.05 versus 30 mg daily pioglitazone + metforminThe therapeutic effect of pioglitazone in combination with metformin was observed in patients regardless of the metformin dose.
-
16 HOW SUPPLIED/STORAGE AND HANDLING
ACTOPLUS MET XR is available in 15 mg pioglitazone (as the base)/1000 mg metformin hydrochloride extended-release and 30 mg pioglitazone (as the base)/1000 mg metformin hydrochloride extended-release tablets as follows:
15 mg/1000 mg tablet: white to off-white, round, film-coated tablets imprinted with "4833X" and "15/1000" in red on one side, available in:
NDC: 64764-510-30 Bottles of 30
NDC: 64764-510-60 Bottles of 60
NDC: 64764-510-90 Bottles of 90
30 mg/1000 mg tablet: white to off-white round, film-coated tablets imprinted with "4833X" and "30/1000" in light blue on one side, available in:
NDC: 64764-310-30 Bottles of 30
NDC: 64764-310-60 Bottles of 60
NDC: 64764-310-90 Bottles of 90
Storage
Store at 25°C (77°F); excursions permitted to 15° to 30°C (59° to 86°F) [see USP Controlled Room Temperature]. Keep container tightly closed, and protect from moisture and humidity.
-
17 PATIENT COUNSELING INFORMATION
See FDA-approved patient labeling (Medication Guide)
- It is important to instruct patients to adhere to dietary instructions and to have blood glucose and glycosylated hemoglobin tested regularly. During periods of stress such as fever, trauma, infection, or surgery, medication requirements may change and patients should be reminded to seek medical advice promptly.
- Tell patients to promptly report any sign of macroscopic hematuria or other symptoms such as dysuria or urinary urgency that develop or increase during treatment as these may be due to bladder cancer.
- Explain to patients the risks of lactic acidosis, its symptoms and conditions that predispose to its development, as noted in the Warnings and Precautions (5.2) section. Advise patients to discontinue ACTOPLUS MET XR immediately and to promptly notify their healthcare professional if unexplained hyperventilation, myalgia, gastrointestinal symptoms, malaise, unusual somnolence or other nonspecific symptoms occur. Instruct patients to inform their doctor that they are taking ACTOPLUS MET XR prior to any surgical or radiological procedure, as temporary discontinuation of ACTOPLUS MET XR may be required until renal function has been confirmed to be normal.
- Counsel patients against excessive alcohol intake while receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR.
- Inform patients to immediately report symptoms of an unusually rapid increase in weight or edema, shortness of breath or other symptoms of heart failure while receiving ACTOPLUS MET XR.
- Tell patients to promptly stop taking ACTOPLUS MET XR and seek immediate medical advice if there is unexplained nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fatigue, anorexia, or dark urine as these symptoms may be due to hepatotoxicity.
- Inform patients about the importance of regular testing of renal function and hematologic parameters when receiving treatment with ACTOPLUS MET XR.
- Inform female patients that treatment with ACTOPLUS MET XR may result in an unintended pregnancy in some premenopausal anovulatory females due to its effect on ovulation [see Use in Specific Populations (8.3)].
- Patients should be advised to notify their health practitioner or call the Poison Control Center immediately in case of ACTOPLUS MET XR overdose.
- Combination antihyperglycemic therapy may cause hypoglycemia. When initiating ACTOPLUS MET XR, the risks of hypoglycemia, its symptoms and treatment, and conditions that predispose to its development should be explained to patients and their family members.
- Patients should be told to take ACTOPLUS MET XR as prescribed and instructed that any change in dosing should only be done if directed by their physician. If a dose is missed on one day, the dose should not be doubled the following day.
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Deerfield, IL 60015
ACTOS and ACTOPLUS MET XR are trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
All other trademarks are the property of their respective owners.
©2009 - 2017 Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
AMX002 R11
-
MEDICATION GUIDE
MEDICATION GUIDE
ACTOPLUS MET XR (ak-TŌ-plus-met eX-R)
(pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride extended-release) tabletsRead this Medication Guide carefully before you start taking ACTOPLUS MET XR and each time you get a refill. There may be new information. This information does not take the place of talking with your doctor about your medical condition or your treatment. If you have any questions about ACTOPLUS MET XR, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
What is the most important information I should know about ACTOPLUS MET XR?
ACTOPLUS MET XR can cause serious side effects, including:
- new or worse heart failure. Pioglitazone, one of the medicines in ACTOPLUS MET XR, can cause your body to keep extra fluid (fluid retention), which leads to swelling (edema) and weight gain. Extra body fluid can make some heart problems worse or lead to heart failure. Heart failure means your heart does not pump blood well enough
- Do not take ACTOPLUS MET XR if you have severe heart failure
- If you have heart failure with symptoms (such as shortness of breath or swelling), even if these symptoms are not severe, ACTOPLUS MET XR may not be right for you
Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following:
- swelling or fluid retention, especially in the ankles or legs
- shortness of breath or trouble breathing, especially when you lie down
- an unusually fast increase in weight
- unusual tiredness
- lactic acidosis. Metformin, one of the medicines in ACTOPLUS MET XR, can cause a rare but serious condition called lactic acidosis (a buildup of an acid in the blood) that can cause death. Lactic acidosis is a medical emergency and must be treated in the hospital.
- Call your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms, which could be signs of lactic acidosis:
- you feel cold in your hands or feet
- you feel dizzy or lightheaded
- you have a slow or irregular heartbeat
- you feel very weak or tired
- you have unusual (not normal) muscle pain
- you have trouble breathing
- you feel sleepy or drowsy
- you have stomach pains, nausea or vomiting
Most people who have had lactic acidosis with metformin have other things that, combined with the metformin, led to the lactic acidosis. Tell your doctor if you have any of the following, because you have a higher chance for getting lactic acidosis with ACTOPLUS MET XR if you:
- have severe kidney problems or your kidneys are affected by certain x-ray tests that use injectable dye
- have liver problems
- drink alcohol very often, or drink a lot of alcohol in short-term "binge" drinking
- get dehydrated (lose a large amount of body fluids). This can happen if you are sick with a fever, vomiting, or diarrhea. Dehydration can also happen when you sweat a lot with activity or exercise and do not drink enough fluids
- have surgery
- have a heart attack, severe infection, or stroke
The best way to keep from having a problem with lactic acidosis from metformin is to tell your doctor if you have any of the problems in the list above. Your doctor may decide to stop your ACTOPLUS MET XR for a while if you have any of these things.
ACTOPLUS MET XR can have other serious side effects. See "What are the possible side effects of ACTOPLUS MET XR?"
What is ACTOPLUS MET XR?
ACTOPLUS MET XR contains 2 prescription diabetes medicines called pioglitazone (ACTOS) and metformin hydrochloride extended-release. ACTOPLUS MET XR can be used with diet and exercise to improve blood sugar (glucose) control in adults with type 2 diabetes.
ACTOPLUS MET XR is not for people with type 1 diabetes.
ACTOPLUS MET XR is not for people with diabetic ketoacidosis (increased ketones in your blood or urine).
It is not known if ACTOPLUS MET XR is safe and effective in children under the age of 18. ACTOPLUS MET XR is not recommended for use in children.
Who should not take ACTOPLUS MET XR?
See "What is the most important information I should know about ACTOPLUS MET XR?"
Do not take ACTOPLUS MET XR if you:
- have severe heart failure
- are allergic to pioglitazone, metformin or any of the ingredients in ACTOPLUS MET XR. See the end of this Medication Guide for a complete list of ingredients in ACTOPLUS MET XR
- have severe kidney problems
- have a condition called metabolic acidosis, including diabetic ketoacidosis. Diabetic ketoacidosis should be treated with insulin
Tell your doctor before taking ACTOPLUS MET XR if you have any of these conditions.
What should I tell my doctor before taking ACTOPLUS MET XR?
Before you take ACTOPLUS MET XR, tell your doctor if you:
- have heart failure
- have severe kidney problems
- are going to have dye injected into a vein for an x-ray, CAT scan, heart study, or other type of scanning
- will be undergoing a surgical procedure
- drink a lot of alcohol (all the time or short binge drinking)
- have type 1 ("juvenile") diabetes or had diabetic ketoacidosis
- have a type of diabetic eye disease that causes swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema)
- have liver problems
- have or have had cancer of the bladder
- are pregnant or plan to become pregnant. It is not known if ACTOPLUS MET XR can harm your unborn baby. Talk to your doctor if you are pregnant or plan to become pregnant about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while pregnant
- are a premenopausal woman (before the "change of life"), who does not have periods regularly or at all. ACTOPLUS MET XR may increase your chance of becoming pregnant. Talk to your doctor about birth control choices while taking ACTOPLUS MET XR. Tell your doctor right away if you become pregnant while taking ACTOPLUS MET XR
- are breast-feeding or plan to breast-feed. It is not known if ACTOPLUS MET XR passes into your milk and if it can harm your baby. Talk to your doctor about the best way to control your blood glucose levels while breast-feeding
Tell your doctor about all the medicines you take including prescription and over the counter medicines, vitamins, and herbal supplements.
ACTOPLUS MET XR and some of your other medicines can affect each other. You may need to have your dose of ACTOPLUS MET XR or certain other medicines changed.
Know the medicines you take. Keep a list of your medicines and show it to your doctor and pharmacist before you start a new medicine. They will tell you if it is okay to take ACTOPLUS MET XR with other medicines.
How should I take ACTOPLUS MET XR?
- Take ACTOPLUS MET XR exactly as your doctor tells you to take it
- Your doctor may need to change your dose of ACTOPLUS MET XR. Do not change your ACTOPLUS MET XR dose unless your doctor tells you to
- ACTOPLUS MET XR may be prescribed alone or with other diabetes medicines. This will depend on how well your blood sugar is controlled
- Take ACTOPLUS MET XR once a day with meals to lower your chance of an upset stomach
- Take ACTOPLUS MET XR tablets whole. Do not chew, cut, or crush the tablets. If you cannot swallow ACTOPLUS MET XR whole, tell your doctor. You may need a different medicine.
- If you take ACTOPLUS MET XR, you may see something that looks like the ACTOPLUS MET XR tablet in your stools. This is normal.
- If you miss a dose of ACTOPLUS MET XR, take your next dose as prescribed unless your doctor tells you differently. Do not take two doses at one time the next day
- If you take too much ACTOPLUS MET XR, call your doctor or go to the nearest hospital emergency room right away
- If your body is under stress, such as from a fever, infection, accident or surgery, the dose of your diabetes medicines may need to be changed. Call your doctor right away
- Stay on your diet and exercise programs and test your blood sugar regularly while taking ACTOPLUS MET XR
- Your doctor should do certain blood tests before you start and while you take ACTOPLUS MET XR
- Your doctor should also do hemoglobin A1C testing to check how well your blood sugar is controlled with ACTOPLUS MET XR
- Your doctor should check your eyes regularly while you take ACTOPLUS MET XR
What are the possible side effects of ACTOPLUS MET XR?
ACTOPLUS MET XR may cause serious side effects including:
- See "What is the most important information I should know about ACTOPLUS MET XR?"
- low blood sugar (hypoglycemia). This can happen if you skip meals, if you also use another medicine that lowers blood sugar, or if you have certain medical problems. Lightheadedness, dizziness, shakiness, or hunger may happen if your blood sugar is too low. Call your doctor if low blood sugar levels are a problem for you
- liver problems. Call your doctor right away if you have:
- nausea or vomiting
- stomach pain
- unusual or unexplained tiredness
- loss of appetite
- dark urine
- yellowing of your skin or the whites of your eyes
-
bladder cancer. There may be an increased chance of having bladder cancer when you take ACTOPLUS MET XR. You should not take ACTOPLUS MET XR if you are receiving treatment for bladder cancer. Tell your doctor right away if you have any of the following symptoms of bladder cancer:
- o blood or a red color in your urine
- o an increased need to urinate
- o pain while you urinate
- broken bones (fractures). Usually in the hand, upper arm, or foot in women. Talk to your doctor for advice on how to keep your bones healthy
- diabetic eye disease with swelling in the back of the eye (macular edema). Tell your doctor right away if you have any changes in your vision. Your doctor should check your eyes regularly
- release of an egg from an ovary in a woman (ovulation) leading to pregnancy. Ovulation may happen when premenopausal women who do not have regular monthly periods take ACTOPLUS MET XR. This can increase your chance of getting pregnant
- low red blood cell count (anemia)
The most common side effects of ACTOPLUS MET XR include:
- cold-like symptoms (upper respiratory tract infection)
- swelling (edema)
- diarrhea
- headache
- increased weight
Tell your doctor if you have any side effect that bothers you or that does not go away. These are not all the side effects of ACTOPLUS MET XR. For more information, ask your doctor or pharmacist.
Call your doctor for medical advice about side effects. You may report side effects to FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088.
How should I store ACTOPLUS MET XR?
- Store ACTOPLUS MET XR at 68°F to 77°F (20°C to 25°C). Keep ACTOPLUS MET XR in the original container to protect from light
- Keep the ACTOPLUS MET XR bottle tightly closed and keep tablets dry
Keep ACTOPLUS MET XR and all medicines out of the reach of children.
General information about the safe and effective use of ACTOPLUS MET XR
Medicines are sometimes prescribed for purposes other than those listed in a Medication Guide. Do not use ACTOPLUS MET XR for a condition for which it was not prescribed. Do not give ACTOPLUS MET XR to other people, even if they have the same symptoms you have. It may harm them.
This Medication Guide summarizes the most important information about ACTOPLUS MET XR. If you would like more information, talk with your doctor. You can ask your doctor or pharmacist for information about ACTOPLUS MET XR that is written for healthcare professionals. For more information, go to www.actoplusmetxr.com or call 1-877-825-3327.
What are the ingredients in ACTOPLUS MET XR?
Active Ingredients: pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride.
Inactive Ingredients: candelilla wax, cellulose acetate, povidone, hydroxypropyl cellulose, lactose monohydrate, magnesium stearate, hypromellose, polyethylene glycols (PEG 400, PEG 8000), sodium lauryl sulfate, titanium dioxide, and triacetin. Ink contains shellac, iron-oxide red (15 mg/1000 mg tablet strength), FD&C Blue No. 2 Lake (30 mg/1000 mg tablet strength), propylene glycol, and ammonium hydroxide.
ACTOS and ACTOPLUS MET XR are trademarks of Takeda Pharmaceutical Company Limited registered with the U.S. Patent and Trademark Office and used under license by Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
This Medication Guide has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Distributed by:
Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
Deerfield, IL 60015
Revised: December 2016
©2009 - 2017 Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc.
AMX002 R11
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL – 15 mg/1000 mg Tablet Bottle Label
30 Tablets NDC 64764-510-30
actoplus met XR
(pioglitazone and metformin HCl
extended-release) Tablets15 mg/1000 mg
Each film-coated tablet contains
pioglitazone hydrochloride equivalent
to 15 mg pioglitazone and 1000 mg
metformin hydrochloride.Dispense with Medication Guide
available in package insert or at
www.actoplusmetxr.comTakeda logo
Rx Only
-
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL
PRINCIPAL DISPLAY PANEL - 30 mg/1000 mg Tablet Bottle Label
30 Tablets NDC 64764-310-30
actoplus met XR
(pioglitazone and metformin HCl
extended-release) Tablets30 mg/1000 mg
Each film-coated tablet contains
pioglitazone hydrochloride equivalent
to 30 mg pioglitazone and 1000 mg
metformin hydrochloride.Dispense with Medication Guide
available in package insert or at
www.actoplusmetxr.comTakeda logo
Rx Only
-
INGREDIENTS AND APPEARANCE
ACTOPLUS MET XR
pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 64764-510 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength pioglitazone hydrochloride (UNII: JQT35NPK6C) (pioglitazone - UNII:X4OV71U42S) pioglitazone 15 mg metformin hydrochloride (UNII: 786Z46389E) (metformin - UNII:9100L32L2N) metformin hydrochloride 1000 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength candelilla wax (UNII: WL0328HX19) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (1600000 WAMW) (UNII: RFW2ET671P) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) polyethylene glycol 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) polyethylene glycol 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) sodium lauryl sulfate (UNII: 368GB5141J) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) ferric oxide red (UNII: 1K09F3G675) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code 4833X;15;1000 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 64764-510-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 2 NDC: 64764-510-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 3 NDC: 64764-510-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 4 NDC: 64764-510-07 1 in 1 CARTON 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 4 7 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 5 NDC: 64764-510-33 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022024 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 ACTOPLUS MET XR
pioglitazone and metformin hydrochloride tablet, film coated, extended releaseProduct Information Product Type HUMAN PRESCRIPTION DRUG Item Code (Source) NDC: 64764-310 Route of Administration ORAL Active Ingredient/Active Moiety Ingredient Name Basis of Strength Strength pioglitazone hydrochloride (UNII: JQT35NPK6C) (pioglitazone - UNII:X4OV71U42S) pioglitazone 30 mg metformin hydrochloride (UNII: 786Z46389E) (metformin - UNII:9100L32L2N) metformin hydrochloride 1000 mg Inactive Ingredients Ingredient Name Strength candelilla wax (UNII: WL0328HX19) cellulose acetate (UNII: 3J2P07GVB6) POVIDONE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: FZ989GH94E) HYDROXYPROPYL CELLULOSE (1600000 WAMW) (UNII: RFW2ET671P) lactose monohydrate (UNII: EWQ57Q8I5X) magnesium stearate (UNII: 70097M6I30) HYPROMELLOSE, UNSPECIFIED (UNII: 3NXW29V3WO) polyethylene glycol 400 (UNII: B697894SGQ) polyethylene glycol 8000 (UNII: Q662QK8M3B) sodium lauryl sulfate (UNII: 368GB5141J) titanium dioxide (UNII: 15FIX9V2JP) triacetin (UNII: XHX3C3X673) shellac (UNII: 46N107B71O) propylene glycol (UNII: 6DC9Q167V3) ammonia (UNII: 5138Q19F1X) FD&C Blue No. 2 (UNII: L06K8R7DQK) Aluminum Oxide (UNII: LMI26O6933) Product Characteristics Color WHITE (white to off-white) Score no score Shape ROUND Size 13mm Flavor Imprint Code 4833X;30;1000 Contains Packaging # Item Code Package Description Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date 1 NDC: 64764-310-30 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 2 NDC: 64764-310-60 60 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 3 NDC: 64764-310-90 90 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 4 NDC: 64764-310-07 1 in 1 CARTON 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 4 7 in 1 BLISTER PACK; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 5 NDC: 64764-310-33 30 in 1 BOTTLE, PLASTIC; Type 0: Not a Combination Product 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 Marketing Information Marketing Category Application Number or Monograph Citation Marketing Start Date Marketing End Date NDA NDA022024 06/11/2010 09/30/2022 Labeler - Takeda Pharmaceuticals America, Inc. (830134016)
Trademark Results [Actoplus Met]
Mark Image Registration | Serial | Company Trademark Application Date |
|---|---|
 ACTOPLUS MET 78218773 3149378 Live/Registered |
TAKEDA PHARMACEUTICAL COMPANY LIMITED 2003-02-25 |
 ACTOPLUS MET 78174989 not registered Dead/Abandoned |
Takeda Chemical Industries, Ltd. 2002-10-16 |
© 2026 FDA.report
This site is not affiliated with or endorsed by the FDA.